f06ff31d2f47513114e7733cc4bfad09.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Developments Advanced in Risk Analysis and Risk Management Lori Brown, Seton Hall University Robert Roach, New York University Jean Demchak, Marsh
Developments Advanced in Risk Analysis and Risk Management Lori Brown, Seton Hall University Robert Roach, New York University Jean Demchak, Marsh
 Program Speakers: Lori Brown Director of Compliance & Risk Management Seton Hall University South Orange, NJ Jean Demchak Managing Director Global Education Leader Marsh, Inc. New York, NY Robert F. Roach Chief Compliance Officer New York University New York, NY
Program Speakers: Lori Brown Director of Compliance & Risk Management Seton Hall University South Orange, NJ Jean Demchak Managing Director Global Education Leader Marsh, Inc. New York, NY Robert F. Roach Chief Compliance Officer New York University New York, NY
 “It wasn’t the risk we knew about that concerned us, but the risks we were unaware of that worried us the most” Chris Mc. Alary, VP Finance, Mount St Mary’s College
“It wasn’t the risk we knew about that concerned us, but the risks we were unaware of that worried us the most” Chris Mc. Alary, VP Finance, Mount St Mary’s College
 Program Overview 1. Trends in risk management and impact of ERM on credit ratings. 2. Developing an Institutional ERM program. 3. Practical Risk Management tools for Compliance and ERM programs
Program Overview 1. Trends in risk management and impact of ERM on credit ratings. 2. Developing an Institutional ERM program. 3. Practical Risk Management tools for Compliance and ERM programs
 Risk: Upside and Downside All organizations face internal and external factors that make it uncertain whether and when they will meet their objectives. The effect of this uncertainty on achieving objectives is called risk.
Risk: Upside and Downside All organizations face internal and external factors that make it uncertain whether and when they will meet their objectives. The effect of this uncertainty on achieving objectives is called risk.
 Risk Management in Application Risk Management principles can be applied to any type of risk, whatever its nature, whether having positive or negative consequences. Compliance Programs: Use Risk Management principles to help identify, assess, evaluate, and treat ethical and regulatory risks. Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): Is a coordinated program applied throughout the life of an organization and to a wide range of activities, including strategies and decisions, operations, processes, functions, projects, and services.
Risk Management in Application Risk Management principles can be applied to any type of risk, whatever its nature, whether having positive or negative consequences. Compliance Programs: Use Risk Management principles to help identify, assess, evaluate, and treat ethical and regulatory risks. Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): Is a coordinated program applied throughout the life of an organization and to a wide range of activities, including strategies and decisions, operations, processes, functions, projects, and services.
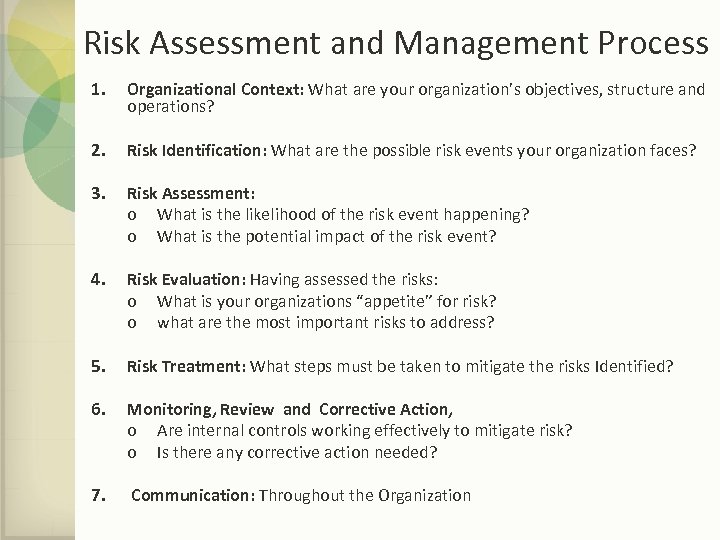 Risk Assessment and Management Process 1. Organizational Context: What are your organization’s objectives, structure and operations? 2. Risk Identification: What are the possible risk events your organization faces? 3. Risk Assessment: o What is the likelihood of the risk event happening? o What is the potential impact of the risk event? 4. Risk Evaluation: Having assessed the risks: o What is your organizations “appetite” for risk? o what are the most important risks to address? 5. Risk Treatment: What steps must be taken to mitigate the risks Identified? 6. Monitoring, Review and Corrective Action, o Are internal controls working effectively to mitigate risk? o Is there any corrective action needed? 7. Communication: Throughout the Organization
Risk Assessment and Management Process 1. Organizational Context: What are your organization’s objectives, structure and operations? 2. Risk Identification: What are the possible risk events your organization faces? 3. Risk Assessment: o What is the likelihood of the risk event happening? o What is the potential impact of the risk event? 4. Risk Evaluation: Having assessed the risks: o What is your organizations “appetite” for risk? o what are the most important risks to address? 5. Risk Treatment: What steps must be taken to mitigate the risks Identified? 6. Monitoring, Review and Corrective Action, o Are internal controls working effectively to mitigate risk? o Is there any corrective action needed? 7. Communication: Throughout the Organization
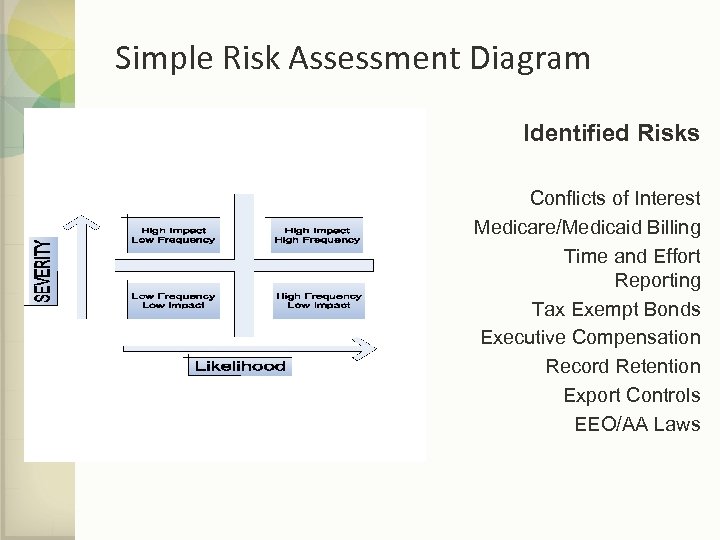 Simple Risk Assessment Diagram Identified Risks Conflicts of Interest Medicare/Medicaid Billing Time and Effort Reporting Tax Exempt Bonds Executive Compensation Record Retention Export Controls EEO/AA Laws
Simple Risk Assessment Diagram Identified Risks Conflicts of Interest Medicare/Medicaid Billing Time and Effort Reporting Tax Exempt Bonds Executive Compensation Record Retention Export Controls EEO/AA Laws
 Risk Evaluation Having assessed the risks: o What are the most important risks to address? o What is your organizations “appetite” for risk?
