312ec43146b3733d6ff583373a48aaa3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Development through ICT: Egyptian Information Society Initiative Amr HASHEM Ministry of Communications & Information Technology Arab Republic of Egypt
Development through ICT: Egyptian Information Society Initiative Amr HASHEM Ministry of Communications & Information Technology Arab Republic of Egypt
 Agenda £ Introduction £ £ £ ICT Industry £ £ £ Egypt’s Outlook Information Society Initiative Creating Favorable Environment WTO Commitments Way Forward £ £ National Action Plans Regional & International Coordination
Agenda £ Introduction £ £ £ ICT Industry £ £ £ Egypt’s Outlook Information Society Initiative Creating Favorable Environment WTO Commitments Way Forward £ £ National Action Plans Regional & International Coordination
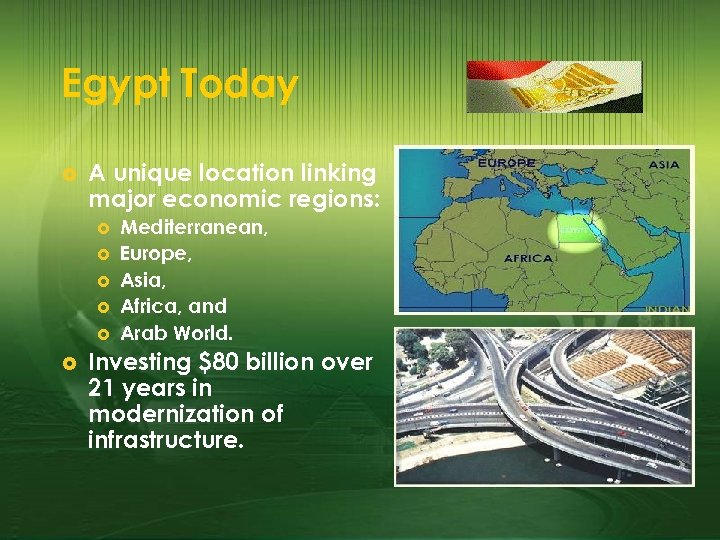 Egypt Today £ A unique location linking major economic regions: £ £ £ Mediterranean, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Arab World. Investing $80 billion over 21 years in modernization of infrastructure.
Egypt Today £ A unique location linking major economic regions: £ £ £ Mediterranean, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Arab World. Investing $80 billion over 21 years in modernization of infrastructure.
 Egypt Today £ £ 65% under age of 25 Preparing young generations by investing in: £ £ education, skills development, and professional training. Ranking 17 th worldwide in number of yearly graduates
Egypt Today £ £ 65% under age of 25 Preparing young generations by investing in: £ £ education, skills development, and professional training. Ranking 17 th worldwide in number of yearly graduates
 Egypt Today £ Egypt is reincarnating into a modern, liberal & private sector led market driven economy. £ A remarkable recovery through an extensive economic and social reform programs
Egypt Today £ Egypt is reincarnating into a modern, liberal & private sector led market driven economy. £ A remarkable recovery through an extensive economic and social reform programs
 Egyptian Information Society Initiative Coordinating the efforts of the Government, the business sector and the Civil Society in deployment and utilization of ICT for economic and social development through various forms of Public-Private. Partnerships
Egyptian Information Society Initiative Coordinating the efforts of the Government, the business sector and the Civil Society in deployment and utilization of ICT for economic and social development through various forms of Public-Private. Partnerships
 ICT & Economic Growth £ Higher productivity: £ making it possible to adopt different structures and locations £ New technologies allow for new methods of production £ Social Services: £ social services promoting economic growth, such as health and education. £ Investment: £ Investment in ICT is also significantly correlated with growth (Easterly and Rebelo, 1993) £ Rural Development: £ There is evidence that teledensity is positively correlated with the level of income.
ICT & Economic Growth £ Higher productivity: £ making it possible to adopt different structures and locations £ New technologies allow for new methods of production £ Social Services: £ social services promoting economic growth, such as health and education. £ Investment: £ Investment in ICT is also significantly correlated with growth (Easterly and Rebelo, 1993) £ Rural Development: £ There is evidence that teledensity is positively correlated with the level of income.
