57b13472a4d88065dff3fd4c38aaa35b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
 Differential Advantage Analysis, Market Potential & Sales Forecasting Session 3 By: - Neeraj Gupta
Differential Advantage Analysis, Market Potential & Sales Forecasting Session 3 By: - Neeraj Gupta
 Differential Advantage Analysis n A useful way to examine competitors capabilities is to divide the necessary information into five categories q q q Competitors abilities to conceive and design To produce To market To finance To manage
Differential Advantage Analysis n A useful way to examine competitors capabilities is to divide the necessary information into five categories q q q Competitors abilities to conceive and design To produce To market To finance To manage
 Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors abilities to conceive and design q Technical resources n n q Human Resources n n q Concepts Patents and copyrights Key people and skills Use of external technical groups R&D funding n n n Total Percentage of sales Consistency over time Internally generated Government supplied
Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors abilities to conceive and design q Technical resources n n q Human Resources n n q Concepts Patents and copyrights Key people and skills Use of external technical groups R&D funding n n n Total Percentage of sales Consistency over time Internally generated Government supplied
 Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors abilities to conceive and design q Technological strategy n n q Specialization Competence Source of capability Timing: initiate versus imitate Management processes n n TQM House of Quality
Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors abilities to conceive and design q Technological strategy n n q Specialization Competence Source of capability Timing: initiate versus imitate Management processes n n TQM House of Quality
 Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors ability to Produce q Physical resources n n n q Human Resources n n q Capacity Plant Equipment Processes Degree of integration Key people and skills Workforce Suppliers n n n Capacity Quality Commitment
Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors ability to Produce q Physical resources n n n q Human Resources n n q Capacity Plant Equipment Processes Degree of integration Key people and skills Workforce Suppliers n n n Capacity Quality Commitment
 Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors ability to Market q q q Sales Force Distribution Network Service and Sales Policies Advertising Human Resources Funding
Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors ability to Market q q q Sales Force Distribution Network Service and Sales Policies Advertising Human Resources Funding
 Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors ability to Finance q Long-Term n n q Short-term n n n q q n n Days of receivables Inventory turnover Accounting practices Human resources n n q Cash or equivalent Line of credit Cost of debt Liquidity Cash flow n q Debt/equity ratio Cost of debt Key people and skills Turnover Systems n n n Budgeting Forecasting Controlling
Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors ability to Finance q Long-Term n n q Short-term n n n q q n n Days of receivables Inventory turnover Accounting practices Human resources n n q Cash or equivalent Line of credit Cost of debt Liquidity Cash flow n q Debt/equity ratio Cost of debt Key people and skills Turnover Systems n n n Budgeting Forecasting Controlling
 Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors ability to Manage q Key people n n n q Decision making n n n q n n Type Emphasis Time span Staffing n n n q (i) Location (ii) Type (iii) Speed Planning n q Objectives and priorities Values Reward systems Longevity and turnover Experience Replacement policies Organization n Centralization Functions Use of staff
Differential Advantage Analysis n Competitors ability to Manage q Key people n n n q Decision making n n n q n n Type Emphasis Time span Staffing n n n q (i) Location (ii) Type (iii) Speed Planning n q Objectives and priorities Values Reward systems Longevity and turnover Experience Replacement policies Organization n Centralization Functions Use of staff
 Customer Analysis Purpose n n n Customer analysis is an activity that is or should be performed by organizations. The Customer Analysis section of the business plan assesses the customer segments that the company serves. In it, the company must: 1. Identify its target customers 2. Convey the needs of these customers 3. Show its products and services satisfy these needs
Customer Analysis Purpose n n n Customer analysis is an activity that is or should be performed by organizations. The Customer Analysis section of the business plan assesses the customer segments that the company serves. In it, the company must: 1. Identify its target customers 2. Convey the needs of these customers 3. Show its products and services satisfy these needs
 Customer Segmentation n Segmentation: - Creating clusters in the market of buyers with similar needs and preferences
Customer Segmentation n Segmentation: - Creating clusters in the market of buyers with similar needs and preferences
 Differentiated Marketing can be operated at Various Levels n Segment Marketing: -similar set of wants q q n Can be enhanced by providing a naked solution containing the product and service elements that all segment members value. Discretionary elements that some segment members value. Niche Marketing: -narrow but attractive, requiring distinctive mix of market offering. Sub segment of a segment
Differentiated Marketing can be operated at Various Levels n Segment Marketing: -similar set of wants q q n Can be enhanced by providing a naked solution containing the product and service elements that all segment members value. Discretionary elements that some segment members value. Niche Marketing: -narrow but attractive, requiring distinctive mix of market offering. Sub segment of a segment
 Identifying Market segments and Target Market Positioning n Market Segment: - group of customers with similar needs, preferences or buying habits. q Market divided into smaller groups in which members are similar with respect to factors that influence demand. q Major element in success of a company. n Target market Consists of group of customers for whom seller designs a particular marketing mix.
Identifying Market segments and Target Market Positioning n Market Segment: - group of customers with similar needs, preferences or buying habits. q Market divided into smaller groups in which members are similar with respect to factors that influence demand. q Major element in success of a company. n Target market Consists of group of customers for whom seller designs a particular marketing mix.
 Benefits of Segmentation n n Application of the “divide and rule” principle, or divide the markets and conquer them. Marketing effort becomes effective and efficient. Specific marketing mix can be effectively designed for specific market segments. Focussed attention can be given to complex but attractive segments
Benefits of Segmentation n n Application of the “divide and rule” principle, or divide the markets and conquer them. Marketing effort becomes effective and efficient. Specific marketing mix can be effectively designed for specific market segments. Focussed attention can be given to complex but attractive segments
 Factors Affecting the Feasibility of Segmentation n n n Measurable Accessible Substantial Unique/Differentiable Appropriate Actionable Stable
Factors Affecting the Feasibility of Segmentation n n n Measurable Accessible Substantial Unique/Differentiable Appropriate Actionable Stable
 Evaluating Market Segments Segment size and growth n Segment structural attractiveness w Level of competition n w Substitute products w Power of buyers w Powerful suppliers n Company objectives and resources
Evaluating Market Segments Segment size and growth n Segment structural attractiveness w Level of competition n w Substitute products w Power of buyers w Powerful suppliers n Company objectives and resources
 Basis of Segmentation n Geographic q Region q City or metro size q Population density q Climate Geo-Demographic q Age and Life-Cycle Stage q Life Stage q Gender q Income q Generation q Lifestage Analytic Matrix q Social class
Basis of Segmentation n Geographic q Region q City or metro size q Population density q Climate Geo-Demographic q Age and Life-Cycle Stage q Life Stage q Gender q Income q Generation q Lifestage Analytic Matrix q Social class
 Benefit Segments- Computers* n n The Germans – “We want the best” The Indians – “We want the best today and tomorrow” The Taiwanese – “We want it cheap with a name” The Americans – “We want service too” *Customer-focused product planning: Personal Computers in India Jagrook Dawra, Kanupriya Katyal, Vishal Mishra, Seerisha M.
