dc4c0b7abee958cf8f540a62b841004a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 DICOM Singapore Seminar: Consistent Presentation of Images: Author: Rob Horn Agfa Healthcare Chair, DICOM WG-06 Presenter: Kevin O’Donnell Toshiba Medical Systems Company Member, DICOM WG-06
DICOM Singapore Seminar: Consistent Presentation of Images: Author: Rob Horn Agfa Healthcare Chair, DICOM WG-06 Presenter: Kevin O’Donnell Toshiba Medical Systems Company Member, DICOM WG-06
 The Grayscale Image Presentation Problem: The appearance of grayscale images displayed on different types of softcopy display devices or printed on different types of hardcopy output devices has often been inconsistent.
The Grayscale Image Presentation Problem: The appearance of grayscale images displayed on different types of softcopy display devices or printed on different types of hardcopy output devices has often been inconsistent.
 The Grayscale Consistency Problem: n n Optimal image viewing parameters (e. g. window/ level) selected on one device appear different when displayed on a different device Device capabilities/ characteristics vary - the same number of gray levels cannot be rendered or perceived on different devices Displayed images look different from printed images …other
The Grayscale Consistency Problem: n n Optimal image viewing parameters (e. g. window/ level) selected on one device appear different when displayed on a different device Device capabilities/ characteristics vary - the same number of gray levels cannot be rendered or perceived on different devices Displayed images look different from printed images …other
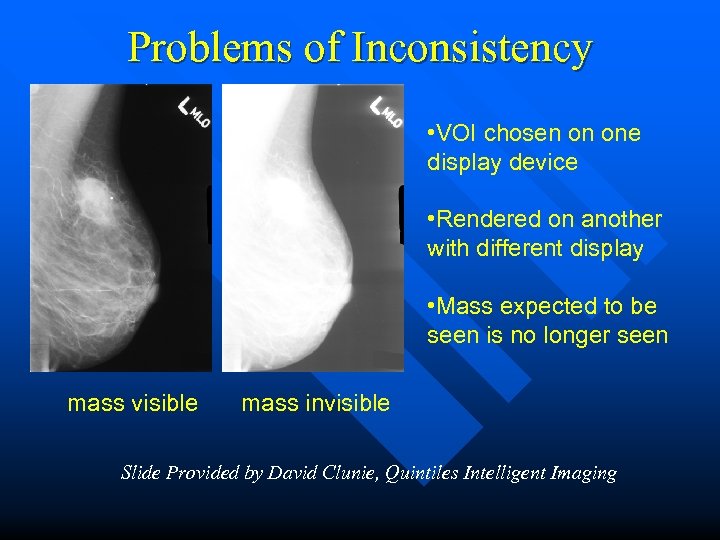 Problems of Inconsistency • VOI chosen on one display device • Rendered on another with different display • Mass expected to be seen is no longer seen mass visible mass invisible Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Problems of Inconsistency • VOI chosen on one display device • Rendered on another with different display • Mass expected to be seen is no longer seen mass visible mass invisible Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
