f2b0083a751153b67bd22c0b0cf0dde8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 107

Development, database and results of the Historical Sample of the Netherlands Kees Mandemakers Les Grandes Bases de Données et l’Histoire Sociale des Populations Bordeaux, Université Michel de Montagne, 7 -9 th of February 2008

HSN - What’s the HSN ? GENLIAS-index of civil certificates Best practices of large databases International data model Historical Sample of Europe

HSN - What’s the HSN ? - Sources and development database - Projects - Results


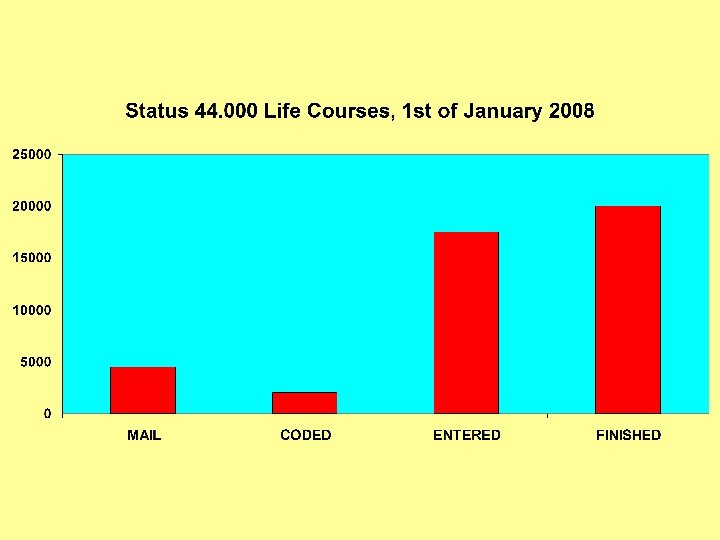
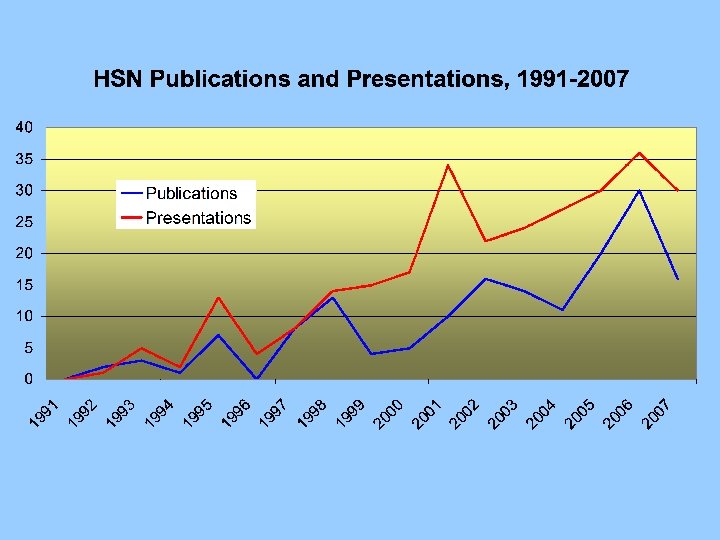
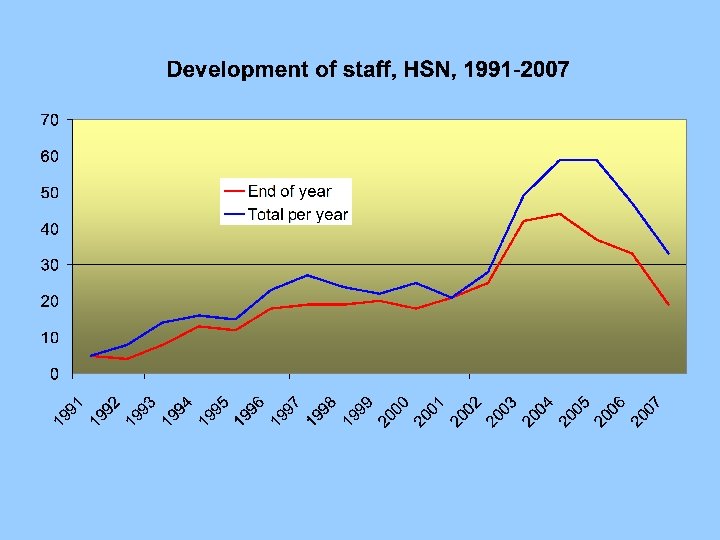
HSN Five periods of Investment 1987 -1990 1991 -1993 -1995 1996 -2002 2003 -2007 Conceptual stage Pilot project province of Utrecht Extension pilot, first collaboratory projects Extension to the whole country Life courses 1850/1863 -1922


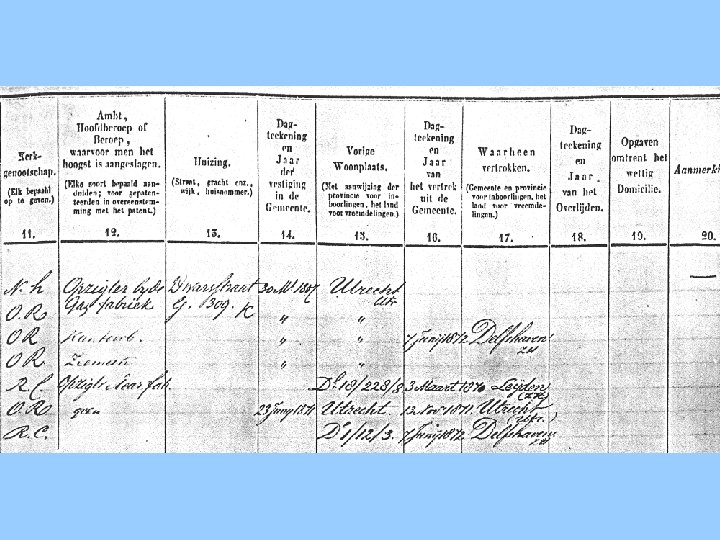
Typical Sequence of Entries in Population Registers Parental family On the road lodger maid servant soldier Own family

HSN IN CONNECTION WITH OUTPUT REGISTER 1850 -1940 Adding Personal Card/List RP Adding Marriage Certificates RP

HSN Collaboratory projects Extension datasets - Other kind of data - Other (related) persons Upkeeping HSN-infrastructure Widening circle HSN-users

Migration Dutch East Indies 1820 – 1940 Ulbe Bosma Retrieving HSN-research persons - - - Indian archives (Directories) Registers Military, Civil Servants Shipping Lists etc

Migration Dutch East Indies 1820 – 1940 Ulbe Bosma Comparison Indian and Dutch Careers (HSN Control Group)


HSN Unique position HSN . Sampling birth certificates . A whole nation (not regional) . Following persons all over the country

HSN Spanning Past and Present (SPAN) . Combination NKPS (sample 1923 -1985) Completing Families RP’s Sampling and Following Siblings Sampling from Period 1923 -1938 Reinforcement technical infrastructure (e. g. integrated SPAN-database)

HSN Future . Life courses 1812 -1862 . . Back into 18 th century Simulating census 1850 -1920 New sources: land registers, tax registers, poor law files, personal records army Enrichment geo-referencing all addresses