Benefit Segments- Computers* n n The Germans – “We want the best” The Indians – “We want the best today and tomorrow” The Taiwanese – “We want it cheap with a name” The Americans – “We want service too” *Customer-focused product planning: Personal Computers in India Jagrook Dawra, Kanupriya Katyal, Vishal Mishra, Seerisha M.
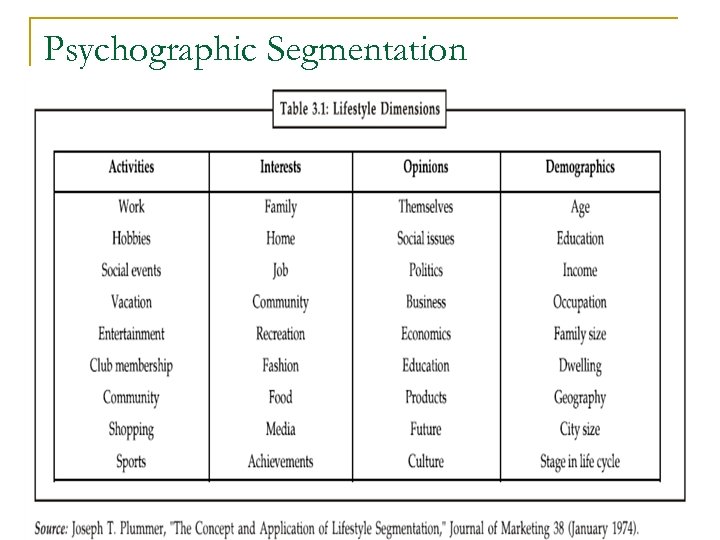
 Basis of Segmentation n Psychographic Segmentation q Lifestyle n Time-constrained q n q Money-constrained Personality n “Brand personality” examples: q q q multitasking Sincere Exciting Competent Sophisticated Rugged Values n Core values
Basis of Segmentation n Psychographic Segmentation q Lifestyle n Time-constrained q n q Money-constrained Personality n “Brand personality” examples: q q q multitasking Sincere Exciting Competent Sophisticated Rugged Values n Core values
 Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic Segmentation
 Basis of Segmentation-Psychographic
Basis of Segmentation-Psychographic
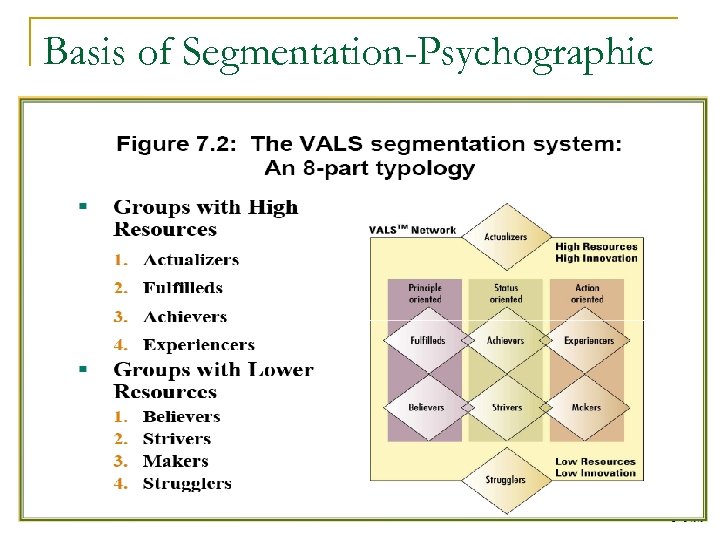
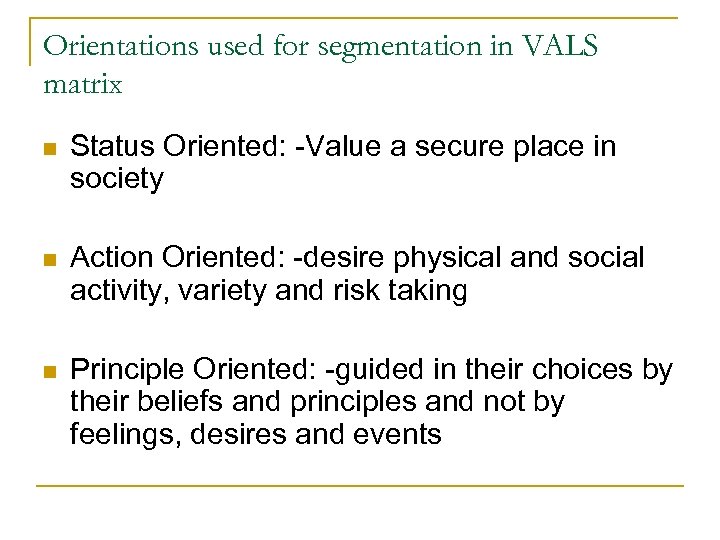 Orientations used for segmentation in VALS matrix n Status Oriented: -Value a secure place in society n Action Oriented: -desire physical and social activity, variety and risk taking n Principle Oriented: -guided in their choices by their beliefs and principles and not by feelings, desires and events
Orientations used for segmentation in VALS matrix n Status Oriented: -Value a secure place in society n Action Oriented: -desire physical and social activity, variety and risk taking n Principle Oriented: -guided in their choices by their beliefs and principles and not by feelings, desires and events
 Psychographic Segmentation n ACTULIZERS: q Successful, sophisticated, take-charge people with high self-esteem. q q Established and emerging leaders in business and government q n Image is important to Innovators seek challenges, variety FULFILLEDS q Motivated by ideals q Mature, satisfied, comfortable , and reflective people who value order, knowledge, and responsibility q well educated and actively seek out information in the decision-making
Psychographic Segmentation n ACTULIZERS: q Successful, sophisticated, take-charge people with high self-esteem. q q Established and emerging leaders in business and government q n Image is important to Innovators seek challenges, variety FULFILLEDS q Motivated by ideals q Mature, satisfied, comfortable , and reflective people who value order, knowledge, and responsibility q well educated and actively seek out information in the decision-making
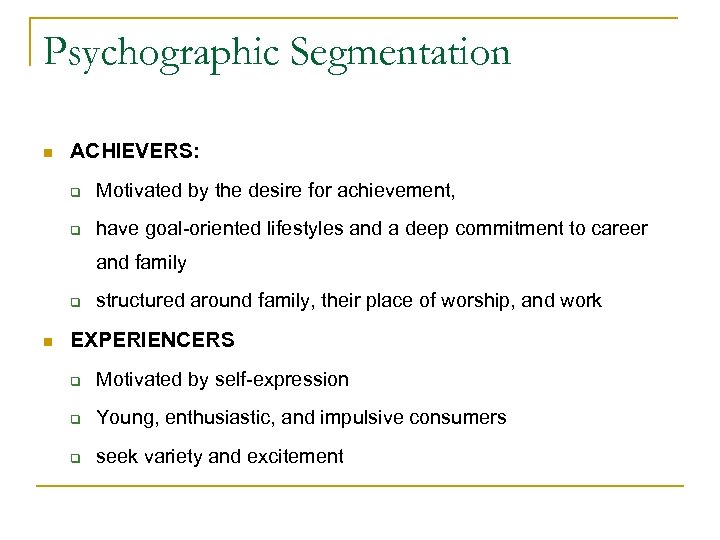 Psychographic Segmentation n ACHIEVERS: q Motivated by the desire for achievement, q have goal-oriented lifestyles and a deep commitment to career and family q n structured around family, their place of worship, and work EXPERIENCERS q Motivated by self-expression q Young, enthusiastic, and impulsive consumers q seek variety and excitement
Psychographic Segmentation n ACHIEVERS: q Motivated by the desire for achievement, q have goal-oriented lifestyles and a deep commitment to career and family q n structured around family, their place of worship, and work EXPERIENCERS q Motivated by self-expression q Young, enthusiastic, and impulsive consumers q seek variety and excitement