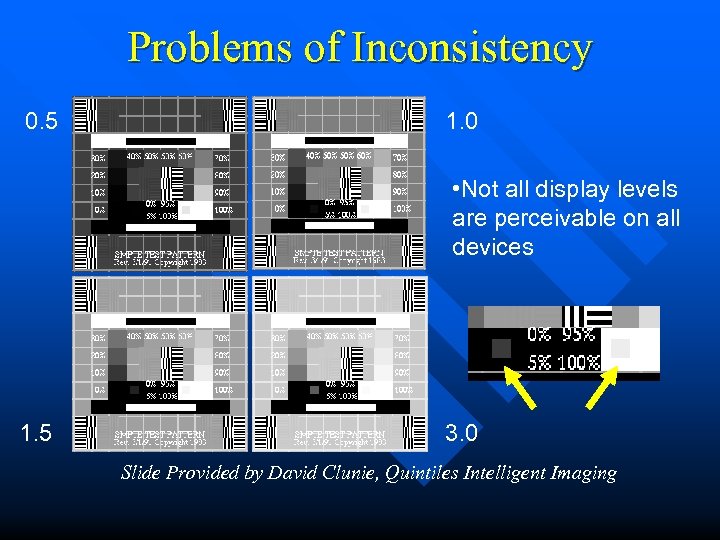 Problems of Inconsistency 0. 5 1. 0 • Not all display levels are perceivable on all devices 1. 5 3. 0 Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Problems of Inconsistency 0. 5 1. 0 • Not all display levels are perceivable on all devices 1. 5 3. 0 Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
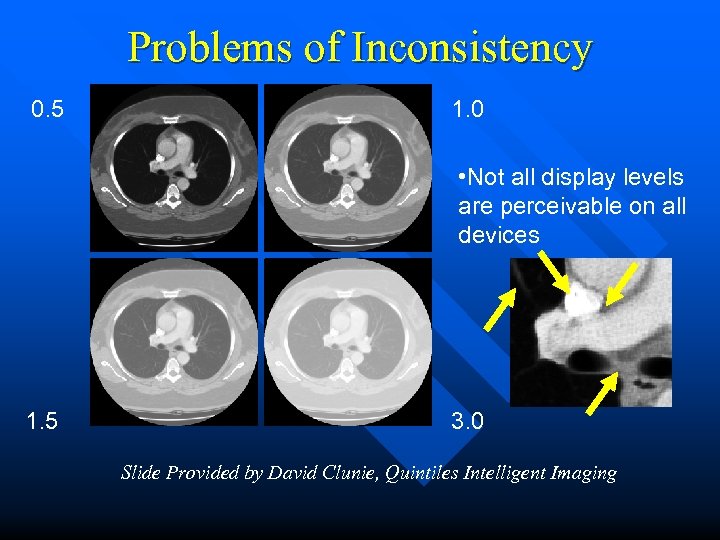 Problems of Inconsistency 0. 5 1. 0 • Not all display levels are perceivable on all devices 1. 5 3. 0 Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Problems of Inconsistency 0. 5 1. 0 • Not all display levels are perceivable on all devices 1. 5 3. 0 Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
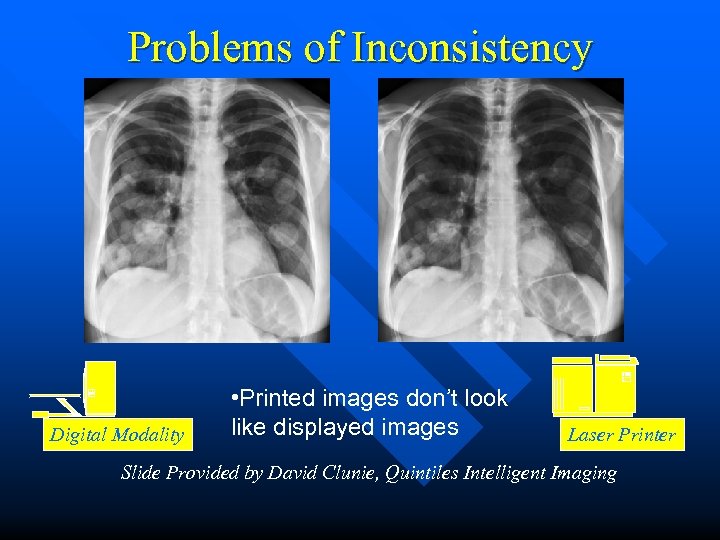 Problems of Inconsistency Digital Modality • Printed images don’t look like displayed images Laser Printer Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Problems of Inconsistency Digital Modality • Printed images don’t look like displayed images Laser Printer Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
 Causes of Inconsistency n Gamut of device – Minimum/maximum luminance/density n Characteristic curve – Mapping digital input to luminance/density – Shape – Linearity n Ambient light or illumination
Causes of Inconsistency n Gamut of device – Minimum/maximum luminance/density n Characteristic curve – Mapping digital input to luminance/density – Shape – Linearity n Ambient light or illumination
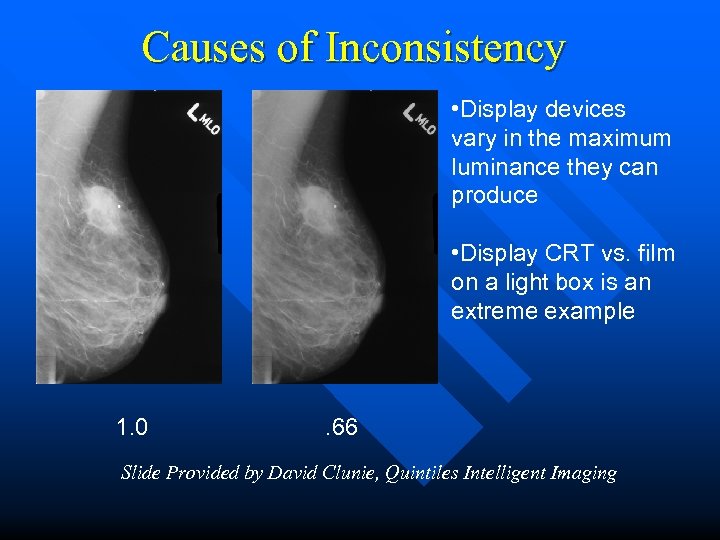 Causes of Inconsistency • Display devices vary in the maximum luminance they can produce • Display CRT vs. film on a light box is an extreme example 1. 0 . 66 Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Causes of Inconsistency • Display devices vary in the maximum luminance they can produce • Display CRT vs. film on a light box is an extreme example 1. 0 . 66 Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