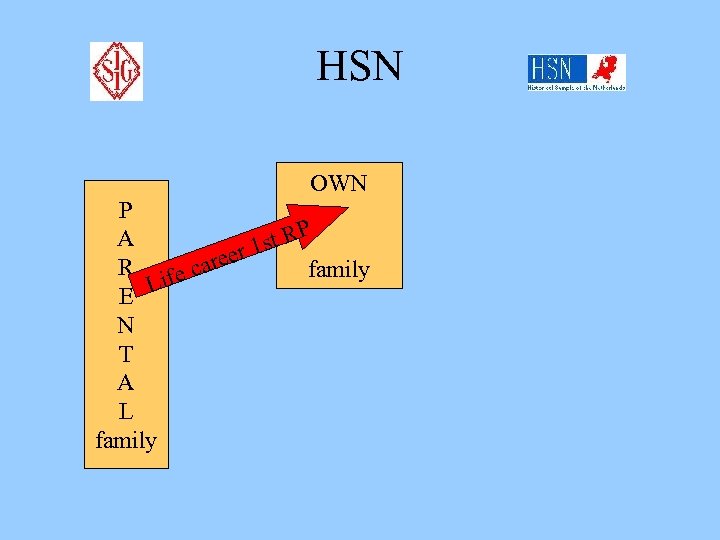
HSN P A R E N T A L family Standard HSN-data OWN Life career RP family
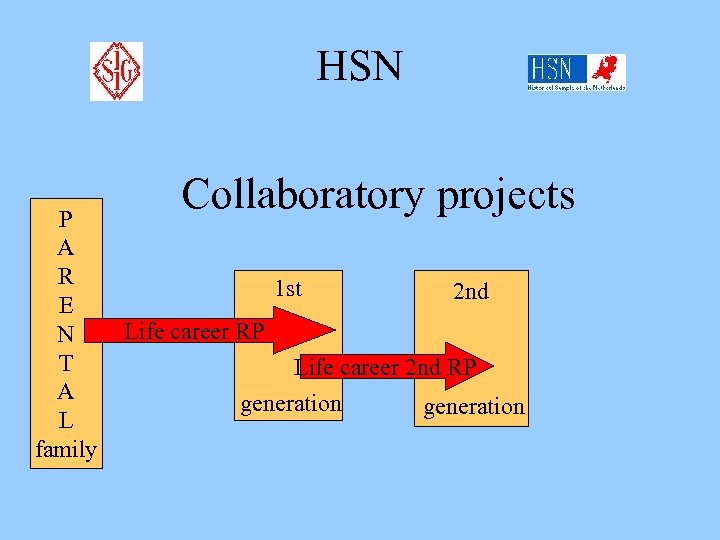
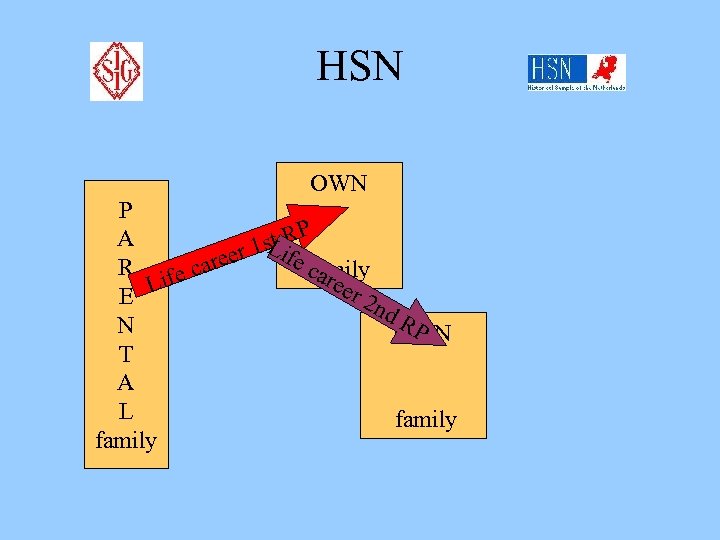
HSN P A R E N T A L family Collaboratory projects 1 st 2 nd Life career RP Life career 2 nd RP generation
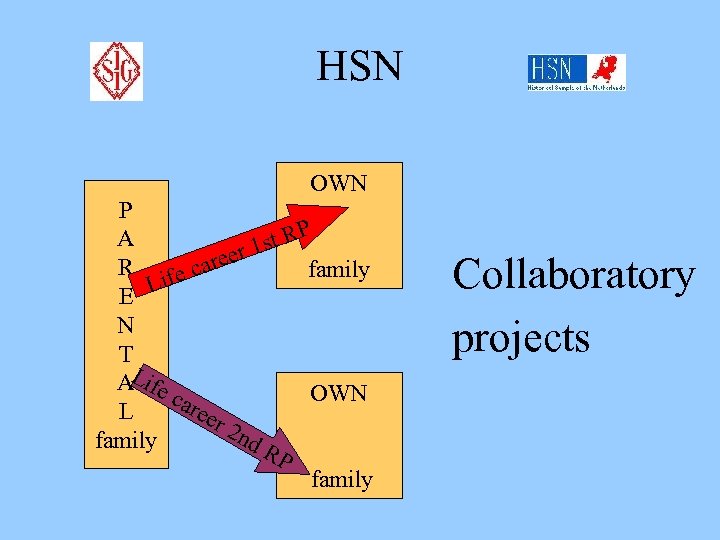
HSN OWN P P A st R 1 eer R fe car family i E L N T L A ife OWN car eer L 2 n d R family P family Collaboratory projects


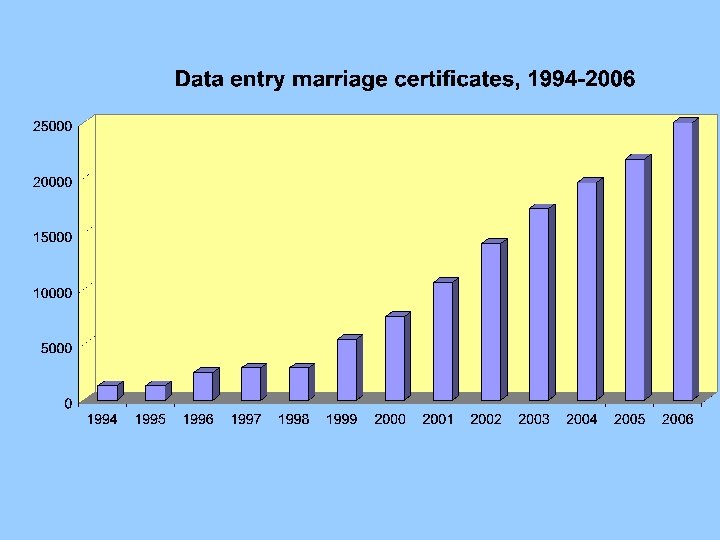
Index names from 2, 5 million marriage certificates 1812 -1922 70 % 4, 0 million death certificates 1812 -1950 40 % 2, 0 million birth certificates 1812 -1902 20 % 0, 6 million from sources before 1812
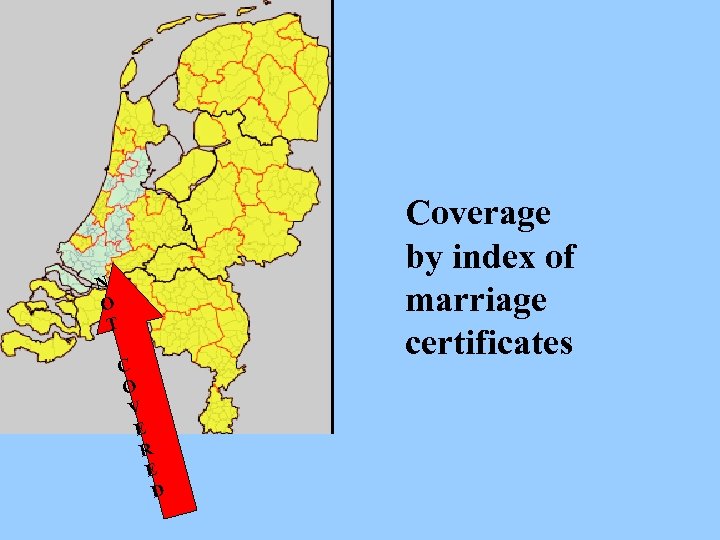
N O T C O V E R E D Coverage by index of marriage certificates
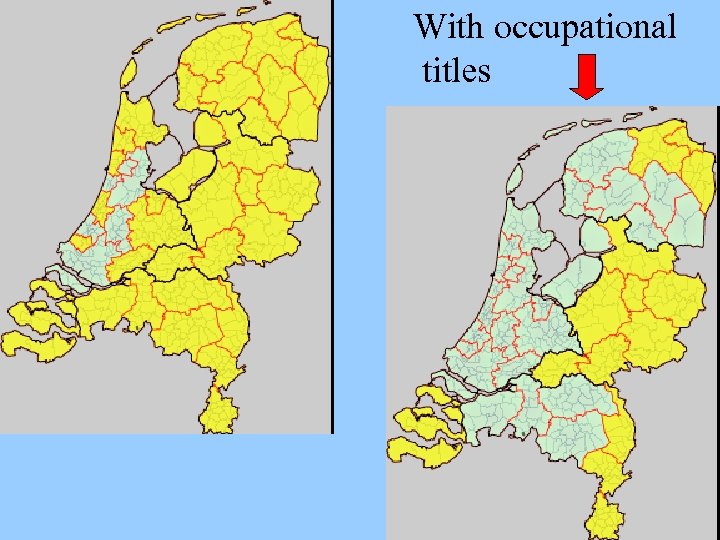
With occupational titles

