DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1-st part General description The
















9882-digestive_system_part_1_med_2014.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1-st part
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1-st part
 General description The digestive tract is a long tube extending from oral cavity to the anus and associated glands. Maim functions are: ingestion, fragmentation, digestion, absorption of nutrients and elimination of waste products.
General description The digestive tract is a long tube extending from oral cavity to the anus and associated glands. Maim functions are: ingestion, fragmentation, digestion, absorption of nutrients and elimination of waste products.
 3 compartments: Anterior. Oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus Middle. Gastrointestinal tract Posterior. Last 1/3 rectum, anus
3 compartments: Anterior. Oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus Middle. Gastrointestinal tract Posterior. Last 1/3 rectum, anus
 + Embryogenesis
+ Embryogenesis
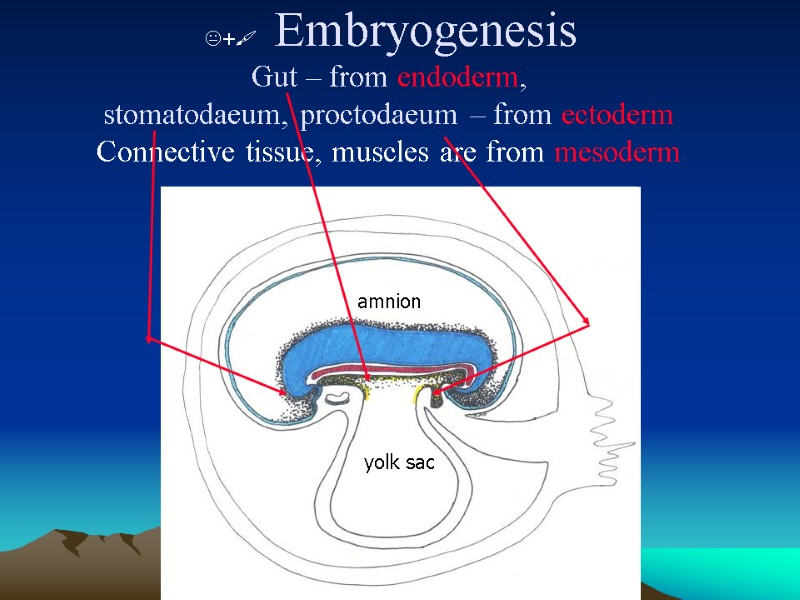
 + Embryogenesis Gut – from endoderm, stomatodaeum, proctodaeum – from ectoderm Connective tissue, muscles are from mesoderm amnion yolk sac
+ Embryogenesis Gut – from endoderm, stomatodaeum, proctodaeum – from ectoderm Connective tissue, muscles are from mesoderm amnion yolk sac
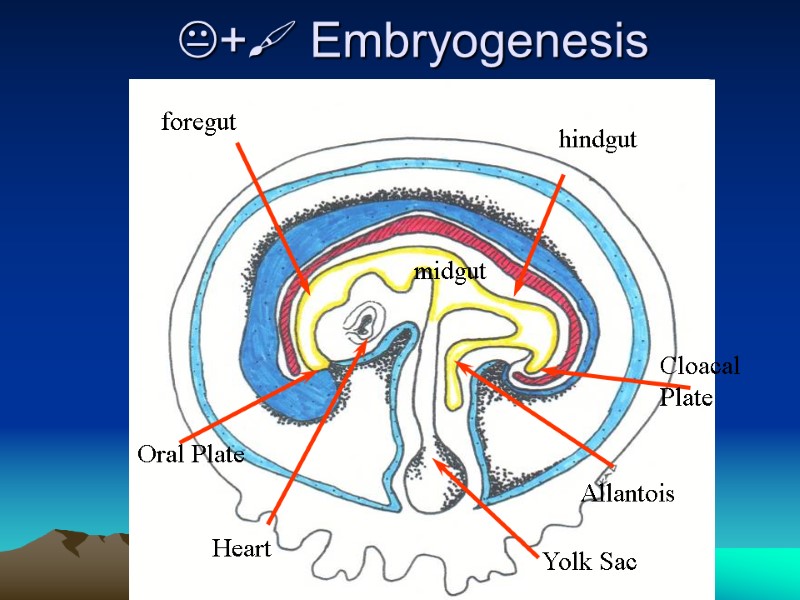
 + Embryogenesis Yolk Sac Oral Plate Cloacal Plate foregut midgut hindgut Allantois Heart +
+ Embryogenesis Yolk Sac Oral Plate Cloacal Plate foregut midgut hindgut Allantois Heart +
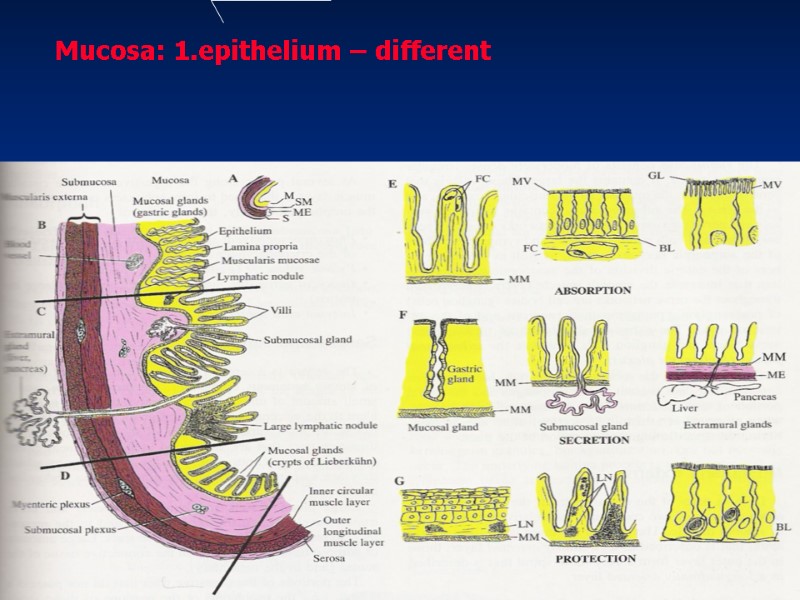
 General plan of structure FOUR principal membranes: Mucosa: a- Epithelium b- Lamina propria c -Muscularis mucosae Submucosa Muscularis externa Serosa or adventitia
General plan of structure FOUR principal membranes: Mucosa: a- Epithelium b- Lamina propria c -Muscularis mucosae Submucosa Muscularis externa Serosa or adventitia
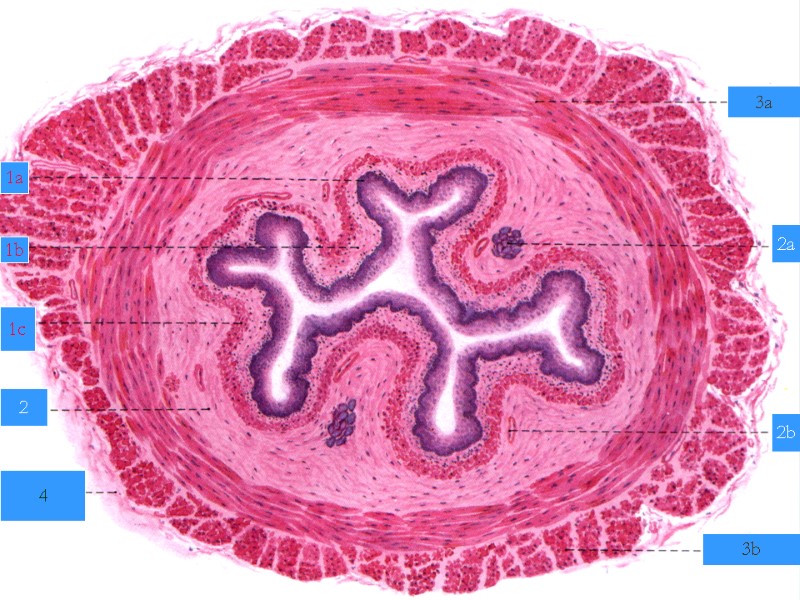
 1c 2 4 3a 2a 2b 3b 1a 1b
1c 2 4 3a 2a 2b 3b 1a 1b
 Mucosa: 1.epithelium – different
Mucosa: 1.epithelium – different
 2. lamina propria – connective tissue – has glands, lymphatic nodules, form core of villi 3. muscularis mucosae – smooth muscle tis. Submucosa - con. t. - big blood vessels, glands, nerve plexuses, lymphatic nodules, provides motility of mucosa, form FOLDS Muscularis externa – circular, longitudinal layers Serosa – peritoneum or adventitia – con. Tis.
2. lamina propria – connective tissue – has glands, lymphatic nodules, form core of villi 3. muscularis mucosae – smooth muscle tis. Submucosa - con. t. - big blood vessels, glands, nerve plexuses, lymphatic nodules, provides motility of mucosa, form FOLDS Muscularis externa – circular, longitudinal layers Serosa – peritoneum or adventitia – con. Tis.
