ed990f708590155ccfbf055b13ed23d1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Development of Advanced Nursing Practice in Hong Kong: a celebration of ten years’ work Frances Kam Yuet Wong Professor & Associate Head School of Nursing The Hong Kong Polytechnic University 1
Development of Advanced Nursing Practice in Hong Kong: a celebration of ten years’ work Frances Kam Yuet Wong Professor & Associate Head School of Nursing The Hong Kong Polytechnic University 1
 Outline • Factors that contribute to the development of Advanced Nursing Practice (ANP) • The scenario of practice by Nurse Specialists (NSs) in the early 1990 s • The development of NS practice in the late 1990 s to early 2000 2
Outline • Factors that contribute to the development of Advanced Nursing Practice (ANP) • The scenario of practice by Nurse Specialists (NSs) in the early 1990 s • The development of NS practice in the late 1990 s to early 2000 2
 Factors Contributing to the Development of Advanced Nursing Practice (ANPs) • Differentiation of nursing work • Nexus of work and profession in a cost containment environment • Specialization of patient groups • Enhancement of nursing education (Wong, 1996) 3
Factors Contributing to the Development of Advanced Nursing Practice (ANPs) • Differentiation of nursing work • Nexus of work and profession in a cost containment environment • Specialization of patient groups • Enhancement of nursing education (Wong, 1996) 3
 (1) Differentiation of Nursing Work Proletarianization Nursing work less skilled worker Professionalization Upgrading of nursing education and autonomy 4
(1) Differentiation of Nursing Work Proletarianization Nursing work less skilled worker Professionalization Upgrading of nursing education and autonomy 4
 (2) Nexus of Work and Profession in a Cost Containment Environment 5
(2) Nexus of Work and Profession in a Cost Containment Environment 5
 (2) Nexus of Work and Profession in a Cost Containment Environment Human institution helps to mediate between Knowledge and Power 6
(2) Nexus of Work and Profession in a Cost Containment Environment Human institution helps to mediate between Knowledge and Power 6
 (3) Specialization of Patients • Chronically ill patients become experts of their own illnesses • Increased level of education • Increased availability of health knowledge in the mass media and the web 7
(3) Specialization of Patients • Chronically ill patients become experts of their own illnesses • Increased level of education • Increased availability of health knowledge in the mass media and the web 7
 (4) Enhancement of Nursing Education • Over 50% nurses possess a first degree • Many studying for masters degree and doctorate degree 8
(4) Enhancement of Nursing Education • Over 50% nurses possess a first degree • Many studying for masters degree and doctorate degree 8
 Scenario of Practice by NSs in the Early 1990 s Identity searching Being distinguished from RNs 9
Scenario of Practice by NSs in the Early 1990 s Identity searching Being distinguished from RNs 9
 Scenario of Practice by NSs in the Early 1990 s The main work involvement of NSs: • • Client care Patient education Staff development Quality improvement and research Hospital Authority, 1996 and Wong, 1997 10
Scenario of Practice by NSs in the Early 1990 s The main work involvement of NSs: • • Client care Patient education Staff development Quality improvement and research Hospital Authority, 1996 and Wong, 1997 10
 NS vs RN • Work is NOT subject to routinization • See clients by referrals 11
NS vs RN • Work is NOT subject to routinization • See clients by referrals 11