 Towards a Standard Display Can’t use absolute luminance since display capabilities different n Can’t use relative luminance since shape of characteristic curves vary n Solution: exploit known characteristics of the contrast sensitivity of human visual system - contrast perception is different at different levels of luminance n
Towards a Standard Display Can’t use absolute luminance since display capabilities different n Can’t use relative luminance since shape of characteristic curves vary n Solution: exploit known characteristics of the contrast sensitivity of human visual system - contrast perception is different at different levels of luminance n
 Human Visual System n Model contrast sensitivity – assume a target similar to image features – confirm model with measurements – Barten’s model n Grayscale Standard Display Function: – Input: Just Noticeable Differences (JNDs) – Output: absolute luminance
Human Visual System n Model contrast sensitivity – assume a target similar to image features – confirm model with measurements – Barten’s model n Grayscale Standard Display Function: – Input: Just Noticeable Differences (JNDs) – Output: absolute luminance
 Printer Calibration Tools (Densitometer)
Printer Calibration Tools (Densitometer)
 Display Calibration Tools (Photometer) Slide Provided by Jerry Gaskill, Image Smiths Inc.
Display Calibration Tools (Photometer) Slide Provided by Jerry Gaskill, Image Smiths Inc.
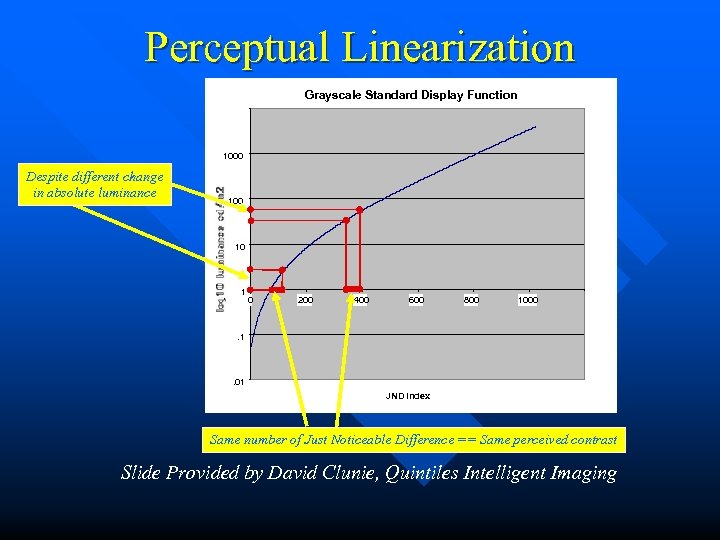 Perceptual Linearization Grayscale Standard Display Function 1000 Despite different change in absolute luminance 100 10 1 0 200 400 600 800 1000 . 1 . 01 JND Index Same number of Just Noticeable Difference == Same perceived contrast Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Perceptual Linearization Grayscale Standard Display Function 1000 Despite different change in absolute luminance 100 10 1 0 200 400 600 800 1000 . 1 . 01 JND Index Same number of Just Noticeable Difference == Same perceived contrast Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