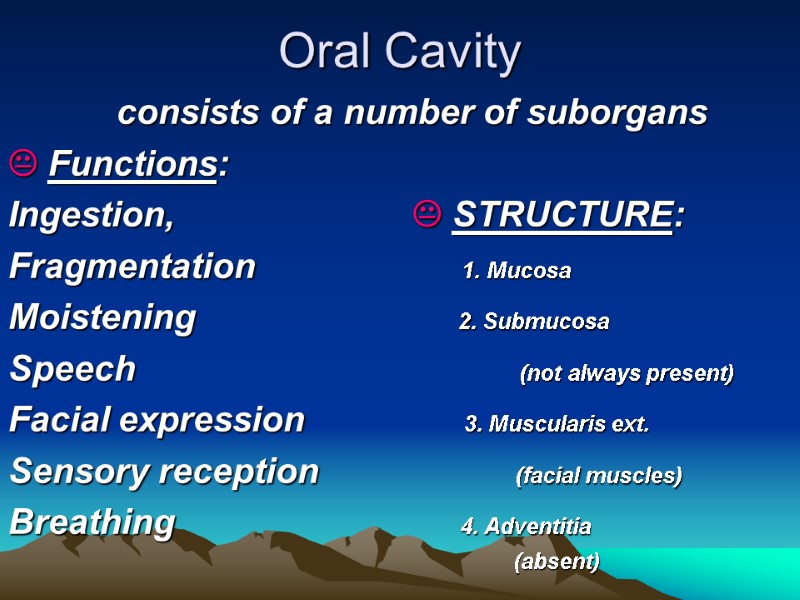
 Oral Cavity consists of a number of suborgans Functions: Ingestion, STRUCTURE: Fragmentation 1. Mucosa Moistening 2. Submucosa Speech (not always present) Facial expression 3. Muscularis ext. Sensory reception (facial muscles) Breathing 4. Adventitia (absent)
Oral Cavity consists of a number of suborgans Functions: Ingestion, STRUCTURE: Fragmentation 1. Mucosa Moistening 2. Submucosa Speech (not always present) Facial expression 3. Muscularis ext. Sensory reception (facial muscles) Breathing 4. Adventitia (absent)
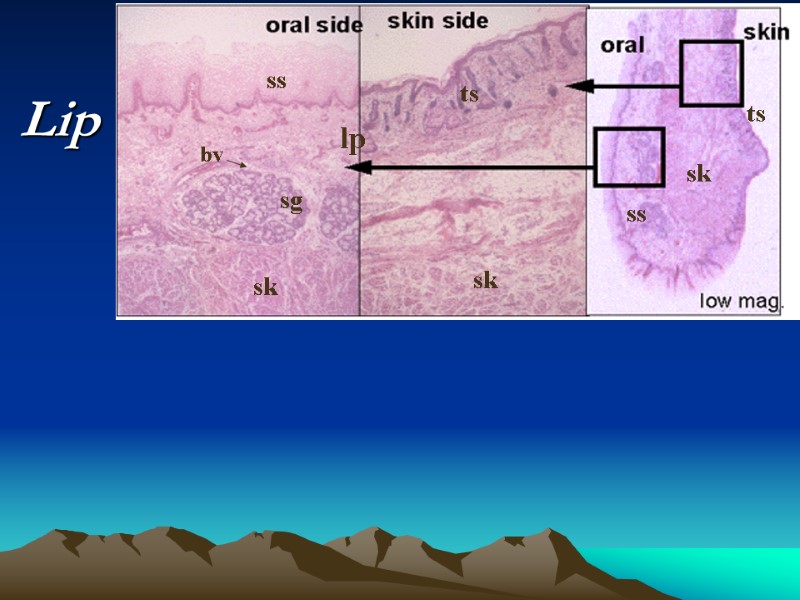
 Lip The outer surface of the lip is covered by thin skin. The inner surface (oral) is lined by a thick stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium. In the submucosal connective tissue lie minor salivary glands The transitional zone - red
Lip The outer surface of the lip is covered by thin skin. The inner surface (oral) is lined by a thick stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium. In the submucosal connective tissue lie minor salivary glands The transitional zone - red
 oral side skin side low mag. oral skin sk sk sk ts ts ss ss bv sg lp Lip
oral side skin side low mag. oral skin sk sk sk ts ts ss ss bv sg lp Lip
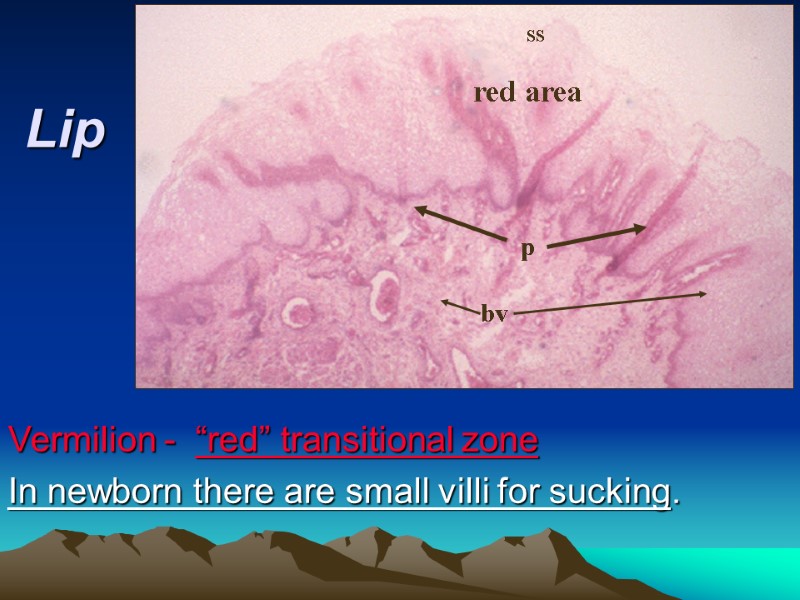
 Lip Vermilion - “red” transitional zone In newborn there are small villi for sucking. red area ss p bv
Lip Vermilion - “red” transitional zone In newborn there are small villi for sucking. red area ss p bv
 The cheek is similar to the lip.
The cheek is similar to the lip.
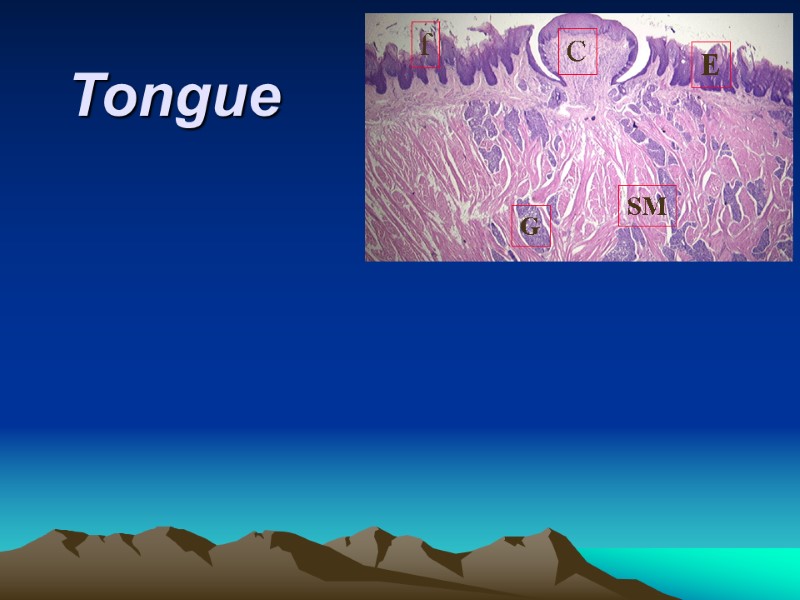
 Tongue E SM G C f
Tongue E SM G C f
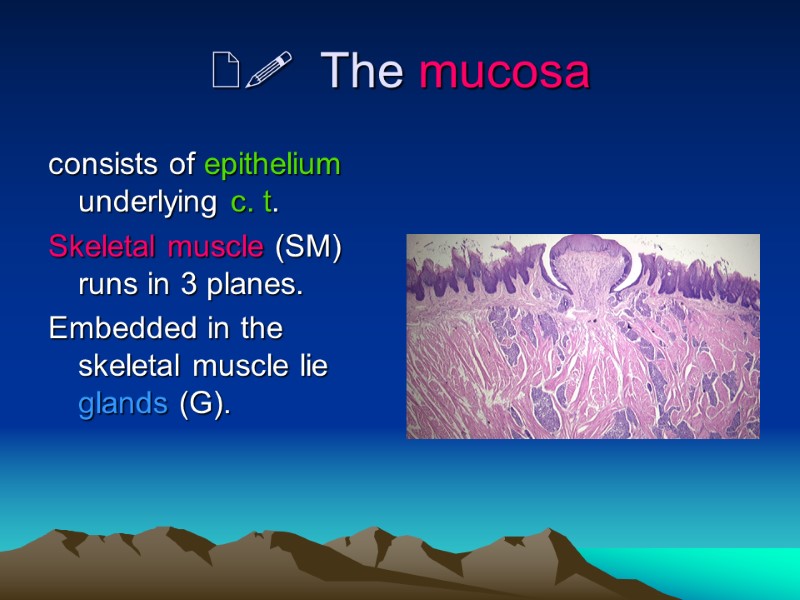
 The mucosa consists of epithelium underlying c. t. Skeletal muscle (SM) runs in 3 planes. Embedded in the skeletal muscle lie glands (G).
The mucosa consists of epithelium underlying c. t. Skeletal muscle (SM) runs in 3 planes. Embedded in the skeletal muscle lie glands (G).
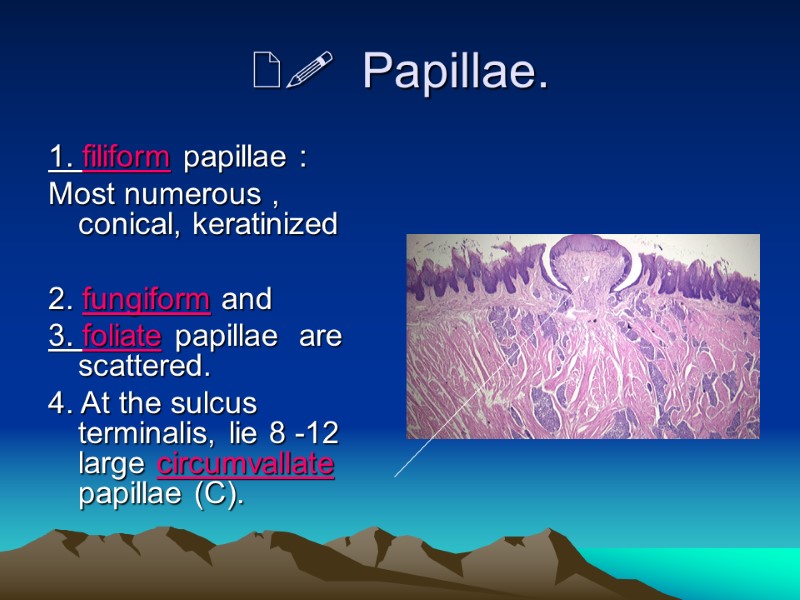
 Papillae. 1. filiform papillae : Most numerous , conical, keratinized 2. fungiform and 3. foliate papillae are scattered. 4. At the sulcus terminalis, lie 8 -12 large circumvallate papillae (C).