Risk Evaluation Having assessed the risks: o What are the most important risks to address? o What is your organizations “appetite” for risk?
 Risk Response • Avoidance • Reduction/Mitigation (Internal Controls) • Sharing (e. g. Insurance) • Acceptance o Crisis Management Plans o Business Continuity Plans o Other Operational Plans
Risk Response • Avoidance • Reduction/Mitigation (Internal Controls) • Sharing (e. g. Insurance) • Acceptance o Crisis Management Plans o Business Continuity Plans o Other Operational Plans
 Control Activities • Organizational/Process Controls o E. g. Separation of Duties • Documentation o Written Policies and Procedures Essential • Training • Audit Trails o Final Results should be traceable back to originating transactions • Security and Integrity o Access Controls
Control Activities • Organizational/Process Controls o E. g. Separation of Duties • Documentation o Written Policies and Procedures Essential • Training • Audit Trails o Final Results should be traceable back to originating transactions • Security and Integrity o Access Controls
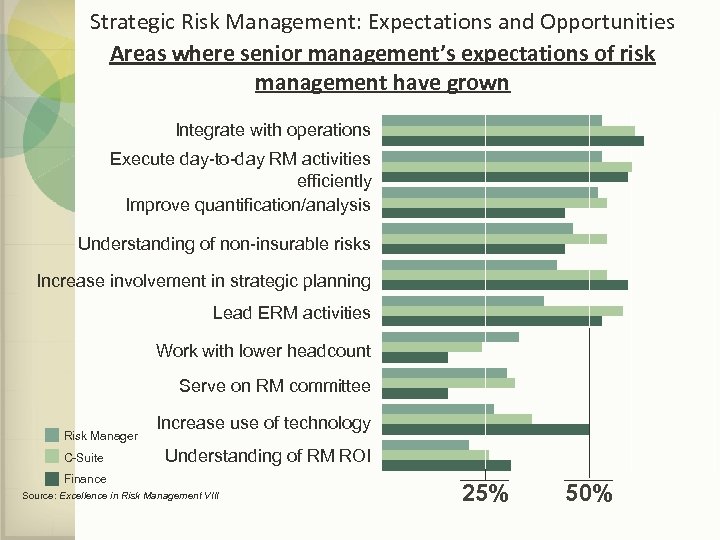 Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Areas where senior management’s expectations of risk management have grown Integrate with operations Execute day-to-day RM activities efficiently Improve quantification/analysis Understanding of non-insurable risks Increase involvement in strategic planning Lead ERM activities Work with lower headcount Serve on RM committee Risk Manager C-Suite Increase use of technology Understanding of RM ROI Finance Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII 25% 50%
Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Areas where senior management’s expectations of risk management have grown Integrate with operations Execute day-to-day RM activities efficiently Improve quantification/analysis Understanding of non-insurable risks Increase involvement in strategic planning Lead ERM activities Work with lower headcount Serve on RM committee Risk Manager C-Suite Increase use of technology Understanding of RM ROI Finance Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII 25% 50%
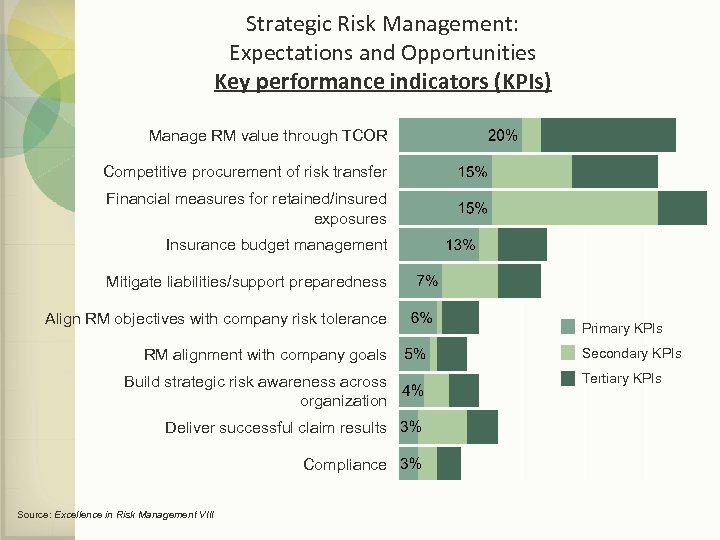 Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Key performance indicators (KPIs) Manage RM value through TCOR Competitive procurement of risk transfer Financial measures for retained/insured exposures Insurance budget management Mitigate liabilities/support preparedness Align RM objectives with company risk tolerance RM alignment with company goals Build strategic risk awareness across organization Deliver successful claim results Compliance Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII Primary KPIs Secondary KPIs Tertiary KPIs
Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Key performance indicators (KPIs) Manage RM value through TCOR Competitive procurement of risk transfer Financial measures for retained/insured exposures Insurance budget management Mitigate liabilities/support preparedness Align RM objectives with company risk tolerance RM alignment with company goals Build strategic risk awareness across organization Deliver successful claim results Compliance Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII Primary KPIs Secondary KPIs Tertiary KPIs