 (1) Work is Not Routinized When I was working on the ward as an RN, if the patient in the next bed has a physical need, I needed to see him right away. This interrupted the health education session. Now I have the freedom to telephone the patients for follow up, and put time in cases which are of higher priority. The satisfaction is greater. (Wong 1998: 477) 12
(1) Work is Not Routinized When I was working on the ward as an RN, if the patient in the next bed has a physical need, I needed to see him right away. This interrupted the health education session. Now I have the freedom to telephone the patients for follow up, and put time in cases which are of higher priority. The satisfaction is greater. (Wong 1998: 477) 12
 (2) Consultation by Referrals Professional tion sulta Con A Professional B 13
(2) Consultation by Referrals Professional tion sulta Con A Professional B 13
![DMNS’ Notes. . . The patient demonstrated [basic skills in using the] Novopen … DMNS’ Notes. . . The patient demonstrated [basic skills in using the] Novopen …](https://present5.com/presentation/ed990f708590155ccfbf055b13ed23d1/image-14.jpg) DMNS’ Notes. . . The patient demonstrated [basic skills in using the] Novopen … I would make an appointment to see her [in OPD]… To practice Novopen under skill supervision in ward. 14
DMNS’ Notes. . . The patient demonstrated [basic skills in using the] Novopen … I would make an appointment to see her [in OPD]… To practice Novopen under skill supervision in ward. 14
![DMNS’ Notes. . . The patient demonstrated Dr’s Notes [basic skills in using the] DMNS’ Notes. . . The patient demonstrated Dr’s Notes [basic skills in using the]](https://present5.com/presentation/ed990f708590155ccfbf055b13ed23d1/image-15.jpg) DMNS’ Notes. . . The patient demonstrated Dr’s Notes [basic skills in using the] Novopen … … to practice [injection] skill on ward. I would make an appointment to see her [in OPD]… Home until ready. To practice Novopen under skill supervision in ward. 15
DMNS’ Notes. . . The patient demonstrated Dr’s Notes [basic skills in using the] Novopen … … to practice [injection] skill on ward. I would make an appointment to see her [in OPD]… Home until ready. To practice Novopen under skill supervision in ward. 15
 Scenario of Practice in NSs in the Early 1990 s 16
Scenario of Practice in NSs in the Early 1990 s 16
 Scenario of Practice in NSs in the Early 1990 s 17
Scenario of Practice in NSs in the Early 1990 s 17
 Scenario of Practice in NSs in the Early 1990 s 18
Scenario of Practice in NSs in the Early 1990 s 18
 Scenario of Practice in NSs in the Early 1990 s • 22 NSs appointed in 14 clinical areas in 1993 • Definition of nursing specialties was somewhat arbitrary • No credentialing and regulatory body to scrutinize the qualifications of the NSs and monitor their clinical competence 19
Scenario of Practice in NSs in the Early 1990 s • 22 NSs appointed in 14 clinical areas in 1993 • Definition of nursing specialties was somewhat arbitrary • No credentialing and regulatory body to scrutinize the qualifications of the NSs and monitor their clinical competence 19
 The Development of NS Practice in the Late 1990 s to Early 2000 s 20
The Development of NS Practice in the Late 1990 s to Early 2000 s 20
 The Development of NS Practice in the Late 1990 s to Early 2000 • Exemplary work of NS practice, with support of research • Service well recognized by the nursing peers and doctors • Nurse-led clinics • The issue of regulation • Room for the APN to be developed in the community 21
The Development of NS Practice in the Late 1990 s to Early 2000 • Exemplary work of NS practice, with support of research • Service well recognized by the nursing peers and doctors • Nurse-led clinics • The issue of regulation • Room for the APN to be developed in the community 21
