783a00912ef99b594850df5333a06591.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89

Diabetes as a Global Health Problem The IDF meets the Challenge By Prof. Morsi Arab IDF Chairman MENA Region






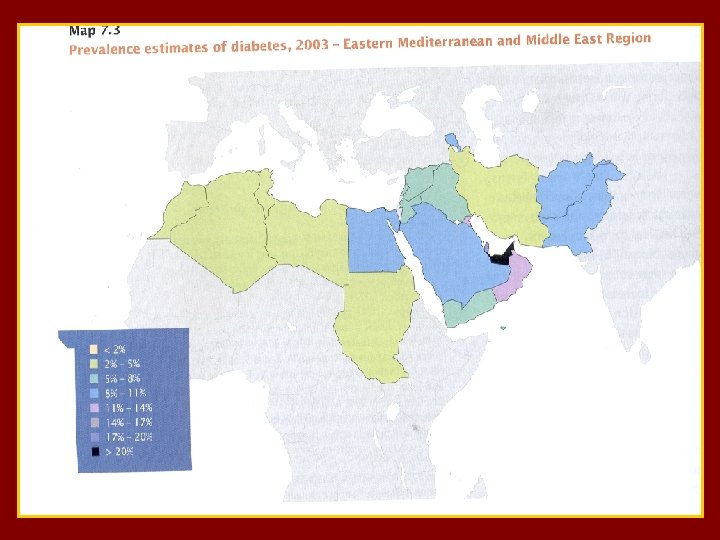
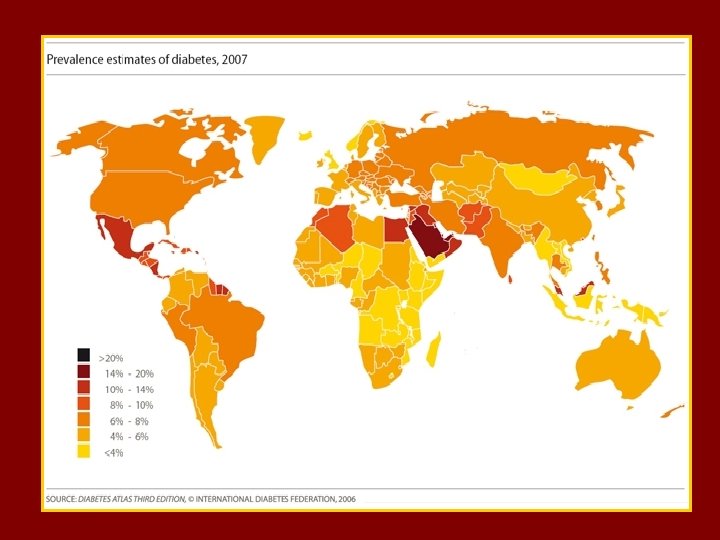
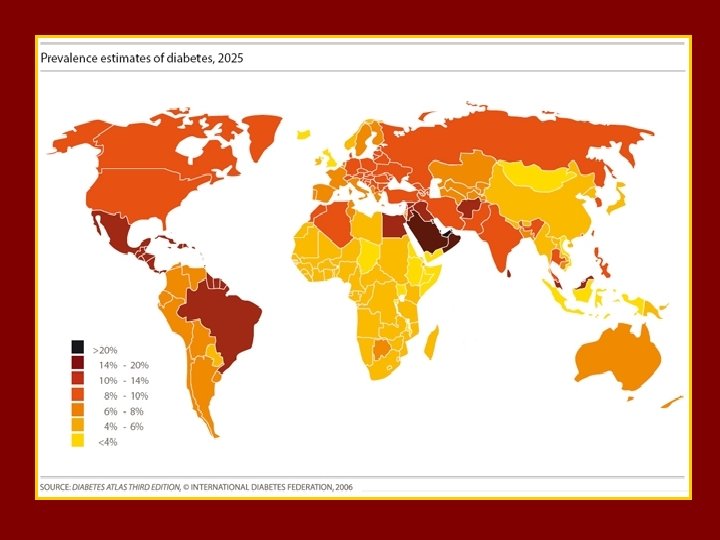
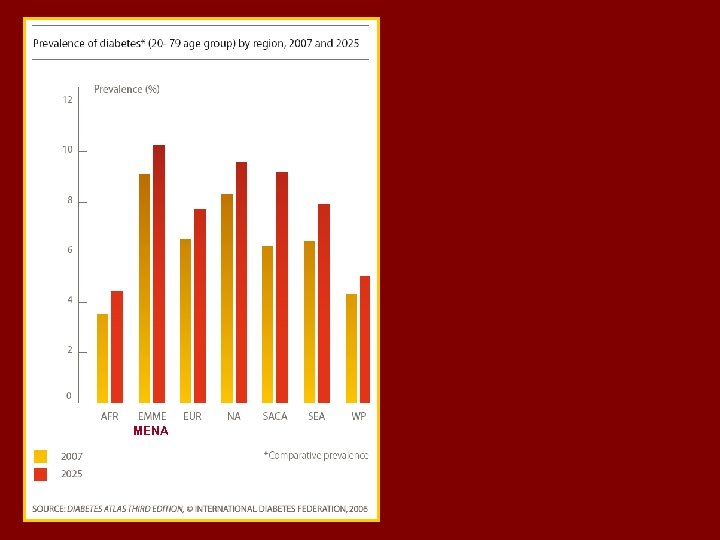
MENA
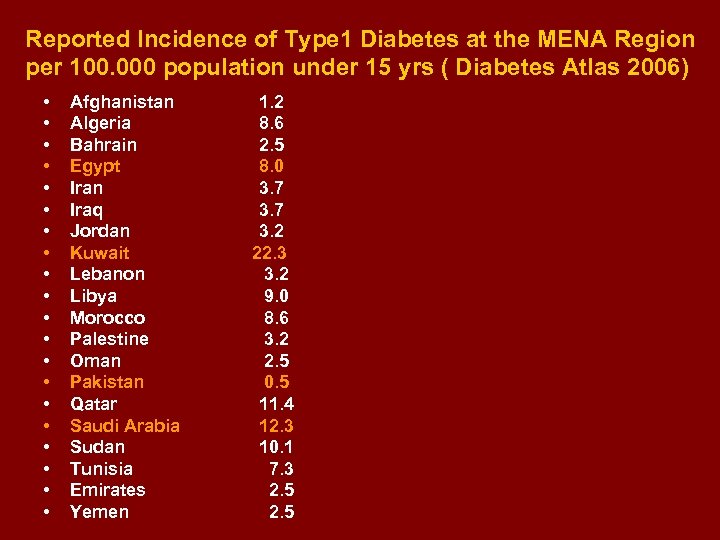
Reported Incidence of Type 1 Diabetes at the MENA Region per 100. 000 population under 15 yrs ( Diabetes Atlas 2006) • • • • • Afghanistan Algeria Bahrain Egypt Iran Iraq Jordan Kuwait Lebanon Libya Morocco Palestine Oman Pakistan Qatar Saudi Arabia Sudan Tunisia Emirates Yemen 1. 2 8. 6 2. 5 8. 0 3. 7 3. 2 22. 3 3. 2 9. 0 8. 6 3. 2 2. 5 0. 5 11. 4 12. 3 10. 1 7. 3 2. 5


