7b548ab60cc37d850b2d35f648445e37.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Closed Head Injury: Sifting through the Quagmire of Concussions/Mild TBI Alina K. Fong, Ph. D Clinical Neuropsychologist
Diagnosis and Treatment of Closed Head Injury: Sifting through the Quagmire of Concussions/Mild TBI Alina K. Fong, Ph. D Clinical Neuropsychologist
 1) Identifying the differences between structural and functional MRI 2)Not all f. MRIs are created equal: Learning about functional NCI and its implications for diagnosis with concussions 3) Sensivity and Specificity of CFX m. TBI diagnoses 4) Determining some facts and fictions re: m. TBI 5)Learning about the Cognitive. FX Concussion Treatment Method BONUS: Can we detect Malingering in this population? ? ?
1) Identifying the differences between structural and functional MRI 2)Not all f. MRIs are created equal: Learning about functional NCI and its implications for diagnosis with concussions 3) Sensivity and Specificity of CFX m. TBI diagnoses 4) Determining some facts and fictions re: m. TBI 5)Learning about the Cognitive. FX Concussion Treatment Method BONUS: Can we detect Malingering in this population? ? ?
 Structural MRI vs. Functional NCI Structural MRI reveals brain anatomy. Functional NCI (f. NCI) reveals brain function.
Structural MRI vs. Functional NCI Structural MRI reveals brain anatomy. Functional NCI (f. NCI) reveals brain function.
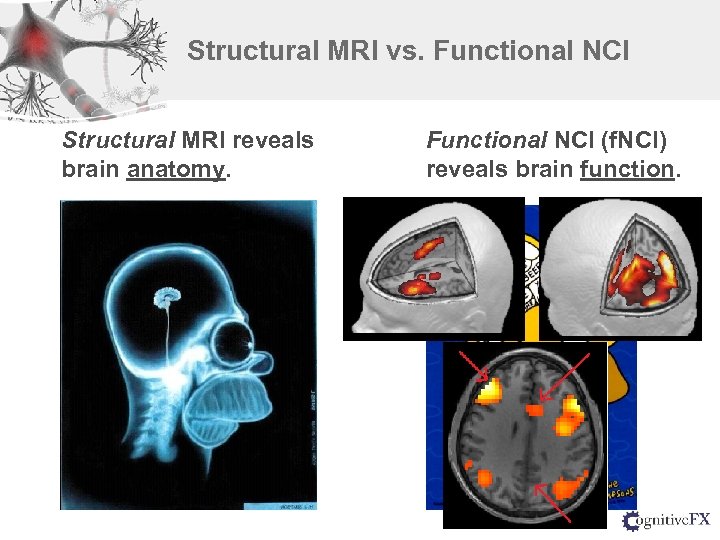 Structural MRI vs. Functional NCI Structural MRI reveals brain anatomy. Functional NCI (f. NCI) reveals brain function.
Structural MRI vs. Functional NCI Structural MRI reveals brain anatomy. Functional NCI (f. NCI) reveals brain function.
 Functional NCI
Functional NCI
 We offer unique f. NCI application f. NCI Standard f. MRI § 10 years of development § 6 comprehensive tasks that measure all areas of cognition §Our tests cover 57 distinct brain regions §Normative Database - We know what NORMAL IS! §Encapsulates all forms of brain injury §Concussion database (+1, 000 tests administered and collected data) §Diagnostic accuracy for concussion over 98% §Used to target treatment on specific cognitive areas, speeding up return to play §Recovery can be objectively measured §Unlimited applications: ADD, MS, Medication Effects, Alzheimer’s, "Chemo Brain, " etc. §Pre-surgical brain mapping §Research (group averaging) §Limited clinical use § 1, maybe 2 tasks and limited areas of focus
We offer unique f. NCI application f. NCI Standard f. MRI § 10 years of development § 6 comprehensive tasks that measure all areas of cognition §Our tests cover 57 distinct brain regions §Normative Database - We know what NORMAL IS! §Encapsulates all forms of brain injury §Concussion database (+1, 000 tests administered and collected data) §Diagnostic accuracy for concussion over 98% §Used to target treatment on specific cognitive areas, speeding up return to play §Recovery can be objectively measured §Unlimited applications: ADD, MS, Medication Effects, Alzheimer’s, "Chemo Brain, " etc. §Pre-surgical brain mapping §Research (group averaging) §Limited clinical use § 1, maybe 2 tasks and limited areas of focus
 Recent Notus Publications Bigler, E. D. , Allen, M. D. , Stimac, G. K, (2012). MRI and functional MRI. In Simpson, J. R. (Ed. ) Neuroimaging in Forensic Psychiatry: From the clinic to the courtroom. Wiley-Blackwell Press. Abstract Woon, F. L. , Allen, M. D. , Hedges, D. , Miller, C. (2012). The functional magnetic resonance imaging-based verbal fluency test in Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. Neurocase. Abstract Allen, M. D. , Hedges, D. W. , Farrer, T. J. , and Larson, M. J. (2012). Assessment of Brain Activity during Memory Encoding in a Narcolepsy Patient On and Off Modafinil using Normative f. MRI data. Neurocase, 18, 13 -25. Abstract Allen, M. D. , Owens, T. E. , Fong, A. K. , Richards, D. R. (2011). A Functional Neuroimaging Analysis of the Trail Making Test-B: Implications for Clinical Application. Behavioural Neurology, 24, 159 -171. Abstract Allen, M. D. , Wu, T. C. , & Bigler, E. , (2011). Traumatic Brain Injury Alters Word Memory Test Performance by Slowing Response Time and Increasing Cortical Activation: An f. MRI Study of a Symptom Validity Test. Psychological Injury and Law, 4, 140 -146. Abstract Larsen, J. D. , Allen, M. D. , Bigler, E. , Goodrich-Hunsaker, N. , & Hopkins, R. (2010) Different patterns of cerebral activation in genuine and malingered cognitive effort during performance on the Word Memory Test. Brain Injury, 24, 89 -99. Abstract Wu, T. C. , Allen, et al. (2010). Functional Neuroimaging of Symptom Validity Testing in Traumatic Brain Injury. Psychological Injury and Law, 3, 50 -62. Abstract Garn, C. L. , Allen, M. D. , Larsen, J. D. (2009). An f. MRI study of sex differences in brain activation during object naming. Cortex, 45, 610 -618. Abstract Allen, M. D. & Fong A. (2008 a). Clinical Application of Standardized Cognitive Assessment using f. MRI. I. Matrix Reasoning. Behavioural Neurology, 20, 127 -140. Abstract Allen, M. D. & Fong A. (2008 b). Clinical Application of Standardized Cognitive Assessment using f. MRI. II. Verbal Fluency. Behavioural Neurology, 20, 141 -152. Abstract Allen, M. D. , Bigler, E. , Larsen, J. , Goodrich-Hunsaker, N. , & Hopkins, R. (2007). Functional neuroimaging evidence for high cognitive effort on the Word Memory Test in the absence of external incentives. Brain Injury, 21, 1425 -1428. Abstract