 Exemplary Work - Research Evidence • From Senior NS (SNS) Scheme by HA, HK • Positive results of SNS from an independent evaluation (HA, 1996; Wong, 2001) • Economic downturn position not established Examples on cost-effective and quality care by renal SNS 22
Exemplary Work - Research Evidence • From Senior NS (SNS) Scheme by HA, HK • Positive results of SNS from an independent evaluation (HA, 1996; Wong, 2001) • Economic downturn position not established Examples on cost-effective and quality care by renal SNS 22
 Cost-effective Care (1) Renal SNS Erythropoietin Selfinjection Program • 26 chronic renal failure patients • Saving 225 nurse hours annually 23
Cost-effective Care (1) Renal SNS Erythropoietin Selfinjection Program • 26 chronic renal failure patients • Saving 225 nurse hours annually 23
 Cost-effective Care (1) Renal SNS Braunoderm Vs Betadine Spray • Same effect • Braunoderm costs HK$0. 8 (0. 0067 Hr) • Betadine costs HK$6. 0 (0. 233 Hr) 24
Cost-effective Care (1) Renal SNS Braunoderm Vs Betadine Spray • Same effect • Braunoderm costs HK$0. 8 (0. 0067 Hr) • Betadine costs HK$6. 0 (0. 233 Hr) 24
 Cost-effective Care (2) • • Senior Diabetes NS Seeing 108 poorly controlled diabetic patients 10 (9%) physicians 98 (91%) managed by Senior Diabetes NS (HA, 1996; Wong 2001) 25
Cost-effective Care (2) • • Senior Diabetes NS Seeing 108 poorly controlled diabetic patients 10 (9%) physicians 98 (91%) managed by Senior Diabetes NS (HA, 1996; Wong 2001) 25
 Leadership Clinical Leader Care Engineer 26
Leadership Clinical Leader Care Engineer 26
 Nurse-led Clinic What is a nurse-led clinic Initial assessment See doctor by nurse See doctor To nurse for education 27
Nurse-led Clinic What is a nurse-led clinic Initial assessment See doctor by nurse See doctor To nurse for education 27
 The Definition of A Nurse-led Clinic A NURSE CLINIC is a formalized and structured health care delivery mode involving a nurse and a client. THE CLIENT is an individual and his/her family with health care needs that can be addressed by the nurse. THE CONSULTATION is initiated through referrals from nurses, doctors or other health care professionals. THE NURSE has demonstrated advanced competence to practice in the specific health area. 28
The Definition of A Nurse-led Clinic A NURSE CLINIC is a formalized and structured health care delivery mode involving a nurse and a client. THE CLIENT is an individual and his/her family with health care needs that can be addressed by the nurse. THE CONSULTATION is initiated through referrals from nurses, doctors or other health care professionals. THE NURSE has demonstrated advanced competence to practice in the specific health area. 28
 The Definition of A Nurse-led Clinic THE NURSE functions independently and/or interdependently with other health care team members for at least 80% of his/her work involvement. HE/SHE is supported by a multidisciplinary team, and can make referrals to other health care professionals to address the health care needs of the clients. THE MOST important and key interventions are nursing therapeutics which encompass assessment and evaluation, treatment and procedures, health teaching/counseling, and case management. 29
The Definition of A Nurse-led Clinic THE NURSE functions independently and/or interdependently with other health care team members for at least 80% of his/her work involvement. HE/SHE is supported by a multidisciplinary team, and can make referrals to other health care professionals to address the health care needs of the clients. THE MOST important and key interventions are nursing therapeutics which encompass assessment and evaluation, treatment and procedures, health teaching/counseling, and case management. 29