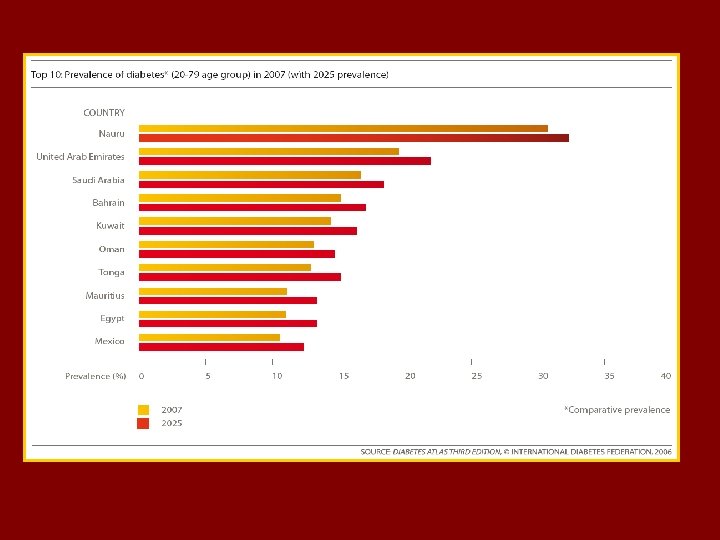
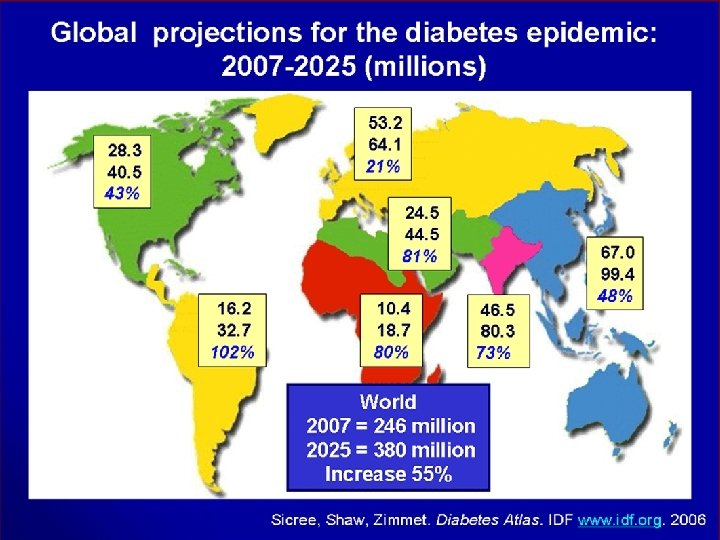
t The MENA Region. A Prevalence of Diabetes is 9. 2 % (age 20 -79) Prevalence of IGT ……. is 8. 1 % 24. 5 millions with Diabetes & 22. 4 with IGT out of the top 10 highest diabetes prevalence rate countries 6 are MENA countries Estimated death due to DM as % of all deaths is 11. 5% ( 11. 1% in Europe and 11. 8 % in MENA )

Diabetes Mortality World wide = 3. 2 millions die from complications associated with diabetes In the ME : ( with high prev. of diab. ) one in 4 deaths in adults 35 -64 years is related to diabetes
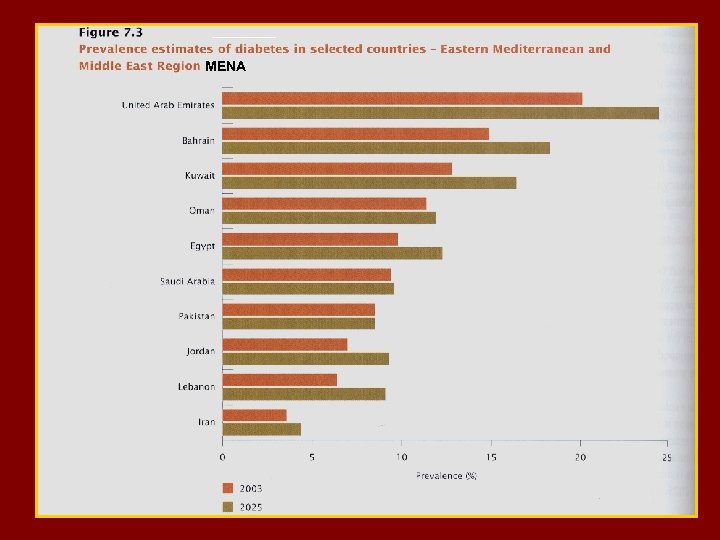
MENA
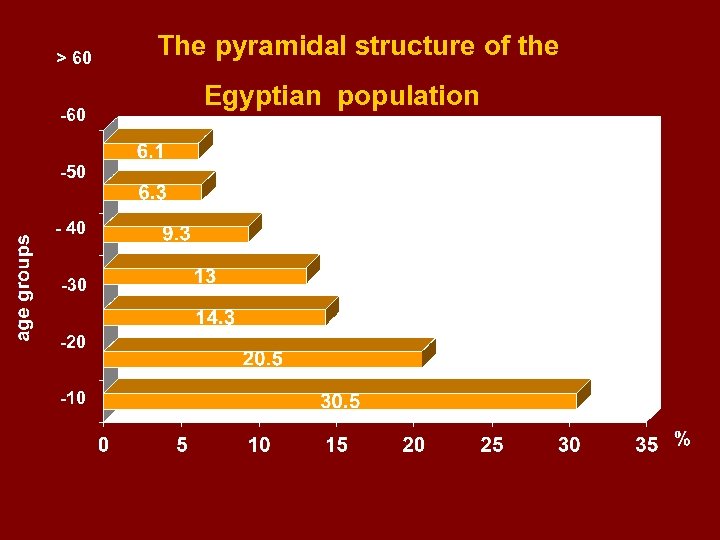
> 60 -50 - 40 -30 -20 -10 The pyramidal structure of the Egyptian population