Recent Notus Publications Bigler, E. D. , Allen, M. D. , Stimac, G. K, (2012). MRI and functional MRI. In Simpson, J. R. (Ed. ) Neuroimaging in Forensic Psychiatry: From the clinic to the courtroom. Wiley-Blackwell Press. Abstract Woon, F. L. , Allen, M. D. , Hedges, D. , Miller, C. (2012). The functional magnetic resonance imaging-based verbal fluency test in Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. Neurocase. Abstract Allen, M. D. , Hedges, D. W. , Farrer, T. J. , and Larson, M. J. (2012). Assessment of Brain Activity during Memory Encoding in a Narcolepsy Patient On and Off Modafinil using Normative f. MRI data. Neurocase, 18, 13 -25. Abstract Allen, M. D. , Owens, T. E. , Fong, A. K. , Richards, D. R. (2011). A Functional Neuroimaging Analysis of the Trail Making Test-B: Implications for Clinical Application. Behavioural Neurology, 24, 159 -171. Abstract Allen, M. D. , Wu, T. C. , & Bigler, E. , (2011). Traumatic Brain Injury Alters Word Memory Test Performance by Slowing Response Time and Increasing Cortical Activation: An f. MRI Study of a Symptom Validity Test. Psychological Injury and Law, 4, 140 -146. Abstract Larsen, J. D. , Allen, M. D. , Bigler, E. , Goodrich-Hunsaker, N. , & Hopkins, R. (2010) Different patterns of cerebral activation in genuine and malingered cognitive effort during performance on the Word Memory Test. Brain Injury, 24, 89 -99. Abstract Wu, T. C. , Allen, et al. (2010). Functional Neuroimaging of Symptom Validity Testing in Traumatic Brain Injury. Psychological Injury and Law, 3, 50 -62. Abstract Garn, C. L. , Allen, M. D. , Larsen, J. D. (2009). An f. MRI study of sex differences in brain activation during object naming. Cortex, 45, 610 -618. Abstract Allen, M. D. & Fong A. (2008 a). Clinical Application of Standardized Cognitive Assessment using f. MRI. I. Matrix Reasoning. Behavioural Neurology, 20, 127 -140. Abstract Allen, M. D. & Fong A. (2008 b). Clinical Application of Standardized Cognitive Assessment using f. MRI. II. Verbal Fluency. Behavioural Neurology, 20, 141 -152. Abstract Allen, M. D. , Bigler, E. , Larsen, J. , Goodrich-Hunsaker, N. , & Hopkins, R. (2007). Functional neuroimaging evidence for high cognitive effort on the Word Memory Test in the absence of external incentives. Brain Injury, 21, 1425 -1428. Abstract
 Scientific and Clinical Acceptance Tests used for neuropsychological assessments are being adapted for administration during functional neuroimaging (Allen & Fong, 2008) such that … neuropsychologists … will be able to visualize brain activation patterns related to specific tests.
Scientific and Clinical Acceptance Tests used for neuropsychological assessments are being adapted for administration during functional neuroimaging (Allen & Fong, 2008) such that … neuropsychologists … will be able to visualize brain activation patterns related to specific tests.
 Ø Signs & symptoms vary widely Ø May/may not be obvious signs Ø Post-concussion symptoms: subtle, unnoticed by patient, doctors, family members Ø Varied training of medical professionals who claim to "treat" concussions Ø Patient's reluctance to report symptoms
Ø Signs & symptoms vary widely Ø May/may not be obvious signs Ø Post-concussion symptoms: subtle, unnoticed by patient, doctors, family members Ø Varied training of medical professionals who claim to "treat" concussions Ø Patient's reluctance to report symptoms
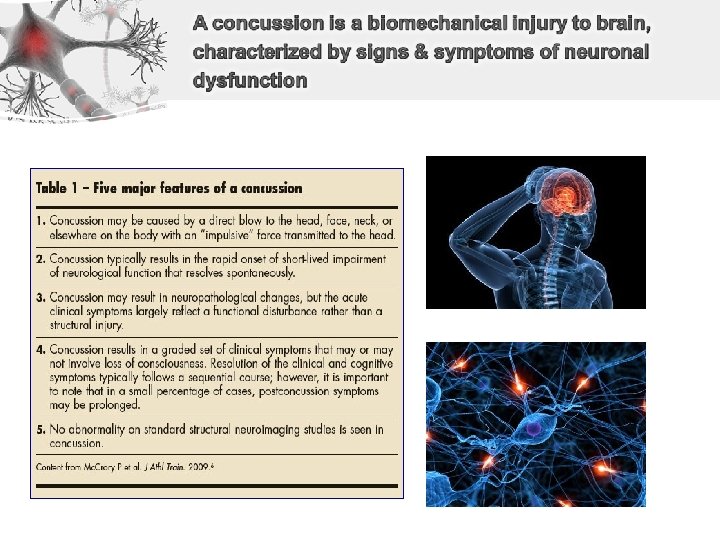
 • Temporary confusion or amnesia in absence of loss of consciousness is more common • LOC is not always predictive of recovery after mild TBI [Guskiewicz et al. , 2003; Lovell et al. , 1999]
• Temporary confusion or amnesia in absence of loss of consciousness is more common • LOC is not always predictive of recovery after mild TBI [Guskiewicz et al. , 2003; Lovell et al. , 1999]
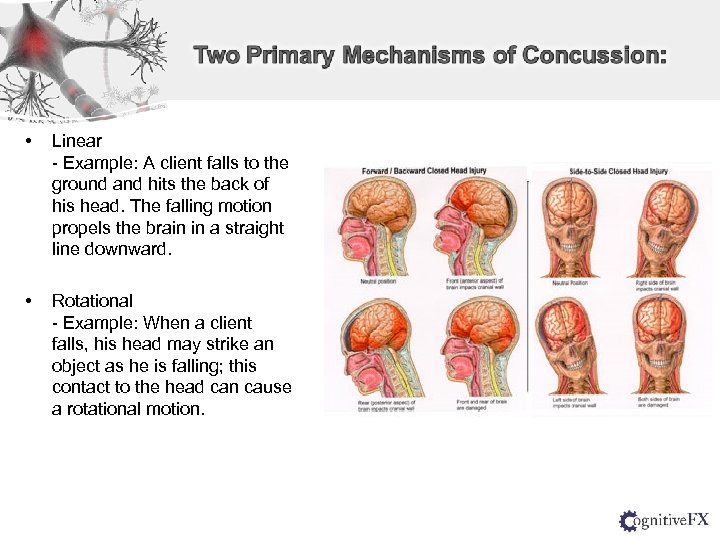 • Linear - Example: A client falls to the ground and hits the back of his head. The falling motion propels the brain in a straight line downward. • Rotational - Example: When a client falls, his head may strike an object as he is falling; this contact to the head can cause a rotational motion.
