e89e2d491f743366aadffe35ec46e656.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Developing Secure, Multi-lateral Peer to Peer SIP Applications Jim. Dalton@Trans. Nexus. com
Developing Secure, Multi-lateral Peer to Peer SIP Applications Jim. Dalton@Trans. Nexus. com
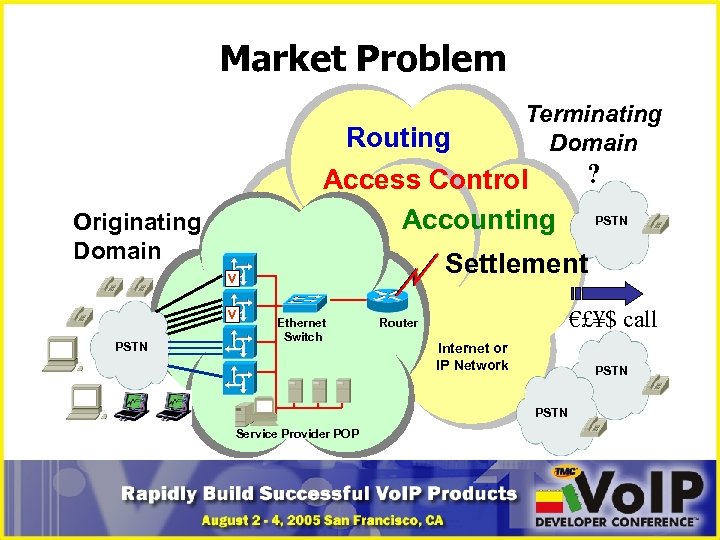 Market Problem Routing Access Control Accounting Originating Domain V ? PSTN Settlement V PSTN Terminating Domain Ethernet Switch €£¥$ call Router Internet or IP Network PSTN Service Provider POP
Market Problem Routing Access Control Accounting Originating Domain V ? PSTN Settlement V PSTN Terminating Domain Ethernet Switch €£¥$ call Router Internet or IP Network PSTN Service Provider POP
 Current Status of Peering • Ad hoc bilateral peering arrangements • ENUM provides a solution for peer to peer route discovery But how to handle? o o o Inter-domain Access control Accounting Settlement disputes Backwards compatibility with Operations and Billing Support Systems for H. 323 networks Evolution to new services
Current Status of Peering • Ad hoc bilateral peering arrangements • ENUM provides a solution for peer to peer route discovery But how to handle? o o o Inter-domain Access control Accounting Settlement disputes Backwards compatibility with Operations and Billing Support Systems for H. 323 networks Evolution to new services
 Benefits of secure multi-lateral peering • Efficient peer to peer communications eliminates signaling bottlenecks • Access control is greatly simplified o o IP access lists are eliminated Asymmetric key management is simpler and more secure than shared secrets • Eliminates costly overhead of managing many bilateral interconnect agreements
Benefits of secure multi-lateral peering • Efficient peer to peer communications eliminates signaling bottlenecks • Access control is greatly simplified o o IP access lists are eliminated Asymmetric key management is simpler and more secure than shared secrets • Eliminates costly overhead of managing many bilateral interconnect agreements
 Solution: Open Settlement Protocol • Open Settlement Protocol (OSP): o o o Global standard for inter-domain transaction authorization and usage reporting. Developed by ETSI in 1998, now in version 4. 1. 1 Based on existing standards Uses Asymmetric Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) services for non-repudiation of transactions Broad support: Asterisk, SER, Cisco, Alcatel, Radvision, UTStarcom, Mediaring, ISDN Communications, Veraz, Vovida, Teles Protocol Independent • Works with SIP, H. 323, SMS, MMS, IAX …