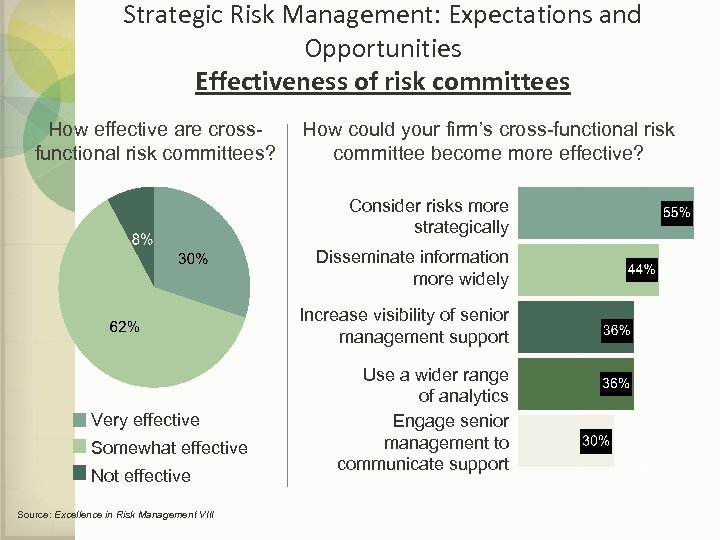 Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Effectiveness of risk committees How effective are crossfunctional risk committees? How could your firm’s cross-functional risk committee become more effective? Consider risks more strategically Disseminate information more widely Increase visibility of senior management support Very effective Somewhat effective Not effective Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII Use a wider range of analytics Engage senior management to communicate support
Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Effectiveness of risk committees How effective are crossfunctional risk committees? How could your firm’s cross-functional risk committee become more effective? Consider risks more strategically Disseminate information more widely Increase visibility of senior management support Very effective Somewhat effective Not effective Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII Use a wider range of analytics Engage senior management to communicate support
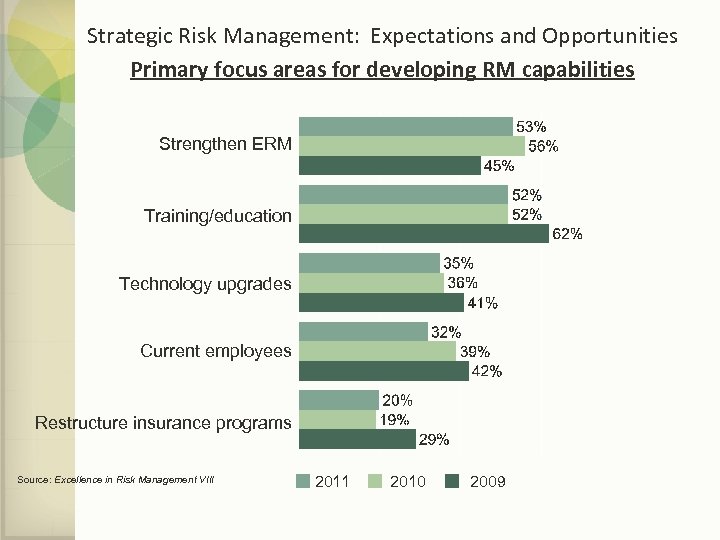 Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Primary focus areas for developing RM capabilities Strengthen ERM Training/education Technology upgrades Current employees Restructure insurance programs Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII 2011 2010 2009
Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Primary focus areas for developing RM capabilities Strengthen ERM Training/education Technology upgrades Current employees Restructure insurance programs Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII 2011 2010 2009
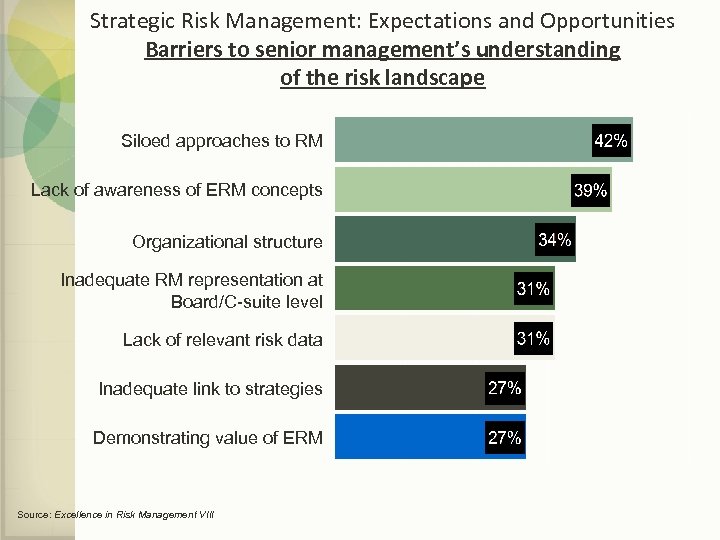 Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Barriers to senior management’s understanding of the risk landscape Siloed approaches to RM Lack of awareness of ERM concepts Organizational structure Inadequate RM representation at Board/C-suite level Lack of relevant risk data Inadequate link to strategies Demonstrating value of ERM Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII
Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Barriers to senior management’s understanding of the risk landscape Siloed approaches to RM Lack of awareness of ERM concepts Organizational structure Inadequate RM representation at Board/C-suite level Lack of relevant risk data Inadequate link to strategies Demonstrating value of ERM Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII
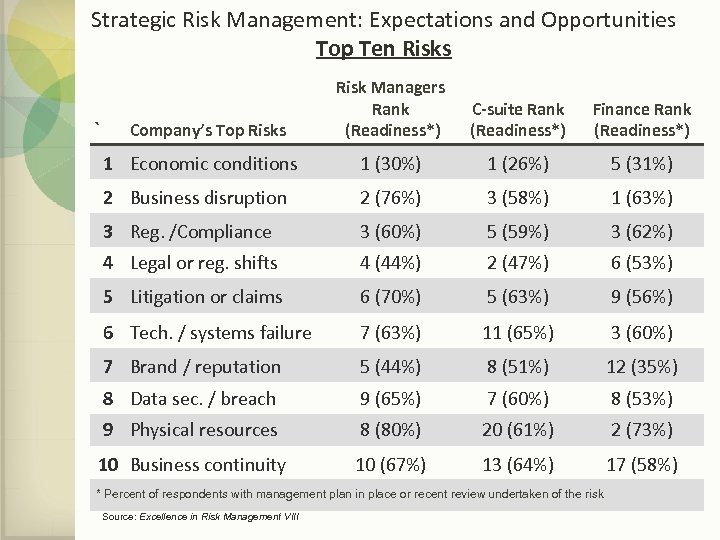 Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Top Ten Risks Risk Managers Rank (Readiness*) C-suite Rank (Readiness*) Finance Rank (Readiness*) 1 Economic conditions 1 (30%) 1 (26%) 5 (31%) 2 Business disruption 2 (76%) 3 (58%) 1 (63%) 3 Reg. /Compliance 3 (60%) 5 (59%) 3 (62%) 4 Legal or reg. shifts 4 (44%) 2 (47%) 6 (53%) 5 Litigation or claims 6 (70%) 5 (63%) 9 (56%) 6 Tech. / systems failure 7 (63%) 11 (65%) 3 (60%) 7 Brand / reputation 5 (44%) 8 (51%) 12 (35%) 8 Data sec. / breach 9 (65%) 7 (60%) 8 (53%) 9 Physical resources 8 (80%) 20 (61%) 2 (73%) 10 Business continuity 10 (67%) 13 (64%) 17 (58%) ` Company’s Top Risks * Percent of respondents with management plan in place or recent review undertaken of the risk Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII
Strategic Risk Management: Expectations and Opportunities Top Ten Risks Risk Managers Rank (Readiness*) C-suite Rank (Readiness*) Finance Rank (Readiness*) 1 Economic conditions 1 (30%) 1 (26%) 5 (31%) 2 Business disruption 2 (76%) 3 (58%) 1 (63%) 3 Reg. /Compliance 3 (60%) 5 (59%) 3 (62%) 4 Legal or reg. shifts 4 (44%) 2 (47%) 6 (53%) 5 Litigation or claims 6 (70%) 5 (63%) 9 (56%) 6 Tech. / systems failure 7 (63%) 11 (65%) 3 (60%) 7 Brand / reputation 5 (44%) 8 (51%) 12 (35%) 8 Data sec. / breach 9 (65%) 7 (60%) 8 (53%) 9 Physical resources 8 (80%) 20 (61%) 2 (73%) 10 Business continuity 10 (67%) 13 (64%) 17 (58%) ` Company’s Top Risks * Percent of respondents with management plan in place or recent review undertaken of the risk Source: Excellence in Risk Management VIII
 What is ERM And Why Does it Matter to Higher Education?
What is ERM And Why Does it Matter to Higher Education?
 Definition of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) A structured, consistent, and continuous risk management process applied across the entire organization that brings value by: 1. Proactively identifying, assessing, and prioritizing material risks 2. Developing and deploying effective mitigation strategies 3. Aligning with strategic objectives and administrative processes 4. Embedding key components into the organization’s culture: 1. Risk ownership, governance, and oversight 2. Reporting and communications 3. Leveraging technology and tools 5. S&P incorporating ERM reference into industry credit rating reports
Definition of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) A structured, consistent, and continuous risk management process applied across the entire organization that brings value by: 1. Proactively identifying, assessing, and prioritizing material risks 2. Developing and deploying effective mitigation strategies 3. Aligning with strategic objectives and administrative processes 4. Embedding key components into the organization’s culture: 1. Risk ownership, governance, and oversight 2. Reporting and communications 3. Leveraging technology and tools 5. S&P incorporating ERM reference into industry credit rating reports
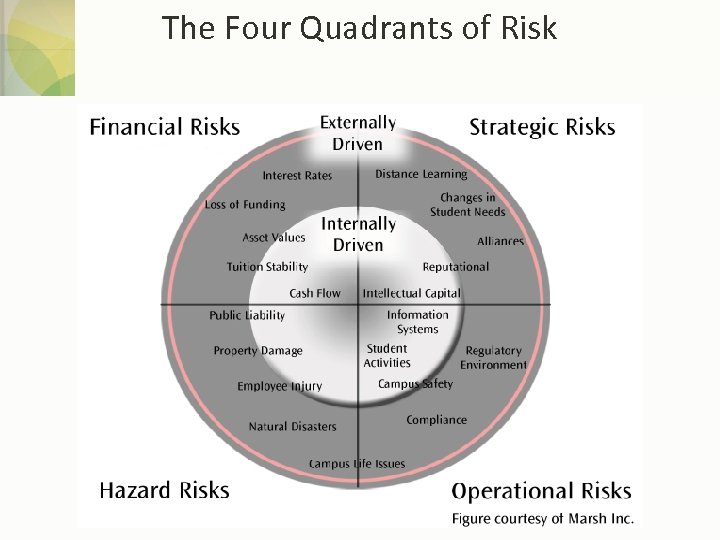 The Four Quadrants of Risk
The Four Quadrants of Risk
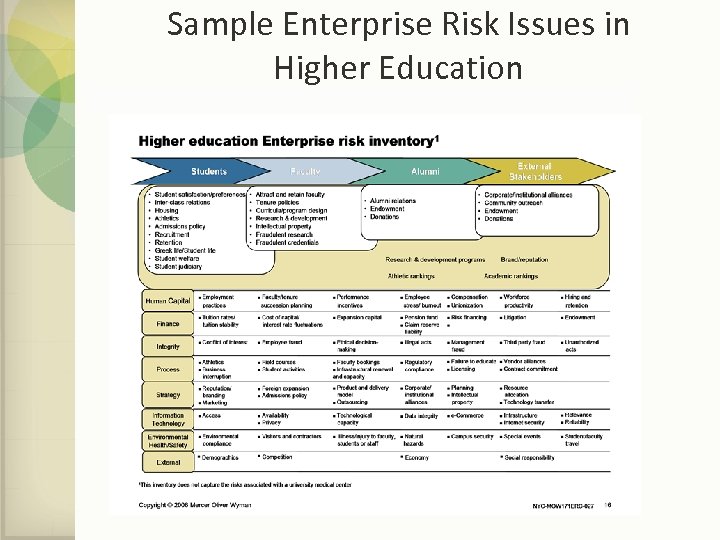 Sample Enterprise Risk Issues in Higher Education
Sample Enterprise Risk Issues in Higher Education
 ERM Compliance Factors: Commentary • Compliance and ethics oversight has traditionally been the responsibility of an institution’s legal department • Risk management procedures of institutions are under increasing regulatory and private scrutiny • There has been a shift from a defensive function focused on policies, procedures and expenditures, to a strategic function focused on optimizing resource allocation and effectiveness • Recent mandates and guidelines are fueling the momentum
ERM Compliance Factors: Commentary • Compliance and ethics oversight has traditionally been the responsibility of an institution’s legal department • Risk management procedures of institutions are under increasing regulatory and private scrutiny • There has been a shift from a defensive function focused on policies, procedures and expenditures, to a strategic function focused on optimizing resource allocation and effectiveness • Recent mandates and guidelines are fueling the momentum
 ERM Compliance Factors: Current and Emerging Standards and Guidelines GUIDELINES & BEST PRACTICES: • Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission’s (COSO) ERM Framework • Standard & Poor's (S&P) ERM Ratings Criteria for Non. Financial Organizations • ISO 31000 EMERGING REGULATIONS & GUIDELINES: • Accreditation requirements?