Papillae. 1. filiform papillae : Most numerous , conical, keratinized 2. fungiform and 3. foliate papillae are scattered. 4. At the sulcus terminalis, lie 8 -12 large circumvallate papillae (C).
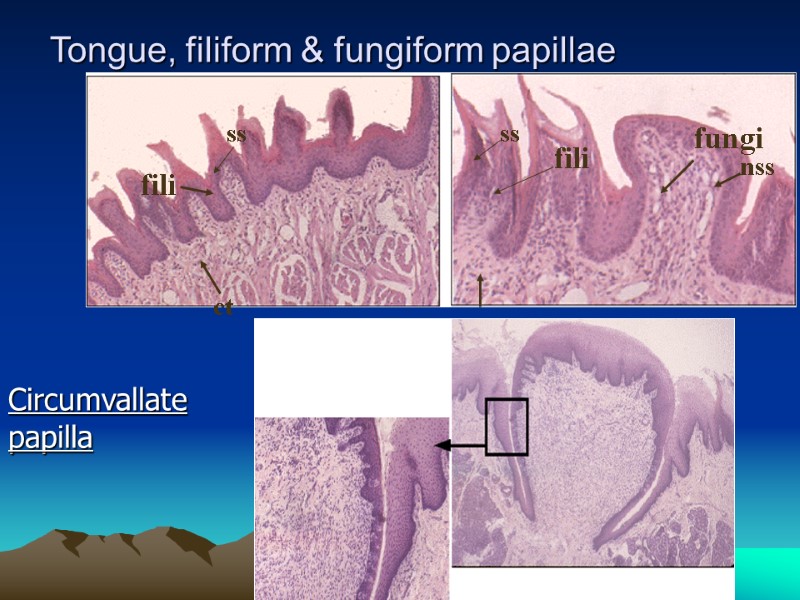
 Tongue, filiform & fungiform papillae fili fili ct ct ss ss fungi nss Circumvallate papilla
Tongue, filiform & fungiform papillae fili fili ct ct ss ss fungi nss Circumvallate papilla
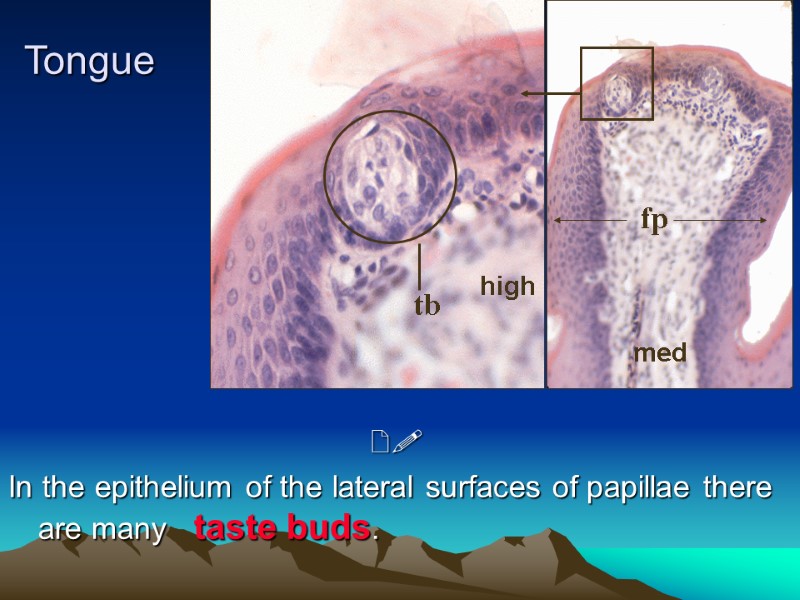
 Tongue In the epithelium of the lateral surfaces of papillae there are many taste buds. high med fp tb
Tongue In the epithelium of the lateral surfaces of papillae there are many taste buds. high med fp tb
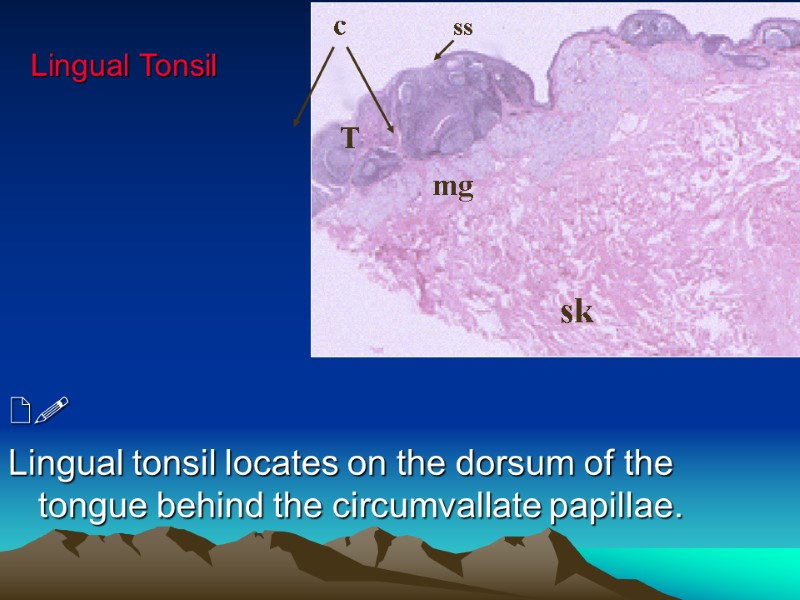
 Lingual Tonsil Lingual tonsil locates on the dorsum of the tongue behind the circumvallate papillae. ss c mg sk T
Lingual Tonsil Lingual tonsil locates on the dorsum of the tongue behind the circumvallate papillae. ss c mg sk T
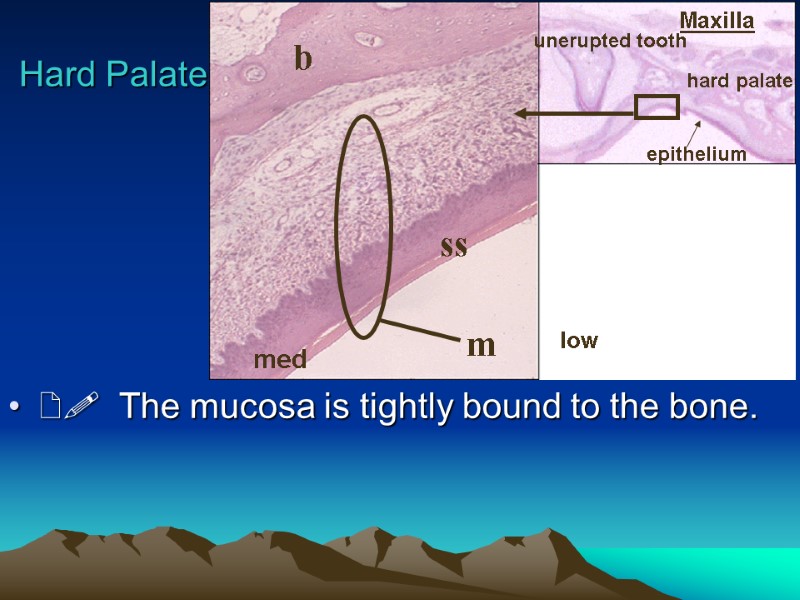
 The mucosa is tightly bound to the bone. Hard Palate Maxilla unerupted tooth hard palate epithelium m b ss low med
The mucosa is tightly bound to the bone. Hard Palate Maxilla unerupted tooth hard palate epithelium m b ss low med
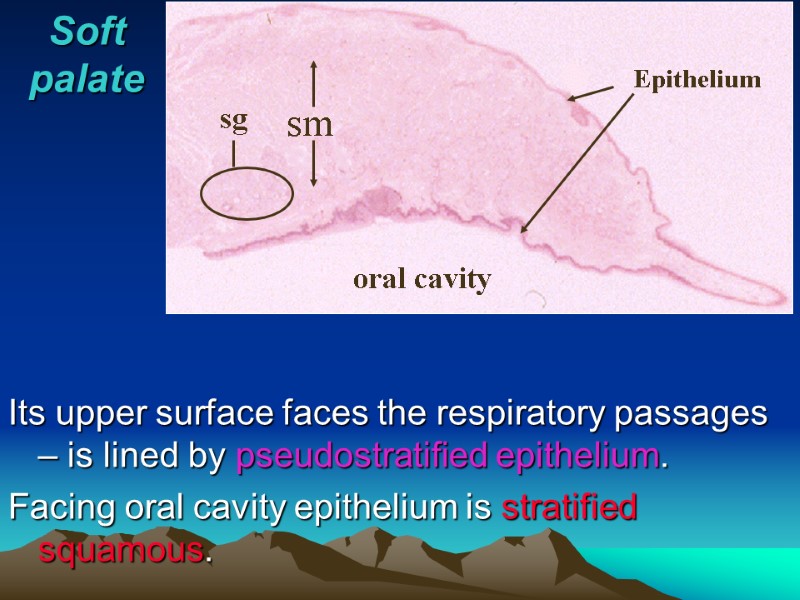
 Soft palate sm Epithelium sg oral cavity Its upper surface faces the respiratory passages – is lined by pseudostratified epithelium. Facing oral cavity epithelium is stratified squamous.
Soft palate sm Epithelium sg oral cavity Its upper surface faces the respiratory passages – is lined by pseudostratified epithelium. Facing oral cavity epithelium is stratified squamous.