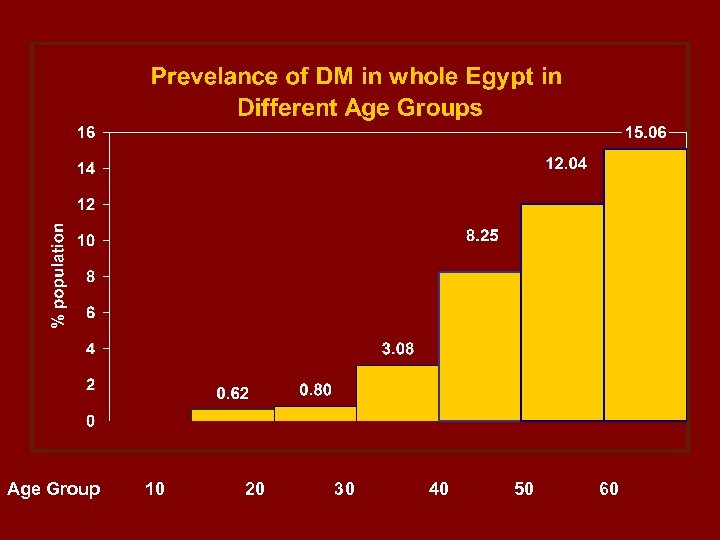
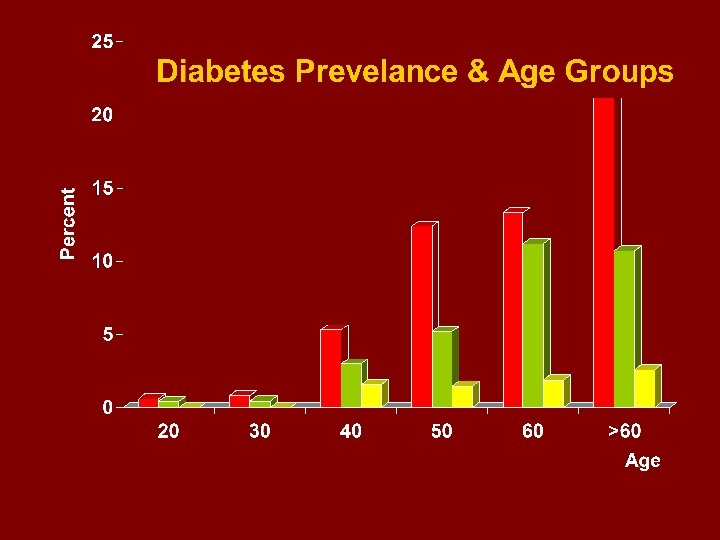
Age Group 10 20 30 40 50 60
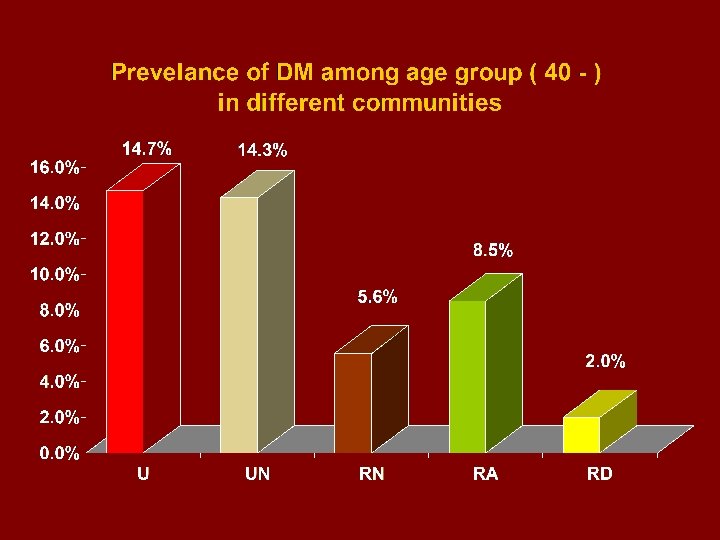
Saini Eastern desert Western desert Nubia
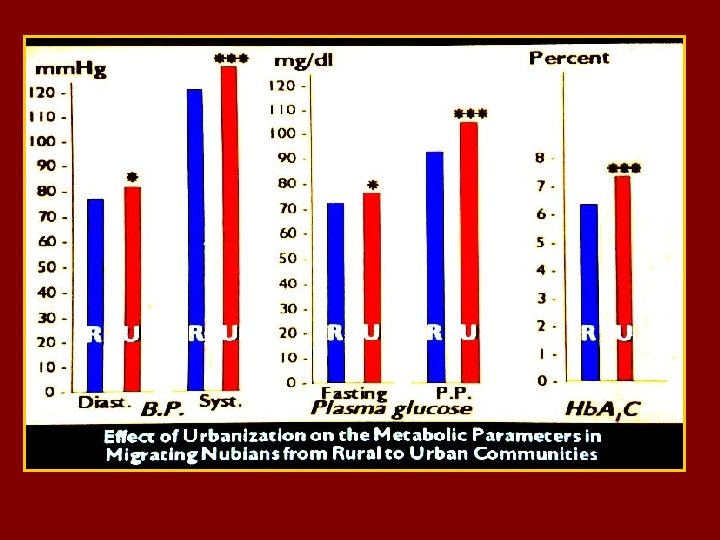
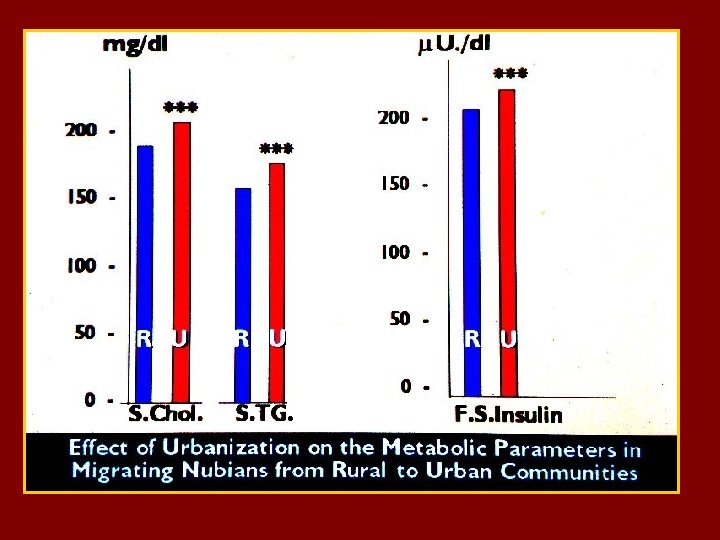

DIABETES IS PART OF THE WIDER HEALTH PROBLEM : THE METABOLIC SYNDROME 20 -25 % of the world adult population have the metabolic syndrome ( MTS) , and these are : - 5 times at risk to develop diabetes type 2 - 3 times likely to have a heart attack or stroke - twice likely to die

Obesity” is always involved , or associated with all elements of the Metabolic Syndrome : But Which type of Obesity ?


“ Abdominal Obesity “ as measured by waist circumference is more indicative of the Metabolic Syndrome profile than increased BMI


The new international Diabetes Federation (IDF) definition According to the new IDF definition , for a person to be defined as having the metabolic syndrome he/she must have : Central Obesity ( defined as waist circumference * with ethnicity specific values ) plus any two of the following four factors : Raised triglycerides 150 mg/d. L (1. 7 mmol/L ) or specific treatment for this lipid abnormality. Reduced HDL Cholesterol 40 mg/dl ( 1. 03 mmol/L ) in males 50 mg/d. L (1. 29 mmol/L) in females or specific treatment for this lipid abnormality Raised blood pressure Systolic BP 130 or diastolic BP 85 mm. Hg Or treatment of previously diagnosed hypertension Raised fasting plasma glucose ( FPG) 100 mg/d. L (5. 6 mmol/L) or previously diagnosed type 2 diabetes

