Diabetic Foot syndrome 1.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 33

DIABETIC FOOT EXAMINATION
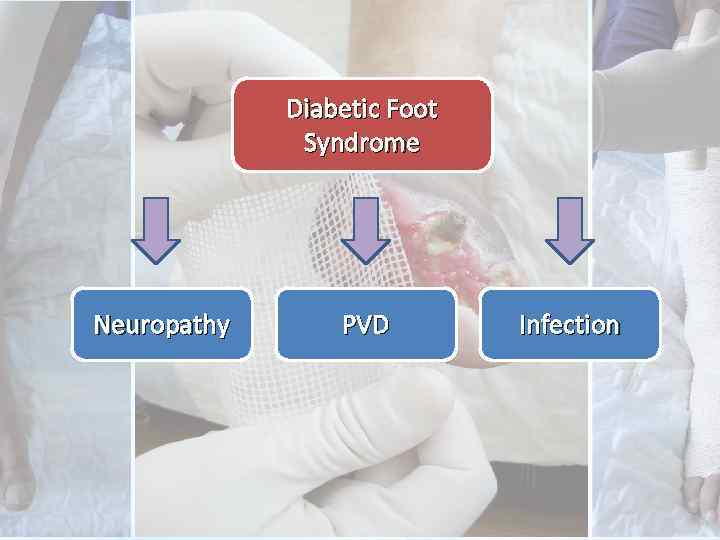
Diabetic Foot Syndrome Neuropathy PVD Infection
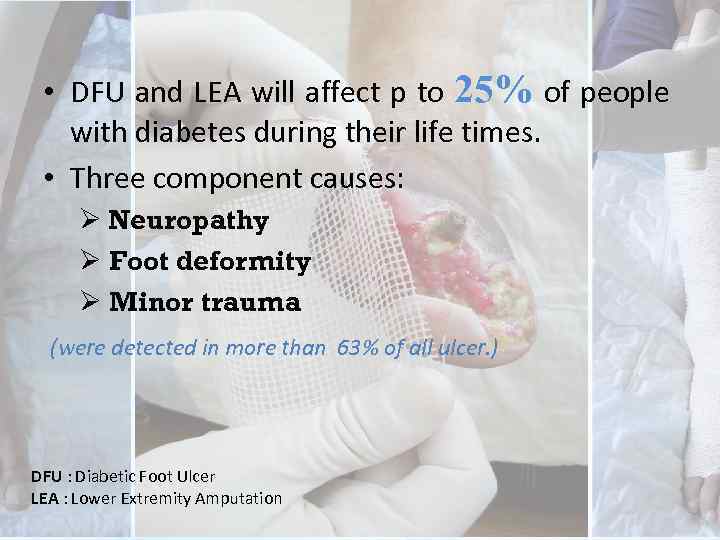
• DFU and LEA will affect p to 25% of people with diabetes during their life times. • Three component causes: Ø Neuropathy Ø Foot deformity Ø Minor trauma (were detected in more than 63% of all ulcer. ) DFU : Diabetic Foot Ulcer LEA : Lower Extremity Amputation
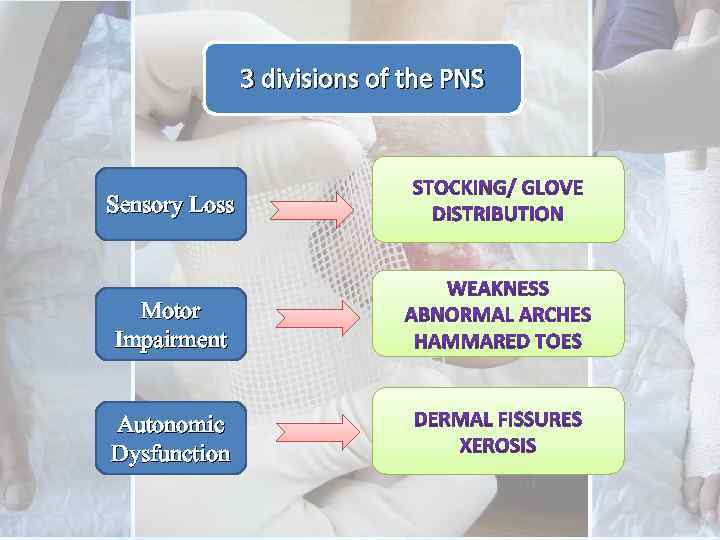
3 divisions of the PNS Sensory Loss Motor Impairment Autonomic Dysfunction

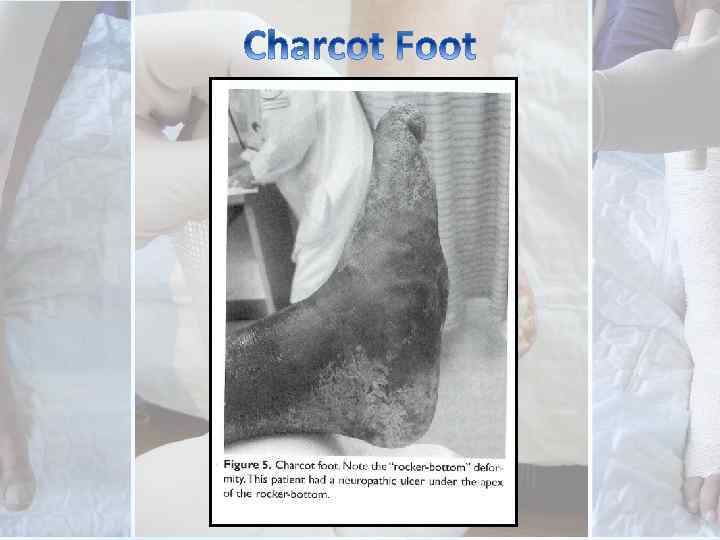
