661703a4d84009b0c596ae0f371cdb3b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Development Plan for Green Port President CEO YB, Choi Hanjin New Port Co. 한진해운 신항만㈜ 대표이사 최 영 배 Nov. 12 th, 2009

Contents 1. Environmental issues and Global warming 2. International concern and Trends 3. Domestic Situation and Response 4. Environmental issues in Logistics 5. Green port status and Action plan for domestic ports 6. HJNC’s action plan for Green port 7. Conclusion
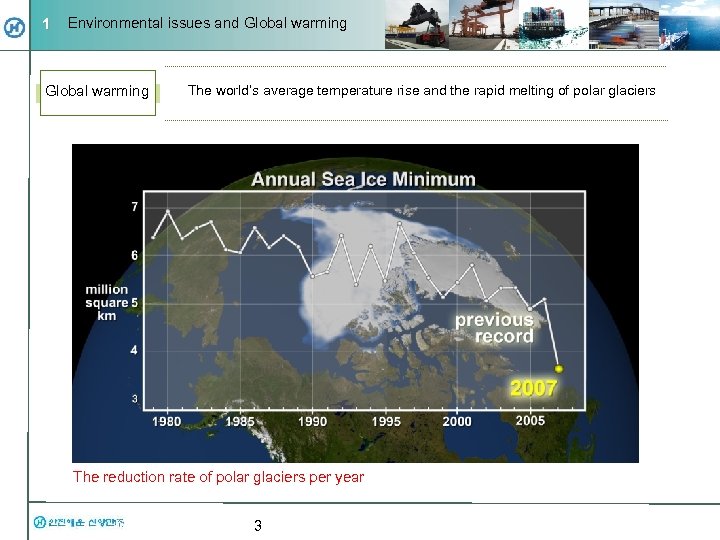
1 Environmental issues and Global warming The world’s average temperature rise and the rapid melting of polar glaciers The reduction rate of polar glaciers per year 3
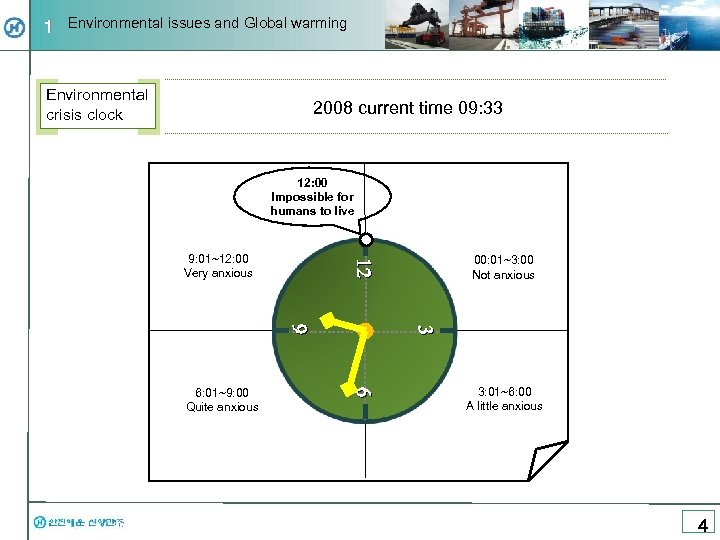
1 Environmental issues and Global warming Environmental crisis clock 2008 current time 09: 33 12: 00 Impossible for humans to live 3 3 9 9 6 6 6: 01~9: 00 Quite anxious 00: 01~3: 00 Not anxious 12 12 9: 01~12: 00 Very anxious 3: 01~6: 00 A little anxious 4
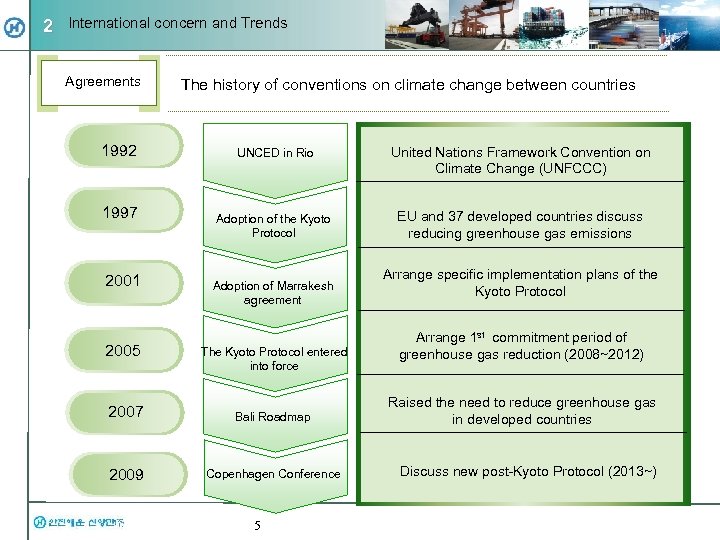
2 International concern and Trends Agreements 1992 1997 2001 2005 The history of conventions on climate change between countries UNCED in Rio United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Adoption of the Kyoto Protocol EU and 37 developed countries discuss reducing greenhouse gas emissions Adoption of Marrakesh agreement The Kyoto Protocol entered into force 2007 Bali Roadmap 2009 Copenhagen Conference 5 Arrange specific implementation plans of the Kyoto Protocol Arrange 1 st commitment period of greenhouse gas reduction (2008~2012) Raised the need to reduce greenhouse gas in developed countries Discuss new post-Kyoto Protocol (2013~)
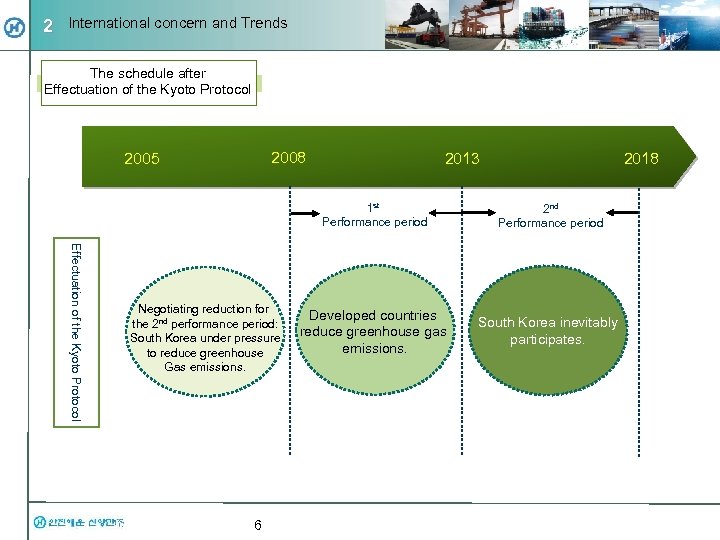