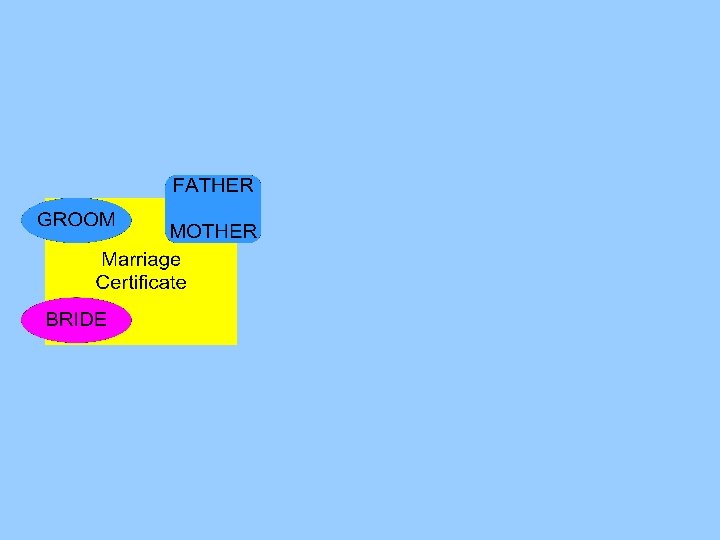
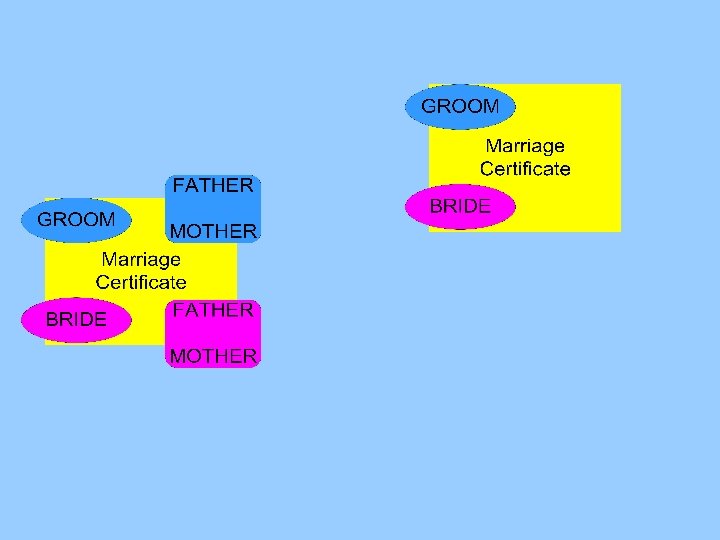
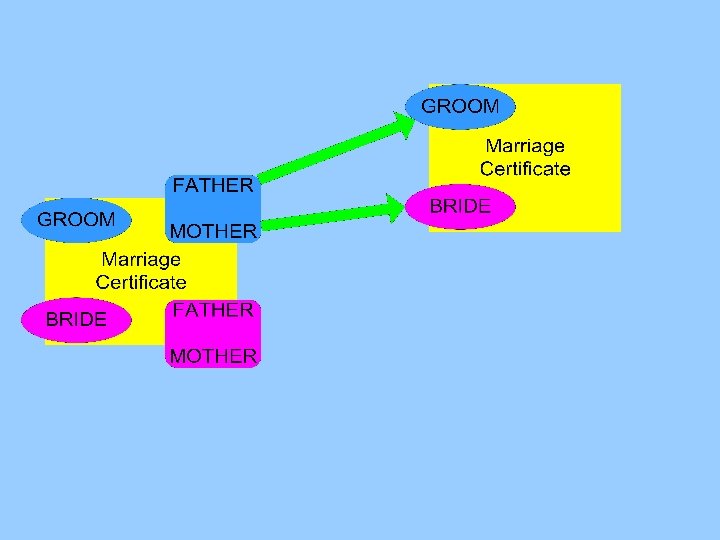
Marriage certificates Bride and groom Lastname, First name, Age at marriage Parents of bride and groom Lastname, First name

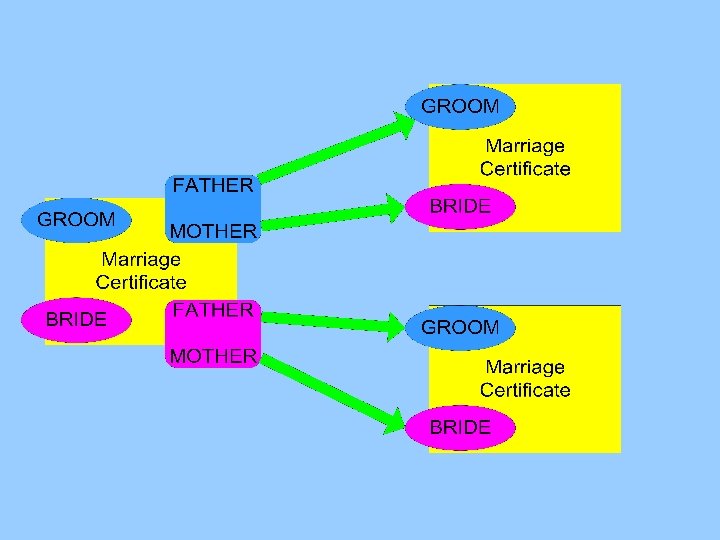
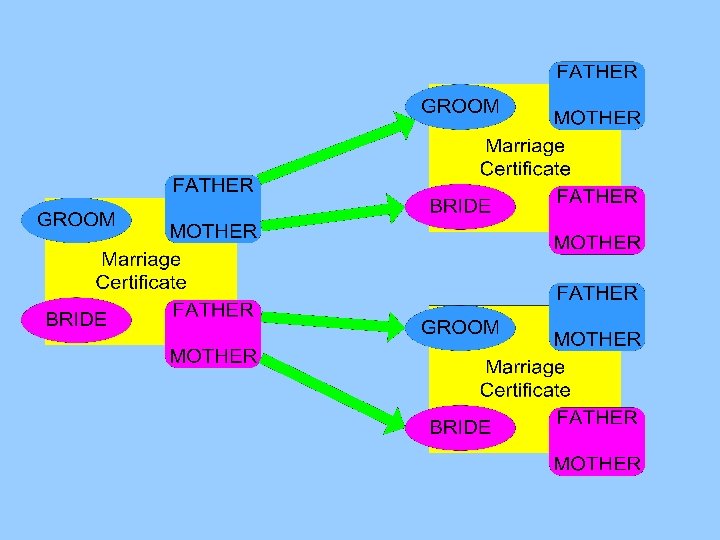
Marriage certificates Linking parents of bride and groom with their own certificate between 15 and 50 years earlier matching on combination of two persons (last name and first name)

