DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2 Intestine LIVER PANCREAS Small intestine









9880-digestive_system_part_2_med_2014.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2 Intestine LIVER PANCREAS
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2 Intestine LIVER PANCREAS
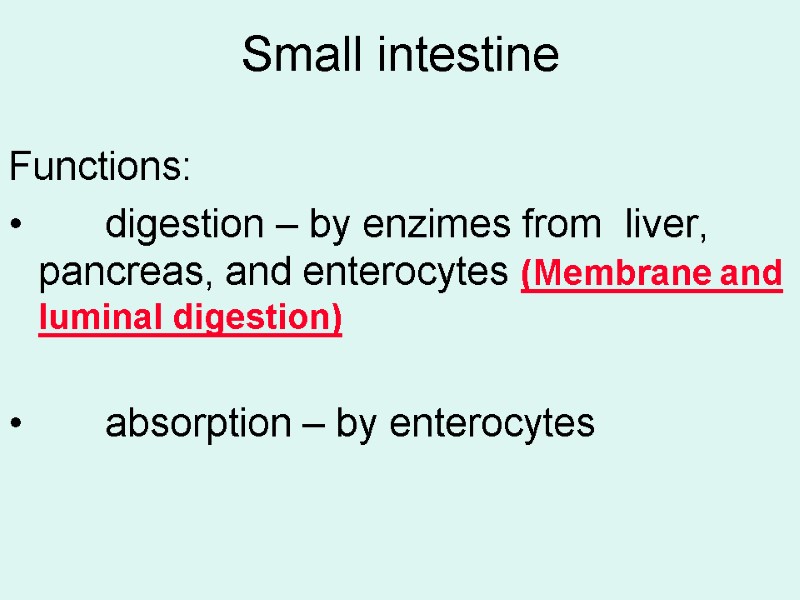
 Small intestine Functions: digestion – by enzimes from liver, pancreas, and enterocytes (Membrane and luminal digestion) absorption – by enterocytes
Small intestine Functions: digestion – by enzimes from liver, pancreas, and enterocytes (Membrane and luminal digestion) absorption – by enterocytes
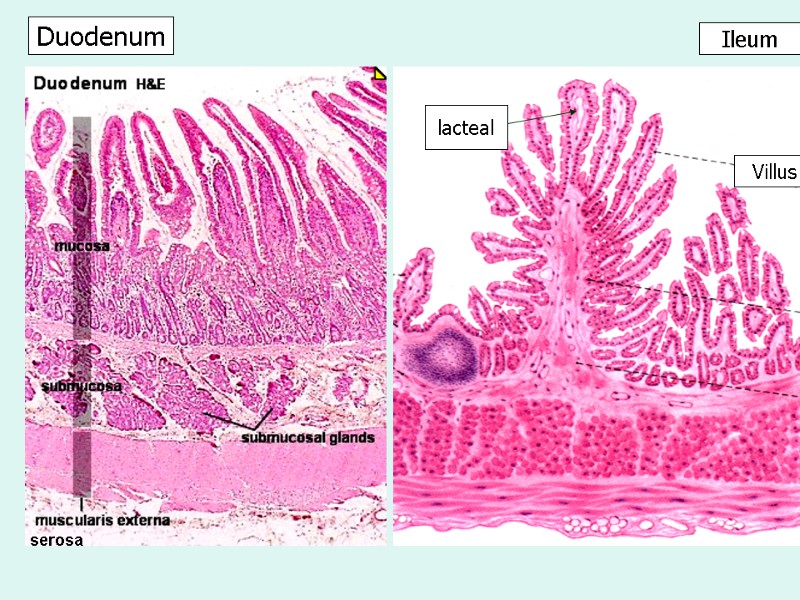
 Ileum Duodenum Villus lacteal serosa
Ileum Duodenum Villus lacteal serosa
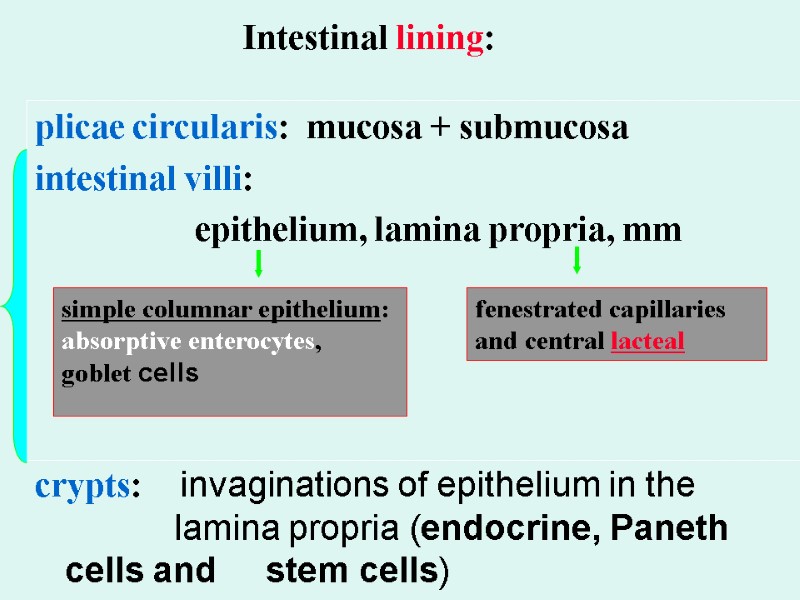
 Intestinal lining: plicae circularis: mucosa + submucosa intestinal villi: epithelium, lamina propria, mm crypts: invaginations of epithelium in the lamina propria (endocrine, Paneth cells and stem cells) simple columnar epithelium: absorptive enterocytes, goblet cells fenestrated capillaries and central lacteal
Intestinal lining: plicae circularis: mucosa + submucosa intestinal villi: epithelium, lamina propria, mm crypts: invaginations of epithelium in the lamina propria (endocrine, Paneth cells and stem cells) simple columnar epithelium: absorptive enterocytes, goblet cells fenestrated capillaries and central lacteal
 Intestinal lining: plicae circularis (folds): mucosa + submucosa intestinal villi: epithelium + lamina propria with muscularis mucosae (increased surface)
Intestinal lining: plicae circularis (folds): mucosa + submucosa intestinal villi: epithelium + lamina propria with muscularis mucosae (increased surface)
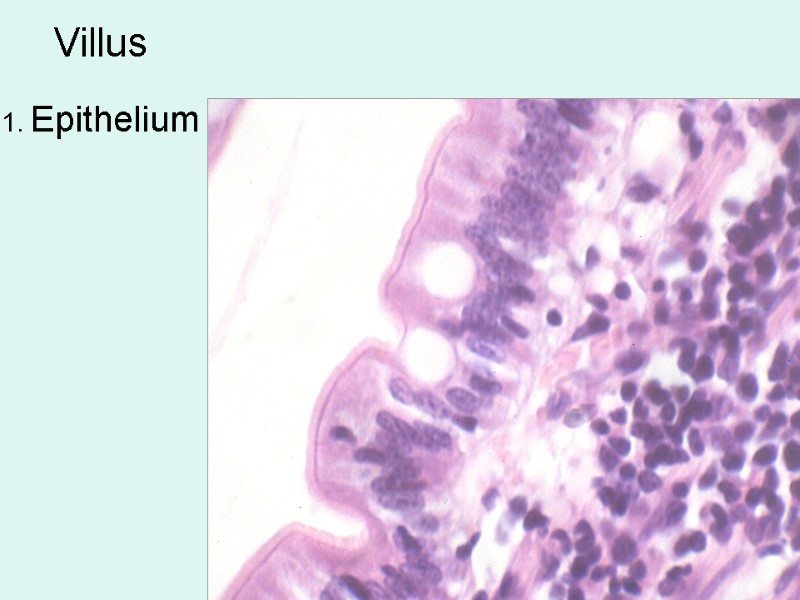
 Villus 1. Epithelium
Villus 1. Epithelium
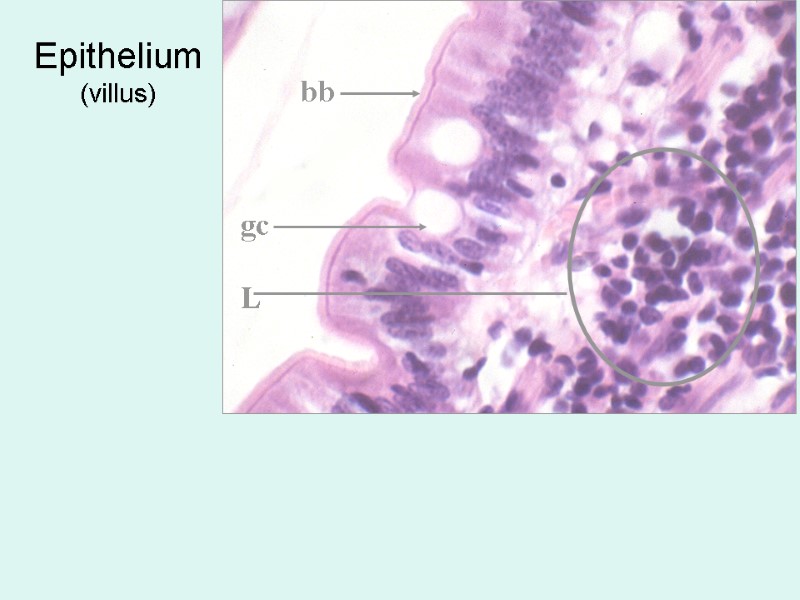
 Epithelium: simple columnar . Cells: 1. Enterocytes -- Columnar absorptive cells --have microvilli = brush border for absorption of digested food. 2. Goblet cells produce a protective mucus. Lamina propria: Connective tissue, has fenestrated capillaries and central lacteal -- lymphatic capillary Lymphocytes and plasma cells are very numerous.
Epithelium: simple columnar . Cells: 1. Enterocytes -- Columnar absorptive cells --have microvilli = brush border for absorption of digested food. 2. Goblet cells produce a protective mucus. Lamina propria: Connective tissue, has fenestrated capillaries and central lacteal -- lymphatic capillary Lymphocytes and plasma cells are very numerous.
