083d2c106e0ece5815fe46d316ad5e01.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Diabetes Structured Patient Education Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse June 2016
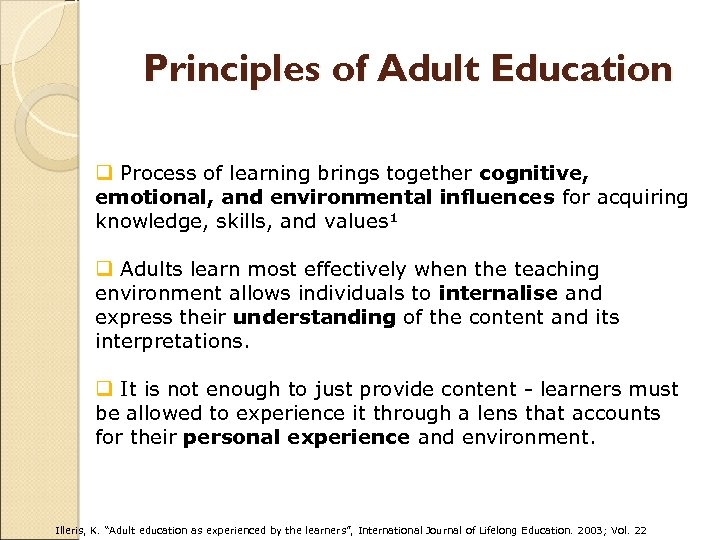
Principles of Adult Education q Process of learning brings together cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences for acquiring knowledge, skills, and values¹ q Adults learn most effectively when the teaching environment allows individuals to internalise and express their understanding of the content and its interpretations. q It is not enough to just provide content - learners must be allowed to experience it through a lens that accounts for their personal experience and environment. Illeris, K. “Adult education as experienced by the learners”, International Journal of Lifelong Education. 2003; Vol. 22

Key criteria of a structured education programme • A clear underlying philosophy on which the programme is based • A structured written curriculum • Trained educators familiar with the programme and its delivery • A quality assurance system applied to the structure, process, content, and delivery of the programme • A process of audit of programme outcomes including biomedical, psychosocial, and patient experience Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Ongoing Diabetes Education Work in GGC Diabetes MCN developed patient pathways for Type 1 and Type 2 education with a move towards quality assurance for all courses now being provided. Multi-disciplinary working groups are reviewing current provision and developing action plans to improve provision of Type 1 & Type 2 patient education. New Continuing education programme developed by dietician Valerie Laszlo called “Mastering Type 2 DM” Expected restart after April 2016. Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Type 2 Patient Education Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Conversation Maps Good to talk Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Diabetes Conversation Maps • A comprehensive and unique set of educational tools known as Conversation Maps • Designed to engage patients in the learning process and help them become better self managers through group sessions • Developed in accordance with Clinical Practice Guidelines Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Diabetes self-management education and ongoing self-management support are crucial components of effective diabetes care and significant contributors to the metabolic and psychological outcomes of people with type 2 diabetes Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Conversation Map™ (CM) education tools are a series of tools for facilitated group education that were developed by Healthy Interactions in collaboration with the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and are sponsored by Lilly Diabetes. Different CM versions have been developed for specific regions or countries (United States, Canada, Europe, Asia, Australia, Latin America, and Africa) in cooperation with national and international diabetes associations (IDF and the Canadian, American, and U. K. diabetes associations) to reflect differences in culture and background. CM-based education guides people with diabetes through a process with the aim of helping them understand internalise information about their disease and generate insightful conclusions, which may then result in improved selfmanagement decisions and actions Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016
Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016
Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