Linking three or more generations ? ?
Linking three or more generations ? ? They have already been linked !!!
BUT HOW ? ? ?
EASILY
A B
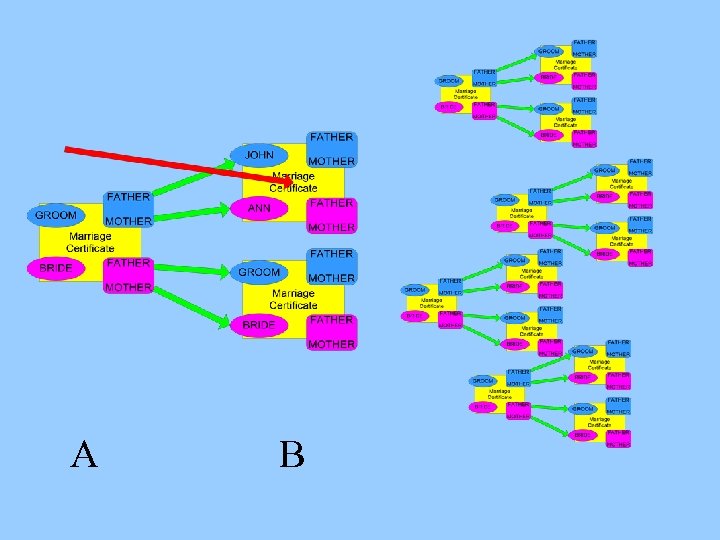
A B
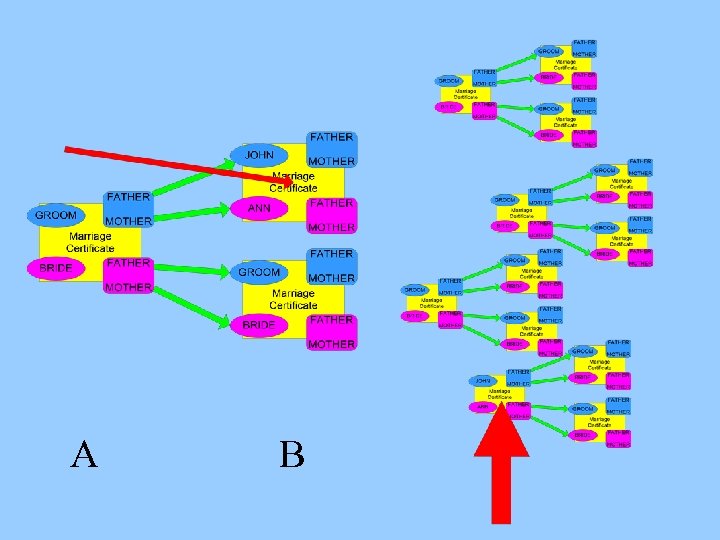
A B
![A B [= A] C [=B] A B [= A] C [=B]](https://present5.com/presentation/f2b0083a751153b67bd22c0b0cf0dde8/image-50.jpg)
A B [= A] C [=B]

Marriage certificates Chains of three generations • • • . Research on social mobility Marriages of cousins Marriages of uncles/aunts with nieces/newphews Passing down of the age of marriage

HSN P A R E N T A L family Standard HSN-data OWN Life career RP family
HSN P A R OWN E N Life career RP T family A L family
HSN P A R OWN E N Life career RP T family A L family
HSN P A R OWN E N Life career RP T family A L family
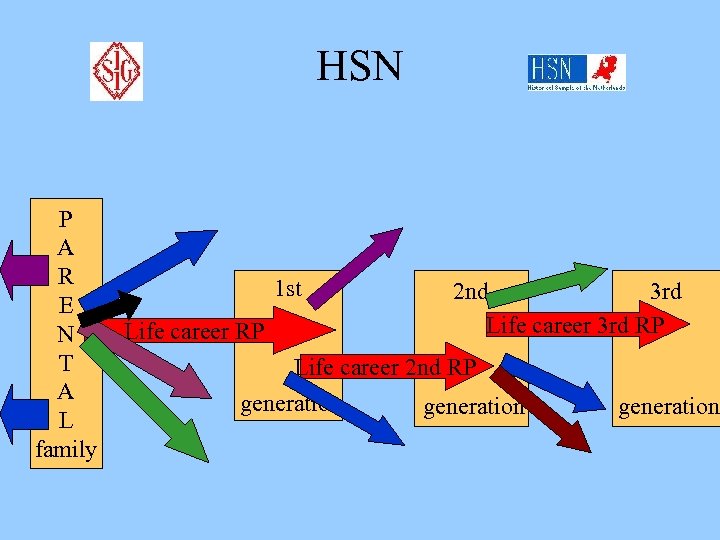
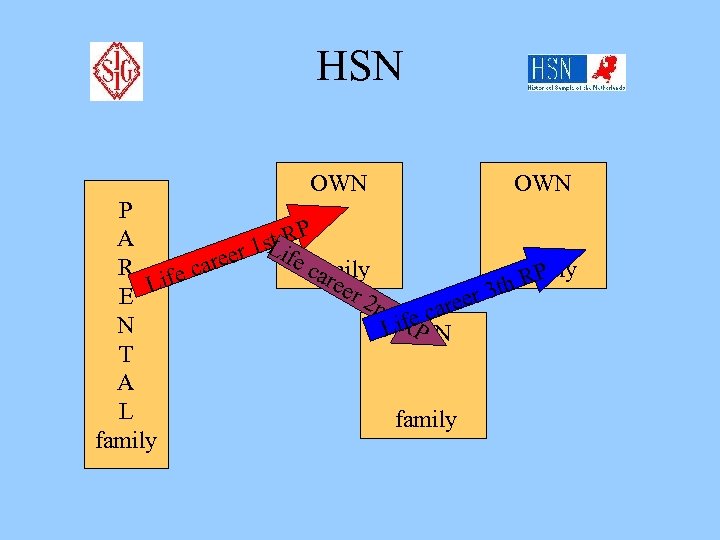
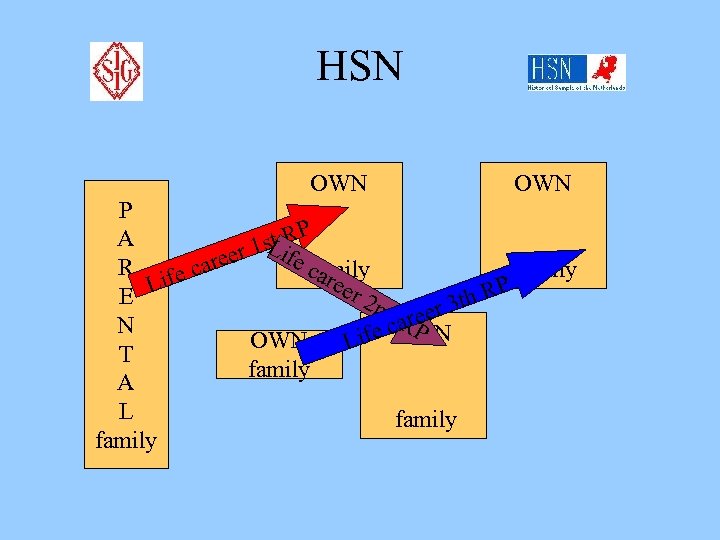
HSN P A R E N T A L family 1 st Life career RP 2 nd 3 rd Life career 3 rd RP Life career 2 nd RP generation

Best practices with large databases on historical populations Kees Mandemakers and Lisa Dillon Historical Methods 37 (2004), nr. 1, 34 -38. History and Computing 13 (2001, published 2004), 2, 207 -216