• Linear - Example: A client falls to the ground and hits the back of his head. The falling motion propels the brain in a straight line downward. • Rotational - Example: When a client falls, his head may strike an object as he is falling; this contact to the head can cause a rotational motion.
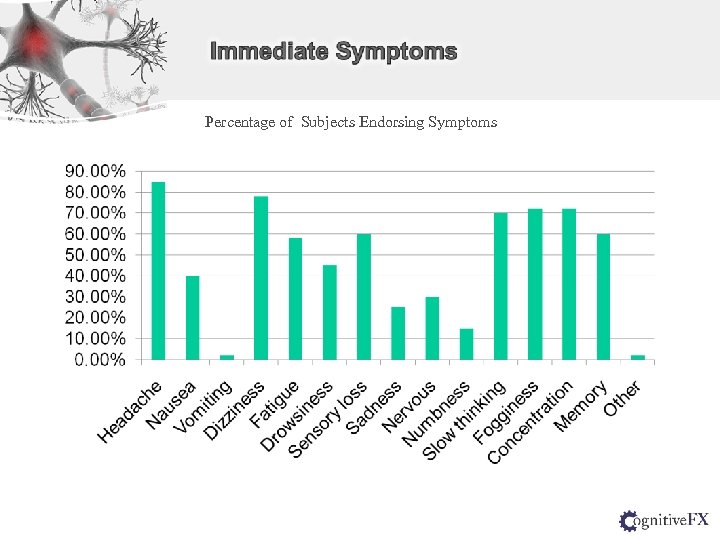 Percentage of Subjects Endorsing Symptoms
Percentage of Subjects Endorsing Symptoms
 • Impaired attention -- vacant stare, delayed responses, inability to focus • Slurred or incoherent speech • Gross incoordination • Disorientation • Emotional reactions out of proportion • Memory deficits • "Altered" consciousness
• Impaired attention -- vacant stare, delayed responses, inability to focus • Slurred or incoherent speech • Gross incoordination • Disorientation • Emotional reactions out of proportion • Memory deficits • "Altered" consciousness
 Later Signs of Concussion - Occuring from days to weeks • • • • Persistent headache Dizziness/vertigo Poor attention and concentration Memory dysfunction Nausea or vomiting Fatigue easily Irritability Intolerance of bright lights Intolerance of loud noises Anxiety and/or depression Sleep/Eating disturbances Behavioral Changes Poor academic performance
Later Signs of Concussion - Occuring from days to weeks • • • • Persistent headache Dizziness/vertigo Poor attention and concentration Memory dysfunction Nausea or vomiting Fatigue easily Irritability Intolerance of bright lights Intolerance of loud noises Anxiety and/or depression Sleep/Eating disturbances Behavioral Changes Poor academic performance
 Ø Methods & tools to detect concussion & make accurate return-to-play decisions are inadequate when used independently of each other Ø Traditional neurological exam & imaging (CT, MRI) are not consistently useful Ø Lack of data on youngest age groups affected by concussions
Ø Methods & tools to detect concussion & make accurate return-to-play decisions are inadequate when used independently of each other Ø Traditional neurological exam & imaging (CT, MRI) are not consistently useful Ø Lack of data on youngest age groups affected by concussions
 Fiction: “A concussion is a minor head injury with no long-term effects. ” Fact: § A concussion is a minor or mild brain injury. § Symptoms of a concussion can last hours, days, weeks, months or indefinitely. § Long-term problems can include: memory loss, poor concentration, anxiety, depression, & personality changes.
Fiction: “A concussion is a minor head injury with no long-term effects. ” Fact: § A concussion is a minor or mild brain injury. § Symptoms of a concussion can last hours, days, weeks, months or indefinitely. § Long-term problems can include: memory loss, poor concentration, anxiety, depression, & personality changes.
 § § Fiction: “If there is no visible injury, everything is okay!” Fact: Concussions often do not result in any obvious signs & symptoms. Signs may be subtle & may not appear for hours or days following injury.
§ § Fiction: “If there is no visible injury, everything is okay!” Fact: Concussions often do not result in any obvious signs & symptoms. Signs may be subtle & may not appear for hours or days following injury.
 Fiction: “Symptoms of a concussion will always clear up, usually within a few days. ” Fact: • Most patients report significant recoverywithin a short timeframe of 7 to 10 days; however full recovery from a first time concussion may take up to 45 days. Approximately 15 -20% will experience symptoms lasting for weeks, months, or longer • Post-concussion syndrome (post-concussive signs & symptoms > 3 weeks duration) may develop, further delaying recovery
Fiction: “Symptoms of a concussion will always clear up, usually within a few days. ” Fact: • Most patients report significant recoverywithin a short timeframe of 7 to 10 days; however full recovery from a first time concussion may take up to 45 days. Approximately 15 -20% will experience symptoms lasting for weeks, months, or longer • Post-concussion syndrome (post-concussive signs & symptoms > 3 weeks duration) may develop, further delaying recovery
 Fiction: “A normal CT (computed tomography) scan rule ou concussion. ” Fact: Ø CT scan only identifies structural damage Ø A concussion is an alteration of the brain’s normal functioning Ø Advanced neuroimaging techniques (e. g. f. MRI, DTI)
Fiction: “A normal CT (computed tomography) scan rule ou concussion. ” Fact: Ø CT scan only identifies structural damage Ø A concussion is an alteration of the brain’s normal functioning Ø Advanced neuroimaging techniques (e. g. f. MRI, DTI)
 Fiction : “All concussion grading scales are the same” Fact: Ø There are over 17 different concussion severity grading scales Ø Concussion severity should be graded on basis of presence and overall duration of symptoms (i. e. after all symptoms have cleared) [Guskiewicz et al. , 2004] Ø Focus attention on patient's recovery w/o too much emphasis on grading system.
