- Количество слайдов: 29

Developments in Borderless Higher Education Top Management Programme November 22, 2005 Svava Bjarnason Director of Research and Strategy Association of Commonwealth Universities and Director Observatory on Borderless Higher Education

Today’s Presentation: • • • Context Transnational activities Regulatory frameworks Online learning Issues

The Business of Borderless Education: UK Perspectives 2000

Borderless Education Report: “. . . We consider that the drivers behind borderless developments are strong and will strengthen. As such, the picture as it exists today is not a good predictor of the future. The opportunities are real and the threats, both direct and indirect, are already present. ” Business of Borderless Education: UK Perspectives 2000
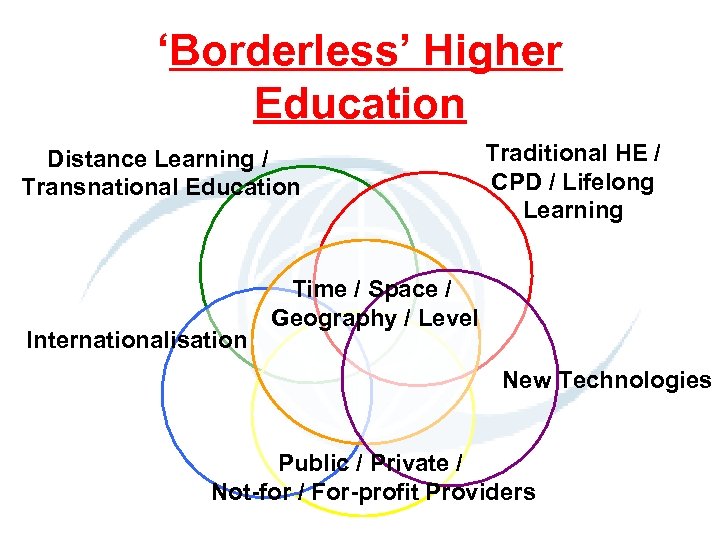
‘Borderless’ Higher Education Distance Learning / Transnational Education Internationalisation Traditional HE / CPD / Lifelong Learning Time / Space / Geography / Level New Technologies Public / Private / Not-for / For-profit Providers

Demand for Higher Education • Worldwide HE places to be 125 million in 2020 • Demand for international education places predicted to be: – 2. 1 million in 2003 – 5. 8 million by 2020 • Age participation rate: – 40% – 50% in ‘north’ – Below 5% in many developing and emerging economies
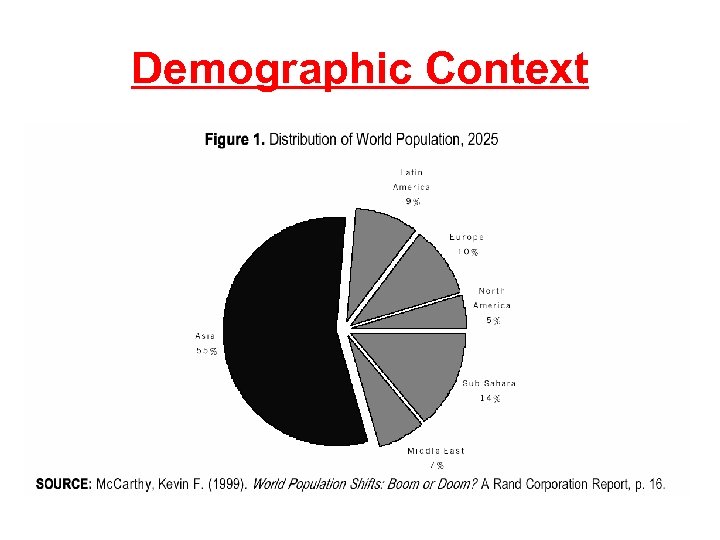
Demographic Context

Transnational Education (TNE) “. . . where the learners are located in a country different from the one where the awarding institution is based. ” UNESCO and Council of Europe 2005

World Trade Organisation General Agreement on Trade in Services: – Mode 1 ~ Cross-border Supply – Mode 2 ~ Consumption Abroad – Mode 3 ~ Commercial Presence – Mode 4 ~ Presence of Natural Persons

Global Players • • Global ‘mega’ universities Traditional public universities Private universities (for/not for profit) Corporate universities Media & Publishing Houses Professional Associations Public & private companies