2 International concern and Trends The schedule after Effectuation of the Kyoto Protocol 2008 2005 2013 2018 Effectuation of the Kyoto Protocol 1 st Performance period Negotiating reduction for the 2 nd performance period: South Korea under pressure to reduce greenhouse Gas emissions. 6 2 nd Performance period Developed countries reduce greenhouse gas emissions. South Korea inevitably participates.

2 International concern and Trends Obama, President of U. S. 1 • 80% reduction in greenhouse gas(CO 2) emissions by 2050 2 • Approving the global warming treaty 3 • Investing in alternative energy 4 • creating 5 million ‘green jobs’ World-wide environmental declaration 1 • In Journalism: Rupert Murdoch 2 • In Shipping: MAERSK, Evergreen, MOL 3 • In Industry: GE의 Ecomagination (Toyota, BP) 4 • In distributing: Wal-Mart, Tesco 7

3 Domestic situation and Response Domestic Reality Energy consumption and Pollutant emissions in South Korea • Increase greenhouse gas emissions continuously • The average annual growth rate of 7. 9% in greenhouse gas from 1990 to 1997, higher than the growth rate of 7. 1% in GDP • Continuously increase proportion of energy-guzzling industries (steel, petrochemical industry) since 1990 • Rapidly increase greenhouse gas emissions per capita from 1. 9 TC/Capita in 1990 to 3. 1 TC/Capita in 1997 (World lanking) Greenhouse gas emissions (2005) 16 th(OECD 6 th) Greenhouse gas emissions per capita (2005) 28 th CO 2 emissions (2006) 9 th Growth rate of CO 2 emissions (2006) OECD 1 st If obligations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are charged hereafter, Korean economic growth could shrink concerning the difficulty of its Reduction in Korean circumstances. 8
3 Domestic situation and Response Domestic reality and Respond Korean President’s “Green growth” Declaration : Selected as a national challenge Aug 5 th, 2008 Forming eco-friendly business & Developing new industries energy-saving infrastructure to respond to climate change Improving independent energy & Developing renewable energy & Creating green Korean Peninsula clean energy Included in parties to UNFCCC from 2013 Research actual emissions of greenhouse gas in logistics and accept plans and road map to attain target for greenhouse gas reduction. 9