Fiction : “All concussion grading scales are the same” Fact: Ø There are over 17 different concussion severity grading scales Ø Concussion severity should be graded on basis of presence and overall duration of symptoms (i. e. after all symptoms have cleared) [Guskiewicz et al. , 2004] Ø Focus attention on patient's recovery w/o too much emphasis on grading system.
 Fiction: “The harder someone is hit, the worse the concussion. ” Fact: Ø Any contact to head or body causing rapid head movement can cause a concussion Ø Several low impact hits over time might be more serious than a single high force collision.
Fiction: “The harder someone is hit, the worse the concussion. ” Fact: Ø Any contact to head or body causing rapid head movement can cause a concussion Ø Several low impact hits over time might be more serious than a single high force collision.
 Fiction: “Helmets prevent concussions. ” Fact: Ø Helmets are designed to prevent skull fracture & other serious head injuries; they are not designed to prevent concussions. Ø A properly fitted helmet may reduce risk or severity of a concussion.
Fiction: “Helmets prevent concussions. ” Fact: Ø Helmets are designed to prevent skull fracture & other serious head injuries; they are not designed to prevent concussions. Ø A properly fitted helmet may reduce risk or severity of a concussion.
 Fiction: “A patient should be completely restricted from activity after a concussion. ” Fact: Ø Current clinical recommendations: complete rest from physical & cognitive activities. Ø No evidence that cognitive activity following injury increases risk for further concussions or that complete restriction of all activity accelerates recovery. Ø Brain can benefit from appropriately-timed voluntary exercise [Griesbach et al. , 2004; Majerske et al. , 2008]
Fiction: “A patient should be completely restricted from activity after a concussion. ” Fact: Ø Current clinical recommendations: complete rest from physical & cognitive activities. Ø No evidence that cognitive activity following injury increases risk for further concussions or that complete restriction of all activity accelerates recovery. Ø Brain can benefit from appropriately-timed voluntary exercise [Griesbach et al. , 2004; Majerske et al. , 2008]
 the Facts about concussion Ø Ø Ø A concussion is a brain injury All concussions are serious Concussions can occur without loss of consciousness Concussions can occur in any sport or activity Recognition & management of concussions when they first occur can help prevent further injury or death, & possible long-term complications