How does it work? • It hopes to promote understanding of type 2 diabetes, allowing patients to be more knowledgeable about what will positively benefit their long-term health as they live with the condition. • The course aims to dispel any myths about the condition, and any illness beliefs that are false or potentially damaging. • It should help patients to see their illness in a biomedical model, as well as the personal functional and social model that most use as their initial conceptual framework for understanding the impact of the illness. • It should enable patients to monitor their type 2 diabetes effectively, realise when their control is inadequate, and enable them to self-manage their lifestyle, nutrition and medication to bring about improvement in diabetic control, or know when to seek professional help. • It should enable them to be an active partner in the management of their type 2 diabetes, along with healthcare professionals. Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Patient share if they wish through pier conversation their. . • Thoughts and feelings of the participants around diabetes. • Discussion helps them understand their diabetes and glucose: what happens in the body. • Gives them insight and understanding about the risk factors and complications associated with diabetes. • More understanding about monitoring and medication. • Encouraging patients on how to take control discussing. . . • Food Choices • Physical Activity. • Planning for the future. • Setting goals. • Knowing their numbers Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Training Educators After completing the Conversation Map training, facilitators are able to incorporate new education techniques into their practice, which can help drive greater information retention and help positively affect behaviour. The training can expand the skill set of healthcare professionals by enhancing group-session facilitation skills. A new role for educators – that of a facilitator rather than just a dispenser of facts. Educators are there to ensure that information shared within the group is correct. Training workshops – 4 hours arranged through Lilly representative Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Do you know how to refer patients locally to diabetes structured education classes ? Type 2: Paper referral to local CHP Diabetes Education co-ordinator for Conversation Map or one to one Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016
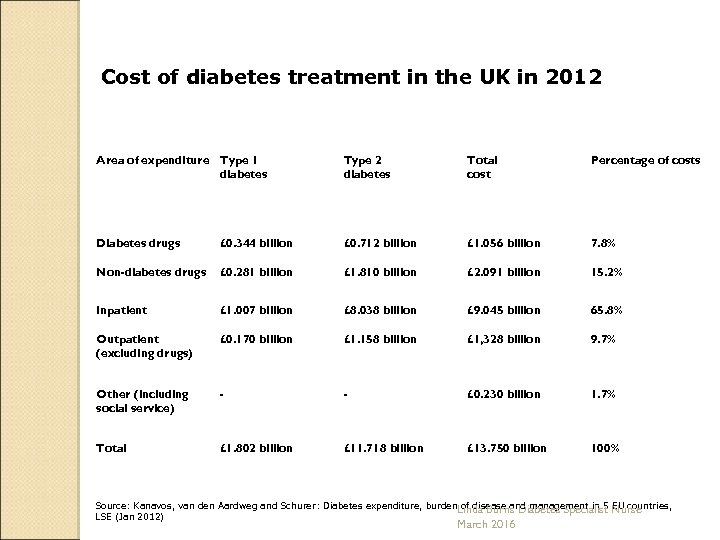
Cost of diabetes treatment in the UK in 2012 Area of expenditure Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Total cost Percentage of costs Diabetes drugs £ 0. 344 billion £ 0. 712 billion £ 1. 056 billion 7. 8% Non-diabetes drugs £ 0. 281 billion £ 1. 810 billion £ 2. 091 billion 15. 2% Inpatient £ 1. 007 billion £ 8. 038 billion £ 9. 045 billion 65. 8% Outpatient (excluding drugs) £ 0. 170 billion £ 1. 158 billion £ 1, 328 billion 9. 7% Other (including social service) - - £ 0. 230 billion 1. 7% Total £ 1. 802 billion £ 11. 718 billion £ 13. 750 billion 100% Source: Kanavos, van den Aardweg and Schurer: Diabetes expenditure, burden. Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse of disease and management in 5 EU countries, LSE (Jan 2012) March 2016

The cost of diabetes to the NHS is over £ 1. 5 m an hour or 10% of the NHS budget for England Wales. This equates to over £ 25, 000 being spent on diabetes every minute. This equates to £ 416. 66 every second. In total, an estimated £ 14 billion pounds is spent a year on treating diabetes and its complications, with the cost of treating complications representing the much higher cost. The prevalence of diabetes is estimated to rise to 4 million by 2025. Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Although knowledge alone is likely insufficient to achieve changes in A 1 C, it is evident from prior research that behaviour and ultimately clinical outcomes are unlikely to change unless there is knowledge together with an understanding of the need to change, what to change, and how to change it. Knowledge is necessary for diabetes self-management behavior, physical and psychological well-being, glycemic control (A 1 C), body weight, attainment of personal therapeutic goals Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016

Thank you Any questions? Linda Burns Diabetes Specialist Nurse March 2016
083d2c106e0ece5815fe46d316ad5e01.ppt