4 Environmental issues in Logistics Trends in domestic private companies Hanjin Shipping 1 • Operate fuel-saving service lanes (BSP : Bunker Saving Program) 2 • Streamlined routes, Vessel speed reduction 3 • Install new shipbuilding AMP (Alternative Maritime Power) POSCO 1 • Steadily expand volume of eco-friendly marine & rail transportation 2 • Secure competitiveness through diversification of transportation 3 • Reduce distribution costs by road damage & mass transportation Domestic companies haven’t recognized environmental issues yet. Government’s measure also isn’t specific. 1
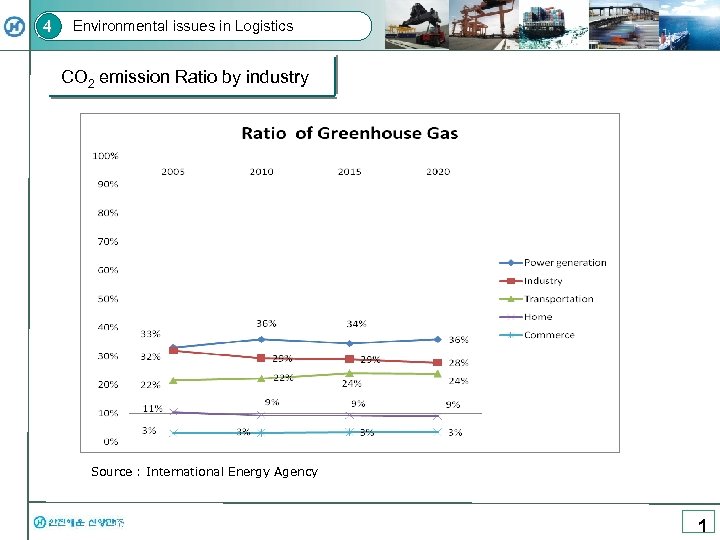
4 Environmental issues in Logistics CO 2 emission Ratio by industry Source : International Energy Agency 1
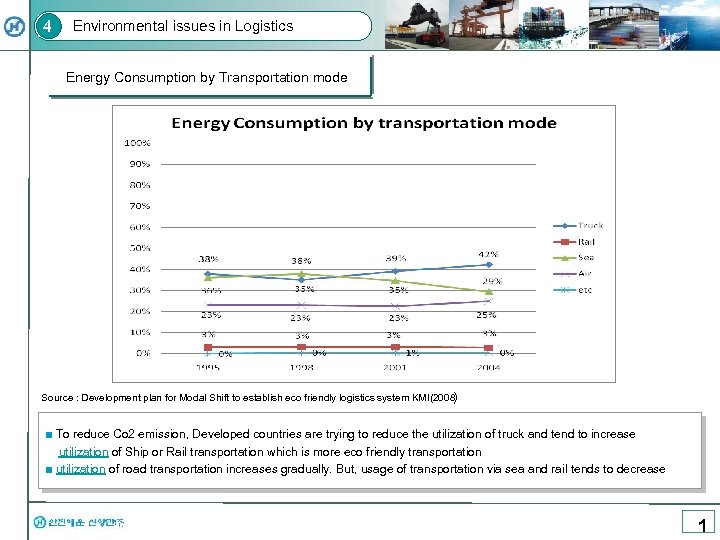
4 Environmental issues in Logistics Energy Consumption by Transportation mode Source : Development plan for Modal Shift to establish eco friendly logistics system KMI(2008) ■ To reduce Co 2 emission, Developed countries are trying to reduce the utilization of truck and tend to increase utilization of Ship or Rail transportation which is more eco friendly transportation ■ utilization of road transportation increases gradually. But, usage of transportation via sea and rail tends to decrease 1

4 Environmental issues in Logistics Global Warming Ozone Depletion It caused by CO 2 from vehicles and Vessels Causing from Air conditioner of Vehicle, Reefer Container, refrigeration/freezer Tank Acid Rain It caused by Sox, Nox from Vehicles and Vessels Marine Pollution Oil Spills by Marine Accident Destruction of Rainforest Exhaustion of resources Using packing material for transit & Pallet Exhaustion of petroleum resources 1