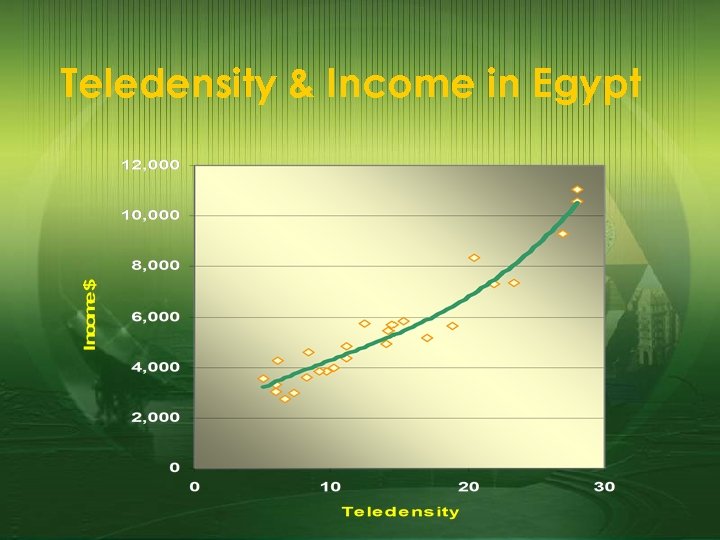 Teledensity & Income in Egypt
Teledensity & Income in Egypt
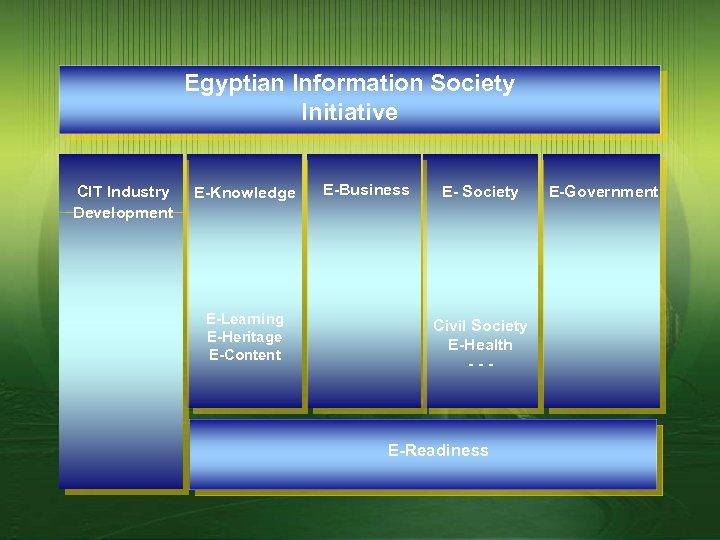 Egyptian Information Society Initiative CIT Industry Development E-Knowledge E-Learning E-Heritage E-Content E-Business E- Society Civil Society E-Health --- E-Readiness E-Government
Egyptian Information Society Initiative CIT Industry Development E-Knowledge E-Learning E-Heritage E-Content E-Business E- Society Civil Society E-Health --- E-Readiness E-Government
 Legal ICT Framework £ 1997: 1998: £ 1999: £ 2002: £ 2003: £ 2004: £ Investment Incentives Law Separation of Operation and Regulation Establishment of an Independent Regulatory Authority Establishment of Ministry of Communications & Information Technology Development of 1 st National CIT-Plan Intellectual Property Law WTO- Basic Telecommunications Agreement New Telecom Law WTO-Information Technology Agreement E- Signature Law
Legal ICT Framework £ 1997: 1998: £ 1999: £ 2002: £ 2003: £ 2004: £ Investment Incentives Law Separation of Operation and Regulation Establishment of an Independent Regulatory Authority Establishment of Ministry of Communications & Information Technology Development of 1 st National CIT-Plan Intellectual Property Law WTO- Basic Telecommunications Agreement New Telecom Law WTO-Information Technology Agreement E- Signature Law
 Basic Telecom Agreement (BTA) £ Arab Countries with BTA Commitments Morocco (Apr. 94, Apr. 97, Oct. 00) Jordan (Oct. 00) Egypt (Jun. 02) £ £ £ Tunisia (Apr. 97) Oman (Dec. 00) Bahrain MCIT and TRA studying the requirements of BTA (Winter/Spring 2001) MCIT, TRA, Mo. FA and Mo. E Preparing the Final Draft of BTA proposal (June 2001) Clarifying issues related to the BTA proposal (Fall 2001/Winter 2002) Meetings for discussing Egypt’s BTA proposal (February 2002) BTA proposal circulated among WTO members for approval (April 2002) BTA commitments integrated into Egypt’s schedule (June 2002)
