Диф_ диа_ желт.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Дифференциальная диагностика желтух (Jaundice) • М Г У им М. В. Ломоносова • Факультет фундаментальной медицины • Кафедра • хирургических болезней www. drsarma. in 1
Дифференциальная диагностика желтух (Jaundice) • М Г У им М. В. Ломоносова • Факультет фундаментальной медицины • Кафедра • хирургических болезней www. drsarma. in 1
 ЖЕЛТУХА Пропитывание и окрашивание всех тканей организма человека в желтый цвет в результате избыточного накопления в крови желчного пигмента — билирубина
ЖЕЛТУХА Пропитывание и окрашивание всех тканей организма человека в желтый цвет в результате избыточного накопления в крови желчного пигмента — билирубина
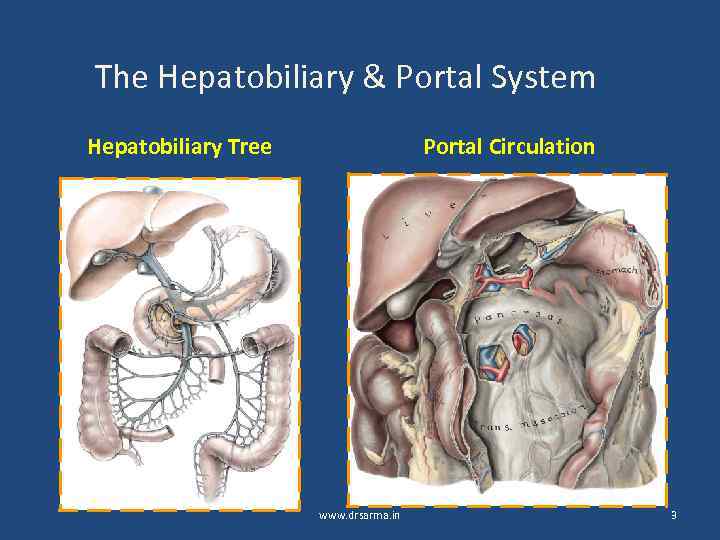 The Hepatobiliary & Portal System Hepatobiliary Tree Portal Circulation www. drsarma. in 3
The Hepatobiliary & Portal System Hepatobiliary Tree Portal Circulation www. drsarma. in 3
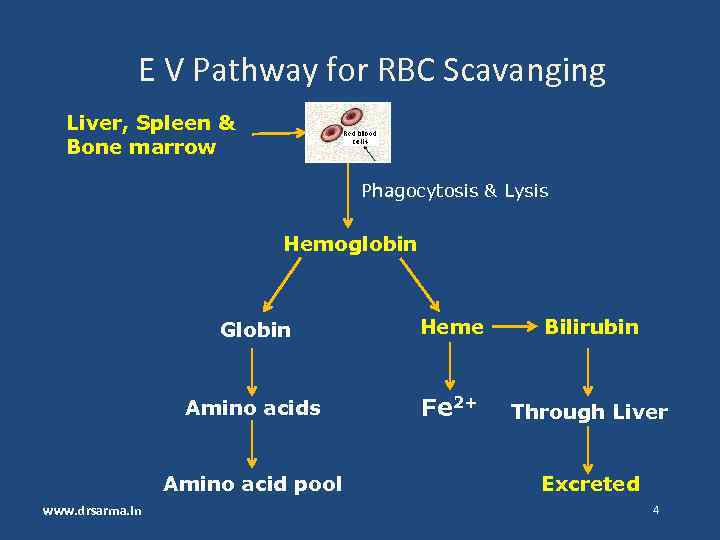 E V Pathway for RBC Scavanging Liver, Spleen & Bone marrow Phagocytosis & Lysis Hemoglobin Globin Heme Bilirubin Amino acids Fe 2+ Through Liver Amino acid pool www. drsarma. in Excreted 4
E V Pathway for RBC Scavanging Liver, Spleen & Bone marrow Phagocytosis & Lysis Hemoglobin Globin Heme Bilirubin Amino acids Fe 2+ Through Liver Amino acid pool www. drsarma. in Excreted 4
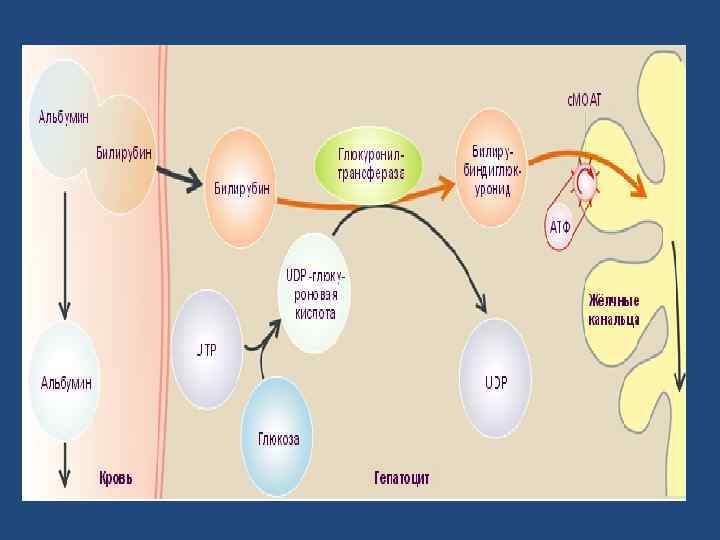
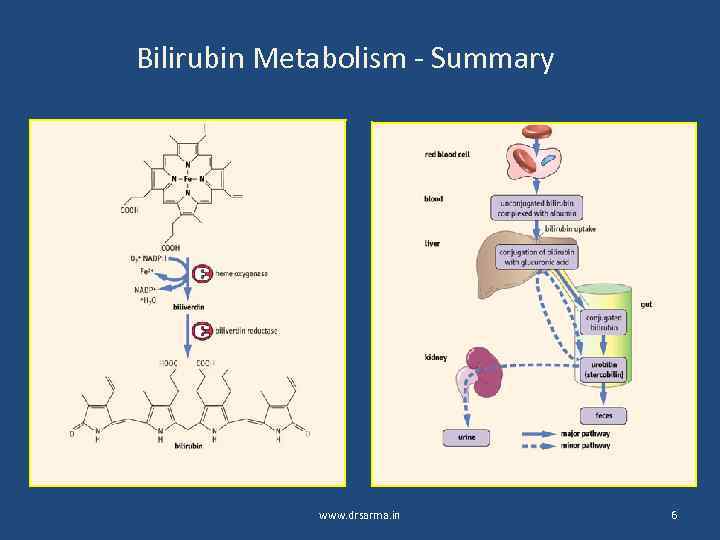 Bilirubin Metabolism - Summary www. drsarma. in 6
Bilirubin Metabolism - Summary www. drsarma. in 6
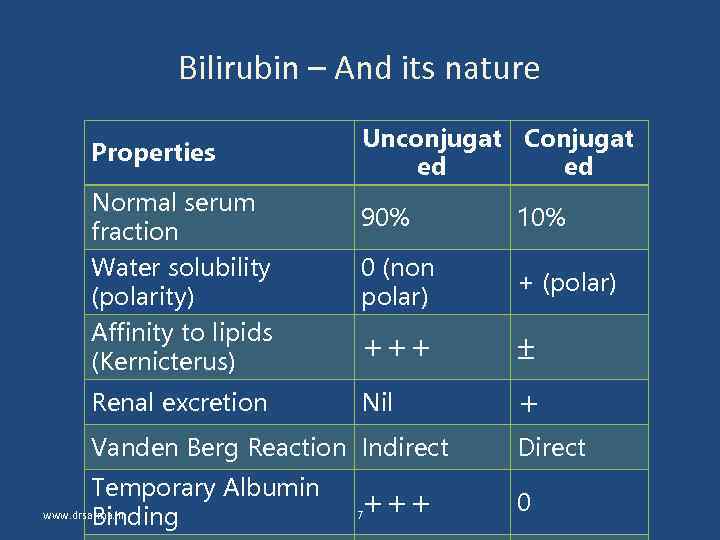 Bilirubin – And its nature Properties Unconjugat Conjugat ed ed Normal serum fraction 90% 10% Water solubility (polarity) Affinity to lipids (Kernicterus) 0 (non polar) + (polar) +++ Renal excretion Nil + Vanden Berg Reaction Indirect Temporary Albumin www. drsarma. in Binding +++ 7 Direct 0
Bilirubin – And its nature Properties Unconjugat Conjugat ed ed Normal serum fraction 90% 10% Water solubility (polarity) Affinity to lipids (Kernicterus) 0 (non polar) + (polar) +++ Renal excretion Nil + Vanden Berg Reaction Indirect Temporary Albumin www. drsarma. in Binding +++ 7 Direct 0
 Неконъюгированный билирубин (непрямой) конъюгированный (прямой)
Неконъюгированный билирубин (непрямой) конъюгированный (прямой)
 Neonatal Jaundice Neonatal jaundice is common 50% healthy term infants Re-emergence of kernicterus In utero bilirubin is handled by placenta and mother’s liver • After birth, neonate to has cope with increase in bilirubin production and the immature liver cannot • • www. drsarma. in 9
Neonatal Jaundice Neonatal jaundice is common 50% healthy term infants Re-emergence of kernicterus In utero bilirubin is handled by placenta and mother’s liver • After birth, neonate to has cope with increase in bilirubin production and the immature liver cannot • • www. drsarma. in 9
 Jaundice – Classification Normal Serum Bilirubin (SB) is 0. 3 to 1. 0 mg% Jaundice is increased levels of SB > 1. 0 mg% Over production of Bilirubin (Hemolytic) From hemolysis of RBC Lysis of RBC precursors – Ineffective erythropoesis Impaired hepatic function (Hepatitic) Hepatocellular dysfunction in handling bilirubin Uptake, Metabolism and Excretion of bilirubin Obstruction to bile flow (Obstructive) Intrahepatic cholestasis Extrahepatic Obstruction (Surgical Jaundice) www. drsarma. in 10