Types of Relationship with Higher Education • • Competitive Software services & sales Materials sales Core and non-core course sales Franchising/ marketing Funding Accreditation Joint content development
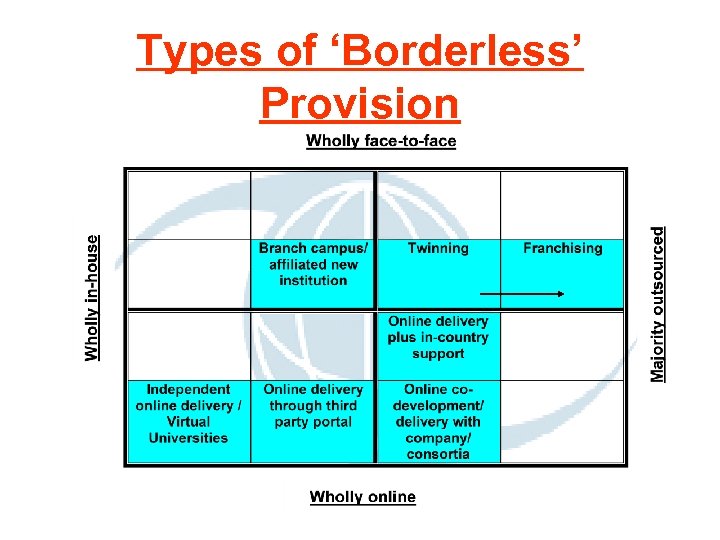
Types of ‘Borderless’ Provision

Current Choices… Face-to-face Generic Mass-market Low cost In-house Online Bespoke Personalised High cost Third party
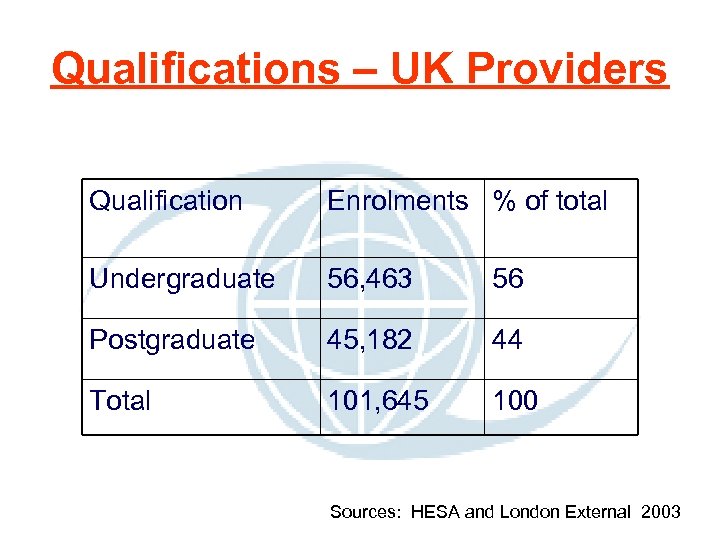
Qualifications – UK Providers Qualification Enrolments % of total Undergraduate 56, 463 56 Postgraduate 45, 182 44 Total 101, 645 100 Sources: HESA and London External 2003
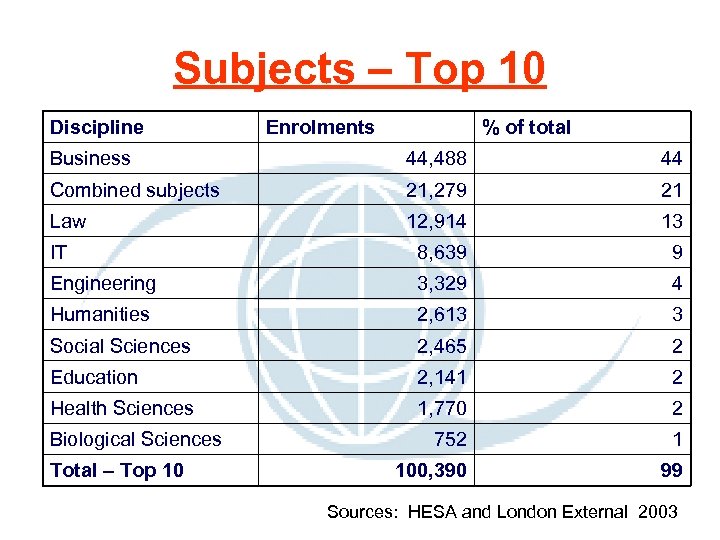
Subjects – Top 10 Discipline Enrolments % of total Business 44, 488 44 Combined subjects 21, 279 21 Law 12, 914 13 IT 8, 639 9 Engineering 3, 329 4 Humanities 2, 613 3 Social Sciences 2, 465 2 Education 2, 141 2 Health Sciences 1, 770 2 752 1 100, 390 99 Biological Sciences Total – Top 10 Sources: HESA and London External 2003
