 Diffraction from cystals Ps: I put things on the comment block below so please make sure you are in edit status Fan Ziyi
Diffraction from cystals Ps: I put things on the comment block below so please make sure you are in edit status Fan Ziyi
 Main topic: DP: diffraction pattern Reciprocal lattice Bragger’s law Structure factor Amplitude of electron beam scattered by a unit cell
Main topic: DP: diffraction pattern Reciprocal lattice Bragger’s law Structure factor Amplitude of electron beam scattered by a unit cell
 How can Diffraction occur Using bragger’s law and reciprocal lattice
How can Diffraction occur Using bragger’s law and reciprocal lattice
 Something about X-RAY When x ray hit the electrons, it makes electrons to vibrate in the same frequency. those electrons become the new source of X-ray. We call beams which given by electrons SCATTERING BEAM.
Something about X-RAY When x ray hit the electrons, it makes electrons to vibrate in the same frequency. those electrons become the new source of X-ray. We call beams which given by electrons SCATTERING BEAM.
 Bragger’s law
Bragger’s law
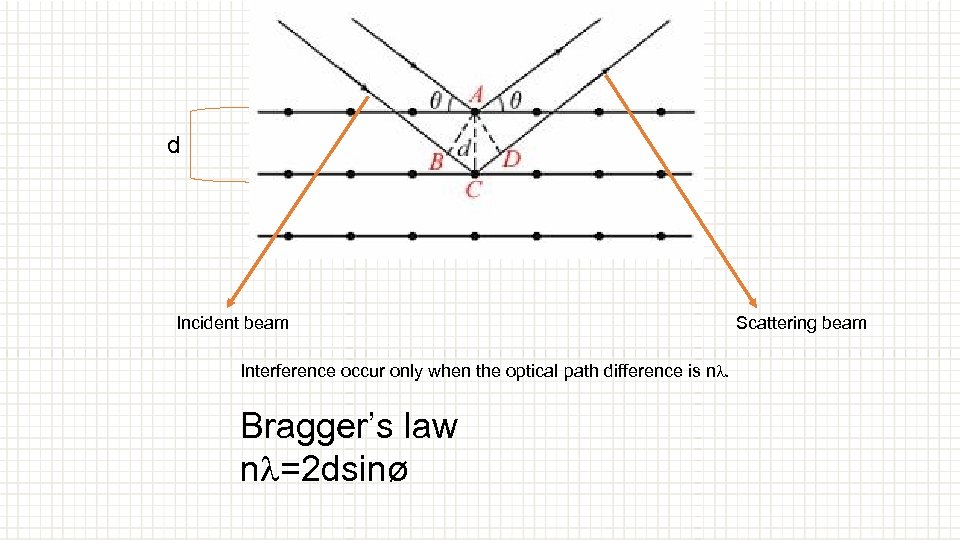 d Incident beam Interference occur only when the optical path difference is nl. Bragger’s law nl=2 dsinø Scattering beam
d Incident beam Interference occur only when the optical path difference is nl. Bragger’s law nl=2 dsinø Scattering beam
 Reciprocal lattice
Reciprocal lattice
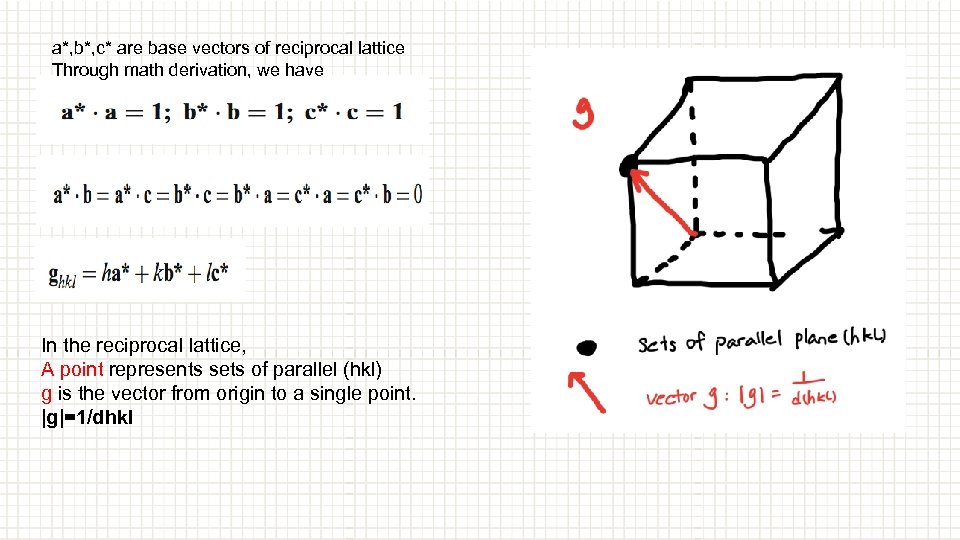 a*, b*, c* are base vectors of reciprocal lattice Through math derivation, we have In the reciprocal lattice, A point represents sets of parallel (hkl) g is the vector from origin to a single point. |g|=1/dhkl