ERM Compliance Factors: Current and Emerging Standards and Guidelines GUIDELINES & BEST PRACTICES: • Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission’s (COSO) ERM Framework • Standard & Poor's (S&P) ERM Ratings Criteria for Non. Financial Organizations • ISO 31000 EMERGING REGULATIONS & GUIDELINES: • Accreditation requirements?
 ERM Guidelines and Best Practices: Overview of S&P’s ERM Ratings Criteria Culture § Organizational structure § Risk management staff roles and accountability § Risk communication (internal and external) Emerging Risk Preparation Strategic Risk Management § Risk limit application and enforcement § Environmental scanning, trending, stress testing, contingency planning and other pre-loss practices § Utilization of risk management and return on risk in strategic decision making § Risk control processes— policies, infrastructure, methodology (PIM) § Expectation planning for negative events pre and post-loss performance Risk Controls § Risk identification, measurement and monitoring § Sector and firmspecific risk control criteria § Risk consideration within capital budgeting and allocation, performance measurement and other administrative practices
ERM Guidelines and Best Practices: Overview of S&P’s ERM Ratings Criteria Culture § Organizational structure § Risk management staff roles and accountability § Risk communication (internal and external) Emerging Risk Preparation Strategic Risk Management § Risk limit application and enforcement § Environmental scanning, trending, stress testing, contingency planning and other pre-loss practices § Utilization of risk management and return on risk in strategic decision making § Risk control processes— policies, infrastructure, methodology (PIM) § Expectation planning for negative events pre and post-loss performance Risk Controls § Risk identification, measurement and monitoring § Sector and firmspecific risk control criteria § Risk consideration within capital budgeting and allocation, performance measurement and other administrative practices
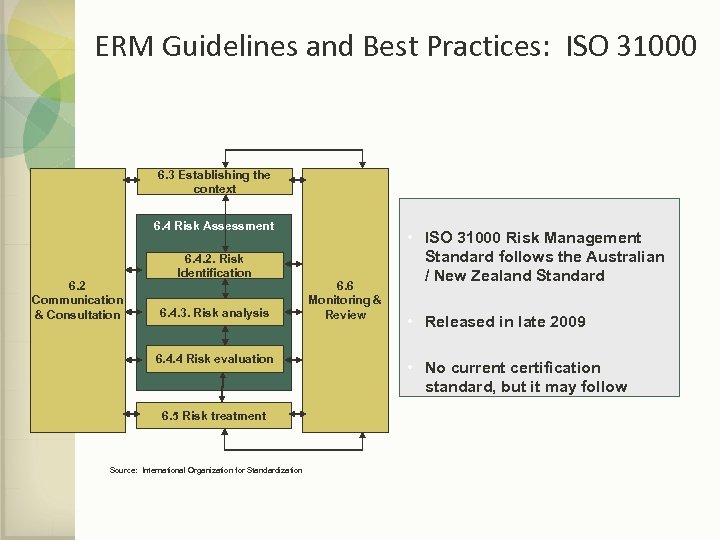 ERM Guidelines and Best Practices: ISO 31000 6. 3 Establishing the context 6. 4 Risk Assessment 6. 2 Communication & Consultation 6. 4. 2. Risk Identification 6. 4. 3. Risk analysis 6. 4. 4 Risk evaluation 6. 5 Risk treatment Source: International Organization for Standardization 6. 6 Monitoring & Review • ISO 31000 Risk Management Standard follows the Australian / New Zealand Standard • Released in late 2009 • No current certification standard, but it may follow
ERM Guidelines and Best Practices: ISO 31000 6. 3 Establishing the context 6. 4 Risk Assessment 6. 2 Communication & Consultation 6. 4. 2. Risk Identification 6. 4. 3. Risk analysis 6. 4. 4 Risk evaluation 6. 5 Risk treatment Source: International Organization for Standardization 6. 6 Monitoring & Review • ISO 31000 Risk Management Standard follows the Australian / New Zealand Standard • Released in late 2009 • No current certification standard, but it may follow
 ERM Compliance Factors: Common Elements of ERM Frameworks • They outline a process for ERM implementation that includes: – Risk identification and assessment – Risk prioritization – Risk solution design and implementation – Routine monitoring and reporting – Communication • They recognize that good risk management must be embedded into the organization’s day to day activities • They consider both the ‘upside’ and ‘downside’ of risk • They are not one size fits all