 The Definition of A Nurse-led Clinic THE NURSE CLINIC differs from the doctor clinic in its less reliance on the use of medications, but the employment of a holistic approach in addressing the needs of the clients and their families. THE NURSE determines the duration of each consultation and the time lapse between consultations according to clients’ needs. 30
The Definition of A Nurse-led Clinic THE NURSE CLINIC differs from the doctor clinic in its less reliance on the use of medications, but the employment of a holistic approach in addressing the needs of the clients and their families. THE NURSE determines the duration of each consultation and the time lapse between consultations according to clients’ needs. 30
 Future Development To link professional recognition with practice To expand the scope of practice of APN 31
Future Development To link professional recognition with practice To expand the scope of practice of APN 31
 Linking Professional Recognition with Practice To develop a certificate process to validate and standardize the qualifications and practice competencies of the advanced practice – To protect the public’s health – To ensure the credibility of advanced nurses practising 32
Linking Professional Recognition with Practice To develop a certificate process to validate and standardize the qualifications and practice competencies of the advanced practice – To protect the public’s health – To ensure the credibility of advanced nurses practising 32
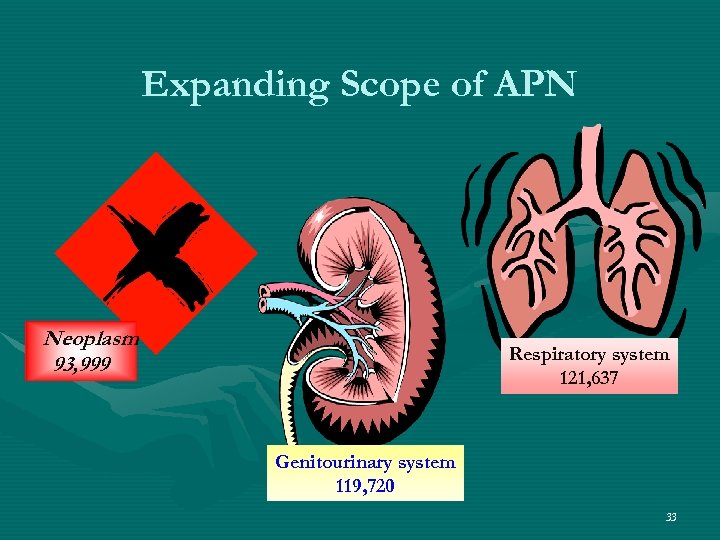 Expanding Scope of APN Neoplasm 93, 999 Respiratory system 121, 637 Genitourinary system 119, 720 33
Expanding Scope of APN Neoplasm 93, 999 Respiratory system 121, 637 Genitourinary system 119, 720 33
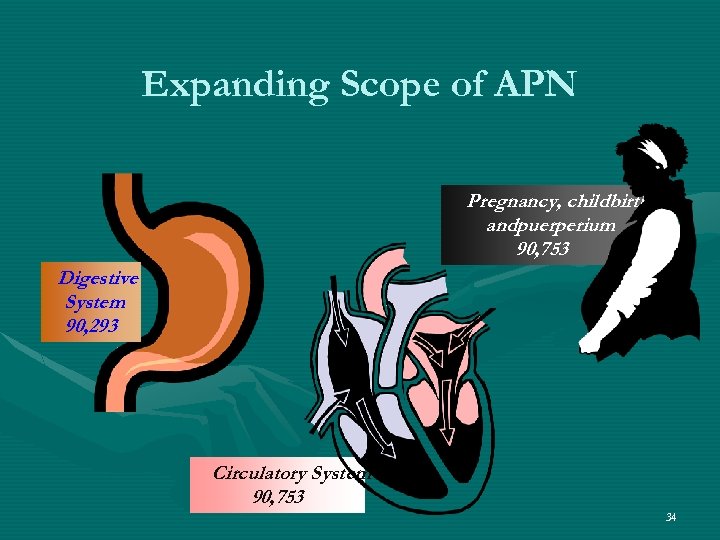 Expanding Scope of APN Pregnancy, childbirth andpuerperium 90, 753 Digestive System 90, 293 Circulatory System 90, 753 34
Expanding Scope of APN Pregnancy, childbirth andpuerperium 90, 753 Digestive System 90, 293 Circulatory System 90, 753 34
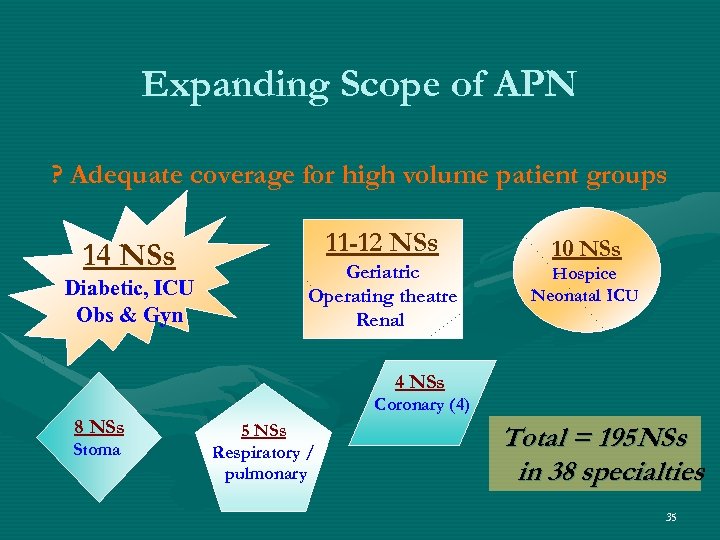 Expanding Scope of APN ? Adequate coverage for high volume patient groups 14 NSs Diabetic, ICU Obs & Gyn 11 -12 NSs Geriatric Operating theatre Renal 10 NSs Hospice Neonatal ICU 4 NSs Coronary (4) 8 NSs Stoma 5 NSs Respiratory / pulmonary Total = 195 NSs in 38 specialties 35
Expanding Scope of APN ? Adequate coverage for high volume patient groups 14 NSs Diabetic, ICU Obs & Gyn 11 -12 NSs Geriatric Operating theatre Renal 10 NSs Hospice Neonatal ICU 4 NSs Coronary (4) 8 NSs Stoma 5 NSs Respiratory / pulmonary Total = 195 NSs in 38 specialties 35
 Expanding Scope of APN • Nurse practitioner (NP) in primary care 36
Expanding Scope of APN • Nurse practitioner (NP) in primary care 36
 Expanding Scope of APN • NPs focus on primary care: family, adult, pediatric or obs & gyn -- life stages – Assessment, promotion of health and prevention of illnesses – Health areas: school, factory, community, GOPD and A&E • NSs focus on well-defined health conditions 37
Expanding Scope of APN • NPs focus on primary care: family, adult, pediatric or obs & gyn -- life stages – Assessment, promotion of health and prevention of illnesses – Health areas: school, factory, community, GOPD and A&E • NSs focus on well-defined health conditions 37
 Conclusions 38
Conclusions 38
 Journey to the West Chapter 27 39
Journey to the West Chapter 27 39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46