Best practices with large databases Purpose of the rules - Articulate standards Trustworthy results Benefit from previous experience Quality standard Read as list of recommendations

Best practices with large databases Three stages database-building A B C Definition object and content Data entry, integration, standardization Enrichment and release data

Best practices with large databases A Definition object and content A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 Description universe database Whole source, unless… Documentation each included source Specific rules in case of samples

Best practices with large databases B Data entry, integration, standardization Components Database SOURCES CENTRAL DATABASE DATA RELEASE

Best practices with large databases B Data entry, integration, standardization B 5 B 6 B 7 B 8 Distinction original and corrected data Clearly distinction of inferred data Archiving in simple format (ASCI) Good back-up system

Best practices with large databases C Enrichment and release data Values C 5 C 6 C 7 Standardized and original values (international standards, e. g. HISCO) Negative standard values missing values Geo-referenced data

Best practices with large databases C Enrichment and release Documentation C 8 List of model studies C 9 Easy user versions (for ‘beginners’) C 10 DDI-based meta-data C 11 Website database C 12 Progress reports

HSN P A R E N T A L family OWN Life career RP family RELEASES Dissemination data
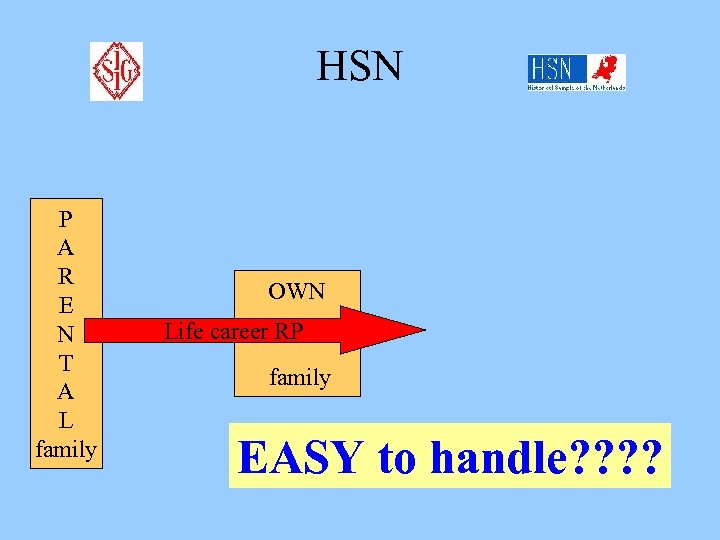
HSN P A R E N T A L family OWN Life career RP family EASY to handle? ?
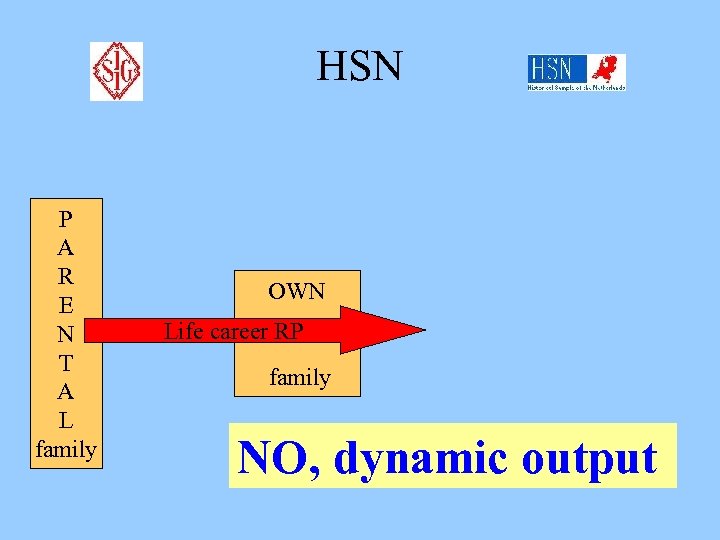
HSN P A R E N T A L family OWN Life career RP family NO, dynamic output
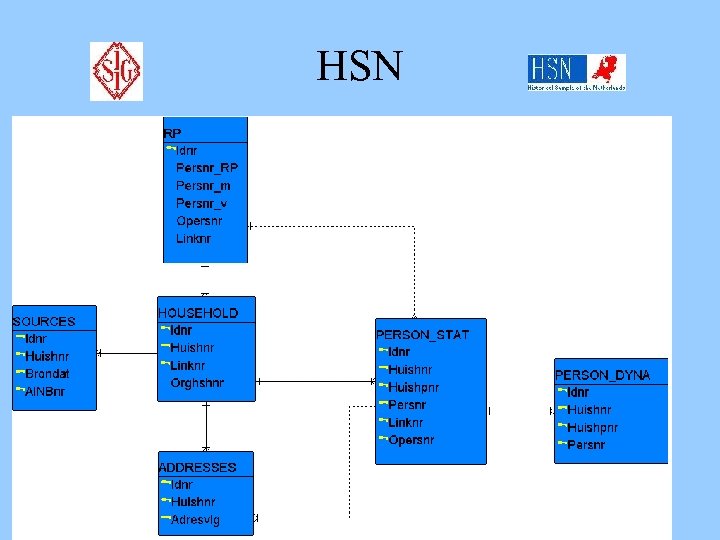
HSN
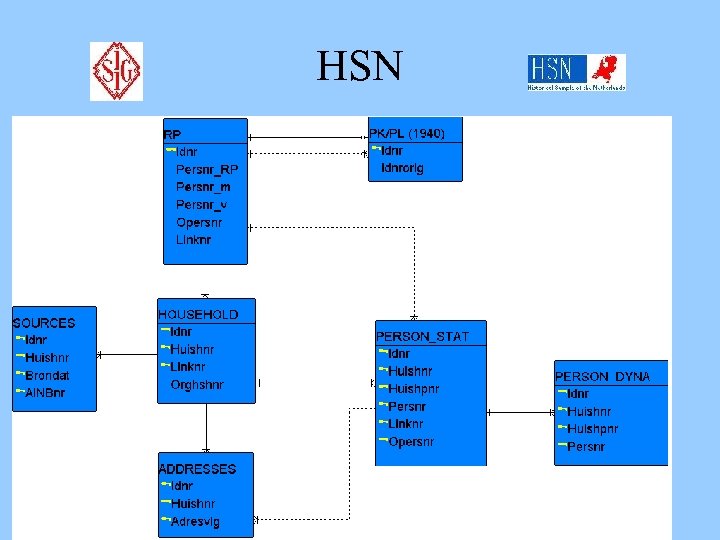
HSN
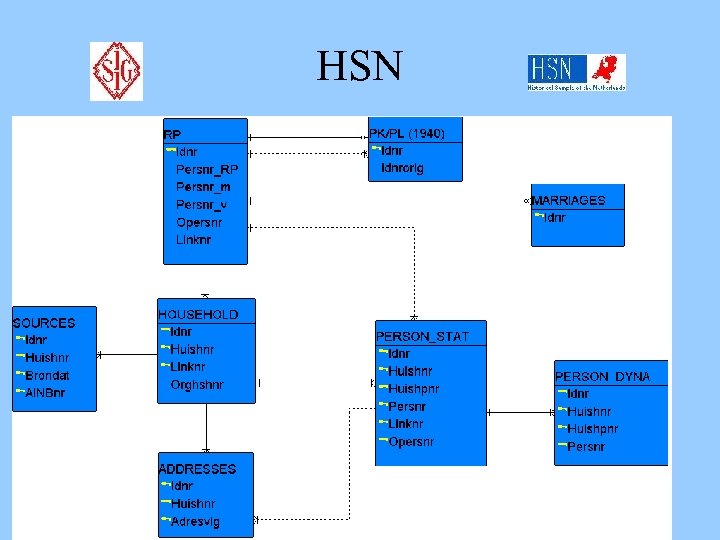
HSN
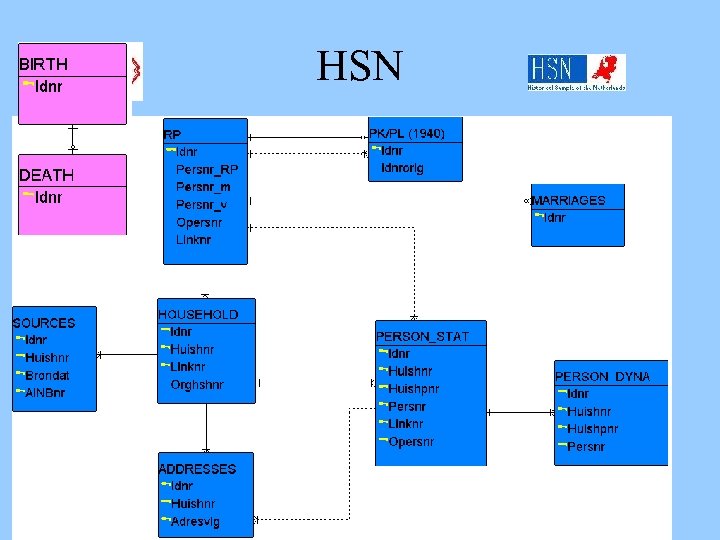
HSN
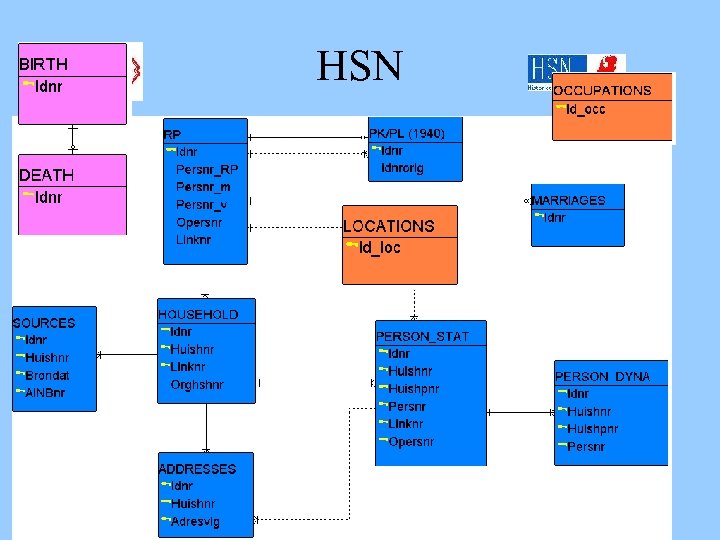
HSN