Diabetes Mellitus and its state of control and complications in the MENA Region

Fasting Hyperglycemia - Controlled (< 120 mg/dl ) - Uncontrolled = 19. 8 % = 80. 2 % ----------------- Hyperglycemic 121 -150 mg/dl Marked hyperglycemia -200 Severe hyperglycemia -220 Very severe hyperglycemia > 220 = 15. 6 % = 31. 3 % = 12. 5 % = 20. 8 %
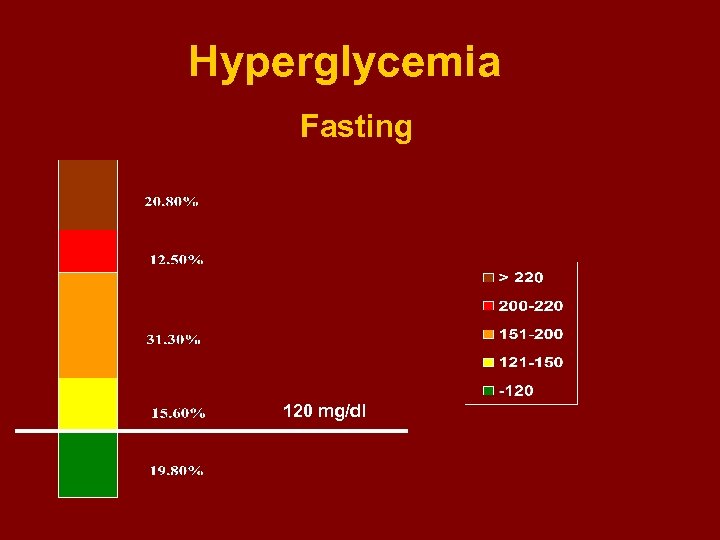
Hyperglycemia Fasting 120 mg/dl
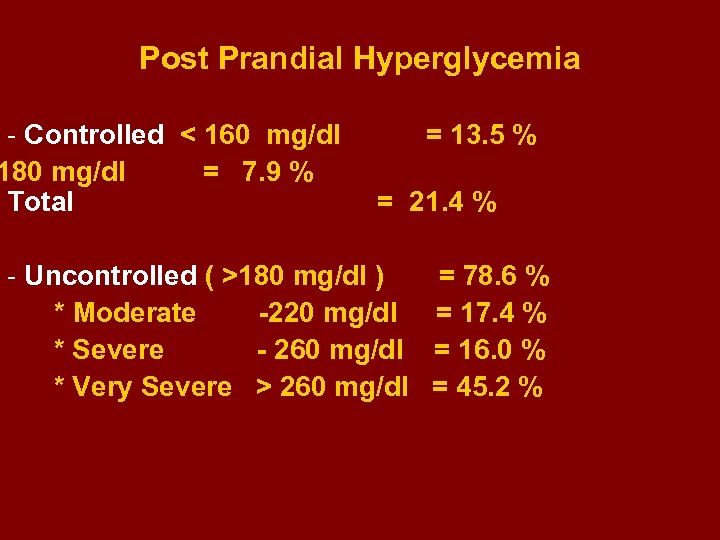
Post Prandial Hyperglycemia - Controlled < 160 mg/dl 180 mg/dl = 7. 9 % Total = 13. 5 % = 21. 4 % - Uncontrolled ( >180 mg/dl ) = 78. 6 % * Moderate -220 mg/dl = 17. 4 % * Severe - 260 mg/dl = 16. 0 % * Very Severe > 260 mg/dl = 45. 2 %
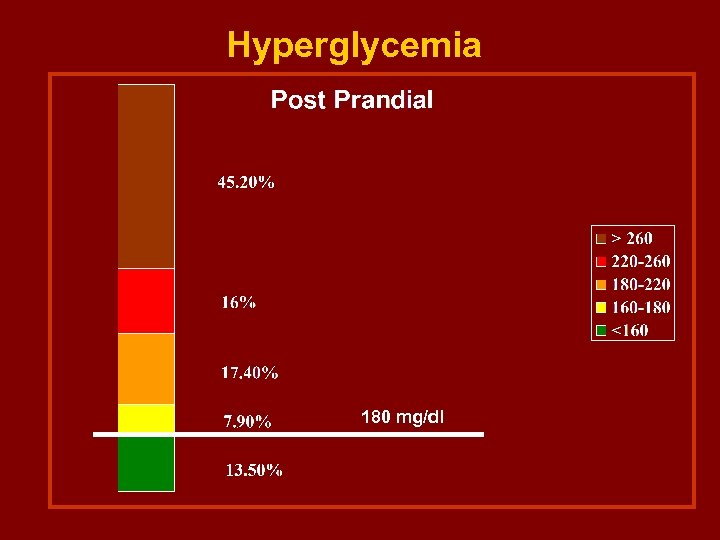
Hyperglycemia 180 mg/dl
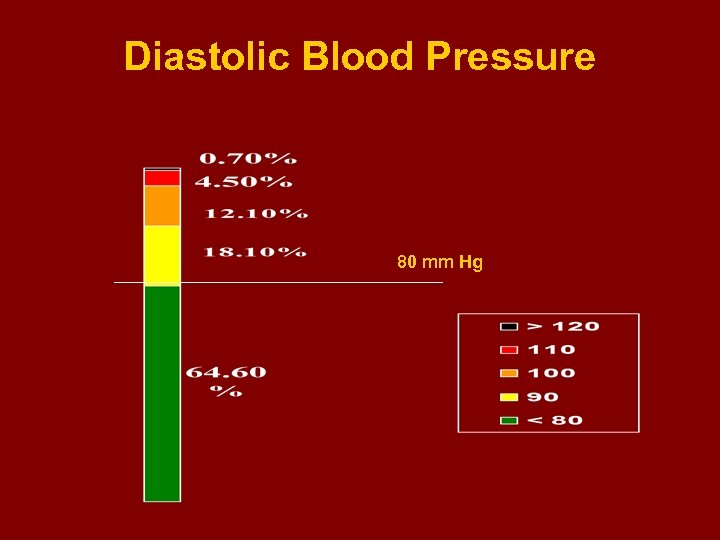
Diastolic Blood Pressure 80 mm Hg
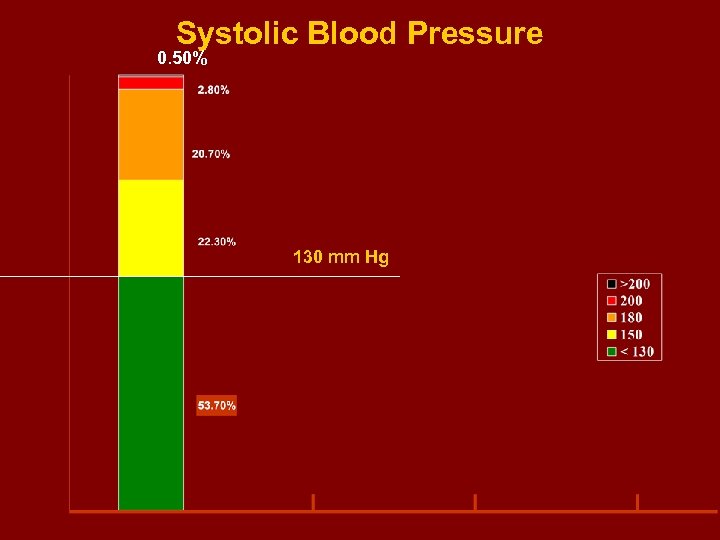
Systolic Blood Pressure 0. 50% 130 mm Hg
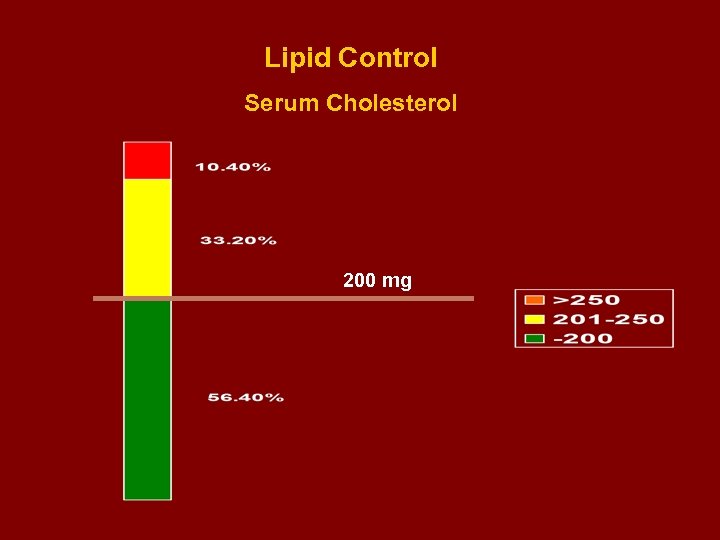
Lipid Control Serum Cholesterol 200 mg
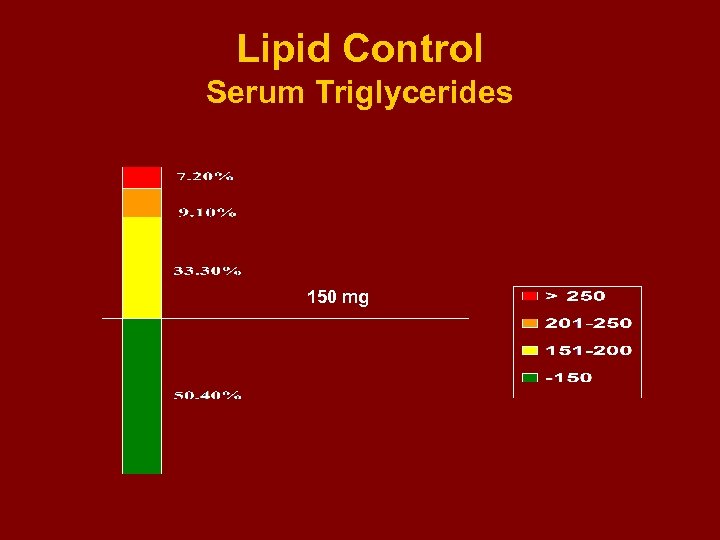
Lipid Control Serum Triglycerides 150 mg
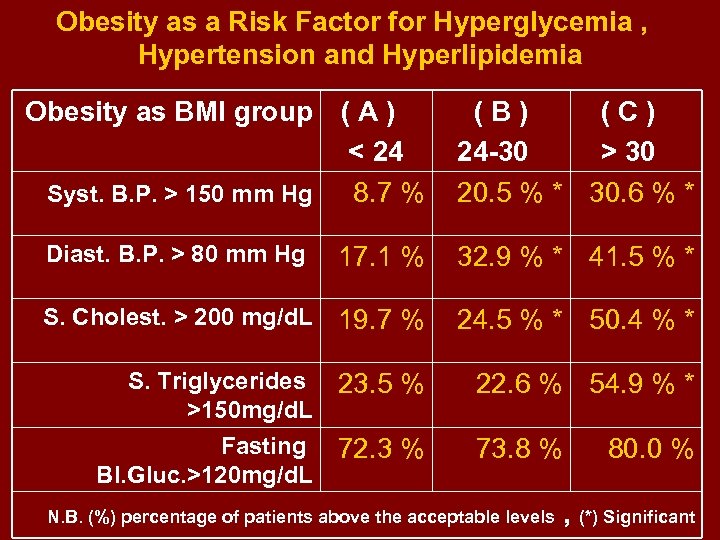
Obesity as a Risk Factor for Hyperglycemia , Hypertension and Hyperlipidemia Obesity as BMI group Syst. B. P. > 150 mm Hg (A) < 24 8. 7 % (B) (C) 24 -30 > 30 20. 5 % * 30. 6 % * Diast. B. P. > 80 mm Hg 17. 1 % 32. 9 % * 41. 5 % * S. Cholest. > 200 mg/d. L 19. 7 % 24. 5 % * 50. 4 % * S. Triglycerides >150 mg/d. L 23. 5 % 22. 6 % 54. 9 % * Fasting Bl. Gluc. >120 mg/d. L 72. 3 % 73. 8 % N. B. (%) percentage of patients above the acceptable levels 80. 0 % , (*) Significant
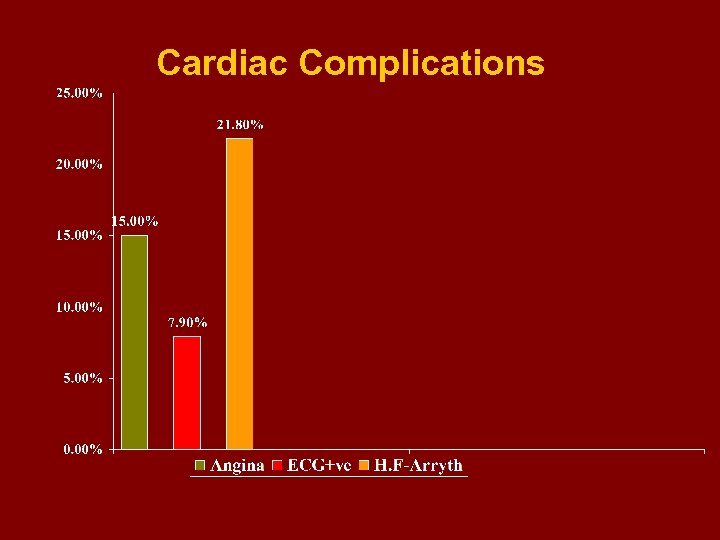
Cardiac Complications