1. Does the patient have loss of protective sensation? 2. Is foot deformity present? 3. Does the patient have a history of ulceration, amputation or Charcot foot?
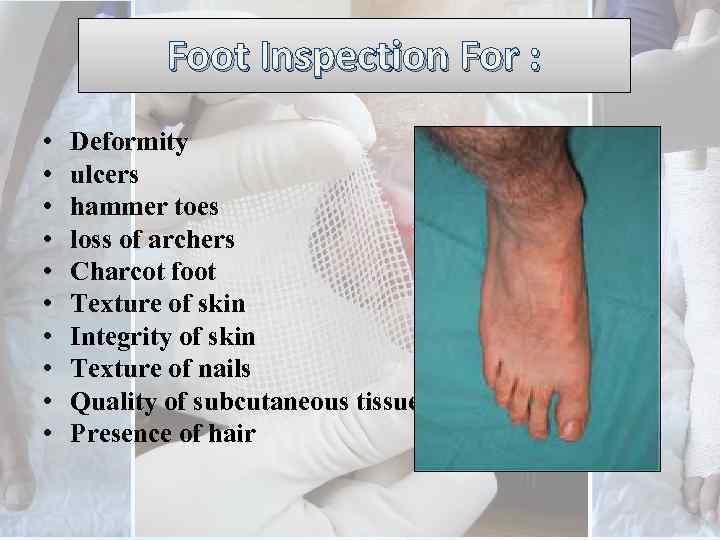
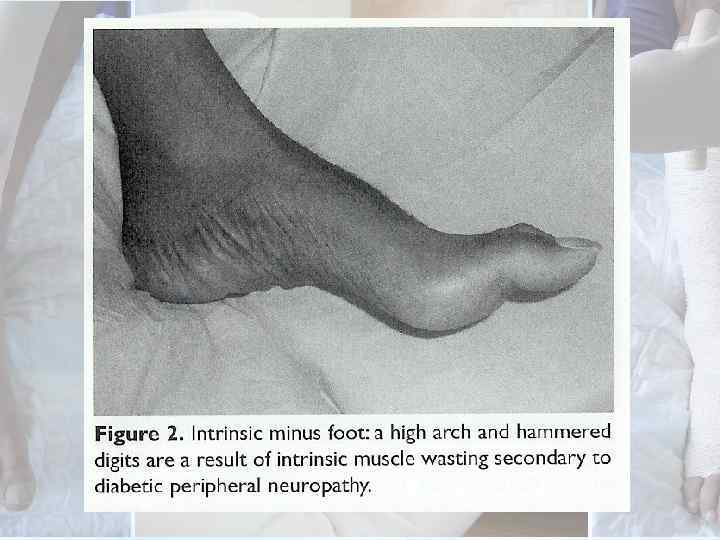
Foot Inspection For : • • • Deformity ulcers hammer toes loss of archers Charcot foot Texture of skin Integrity of skin Texture of nails Quality of subcutaneous tissue Presence of hair
1 - Deformity • One must examine the foot for bony prominences and deformities. • It is important to determine if a deformity is rigid or flexible as rigid deformities are often more difficult to accommodate conservatively and may need surgery.