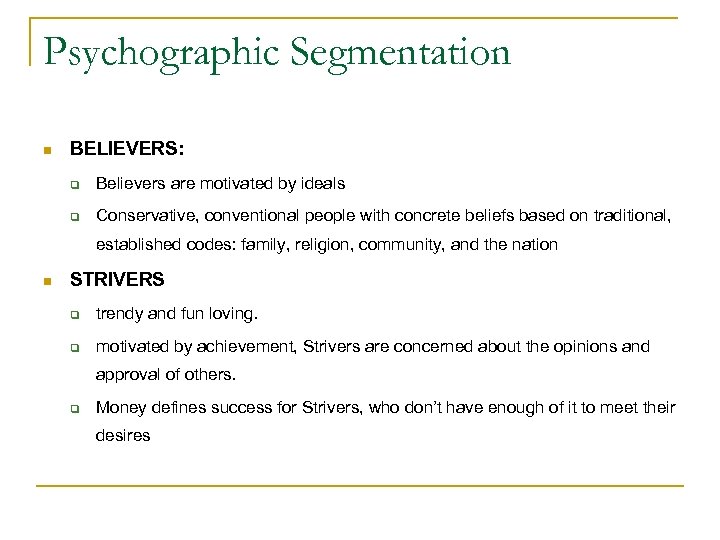 Psychographic Segmentation n BELIEVERS: q Believers are motivated by ideals q Conservative, conventional people with concrete beliefs based on traditional, established codes: family, religion, community, and the nation n STRIVERS q trendy and fun loving. q motivated by achievement, Strivers are concerned about the opinions and approval of others. q Money defines success for Strivers, who don’t have enough of it to meet their desires
Psychographic Segmentation n BELIEVERS: q Believers are motivated by ideals q Conservative, conventional people with concrete beliefs based on traditional, established codes: family, religion, community, and the nation n STRIVERS q trendy and fun loving. q motivated by achievement, Strivers are concerned about the opinions and approval of others. q Money defines success for Strivers, who don’t have enough of it to meet their desires
 Psychographic Segmentation n MAKERS: q Makers are motivated by self-expression q express themselves and experience the world by working on it-building a house, raising children, fixing a car, or canning q n Practical people who have constructive skills and value self-sufficiency. STRUGGLERS q Narrowly focused lives q with the familiar and are primarily concerned with safety and security
Psychographic Segmentation n MAKERS: q Makers are motivated by self-expression q express themselves and experience the world by working on it-building a house, raising children, fixing a car, or canning q n Practical people who have constructive skills and value self-sufficiency. STRUGGLERS q Narrowly focused lives q with the familiar and are primarily concerned with safety and security
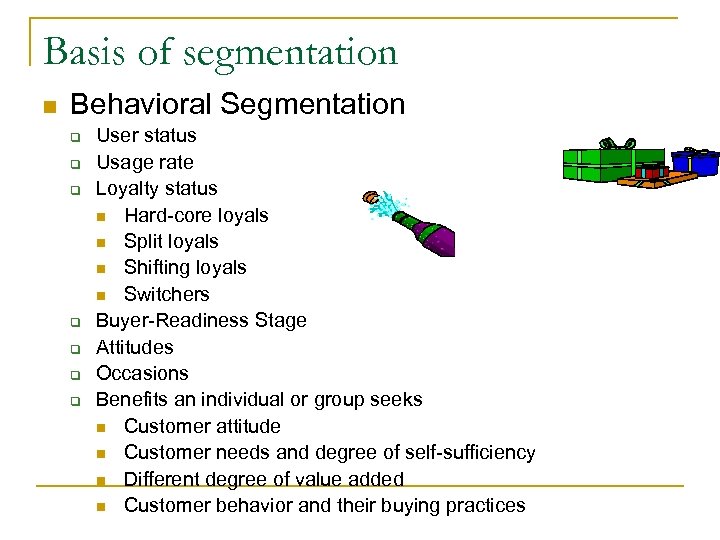 Basis of segmentation n Behavioral Segmentation q q q q User status Usage rate Loyalty status n Hard-core loyals n Split loyals n Shifting loyals n Switchers Buyer-Readiness Stage Attitudes Occasions Benefits an individual or group seeks n Customer attitude n Customer needs and degree of self-sufficiency n Different degree of value added n Customer behavior and their buying practices
Basis of segmentation n Behavioral Segmentation q q q q User status Usage rate Loyalty status n Hard-core loyals n Split loyals n Shifting loyals n Switchers Buyer-Readiness Stage Attitudes Occasions Benefits an individual or group seeks n Customer attitude n Customer needs and degree of self-sufficiency n Different degree of value added n Customer behavior and their buying practices
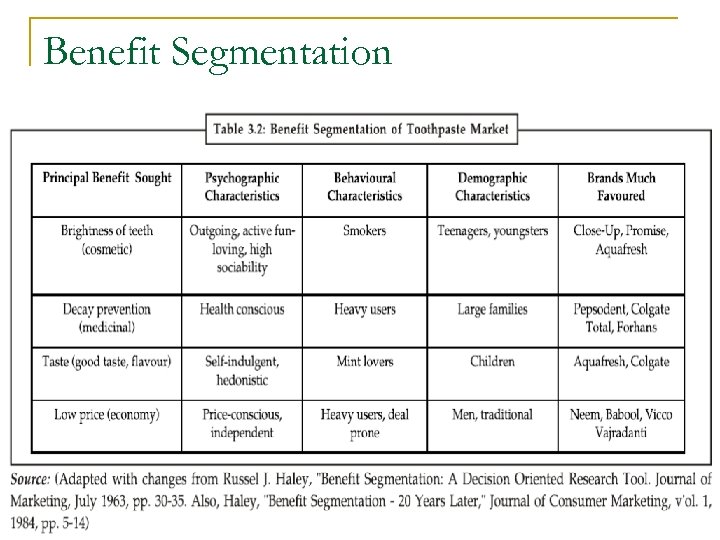 Benefit Segmentation
Benefit Segmentation
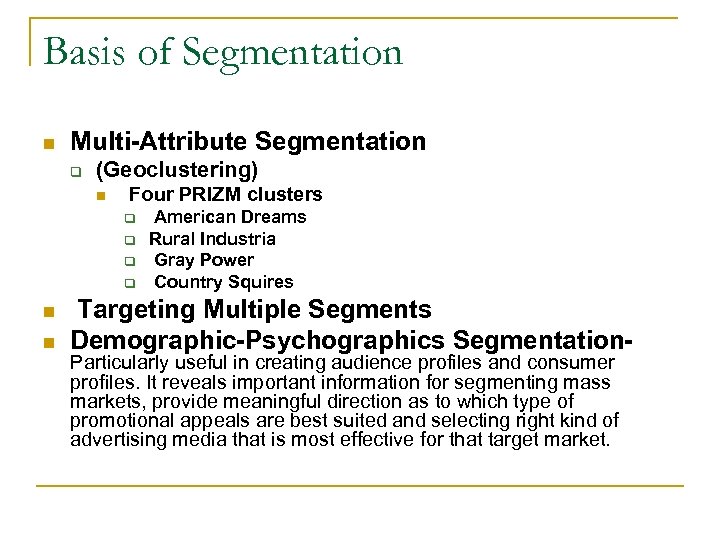 Basis of Segmentation n Multi-Attribute Segmentation q (Geoclustering) n Four PRIZM clusters q q n n American Dreams Rural Industria Gray Power Country Squires Targeting Multiple Segments Demographic-Psychographics Segmentation. Particularly useful in creating audience profiles and consumer profiles. It reveals important information for segmenting mass markets, provide meaningful direction as to which type of promotional appeals are best suited and selecting right kind of advertising media that is most effective for that target market.