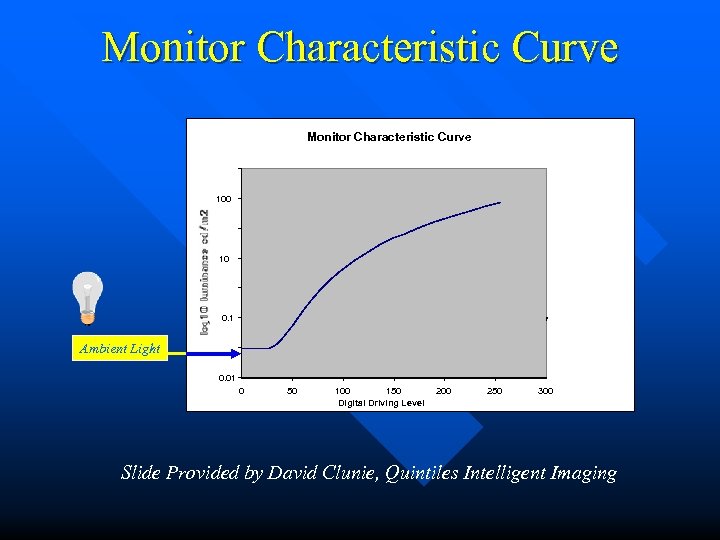 Monitor Characteristic Curve 100 10 0. 1 Ambient Light 0. 01 0 50 100 150 Digital Driving Level 200 250 300 Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Monitor Characteristic Curve 100 10 0. 1 Ambient Light 0. 01 0 50 100 150 Digital Driving Level 200 250 300 Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
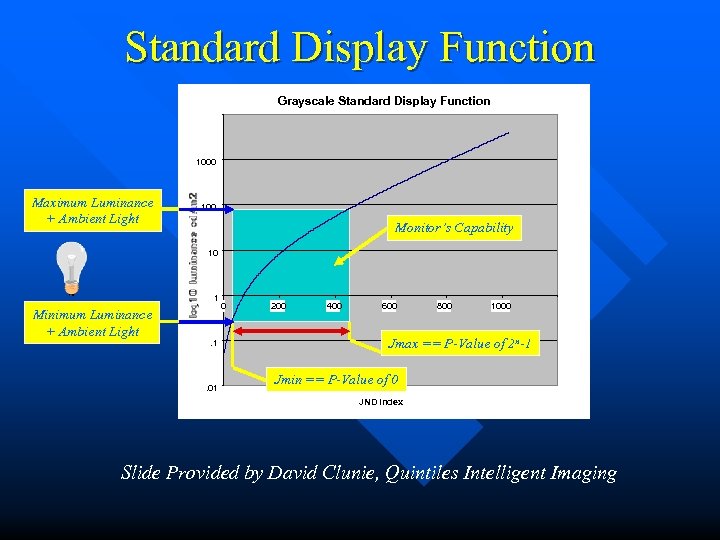 Standard Display Function Grayscale Standard Display Function 1000 Maximum Luminance + Ambient Light 100 Monitor’s Capability 10 1 Minimum Luminance + Ambient Light . 1 . 01 0 200 400 600 800 1000 Jmax == P-Value of 2 n-1 Jmin == P-Value of 0 JND Index Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Standard Display Function Grayscale Standard Display Function 1000 Maximum Luminance + Ambient Light 100 Monitor’s Capability 10 1 Minimum Luminance + Ambient Light . 1 . 01 0 200 400 600 800 1000 Jmax == P-Value of 2 n-1 Jmin == P-Value of 0 JND Index Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
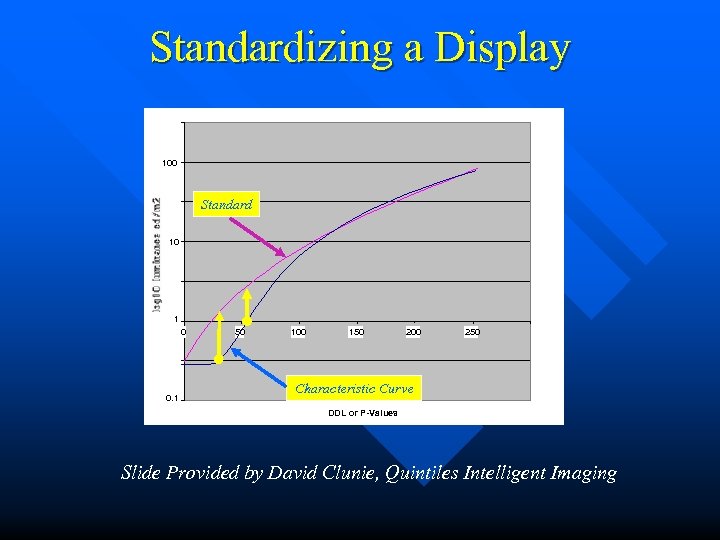 Standardizing a Display 100 Standard 10 1 0 0. 1 50 100 150 200 250 Characteristic Curve DDL or P-Values Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Standardizing a Display 100 Standard 10 1 0 0. 1 50 100 150 200 250 Characteristic Curve DDL or P-Values Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
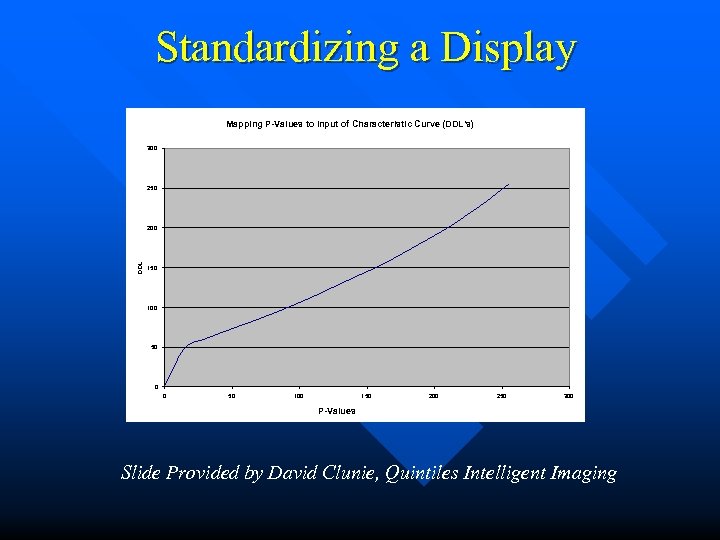 Standardizing a Display Mapping P-Values to Input of Characteristic Curve (DDL’s) 300 250 DDL 200 150 100 50 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 P-Values Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