 Epithelium (villus) bb gc L
Epithelium (villus) bb gc L
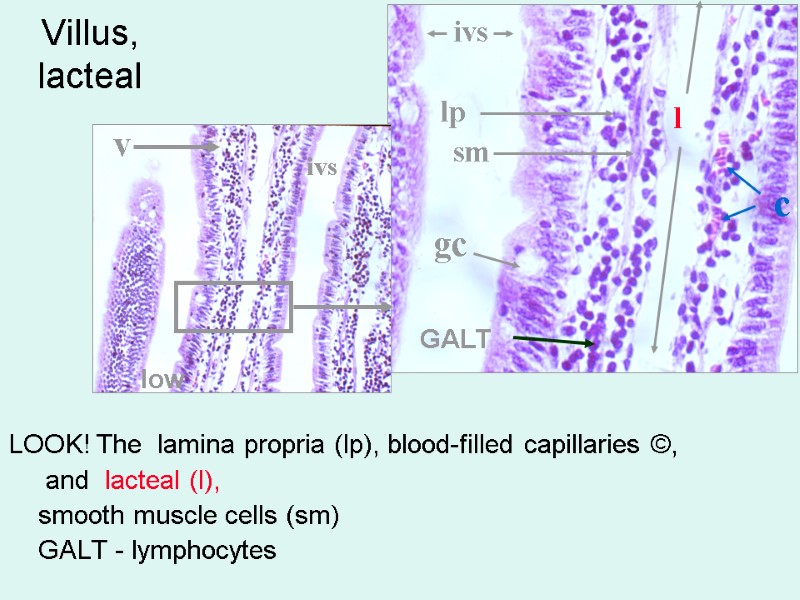
 Villus, lacteal LOOK! The lamina propria (lp), blood-filled capillaries ©, and lacteal (l), smooth muscle cells (sm) GALT - lymphocytes v gc ivs ivs l lp c sm GALT low
Villus, lacteal LOOK! The lamina propria (lp), blood-filled capillaries ©, and lacteal (l), smooth muscle cells (sm) GALT - lymphocytes v gc ivs ivs l lp c sm GALT low
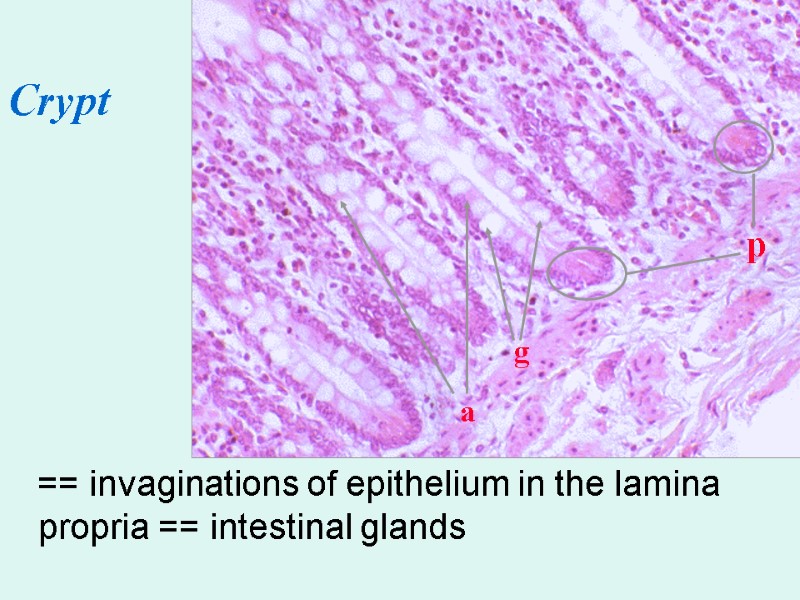
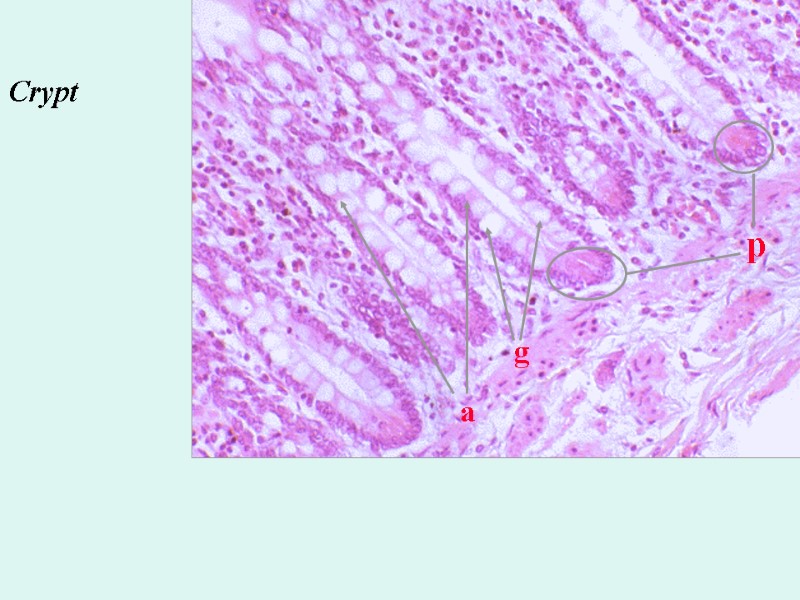
 == invaginations of epithelium in the lamina propria == intestinal glands p g a Crypt
== invaginations of epithelium in the lamina propria == intestinal glands p g a Crypt
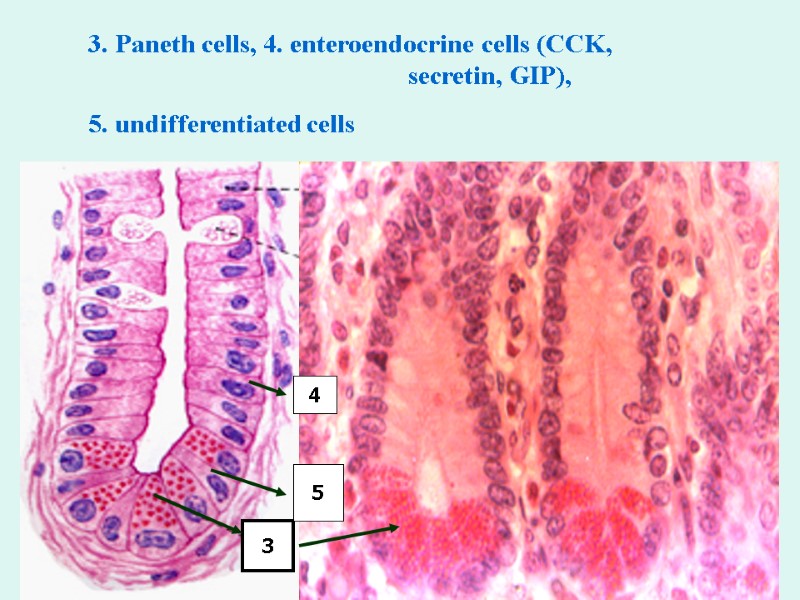
 1.Goblet and 2.absorptive cells. 3. the granule-containing Paneth cells - produce Lysozyme (. at the bottom 4. enteroendocrine cells 5. undifferentiated stem cells Epithelium of crypt
1.Goblet and 2.absorptive cells. 3. the granule-containing Paneth cells - produce Lysozyme (. at the bottom 4. enteroendocrine cells 5. undifferentiated stem cells Epithelium of crypt
 p g a Crypt
p g a Crypt
 3. Paneth cells, 4. enteroendocrine cells (CCK, secretin, GIP), 5. undifferentiated cells 3 4 5
3. Paneth cells, 4. enteroendocrine cells (CCK, secretin, GIP), 5. undifferentiated cells 3 4 5
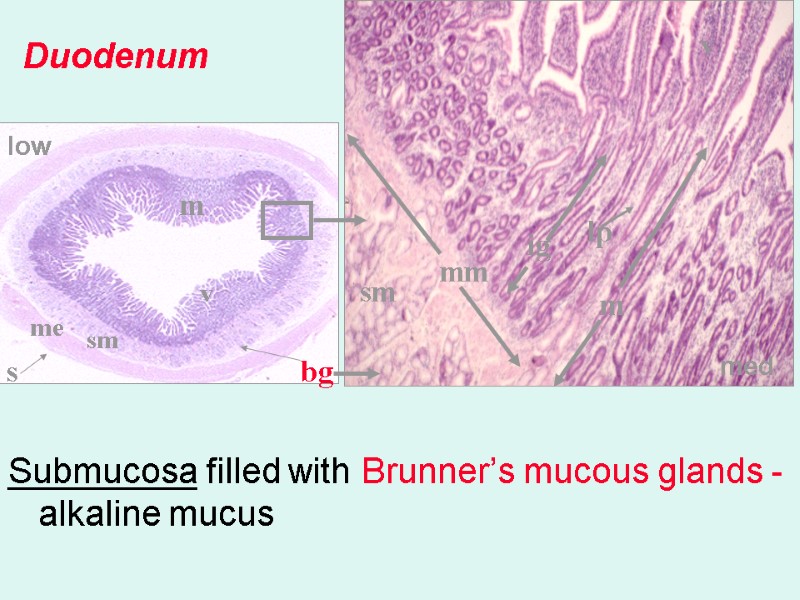
 Submucosa filled with Brunner’s mucous glands - alkaline mucus Duodenum v v m m ig sm sm lp mm bg me s low med v
Submucosa filled with Brunner’s mucous glands - alkaline mucus Duodenum v v m m ig sm sm lp mm bg me s low med v
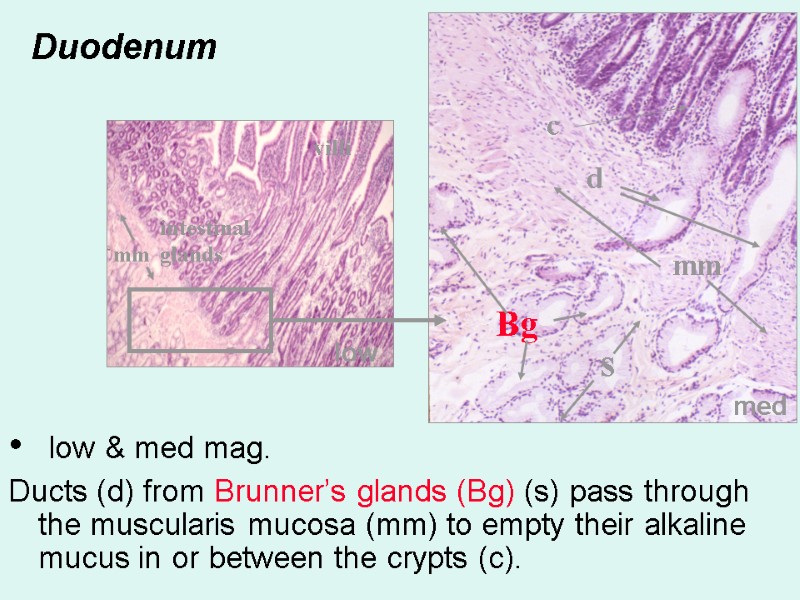