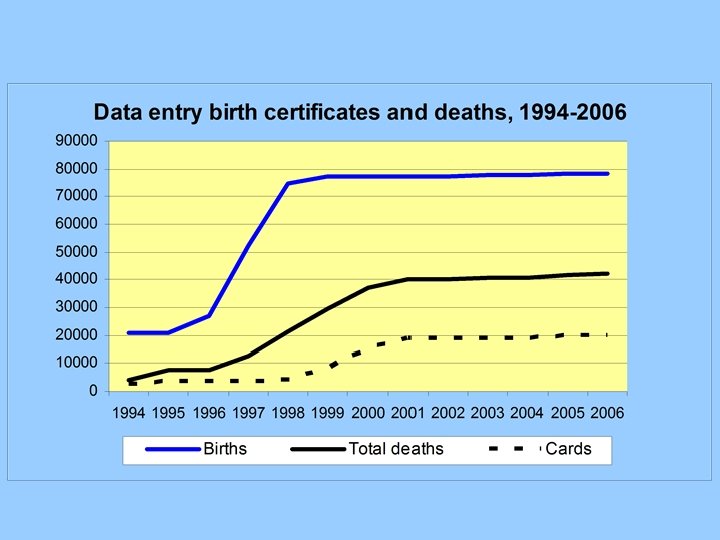
HSN Tough nuts Dynamic output Uncertain dates Cohort/period Definition household Linking research persons

Dynamic Output

HSN UNCERTAIN DATES

HSN Over 20 CODES on day number 33 Arrival date based on interpretation 35 Estimated declaration occupational title, religion e 36 42 Estimated change of address 44 Estimated departure (group departing) 45 46 Estimated departure (based on census date)

HSN COHORT & PERIOD
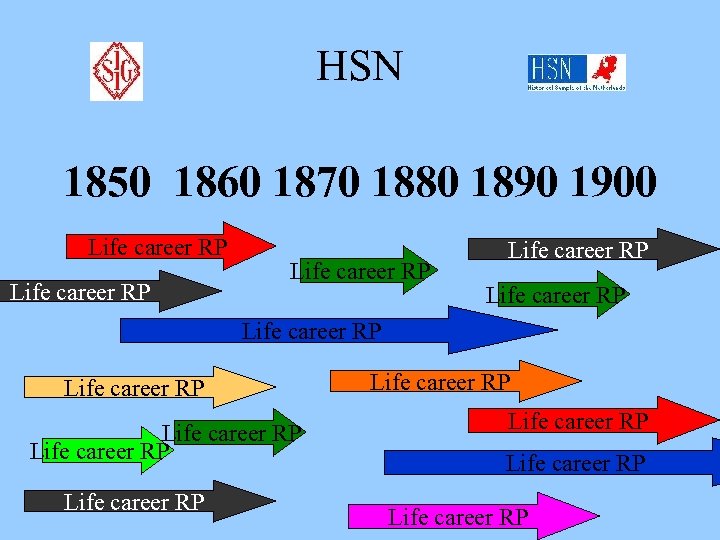
HSN 1850 1860 1870 1880 1890 1900 Life career RP Life career RP Life career RP Life career RP

HSN DEFINITION HOUSEHOLD or where is my RP?
HSN OWN P P A st R 1 eer R fe car family i E L N T A L family
HSN OWN P P A stif L R 1 e eer ca R fe car family ree i L r 2 E nd RP N OWN T A L family
HSN OWN P P A stif L R 1 e eer ca R fe car family P ree i L th R 3 r 2 E eer nd car RP ife N L OWN T A L family
HSN OWN P P A stif L R 1 e eer ca R fe car family ree i r 2 E L h RP nd eer 3 t a N c. Rr. P OWN Life OWN T family A L family