a*, b*, c* are base vectors of reciprocal lattice Through math derivation, we have In the reciprocal lattice, A point represents sets of parallel (hkl) g is the vector from origin to a single point. |g|=1/dhkl
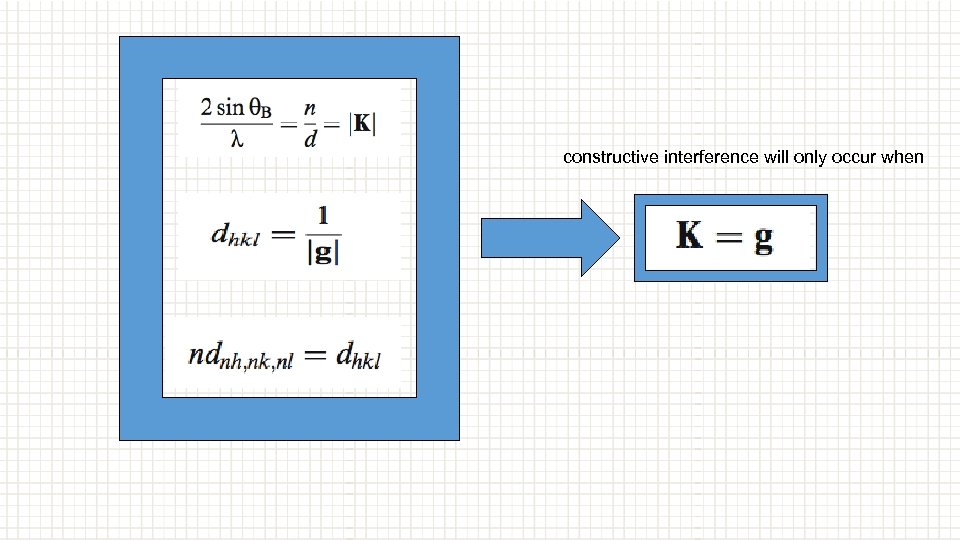 constructive interference will only occur when
constructive interference will only occur when
 What affects the intensity Using amplitude equation and structure factor
What affects the intensity Using amplitude equation and structure factor
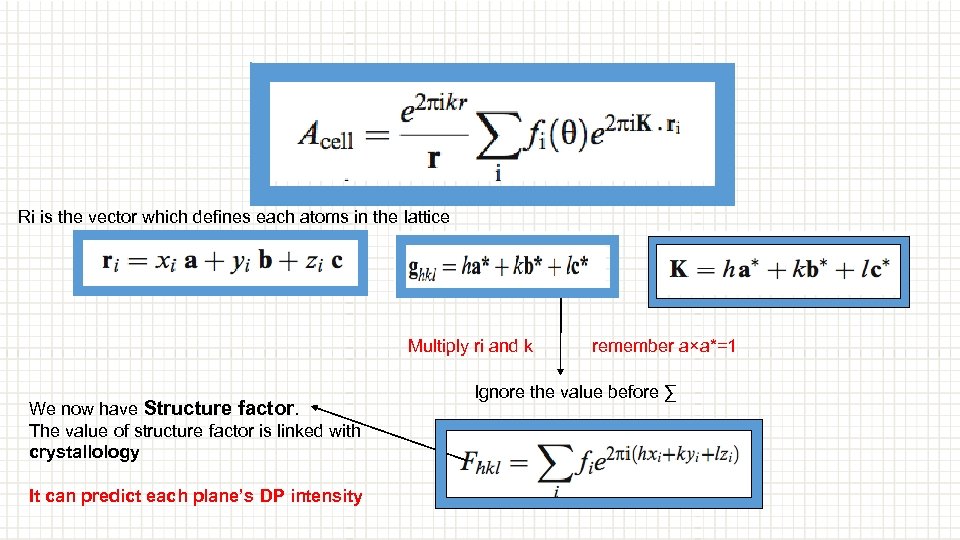 Ri is the vector which defines each atoms in the lattice Multiply ri and k We now have Structure factor. The value of structure factor is linked with crystallology It can predict each plane’s DP intensity remember a×a*=1 Ignore the value before ∑
Ri is the vector which defines each atoms in the lattice Multiply ri and k We now have Structure factor. The value of structure factor is linked with crystallology It can predict each plane’s DP intensity remember a×a*=1 Ignore the value before ∑
 Examples Important structures
Examples Important structures
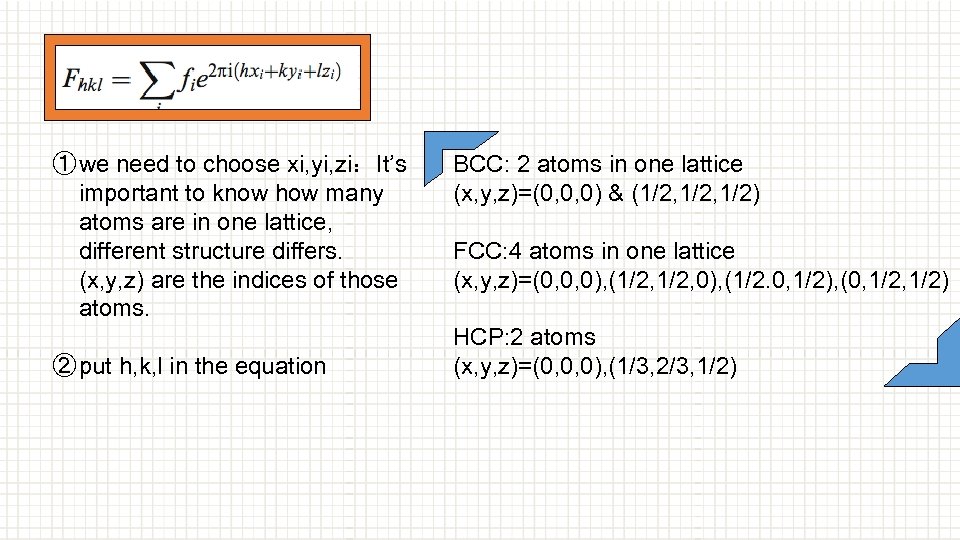 ① we need to choose xi, yi, zi:It’s important to know how many atoms are in one lattice, different structure differs. (x, y, z) are the indices of those atoms. ② put h, k, l in the equation BCC: 2 atoms in one lattice (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0) & (1/2, 1/2) FCC: 4 atoms in one lattice (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0), (1/2, 0), (1/2. 0, 1/2), (0, 1/2) HCP: 2 atoms (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0), (1/3, 2/3, 1/2)