 Duodenum low & med mag. Ducts (d) from Brunner’s glands (Bg) (s) pass through the muscularis mucosa (mm) to empty their alkaline mucus in or between the crypts (c). d s Bg mm mm c med low villi intestinal glands
Duodenum low & med mag. Ducts (d) from Brunner’s glands (Bg) (s) pass through the muscularis mucosa (mm) to empty their alkaline mucus in or between the crypts (c). d s Bg mm mm c med low villi intestinal glands
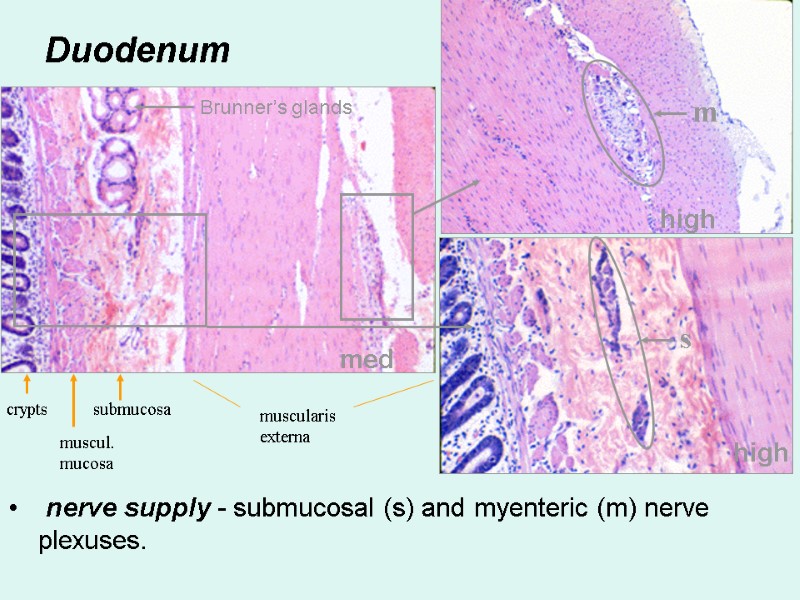
 Duodenum nerve supply - submucosal (s) and myenteric (m) nerve plexuses. med high high s m crypts muscul. mucosa submucosa muscularis externa Brunner’s glands
Duodenum nerve supply - submucosal (s) and myenteric (m) nerve plexuses. med high high s m crypts muscul. mucosa submucosa muscularis externa Brunner’s glands
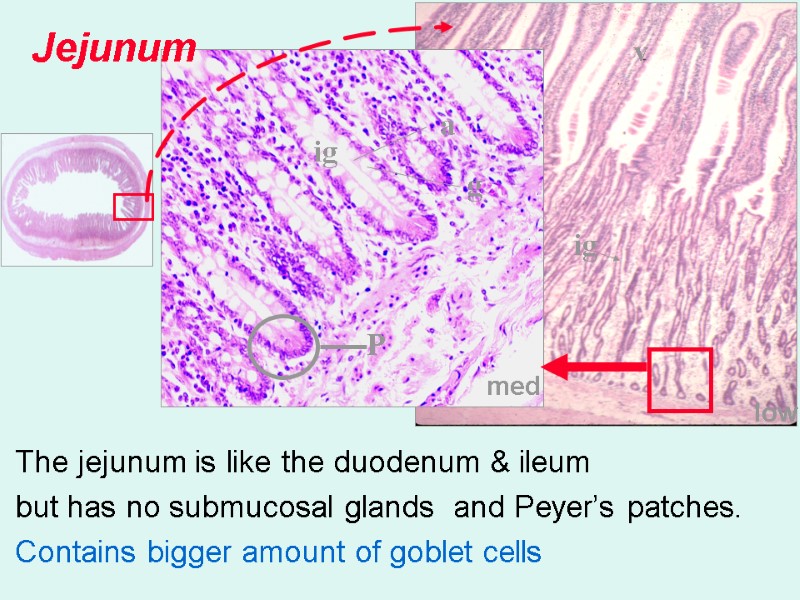
 med low Jejunum The jejunum is like the duodenum & ileum but has no submucosal glands and Peyer’s patches. Contains bigger amount of goblet cells v ig ig g a P
med low Jejunum The jejunum is like the duodenum & ileum but has no submucosal glands and Peyer’s patches. Contains bigger amount of goblet cells v ig ig g a P
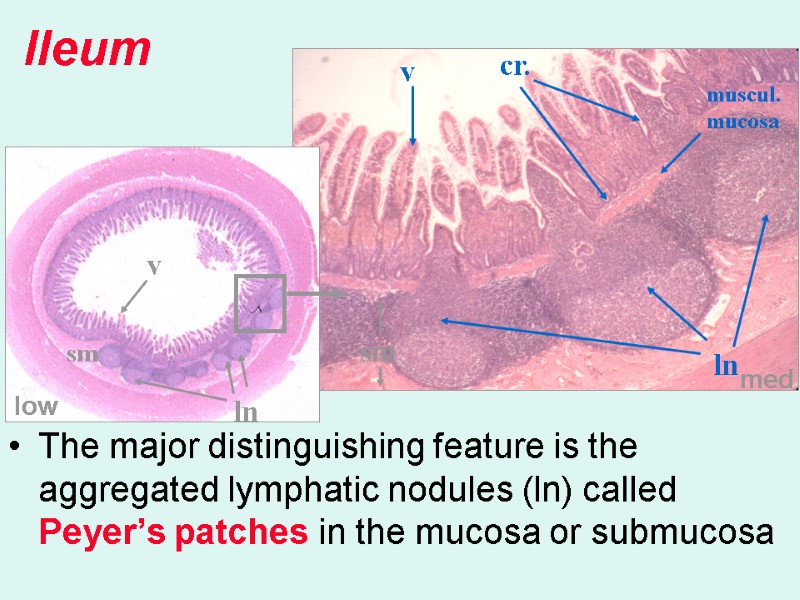
 The major distinguishing feature is the aggregated lymphatic nodules (ln) called Peyer’s patches in the mucosa or submucosa Ileum med low v v cr. sm sm ln ln muscul. mucosa
The major distinguishing feature is the aggregated lymphatic nodules (ln) called Peyer’s patches in the mucosa or submucosa Ileum med low v v cr. sm sm ln ln muscul. mucosa
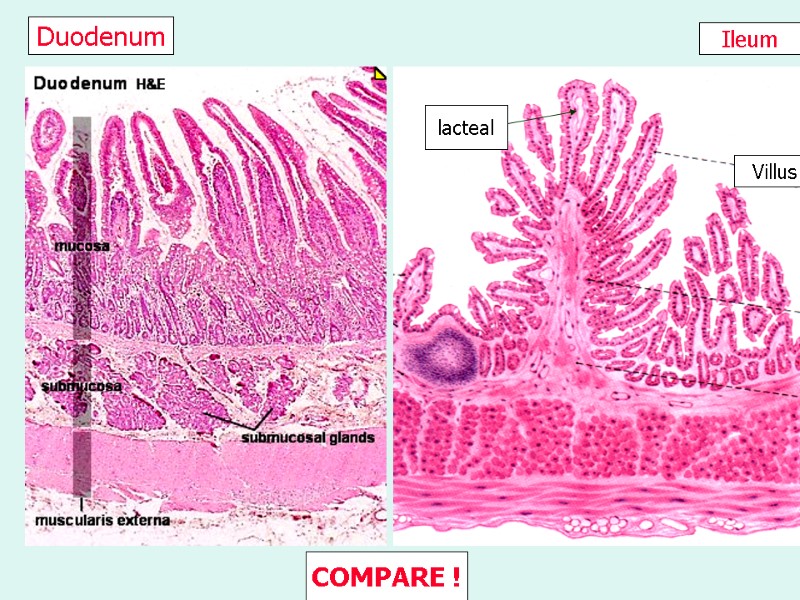
 Ileum Duodenum Villus lacteal COMPARE !
Ileum Duodenum Villus lacteal COMPARE !
