1b1d7c4f2bcc94bbf9288c43a500d448.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Development and Health Singapore
Development and Health Singapore
 Introduction l l l Singapore is classed as a Developing Country or and ELDC. However, it is at the developed end of this classification. In other words it is very developed for a developing country. It is therefore a useful comparison allowing us to look at why developing countries have different levels of development.
Introduction l l l Singapore is classed as a Developing Country or and ELDC. However, it is at the developed end of this classification. In other words it is very developed for a developing country. It is therefore a useful comparison allowing us to look at why developing countries have different levels of development.
 BACKGROUND – Singapore/Bangladesh l Statistics: Singapore Total population: 4, 326, 000 l GDP per capita (Intl $, 2004): 28, 848 l Life expectancy at birth m/f (years): 77. 0/82. 0 l Healthy life expectancy at birth m/f (years, 2002): 68. 8/71. 3 l Child mortality m/f (per 1000): 4/3 l Adult mortality m/f (per 1000): 92/51 l l l Statistics: Total population: 141, 822, 000 l GDP per capita (Intl $, 2004): 2, 098 l Life expectancy at birth m/f (years): 62. 0/63. 0 l Healthy life expectancy at birth m/f (years, 2002): 55. 3/53. 3 l Child mortality m/f (per 1000): 81/73 l Adult mortality m/f (per 1000): 251/258 Total health expenditure per capita (Intl $, 2003): 1, 156 l Total health expenditure per capita (Intl $, 2003): 68 Figures are for 2004 unless indicated. Source: The world health report 2006 l Figures are for 2004 unless indicated. Source: The world health report 2006
BACKGROUND – Singapore/Bangladesh l Statistics: Singapore Total population: 4, 326, 000 l GDP per capita (Intl $, 2004): 28, 848 l Life expectancy at birth m/f (years): 77. 0/82. 0 l Healthy life expectancy at birth m/f (years, 2002): 68. 8/71. 3 l Child mortality m/f (per 1000): 4/3 l Adult mortality m/f (per 1000): 92/51 l l l Statistics: Total population: 141, 822, 000 l GDP per capita (Intl $, 2004): 2, 098 l Life expectancy at birth m/f (years): 62. 0/63. 0 l Healthy life expectancy at birth m/f (years, 2002): 55. 3/53. 3 l Child mortality m/f (per 1000): 81/73 l Adult mortality m/f (per 1000): 251/258 Total health expenditure per capita (Intl $, 2003): 1, 156 l Total health expenditure per capita (Intl $, 2003): 68 Figures are for 2004 unless indicated. Source: The world health report 2006 l Figures are for 2004 unless indicated. Source: The world health report 2006
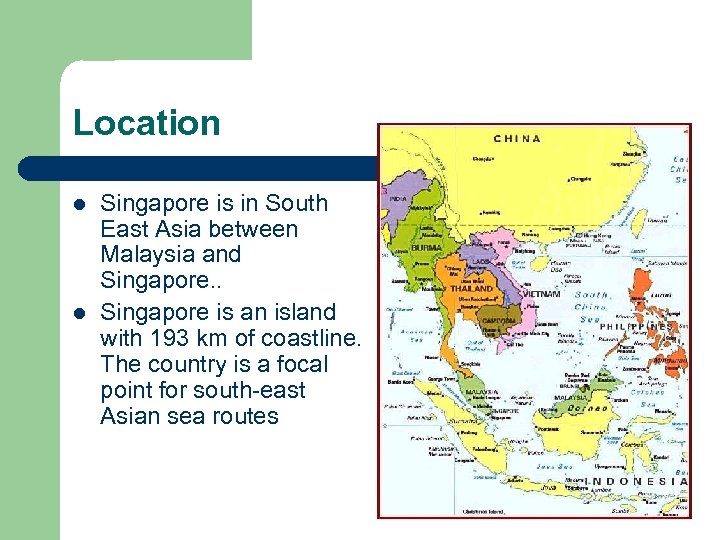 Location l l Singapore is in South East Asia between Malaysia and Singapore. . Singapore is an island with 193 km of coastline. The country is a focal point for south-east Asian sea routes
Location l l Singapore is in South East Asia between Malaysia and Singapore. . Singapore is an island with 193 km of coastline. The country is a focal point for south-east Asian sea routes
 History l l l Singapore was founded as a British Trading Colony in 1819. It became independent in 1965. It has subsequently become one of the world’s most prosperous countries with strong International Trading links. Its capita GDP is similar to that of a leading nation in Western Europe. HOW HAS THIS HAPPENED? ? ? ?