2 - Ulcers : The depth of a wound is much more important for healing than the size of the wound. Wagener Gredes
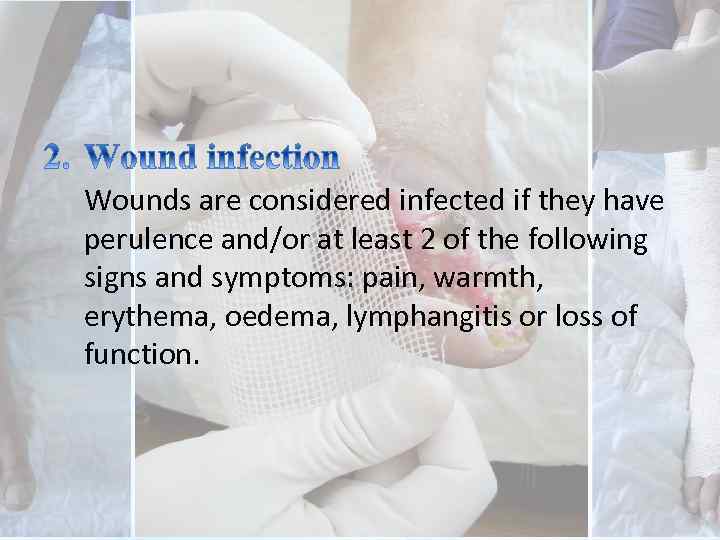
Wounds are considered infected if they have perulence and/or at least 2 of the following signs and symptoms: pain, warmth, erythema, oedema, lymphangitis or loss of function.
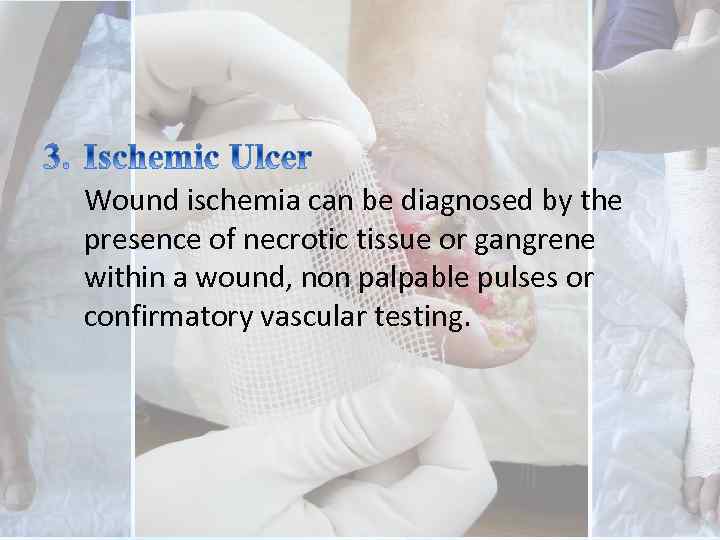
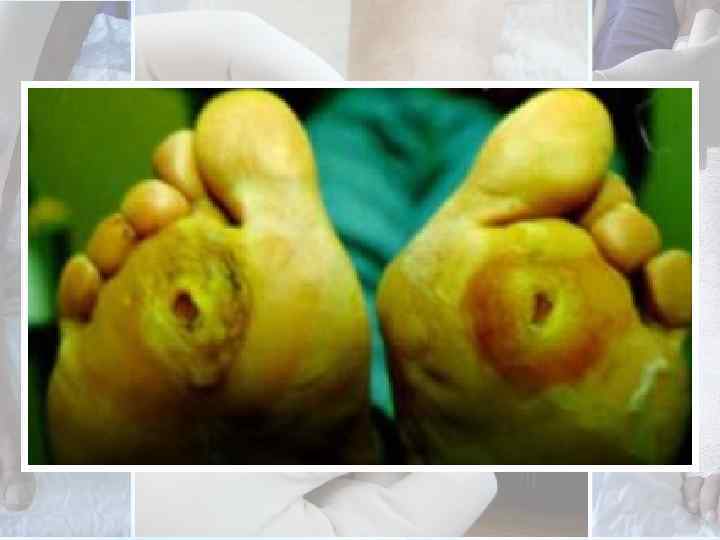
Wound ischemia can be diagnosed by the presence of necrotic tissue or gangrene within a wound, non palpable pulses or confirmatory vascular testing.