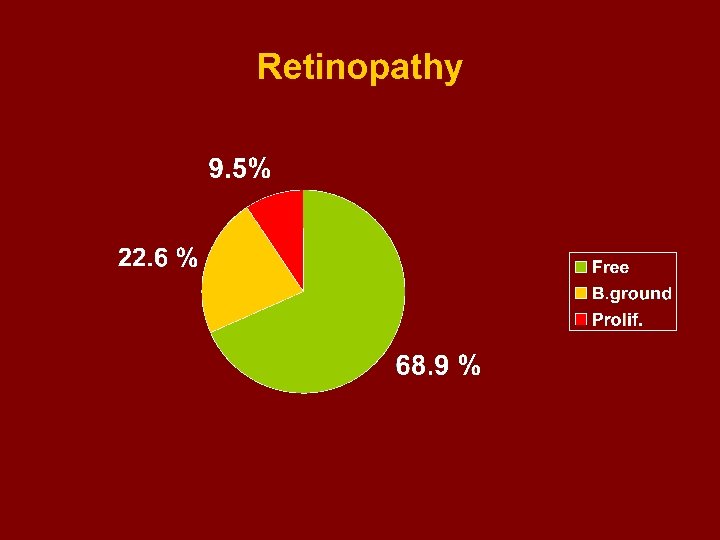
Retinopathy (in 1173 patients ) - Free - Back ground - Proliferative 68. 9 % 22. 6 % 9. 5 %
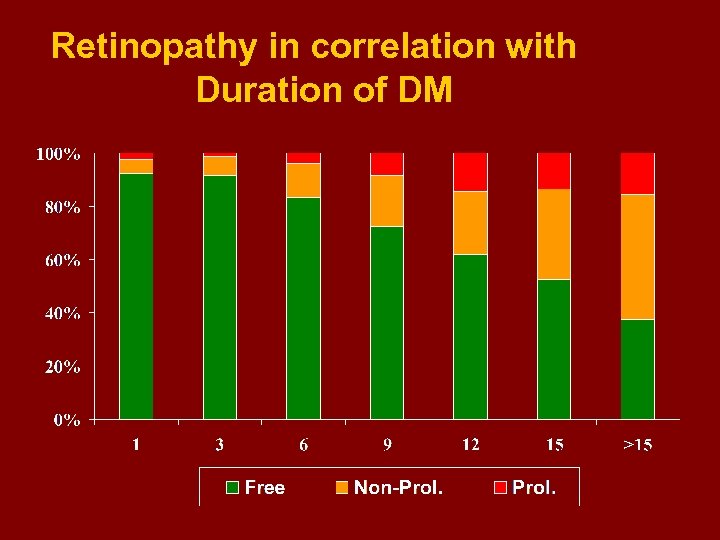
Retinopathy in correlation with Duration of DM
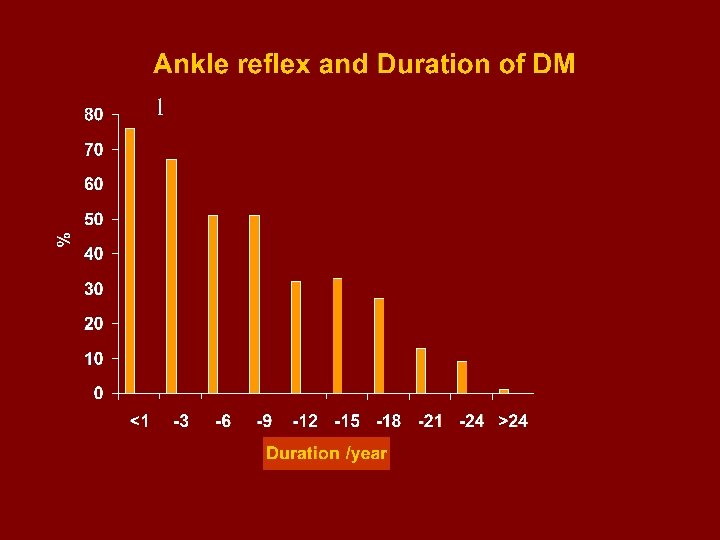
l
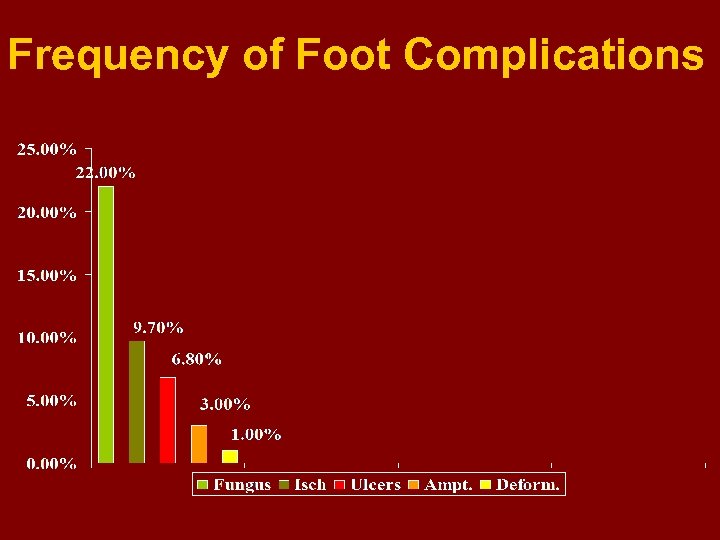
Frequency of Foot Complications