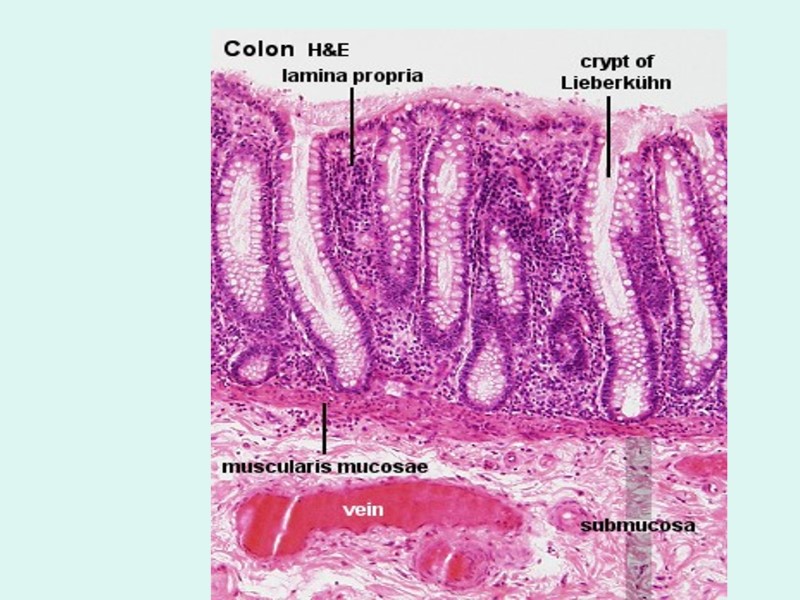
 Large intestine (bowal) - general Function = Reabsorbtion of water and electrolytes + Elimination of wastes Inner lining - permanent internal folds of its mucosa + submucosa called plicae circulares and crypts. Its mucosa lacks of villi. muscularis externa: The inner circular layer is uniform but the outer longitudinal layer has 3 thicker bands, the taenia coli. where the colon faces the abdominal cavity there is a serosa.
Large intestine (bowal) - general Function = Reabsorbtion of water and electrolytes + Elimination of wastes Inner lining - permanent internal folds of its mucosa + submucosa called plicae circulares and crypts. Its mucosa lacks of villi. muscularis externa: The inner circular layer is uniform but the outer longitudinal layer has 3 thicker bands, the taenia coli. where the colon faces the abdominal cavity there is a serosa.
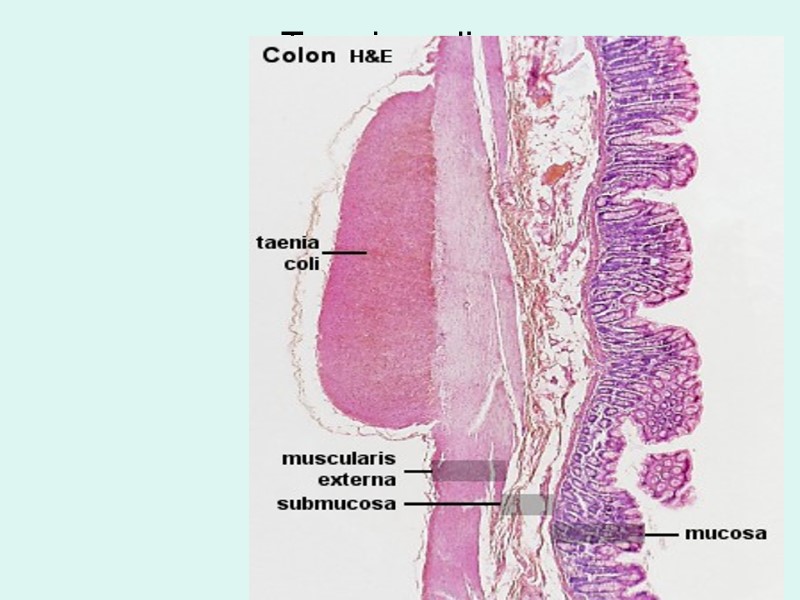
 Taenia coli
Taenia coli
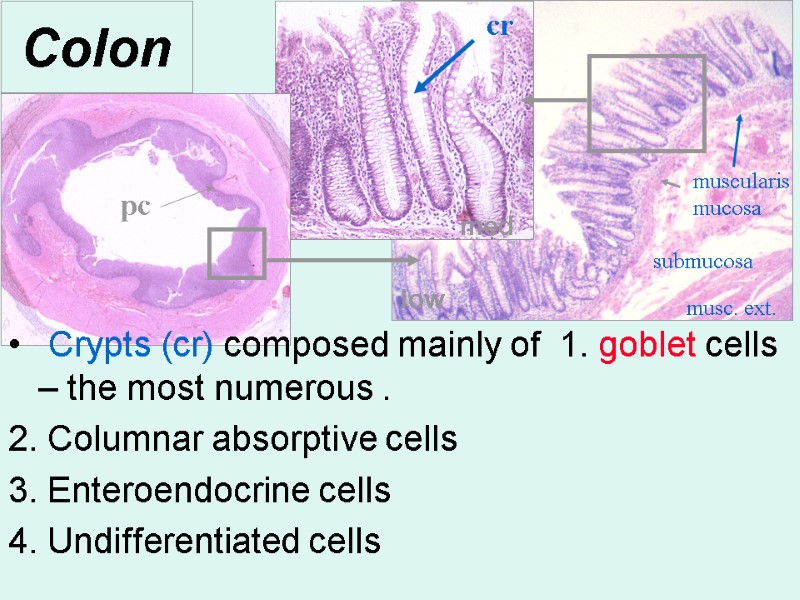
 Colon Crypts (cr) composed mainly of 1. goblet cells – the most numerous . 2. Columnar absorptive cells 3. Enteroendocrine cells 4. Undifferentiated cells pc cr low med muscularis mucosa submucosa musc. ext.
Colon Crypts (cr) composed mainly of 1. goblet cells – the most numerous . 2. Columnar absorptive cells 3. Enteroendocrine cells 4. Undifferentiated cells pc cr low med muscularis mucosa submucosa musc. ext.
 High. Magn.
High. Magn.
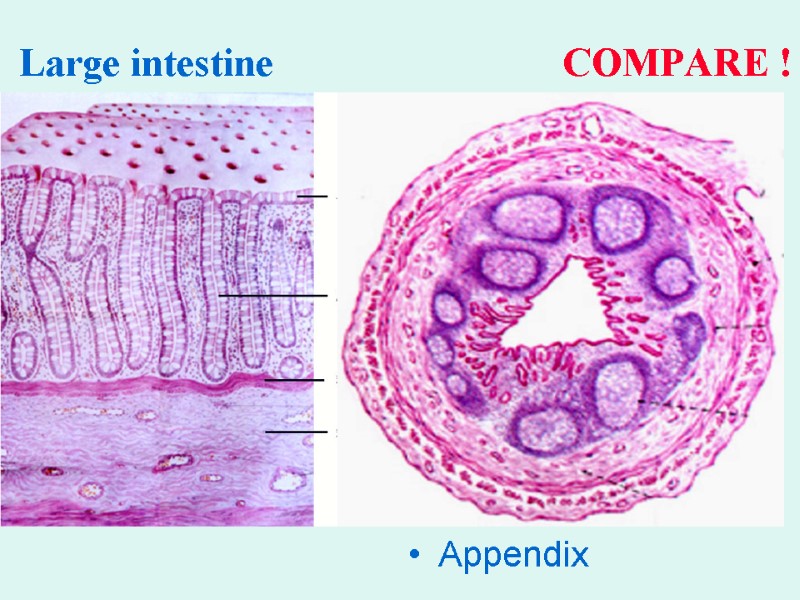
 Large intestine COMPARE ! Appendix
Large intestine COMPARE ! Appendix
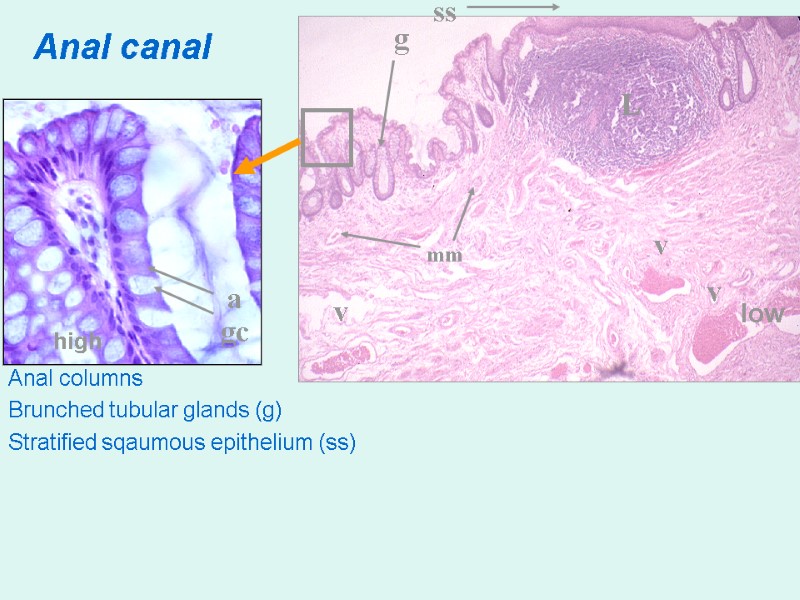
 Anal canal Anal columns Brunched tubular glands (g) Stratified sqaumous epithelium (ss) ig g ss gc a v v v low high L mm
Anal canal Anal columns Brunched tubular glands (g) Stratified sqaumous epithelium (ss) ig g ss gc a v v v low high L mm