Jaundice – Classification Normal Serum Bilirubin (SB) is 0. 3 to 1. 0 mg% Jaundice is increased levels of SB > 1. 0 mg% Over production of Bilirubin (Hemolytic) From hemolysis of RBC Lysis of RBC precursors – Ineffective erythropoesis Impaired hepatic function (Hepatitic) Hepatocellular dysfunction in handling bilirubin Uptake, Metabolism and Excretion of bilirubin Obstruction to bile flow (Obstructive) Intrahepatic cholestasis Extrahepatic Obstruction (Surgical Jaundice) www. drsarma. in 10
 Chronic Liver Disease (CLD) Alcoholic Liver Inherited (ALD) conditions Chronic viral Haemochromatos hepatitis is Hepatitis B Wilson’s Disease Hepatitis C Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Autoimmune liver Deficiency disease: (AATD) Autoimmune Non-alcoholic hepatitis Primary Biliary www. drsarma. in steato-hepatitis 11 (NASH)
Chronic Liver Disease (CLD) Alcoholic Liver Inherited (ALD) conditions Chronic viral Haemochromatos hepatitis is Hepatitis B Wilson’s Disease Hepatitis C Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Autoimmune liver Deficiency disease: (AATD) Autoimmune Non-alcoholic hepatitis Primary Biliary www. drsarma. in steato-hepatitis 11 (NASH)
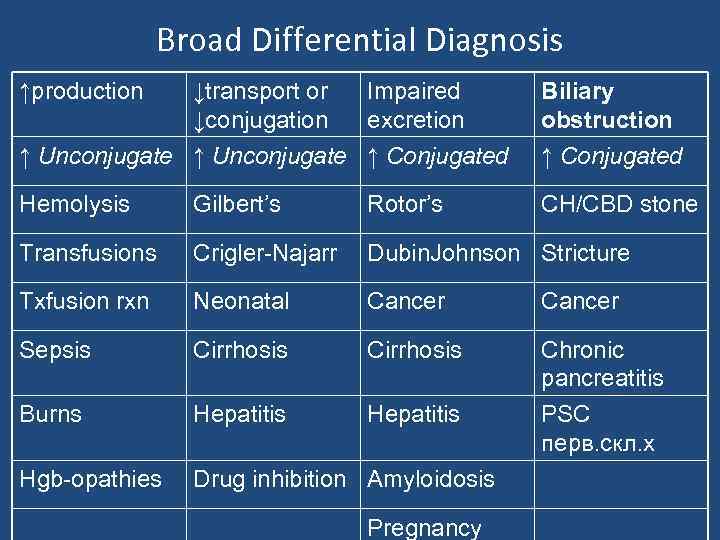 Broad Differential Diagnosis ↑production ↓transport or Impaired ↓conjugation excretion ↑ Unconjugate ↑ Conjugated Biliary obstruction ↑ Conjugated Hemolysis Gilbert’s Rotor’s CH/CBD stone Transfusions Crigler-Najarr Dubin. Johnson Stricture Txfusion rxn Neonatal Cancer Sepsis Cirrhosis Burns Hepatitis Chronic pancreatitis PSC перв. скл. х Hgb-opathies Drug inhibition Amyloidosis Pregnancy
Broad Differential Diagnosis ↑production ↓transport or Impaired ↓conjugation excretion ↑ Unconjugate ↑ Conjugated Biliary obstruction ↑ Conjugated Hemolysis Gilbert’s Rotor’s CH/CBD stone Transfusions Crigler-Najarr Dubin. Johnson Stricture Txfusion rxn Neonatal Cancer Sepsis Cirrhosis Burns Hepatitis Chronic pancreatitis PSC перв. скл. х Hgb-opathies Drug inhibition Amyloidosis Pregnancy
 Causes of Cholestatic Jaundice Intrahepatic Extrahepatic Acute liver injury, Viral hepatitis Choledocholithiasis Alcohol hepatitis, Drugs Stone obstructing CBD, CD Chronic liver injury, PBC, PSC Autoimmune cholangiopathy Drugs, Total parenteral nutrition www. drsarma. in 13 Systemic infection, Biliary strictures Cholangiocarcinoma Pancreatic carcinoma Pancreatitis,
Causes of Cholestatic Jaundice Intrahepatic Extrahepatic Acute liver injury, Viral hepatitis Choledocholithiasis Alcohol hepatitis, Drugs Stone obstructing CBD, CD Chronic liver injury, PBC, PSC Autoimmune cholangiopathy Drugs, Total parenteral nutrition www. drsarma. in 13 Systemic infection, Biliary strictures Cholangiocarcinoma Pancreatic carcinoma Pancreatitis,
 Jaundice Unrelated to Intrinsic Liver Disease • • • Hemolysis (usually T. bili < 4) Massive Transfusion Resorption of Hematoma Ineffective Erythropoesis Disorders of Conjugation – Gilbert’s syndrome • Intrahepatic Cholestasis – Sepsis, TPN, Post-operation
Jaundice Unrelated to Intrinsic Liver Disease • • • Hemolysis (usually T. bili < 4) Massive Transfusion Resorption of Hematoma Ineffective Erythropoesis Disorders of Conjugation – Gilbert’s syndrome • Intrahepatic Cholestasis – Sepsis, TPN, Post-operation
 Alcoholic Liver Disease • The history is the key – 60 grams/day • Gynecomastia, parotids, Dupuytren’s • Lab clues: AST/ALT > 2, MCV > 94 AST < 300 • Alcoholic hepatitis: – Anorexia, fever, jaundice, hepatomegaly – Treatment: • Abstinence • Nutrition • Consider prednisolone or pentoxifylline