Prevalence of foot complications 1 - Fungus infection 2 - Foot ulcers 3 - Evident Ischaemic changes 4 - Amputations 5 - Deformities = 22. 0 % = 6. 8 % = 9. 7 % = 3. 0 % = 1. 0 %
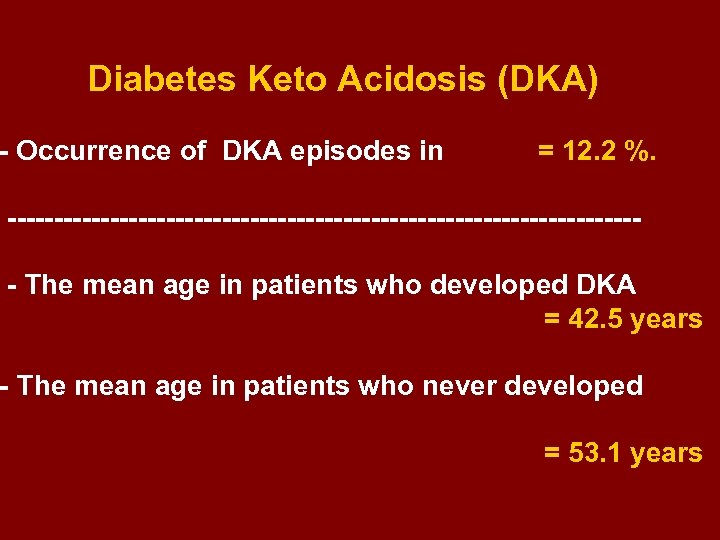
Diabetes Keto Acidosis (DKA) - Occurrence of DKA episodes in = 12. 2 %. ---------------------------------- The mean age in patients who developed DKA = 42. 5 years - The mean age in patients who never developed = 53. 1 years

Hypoglycemia - Occurrence of Hypoglycemic episodes in = 20. 5% ------------------------------------ The mean age of patients who developed hypoglycemic episodes at any time = 50. 8 years The mean age of patients who did not experience hypoglyceamic episodes = 52. 1 years
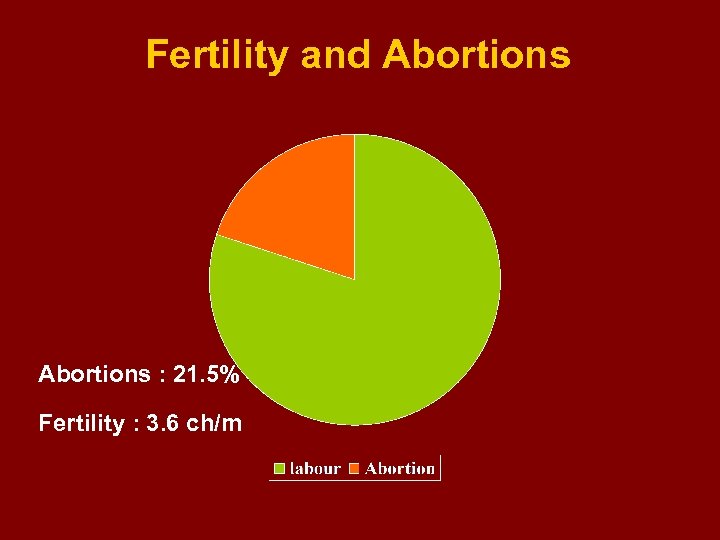
Fertility and Abortions : 21. 5% Fertility : 3. 6 ch/m