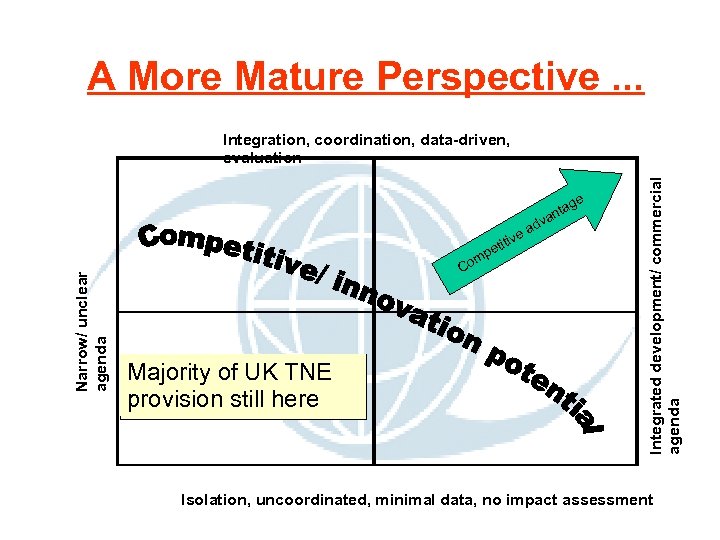
A More Mature Perspective. . . ge v ta an d ea Narrow/ unclear agenda tiv eti p m Co Majority of UK TNE provision still here Integrated development/ commercial agenda Integration, coordination, data-driven, evaluation Isolation, uncoordinated, minimal data, no impact assessment
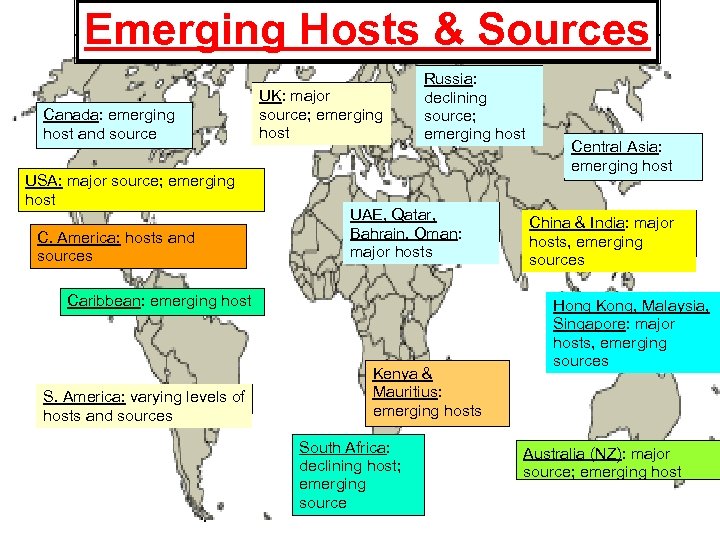
Emerging Hosts & Sources Canada: emerging host and source USA: major source; emerging host C. America: hosts and sources UK: major source; emerging host Russia: declining source; emerging host UAE, Qatar, Bahrain, Oman: major hosts Caribbean: emerging host S. America: varying levels of hosts and sources Kenya & Mauritius: emerging hosts South Africa: declining host; emerging source Central Asia: emerging host China & India: major hosts, emerging sources Hong Kong, Malaysia, Singapore: major hosts, emerging sources Australia (NZ): major source; emerging host