 Liver & Gall Bladder
Liver & Gall Bladder
 Functions: Bile synthesis and secretion (emulsification) Excretion of bilirubin Protein synthesis Gluconeogenesis Storage Detoxification Protective Hemopoietic organ Endocrine
Functions: Bile synthesis and secretion (emulsification) Excretion of bilirubin Protein synthesis Gluconeogenesis Storage Detoxification Protective Hemopoietic organ Endocrine
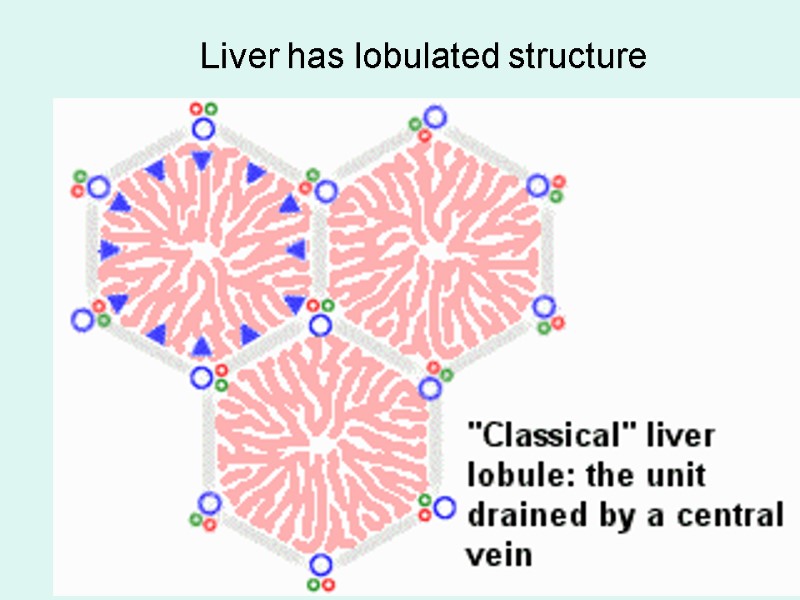
 Liver has lobulated structure
Liver has lobulated structure
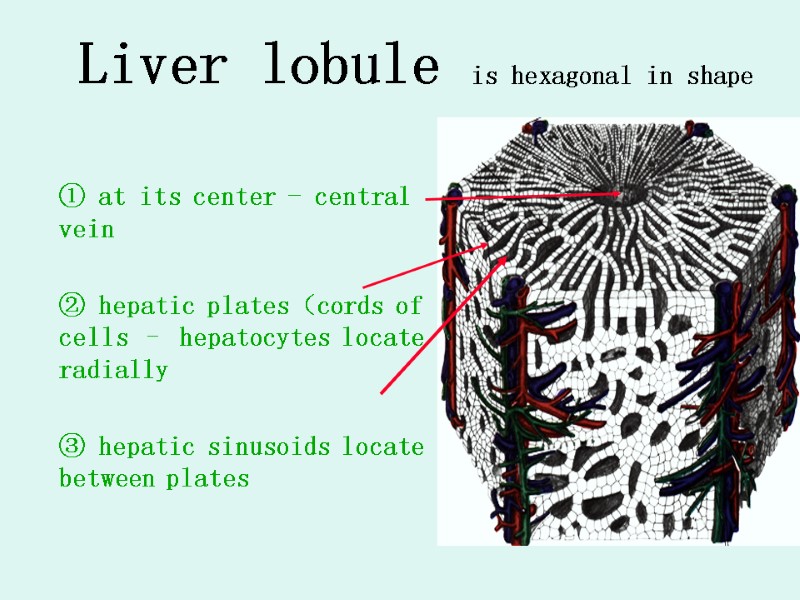
 Liver lobule is hexagonal in shape ① at its center - central vein ② hepatic plates(cords of cells – hepatocytes locate radially ③ hepatic sinusoids locate between plates
Liver lobule is hexagonal in shape ① at its center - central vein ② hepatic plates(cords of cells – hepatocytes locate radially ③ hepatic sinusoids locate between plates
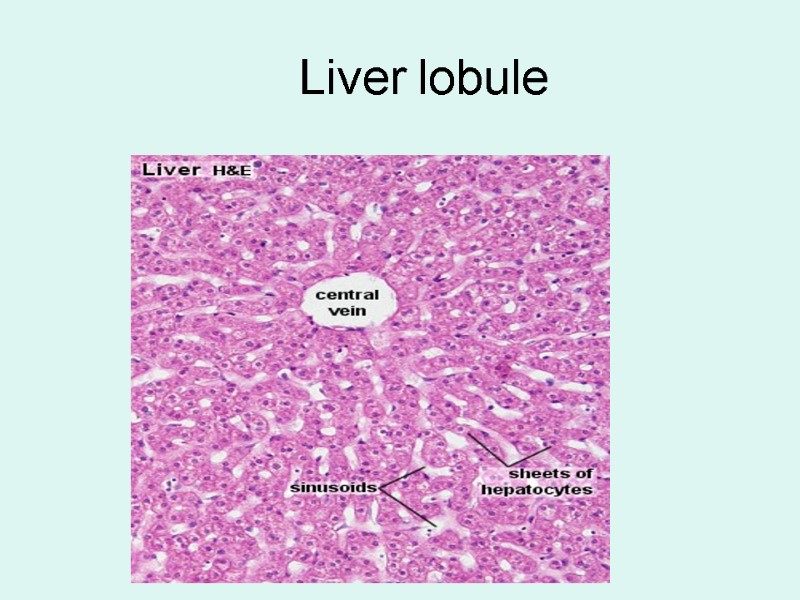
 Liver lobule
Liver lobule
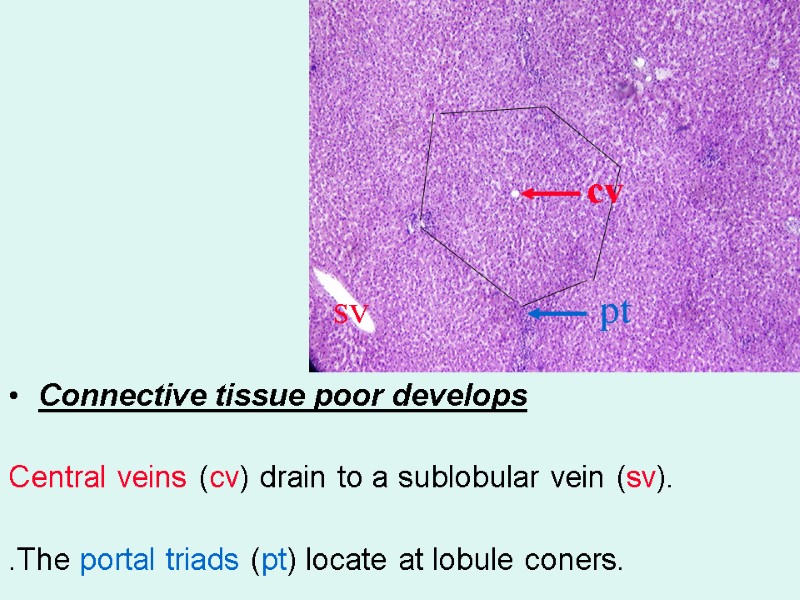
 Connective tissue poor develops Central veins (cv) drain to a sublobular vein (sv). .The portal triads (pt) locate at lobule coners. pt cv sv
Connective tissue poor develops Central veins (cv) drain to a sublobular vein (sv). .The portal triads (pt) locate at lobule coners. pt cv sv
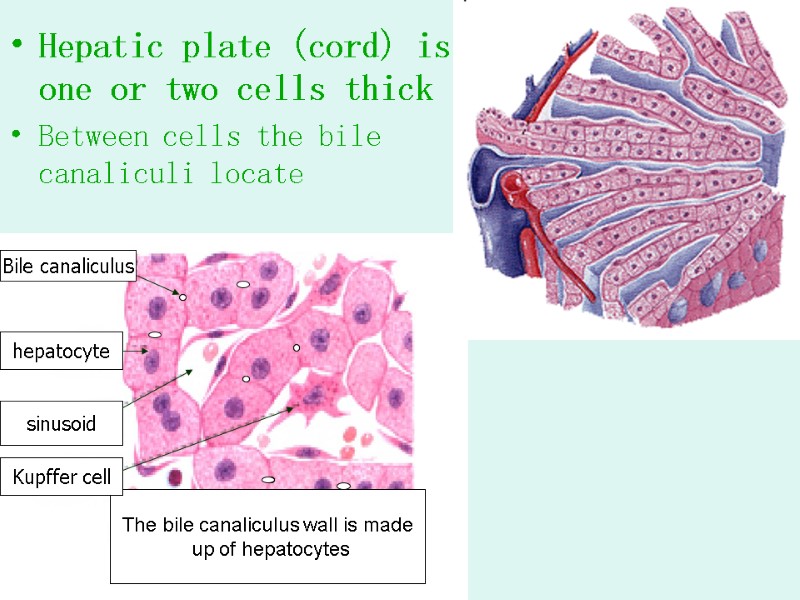
 Hepatic plate (cord) is one or two cells thick Between cells the bile canaliculi locate The bile canaliculus wall is made up of hepatocytes hepatocyte sinusoid Kupffer cell Bile canaliculus
Hepatic plate (cord) is one or two cells thick Between cells the bile canaliculi locate The bile canaliculus wall is made up of hepatocytes hepatocyte sinusoid Kupffer cell Bile canaliculus
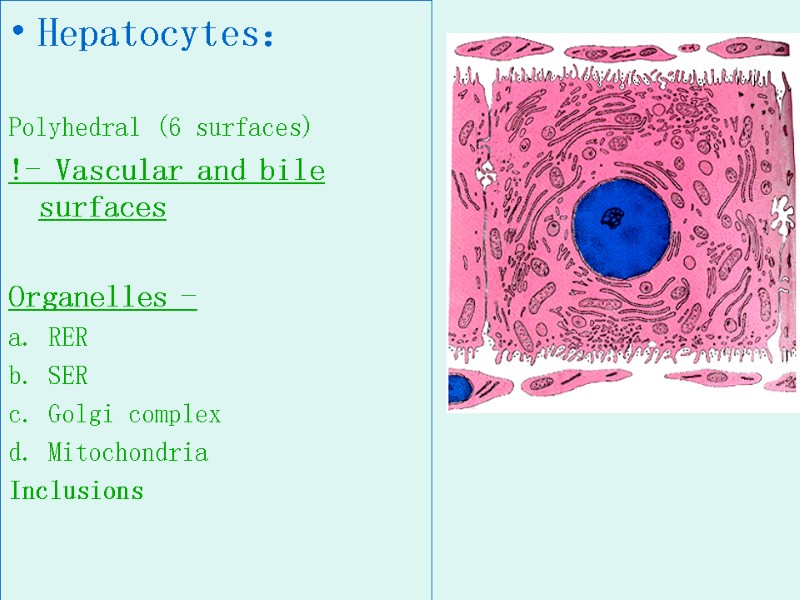