 TOOTH
TOOTH
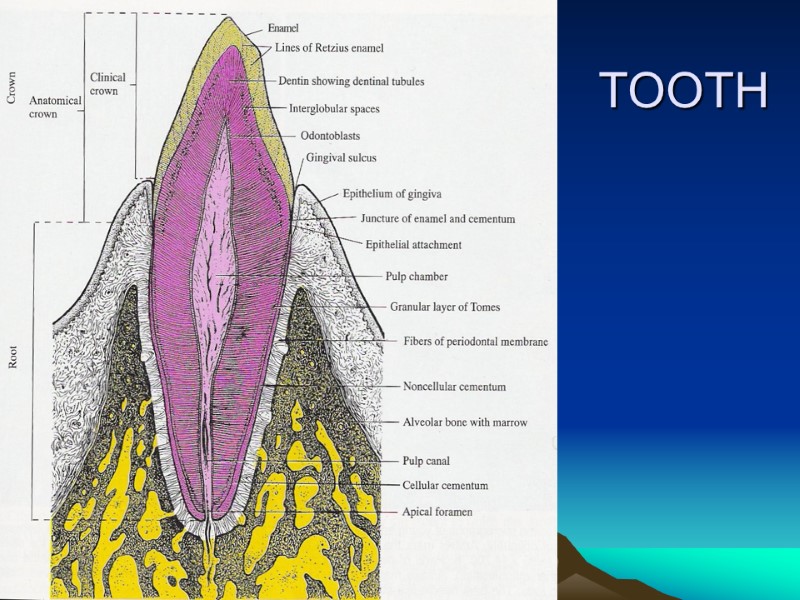
 TOOTH Enamel Dentine Cementum Pulp Periodontal ligament
TOOTH Enamel Dentine Cementum Pulp Periodontal ligament
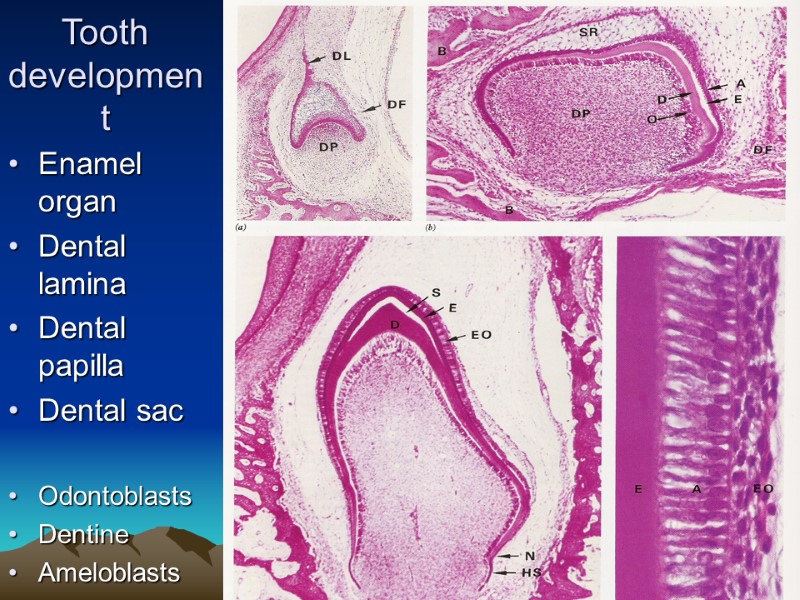
 Tooth development Enamel organ Dental lamina Dental papilla Dental sac Odontoblasts Dentine Ameloblasts Enamel Sheath of Hertwig
Tooth development Enamel organ Dental lamina Dental papilla Dental sac Odontoblasts Dentine Ameloblasts Enamel Sheath of Hertwig
 SALIVARY GLANDS Saliva: water, mucus, amylase, lysozyme, antibodies, ions 2 groups: I. Large salivary glands 3 pairs: parotid, submandibular, sublingual II. Minor salivary glands
SALIVARY GLANDS Saliva: water, mucus, amylase, lysozyme, antibodies, ions 2 groups: I. Large salivary glands 3 pairs: parotid, submandibular, sublingual II. Minor salivary glands
 General structure Compound branched acinar or acino-tubular glands Connective tissue capsule send septae and divide on Lobules Lobules contain secretory units and small ducts Interlobular connective tissue has ducts and vessels
General structure Compound branched acinar or acino-tubular glands Connective tissue capsule send septae and divide on Lobules Lobules contain secretory units and small ducts Interlobular connective tissue has ducts and vessels
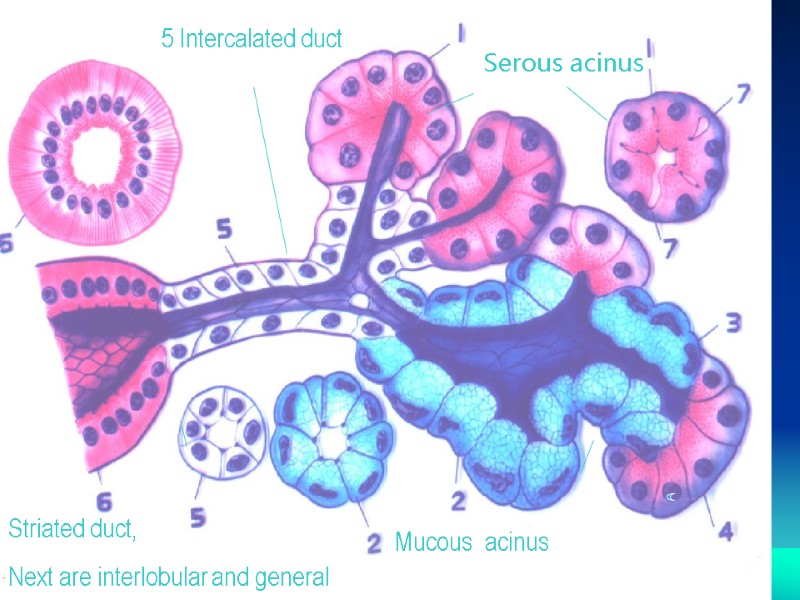
 5 Intercalated duct Striated duct, Next are interlobular and general Mucous acinus Serous acinus
5 Intercalated duct Striated duct, Next are interlobular and general Mucous acinus Serous acinus
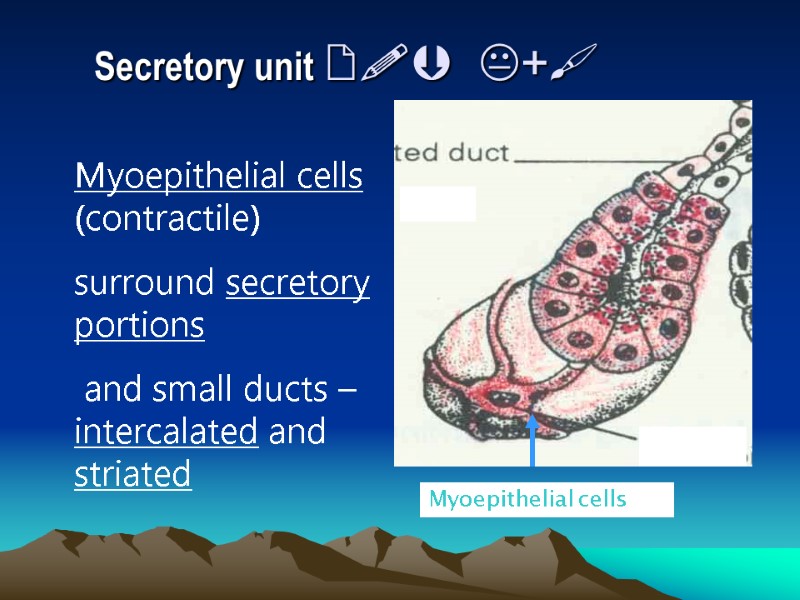
 Secretory unit + Myoepithelial cells (contractile) surround secretory portions and small ducts – intercalated and striated Myoepithelial cells Nucleus
Secretory unit + Myoepithelial cells (contractile) surround secretory portions and small ducts – intercalated and striated Myoepithelial cells Nucleus
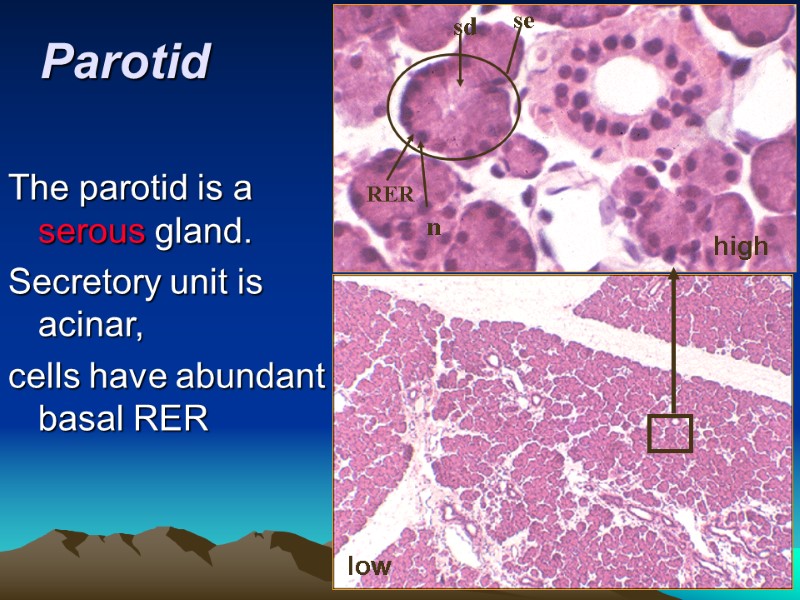
 Parotid high low low se n RER sd The parotid is a serous gland. Secretory unit is acinar, cells have abundant basal RER