Directions of TNE • North to South (vast majority) • North to North (e. g. Charles Sturt University in Ontario, Canada) • South to South (e. g. Manipal Academy of HE in UAE; Al-Azhar University to open in Thailand) • South to North (e. g. University of Sonora to open in Arizona)

Hosts ~ National Examples • Bankroll model: Qatar, Singapore • Economic hub model: Mauritius, UAE • Education hub model: Malaysia, Thailand • Capacity model: China, Hong Kong SAR • ‘Suspicion’ model: South Africa • Ignore/ obstruct model: Greece • Minimal regulation/ no position/ random initiatives model: most countries

Regulatory Models • Majority of countries have little or no regulation • Next most common is minimal source ‘accreditation’ and/ or local registration • Few countries require extensive local QA • ‘Special zone’ approach • Few countries impose specific curricula/ language/ ownership requirements

National Regulatory Frameworks

Guidelines on Provision • UNESCO/OECD – Guidelines for quality provision • Statement on sharing quality HE across borders • AVCC – Code of ethical practice • UK Quality Assurance Agency – Code of practice

Online Learning in Commonwealth Universities • First survey of its kind - May ‘ 02 - second in 2004 • Sent to 500 Executive Heads in 35 countries • Focus on empirical data on institutional strategy, infrastructure, provision • Benchmarking relative position(s)
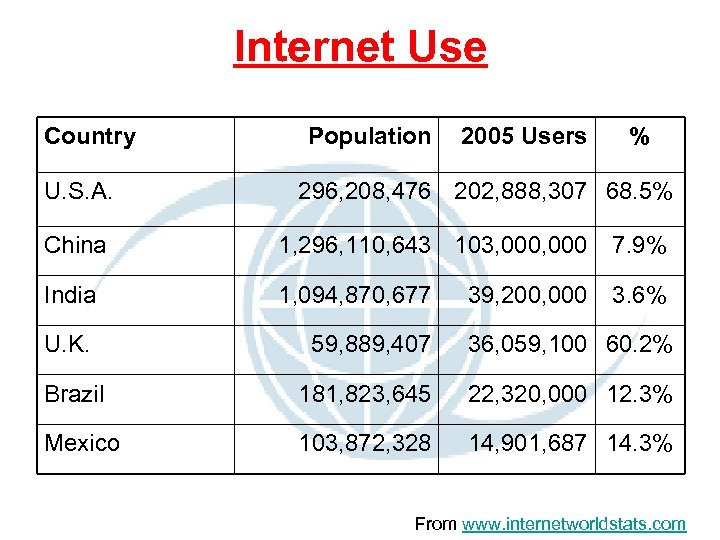
Internet Use Country U. S. A. Population 2005 Users % 296, 208, 476 202, 888, 307 68. 5% China 1, 296, 110, 643 103, 000 7. 9% India 1, 094, 870, 677 3. 6% U. K. 59, 889, 407 36, 059, 100 60. 2% Brazil 181, 823, 645 22, 320, 000 12. 3% Mexico 103, 872, 328 14, 901, 687 14. 3% 39, 200, 000 From www. internetworldstats. com
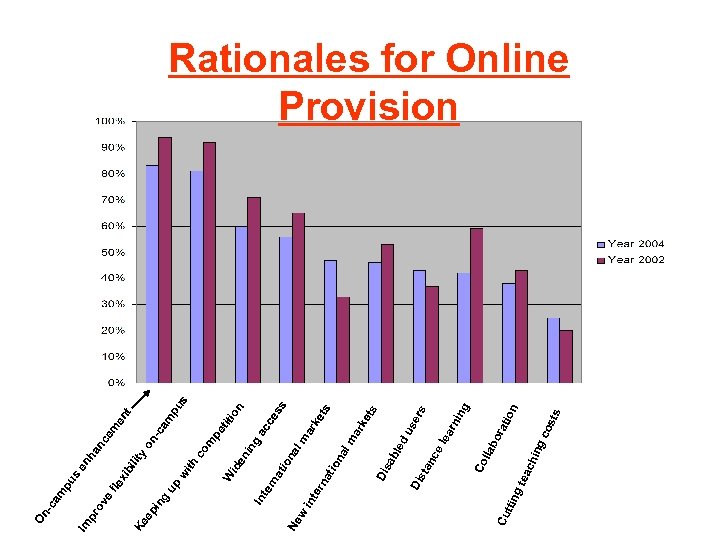
hin g gt eac co sts ion rat bo lla Co ing rn ea ts rs du se el nc sta Di ble sa Di ke ar ke ts ar lm ss ac ce on iti pe t lm na tio na er int Cu ttin w Ne io na rn at co m s pu am -c on en in g id th wi W up y lit en t m nc e en ha bi xi fle In te in g ep ov e pr Ke Im pu s On -c am Rationales for Online Provision
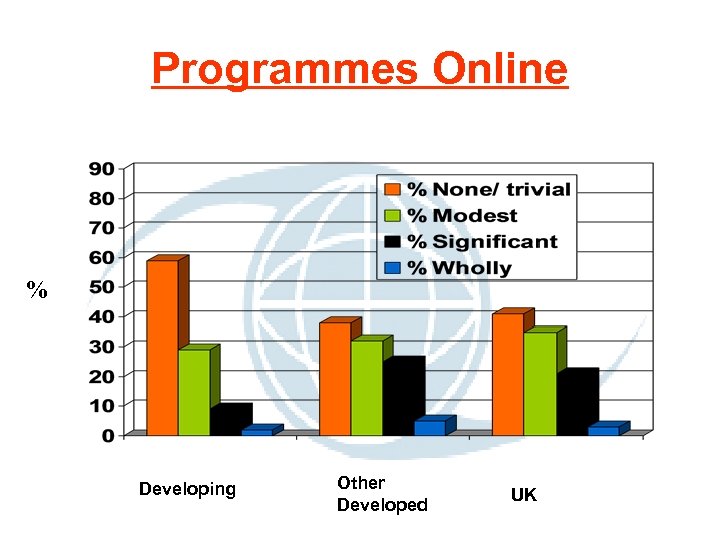
Programmes Online % Developing Other Developed UK

Some of the Issues • Quality assurance • Regulatory • Credit transfer • Recognition of awards • Higher education as a commodity • Working collaboratively with others

Observatory’s Response: Information, Strategy, Reflection • Descriptive Information - news on the latest developments • Strategic Information - an attempt to explore rationales, decision-making processes and organisational change • Reflection - standing back from events to consider implications of trends and developments

www. obhe. ac. uk