ERM Compliance Factors: Common Elements of ERM Frameworks • They outline a process for ERM implementation that includes: – Risk identification and assessment – Risk prioritization – Risk solution design and implementation – Routine monitoring and reporting – Communication • They recognize that good risk management must be embedded into the organization’s day to day activities • They consider both the ‘upside’ and ‘downside’ of risk • They are not one size fits all
 How to Initiate an ERM Program
How to Initiate an ERM Program
 Building Senior-Level Support • Elements of an ERM Value Proposition: – Optimal capital deployment – Continued or improved rating agency confidence – Effective critical event response – Better decision making relative to risks assumed – Enhanced stewardship and governance
Building Senior-Level Support • Elements of an ERM Value Proposition: – Optimal capital deployment – Continued or improved rating agency confidence – Effective critical event response – Better decision making relative to risks assumed – Enhanced stewardship and governance
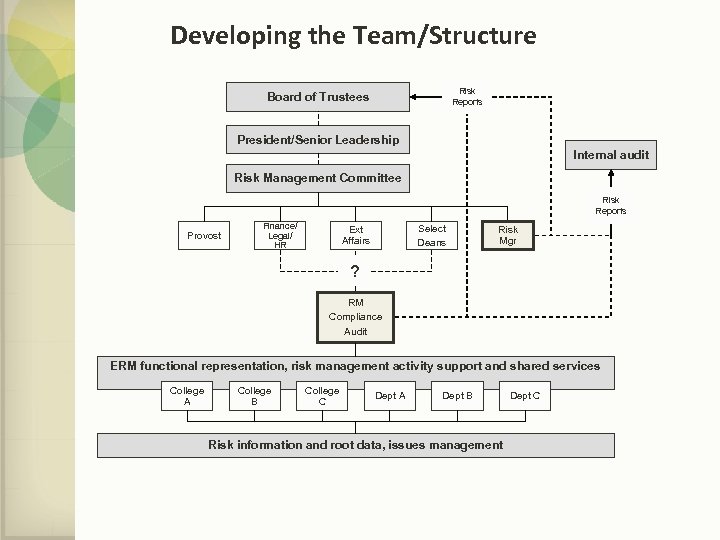 Developing the Team/Structure Risk Reports Board of Trustees President/Senior Leadership Internal audit Risk Management Committee Risk Reports Provost Finance/ Legal/ HR Select Deans Ext Affairs Risk Mgr ? RM Compliance Audit ERM functional representation, risk management activity support and shared services College A College B College C Dept A Dept B Risk information and root data, issues management Dept C
Developing the Team/Structure Risk Reports Board of Trustees President/Senior Leadership Internal audit Risk Management Committee Risk Reports Provost Finance/ Legal/ HR Select Deans Ext Affairs Risk Mgr ? RM Compliance Audit ERM functional representation, risk management activity support and shared services College A College B College C Dept A Dept B Risk information and root data, issues management Dept C
 Understanding Where You Want to Go… Critical success factors • Establish the right vision and realistic plan • Obtain senior leadership buy-in and direction • Align with mission and strategic objectives • Attack silos at the onset • Set objectives / performance / early warning indicators • Stay focused on results • Communicate vision and key outcomes • Develop a sustainable process vs. a one-time a project
Understanding Where You Want to Go… Critical success factors • Establish the right vision and realistic plan • Obtain senior leadership buy-in and direction • Align with mission and strategic objectives • Attack silos at the onset • Set objectives / performance / early warning indicators • Stay focused on results • Communicate vision and key outcomes • Develop a sustainable process vs. a one-time a project
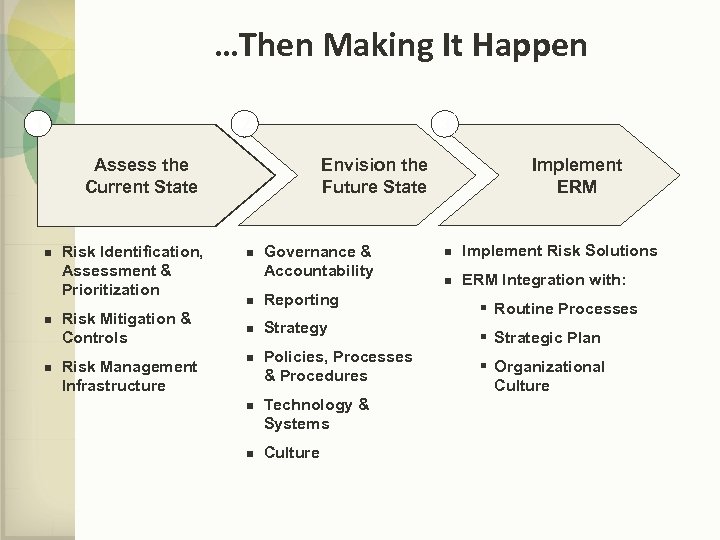 …Then Making It Happen 1 2 3 Envision the Future State Assess the Current State n n n Risk Identification, Assessment & Prioritization Risk Mitigation & Controls Risk Management Infrastructure n Governance & Accountability n Reporting n Strategy n n n Policies, Processes & Procedures Technology & Systems Culture Implement ERM n Implement Risk Solutions n ERM Integration with: § Routine Processes § Strategic Plan § Organizational Culture