Basis of Segmentation n Multi-Attribute Segmentation q (Geoclustering) n Four PRIZM clusters q q n n American Dreams Rural Industria Gray Power Country Squires Targeting Multiple Segments Demographic-Psychographics Segmentation. Particularly useful in creating audience profiles and consumer profiles. It reveals important information for segmenting mass markets, provide meaningful direction as to which type of promotional appeals are best suited and selecting right kind of advertising media that is most effective for that target market.
 What Demographic and Psychographic segment is this ad targeted at? The film opens on a group of guys on their bikes. Seeing a guy walking along the road, they sing, “Thoda hi hai age gap, phir bhi pehne monkey cap. Aaj tumhare saath jawaani, karlo jo chaahe man maani. It’s now or never. ”
What Demographic and Psychographic segment is this ad targeted at? The film opens on a group of guys on their bikes. Seeing a guy walking along the road, they sing, “Thoda hi hai age gap, phir bhi pehne monkey cap. Aaj tumhare saath jawaani, karlo jo chaahe man maani. It’s now or never. ”
 Cut to the shot of a husband getting a scolding from his wife as he stares a young girl. At this our guys continue, “…bachche-kachche. . . raashan-paani, kal hogi yehi kahani. It’s now or never. ” We now see a boss getting mad at his employees. Jingle: “…Ghar se office, office se ghar. . .
Cut to the shot of a husband getting a scolding from his wife as he stares a young girl. At this our guys continue, “…bachche-kachche. . . raashan-paani, kal hogi yehi kahani. It’s now or never. ” We now see a boss getting mad at his employees. Jingle: “…Ghar se office, office se ghar. . .
 . . . Boss ka darr, biwi ka darr. It’s now or never. ” The ad ends on. . . the shot of the bike and VO: “Apache. It’s now or never. ”
. . . Boss ka darr, biwi ka darr. It’s now or never. ” The ad ends on. . . the shot of the bike and VO: “Apache. It’s now or never. ”
 What Demographic and Psychographic segment is this ad targeted at? “Chameli meri jaan, gulabo jalan se lal” says a blind man taking care of his flowers in the garden. Smelling something that’s not part of the garden, he exclaims, “gainda, tu kahan se aaya!” and goes towards a bike.
What Demographic and Psychographic segment is this ad targeted at? “Chameli meri jaan, gulabo jalan se lal” says a blind man taking care of his flowers in the garden. Smelling something that’s not part of the garden, he exclaims, “gainda, tu kahan se aaya!” and goes towards a bike.
 The blind man removes the garland from the brand new bike. As his son comes, he questions him, “arey, tune Splendor chhod di? ” Even as he comes to know that it’s a self-start and “powerful” bike, he still scolds his son for getting rid of the Splendor
The blind man removes the garland from the brand new bike. As his son comes, he questions him, “arey, tune Splendor chhod di? ” Even as he comes to know that it’s a self-start and “powerful” bike, he still scolds his son for getting rid of the Splendor
 “ 125 CC, Quantum Core engine” with a better mileage, informs the son about the new bike. He makes the father more comfortable. . . when he tells him that he has bought a Super Splendor. Cut to the shot of the father who now comes in a surprisingly new get-up.
“ 125 CC, Quantum Core engine” with a better mileage, informs the son about the new bike. He makes the father more comfortable. . . when he tells him that he has bought a Super Splendor. Cut to the shot of the father who now comes in a surprisingly new get-up.
 As the father and son go on the new Super Splendor, the VO. . . plays: “New 125 CC Super Splendor Generation nayi, bharosa wahi.
As the father and son go on the new Super Splendor, the VO. . . plays: “New 125 CC Super Splendor Generation nayi, bharosa wahi.
 Marketing Implications n n n Marketers facing consumers who have a negative attitude toward their product must work to identify the key issues shaping a consumer's attitude then adjust marketing decisions (e. g. , advertising) in an effort to change the attitude. For companies competing against strong rivals to whom loyal consumers exhibit a positive attitude, an important strategy is to work to see why consumers feel positive toward the competitor and then try to meet or beat the competitor on these issues. Alternatively, a company can try to locate customers who feel negatively toward the competitor and then increase awareness among this group.
Marketing Implications n n n Marketers facing consumers who have a negative attitude toward their product must work to identify the key issues shaping a consumer's attitude then adjust marketing decisions (e. g. , advertising) in an effort to change the attitude. For companies competing against strong rivals to whom loyal consumers exhibit a positive attitude, an important strategy is to work to see why consumers feel positive toward the competitor and then try to meet or beat the competitor on these issues. Alternatively, a company can try to locate customers who feel negatively toward the competitor and then increase awareness among this group.