Parotid high low low se n RER sd The parotid is a serous gland. Secretory unit is acinar, cells have abundant basal RER
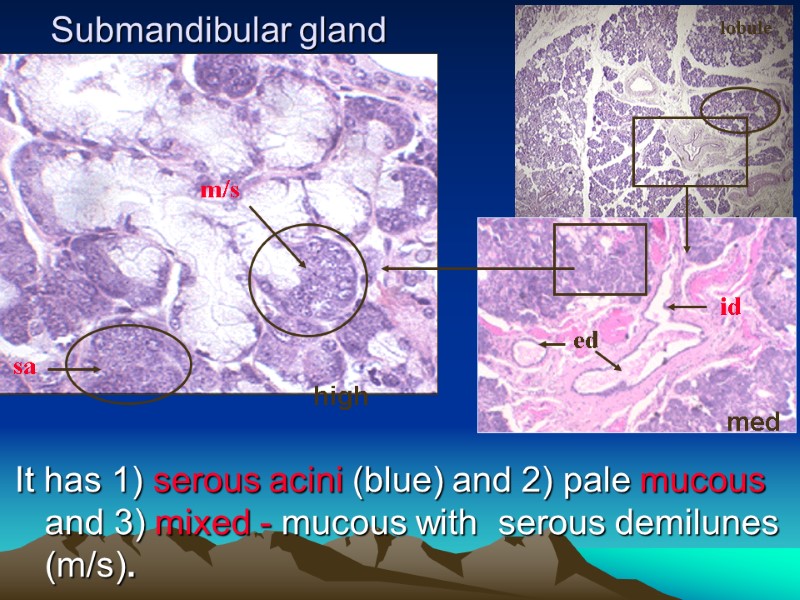
 Submandibular gland It has 1) serous acini (blue) and 2) pale mucous and 3) mixed - mucous with serous demilunes (m/s). low high med lobule id ed sa m/s
Submandibular gland It has 1) serous acini (blue) and 2) pale mucous and 3) mixed - mucous with serous demilunes (m/s). low high med lobule id ed sa m/s
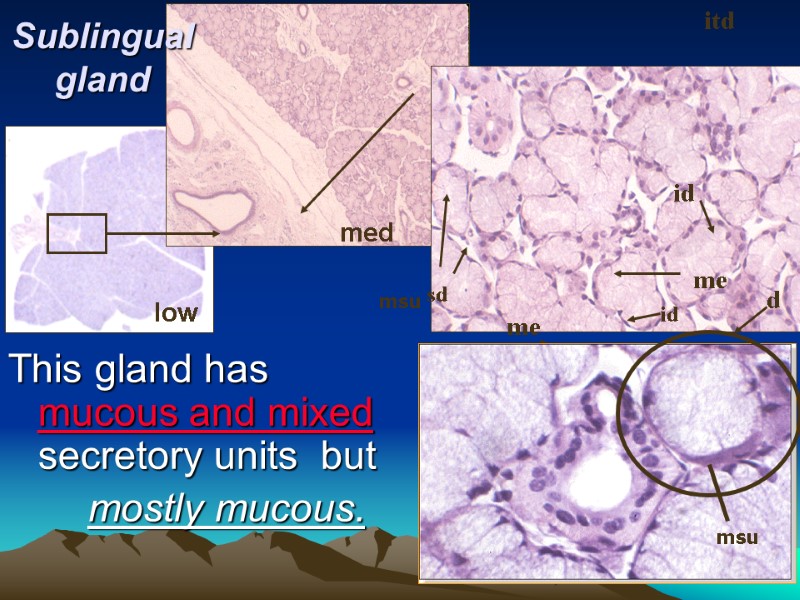
 low med Sublingual gland This gland has mucous and mixed secretory units but mostly mucous. high me me d id itd n id sd msu msu
low med Sublingual gland This gland has mucous and mixed secretory units but mostly mucous. high me me d id itd n id sd msu msu
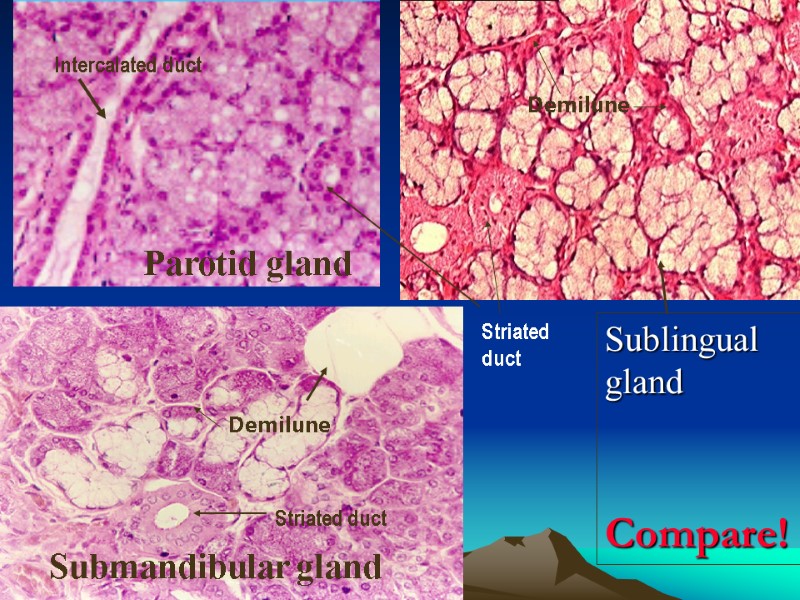
 sublingual gland Submandibular gland Striated duct demilune Demilune Intercalated duct Parotid gland Sublingual gland Compare! Demilune Striated duct
sublingual gland Submandibular gland Striated duct demilune Demilune Intercalated duct Parotid gland Sublingual gland Compare! Demilune Striated duct
 Esophagus
Esophagus
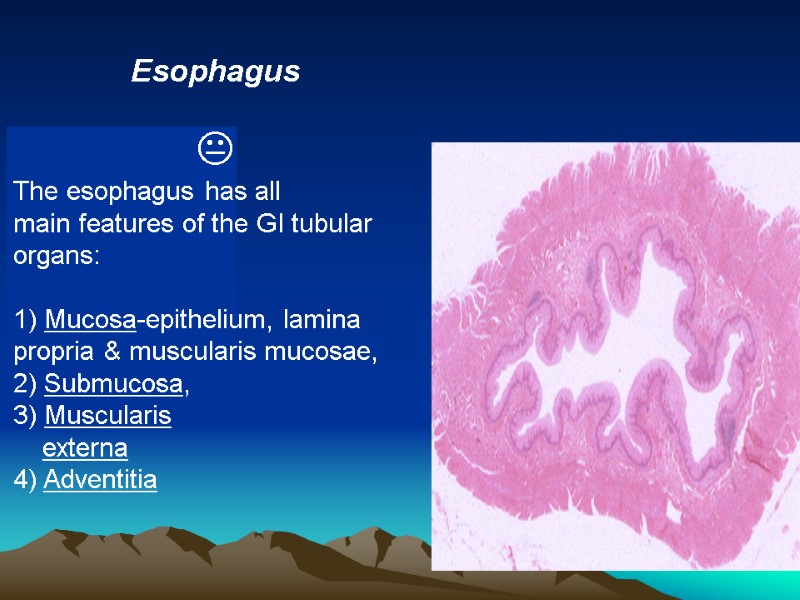
 Esophagus The esophagus has all main features of the GI tubular organs: 1) Mucosa-epithelium, lamina propria & muscularis mucosae, 2) Submucosa, 3) Muscularis externa 4) Adventitia
Esophagus The esophagus has all main features of the GI tubular organs: 1) Mucosa-epithelium, lamina propria & muscularis mucosae, 2) Submucosa, 3) Muscularis externa 4) Adventitia
 Esophagus 1. Epithelium is stratified squamous nonkeratinized 2. 6-7 longitudinal folds. 3. The muscularis externa: The upper 1/3rd is composed of skeletal muscle; the lower 1/3rd - smooth muscle; the middle 1/3rd shows a blending of the two varieties of muscle.
Esophagus 1. Epithelium is stratified squamous nonkeratinized 2. 6-7 longitudinal folds. 3. The muscularis externa: The upper 1/3rd is composed of skeletal muscle; the lower 1/3rd - smooth muscle; the middle 1/3rd shows a blending of the two varieties of muscle.