 Hepatocytes: Polyhedral (6 surfaces) !- Vascular and bile surfaces Organelles - a. RER b. SER c. Golgi complex d. Mitochondria Inclusions
Hepatocytes: Polyhedral (6 surfaces) !- Vascular and bile surfaces Organelles - a. RER b. SER c. Golgi complex d. Mitochondria Inclusions
 The bile canaliculus form a network that eventually empty into bile duct at the periphery of the lobule. h h b
The bile canaliculus form a network that eventually empty into bile duct at the periphery of the lobule. h h b
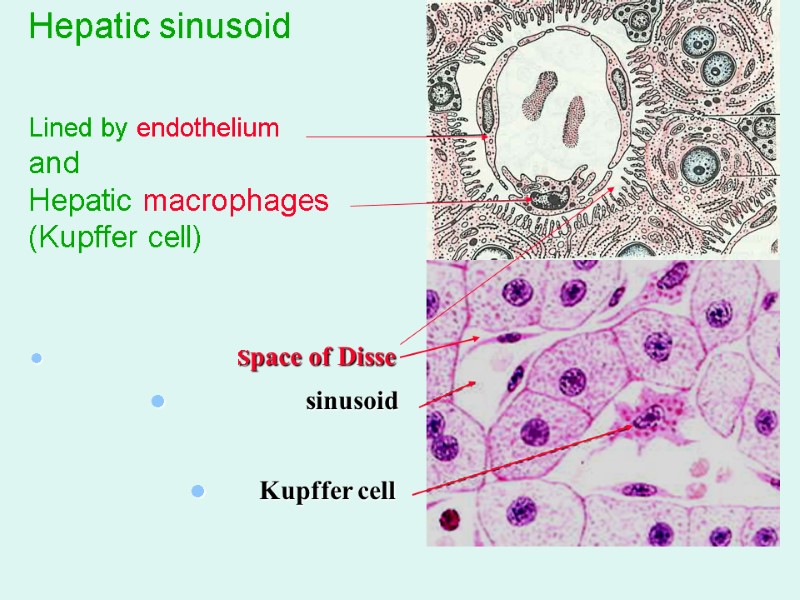
 Hepatic sinusoid Lined by endothelium and Hepatic macrophages (Kupffer cell) Space of Disse sinusoid Kupffer cell
Hepatic sinusoid Lined by endothelium and Hepatic macrophages (Kupffer cell) Space of Disse sinusoid Kupffer cell
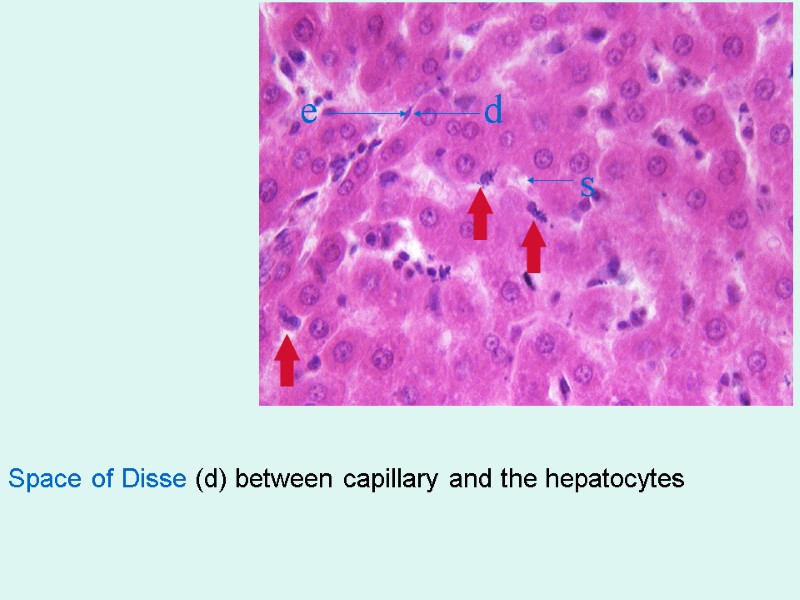
 Space of Disse (d) between capillary and the hepatocytes e d s
Space of Disse (d) between capillary and the hepatocytes e d s
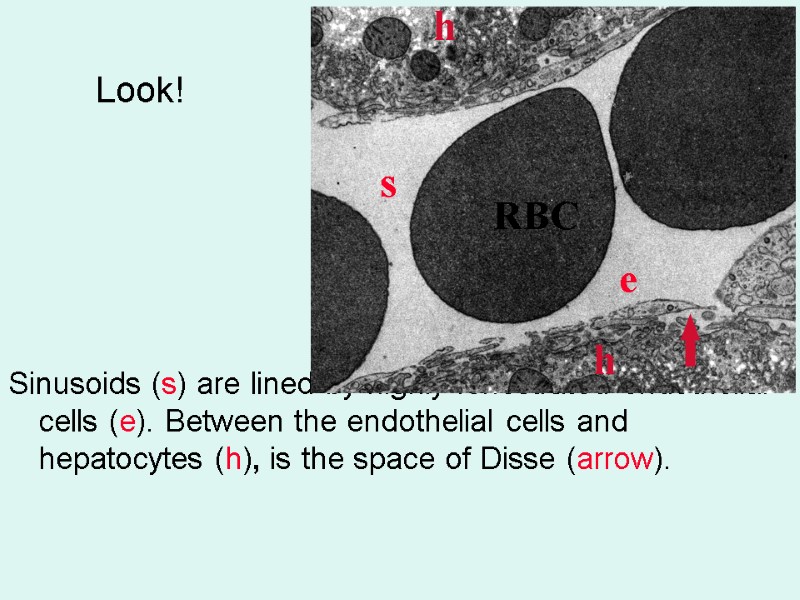
 Look! Sinusoids (s) are lined by highly fenestrated endothelial cells (e). Between the endothelial cells and hepatocytes (h), is the space of Disse (arrow). s e h h RBC
Look! Sinusoids (s) are lined by highly fenestrated endothelial cells (e). Between the endothelial cells and hepatocytes (h), is the space of Disse (arrow). s e h h RBC
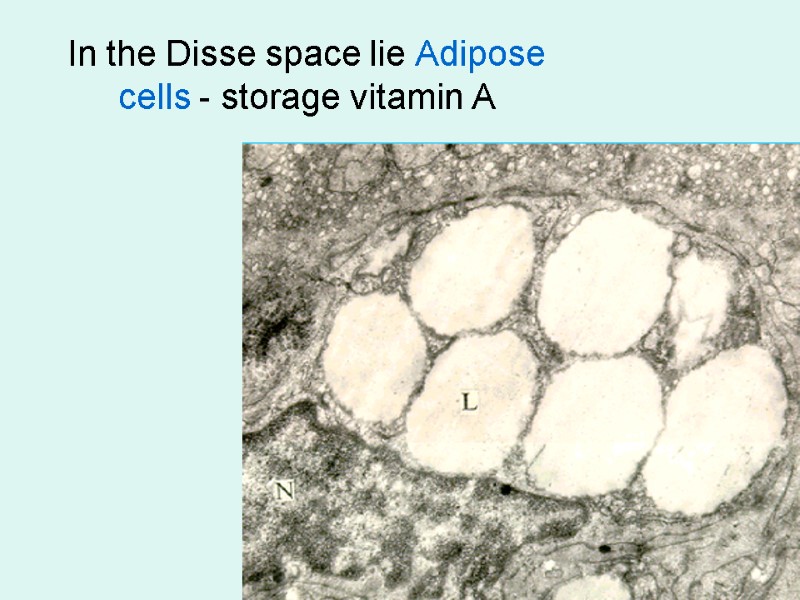
 In the Disse space lie Adipose cells - storage vitamin A
In the Disse space lie Adipose cells - storage vitamin A
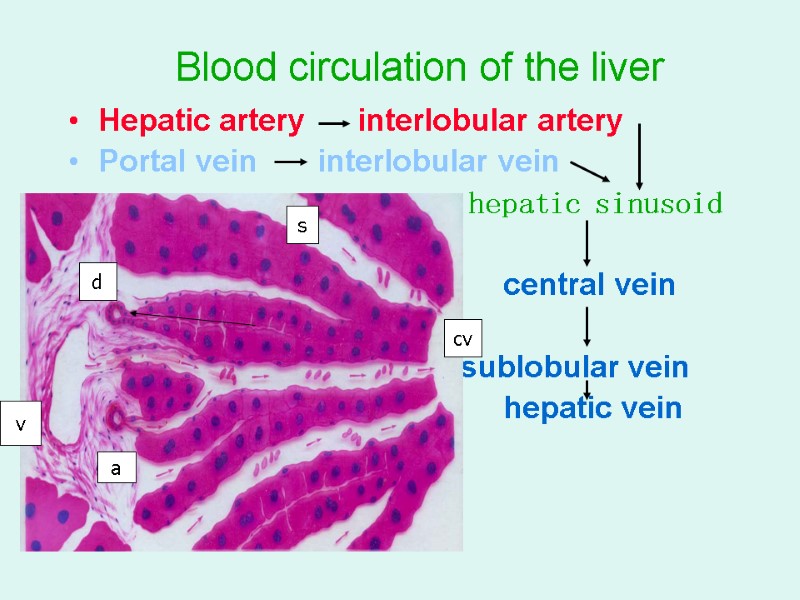
 Blood circulation of the liver Hepatic artery interlobular artery Portal vein interlobular vein hepatic sinusoid central vein cv sublobular vein hepatic vein v a d s cv
Blood circulation of the liver Hepatic artery interlobular artery Portal vein interlobular vein hepatic sinusoid central vein cv sublobular vein hepatic vein v a d s cv