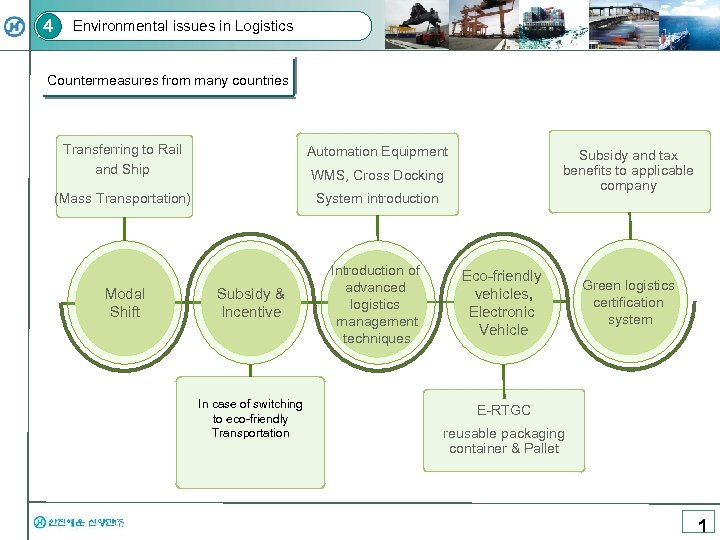
4 Environmental issues in Logistics Countermeasures from many countries Transferring to Rail and Ship Automation Equipment (Mass Transportation) System introduction Modal Shift Introduction of advanced logistics management techniques Subsidy and tax benefits to applicable company WMS, Cross Docking Subsidy & Incentive In case of switching to eco-friendly Transportation Eco-friendly vehicles, Electronic Vehicle Green logistics certification system E-RTGC reusable packaging container & Pallet 1

5 Green port status and Action plan Eco Friendly Port Technology Eco Friendly Port Operation Technology In Charge In short term Liner • Fuel Change • Catalyst • Controller for fuel usage • Automated berth system In long term • AMP • Clean Vessel • C/C unit increase • C/C ability ↑ • new C/C development Terminal • Non peak incentive • Multi spreader • Relocation Operator • 24 hour operation • advanced • proper facility size equipment • Non stop at gate • gate separation Trucking/ Shipper • Modal Shift • Fuel Change • Multi vehicle Eco Friendly Green Terminal • Vessel Speed ↓ In mid term • Clean vehicle input 1
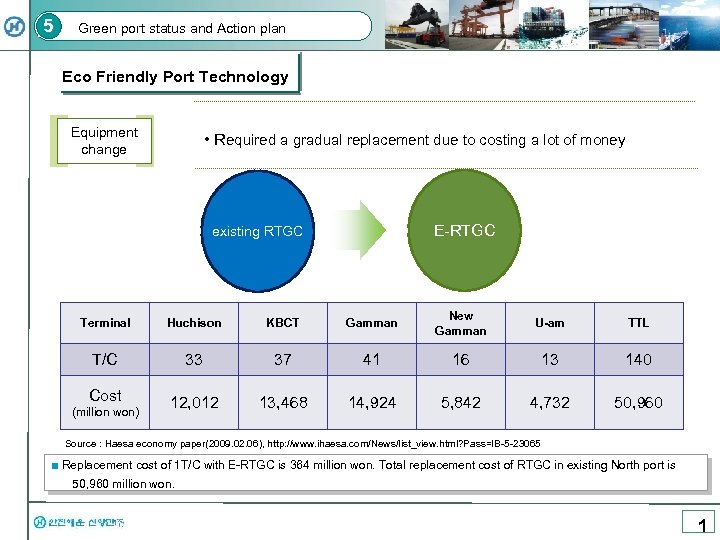
5 Green port status and Action plan Eco Friendly Port Technology Equipment change • Required a gradual replacement due to costing a lot of money E-RTGC existing RTGC Terminal Huchison KBCT Gamman New Gamman U-am TTL T/C 33 37 41 16 13 140 Cost 12, 012 13, 468 14, 924 5, 842 4, 732 50, 960 (million won) Source : Haesa economy paper(2009. 02. 06), http: //www. ihaesa. com/News/list_view. html? Pass=IB-5 -23065 ■ Replacement cost of 1 T/C with E-RTGC is 364 million won. Total replacement cost of RTGC in existing North port is 50, 960 million won. 1
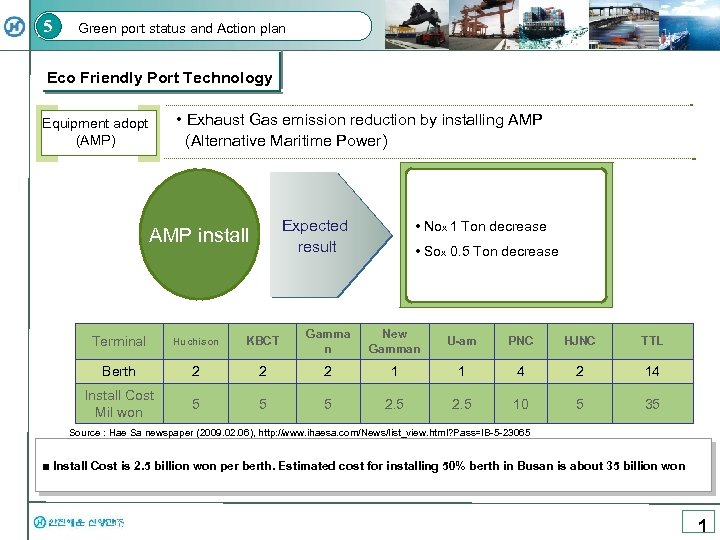