① we need to choose xi, yi, zi:It’s important to know how many atoms are in one lattice, different structure differs. (x, y, z) are the indices of those atoms. ② put h, k, l in the equation BCC: 2 atoms in one lattice (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0) & (1/2, 1/2) FCC: 4 atoms in one lattice (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0), (1/2, 0), (1/2. 0, 1/2), (0, 1/2) HCP: 2 atoms (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0), (1/3, 2/3, 1/2)
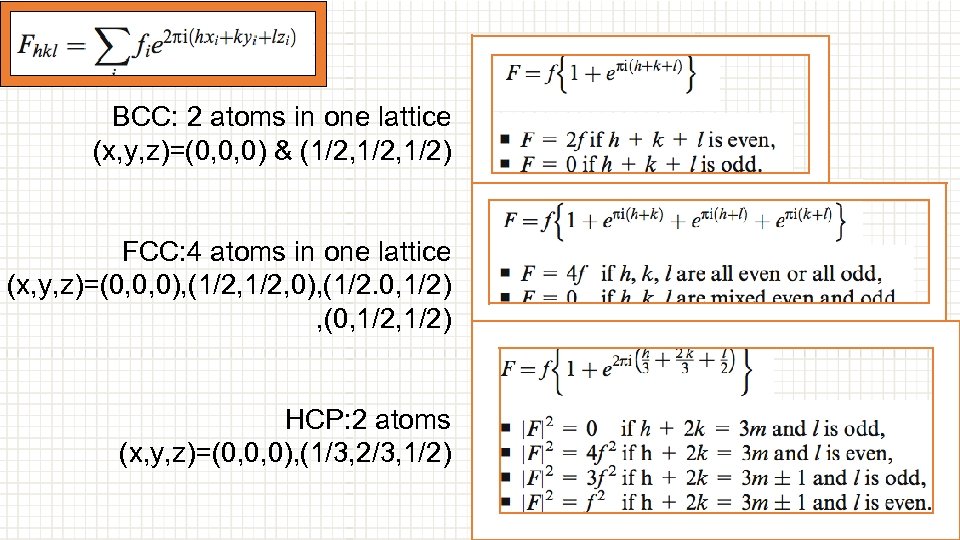 BCC: 2 atoms in one lattice (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0) & (1/2, 1/2) FCC: 4 atoms in one lattice (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0), (1/2, 0), (1/2. 0, 1/2) , (0, 1/2) HCP: 2 atoms (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0), (1/3, 2/3, 1/2)
BCC: 2 atoms in one lattice (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0) & (1/2, 1/2) FCC: 4 atoms in one lattice (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0), (1/2, 0), (1/2. 0, 1/2) , (0, 1/2) HCP: 2 atoms (x, y, z)=(0, 0, 0), (1/3, 2/3, 1/2)
 Examples Extended
Examples Extended
 Na atoms on an fcc site Cl related to it by the basis vector [1/2, 1/2]
Na atoms on an fcc site Cl related to it by the basis vector [1/2, 1/2]
 Ga located on the fcc lattice As related to it by the basis vector [1/4, 1/4]
Ga located on the fcc lattice As related to it by the basis vector [1/4, 1/4]
 Reference 1. Wiiliams, D. B. , &Barry Carter, C. , (1996). transmission electron microscopy. new york: Springer ScienceþBusiness Media
Reference 1. Wiiliams, D. B. , &Barry Carter, C. , (1996). transmission electron microscopy. new york: Springer ScienceþBusiness Media
 THANKS
THANKS