the Facts about concussion Ø Ø Ø A concussion is a brain injury All concussions are serious Concussions can occur without loss of consciousness Concussions can occur in any sport or activity Recognition & management of concussions when they first occur can help prevent further injury or death, & possible long-term complications
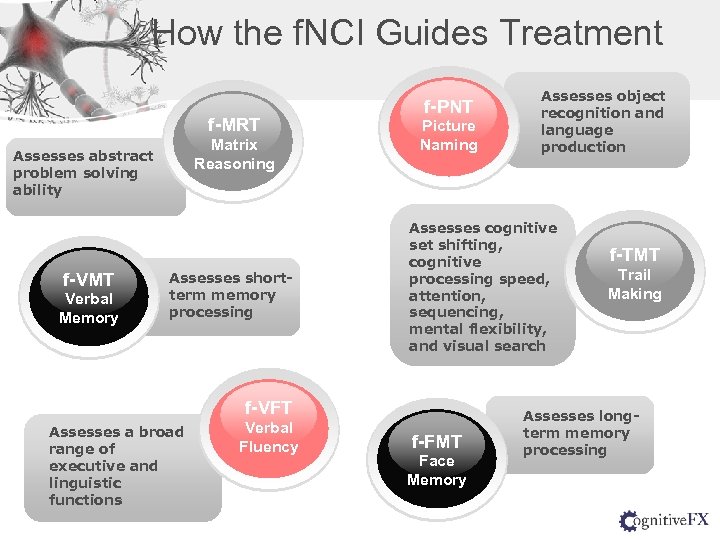 How the f. NCI Guides Treatment f-MRT Matrix Reasoning Assesses abstract problem solving ability f-VMT Verbal Memory Assesses shortterm memory processing f-PNT Picture Naming Assesses cognitive set shifting, cognitive processing speed, attention, sequencing, mental flexibility, and visual search f-VFT Assesses a broad range of executive and linguistic functions Verbal Fluency Assesses object recognition and language production f-FMT Face Memory f-TMT Trail Making Assesses longterm memory processing
How the f. NCI Guides Treatment f-MRT Matrix Reasoning Assesses abstract problem solving ability f-VMT Verbal Memory Assesses shortterm memory processing f-PNT Picture Naming Assesses cognitive set shifting, cognitive processing speed, attention, sequencing, mental flexibility, and visual search f-VFT Assesses a broad range of executive and linguistic functions Verbal Fluency Assesses object recognition and language production f-FMT Face Memory f-TMT Trail Making Assesses longterm memory processing
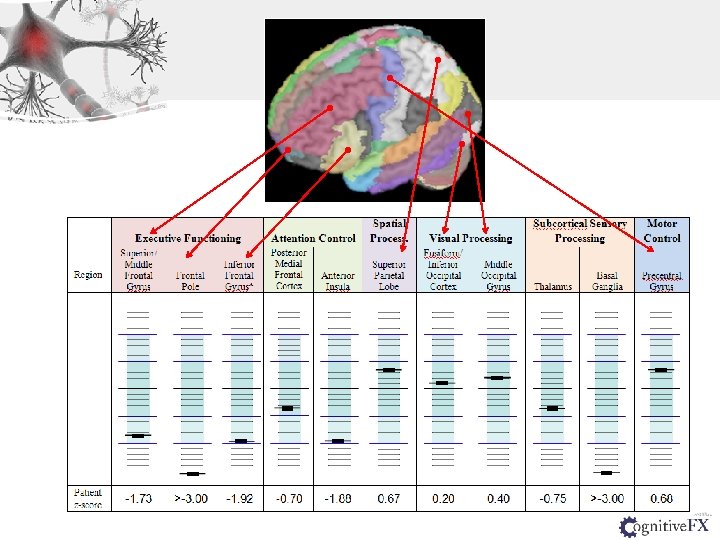
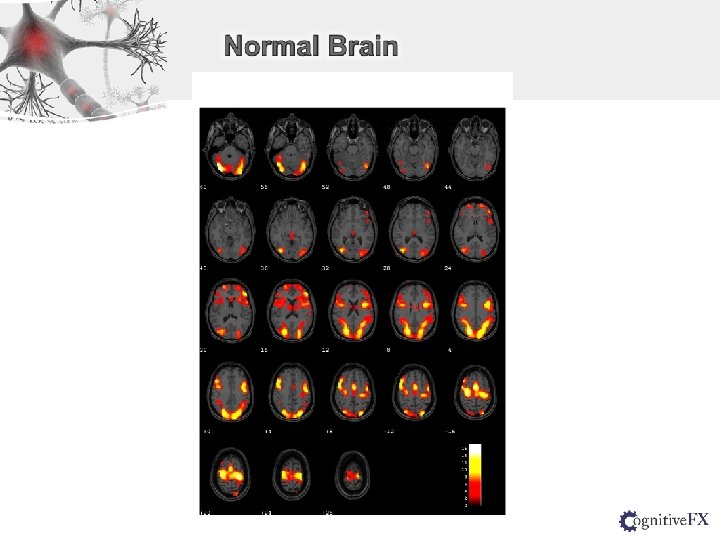
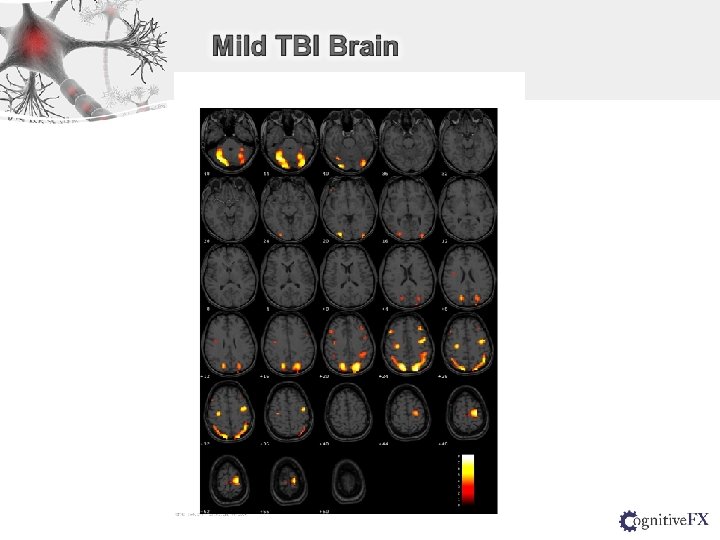
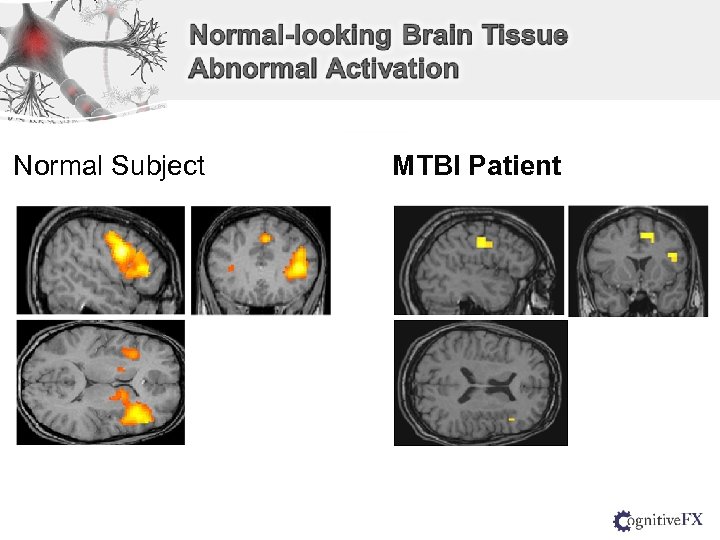 Normal Subject MTBI Patient
Normal Subject MTBI Patient
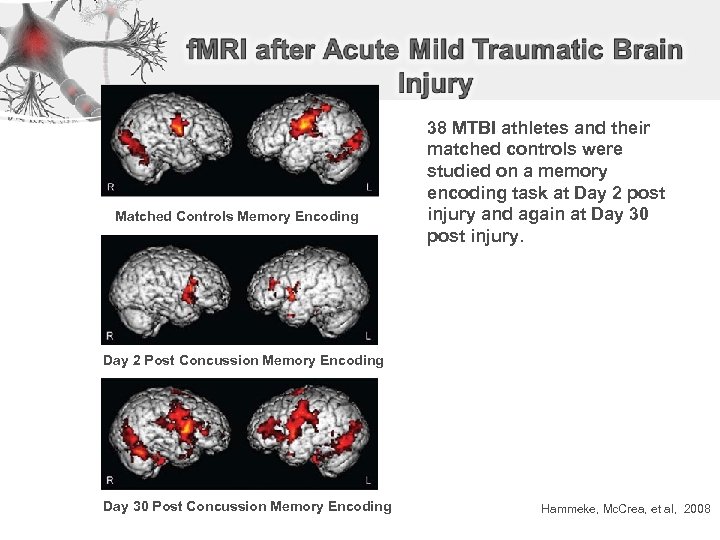 Matched Controls Memory Encoding 38 MTBI athletes and their matched controls were studied on a memory encoding task at Day 2 post injury and again at Day 30 post injury. Day 2 Post Concussion Memory Encoding Day 30 Post Concussion Memory Encoding Hammeke, Mc. Crea, et al, 2008
Matched Controls Memory Encoding 38 MTBI athletes and their matched controls were studied on a memory encoding task at Day 2 post injury and again at Day 30 post injury. Day 2 Post Concussion Memory Encoding Day 30 Post Concussion Memory Encoding Hammeke, Mc. Crea, et al, 2008