5 Green port status and Action plan Eco Friendly Port Technology • Exhaust Gas emission reduction by installing AMP (Alternative Maritime Power) Equipment adopt (AMP) Expected result AMP install • Nox 1 Ton decrease • Sox 0. 5 Ton decrease Terminal Huchison KBCT Gamma n New Gamman U-am PNC HJNC TTL Berth 2 2 2 1 1 4 2 14 Install Cost Mil won 5 5 5 2. 5 10 5 35 Source : Hae Sa newspaper (2009. 02. 06), http: //www. ihaesa. com/News/list_view. html? Pass=IB-5 -23065 ■ Install Cost is 2. 5 billion won per berth. Estimated cost for installing 50% berth in Busan is about 35 billion won 1
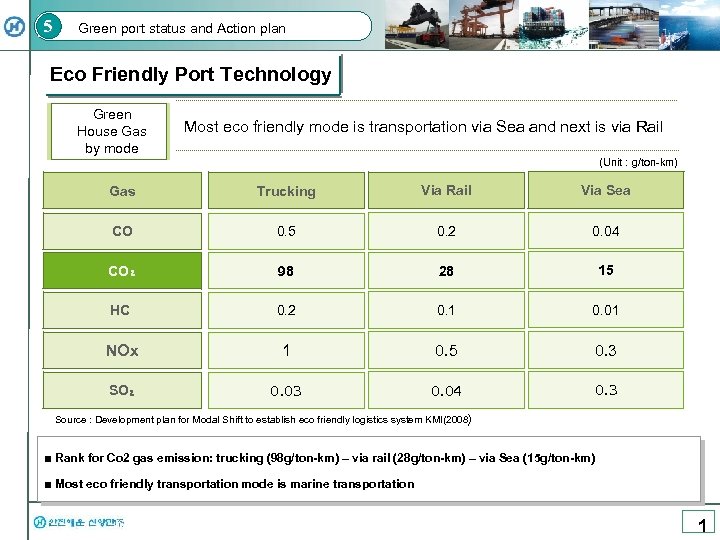
5 Green port status and Action plan Eco Friendly Port Technology Green House Gas by mode Most eco friendly mode is transportation via Sea and next is via Rail (Unit : g/ton-km) Gas Trucking Via Rail Via Sea CO 0. 5 0. 2 0. 04 CO₂ 98 28 15 HC 0. 2 0. 1 0. 01 NOx 1 0. 5 0. 3 SO₂ 0. 03 0. 04 0. 3 Source : Development plan for Modal Shift to establish eco friendly logistics system KMI(2008) ■ Rank for Co 2 gas emission: trucking (98 g/ton-km) – via rail (28 g/ton-km) – via Sea (15 g/ton-km) ■ Most eco friendly transportation mode is marine transportation 1
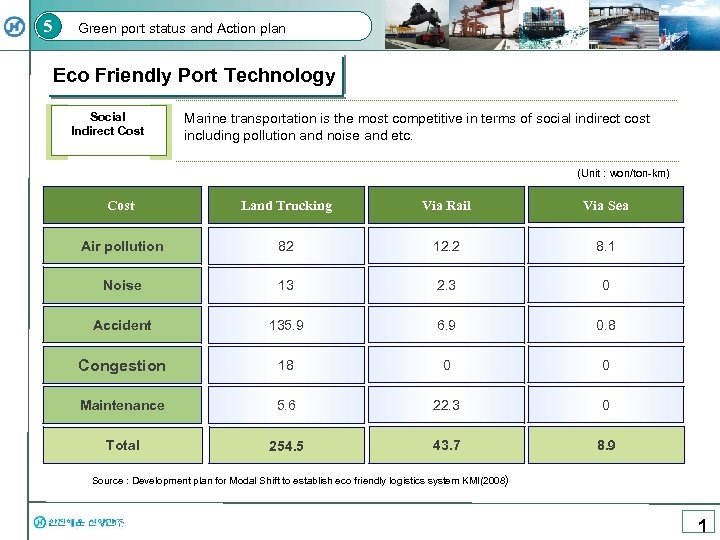
5 Green port status and Action plan Eco Friendly Port Technology Social Indirect Cost Marine transportation is the most competitive in terms of social indirect cost including pollution and noise and etc. (Unit : won/ton-km) Cost Land Trucking Via Rail Via Sea Air pollution 82 12. 2 8. 1 Noise 13 2. 3 0 Accident 135. 9 6. 9 0. 8 Congestion 18 0 0 Maintenance 5. 6 22. 3 0 Total 254. 5 43. 7 8. 9 Source : Development plan for Modal Shift to establish eco friendly logistics system KMI(2008) 1
5 Green port status and Action plan Eco Friendly Port Technology Rear Transportation Tucking takes up 90% of the rear transportation of the port Need for various transportation mode Joint Delivery required Existing Hardware available No need for additional investment Requiring Gov, Subsidy or incentives for stable service 2