 Customer Needs n n n Customer needs are the expectations of the product buyers. There are several needs of customers in this open market and it is also seen that its very difficult to measure the exact needs and demands from customers. Categorise the customer expectations/needs into: q q General Needs Emotional Needs
Customer Needs n n n Customer needs are the expectations of the product buyers. There are several needs of customers in this open market and it is also seen that its very difficult to measure the exact needs and demands from customers. Categorise the customer expectations/needs into: q q General Needs Emotional Needs
 Consumer Buyer Behavior
Consumer Buyer Behavior
 Consumer Behavior Processes a consumer uses to make purchase decisions, as well as to use and dispose of purchased goods or services; also includes factors that influence purchase decisions and the product use Chapter 4 Version 3 e 39
Consumer Behavior Processes a consumer uses to make purchase decisions, as well as to use and dispose of purchased goods or services; also includes factors that influence purchase decisions and the product use Chapter 4 Version 3 e 39
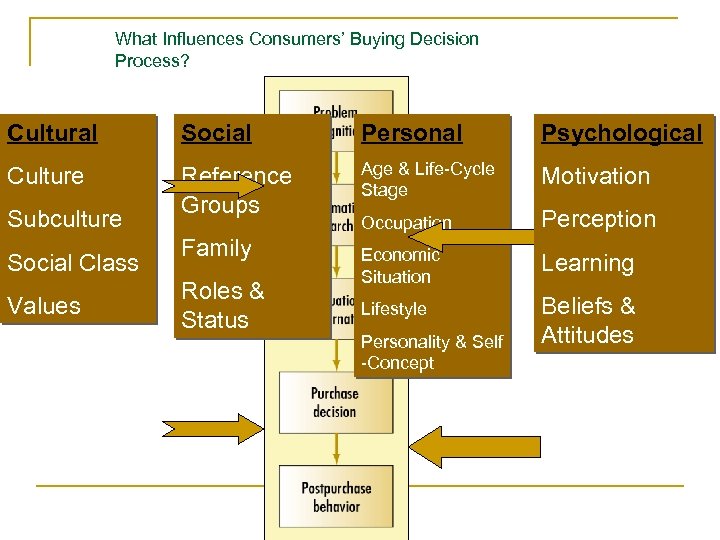 What Influences Consumers’ Buying Decision Process? Cultural Social Personal Psychological Culture Reference Groups Age & Life-Cycle Stage Motivation Occupation Perception Economic Situation Learning Lifestyle Beliefs & Attitudes Subculture Social Class Values Family Roles & Status Personality & Self -Concept
What Influences Consumers’ Buying Decision Process? Cultural Social Personal Psychological Culture Reference Groups Age & Life-Cycle Stage Motivation Occupation Perception Economic Situation Learning Lifestyle Beliefs & Attitudes Subculture Social Class Values Family Roles & Status Personality & Self -Concept

 Marketing to a Subculture Sears is widely considered one of the most successful marketers to the U. S. Hispanic population. Its Spanish-language Web site features content and events carefully tailored to Hispanic consumers.
Marketing to a Subculture Sears is widely considered one of the most successful marketers to the U. S. Hispanic population. Its Spanish-language Web site features content and events carefully tailored to Hispanic consumers.
 Opinion Leaders Marketers use buzz marketing by enlisting or even creating opinion leaders to spread the word about their brands.
Opinion Leaders Marketers use buzz marketing by enlisting or even creating opinion leaders to spread the word about their brands.

 Personal Factors: Self-concept
Personal Factors: Self-concept
 Psychological Factors: Beliefs
Psychological Factors: Beliefs
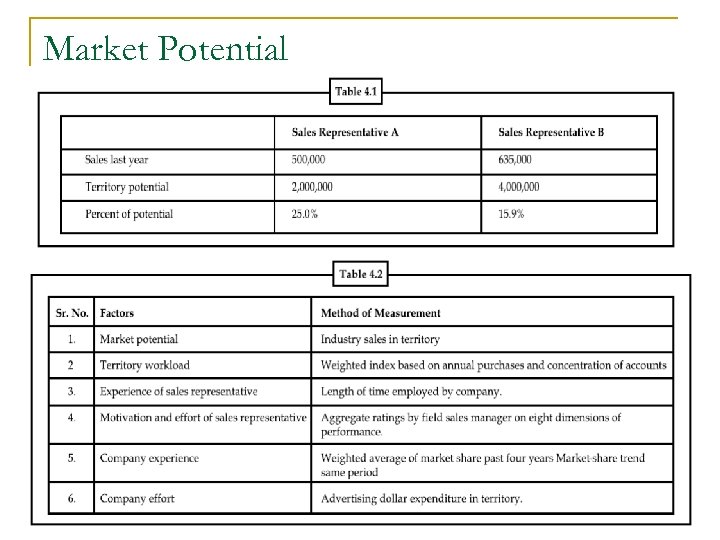
 Market Potential n n Market or sales potential must be stated for a given product or group of products fir a given area for a given period of time, usually a year. Area potentials can be expressed in both absolute terms and as a percent of the total market.
Market Potential n n Market or sales potential must be stated for a given product or group of products fir a given area for a given period of time, usually a year. Area potentials can be expressed in both absolute terms and as a percent of the total market.
 Uses Of Market Potential n n There are three main uses of market potential and these are: Allocation of marketing resources Defining sales techniques Setting sales quotas: -A sales forecast is a prediction based on past sales performance and an analysis of expected market conditions. The true value in making a forecast is that it forces us to look at the future objectively. The company that takes note of the past stays aware of the present and precisely analyzes that information to see into the future.
Uses Of Market Potential n n There are three main uses of market potential and these are: Allocation of marketing resources Defining sales techniques Setting sales quotas: -A sales forecast is a prediction based on past sales performance and an analysis of expected market conditions. The true value in making a forecast is that it forces us to look at the future objectively. The company that takes note of the past stays aware of the present and precisely analyzes that information to see into the future.
 Market Potential
Market Potential
 Sales Forecasting n n n Sales forecasting is the process of organizing and analyzing information in a way that makes it possible to estimate what your sales will be. A sales forecast is a prediction based on past sales performance and an analysis of expected market conditions. The true value in making a forecast is that it forces us to look at the future objectively. The company that takes note of the past stays aware of the present and precisely analyzes that information to see into the future.
Sales Forecasting n n n Sales forecasting is the process of organizing and analyzing information in a way that makes it possible to estimate what your sales will be. A sales forecast is a prediction based on past sales performance and an analysis of expected market conditions. The true value in making a forecast is that it forces us to look at the future objectively. The company that takes note of the past stays aware of the present and precisely analyzes that information to see into the future.