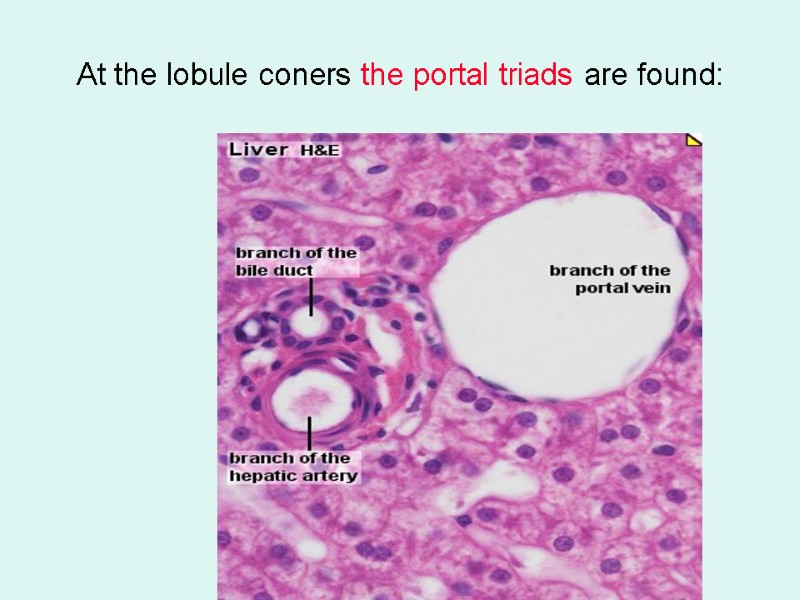
 At the lobule coners the portal triads are found:
At the lobule coners the portal triads are found:
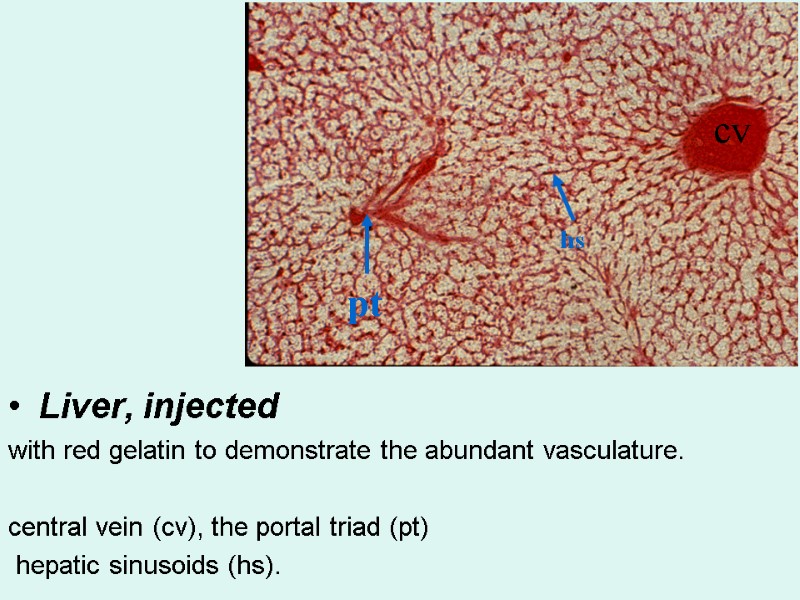
 Liver, injected with red gelatin to demonstrate the abundant vasculature. central vein (cv), the portal triad (pt) hepatic sinusoids (hs). cv pt hs
Liver, injected with red gelatin to demonstrate the abundant vasculature. central vein (cv), the portal triad (pt) hepatic sinusoids (hs). cv pt hs
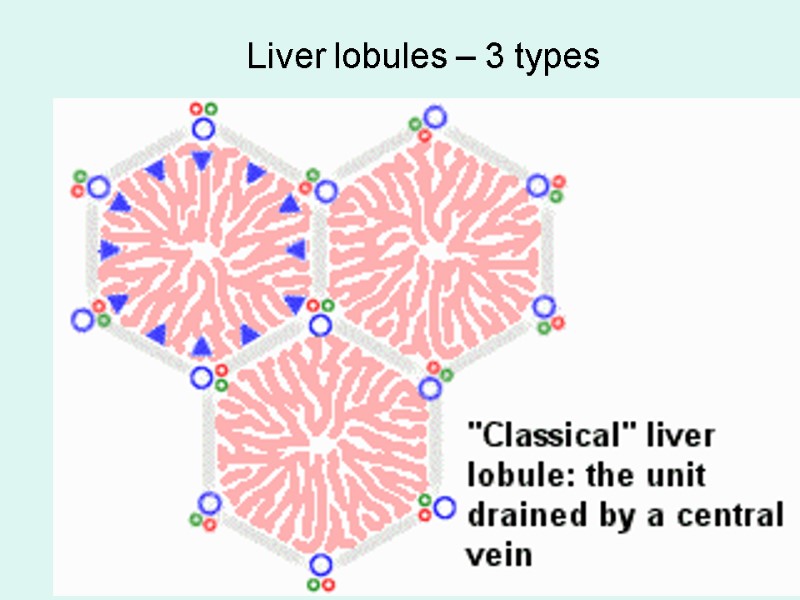
 Liver lobules – 3 types
Liver lobules – 3 types
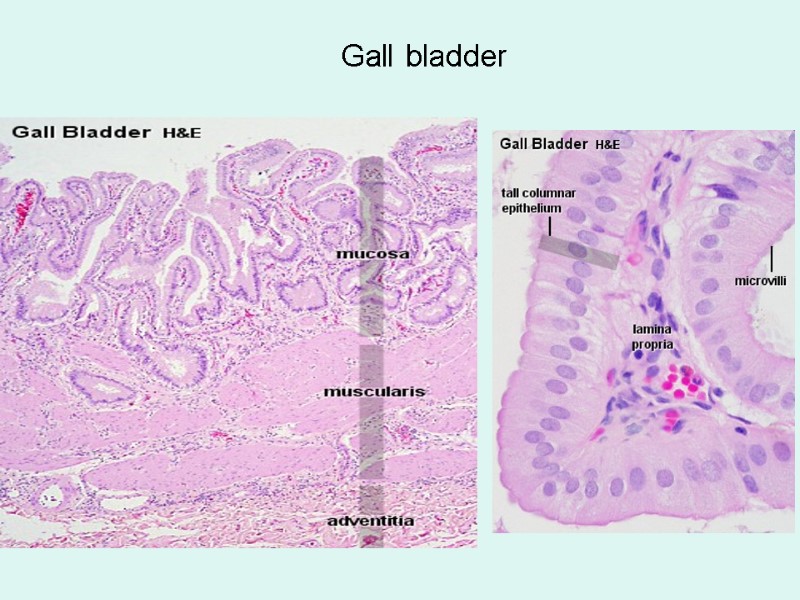
 Gall bladder
Gall bladder
 Pancreas -- mixed gland Functions: Exocrine Trypsinogen, pepsinogen, peptidase Amylase Lipase Deoxyribonuclease, ribonuclease Endocrine
Pancreas -- mixed gland Functions: Exocrine Trypsinogen, pepsinogen, peptidase Amylase Lipase Deoxyribonuclease, ribonuclease Endocrine
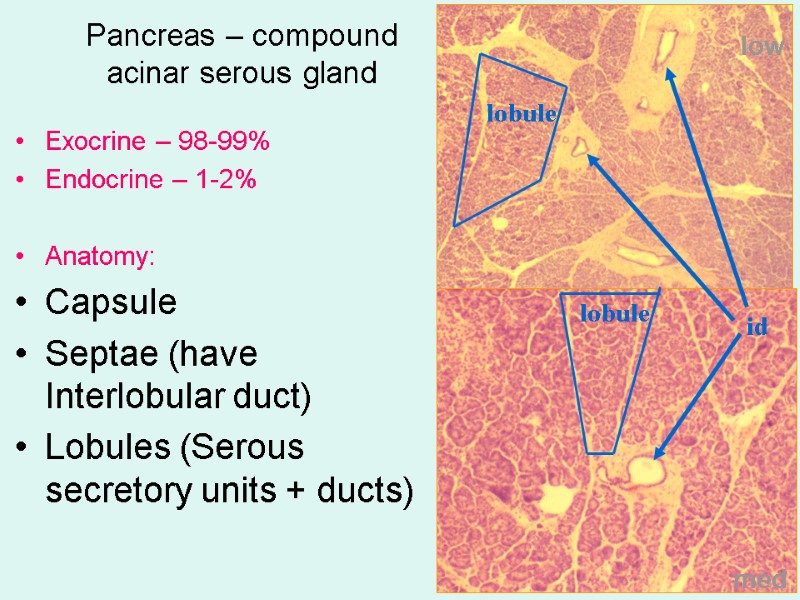
 Pancreas – compound acinar serous gland Exocrine – 98-99% Endocrine – 1-2% Anatomy: Capsule Septae (have Interlobular duct) Lobules (Serous secretory units + ducts) low med lobule id lobule
Pancreas – compound acinar serous gland Exocrine – 98-99% Endocrine – 1-2% Anatomy: Capsule Septae (have Interlobular duct) Lobules (Serous secretory units + ducts) low med lobule id lobule
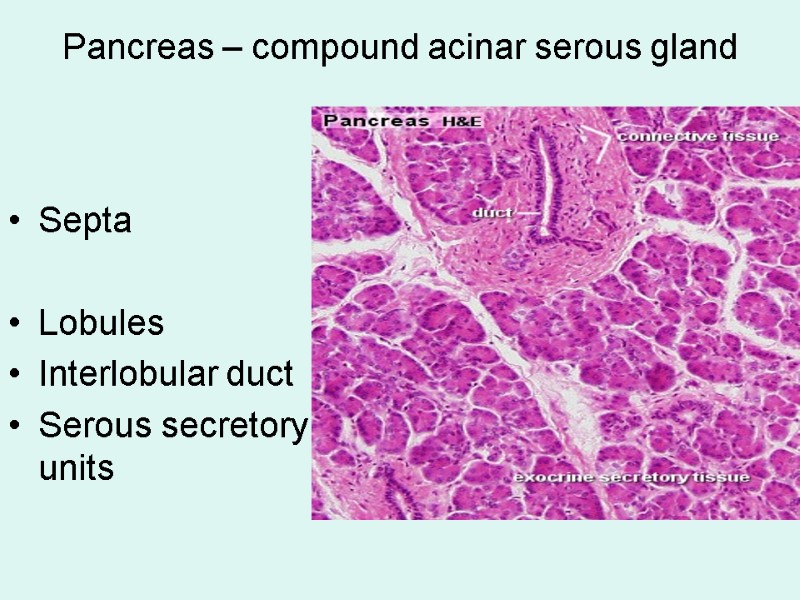
 Pancreas – compound acinar serous gland Septa Lobules Interlobular duct Serous secretory units
Pancreas – compound acinar serous gland Septa Lobules Interlobular duct Serous secretory units
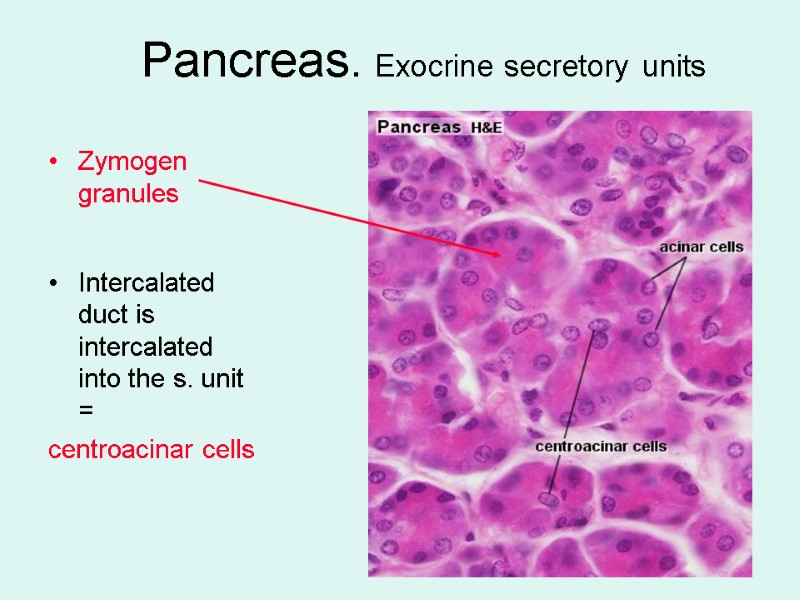
 Pancreas. Exocrine secretory units Zymogen granules Intercalated duct is intercalated into the s. unit = centroacinar cells
Pancreas. Exocrine secretory units Zymogen granules Intercalated duct is intercalated into the s. unit = centroacinar cells