…Then Making It Happen 1 2 3 Envision the Future State Assess the Current State n n n Risk Identification, Assessment & Prioritization Risk Mitigation & Controls Risk Management Infrastructure n Governance & Accountability n Reporting n Strategy n n n Policies, Processes & Procedures Technology & Systems Culture Implement ERM n Implement Risk Solutions n ERM Integration with: § Routine Processes § Strategic Plan § Organizational Culture
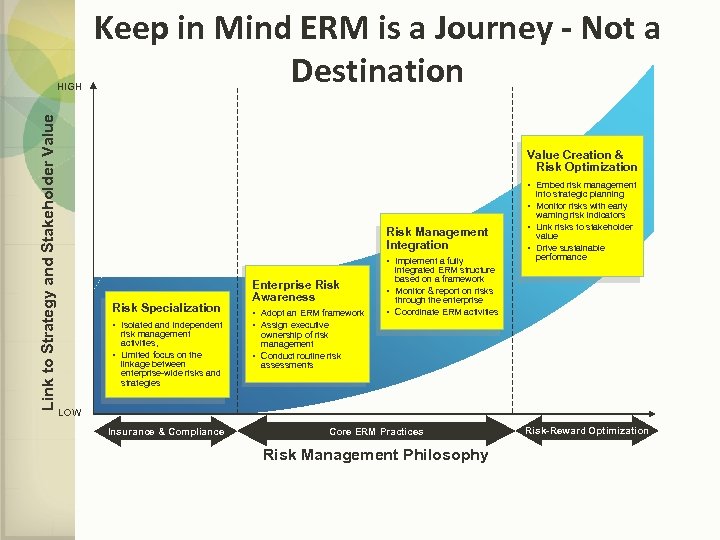 Link to Strategy and Stakeholder Value HIGH Keep in Mind ERM is a Journey - Not a Destination Value Creation & Risk Optimization • Embed risk management into strategic planning • Monitor risks with early warning risk indicators Risk Management Integration • Implement a fully Risk Specialization • Isolated and independent risk management activities, • Limited focus on the linkage between enterprise-wide risks and strategies Enterprise Risk Awareness • Adopt an ERM framework • Assign executive • Link risks to stakeholder value • Drive sustainable performance integrated ERM structure based on a framework • Monitor & report on risks through the enterprise • Coordinate ERM activities ownership of risk management • Conduct routine risk assessments LOW Insurance & Compliance Core ERM Practices Risk Management Philosophy Risk-Reward Optimization
Link to Strategy and Stakeholder Value HIGH Keep in Mind ERM is a Journey - Not a Destination Value Creation & Risk Optimization • Embed risk management into strategic planning • Monitor risks with early warning risk indicators Risk Management Integration • Implement a fully Risk Specialization • Isolated and independent risk management activities, • Limited focus on the linkage between enterprise-wide risks and strategies Enterprise Risk Awareness • Adopt an ERM framework • Assign executive • Link risks to stakeholder value • Drive sustainable performance integrated ERM structure based on a framework • Monitor & report on risks through the enterprise • Coordinate ERM activities ownership of risk management • Conduct routine risk assessments LOW Insurance & Compliance Core ERM Practices Risk Management Philosophy Risk-Reward Optimization
 A Few Practical Tools and Deliverables
A Few Practical Tools and Deliverables
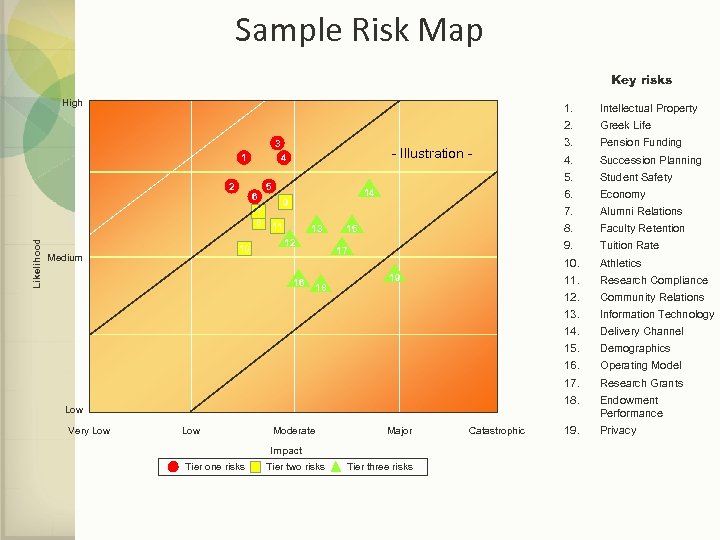 Sample Risk Map Key risks High 3 1 Likelihood 2 4 6 7 8 10 Medium - Illustration - 5 14 9 11 13 12 16 15 17 18 19 Low Very Low Moderate Major Impact Tier one risks Tier two risks Tier three risks Catastrophic 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Intellectual Property 19. Privacy Greek Life Pension Funding Succession Planning Student Safety Economy Alumni Relations Faculty Retention Tuition Rate Athletics Research Compliance Community Relations Information Technology Delivery Channel Demographics Operating Model Research Grants Endowment Performance
Sample Risk Map Key risks High 3 1 Likelihood 2 4 6 7 8 10 Medium - Illustration - 5 14 9 11 13 12 16 15 17 18 19 Low Very Low Moderate Major Impact Tier one risks Tier two risks Tier three risks Catastrophic 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Intellectual Property 19. Privacy Greek Life Pension Funding Succession Planning Student Safety Economy Alumni Relations Faculty Retention Tuition Rate Athletics Research Compliance Community Relations Information Technology Delivery Channel Demographics Operating Model Research Grants Endowment Performance
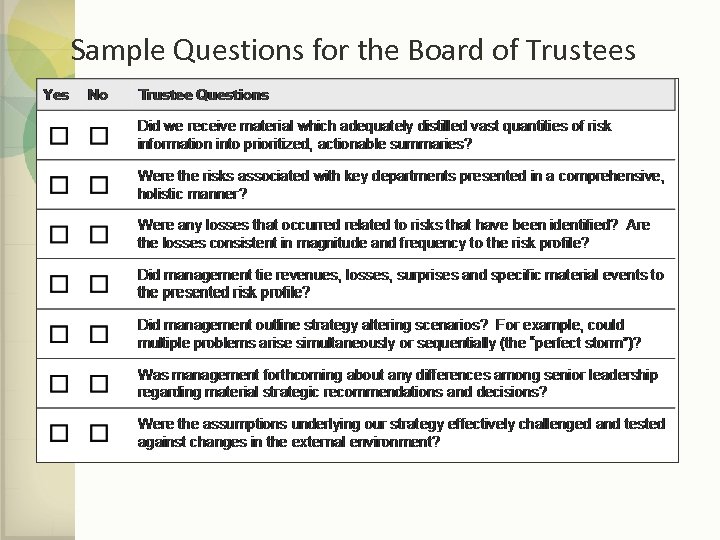 Sample Questions for the Board of Trustees
Sample Questions for the Board of Trustees
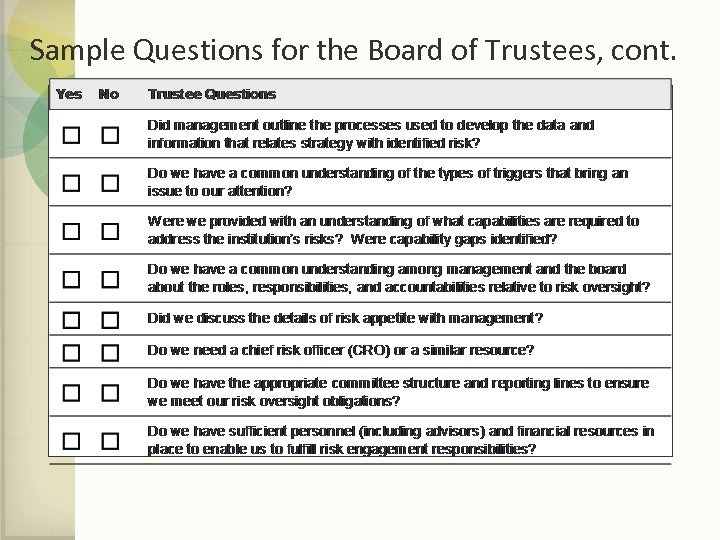 Sample Questions for the Board of Trustees, cont.