History l l l Singapore was founded as a British Trading Colony in 1819. It became independent in 1965. It has subsequently become one of the world’s most prosperous countries with strong International Trading links. Its capita GDP is similar to that of a leading nation in Western Europe. HOW HAS THIS HAPPENED? ? ? ?
 Challenges l l l A small county with no natural resources. High Unemployment rate. A small manufacturing base.
Challenges l l l A small county with no natural resources. High Unemployment rate. A small manufacturing base.
 Code to development l l l l C - CLIMATE H – HISTORY I - INFRASTRUCTURE P – GEOGRAPHICAL POSITION/market P – POPULATION N – NATURAL RESOURCES/industry G – GOVERNMENT
Code to development l l l l C - CLIMATE H – HISTORY I - INFRASTRUCTURE P – GEOGRAPHICAL POSITION/market P – POPULATION N – NATURAL RESOURCES/industry G – GOVERNMENT
 CLIMATE l l A tropical climate with two distinct monsoon seasons. No natural climatic hazards.
CLIMATE l l A tropical climate with two distinct monsoon seasons. No natural climatic hazards.
 HISTORY l l l As a British Trading Colony Singapore had a head start in development. The modern history of Singapore began in 1819 when Englishman Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles established a British port on the island Infrastructure, education and health was established quickly during this period.
HISTORY l l l As a British Trading Colony Singapore had a head start in development. The modern history of Singapore began in 1819 when Englishman Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles established a British port on the island Infrastructure, education and health was established quickly during this period.
 INFRASTRUCTURE l l Excellent transport links. Sea and Air facilities are world class. Investment in airport and port expansion by government. Main stop off for flights to Australia.
INFRASTRUCTURE l l Excellent transport links. Sea and Air facilities are world class. Investment in airport and port expansion by government. Main stop off for flights to Australia.
 GEOGRAPHCIAL POSITION l l Singapore’s location is key to its economic success. It has a strategic position on the trade routed between India and China. It is the centre for export of rubber and tin from Malaysia. It is the busiest port in the world in terms of tonnage.
GEOGRAPHCIAL POSITION l l Singapore’s location is key to its economic success. It has a strategic position on the trade routed between India and China. It is the centre for export of rubber and tin from Malaysia. It is the busiest port in the world in terms of tonnage.
 POPULATION l l l Highly skilled and trained workforce. Low population growth. Lack of ethnic conflict. Strong sense of national identity. Entrepreneurial population.
POPULATION l l l Highly skilled and trained workforce. Low population growth. Lack of ethnic conflict. Strong sense of national identity. Entrepreneurial population.
 Natural Resources l l Naturally deep water ports. Reclaimed flat land. No natural resources for exploitation by MEDC’S. Singapore has an open entrepreneurial economy with strong service and manufacturing sectors
Natural Resources l l Naturally deep water ports. Reclaimed flat land. No natural resources for exploitation by MEDC’S. Singapore has an open entrepreneurial economy with strong service and manufacturing sectors
 Government l l l Free trade. Investment laws to attract foreign investment. Government organisations to promote trade, infrastructure and education. Corrupt free government Political stability
Government l l l Free trade. Investment laws to attract foreign investment. Government organisations to promote trade, infrastructure and education. Corrupt free government Political stability