Standardizing a Display Mapping P-Values to Input of Characteristic Curve (DDL’s) 300 250 DDL 200 150 100 50 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 P-Values Slide Provided by David Clunie, Quintiles Intelligent Imaging
 To Achieve Consistent Presentation of Images, the DICOM Standard Defines: · Basic Print Management with Presentation Look Up Table, for controlling the consistent appearance of preformatted images on printed output · Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State, for controlling the consistent appearance of images on softcopy display
To Achieve Consistent Presentation of Images, the DICOM Standard Defines: · Basic Print Management with Presentation Look Up Table, for controlling the consistent appearance of preformatted images on printed output · Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State, for controlling the consistent appearance of images on softcopy display
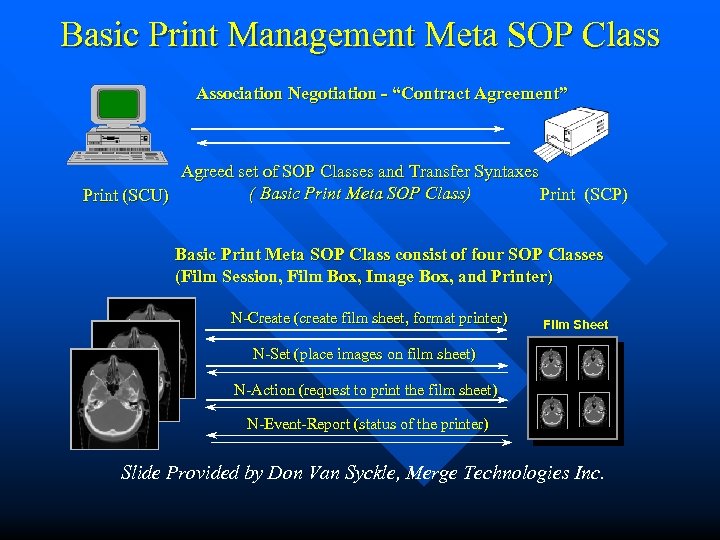 Basic Print Management Meta SOP Class Association Negotiation - “Contract Agreement” Agreed set of SOP Classes and Transfer Syntaxes ( Basic Print Meta SOP Class) Print (SCP) Print (SCU) Basic Print Meta SOP Class consist of four SOP Classes (Film Session, Film Box, Image Box, and Printer) N-Create (create film sheet, format printer) Film Sheet N-Set (place images on film sheet) N-Action (request to print the film sheet) N-Event-Report (status of the printer) Slide Provided by Don Van Syckle, Merge Technologies Inc.
Basic Print Management Meta SOP Class Association Negotiation - “Contract Agreement” Agreed set of SOP Classes and Transfer Syntaxes ( Basic Print Meta SOP Class) Print (SCP) Print (SCU) Basic Print Meta SOP Class consist of four SOP Classes (Film Session, Film Box, Image Box, and Printer) N-Create (create film sheet, format printer) Film Sheet N-Set (place images on film sheet) N-Action (request to print the film sheet) N-Event-Report (status of the printer) Slide Provided by Don Van Syckle, Merge Technologies Inc.