The Socio economic Burden
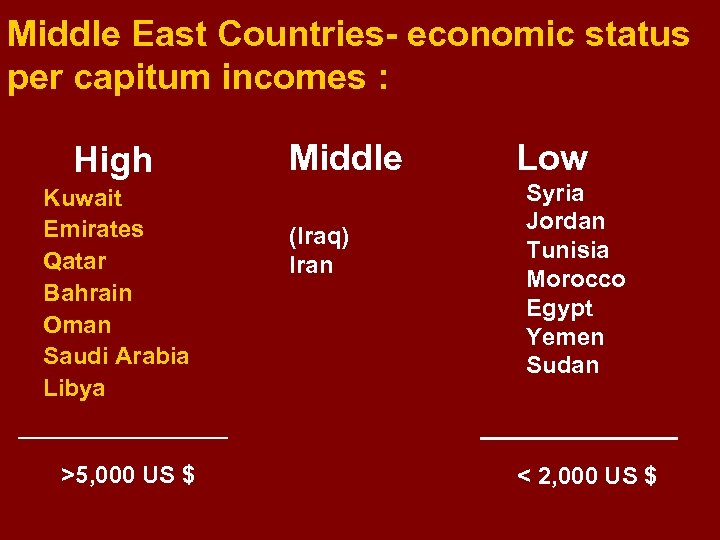
Middle East Countries- economic status per capitum incomes : High Kuwait Emirates Qatar Bahrain Oman Saudi Arabia Libya >5, 000 US $ Middle (Iraq) Iran Low Syria Jordan Tunisia Morocco Egypt Yemen Sudan < 2, 000 US $
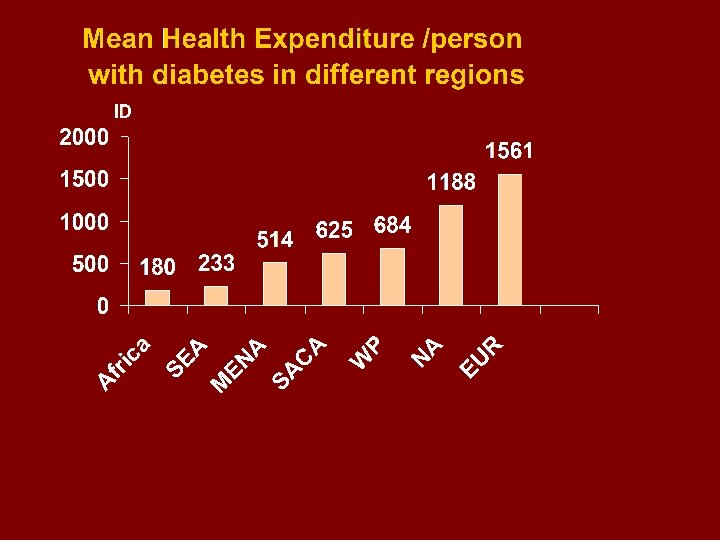
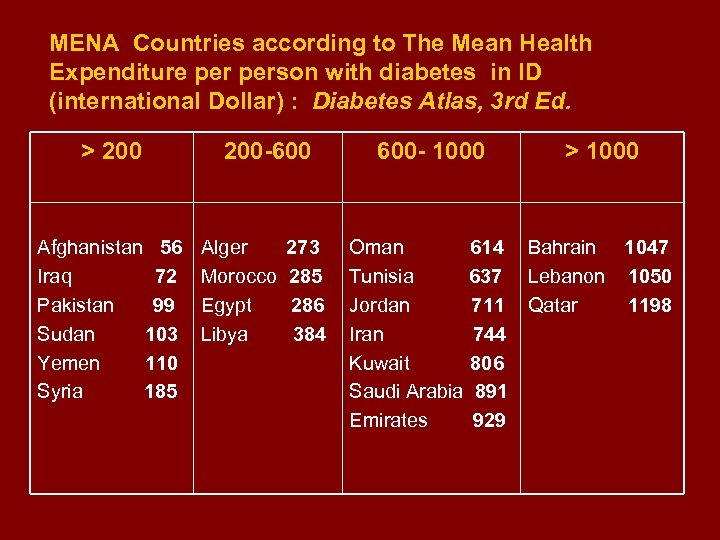
MENA Countries according to The Mean Health Expenditure person with diabetes in ID (international Dollar) : Diabetes Atlas, 3 rd Ed. > 200 Afghanistan 56 Iraq 72 Pakistan 99 Sudan 103 Yemen 110 Syria 185 200 -600 Alger Morocco Egypt Libya 273 285 286 384 600 - 1000 > 1000 Oman 614 Bahrain 1047 Tunisia 637 Lebanon 1050 Jordan 711 Qatar 1198 Iran 744 Kuwait 806 Saudi Arabia 891 Emirates 929
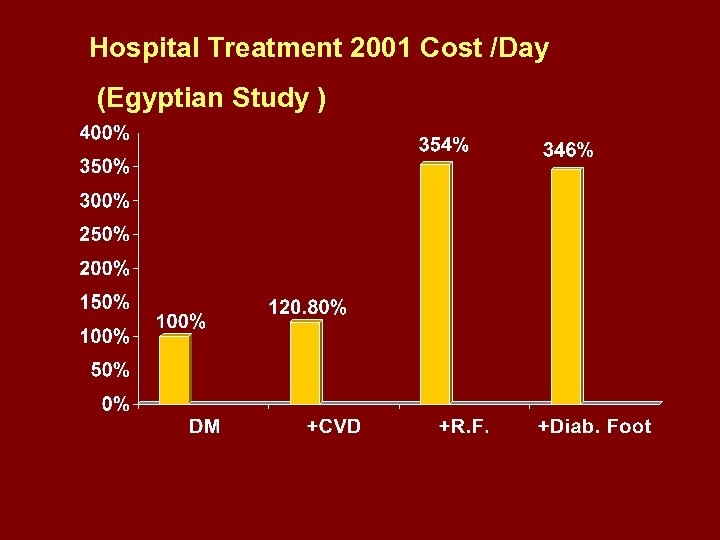
Hospital Treatment 2001 Cost /Day (Egyptian Study )
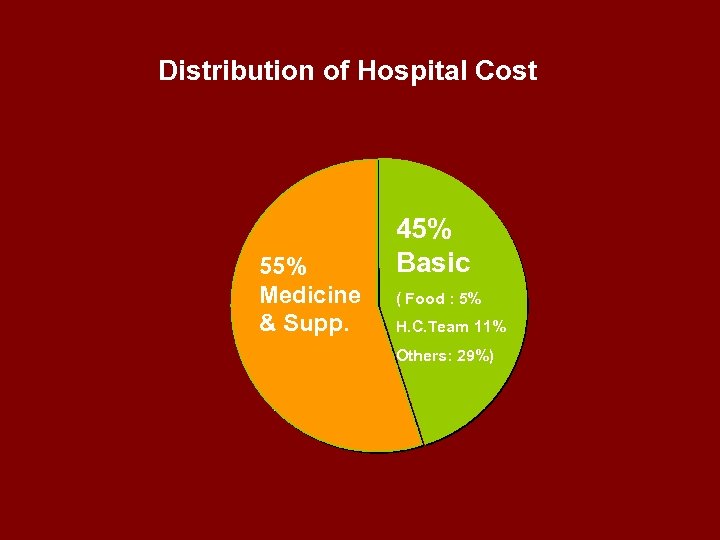
Distribution of Hospital Cost 55% Medicine & Supp. 45% Basic ( Food : 5% H. C. Team 11% Others: 29%)
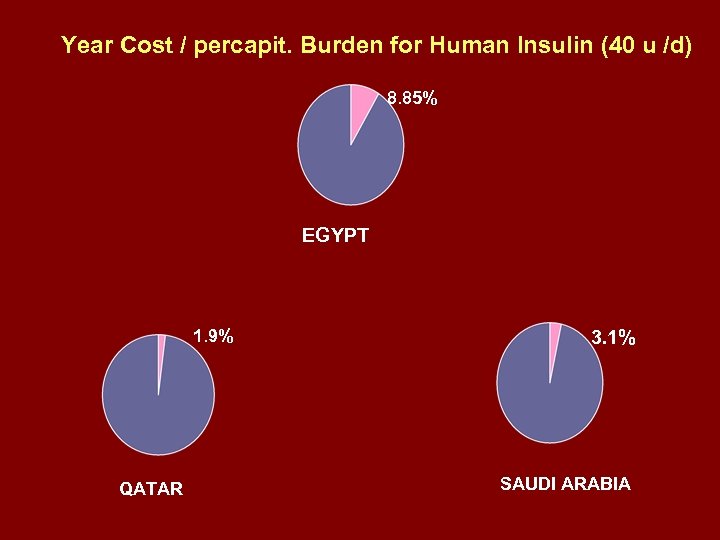
Year Cost / percapit. Burden for Human Insulin (40 u /d) 8. 85% EGYPT 1. 9% QATAR 3. 1% SAUDI ARABIA
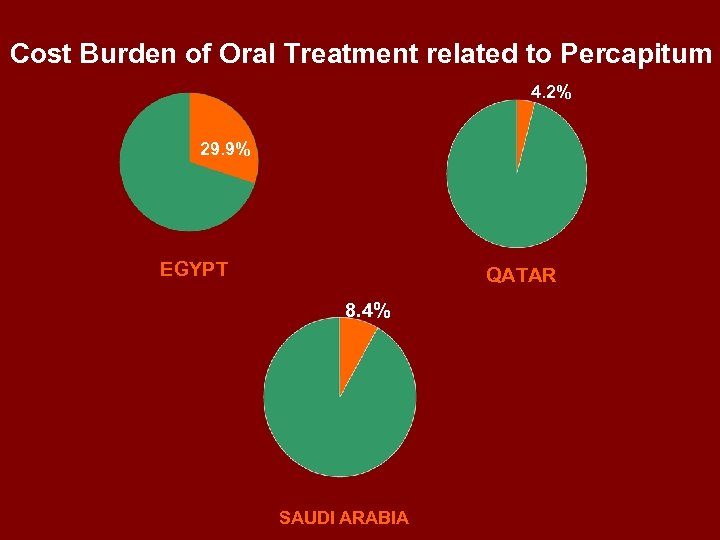
Cost Burden of Oral Treatment related to Percapitum 4. 2% 29. 9% EGYPT QATAR 8. 4% SAUDI ARABIA