 Importance of Sales Forecasting n n Sales forecasting is a self-assessment tool for a company. A sales forecast reports, graphs and analyzes the pulse of your business. The future direction of the company may rest on the accuracy of your sales forecasting. Companies that implement accurate sales forecasting processes realize important benefits such as: q Enhanced cash flow q Knowing when and how much to buy q In-depth knowledge of customers and the products they order q The ability to plan for production and capacity q The ability to identify the pattern or trend of sales q Determine the value of a business above the value of its current assets q Ability to determine the expected return on investment
Importance of Sales Forecasting n n Sales forecasting is a self-assessment tool for a company. A sales forecast reports, graphs and analyzes the pulse of your business. The future direction of the company may rest on the accuracy of your sales forecasting. Companies that implement accurate sales forecasting processes realize important benefits such as: q Enhanced cash flow q Knowing when and how much to buy q In-depth knowledge of customers and the products they order q The ability to plan for production and capacity q The ability to identify the pattern or trend of sales q Determine the value of a business above the value of its current assets q Ability to determine the expected return on investment
 Benefits of Sales Forecasting n n Increased revenue Increased customer retention Decreased costs Increased efficiency
Benefits of Sales Forecasting n n Increased revenue Increased customer retention Decreased costs Increased efficiency
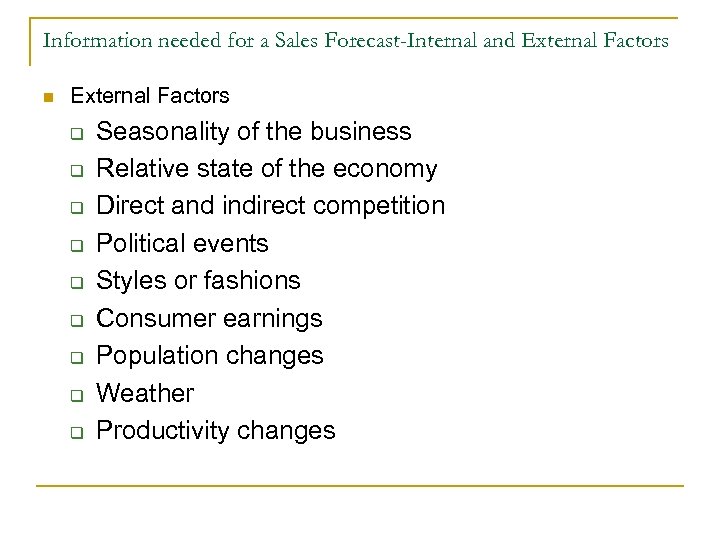 Information needed for a Sales Forecast-Internal and External Factors n External Factors q q q q q Seasonality of the business Relative state of the economy Direct and indirect competition Political events Styles or fashions Consumer earnings Population changes Weather Productivity changes
Information needed for a Sales Forecast-Internal and External Factors n External Factors q q q q q Seasonality of the business Relative state of the economy Direct and indirect competition Political events Styles or fashions Consumer earnings Population changes Weather Productivity changes
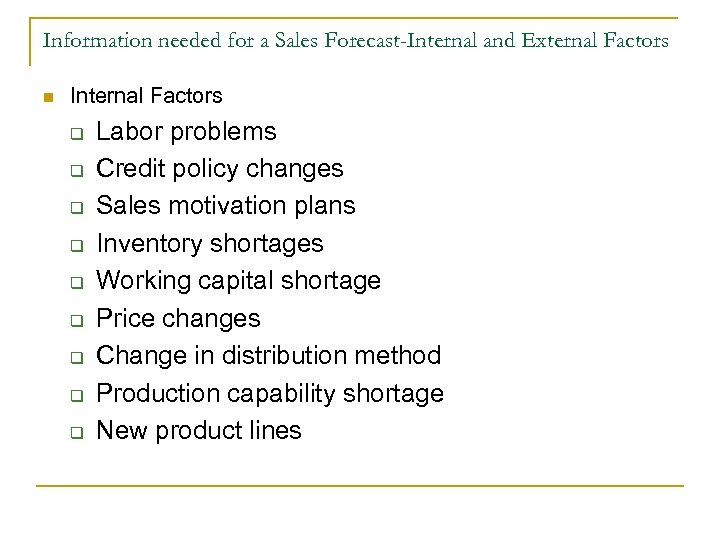 Information needed for a Sales Forecast-Internal and External Factors n Internal Factors q q q q q Labor problems Credit policy changes Sales motivation plans Inventory shortages Working capital shortage Price changes Change in distribution method Production capability shortage New product lines
Information needed for a Sales Forecast-Internal and External Factors n Internal Factors q q q q q Labor problems Credit policy changes Sales motivation plans Inventory shortages Working capital shortage Price changes Change in distribution method Production capability shortage New product lines
 Internal data analysis for a sales forecast n Therefore, this data must be prepared on a consistent basis: q q n Accounting records Financial statements Sales-call reports After-sales service demands from clients How Long and How Often Should One Forecast? q A sales forecast needs to be performed, reviewed and compared with actual performance results on a regular basis. n n n Short-range forecasts are for fewer than three months. Intermediate forecasts have a span of three months to two years. Long-range forecasts cover more than two years.
Internal data analysis for a sales forecast n Therefore, this data must be prepared on a consistent basis: q q n Accounting records Financial statements Sales-call reports After-sales service demands from clients How Long and How Often Should One Forecast? q A sales forecast needs to be performed, reviewed and compared with actual performance results on a regular basis. n n n Short-range forecasts are for fewer than three months. Intermediate forecasts have a span of three months to two years. Long-range forecasts cover more than two years.
 How Sales Forecasting Applies to a New Business n Statistics show that 80 percent of new business startups never survive the first three years. Nine out of 10 of those business failures are caused by poor management decisions. Implementing sales forecasting forces a new business to base decisions on facts rather than hunches. q You need to consider the following: n n How well does your competition satisfy the needs of its potential customers? Note the population and economic growth in your location. Develop a customer profile. Experienced business people will tell you that a good rule of thumb is that 20 percent of your customers account for 80 percent of your sales.
How Sales Forecasting Applies to a New Business n Statistics show that 80 percent of new business startups never survive the first three years. Nine out of 10 of those business failures are caused by poor management decisions. Implementing sales forecasting forces a new business to base decisions on facts rather than hunches. q You need to consider the following: n n How well does your competition satisfy the needs of its potential customers? Note the population and economic growth in your location. Develop a customer profile. Experienced business people will tell you that a good rule of thumb is that 20 percent of your customers account for 80 percent of your sales.
 Software as a Tool for Sales Forecasting n n Projections become even more precise when software programs written specifically for sales forecasting are utilized. When shopping for a good software package, look for the following features: q q q Capability to adjust for special factors, i. e. , promotion and price changes Documents underlying forecasting assumptions An effective management review and communication step Historical data-tracking and plotting of current performance against past trends and future projections Allows multiple parties (e. g. , sales, marketing, manufacturing and logistics) to enhance, manipulate and use the forecast.
Software as a Tool for Sales Forecasting n n Projections become even more precise when software programs written specifically for sales forecasting are utilized. When shopping for a good software package, look for the following features: q q q Capability to adjust for special factors, i. e. , promotion and price changes Documents underlying forecasting assumptions An effective management review and communication step Historical data-tracking and plotting of current performance against past trends and future projections Allows multiple parties (e. g. , sales, marketing, manufacturing and logistics) to enhance, manipulate and use the forecast.