Alcoholic Liver Disease • The history is the key – 60 grams/day • Gynecomastia, parotids, Dupuytren’s • Lab clues: AST/ALT > 2, MCV > 94 AST < 300 • Alcoholic hepatitis: – Anorexia, fever, jaundice, hepatomegaly – Treatment: • Abstinence • Nutrition • Consider prednisolone or pentoxifylline
 Лечебная тактика 1. Исключение механических факторов !!!!! Обычно пациенты с механической желтухой поступают в хирургический стационар из инфекционных стационаров через 2 -3 нед. от начала заболевания. - Инструментальные исследования 1. 2. Лабораторное обследование
Лечебная тактика 1. Исключение механических факторов !!!!! Обычно пациенты с механической желтухой поступают в хирургический стационар из инфекционных стационаров через 2 -3 нед. от начала заболевания. - Инструментальные исследования 1. 2. Лабораторное обследование
 An Approach to Jaundice • Is it isolated elevation of serum bilirubin ? • If so, is the↑unconjugated or conjugated fraction? • Is it accompanied by other liver test abnormalities ? • Is the disorder hepatocellular or cholestatic? • If cholestatic, is it intra- or extrahepatic? • These can be answered with a thoughtful • History and physical examination www. drsarma. in 18
An Approach to Jaundice • Is it isolated elevation of serum bilirubin ? • If so, is the↑unconjugated or conjugated fraction? • Is it accompanied by other liver test abnormalities ? • Is the disorder hepatocellular or cholestatic? • If cholestatic, is it intra- or extrahepatic? • These can be answered with a thoughtful • History and physical examination www. drsarma. in 18
 DDx: Obstructive Jaundice • This is the slide to remember for surgeons • Obstructive Jaundice– extrahepatic cholestasis – Choledocholithiasis (CBD or CHD stone) – Cancer (peri-ampullary or cholangio. CA) – Strictures after invasive procedures – Acute and chronic pancreatitis – Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) – Parasitic infections • Ascaris lumbricoides, liver flukes
DDx: Obstructive Jaundice • This is the slide to remember for surgeons • Obstructive Jaundice– extrahepatic cholestasis – Choledocholithiasis (CBD or CHD stone) – Cancer (peri-ampullary or cholangio. CA) – Strictures after invasive procedures – Acute and chronic pancreatitis – Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) – Parasitic infections • Ascaris lumbricoides, liver flukes
 Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient PHYSICAL EXAM • • BP/HR/Temp Mental status Asterixis Abd tenderness Liver size Splenomegaly Ascites Edema • • • Spider angiomata Hyperpigmentation Kayser-Fleischer rings Xanthomas Gynecomastia Left supraclavicular adenopathy (Virchow’s node)
Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient PHYSICAL EXAM • • BP/HR/Temp Mental status Asterixis Abd tenderness Liver size Splenomegaly Ascites Edema • • • Spider angiomata Hyperpigmentation Kayser-Fleischer rings Xanthomas Gynecomastia Left supraclavicular adenopathy (Virchow’s node)
 Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient • Ultrasound: – More sensitive than CT for gallbladder stones – Equally sensitive for dilated ducts – Portable, cheap, no radiation, no IV contrast • CT: – Better imaging of the pancreas and abdomen • MRCP: – Imaging of biliary tree comparable to ERCP • ERCP: – Therapeutic intervention for stones – Brushing and biopsy for malignancy
Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient • Ultrasound: – More sensitive than CT for gallbladder stones – Equally sensitive for dilated ducts – Portable, cheap, no radiation, no IV contrast • CT: – Better imaging of the pancreas and abdomen • MRCP: – Imaging of biliary tree comparable to ERCP • ERCP: – Therapeutic intervention for stones – Brushing and biopsy for malignancy
 Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient HISTORY • • Pain Fever Confusion Weight loss Sex, drugs, R&R Alcohol Medications • • • pruritus malaise, myalgias dark urine abdominal girth edema other autoimmune dz HIV status prior biliary surgery family history liver dz
Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient HISTORY • • Pain Fever Confusion Weight loss Sex, drugs, R&R Alcohol Medications • • • pruritus malaise, myalgias dark urine abdominal girth edema other autoimmune dz HIV status prior biliary surgery family history liver dz
 Jaundiced Emergencies • Acetaminophen Toxicity • Fulminant Hepatic Failure • Ascending Cholangitis
Jaundiced Emergencies • Acetaminophen Toxicity • Fulminant Hepatic Failure • Ascending Cholangitis
 Initial Evaluation: Physical Exam • Signs of end stage liver disease (cirrhosis) – Ascites, splenomegaly, spider angiomata, and gynecomastia • Jaundice evident first underneath the tongue, also evident in sclerae or skin • Courvoisier’s sign = painless, but palpable or distended gallbladder on exam – Could indicate malignant obstruction
Initial Evaluation: Physical Exam • Signs of end stage liver disease (cirrhosis) – Ascites, splenomegaly, spider angiomata, and gynecomastia • Jaundice evident first underneath the tongue, also evident in sclerae or skin • Courvoisier’s sign = painless, but palpable or distended gallbladder on exam – Could indicate malignant obstruction
 Clinical History – Imp clues Duration of jaundice – Acute / Chronic Abdominal pain v/s painless jaundice Fever – Viral / bacteria /sepsis Arthralgia, rash, glands; Pruritus - obstructive Appetite – Hepatocellular / Malignancy Weight loss – Malignancy – CAH Colour of stools –chalky white –obstructive Family history – Hemolytic – Inherited dis. H/o transfusion, promiscuity, IDU Alcohol abuse, Medications – INH, EM, Largactil www. drsarma. in 25
Clinical History – Imp clues Duration of jaundice – Acute / Chronic Abdominal pain v/s painless jaundice Fever – Viral / bacteria /sepsis Arthralgia, rash, glands; Pruritus - obstructive Appetite – Hepatocellular / Malignancy Weight loss – Malignancy – CAH Colour of stools –chalky white –obstructive Family history – Hemolytic – Inherited dis. H/o transfusion, promiscuity, IDU Alcohol abuse, Medications – INH, EM, Largactil www. drsarma. in 25
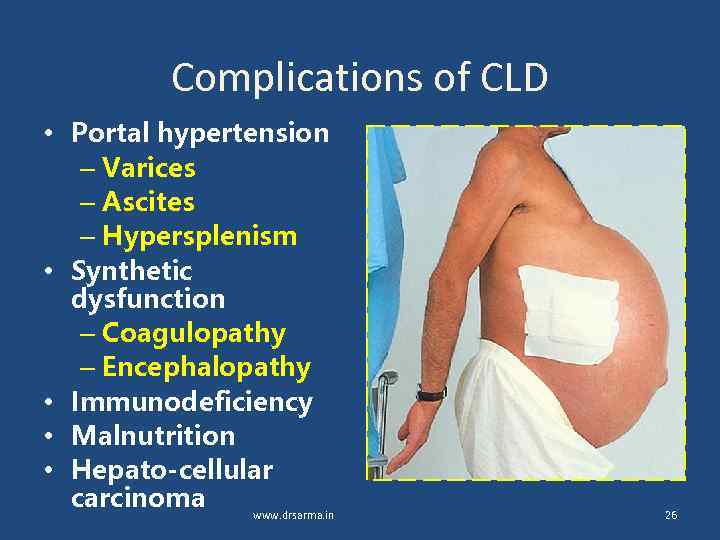 Complications of CLD • Portal hypertension – Varices – Ascites – Hypersplenism • Synthetic dysfunction – Coagulopathy – Encephalopathy • Immunodeficiency • Malnutrition • Hepato-cellular carcinoma www. drsarma. in 26
Complications of CLD • Portal hypertension – Varices – Ascites – Hypersplenism • Synthetic dysfunction – Coagulopathy – Encephalopathy • Immunodeficiency • Malnutrition • Hepato-cellular carcinoma www. drsarma. in 26