Sample Questions for the Board of Trustees, cont.
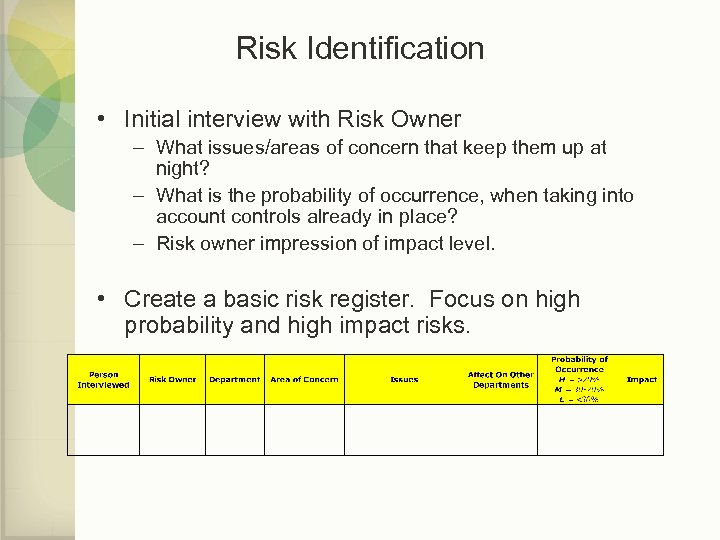 Risk Identification • Initial interview with Risk Owner – What issues/areas of concern that keep them up at night? – What is the probability of occurrence, when taking into account controls already in place? – Risk owner impression of impact level. • Create a basic risk register. Focus on high probability and high impact risks.
Risk Identification • Initial interview with Risk Owner – What issues/areas of concern that keep them up at night? – What is the probability of occurrence, when taking into account controls already in place? – Risk owner impression of impact level. • Create a basic risk register. Focus on high probability and high impact risks.
 Arthur Anderson LLP v. United States • US Supreme Court recognized the legitimacy of managing and systematically disposing of records in accordance pursuant to a records retention policy • The Supreme Court held: “Document retention policies, ’ which are created in part to keep certain information from getting into the hands of others, including the Government, are common in business. It is, of course, not wrongful for a manager to instruct his employees to comply with a valid document retention policy under ordinary circumstances. ”* *544 U. S. 696, 704 (2005)
Arthur Anderson LLP v. United States • US Supreme Court recognized the legitimacy of managing and systematically disposing of records in accordance pursuant to a records retention policy • The Supreme Court held: “Document retention policies, ’ which are created in part to keep certain information from getting into the hands of others, including the Government, are common in business. It is, of course, not wrongful for a manager to instruct his employees to comply with a valid document retention policy under ordinary circumstances. ”* *544 U. S. 696, 704 (2005)
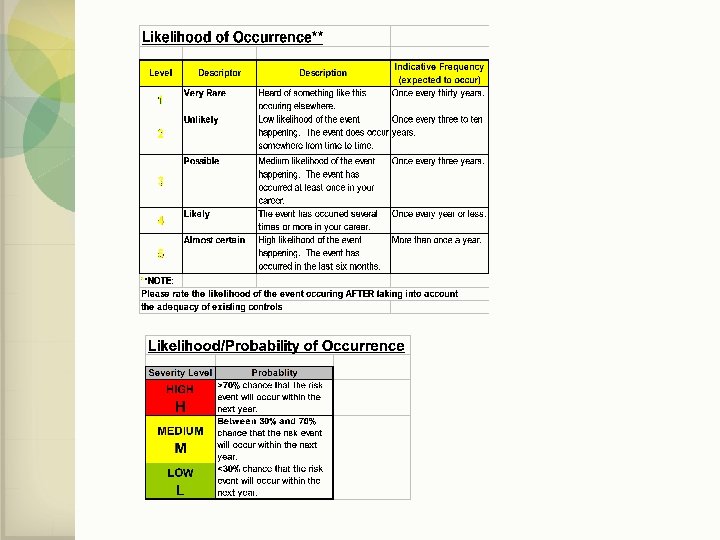
 Communication • Each risk owner creates a project plan, including timelines for mitigating that risk. • The risk owner provides semi-annual progress updates on risk mitigation projects. • This information is provided to the Audit Committee of the Board of Trustees.
Communication • Each risk owner creates a project plan, including timelines for mitigating that risk. • The risk owner provides semi-annual progress updates on risk mitigation projects. • This information is provided to the Audit Committee of the Board of Trustees.
 “Meeting challenges gives rise to opportunities. ”
“Meeting challenges gives rise to opportunities. ”
 QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS