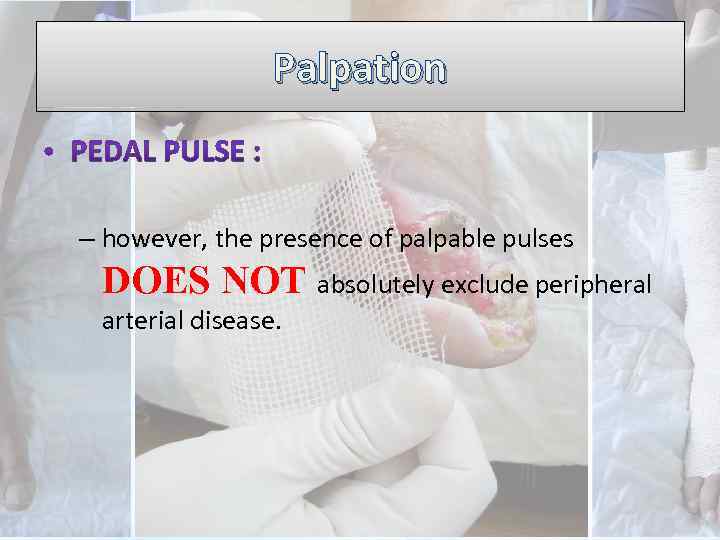
Palpation – however, the presence of palpable pulses DOES NOT absolutely exclude peripheral arterial disease.
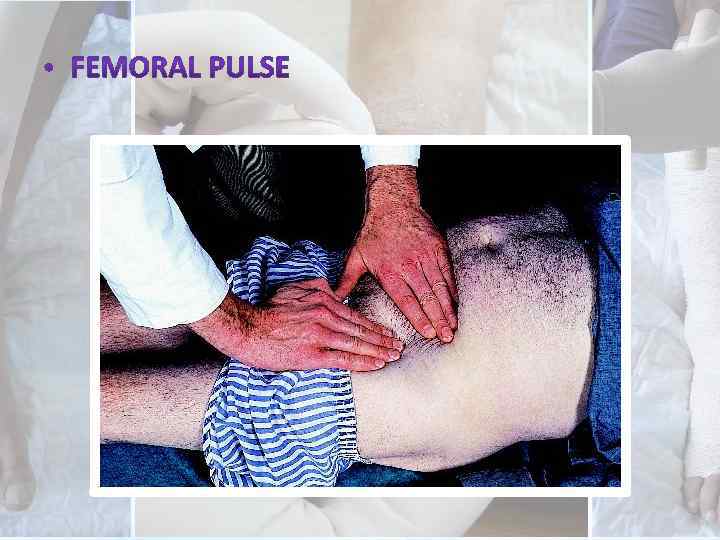
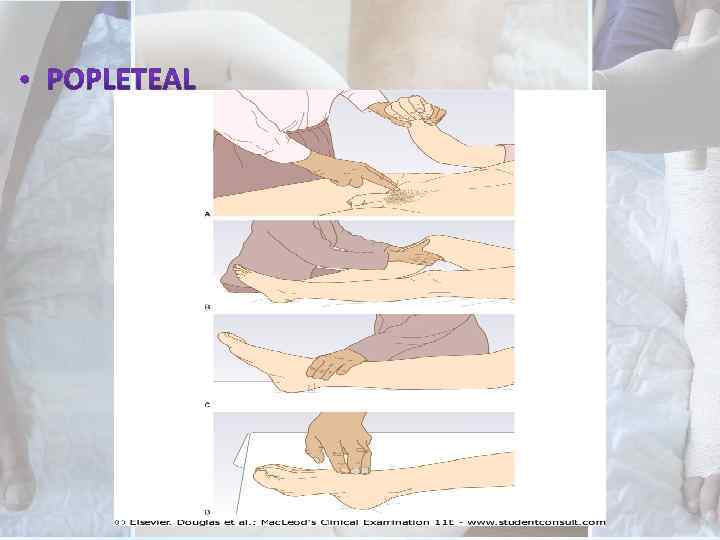
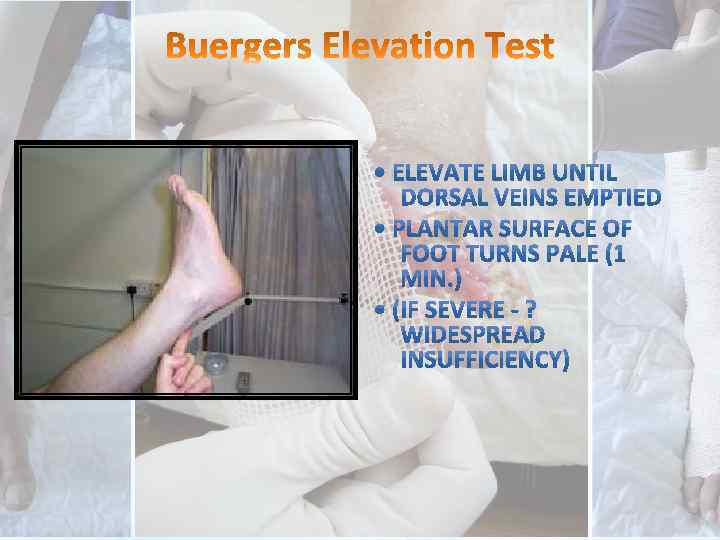
Special Tests

Monofilament Test: • The monofilament should be placed against intact skin (without callus) and allowed to buckle. • The patient should have his or her eyes closed during testing and be given a forced choice i. e. asked “ Do you feel the pressure at time A or time B? ”
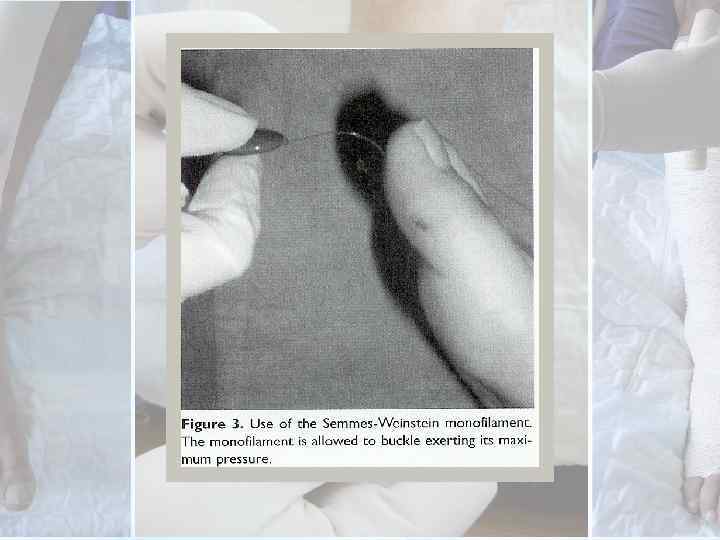
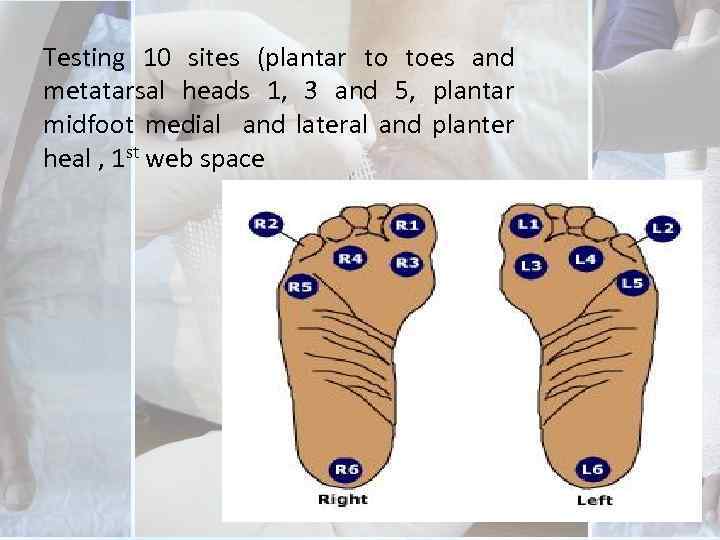
Testing 10 sites (plantar to toes and metatarsal heads 1, 3 and 5, plantar midfoot medial and lateral and planter heal , 1 st web space

• The person who cannot feel at least 7 of 10 pedal sites tested is considered to have an absent protective threshold.