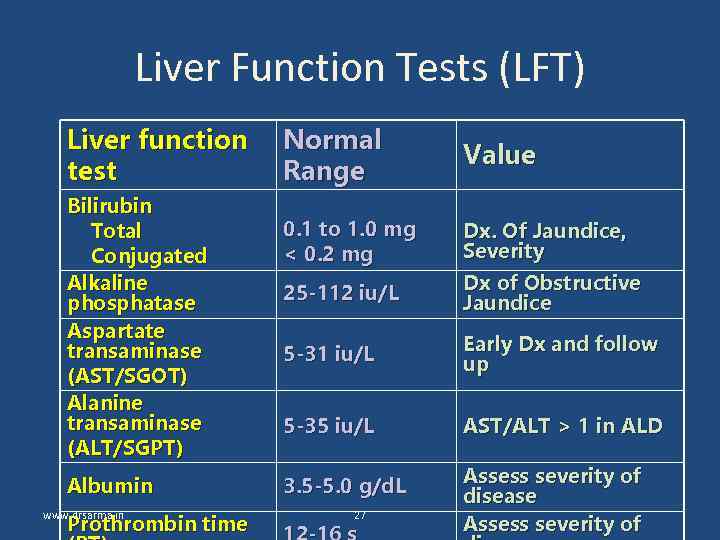 Liver Function Tests (LFT) Liver function test Bilirubin Total Conjugated Alkaline phosphatase Aspartate transaminase (AST/SGOT) Alanine transaminase (ALT/SGPT) Albumin www. drsarma. in Prothrombin time Normal Range Value 0. 1 to 1. 0 mg < 0. 2 mg Dx. Of Jaundice, Severity 25 -112 iu/L Dx of Obstructive Jaundice 5 -31 iu/L Early Dx and follow up 5 -35 iu/L AST/ALT > 1 in ALD 3. 5 -5. 0 g/d. L Assess severity of disease Assess severity of 27
Liver Function Tests (LFT) Liver function test Bilirubin Total Conjugated Alkaline phosphatase Aspartate transaminase (AST/SGOT) Alanine transaminase (ALT/SGPT) Albumin www. drsarma. in Prothrombin time Normal Range Value 0. 1 to 1. 0 mg < 0. 2 mg Dx. Of Jaundice, Severity 25 -112 iu/L Dx of Obstructive Jaundice 5 -31 iu/L Early Dx and follow up 5 -35 iu/L AST/ALT > 1 in ALD 3. 5 -5. 0 g/d. L Assess severity of disease Assess severity of 27
 Common causes • Gallstones and carcinoma of pancreas • Rare cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatitis • USS > 90% gallstones • No gallstones or significant pain – CT • Avoid knee-jerk ERCP • GS in GB but history equivocal - MRCP
Common causes • Gallstones and carcinoma of pancreas • Rare cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatitis • USS > 90% gallstones • No gallstones or significant pain – CT • Avoid knee-jerk ERCP • GS in GB but history equivocal - MRCP
 Acute on call Deranged LFTs, esp Alk Ph and GGT Conjugated Bilirubin high Take a good history Onset, drugs, pain, previous attacks, alcohol, gallstones, pale stools, dark urine, wt loss • Look for signs of liver failure • USS - gallstones? - dilated CBD +/- dilated IH ducts • •
Acute on call Deranged LFTs, esp Alk Ph and GGT Conjugated Bilirubin high Take a good history Onset, drugs, pain, previous attacks, alcohol, gallstones, pale stools, dark urine, wt loss • Look for signs of liver failure • USS - gallstones? - dilated CBD +/- dilated IH ducts • •
 Post hepatic Obstructive Jaundice • Painful v/s painless • Obstruction can be – Luminal (stone) – Stricture (benign v/s cholangiocarcinoma) – Extra luminal pancreatic cancer, Sec. lymph nodes • Investigate & treat with – Radiology (US, CT, MRCP) – ERCP / PTC www. drsarma. in 30
Post hepatic Obstructive Jaundice • Painful v/s painless • Obstruction can be – Luminal (stone) – Stricture (benign v/s cholangiocarcinoma) – Extra luminal pancreatic cancer, Sec. lymph nodes • Investigate & treat with – Radiology (US, CT, MRCP) – ERCP / PTC www. drsarma. in 30
 What imaging we need • Ultrasonography – 98% Sp, 90% Sen. • For GB stones USG better than CT • For duct stones –only 40% seen in USG • PTC – Extrahepatic obstr. – drainage • ERCP – Distal biliary obstruction Dx. Rx. • MRCP – Most useful for duct stones www. drsarma. in 31
What imaging we need • Ultrasonography – 98% Sp, 90% Sen. • For GB stones USG better than CT • For duct stones –only 40% seen in USG • PTC – Extrahepatic obstr. – drainage • ERCP – Distal biliary obstruction Dx. Rx. • MRCP – Most useful for duct stones www. drsarma. in 31
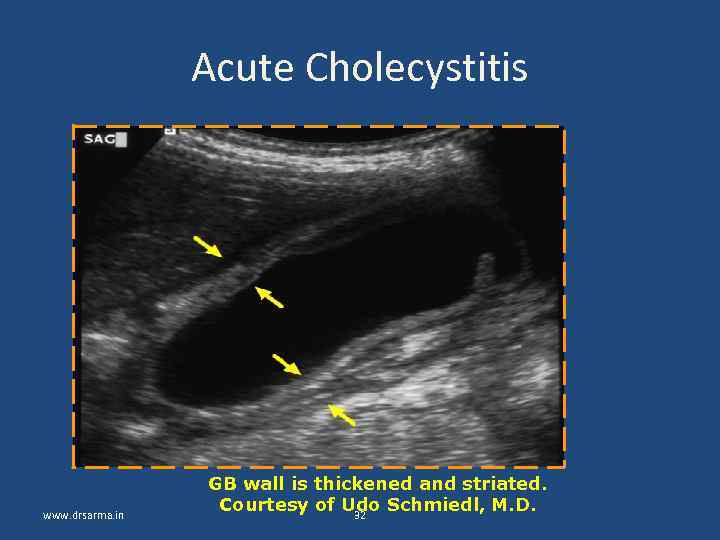 Acute Cholecystitis www. drsarma. in GB wall is thickened and striated. Courtesy of Udo Schmiedl, M. D. 32
Acute Cholecystitis www. drsarma. in GB wall is thickened and striated. Courtesy of Udo Schmiedl, M. D. 32
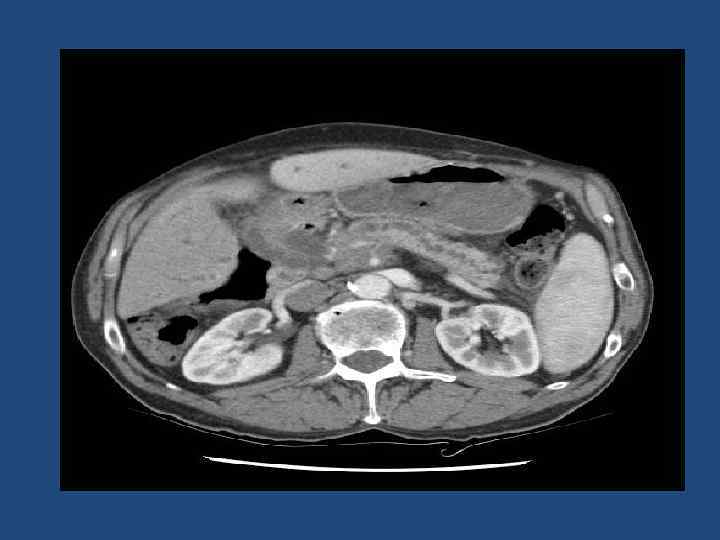
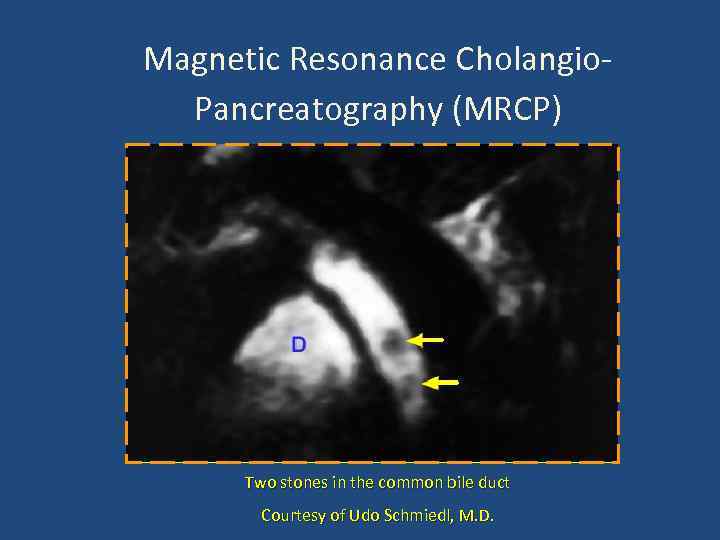 Magnetic Resonance Cholangio. Pancreatography (MRCP) Two stones in the common bile duct Courtesy of Udo Schmiedl, M. D.