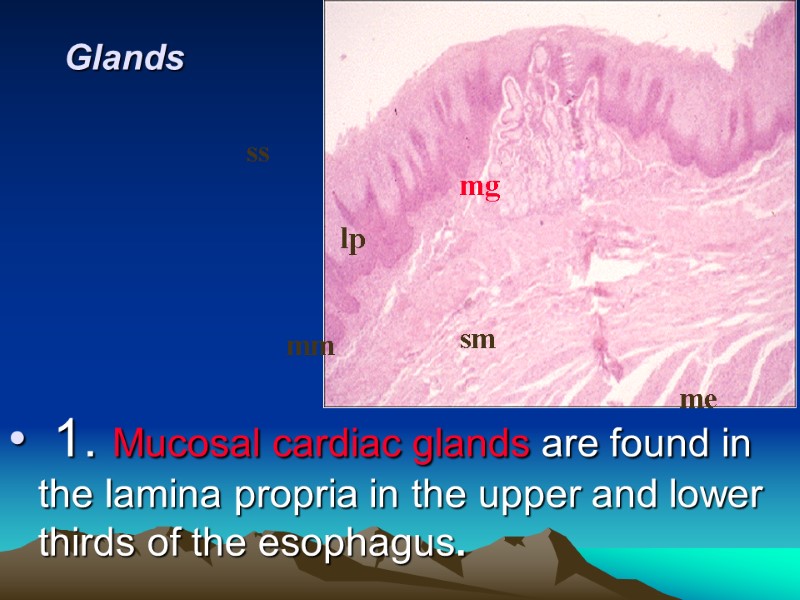
 Glands 1. Mucosal cardiac glands are found in the lamina propria in the upper and lower thirds of the esophagus. mg lp ss mm sm me
Glands 1. Mucosal cardiac glands are found in the lamina propria in the upper and lower thirds of the esophagus. mg lp ss mm sm me
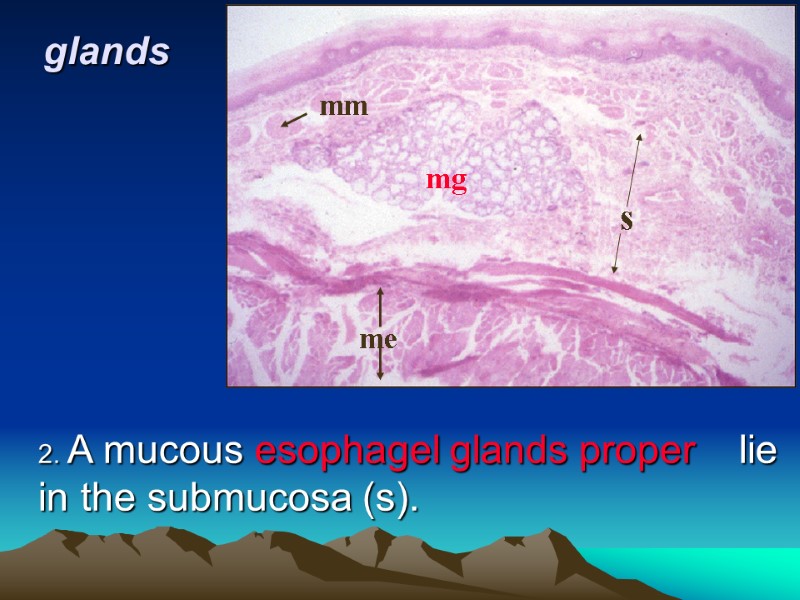
 glands 2. A mucous esophagel glands proper lie in the submucosa (s). mg s mm me
glands 2. A mucous esophagel glands proper lie in the submucosa (s). mg s mm me
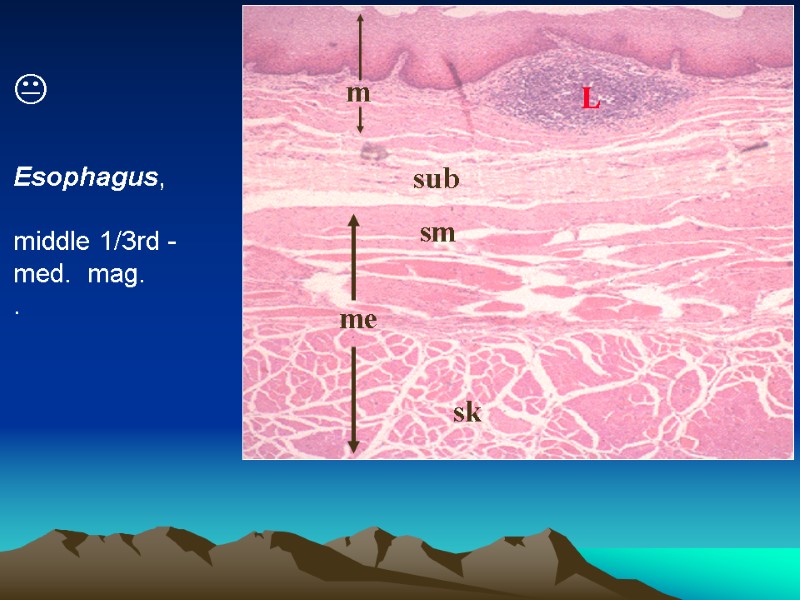
 L sub me sm sk m Esophagus, middle 1/3rd - med. mag. .
L sub me sm sk m Esophagus, middle 1/3rd - med. mag. .
 Nerve supply The enteric nervous system lie in 1- submucosa (Meissner’s plexus) and 2 - in the muscularis externa (Auerbach’s plexus)
Nerve supply The enteric nervous system lie in 1- submucosa (Meissner’s plexus) and 2 - in the muscularis externa (Auerbach’s plexus)
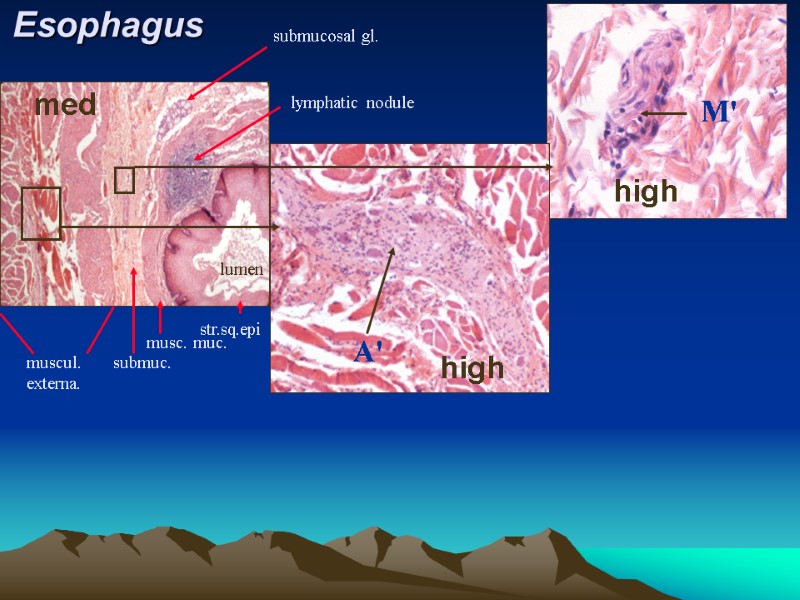
 Esophagus M' A' str.sq.epi musc. muc. submuc. muscul. externa. submucosal gl. lymphatic nodule lumen med high high
Esophagus M' A' str.sq.epi musc. muc. submuc. muscul. externa. submucosal gl. lymphatic nodule lumen med high high
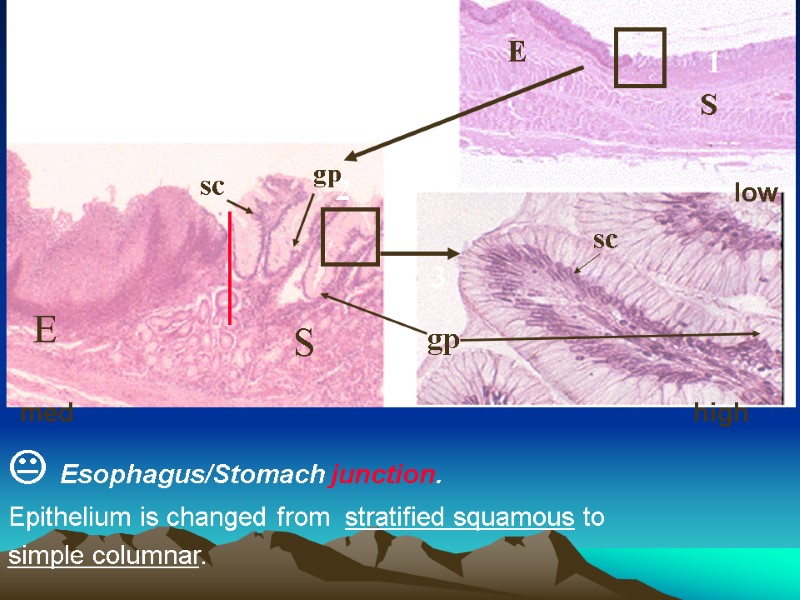
 Esophagus/Stomach junction. Epithelium is changed from stratified squamous to simple columnar. 1 2 3 E E S S sc sc gp gp low med high
Esophagus/Stomach junction. Epithelium is changed from stratified squamous to simple columnar. 1 2 3 E E S S sc sc gp gp low med high
 Stomach - general The process of digestion essentially begins in the stomach; little absorption and excretion also occur here. The stomach is composed of a mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa & serosa. The mucosal lining is a simple columnar secretory epithelium – produce viscous mucous. The mucus protects the lining from stomach acids. Folds (rugae), gastric pits (invaginations lined by epithelium), mammilated areas.
Stomach - general The process of digestion essentially begins in the stomach; little absorption and excretion also occur here. The stomach is composed of a mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa & serosa. The mucosal lining is a simple columnar secretory epithelium – produce viscous mucous. The mucus protects the lining from stomach acids. Folds (rugae), gastric pits (invaginations lined by epithelium), mammilated areas.