Vibration Test : Ø A 128 Hz tuning fork can be applied to the tip of the hallux and bony prominences. Ø It is important to give a non vibrating stimulus such as touch to verify that the person is giving a positive response to the vibration sense and not just to the touch sensation.
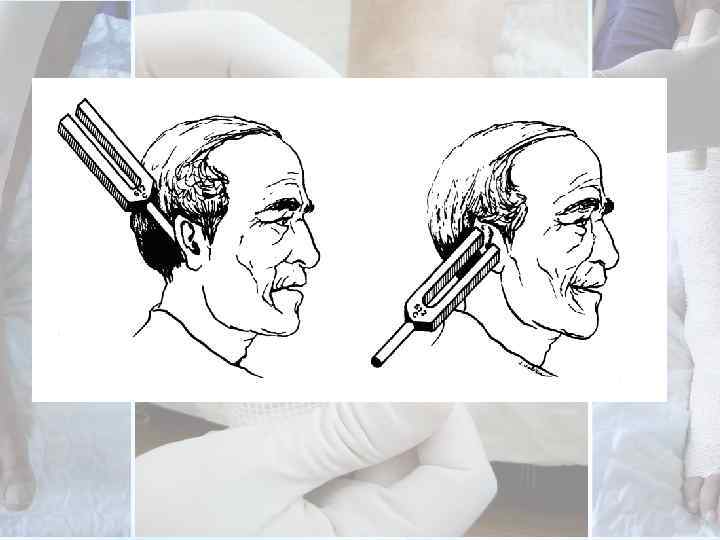
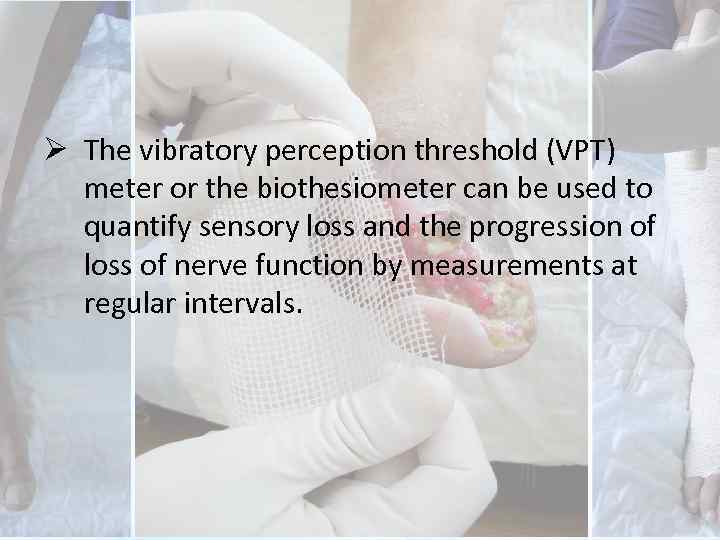
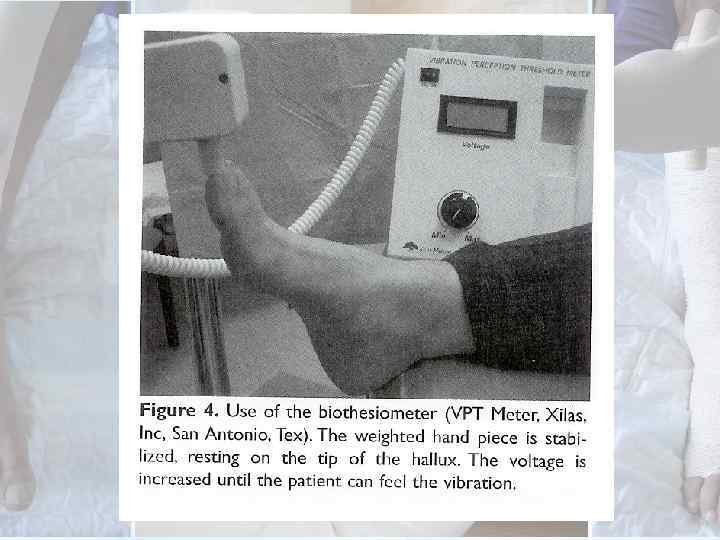
Ø The vibratory perception threshold (VPT) meter or the biothesiometer can be used to quantify sensory loss and the progression of loss of nerve function by measurements at regular intervals.