Magnetic Resonance Cholangio. Pancreatography (MRCP) Two stones in the common bile duct Courtesy of Udo Schmiedl, M. D.
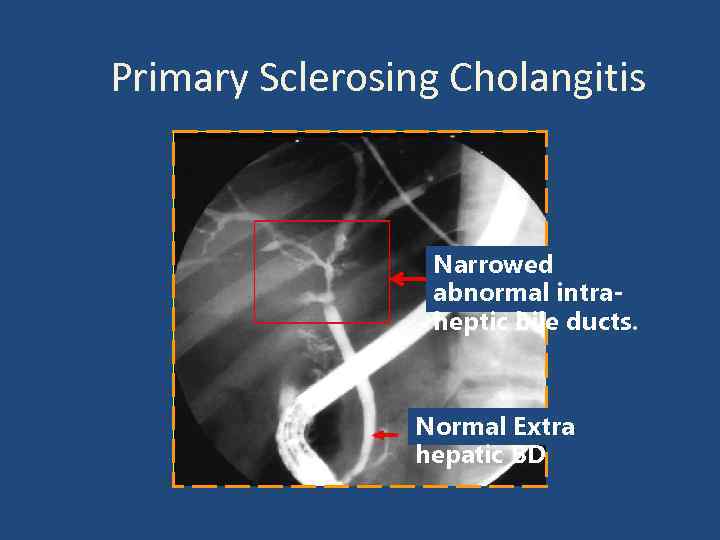 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Narrowed abnormal intraheptic bile ducts. Normal Extra hepatic BD
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Narrowed abnormal intraheptic bile ducts. Normal Extra hepatic BD
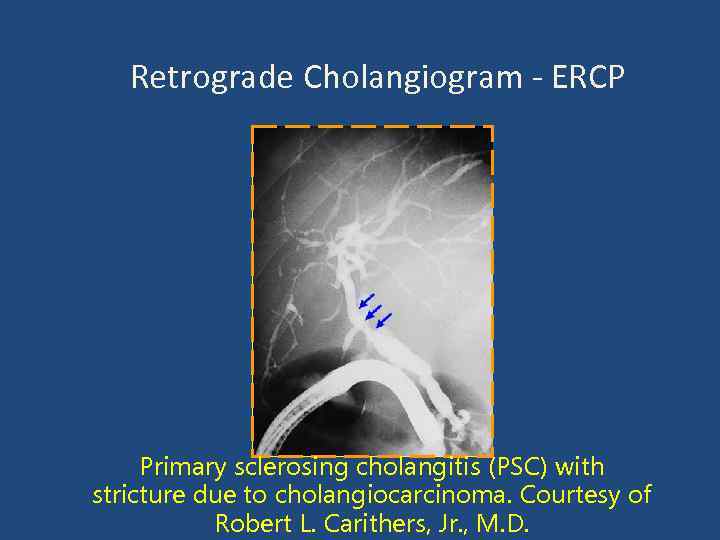 Retrograde Cholangiogram - ERCP Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) with stricture due to cholangiocarcinoma. Courtesy of Robert L. Carithers, Jr. , M. D.
Retrograde Cholangiogram - ERCP Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) with stricture due to cholangiocarcinoma. Courtesy of Robert L. Carithers, Jr. , M. D.
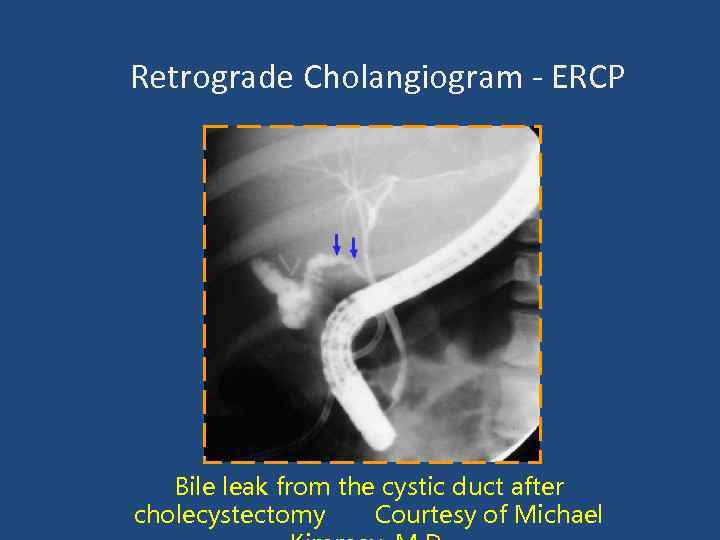 Retrograde Cholangiogram - ERCP Bile leak from the cystic duct after cholecystectomy Courtesy of Michael
Retrograde Cholangiogram - ERCP Bile leak from the cystic duct after cholecystectomy Courtesy of Michael
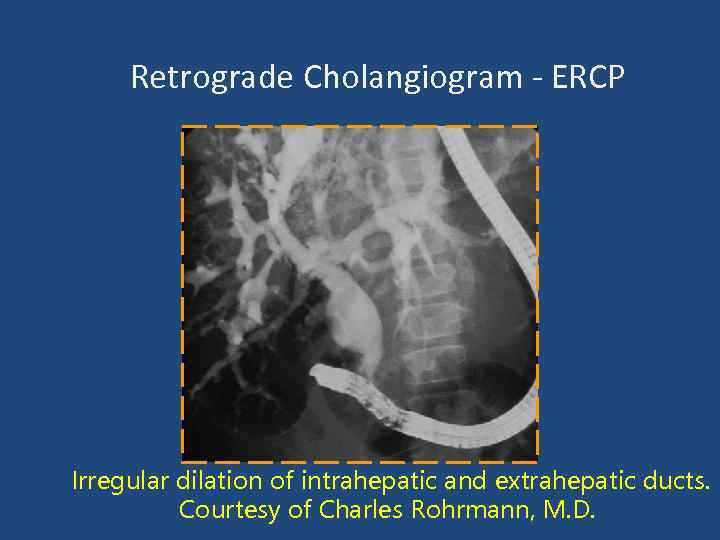 Retrograde Cholangiogram - ERCP Irregular dilation of intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts. Courtesy of Charles Rohrmann, M. D.
Retrograde Cholangiogram - ERCP Irregular dilation of intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts. Courtesy of Charles Rohrmann, M. D.