Basic Telecom Agreement (BTA) £ Arab Countries with BTA Commitments Morocco (Apr. 94, Apr. 97, Oct. 00) Jordan (Oct. 00) Egypt (Jun. 02) £ £ £ Tunisia (Apr. 97) Oman (Dec. 00) Bahrain MCIT and TRA studying the requirements of BTA (Winter/Spring 2001) MCIT, TRA, Mo. FA and Mo. E Preparing the Final Draft of BTA proposal (June 2001) Clarifying issues related to the BTA proposal (Fall 2001/Winter 2002) Meetings for discussing Egypt’s BTA proposal (February 2002) BTA proposal circulated among WTO members for approval (April 2002) BTA commitments integrated into Egypt’s schedule (June 2002)
 BTA Commitments (Cont. ) £ Reference Paper on Regulatory Principles £ Table of Specific Commitments £ Grace Period for Market Reform £ Technology-Neutral approach to services £ Development of Local Industry £ No Limitations on Foreign Capital £ Opening up the market for new services
BTA Commitments (Cont. ) £ Reference Paper on Regulatory Principles £ Table of Specific Commitments £ Grace Period for Market Reform £ Technology-Neutral approach to services £ Development of Local Industry £ No Limitations on Foreign Capital £ Opening up the market for new services
 Competition in ICT 1996: £ 1997: £ 1998: £ 2000: £ 2002: £ 2003: £ 2004: £ Internet services provision public payphone services mobile telephony services - GSM provision of public data services for business sector VSAT services Internet backbone infrastructure rollout and wholesale services high-speed access – x. DSL pre-paid calling cards
Competition in ICT 1996: £ 1997: £ 1998: £ 2000: £ 2002: £ 2003: £ 2004: £ Internet services provision public payphone services mobile telephony services - GSM provision of public data services for business sector VSAT services Internet backbone infrastructure rollout and wholesale services high-speed access – x. DSL pre-paid calling cards