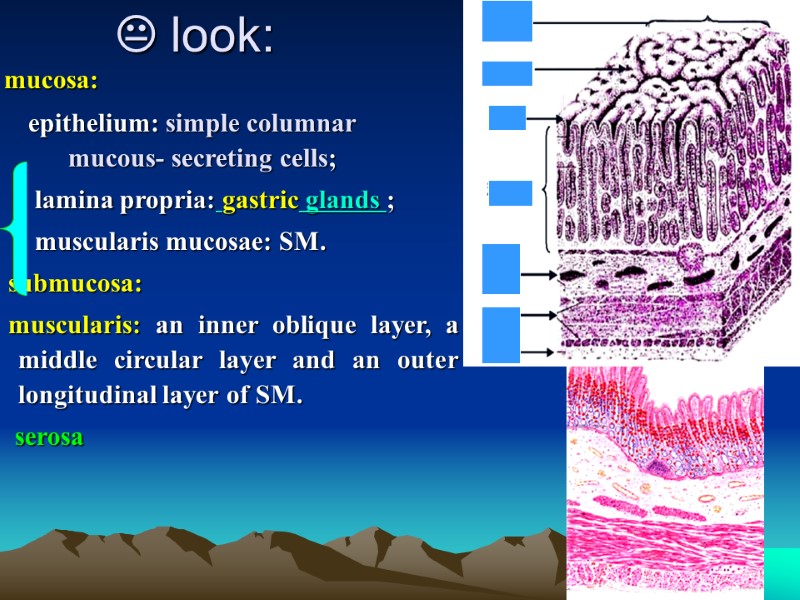
 look: mucosa: epithelium: simple columnar mucous- secreting cells; lamina propria: gastric glands ; muscularis mucosae: SM. submucosa: muscularis: an inner oblique layer, a middle circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer of SM. serosa
look: mucosa: epithelium: simple columnar mucous- secreting cells; lamina propria: gastric glands ; muscularis mucosae: SM. submucosa: muscularis: an inner oblique layer, a middle circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer of SM. serosa
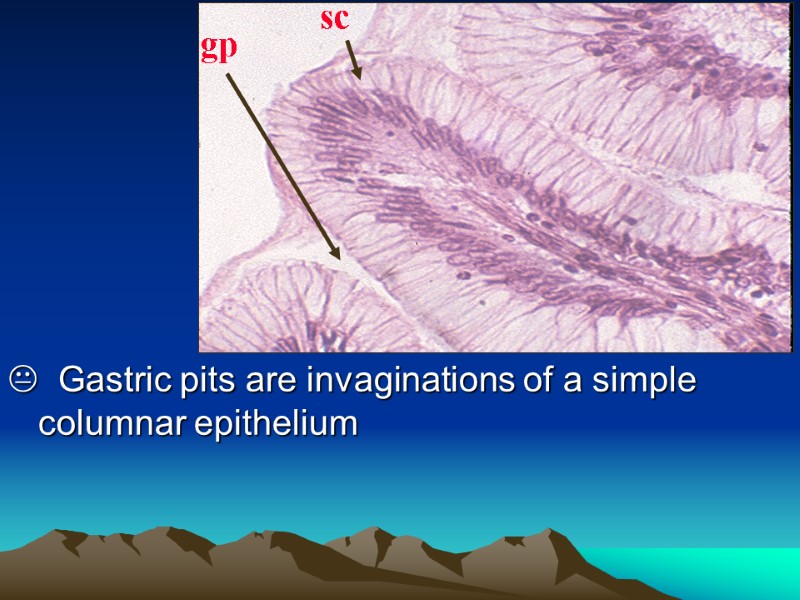
 Gastric pits are invaginations of a simple columnar epithelium gp sc
Gastric pits are invaginations of a simple columnar epithelium gp sc
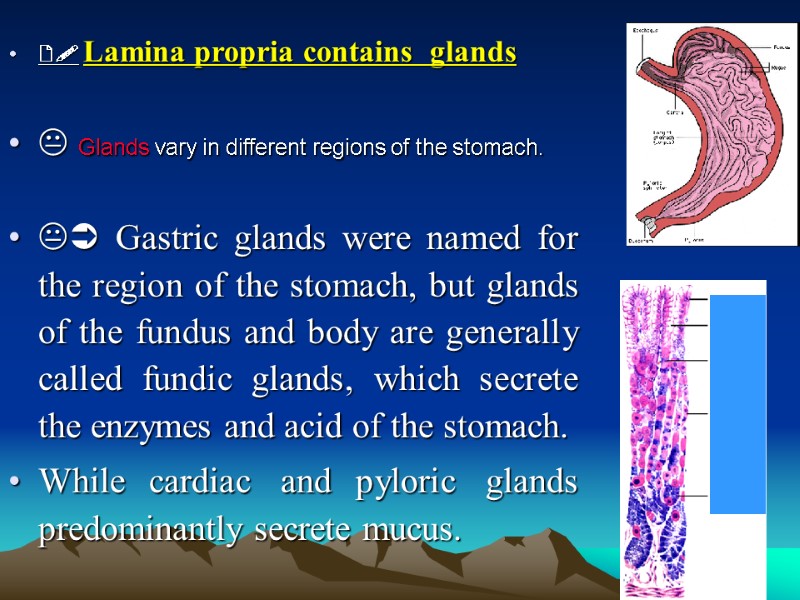
 Lamina propria contains glands Glands vary in different regions of the stomach. Gastric glands were named for the region of the stomach, but glands of the fundus and body are generally called fundic glands, which secrete the enzymes and acid of the stomach. While cardiac and pyloric glands predominantly secrete mucus.
Lamina propria contains glands Glands vary in different regions of the stomach. Gastric glands were named for the region of the stomach, but glands of the fundus and body are generally called fundic glands, which secrete the enzymes and acid of the stomach. While cardiac and pyloric glands predominantly secrete mucus.
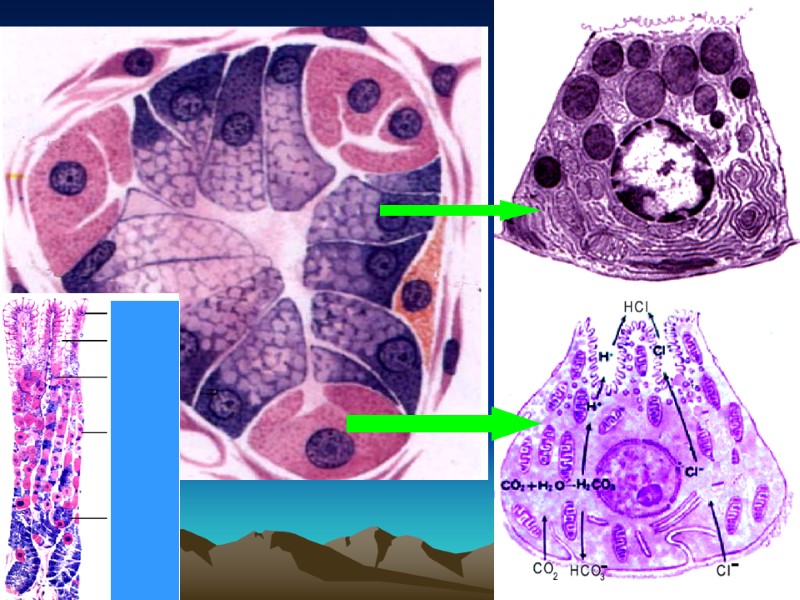
 The fundic glands are simple tubular. They contain 4 cell types: chief, parietal, mucous neck cells (stem), endocrine cells
The fundic glands are simple tubular. They contain 4 cell types: chief, parietal, mucous neck cells (stem), endocrine cells
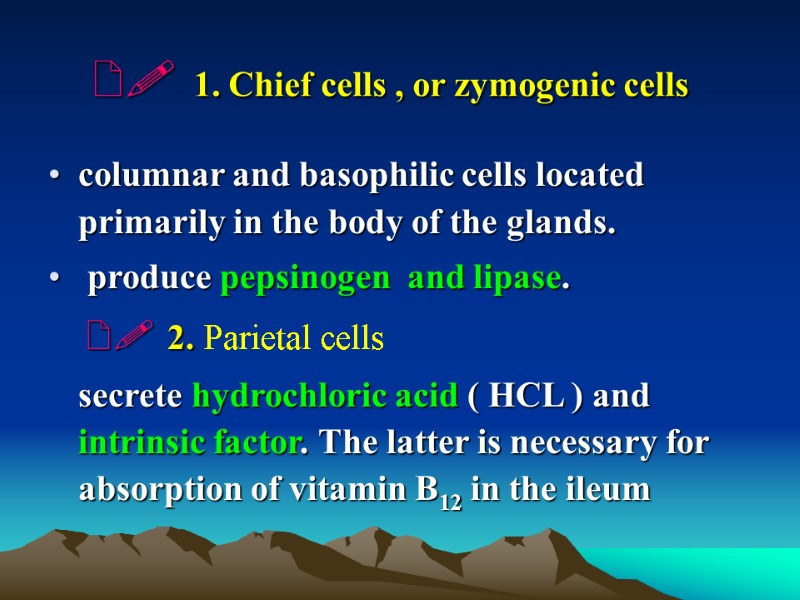
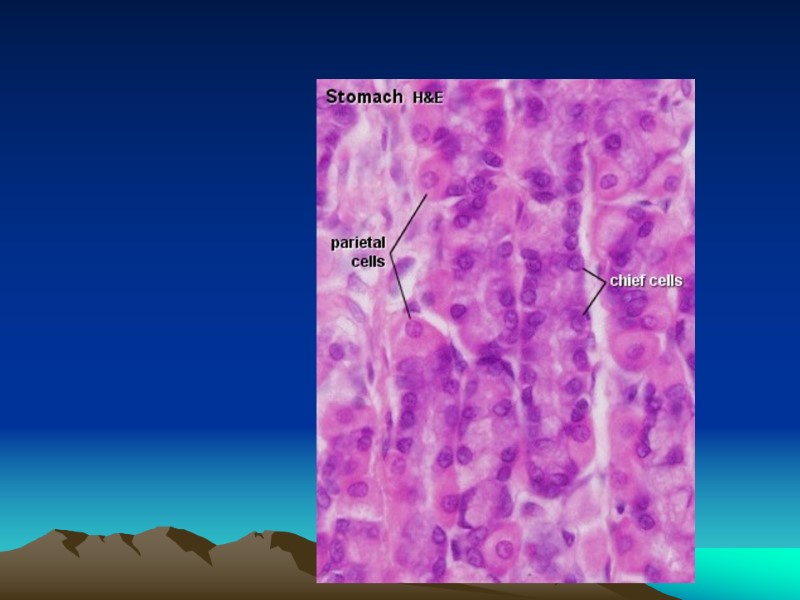
 1. Chief cells , or zymogenic cells columnar and basophilic cells located primarily in the body of the glands. produce pepsinogen and lipase. 2. Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid ( HCL ) and intrinsic factor. The latter is necessary for absorption of vitamin B12 in the ileum
1. Chief cells , or zymogenic cells columnar and basophilic cells located primarily in the body of the glands. produce pepsinogen and lipase. 2. Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid ( HCL ) and intrinsic factor. The latter is necessary for absorption of vitamin B12 in the ileum

 3. Enteroendocrine cells (APUD) 20 different types 4 principal hormones: Gastrin Secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK), gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
3. Enteroendocrine cells (APUD) 20 different types 4 principal hormones: Gastrin Secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK), gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
 Pernicious anemia follows the absence of parietal cells (f.e. loss of epithelium due to gastric ulcer) Disturbance of different cells may call the different pathology. Digestion of different substances begins in different regions.
Pernicious anemia follows the absence of parietal cells (f.e. loss of epithelium due to gastric ulcer) Disturbance of different cells may call the different pathology. Digestion of different substances begins in different regions.