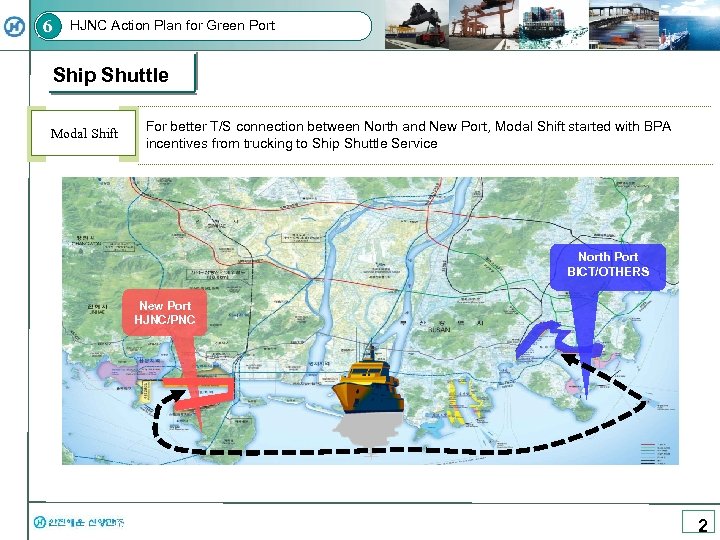
6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Ship Shuttle Modal Shift For better T/S connection between North and New Port, Modal Shift started with BPA incentives from trucking to Ship Shuttle Service North Port BICT/OTHERS New Port HJNC/PNC 2
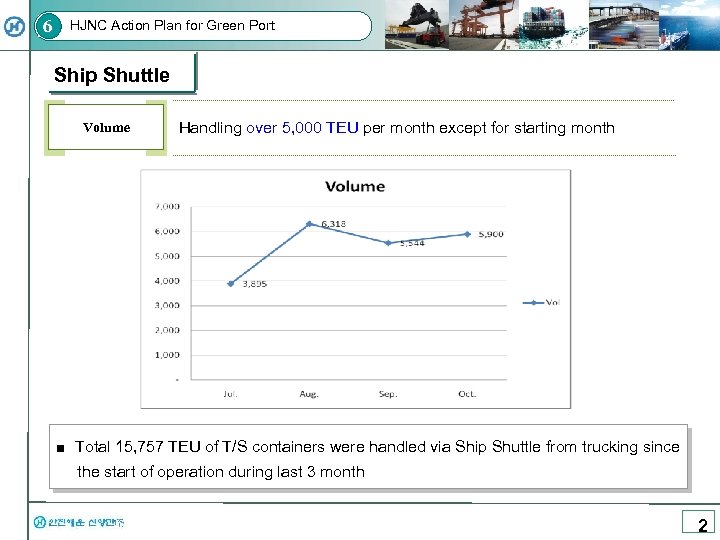
6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Ship Shuttle Volume Handling over 5, 000 TEU per month except for starting month ■ Total 15, 757 TEU of T/S containers were handled via Ship Shuttle from trucking since the start of operation during last 3 month 2
6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Ship Shuttle Social Indirect Cost Saving Social indirect cost reduction is about 1. 9 billion won by transferring to Ship Shuttle Month Vol. (TEU) R/T Trucking (Won) Ship Shuttle (Won) Reduction (Won) Jul 3, 895 77, 900 495, 638, 750 16, 943, 250 478, 695, 500 Aug 6, 318 126, 360 803, 965, 500 27, 483, 300 776, 482, 200 Sep 5, 544 110, 880 705, 474, 000 24, 116, 400 681, 357, 600 Oct 5, 900 118, 000 750, 775, 000 25, 665, 000 725, 110, 000 15, 757 315, 140 2, 005, 078, 250 68, 542, 950 1, 936, 535, 300 Total Source: Considered Air pollution, Noise, Accident, Congestions, M&R Cost (referring to Page 19) 2
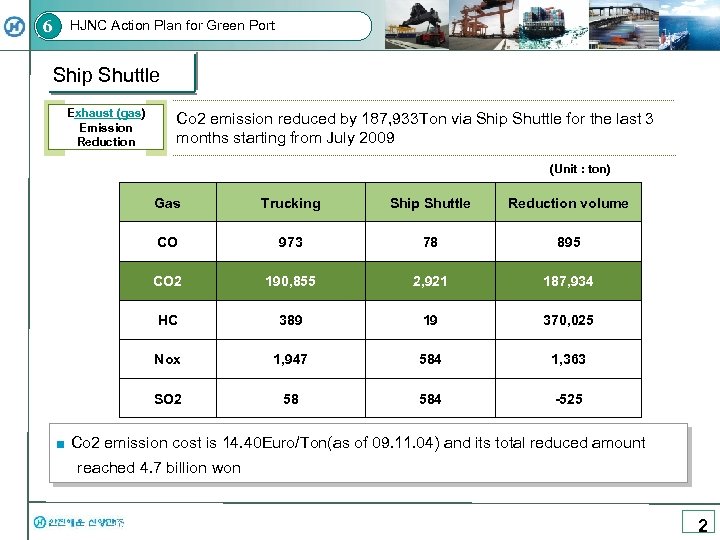
6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Ship Shuttle Exhaust (gas) Emission Reduction Co 2 emission reduced by 187, 933 Ton via Ship Shuttle for the last 3 months starting from July 2009 (Unit : ton) Gas Trucking Ship Shuttle Reduction volume CO 973 78 895 CO 2 190, 855 2, 921 187, 934 HC 389 19 370, 025 Nox 1, 947 584 1, 363 SO 2 58 584 -525 ■ Co 2 emission cost is 14. 40 Euro/Ton(as of 09. 11. 04) and its total reduced amount reached 4. 7 billion won 2