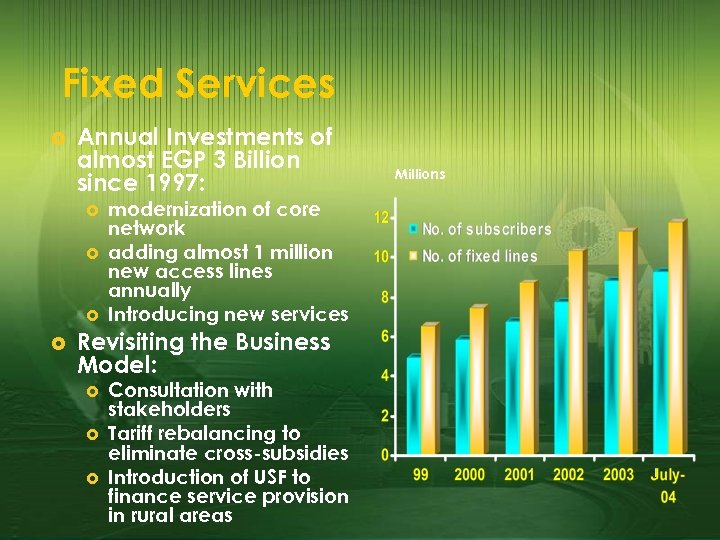 Fixed Services £ Annual Investments of almost EGP 3 Billion since 1997: £ £ modernization of core network adding almost 1 million new access lines annually Introducing new services Revisiting the Business Model: £ £ £ Consultation with stakeholders Tariff rebalancing to eliminate cross-subsidies Introduction of USF to finance service provision in rural areas Millions
Fixed Services £ Annual Investments of almost EGP 3 Billion since 1997: £ £ modernization of core network adding almost 1 million new access lines annually Introducing new services Revisiting the Business Model: £ £ £ Consultation with stakeholders Tariff rebalancing to eliminate cross-subsidies Introduction of USF to finance service provision in rural areas Millions
 Mobile Telephony £ 2 Egyptian. International consortia: £ £ £ Vodafone: Vodafone PLC + Egyptian Investors Mobi. Nil: Orange + Egyptian Investors (Orascom Telecom + others) Impact of deregulation: £ £ Employment: 4000 jobs Investments: EGP 10 Bil. Wealth Creation: EGP 16 Bil. Governmental proceedings of almost: EGP 7. 4 Bil. Millions
Mobile Telephony £ 2 Egyptian. International consortia: £ £ £ Vodafone: Vodafone PLC + Egyptian Investors Mobi. Nil: Orange + Egyptian Investors (Orascom Telecom + others) Impact of deregulation: £ £ Employment: 4000 jobs Investments: EGP 10 Bil. Wealth Creation: EGP 16 Bil. Governmental proceedings of almost: EGP 7. 4 Bil. Millions
 Internet Access £ Subscription-Free Internet Services: £ Launched in Jan ’ 02 £ Interconnection between NSP and TE £ Internet at cost of local calls(0. 2 $ per hour) Improved Qo. S - Reduced Costs - Utilization Growth £ £ Broadband Initiative £ £ Launched in May ’ 04 Unbundling of the local loop Increase ADSL Penetration – Promote Wi. Fi Hotspots 50, 000 ADSL Subscriber during First Year
Internet Access £ Subscription-Free Internet Services: £ Launched in Jan ’ 02 £ Interconnection between NSP and TE £ Internet at cost of local calls(0. 2 $ per hour) Improved Qo. S - Reduced Costs - Utilization Growth £ £ Broadband Initiative £ £ Launched in May ’ 04 Unbundling of the local loop Increase ADSL Penetration – Promote Wi. Fi Hotspots 50, 000 ADSL Subscriber during First Year