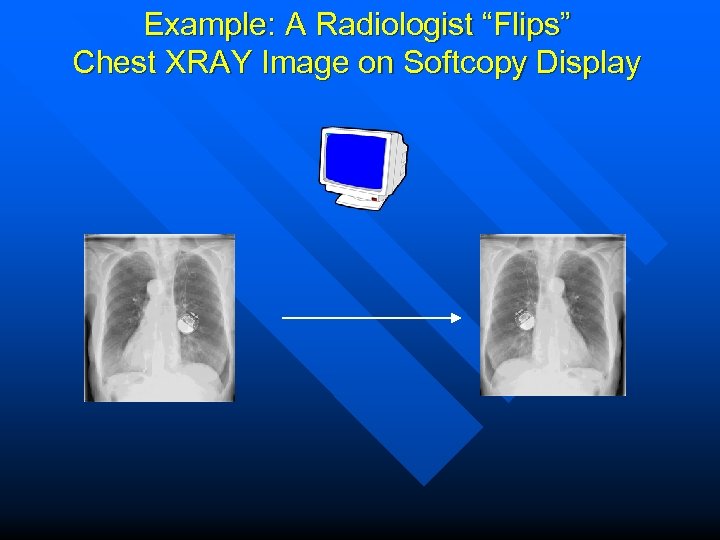 Example: A Radiologist “Flips” Chest XRAY Image on Softcopy Display
Example: A Radiologist “Flips” Chest XRAY Image on Softcopy Display
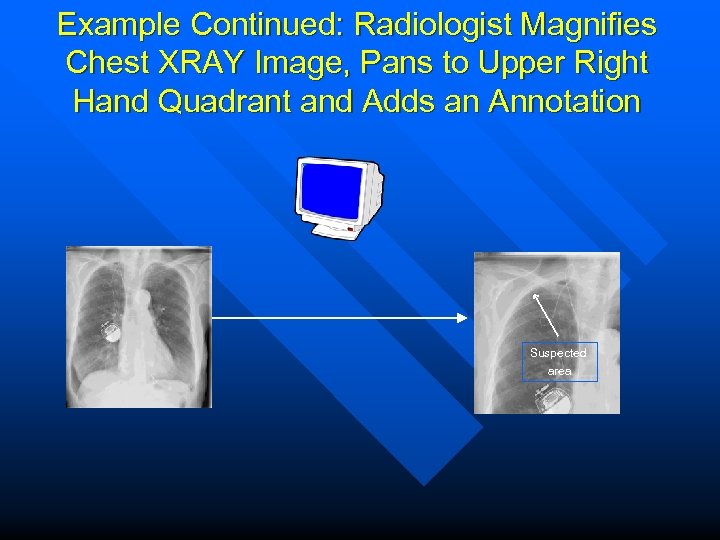 Example Continued: Radiologist Magnifies Chest XRAY Image, Pans to Upper Right Hand Quadrant and Adds an Annotation Suspected area
Example Continued: Radiologist Magnifies Chest XRAY Image, Pans to Upper Right Hand Quadrant and Adds an Annotation Suspected area
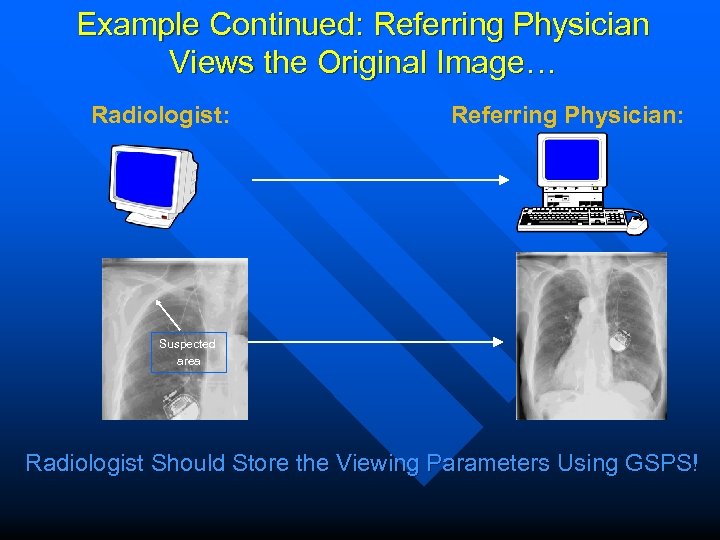 Example Continued: Referring Physician Views the Original Image… Radiologist: Referring Physician: Suspected area Radiologist Should Store the Viewing Parameters Using GSPS!