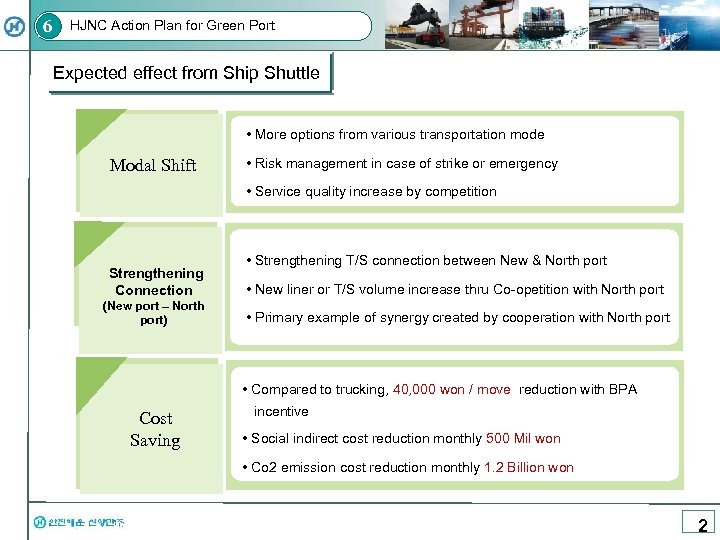
6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Expected effect from Ship Shuttle • More options from various transportation mode Modal Shift • Risk management in case of strike or emergency • Service quality increase by competition Strengthening • Strengthening T/S connection between New & North port Connection • New liner or T/S volume increase thru Co-opetition with North port (New port – North port) • Primary example of synergy created by cooperation with North port • Compared to trucking, 40, 000 won / move reduction with BPA Cost Saving incentive • Social indirect cost reduction monthly 500 Mil won • Co 2 emission cost reduction monthly 1. 2 Billion won 2
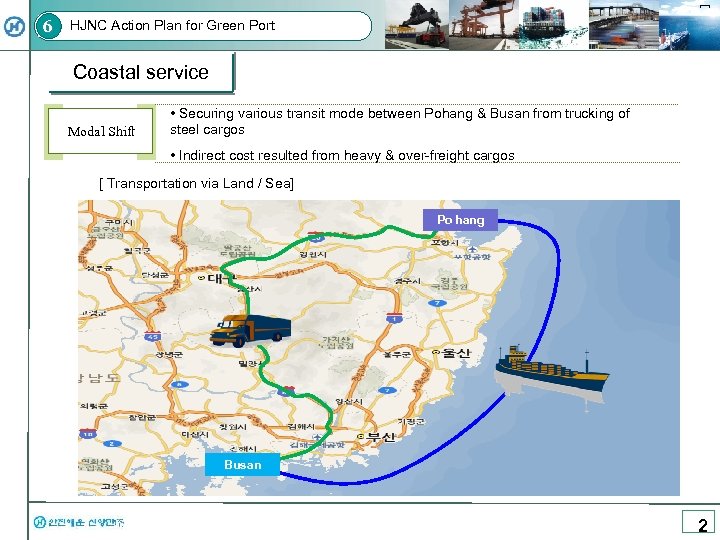
[ 6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Coastal service Modal Shift • Securing various transit mode between Pohang & Busan from trucking of steel cargos • Indirect cost resulted from heavy & over-freight cargos [ Transportation via Land / Sea] Po hang Busan 2
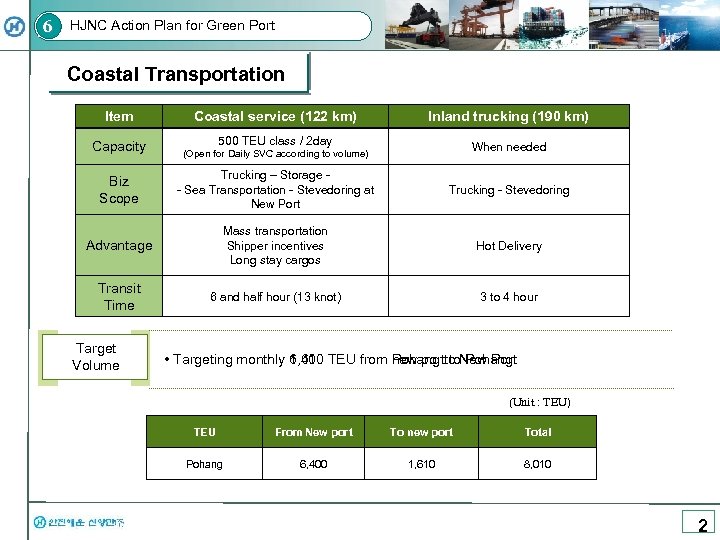
6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Coastal Transportation Item Coastal service (122 km) Inland trucking (190 km) Capacity 500 TEU class / 2 day (Open for Daily SVC according to volume) When needed Biz Scope Trucking – Storage - Sea Transportation - Stevedoring at New Port Trucking - Stevedoring Advantage Mass transportation Shipper incentives Long stay cargos Hot Delivery Transit Time 6 and half hour (13 knot) 3 to 4 hour Target Volume • Targeting monthly 6, 400 TEU from new port to Pohang Targeting monthly 1, 610 TEU from Pohang to New Port (Unit : TEU) TEU From New port To new port Total Pohang 6, 400 1, 610 8, 010 2
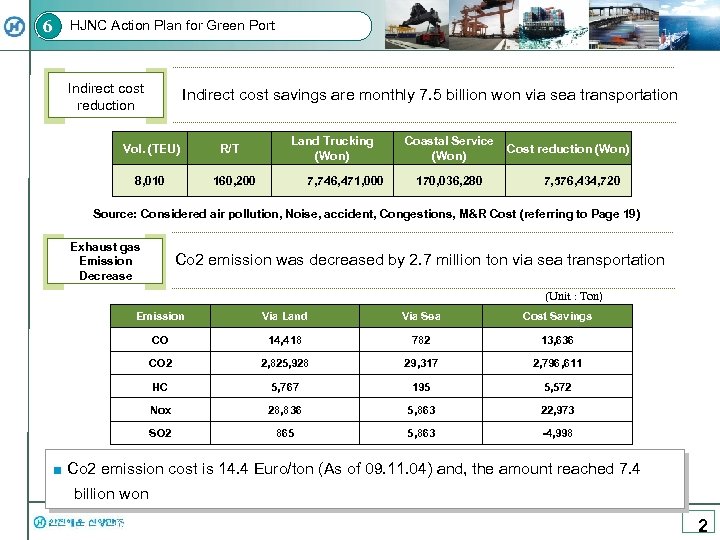