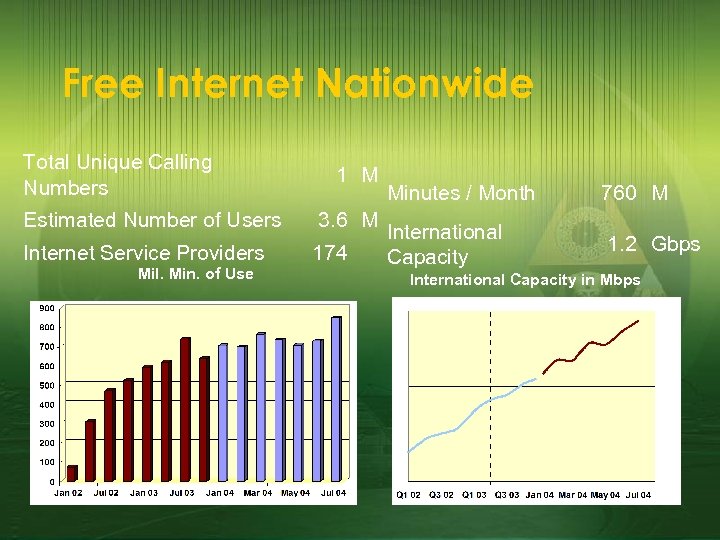 Free Internet Nationwide Total Unique Calling Numbers 1 M Estimated Number of Users 3. 6 M Internet Service Providers 174 Mil. Min. of Use Minutes / Month 760 M International Capacity 1. 2 Gbps International Capacity in Mbps
Free Internet Nationwide Total Unique Calling Numbers 1 M Estimated Number of Users 3. 6 M Internet Service Providers 174 Mil. Min. of Use Minutes / Month 760 M International Capacity 1. 2 Gbps International Capacity in Mbps
 Info Technology Agreement (ITA) £ £ Extension of the implementation for developing countries till 2005 MCIT, Mo. F, Mo. I&FT and MOFA studying the ITA in respect to: £ £ Impact on the sovereign income of taxes Impact on industry development Reaching an initial proposal for phasing-in the items under the ITA The goal is to promote the ICT sector by: £ £ Reducing producers’ costs of deploying ICT Encouraging consumer demand Encouraging innovation and development Creating job opportunities
Info Technology Agreement (ITA) £ £ Extension of the implementation for developing countries till 2005 MCIT, Mo. F, Mo. I&FT and MOFA studying the ITA in respect to: £ £ Impact on the sovereign income of taxes Impact on industry development Reaching an initial proposal for phasing-in the items under the ITA The goal is to promote the ICT sector by: £ £ Reducing producers’ costs of deploying ICT Encouraging consumer demand Encouraging innovation and development Creating job opportunities
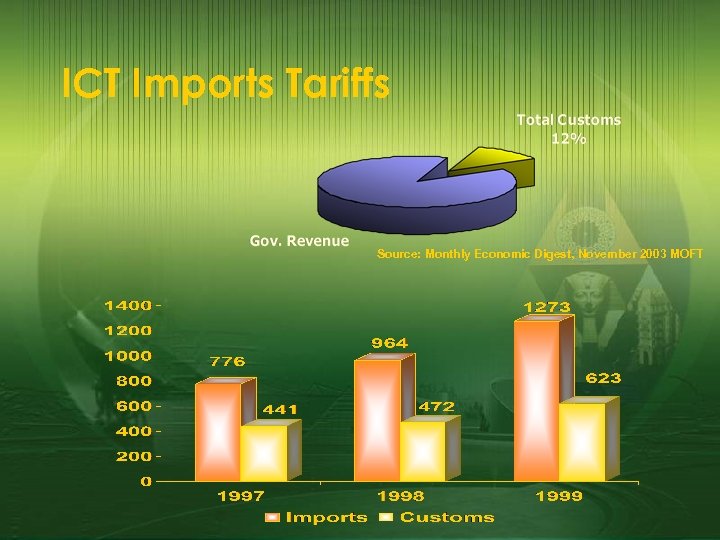 ICT Imports Tariffs Source: Monthly Economic Digest, November 2003 MOFT
ICT Imports Tariffs Source: Monthly Economic Digest, November 2003 MOFT
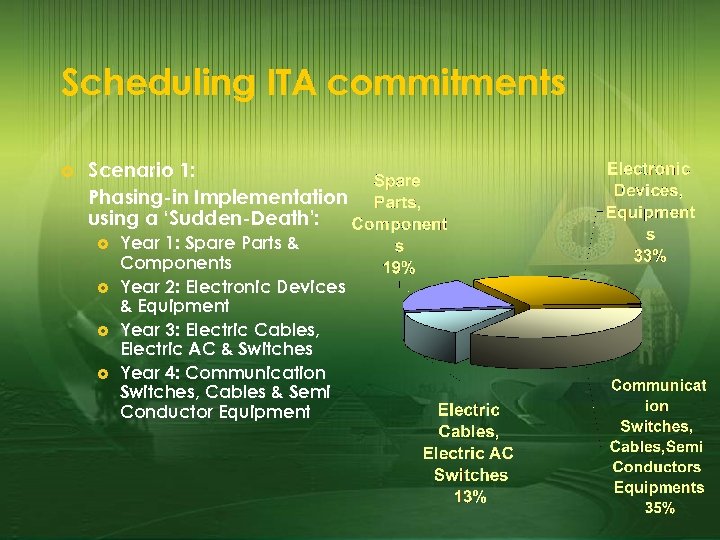 Scheduling ITA commitments £ Scenario 1: Phasing-in Implementation using a ‘Sudden-Death’: £ £ Year 1: Spare Parts & Components Year 2: Electronic Devices & Equipment Year 3: Electric Cables, Electric AC & Switches Year 4: Communication Switches, Cables & Semi Conductor Equipment