 Estimating Market Potential n n Estimating the market or market potential for a new business or business expansion is critical in determining the economic feasibility of a venture. Estimating the market potential will determine if the market is large enough to support your businesses. Once the estimated market potential has been calculated, it is possible to determine if the market is large enough to sustain your proposed business or sustain an addition competitor in the marketplace. Key Steps in Estimating Market Potential q Define your target market and market segments. q Define the geographic boundaries of your market. q Derive an average selling price. q Determine the average annual consumption. Estimating Market Potential: MP = N x P x Q; q q MP = market potential N = number of possible buyers P = average selling price Q = average annual consumption
Estimating Market Potential n n Estimating the market or market potential for a new business or business expansion is critical in determining the economic feasibility of a venture. Estimating the market potential will determine if the market is large enough to support your businesses. Once the estimated market potential has been calculated, it is possible to determine if the market is large enough to sustain your proposed business or sustain an addition competitor in the marketplace. Key Steps in Estimating Market Potential q Define your target market and market segments. q Define the geographic boundaries of your market. q Derive an average selling price. q Determine the average annual consumption. Estimating Market Potential: MP = N x P x Q; q q MP = market potential N = number of possible buyers P = average selling price Q = average annual consumption
 Retail Market Potential n n If you are evaluating a retail establishment, a more refined method of calculating the retail trade area market potential is available. The market potential for a retail establishment provided an estimate of the maximum total sales potential for a specific retail operation in a given market. The key steps in estimating retail market potential are: q q q Define your target market and market segments. Define the geographic boundaries of your market. Derive average expenditures for the category. Determine the average household income for the area and state. Estimate market share.
Retail Market Potential n n If you are evaluating a retail establishment, a more refined method of calculating the retail trade area market potential is available. The market potential for a retail establishment provided an estimate of the maximum total sales potential for a specific retail operation in a given market. The key steps in estimating retail market potential are: q q q Define your target market and market segments. Define the geographic boundaries of your market. Derive average expenditures for the category. Determine the average household income for the area and state. Estimate market share.
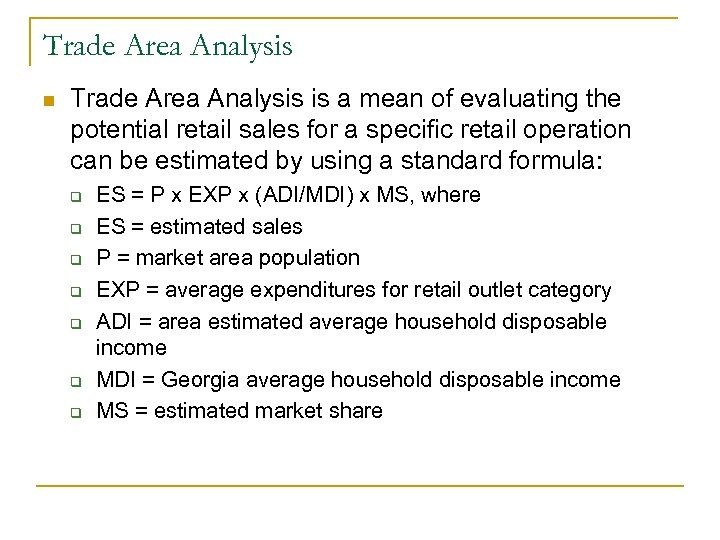 Trade Area Analysis n Trade Area Analysis is a mean of evaluating the potential retail sales for a specific retail operation can be estimated by using a standard formula: q q q q ES = P x EXP x (ADI/MDI) x MS, where ES = estimated sales P = market area population EXP = average expenditures for retail outlet category ADI = area estimated average household disposable income MDI = Georgia average household disposable income MS = estimated market share
Trade Area Analysis n Trade Area Analysis is a mean of evaluating the potential retail sales for a specific retail operation can be estimated by using a standard formula: q q q q ES = P x EXP x (ADI/MDI) x MS, where ES = estimated sales P = market area population EXP = average expenditures for retail outlet category ADI = area estimated average household disposable income MDI = Georgia average household disposable income MS = estimated market share
 Target Market n n A target market can be thought of as the customers who are most likely to buy from you and generally are described using demographic variables (gender, age, education) as well as psychographic variables (lifestyle and belief system variables). The first method of describing your target market segments is using a set of demographic descriptors like the following: q Age q Marital status q HH income q Gender q Race/Ethnicity q Family life cycle q Education q Religious affiliation
Target Market n n A target market can be thought of as the customers who are most likely to buy from you and generally are described using demographic variables (gender, age, education) as well as psychographic variables (lifestyle and belief system variables). The first method of describing your target market segments is using a set of demographic descriptors like the following: q Age q Marital status q HH income q Gender q Race/Ethnicity q Family life cycle q Education q Religious affiliation
 Target Market n Failure to meet these needs will result in loss of business. The following are a few psychological descriptors: q Political affiliation q Socially conscious q Cutting-edge q Family-oriented q Conformist q Power-wielding q Trend follower q Thrill seeker q "Green" q Fun-loving q Fashion-forward q Sports enthusiast
Target Market n Failure to meet these needs will result in loss of business. The following are a few psychological descriptors: q Political affiliation q Socially conscious q Cutting-edge q Family-oriented q Conformist q Power-wielding q Trend follower q Thrill seeker q "Green" q Fun-loving q Fashion-forward q Sports enthusiast
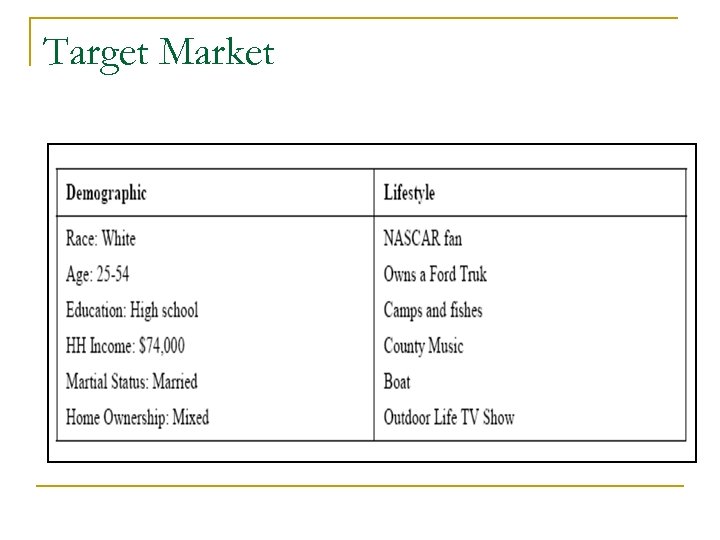 Target Market
Target Market
 Target Market n n n Market or Trade Area: -The market area can be thought of as the geographic area where the business intends to operate, i. e. , a city block, between the rivers or the globe. As a result, it is important to compare your target market profile, generally described using demographics, to the population in the market area. There a number of ways to define a market area, some are easy and others are more difficult and require the services of a marketing professional.
Target Market n n n Market or Trade Area: -The market area can be thought of as the geographic area where the business intends to operate, i. e. , a city block, between the rivers or the globe. As a result, it is important to compare your target market profile, generally described using demographics, to the population in the market area. There a number of ways to define a market area, some are easy and others are more difficult and require the services of a marketing professional.