Example Continued: Referring Physician Views the Original Image… Radiologist: Referring Physician: Suspected area Radiologist Should Store the Viewing Parameters Using GSPS!
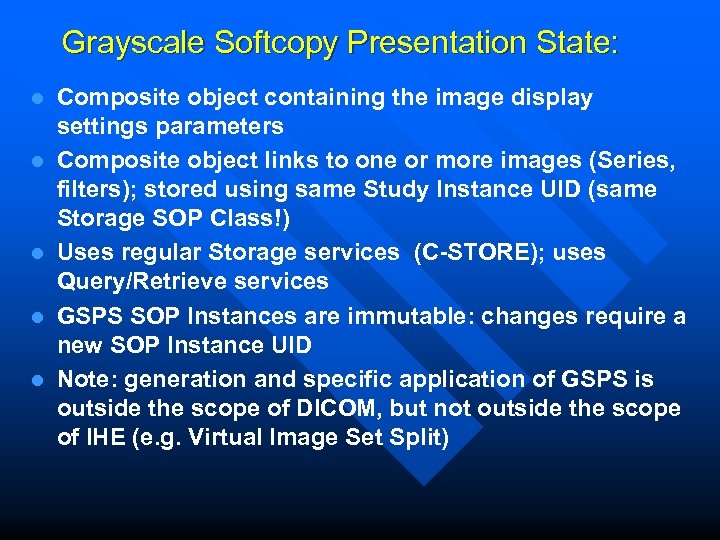 Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State: l l l Composite object containing the image display settings parameters Composite object links to one or more images (Series, filters); stored using same Study Instance UID (same Storage SOP Class!) Uses regular Storage services (C-STORE); uses Query/Retrieve services GSPS SOP Instances are immutable: changes require a new SOP Instance UID Note: generation and specific application of GSPS is outside the scope of DICOM, but not outside the scope of IHE (e. g. Virtual Image Set Split)
Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State: l l l Composite object containing the image display settings parameters Composite object links to one or more images (Series, filters); stored using same Study Instance UID (same Storage SOP Class!) Uses regular Storage services (C-STORE); uses Query/Retrieve services GSPS SOP Instances are immutable: changes require a new SOP Instance UID Note: generation and specific application of GSPS is outside the scope of DICOM, but not outside the scope of IHE (e. g. Virtual Image Set Split)
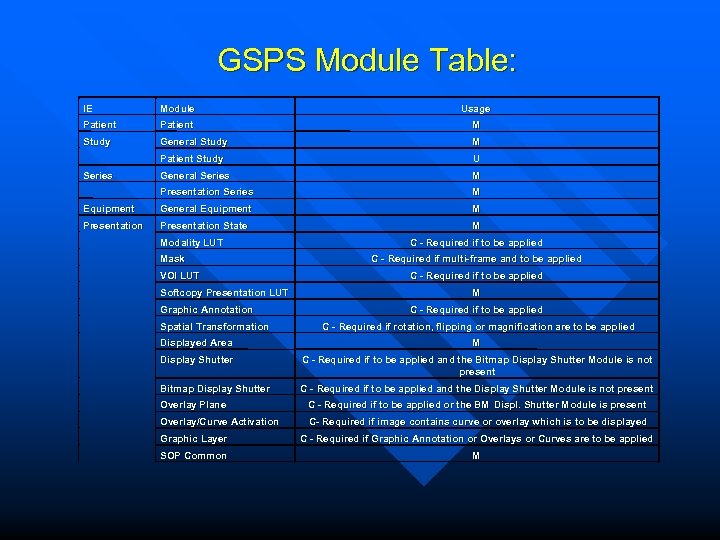 GSPS Module Table: IE Module Usage Patient M Study General Study M Patient Study U General Series M Presentation Series M Equipment General Equipment M Presentation State M Series Modality LUT Mask VOI LUT Softcopy Presentation LUT Graphic Annotation Spatial Transformation C - Required if to be applied C - Required if multi-frame and to be applied C - Required if to be applied M C - Required if to be applied C - Required if rotation, flipping or magnification are to be applied Displayed Area M Display Shutter C - Required if to be applied and the Bitmap Display Shutter Module is not present Bitmap Display Shutter C - Required if to be applied and the Display Shutter Module is not present Overlay Plane C - Required if to be applied or the BM Displ. Shutter Module is present Displ. Overlay/Curve Activation C- Required if image contains curve or overlay which is to be displayed Graphic Layer C - Required if Graphic Annotation or Overlays or Curves are to be applied SOP Common M
GSPS Module Table: IE Module Usage Patient M Study General Study M Patient Study U General Series M Presentation Series M Equipment General Equipment M Presentation State M Series Modality LUT Mask VOI LUT Softcopy Presentation LUT Graphic Annotation Spatial Transformation C - Required if to be applied C - Required if multi-frame and to be applied C - Required if to be applied M C - Required if to be applied C - Required if rotation, flipping or magnification are to be applied Displayed Area M Display Shutter C - Required if to be applied and the Bitmap Display Shutter Module is not present Bitmap Display Shutter C - Required if to be applied and the Display Shutter Module is not present Overlay Plane C - Required if to be applied or the BM Displ. Shutter Module is present Displ. Overlay/Curve Activation C- Required if image contains curve or overlay which is to be displayed Graphic Layer C - Required if Graphic Annotation or Overlays or Curves are to be applied SOP Common M