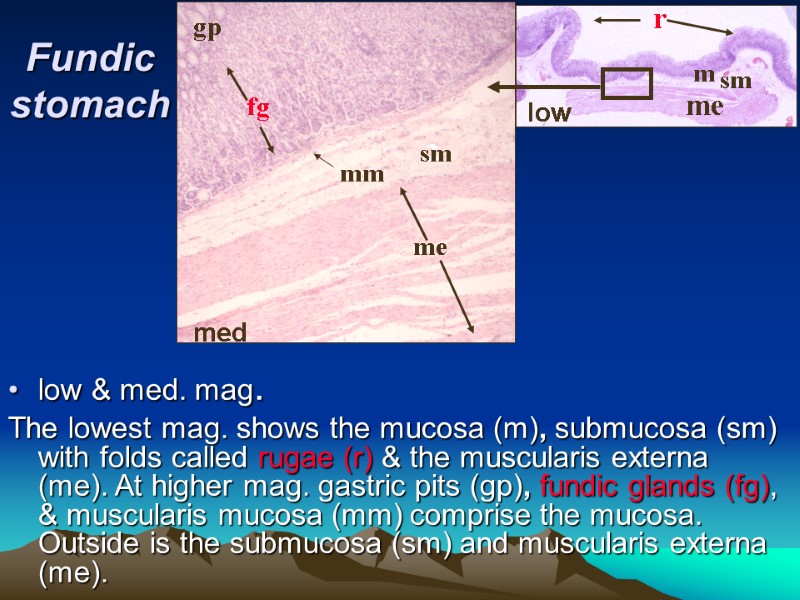
 Fundic stomach low & med. mag. The lowest mag. shows the mucosa (m), submucosa (sm) with folds called rugae (r) & the muscularis externa (me). At higher mag. gastric pits (gp), fundic glands (fg), & muscularis mucosa (mm) comprise the mucosa. Outside is the submucosa (sm) and muscularis externa (me). 2 m sm r me gp fg mm sm me low med
Fundic stomach low & med. mag. The lowest mag. shows the mucosa (m), submucosa (sm) with folds called rugae (r) & the muscularis externa (me). At higher mag. gastric pits (gp), fundic glands (fg), & muscularis mucosa (mm) comprise the mucosa. Outside is the submucosa (sm) and muscularis externa (me). 2 m sm r me gp fg mm sm me low med
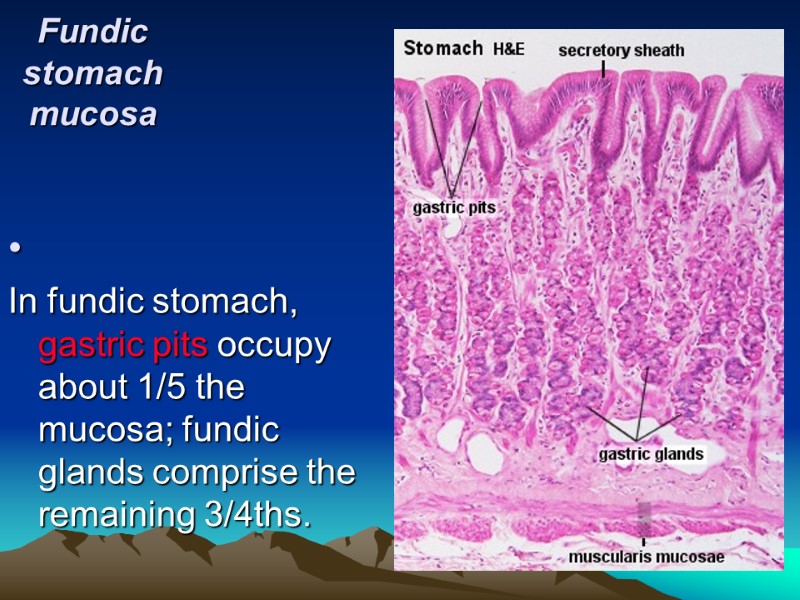
 Fundic stomach mucosa In fundic stomach, gastric pits occupy about 1/5 the mucosa; fundic glands comprise the remaining 3/4ths. gastric pit fundic gland Isthmus Neck Base
Fundic stomach mucosa In fundic stomach, gastric pits occupy about 1/5 the mucosa; fundic glands comprise the remaining 3/4ths. gastric pit fundic gland Isthmus Neck Base

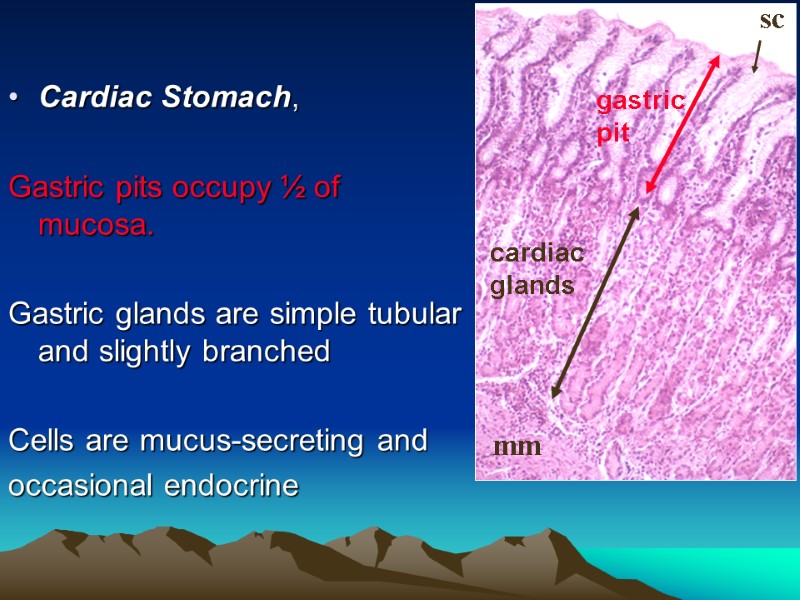
 Cardiac Stomach, Gastric pits occupy ½ of mucosa. Gastric glands are simple tubular and slightly branched Cells are mucus-secreting and occasional endocrine gastric pit cardiac glands sc mm
Cardiac Stomach, Gastric pits occupy ½ of mucosa. Gastric glands are simple tubular and slightly branched Cells are mucus-secreting and occasional endocrine gastric pit cardiac glands sc mm
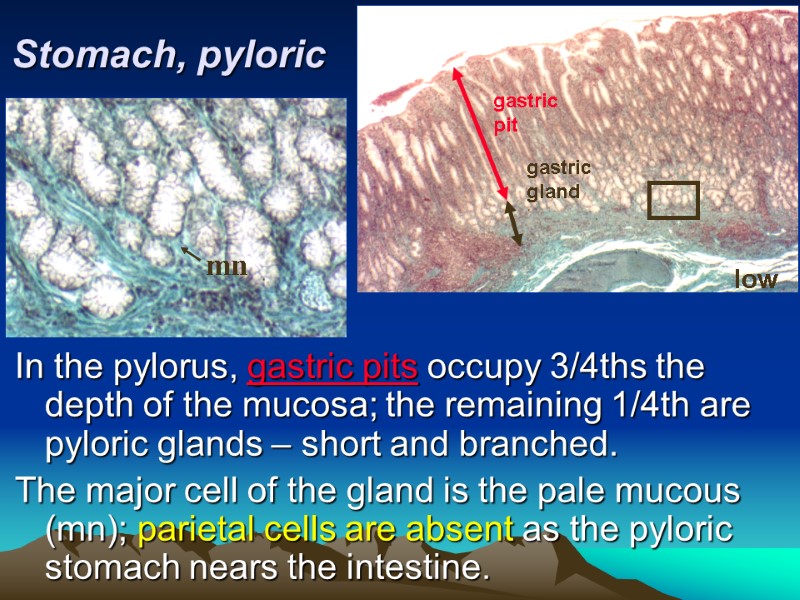
 Stomach, pyloric In the pylorus, gastric pits occupy 3/4ths the depth of the mucosa; the remaining 1/4th are pyloric glands – short and branched. The major cell of the gland is the pale mucous (mn); parietal cells are absent as the pyloric stomach nears the intestine. gastric pit gastric gland mn low
Stomach, pyloric In the pylorus, gastric pits occupy 3/4ths the depth of the mucosa; the remaining 1/4th are pyloric glands – short and branched. The major cell of the gland is the pale mucous (mn); parietal cells are absent as the pyloric stomach nears the intestine. gastric pit gastric gland mn low
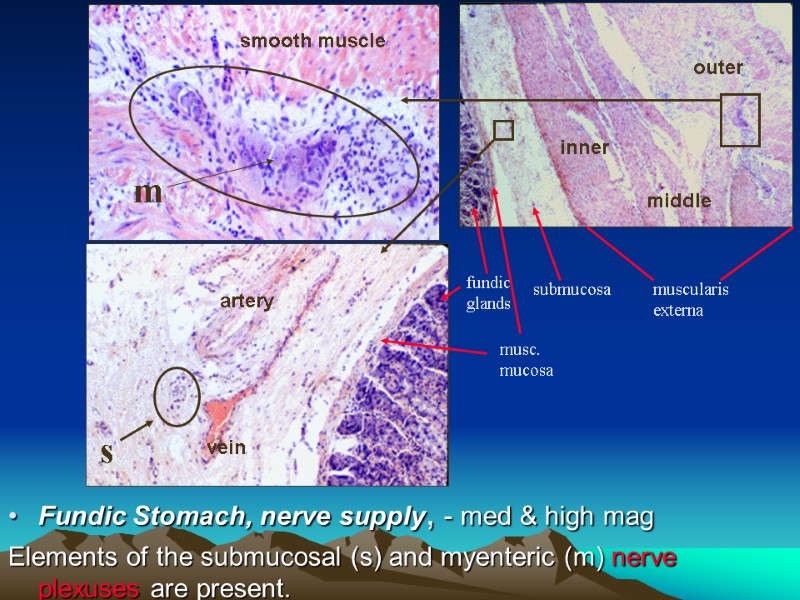
 Fundic Stomach, nerve supply, - med & high mag Elements of the submucosal (s) and myenteric (m) nerve plexuses are present. fundic glands musc. mucosa submucosa muscularis externa inner middle outer s m smooth muscle artery vein
Fundic Stomach, nerve supply, - med & high mag Elements of the submucosal (s) and myenteric (m) nerve plexuses are present. fundic glands musc. mucosa submucosa muscularis externa inner middle outer s m smooth muscle artery vein