 Methods of Defining Target Market n Geography is the simplest form of defining a market area. q q q q n Neighborhoods Zip codes City or County Boundaries Metropolitan Statistical Areas State (multi state) Boarders Nation Continent World A ring or radius defined market area is performed by creating a circle a specified number of miles from a business location. The ring analysis allows a business to evaluate the demographics of people residing within a pre-defined distance from specific business location.
Methods of Defining Target Market n Geography is the simplest form of defining a market area. q q q q n Neighborhoods Zip codes City or County Boundaries Metropolitan Statistical Areas State (multi state) Boarders Nation Continent World A ring or radius defined market area is performed by creating a circle a specified number of miles from a business location. The ring analysis allows a business to evaluate the demographics of people residing within a pre-defined distance from specific business location.
 Methods of Defining Target Market n n Drive Time Analyses: Drive time analysis is a more sophisticated analysis than the radius analysis as a number of variables are used to estimate the drive time to a given location. The analysis takes speed limits, road type, vehicle, time of days, and congestion values. Customers may be willing to drive 15 miles, but given traffic conditions the 15 miles may take 30 minutes to travel.
Methods of Defining Target Market n n Drive Time Analyses: Drive time analysis is a more sophisticated analysis than the radius analysis as a number of variables are used to estimate the drive time to a given location. The analysis takes speed limits, road type, vehicle, time of days, and congestion values. Customers may be willing to drive 15 miles, but given traffic conditions the 15 miles may take 30 minutes to travel.
 Market Size n n Once the market area and target market has been defined, it is possible to determine the number of potential customers for your business. This will allow you to estimate the N (number of potential customers) in the market potential equation. The business has concluded its market area is Wake County which has 101, 768 children under 9 years old. Therefore, N = 101, 600 potential customers. These numbers were obtained from the US Census Bureau. As a result, the 101, 600 kindergarten through 3 rd graders should be adjusted downward by multiplying by 68%. This results in an adjusted market potential of 69, 088 potential students. Adjusted Market Potential = 101, 600*68% = 69, 088
Market Size n n Once the market area and target market has been defined, it is possible to determine the number of potential customers for your business. This will allow you to estimate the N (number of potential customers) in the market potential equation. The business has concluded its market area is Wake County which has 101, 768 children under 9 years old. Therefore, N = 101, 600 potential customers. These numbers were obtained from the US Census Bureau. As a result, the 101, 600 kindergarten through 3 rd graders should be adjusted downward by multiplying by 68%. This results in an adjusted market potential of 69, 088 potential students. Adjusted Market Potential = 101, 600*68% = 69, 088
 Market Size n n Consumption or Usage: -You need to determine how often your target market segment uses your product or service. This figure will have a significant impact on the estimated market potential. Obviously the more frequently the product is purchased, the larger the market potential. Durable goods, products that can be used over a long period of time, are purchased less frequently than perishable items.
Market Size n n Consumption or Usage: -You need to determine how often your target market segment uses your product or service. This figure will have a significant impact on the estimated market potential. Obviously the more frequently the product is purchased, the larger the market potential. Durable goods, products that can be used over a long period of time, are purchased less frequently than perishable items.
 Estimate Sales Potential n n n Survey method Expert opinion method Market studied methods Sales force opinion methods Statistical methods q q Trend method Graphical method Time-series method Regression method
Estimate Sales Potential n n n Survey method Expert opinion method Market studied methods Sales force opinion methods Statistical methods q q Trend method Graphical method Time-series method Regression method
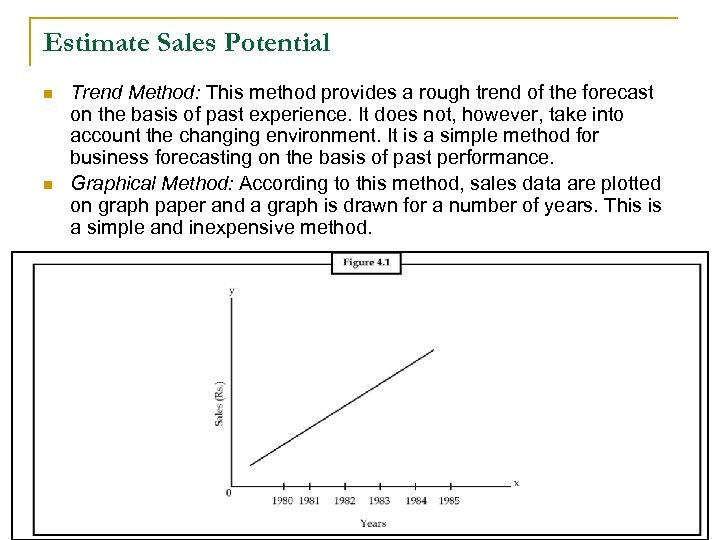 Estimate Sales Potential n n Trend Method: This method provides a rough trend of the forecast on the basis of past experience. It does not, however, take into account the changing environment. It is a simple method for business forecasting on the basis of past performance. Graphical Method: According to this method, sales data are plotted on graph paper and a graph is drawn for a number of years. This is a simple and inexpensive method.
Estimate Sales Potential n n Trend Method: This method provides a rough trend of the forecast on the basis of past experience. It does not, however, take into account the changing environment. It is a simple method for business forecasting on the basis of past performance. Graphical Method: According to this method, sales data are plotted on graph paper and a graph is drawn for a number of years. This is a simple and inexpensive method.
 Estimate Sales Potential n n n Time Series Method: This method is used for long periods duly taking into account cyclical changes, seasonal variation and irregular fluctuation. "A time series may be defined as a collection of magnitudes belonging to different time periods, of some variable or composite variables, such as production of steel, per capita income, gross national product, price of tobacoo, or index of industrial production. “ –Ya-uin-chou The Time Series Method shows the future trends of sales. The various techniques that can be used for determining these trends are: q q n n (i) Freehold or Graphical Method (ii) Semi-Average Method (iii) Moving Average Method (iv) Method of Least Squares Regression Analysis: This is a branch of statistical theory, is popularly used on the principles of sciences. It helps determine the relationship among various variables. According to Ya-uin-chou, "Regression analysis attempt establishing the 'Nature of the relationship' between variables that is to study the functional relationship between the variables and thereby provide a mechanism for prediction, or forecasting".
Estimate Sales Potential n n n Time Series Method: This method is used for long periods duly taking into account cyclical changes, seasonal variation and irregular fluctuation. "A time series may be defined as a collection of magnitudes belonging to different time periods, of some variable or composite variables, such as production of steel, per capita income, gross national product, price of tobacoo, or index of industrial production. “ –Ya-uin-chou The Time Series Method shows the future trends of sales. The various techniques that can be used for determining these trends are: q q n n (i) Freehold or Graphical Method (ii) Semi-Average Method (iii) Moving Average Method (iv) Method of Least Squares Regression Analysis: This is a branch of statistical theory, is popularly used on the principles of sciences. It helps determine the relationship among various variables. According to Ya-uin-chou, "Regression analysis attempt establishing the 'Nature of the relationship' between variables that is to study the functional relationship between the variables and thereby provide a mechanism for prediction, or forecasting".