What are The IDF Goals ? 1. Global Advocacy 2. To raise Global Awareness omote appropriate Diabetes Care & Prevention 4. Encourage finding a Cure



For improving Diabetes Care and Prevention , Education of Health Care Providers should consider expertise in both: I- Clinical Diabetes , II- Educations skills and




The Way to a National Diabetes Program

Minimal requirements : 1 - Insulin and medications availability ( affordable) 2 - Primary centers for diagnosis and care 3 - wide distribution of services allover the country 4 - Basic requirements to manage complications 5 - Education : knowledge & skills to patients – Public orientation 6 - National basic studies in epidemiology and socioeconomics. 7 - Care for Diabetes in School children 8 - Care for diabetes in pregnancy

Potential Adverse Factors 1 - Economic : Poor Financial Res. /per capit. / Government expenditure/ House-hold expend. with High Prev. of diab. 2 - Demographic Extensive areas with poor communications. High population density 3 - Social : Illiteracy- Misconceptions – adverse habits and traditions.
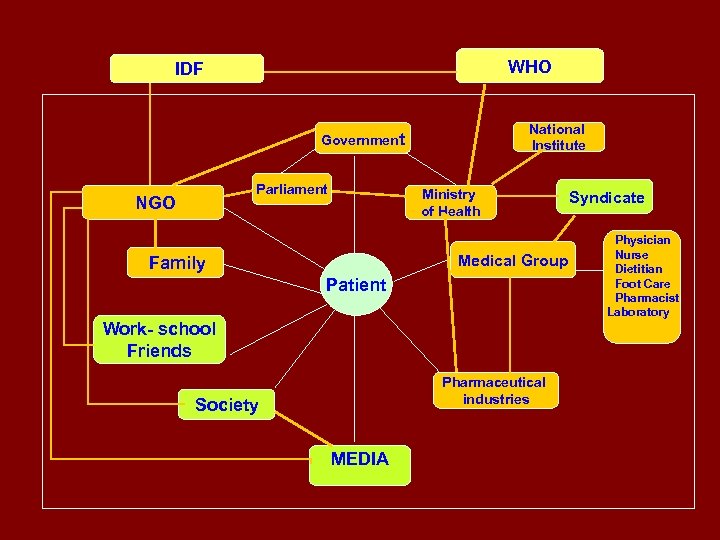
WHO IDF National Institute Government Parliament NGO Ministry of Health Medical Group Family Patient Work- school Friends Pharmaceutical industries Society MEDIA Syndicate Physician Nurse Dietitian Foot Care Pharmacist Laboratory

In Developing a National Diabetes Programme : 1 - Consider the specific needs in the country and available resources to decide priorities 2 - Define the role to be played by each one of the constituents of the community , and Identify Champions for projects. 3 - Seek partnerships with : WHO , Twining , WDF , Rotary , etc. .

Obligations of Different Parties The Government ( Ministry of Health) 1 - Increase Investments in Health/Diabetes 2 - provide Minimal Diabetes Care in Clinics & Hospitals 3 - Insure Insulin & Medications Availability 4 - provide Education : Patient, Health Care Team and Public 5 - Coordinate with Health Care Syndicates 6 - Coordinate with NGOs 7 - attract International Aid programmes 8 - promote National Research ( epidemiol. -socioeconomic)

Parliament (Legislation) 1 - Budget planning to improve diabetes Care 2 - Taxation Exemption for insulin & medical requirements 3 - Put rules and regulations for NGO activities 4 - Maintain and guard Patients’ Human Rights ( anti discrimination, working , children, women , elderly …etc) 5 - Health Insurance Laws

The Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs ) 1 - Advocacy 2 - Education Programs for : -Patients and Families -Health Care Team -Community at large 3 - Rules & Regulations - legally recognized - non profitable - accountable and transparent - coordinated & complementary to government - no unhealthy competition, extravagance , business controlled ( by industries )

The Health Care Team The Physician 1 - is Leader of the HC team 2 - is the Final reference for his patient’s education 3 - keep harmony with others in the HC team 4 - requires continuous training courses and updates 5 - acquire education skills Nurses 1 - Training courses , by whom ? 2 - Knowledge + skills & attitude 3 - skills in education 4 - keep Team work 5 - Continuous education , scientific meetings and workshops

Diabetes Care for Special Groups School Children - Registration at national level - Individual records in schools - basic equipments to manage emergencies - Education courses to school attendants. - protecting special rights : play- recreation treatment. non discrimination …etc

Mothers with Diabetes of Pregnancy - Screening for diabetes of pregnancy - Protocols for management of GD - Care for the N. B. - After-labour follow-up of mothers

The National Diabetes Registry - essential as source of information for planning public services - Central location - paper or computer recordings - contains individual patient data - complemented by local & peripheral registries (in schools - work – Health insurance, etc ) - network connections for exchange information

Diabetes Screening Programmes - Specifically to high risk groups - By central planning and organization - ensure unified criteria for diagnosis - Screening for early detection of complications : - Sending study groups to remote areas.

International Relations The International Diabetes Federation 1 - get moral support from IDF to National Associations & programs 2 - use as source of information & educational material 3 - Benefit from IDF Task forces’ activities and programs 4 - Benefit from WDD events

The WHO 1 - Government / collaborative programmes for promotion of diabetes Care 2 - NGO : collaboration in promoting diabetes care through training & education programmes

The Patient Obligations 1 - Take active role: seek to be educated 2 - follow proper life style 3 - comply 4 - not to accept misconceptions and deceptive propaganda

Thank You Bibliotheca Alexandrina on WDD
783a00912ef99b594850df5333a06591.ppt