6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Indirect cost reduction Indirect cost savings are monthly 7. 5 billion won via sea transportation Vol. (TEU) 8, 010 R/T Land Trucking (Won) 160, 200 7, 746, 471, 000 Coastal Service (Won) 170, 036, 280 Cost reduction (Won) 7, 576, 434, 720 Source: Considered air pollution, Noise, accident, Congestions, M&R Cost (referring to Page 19) Exhaust gas Emission Decrease Co 2 emission was decreased by 2. 7 million ton via sea transportation (Unit : Ton) Emission Via Land Via Sea Cost Savings CO 14, 418 782 13, 636 CO 2 2, 825, 928 29, 317 2, 796, 611 HC 5, 767 195 5, 572 Nox 28, 836 5, 863 22, 973 SO 2 865 5, 863 -4, 998 ■ Co 2 emission cost is 14. 4 Euro/ton (As of 09. 11. 04) and, the amount reached 7. 4 billion won 2
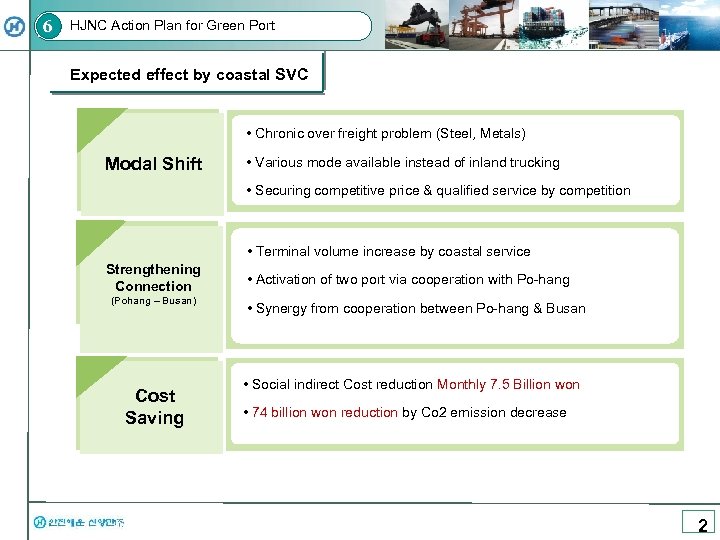
6 HJNC Action Plan for Green Port Expected effect by coastal SVC • Chronic over freight problem (Steel, Metals) 만성적인 과적 문제 수/출입 화물의 대부분이 철강관련 아이템으로 Modal Shift • Various mode available instead of inland trucking 내륙 운송 중심에서 다양한 모드 선택 가능 • Securing competitive price & qualified service by competition 육상운송 경쟁을 통한 서비스 질 향상과 합리적인 가격 • Terminal volume increase by coastal service Strengthening Connection (Pohang – Busan) Cost Saving • Activation of two port via cooperation with Po-hang • Synergy from cooperation between Po-hang & Busan • Social indirect Cost reduction Monthly 7. 5 Billion won • 74 billion won reduction by Co 2 emission decrease 2
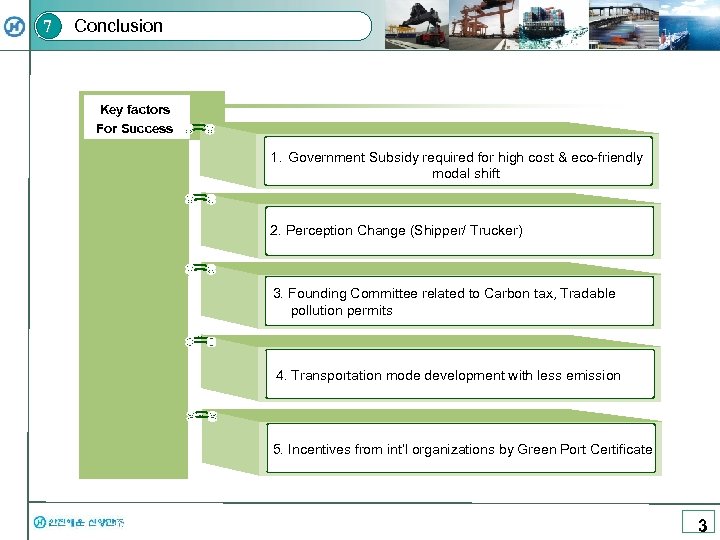
7 Conclusion Key factors For Success 1. Government Subsidy required for high cost & eco-friendly modal shift 2. Perception Change (Shipper/ Trucker) 3. Founding Committee related to Carbon tax, Tradable pollution permits 4. Transportation mode development with less emission 5. Incentives from int’l organizations by Green Port Certificate 3

Thank Your Choice Your success
661703a4d84009b0c596ae0f371cdb3b.ppt