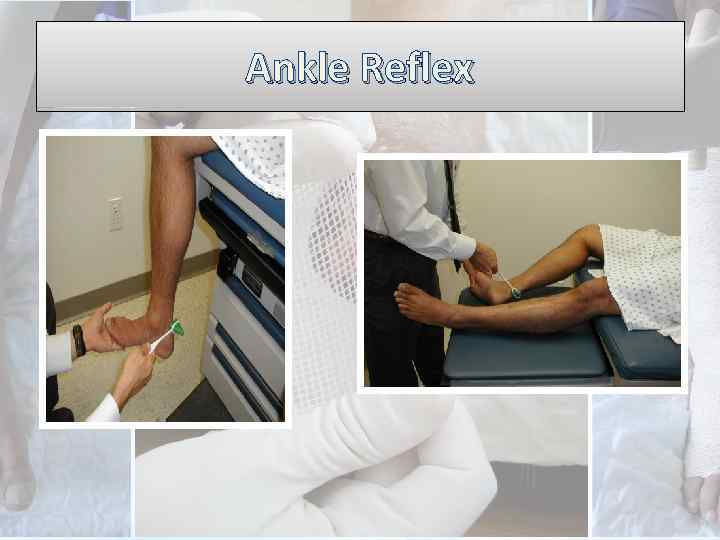
Ankle Reflex

The Ankle Brachial Index systolic ankle pressure ABI = systolic arm pressure The ABI is 95% sensitive and 99% specific for PAD.
• In diabetic patient, the ABI is falsely elevated. • Can assess the peripheral circulation by measuring the toe systolic pressure (normal > 40 mm. Hg) using either a strain gauge sensor or photoplethysmography.
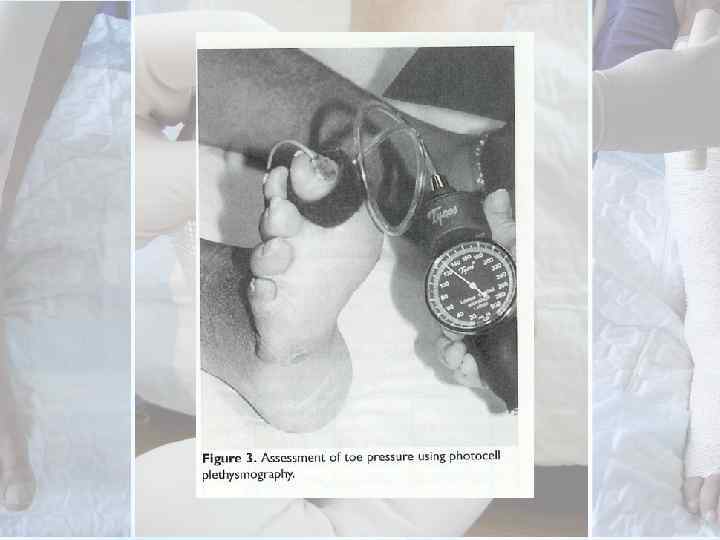
• Transcutaneous oxygen tension (normal > 40 mm. Hg) measurement has been used as non invasive measurement of limb perfusion.
Thank You
Diabetic Foot syndrome 1.pptx