HSN Complicated but TWO SOLUTIONS Internationalising Simplifying
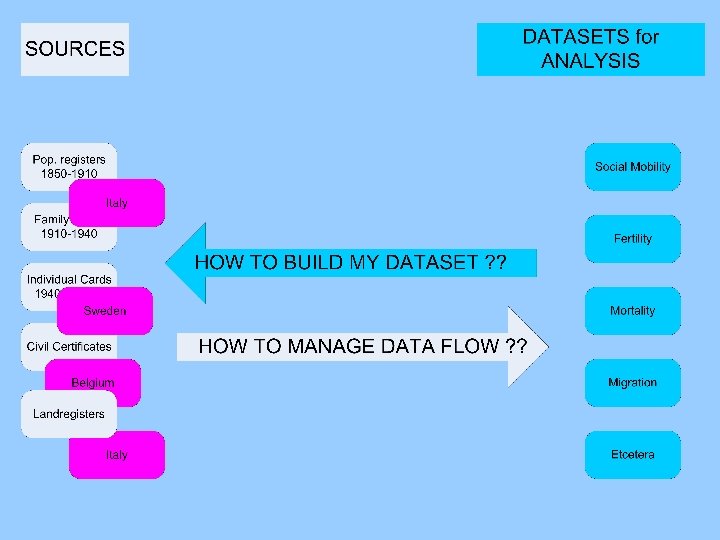
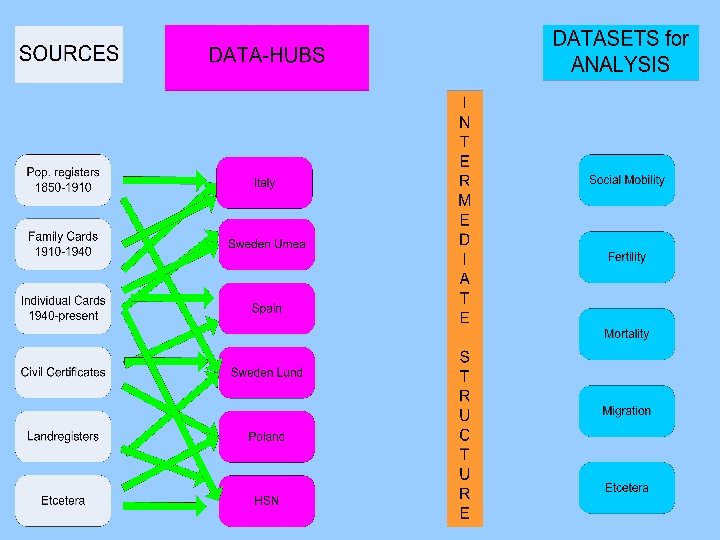
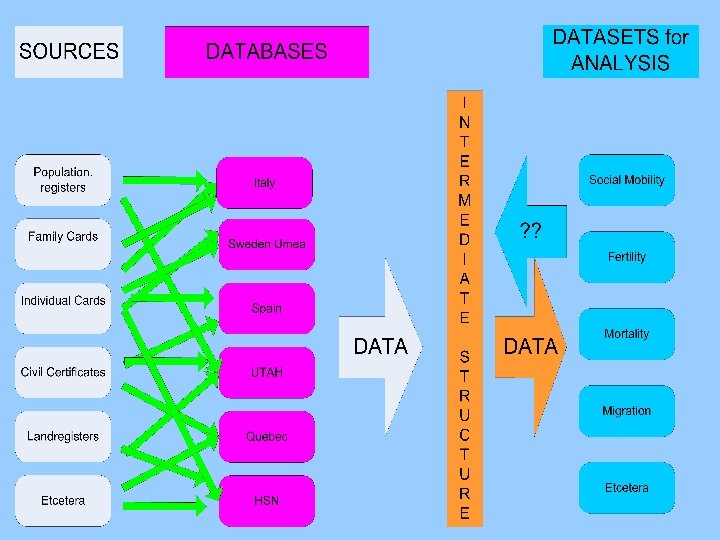
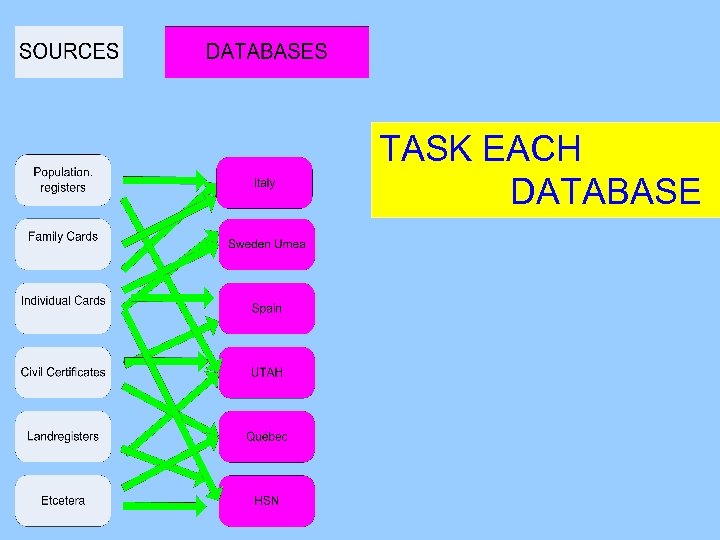
TASK EACH DATABASE
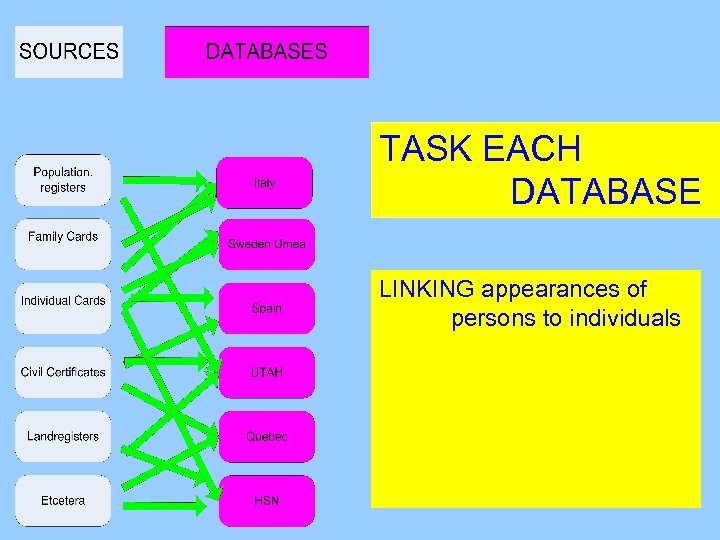
TASK EACH DATABASE LINKING appearances of persons to individuals
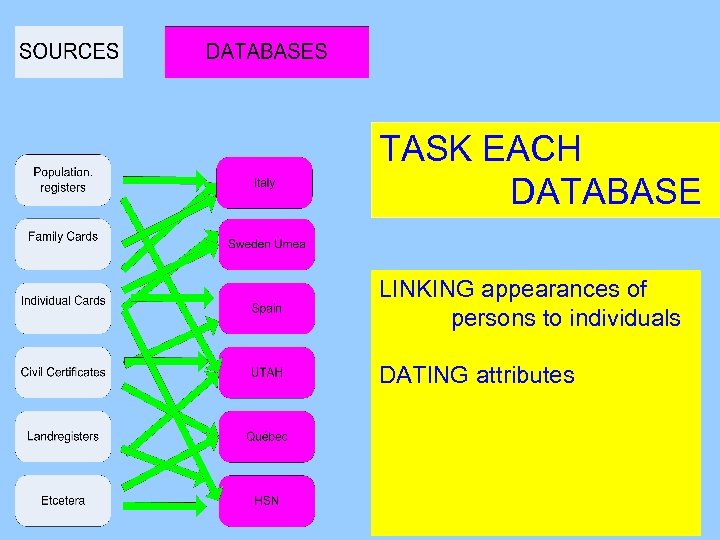
TASK EACH DATABASE LINKING appearances of persons to individuals DATING attributes
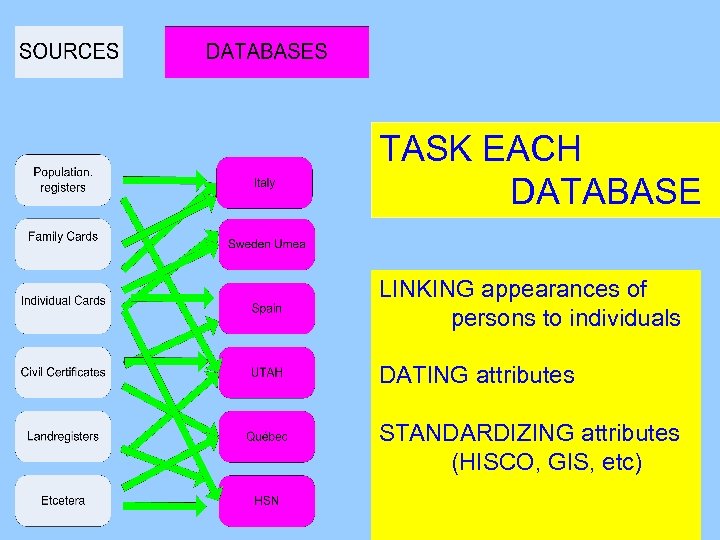
TASK EACH DATABASE LINKING appearances of persons to individuals DATING attributes STANDARDIZING attributes (HISCO, GIS, etc)
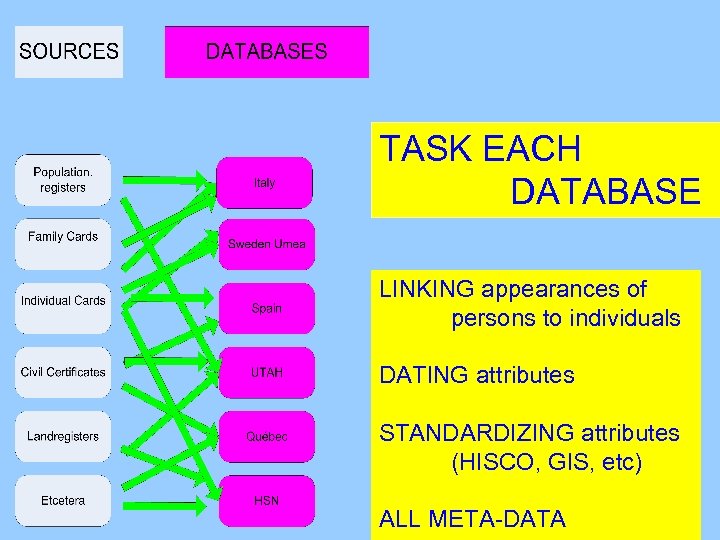
TASK EACH DATABASE LINKING appearances of persons to individuals DATING attributes STANDARDIZING attributes (HISCO, GIS, etc) ALL META-DATA
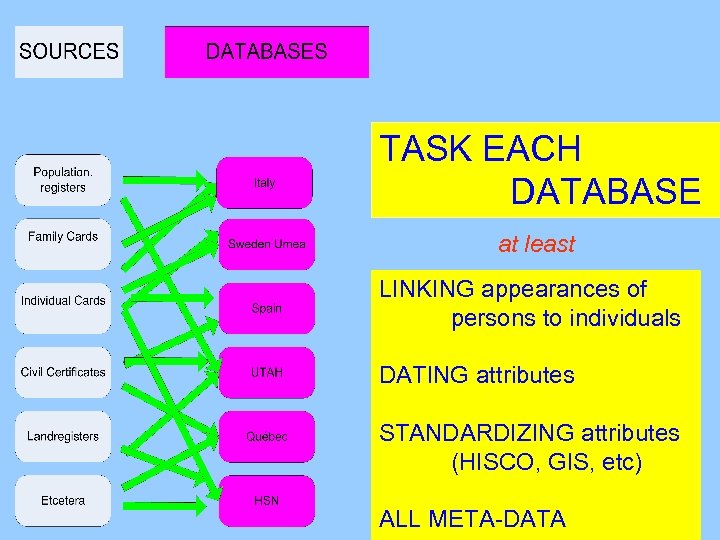
TASK EACH DATABASE at least LINKING appearances of persons to individuals DATING attributes STANDARDIZING attributes (HISCO, GIS, etc) ALL META-DATA