Scheduling ITA commitments £ Scenario 1: Phasing-in Implementation using a ‘Sudden-Death’: £ £ Year 1: Spare Parts & Components Year 2: Electronic Devices & Equipment Year 3: Electric Cables, Electric AC & Switches Year 4: Communication Switches, Cables & Semi Conductor Equipment
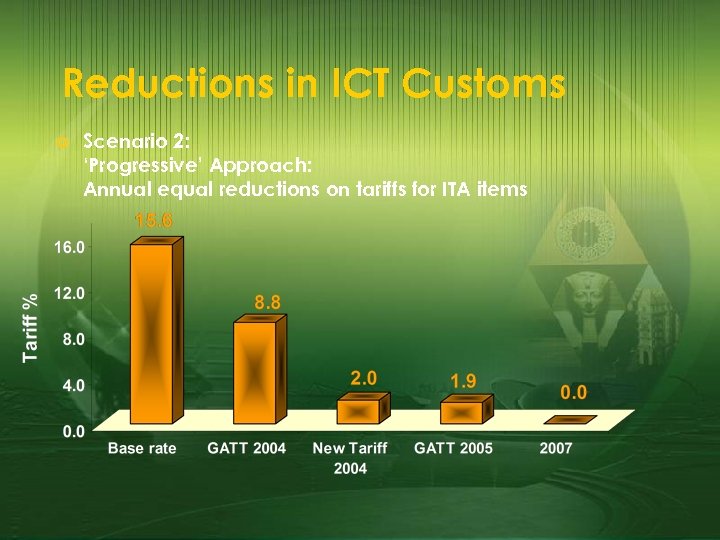 Reductions in ICT Customs £ Scenario 2: ‘Progressive’ Approach: Annual equal reductions on tariffs for ITA items
Reductions in ICT Customs £ Scenario 2: ‘Progressive’ Approach: Annual equal reductions on tariffs for ITA items
 Promoting E-Access £ £ £ Buying a PC on monthly installments and no advance payments Using the phone line as a collateral Highly efficient PCs manufactured or assembled locally 75 thousand PCs were sold since December 2002 Target to reach 200, 000 households within a year
Promoting E-Access £ £ £ Buying a PC on monthly installments and no advance payments Using the phone line as a collateral Highly efficient PCs manufactured or assembled locally 75 thousand PCs were sold since December 2002 Target to reach 200, 000 households within a year
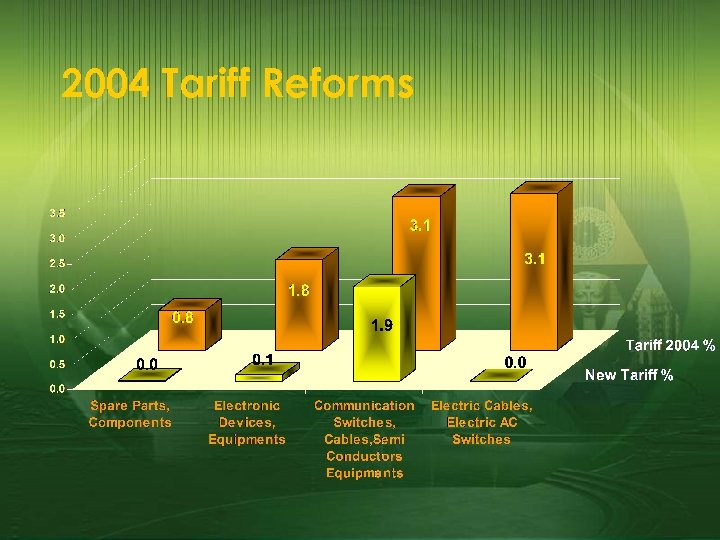 2004 Tariff Reforms
2004 Tariff Reforms
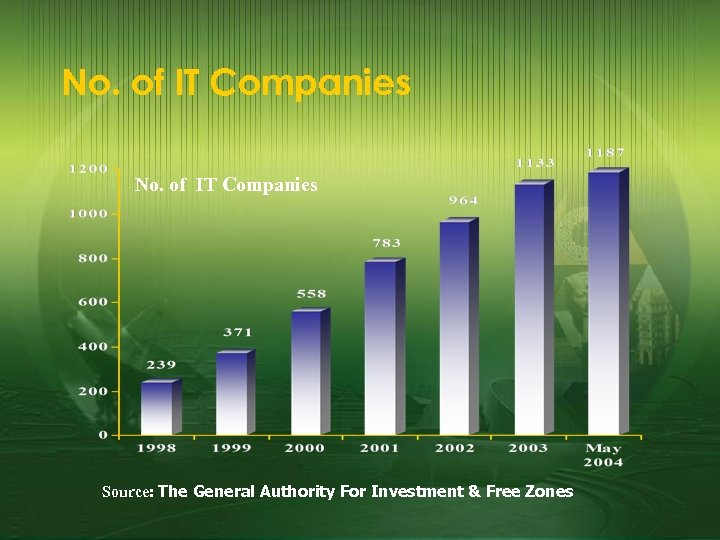 No. of IT Companies Source: The General Authority For Investment & Free Zones
No. of IT Companies Source: The General Authority For Investment & Free Zones
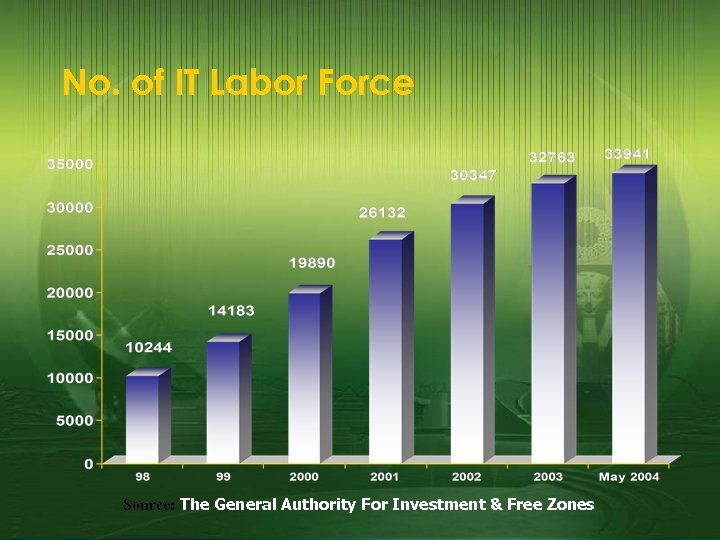 No. of IT Labor Force Source: The General Authority For Investment & Free Zones
No. of IT Labor Force Source: The General Authority For Investment & Free Zones
 Alliance with MNCs Total Investments (in USD Million) Exports 2002 -2006 (in USD Million) Increase in job opportunities Alcatel (French) 135 153 262 Ericsson (Swedish) 112 106 448 Siemens (German) 77 116 515 Nortel (Canadian) 6 15 28 Oracle & their local partners (US) 50 123 3000 IBM (US) 40 99 500 Equant (French) 20 20 400 440 632 5153 Company Total