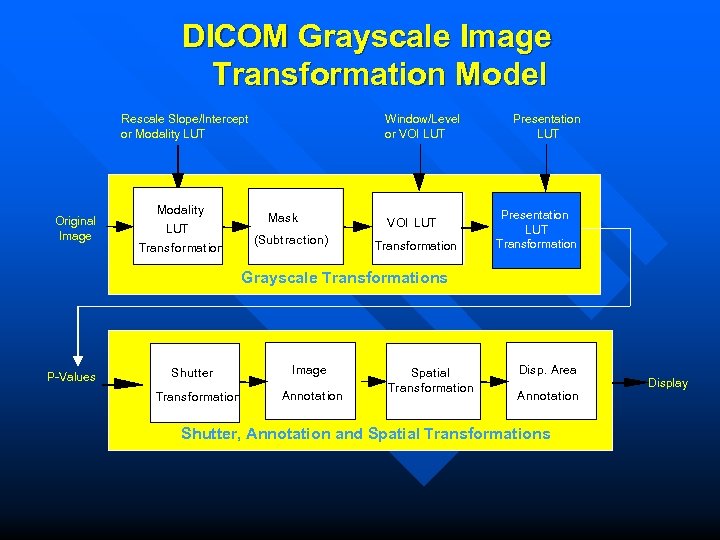 DICOM Grayscale Image Transformation Model Rescale Slope/Intercept or Modality LUT Original Image Modality LUT Transformation Window/Level or VOI LUT Mask (Subtraction) VOI LUT Transformation Presentation LUT Transformation Grayscale Transformations P-Values Shutter Transformation Image Annotation Spatial Transformation Disp. Area Annotation Shutter, Annotation and Spatial Transformations Display
DICOM Grayscale Image Transformation Model Rescale Slope/Intercept or Modality LUT Original Image Modality LUT Transformation Window/Level or VOI LUT Mask (Subtraction) VOI LUT Transformation Presentation LUT Transformation Grayscale Transformations P-Values Shutter Transformation Image Annotation Spatial Transformation Disp. Area Annotation Shutter, Annotation and Spatial Transformations Display
 What about color ? n Consistency is harder to achieve – Not just colorimetry (i. e. not just CIELAB) – Gamut of devices much more variable – Greater influence of psychovisual effects n n Extensive standards efforts e. g. ICC DICOM is defining color presentation in a manner very similar to grayscale, but utilizing the ICC profiles instead of the GSDF, see Supplement 100. – Many display and print devices already have ICC profiles, but few medical imaging devices support color presentation state.
What about color ? n Consistency is harder to achieve – Not just colorimetry (i. e. not just CIELAB) – Gamut of devices much more variable – Greater influence of psychovisual effects n n Extensive standards efforts e. g. ICC DICOM is defining color presentation in a manner very similar to grayscale, but utilizing the ICC profiles instead of the GSDF, see Supplement 100. – Many display and print devices already have ICC profiles, but few medical imaging devices support color presentation state.
 Consistent Presentation is Provided by n n n Use of DICOM GSDF for calibration of monitors Use of Presentation LUT for Grayscale Print Creation of GSPS SOP Instances to capture the presentation of softcopy images. Use of GSPS SOP Instances when displaying images from archives ( Devices that claim conformance to IHE Consistent Presentation of Images provide these functions. )
Consistent Presentation is Provided by n n n Use of DICOM GSDF for calibration of monitors Use of Presentation LUT for Grayscale Print Creation of GSPS SOP Instances to capture the presentation of softcopy images. Use of GSPS SOP Instances when displaying images from archives ( Devices that claim conformance to IHE Consistent Presentation of Images provide these functions. )