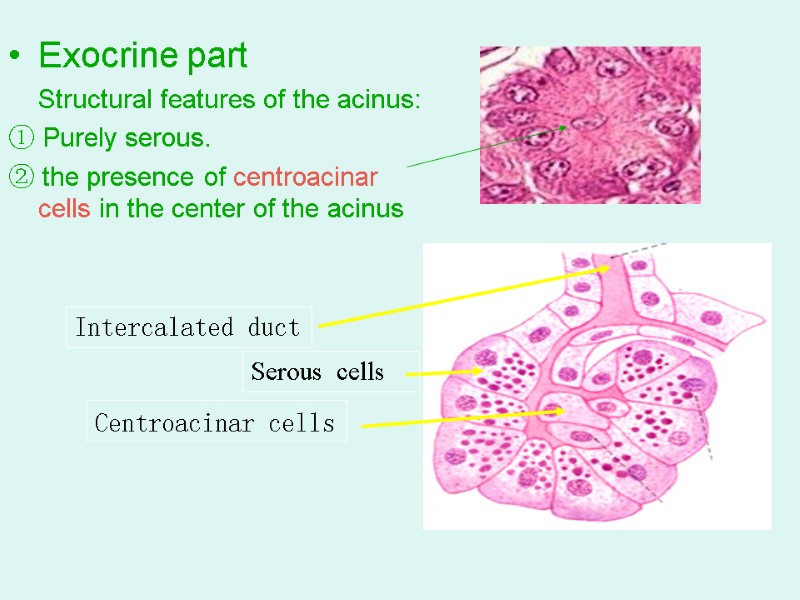
 Exocrine part Structural features of the acinus: ① Purely serous. ② the presence of centroacinar cells in the center of the acinus Centroacinar cells Serous cells Intercalated duct
Exocrine part Structural features of the acinus: ① Purely serous. ② the presence of centroacinar cells in the center of the acinus Centroacinar cells Serous cells Intercalated duct
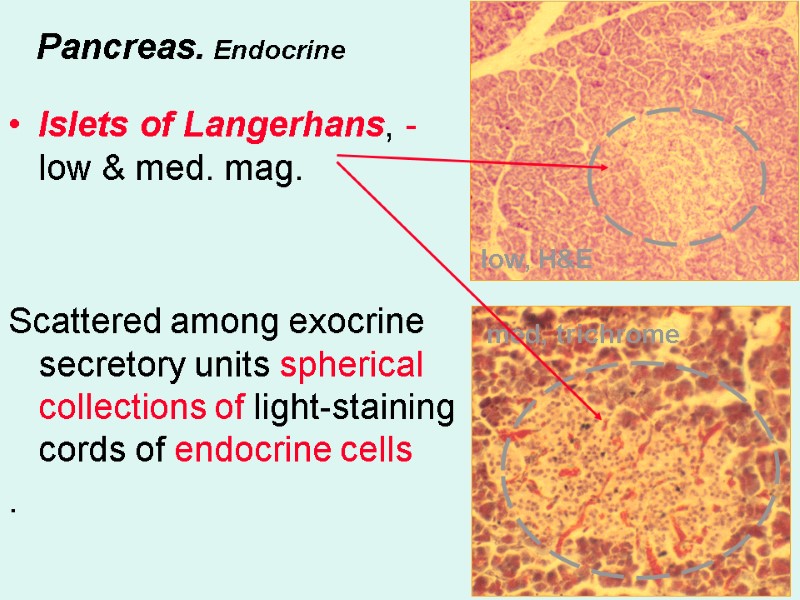
 Pancreas. Endocrine Islets of Langerhans, - low & med. mag. Scattered among exocrine secretory units spherical collections of light-staining cords of endocrine cells . low, H&E med, trichrome
Pancreas. Endocrine Islets of Langerhans, - low & med. mag. Scattered among exocrine secretory units spherical collections of light-staining cords of endocrine cells . low, H&E med, trichrome
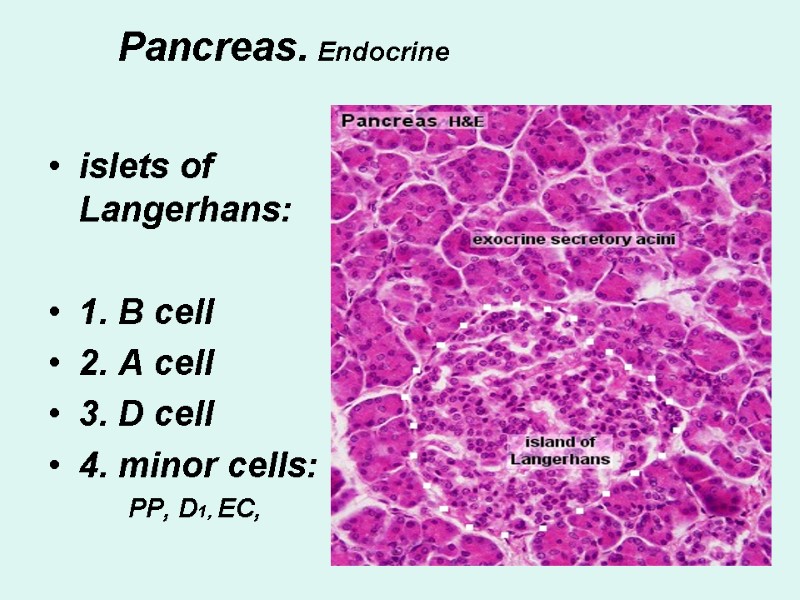
 Pancreas. Endocrine islets of Langerhans: 1. B cell 2. A cell 3. D cell 4. minor cells: PP, D1, EC,
Pancreas. Endocrine islets of Langerhans: 1. B cell 2. A cell 3. D cell 4. minor cells: PP, D1, EC,
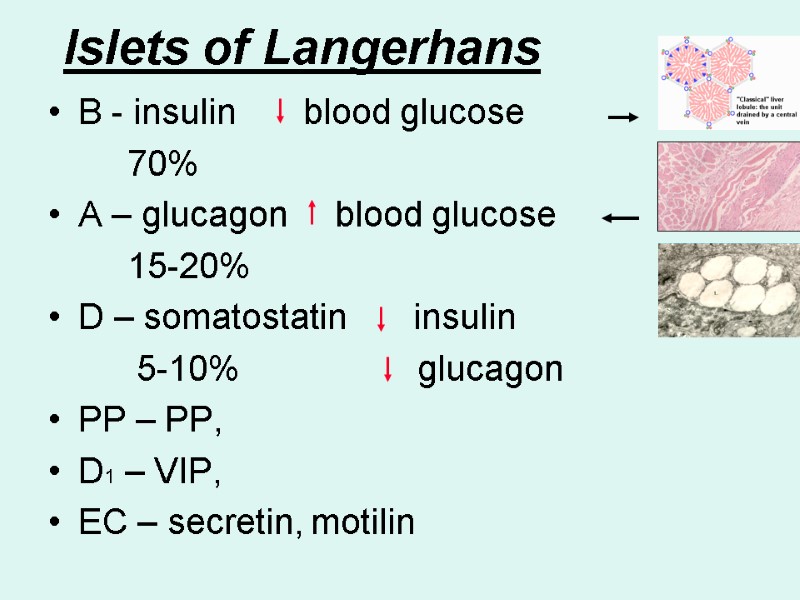
 Islets of Langerhans B - insulin blood glucose 70% A – glucagon blood glucose 15-20% D – somatostatin insulin 5-10% glucagon PP – PP, D1 – VIP, EC – secretin, motilin
Islets of Langerhans B - insulin blood glucose 70% A – glucagon blood glucose 15-20% D – somatostatin insulin 5-10% glucagon PP – PP, D1 – VIP, EC – secretin, motilin
 Control question Group, name 1. Compare Duodenum, Ileum and Colon Transversum 2. Liver: Blood supply. (What peculiar in the blood supply of the Liver?)
Control question Group, name 1. Compare Duodenum, Ileum and Colon Transversum 2. Liver: Blood supply. (What peculiar in the blood supply of the Liver?)