Alliance with MNCs Total Investments (in USD Million) Exports 2002 -2006 (in USD Million) Increase in job opportunities Alcatel (French) 135 153 262 Ericsson (Swedish) 112 106 448 Siemens (German) 77 116 515 Nortel (Canadian) 6 15 28 Oracle & their local partners (US) 50 123 3000 IBM (US) 40 99 500 Equant (French) 20 20 400 440 632 5153 Company Total
 Expectations of Liberalization £ Higher customer focus Bringing-in new services to cater to the needs of various segments £ More efficient service delivery as a result of the technology neutral-approach to regulation £ £ Stronger Industry Promotion High-yield job creation as a result of market growth and development £ Export-oriented industries through transfer of know-how and innovation £
Expectations of Liberalization £ Higher customer focus Bringing-in new services to cater to the needs of various segments £ More efficient service delivery as a result of the technology neutral-approach to regulation £ £ Stronger Industry Promotion High-yield job creation as a result of market growth and development £ Export-oriented industries through transfer of know-how and innovation £
 Way Forward £ £ £ Dialogue within the international community to promote technology transfer and facilitate participation of developing countries in the global information society Regional coordination to promote economic integration and generate opportunities for regional players Ongoing national consultation with market players and stakeholders to resolve various issues of concern regarding further market development
Way Forward £ £ £ Dialogue within the international community to promote technology transfer and facilitate participation of developing countries in the global information society Regional coordination to promote economic integration and generate opportunities for regional players Ongoing national consultation with market players and stakeholders to resolve various issues of concern regarding further market development
 Thank you AHashem@mcit. gov. eg
Thank you AHashem@mcit. gov. eg