 • Functional NCI – Notus Neuro. Cogs with Structural Read Included • Cognitive Treatment • Motor Control, Symmetry, and balance treatment, Optogait • Nutritional and Sleep Program • Psychology • Vestibular and Ocular Treatment • Body Work • Treatment for dizziness, headaches, nausea, and other common physical symptoms of concussion
• Functional NCI – Notus Neuro. Cogs with Structural Read Included • Cognitive Treatment • Motor Control, Symmetry, and balance treatment, Optogait • Nutritional and Sleep Program • Psychology • Vestibular and Ocular Treatment • Body Work • Treatment for dizziness, headaches, nausea, and other common physical symptoms of concussion
 f. NCI guides Treatment Symptoms alone do not reveal areas of damage ● ● ● Visual search/spatial awareness regions of brain Executive/pain symptoms Eye motor Vestibular - inner ear problems Muscular or Joint related
f. NCI guides Treatment Symptoms alone do not reveal areas of damage ● ● ● Visual search/spatial awareness regions of brain Executive/pain symptoms Eye motor Vestibular - inner ear problems Muscular or Joint related
 f. NCI targets therapies to address functional brain regions ● Visual search/tracking regions/data integration regions (S. C. , Thalamus) o motor visual tracking and spatial awareness difficulties § Visual tracking exercises and sensory input exercises ● Visual regions (Occipital) o hyperactivated cortex causing fatigue and light sensitivity § endurance exercises and ocular conditioning ● Executive Dysregulation (Frontal) o pain and executive function impairment comorbidity § destimulation integrated with calibrated visual exercises ● Other Regions (Hippocampal, Brocas, SMA, etc) o Memory, language, motor control, balance, and other impairments § visual exercises integrated with appropriate functional stimuli
f. NCI targets therapies to address functional brain regions ● Visual search/tracking regions/data integration regions (S. C. , Thalamus) o motor visual tracking and spatial awareness difficulties § Visual tracking exercises and sensory input exercises ● Visual regions (Occipital) o hyperactivated cortex causing fatigue and light sensitivity § endurance exercises and ocular conditioning ● Executive Dysregulation (Frontal) o pain and executive function impairment comorbidity § destimulation integrated with calibrated visual exercises ● Other Regions (Hippocampal, Brocas, SMA, etc) o Memory, language, motor control, balance, and other impairments § visual exercises integrated with appropriate functional stimuli
 f. NCI guides overall treatment • • • f. NCI can detect injury and contour treatment Targeted treatments accelerate recovery Return to play/work more quickly and with confidence Players/Patients will feel less pressure to hide injury Players/Patients can provide evidence of recovery Players will feel protected knowing their health and information is more in their control • CFX program gives ex-athletes/players of any age the same opportunities for rehab and improvement • Players can get baselines and track their own brain function over the course of their career and life
f. NCI guides overall treatment • • • f. NCI can detect injury and contour treatment Targeted treatments accelerate recovery Return to play/work more quickly and with confidence Players/Patients will feel less pressure to hide injury Players/Patients can provide evidence of recovery Players will feel protected knowing their health and information is more in their control • CFX program gives ex-athletes/players of any age the same opportunities for rehab and improvement • Players can get baselines and track their own brain function over the course of their career and life
 CFX Hospital §Structural Safety Read Included! Getting two scans for the price of one! §No structural read §Comprehensive 7 test battery § 2 -3 tests administered §Concussion Severity Scale from 0 -6 included! §No Severity Scale included §Full Validity analysis §f. NCI Report integrated with full Neuropsychological Test Battery §Direct referral to in-house therapists fully trained in f. NCI interpretion §f. NCI conducted in-house, on premises for quality assurance, with same-day service in most cases! §No validity analysis §Limited report with general recommendations §Outside, disparate network of therapists
CFX Hospital §Structural Safety Read Included! Getting two scans for the price of one! §No structural read §Comprehensive 7 test battery § 2 -3 tests administered §Concussion Severity Scale from 0 -6 included! §No Severity Scale included §Full Validity analysis §f. NCI Report integrated with full Neuropsychological Test Battery §Direct referral to in-house therapists fully trained in f. NCI interpretion §f. NCI conducted in-house, on premises for quality assurance, with same-day service in most cases! §No validity analysis §Limited report with general recommendations §Outside, disparate network of therapists