 Treatment • If Medical, then treat the etiology • If Obstructive Jaundice: – Should r/o ascending cholangitis, ABC/resusc • For cholangitis: IVF, IV Antibiotics, Decompression – Stones (remove stones vs stent vs drainage) • Done via ERCP or PTC or open (surgery) – Benign stricture (stent vs drainage catheter) – Cancer (Stent vs drainage +/- resect the CA) • The key principle is decompression, either externally(drainage) or internally(stenting) the duct open to allow better drainage
Treatment • If Medical, then treat the etiology • If Obstructive Jaundice: – Should r/o ascending cholangitis, ABC/resusc • For cholangitis: IVF, IV Antibiotics, Decompression – Stones (remove stones vs stent vs drainage) • Done via ERCP or PTC or open (surgery) – Benign stricture (stent vs drainage catheter) – Cancer (Stent vs drainage +/- resect the CA) • The key principle is decompression, either externally(drainage) or internally(stenting) the duct open to allow better drainage
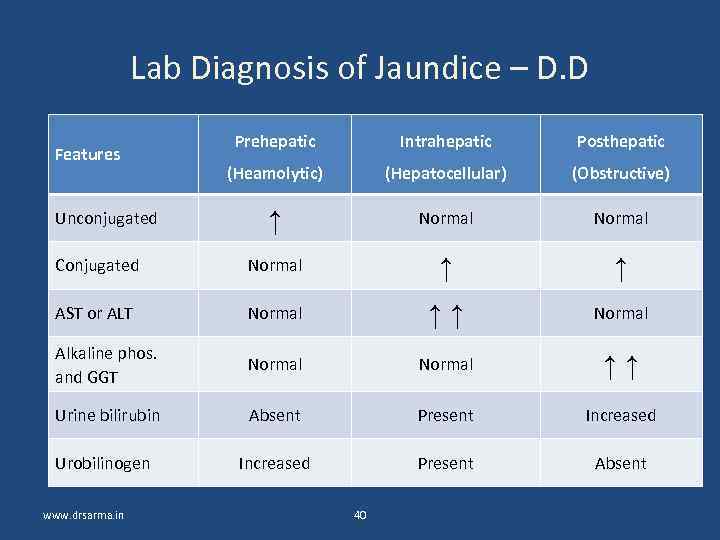 Lab Diagnosis of Jaundice – D. D Prehepatic Intrahepatic Posthepatic (Heamolytic) (Hepatocellular) (Obstructive) ↑ Normal Conjugated Normal ↑ ↑ AST or ALT Normal ↑↑ Normal Alkaline phos. and GGT Normal ↑↑ Urine bilirubin Absent Present Increased Urobilinogen Increased Present Absent Features Unconjugated www. drsarma. in 40
Lab Diagnosis of Jaundice – D. D Prehepatic Intrahepatic Posthepatic (Heamolytic) (Hepatocellular) (Obstructive) ↑ Normal Conjugated Normal ↑ ↑ AST or ALT Normal ↑↑ Normal Alkaline phos. and GGT Normal ↑↑ Urine bilirubin Absent Present Increased Urobilinogen Increased Present Absent Features Unconjugated www. drsarma. in 40
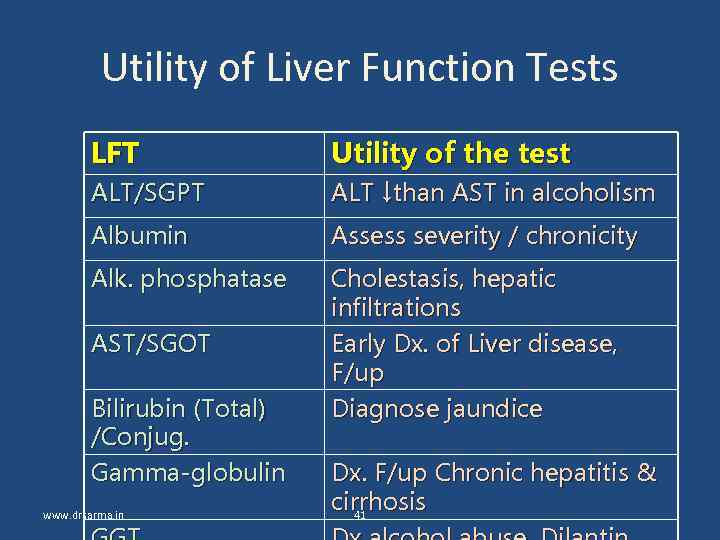 Utility of Liver Function Tests LFT Utility of the test ALT/SGPT ALT ↓than AST in alcoholism Albumin Assess severity / chronicity Alk. phosphatase Cholestasis, hepatic infiltrations Early Dx. of Liver disease, F/up Diagnose jaundice AST/SGOT Bilirubin (Total) /Conjug. Gamma-globulin www. drsarma. in Dx. F/up Chronic hepatitis & cirrhosis 41
Utility of Liver Function Tests LFT Utility of the test ALT/SGPT ALT ↓than AST in alcoholism Albumin Assess severity / chronicity Alk. phosphatase Cholestasis, hepatic infiltrations Early Dx. of Liver disease, F/up Diagnose jaundice AST/SGOT Bilirubin (Total) /Conjug. Gamma-globulin www. drsarma. in Dx. F/up Chronic hepatitis & cirrhosis 41
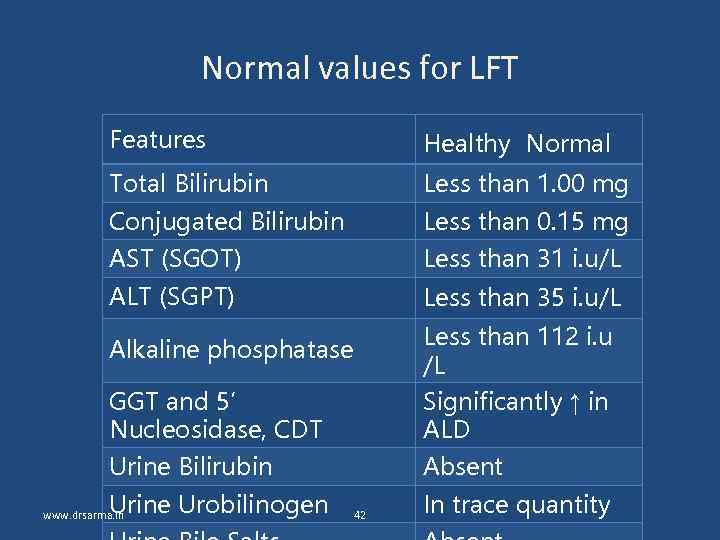 Normal values for LFT Features Healthy Normal Total Bilirubin Less than 1. 00 mg Conjugated Bilirubin Less than 0. 15 mg AST (SGOT) Less than 31 i. u/L ALT (SGPT) Less than 35 i. u/L GGT and 5’ Nucleosidase, CDT Less than 112 i. u /L Significantly ↑ in ALD Urine Bilirubin Absent Alkaline phosphatase Urine Urobilinogen www. drsarma. in 42 In trace quantity
Normal values for LFT Features Healthy Normal Total Bilirubin Less than 1. 00 mg Conjugated Bilirubin Less than 0. 15 mg AST (SGOT) Less than 31 i. u/L ALT (SGPT) Less than 35 i. u/L GGT and 5’ Nucleosidase, CDT Less than 112 i. u /L Significantly ↑ in ALD Urine Bilirubin Absent Alkaline phosphatase Urine Urobilinogen www. drsarma. in 42 In trace quantity
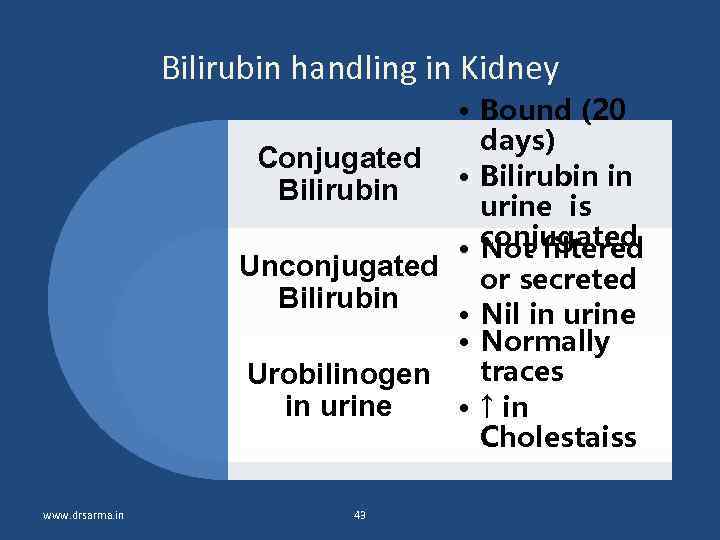 Bilirubin handling in Kidney • Bound (20 days) Conjugated • Bilirubin in Bilirubin urine is • conjugated Not filtered Unconjugated or secreted Bilirubin • Nil in urine • Normally traces Urobilinogen in urine • ↑ in Cholestaiss www. drsarma. in 43
Bilirubin handling in Kidney • Bound (20 days) Conjugated • Bilirubin in Bilirubin urine is • conjugated Not filtered Unconjugated or secreted Bilirubin • Nil in urine • Normally traces Urobilinogen in urine • ↑ in Cholestaiss www. drsarma. in 43
