2db97340a38aeaded16294ff5890c169.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 1
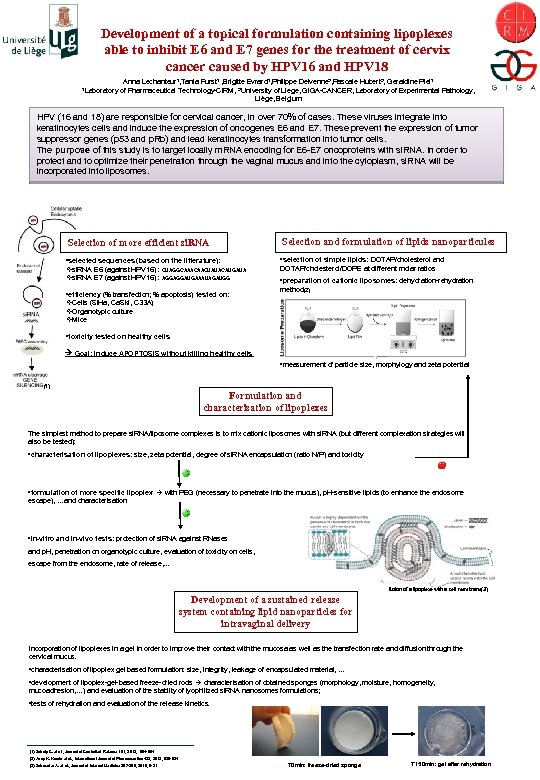
Development of a topical formulation containing lipoplexes able to inhibit E 6 and E 7 genes for the treatment of cervix cancer caused by HPV 16 and HPV 18 1 Laboratory Anna Lechanteur 1, Tania Furst 1 , Brigitte Evrard 1, Philippe Delvenne 2, Pascale Hubert 2, Geraldine Piel 1 of Pharmaceutical Technology-CIRM, 2 University of Liege, GIGA-CANCER, Laboratory of Experimental Pathology, Liège, Belgium HPV (16 and 18) are responsible for cervical cancer, in over 70% of cases. These viruses integrate into keratinocytes cells and induce the expression of oncogenes E 6 and E 7. These prevent the expression of tumor suppressor genes (p 53 and p. Rb) and lead keratinocytes transformation into tumor cells. The purpose of this study is to target locally m. RNA encoding for E 6 -E 7 oncoproteins with si. RNA. In order to protect and to optimize their penetration through the vaginal mucus and into the cytoplasm, si. RNA will be incorporated into liposomes. Selection of more efficient si. RNA Selection and formulation of lipids nanoparticules • selected sequences (based on the litterature): vsi. RNA E 6 (against HPV 16) : CUAGGCAAACAACUAUACAUGAUA vsi. RNA E 7 (against HPV 16) : AGGAGGAUGAAAUAGAUGG • selection of simple lipids: DOTAP/cholesterol and • efficiency (% transfection; % apoptosis) tested on: v. Cells (Si. Ha, Ca. Ski, C 33 A) v. Organotypic culture v. Mice DOTAP/cholesterol/DOPE at different molar ratios • preparation of cationic liposomes: dehydration-rehydration method(2) • toxicity tested on healthy cells Goal: Induce APOPTOSIS without killing healthy cells • measurement of particle size, morphylogy and zeta potential (1) Formulation and characterisation of lipoplexes The simplest method to prepare si. RNA/liposome complexes is to mix cationic liposomes with si. RNA (but different complexation strategies will also be tested): • characterisation of lipoplexes: size, zeta potential, degree of si. RNA encapsulation (ratio N/P) and toxicity • formulation of more specific lipoplex with PEG (necessary to penetrate into the mucus), p. H-sensitive lipids (to enhance the endosome escape), …and characterisation • in-vitro and in-vivo tests: protection of si. RNA against RNases and p. H, penetration on organotypic culture, evaluation of toxicity on cells, escape from the endosome, rate of release, … fusion of a lipoplexe with a cell membrane(3) Development of a sustained release system containing lipid nanoparticles for intravaginal delivery Incorporation of lipoplexes in a gel in order to improve their contact with the mucosa as well as the transfection rate and diffusion through the cervical mucus. • characterisation of lipoplex gel based formulation: size, integrity, leakage of encapsulated material, … • development of lipoplex-gel-based freeze-dried rods characterisation of obtained sponges (morphology, moisture, homogeneity, mucoadhesion, …) and evaluation of the stablity of lyophilized si. RNA nanosomes formulations; • tests of rehydration and evaluation of the release kinetics. (1) Scholy C. et al. , Journal of Controlled Release 161, 2012, 554 -564 (2) Anup K. Kundu et al. , International Journal of Pharmaceutics 423, 2012, 525 -534 (3) Schroeder A. et al. , Journal of Internal Medicine 267 -268, 2010, 9 -21 T 0 min: freeze-dried sponge T 150 min: gel after rehydration
2db97340a38aeaded16294ff5890c169.ppt