 • Dr. Bruce Mc. Iff offers: – Structural MRI reads of other areas of the body: • Cervical, soft tissue neck • Structural Brain • Joints (shoulder, wrist, knee, etc). • Pelvis, Lumbar, Thoracic
• Dr. Bruce Mc. Iff offers: – Structural MRI reads of other areas of the body: • Cervical, soft tissue neck • Structural Brain • Joints (shoulder, wrist, knee, etc). • Pelvis, Lumbar, Thoracic
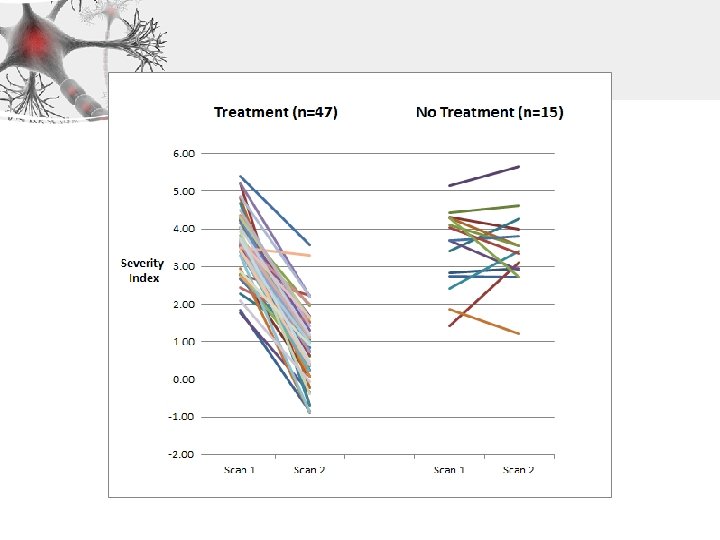
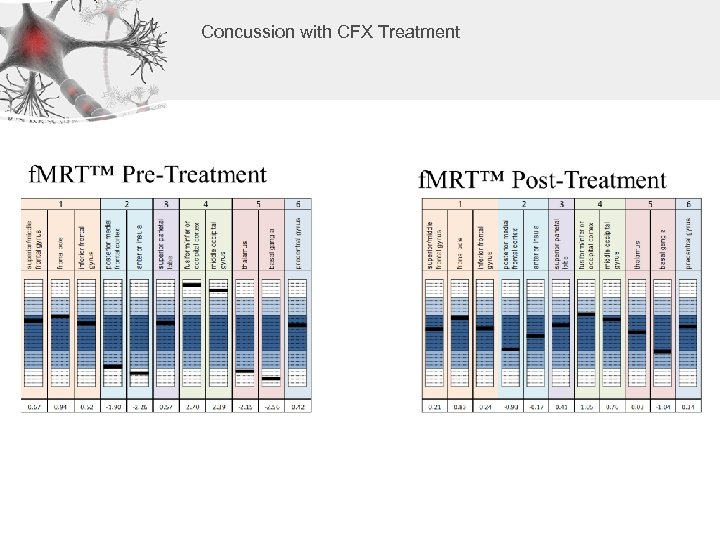 Concussion with CFX Treatment
Concussion with CFX Treatment
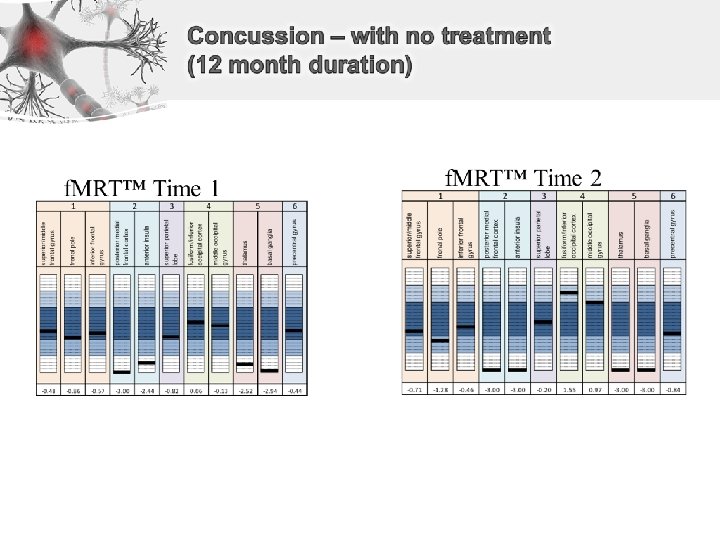
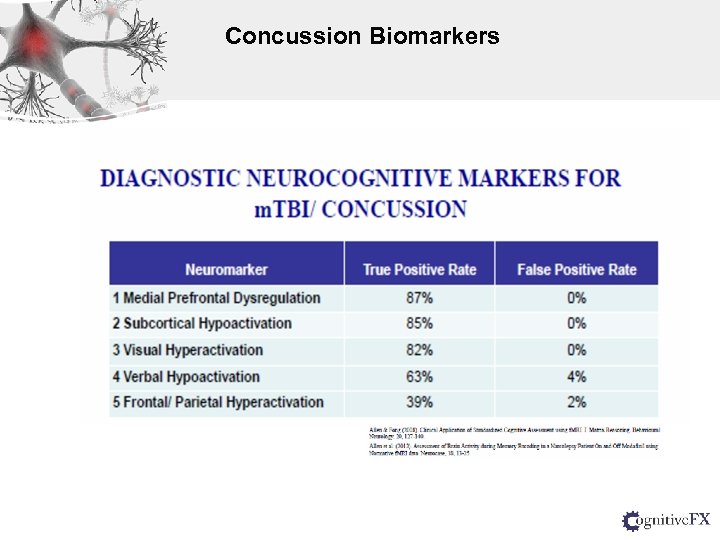 Concussion Biomarkers
Concussion Biomarkers
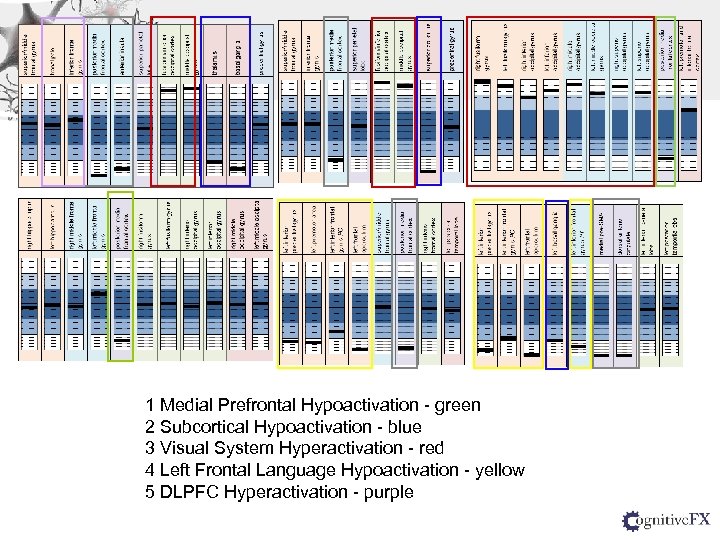 1 Medial Prefrontal Hypoactivation - green 2 Subcortical Hypoactivation - blue 3 Visual System Hyperactivation - red 4 Left Frontal Language Hypoactivation - yellow 5 DLPFC Hyperactivation - purplel Hypoactivation - green
1 Medial Prefrontal Hypoactivation - green 2 Subcortical Hypoactivation - blue 3 Visual System Hyperactivation - red 4 Left Frontal Language Hypoactivation - yellow 5 DLPFC Hyperactivation - purplel Hypoactivation - green
 Misdiagnoses? ? ? • Dementia • Multiple Sclerosis • Schizophrenia • Attention Deficit Disorders • Other Psychiatric Disorders
Misdiagnoses? ? ? • Dementia • Multiple Sclerosis • Schizophrenia • Attention Deficit Disorders • Other Psychiatric Disorders
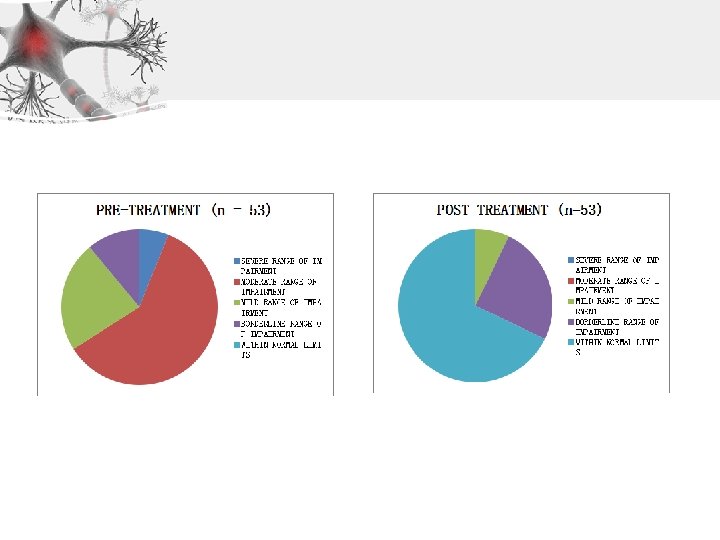
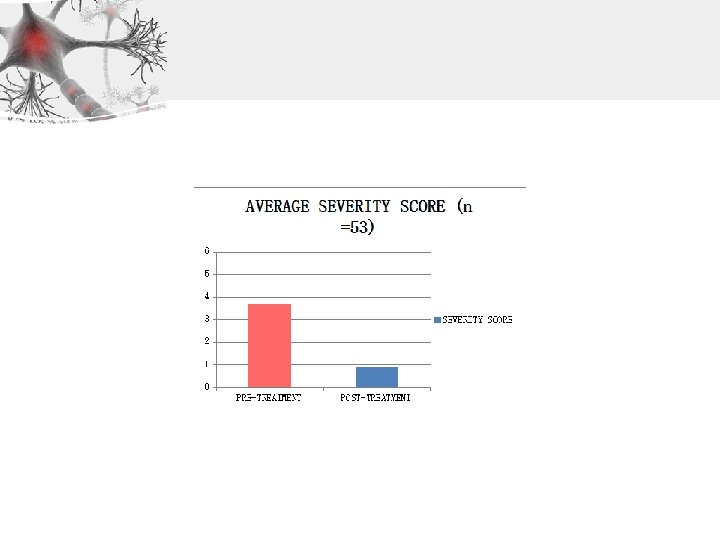
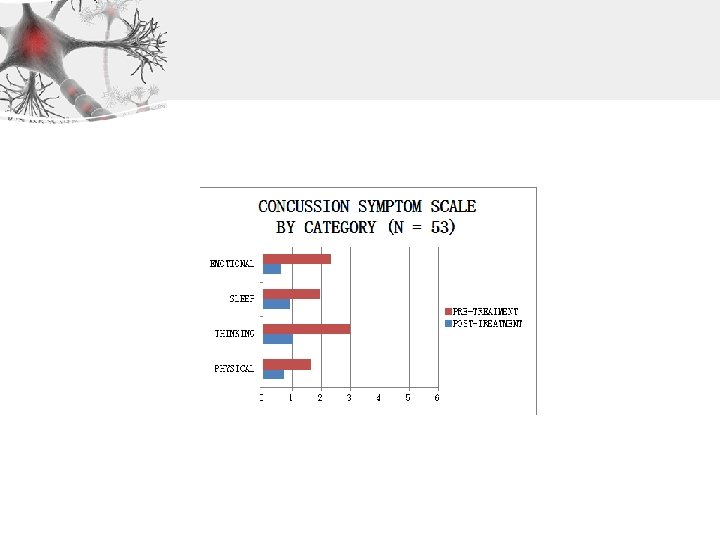
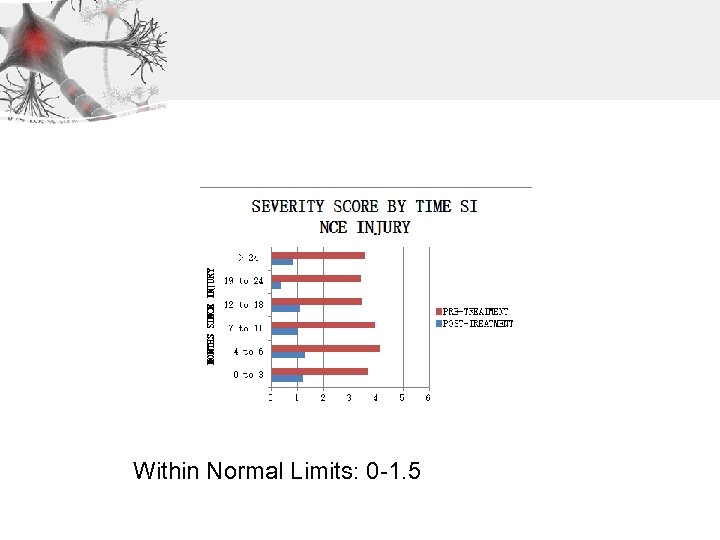 Within Normal Limits: 0 -1. 5
Within Normal Limits: 0 -1. 5
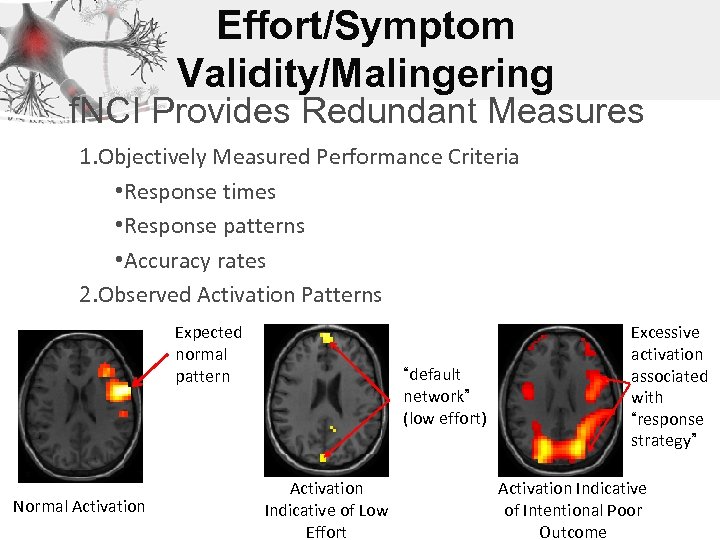 Effort/Symptom Validity/Malingering f. NCI Provides Redundant Measures 1. Objectively Measured Performance Criteria • Response times • Response patterns • Accuracy rates 2. Observed Activation Patterns Expected normal pattern Normal Activation “default network” (low effort) Activation Indicative of Low Effort Excessive activation associated with “response strategy” Activation Indicative of Intentional Poor Outcome
Effort/Symptom Validity/Malingering f. NCI Provides Redundant Measures 1. Objectively Measured Performance Criteria • Response times • Response patterns • Accuracy rates 2. Observed Activation Patterns Expected normal pattern Normal Activation “default network” (low effort) Activation Indicative of Low Effort Excessive activation associated with “response strategy” Activation Indicative of Intentional Poor Outcome