 DDx: Conjugated Bilirubinemia • Intrahepatic cholestasis/impaired excretion – Hepatitis (viral, alcoholic, and non-alcoholic) • Any cause of hepatocellular injury – Primary biliary cirrhosis or end-stage liver dz – Sepsis and hypoperfusion states – TPN – Pregnancy – Infiltrative dz: TB, amyloid, sarcoid, lymphoma – Drugs/toxins i. e. chlorpromazine, arsenic – Post-op patient or post-organ transplantation
DDx: Conjugated Bilirubinemia • Intrahepatic cholestasis/impaired excretion – Hepatitis (viral, alcoholic, and non-alcoholic) • Any cause of hepatocellular injury – Primary biliary cirrhosis or end-stage liver dz – Sepsis and hypoperfusion states – TPN – Pregnancy – Infiltrative dz: TB, amyloid, sarcoid, lymphoma – Drugs/toxins i. e. chlorpromazine, arsenic – Post-op patient or post-organ transplantation
 DDx: Unconjugated bilirubinemia (непрямой бил) • Impaired bilirubin conjugation – Gilbert’s disease – Crigler-Najarr syndrome – Neonatal jaundice (this is physiologic) – Hyperthyroidism – Estrogens – Liver diseases • chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, Wilson’s disease
DDx: Unconjugated bilirubinemia (непрямой бил) • Impaired bilirubin conjugation – Gilbert’s disease – Crigler-Najarr syndrome – Neonatal jaundice (this is physiologic) – Hyperthyroidism – Estrogens – Liver diseases • chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, Wilson’s disease


 Bilirubin in the Intestine 1. CB in bile is excreted into Duodenum CB 10% diffuses in to blood CB excreted is not reabsorbed 2. Conversion of CB into uro & stercobilinogen Urobilinogen excreted in stool Part of the UBG enters EHC 3. From gut, UBG but not CB enters EHC Kidney excretes absorbed UBG www. drsarma. in In biliary obst. UBG absent in urine 48
Bilirubin in the Intestine 1. CB in bile is excreted into Duodenum CB 10% diffuses in to blood CB excreted is not reabsorbed 2. Conversion of CB into uro & stercobilinogen Urobilinogen excreted in stool Part of the UBG enters EHC 3. From gut, UBG but not CB enters EHC Kidney excretes absorbed UBG www. drsarma. in In biliary obst. UBG absent in urine 48
 Fate of Senescent RBC • RBC life span in blood stream is 90 -120 days • Old RBCs are phagocytosed and/or lysed • Lysis occurs extravascularly in the RE system subsequent to RBC phagocytosis • Intravascular Hemolysis of young RBC • This is due to hemolytic diseases of RBC www. drsarma. in 49
Fate of Senescent RBC • RBC life span in blood stream is 90 -120 days • Old RBCs are phagocytosed and/or lysed • Lysis occurs extravascularly in the RE system subsequent to RBC phagocytosis • Intravascular Hemolysis of young RBC • This is due to hemolytic diseases of RBC www. drsarma. in 49
 Coloured Urine – Differ. Diagnosis Bilirubin in urine due to Jaundice (CB) Concentrated urine in dehydration Fluid deprivation syndromes Sulfasalazine use – for Ulcerative colitis Rifampicin, Pyridium and Thiamine use Red urine – Porphyria, Hemoglobin & Myoglobinuria, Hematuria Dark black urine in Ochranosis - HGA Melanin excretion from Melanoma Red sweat in Clofazamine, Rifampicin www. drsarma. in 50
Coloured Urine – Differ. Diagnosis Bilirubin in urine due to Jaundice (CB) Concentrated urine in dehydration Fluid deprivation syndromes Sulfasalazine use – for Ulcerative colitis Rifampicin, Pyridium and Thiamine use Red urine – Porphyria, Hemoglobin & Myoglobinuria, Hematuria Dark black urine in Ochranosis - HGA Melanin excretion from Melanoma Red sweat in Clofazamine, Rifampicin www. drsarma. in 50