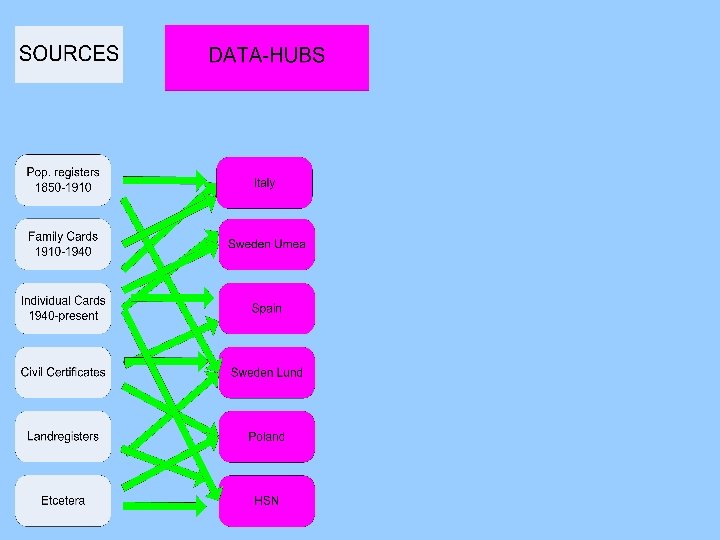
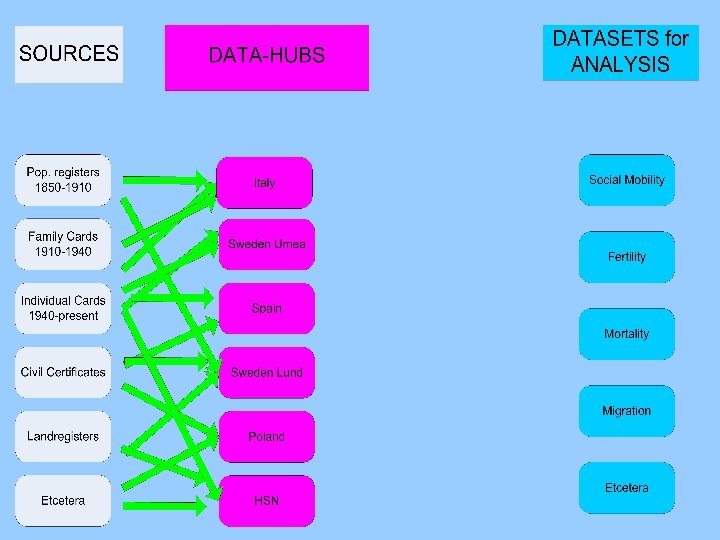
HSN Simplifying with HSN data-machine flat structure only main data no uncertainty documentation per variable
![HSN Simplifying HSN data machine with Umeå Historical Sample of Europe [Clio_infra project] HSN Simplifying HSN data machine with Umeå Historical Sample of Europe [Clio_infra project]](https://present5.com/presentation/f2b0083a751153b67bd22c0b0cf0dde8/image-103.jpg)
HSN Simplifying HSN data machine with Umeå Historical Sample of Europe [Clio_infra project]

Historical Sample of the Netherlands International Institute for Social History
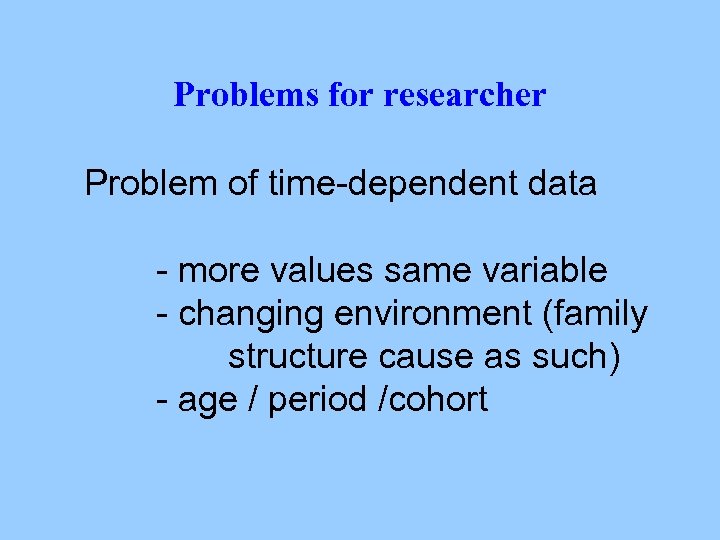
Problems for researcher Problem of time-dependent data - more values same variable - changing environment (family structure cause as such) - age / period /cohort

Problems for researcher. Selection (movers / stayers/ disappearing) . Fuzzy or no dating. Household definition. Multi-level data. Need for rectangularization. Analysing in a comparative way
f2b0083a751153b67bd22c0b0cf0dde8.ppt