Solution: Open Settlement Protocol • Open Settlement Protocol (OSP): o o o Global standard for inter-domain transaction authorization and usage reporting. Developed by ETSI in 1998, now in version 4. 1. 1 Based on existing standards Uses Asymmetric Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) services for non-repudiation of transactions Broad support: Asterisk, SER, Cisco, Alcatel, Radvision, UTStarcom, Mediaring, ISDN Communications, Veraz, Vovida, Teles Protocol Independent • Works with SIP, H. 323, SMS, MMS, IAX …
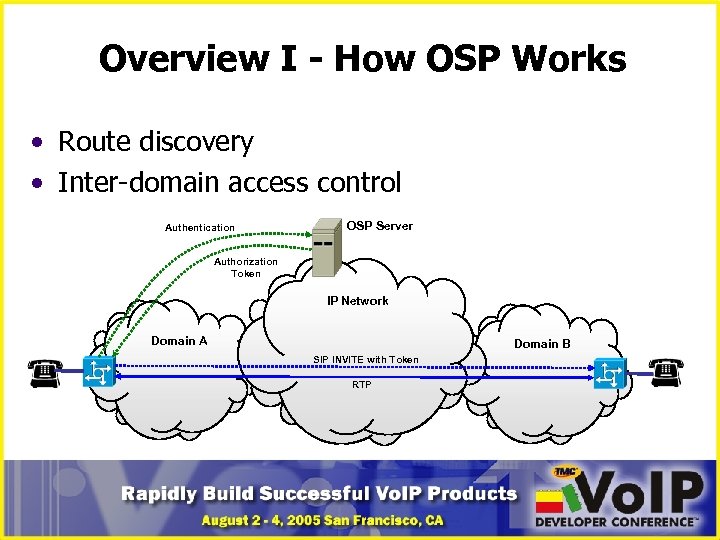 Overview I - How OSP Works • Route discovery • Inter-domain access control Authentication OSP Server Authorization Token IP Network Domain A Domain B SIP INVITE with Token RTP
Overview I - How OSP Works • Route discovery • Inter-domain access control Authentication OSP Server Authorization Token IP Network Domain A Domain B SIP INVITE with Token RTP
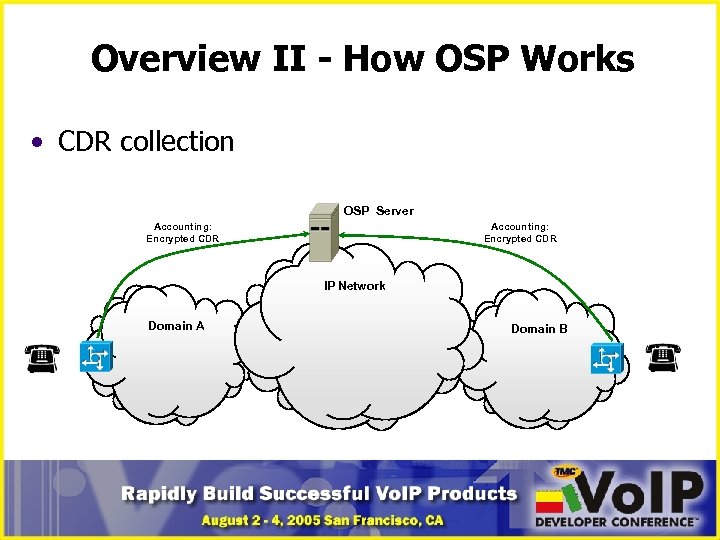 Overview II - How OSP Works • CDR collection OSP Server Accounting: Encrypted CDR IP Network Domain A Domain B
Overview II - How OSP Works • CDR collection OSP Server Accounting: Encrypted CDR IP Network Domain A Domain B
 The Basics of Public-key Cryptosystems Security services between parties rely on exchange of public keys and security of private keys. Critical Points: • Public / Private keys used for encryption / decryption and digital signatures • Public keys are public – easy to distribute • A digital certificate signed by a trusted 3 rd party ensures the public-key is legitimate • Digital signatures provide data integrity, authentication and non-repudiation • Certificates may be chained from a root authority
The Basics of Public-key Cryptosystems Security services between parties rely on exchange of public keys and security of private keys. Critical Points: • Public / Private keys used for encryption / decryption and digital signatures • Public keys are public – easy to distribute • A digital certificate signed by a trusted 3 rd party ensures the public-key is legitimate • Digital signatures provide data integrity, authentication and non-repudiation • Certificates may be chained from a root authority
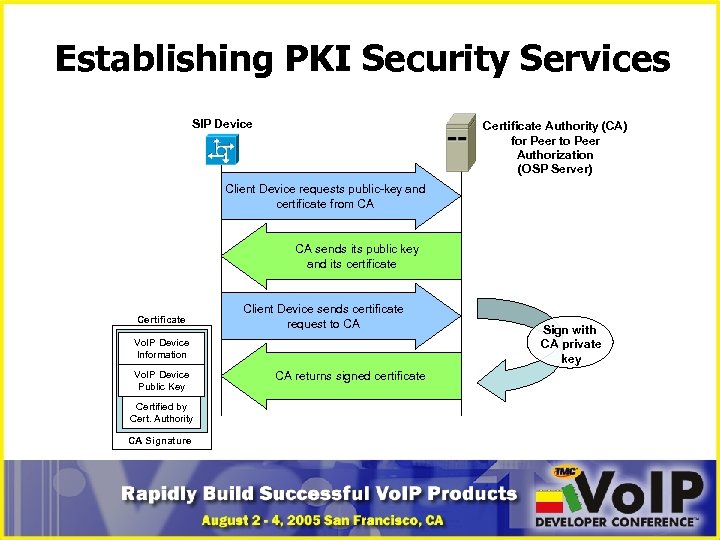 Establishing PKI Security Services SIP Device Certificate Authority (CA) for Peer to Peer Authorization (OSP Server) Client Device requests public-key and certificate from CA CA sends its public key and its certificate Client Device sends certificate request to CA Vo. IP Device Information Vo. IP Device Public Key Certified by Cert. Authority CA Signature CA returns signed certificate Sign with CA private key
Establishing PKI Security Services SIP Device Certificate Authority (CA) for Peer to Peer Authorization (OSP Server) Client Device requests public-key and certificate from CA CA sends its public key and its certificate Client Device sends certificate request to CA Vo. IP Device Information Vo. IP Device Public Key Certified by Cert. Authority CA Signature CA returns signed certificate Sign with CA private key
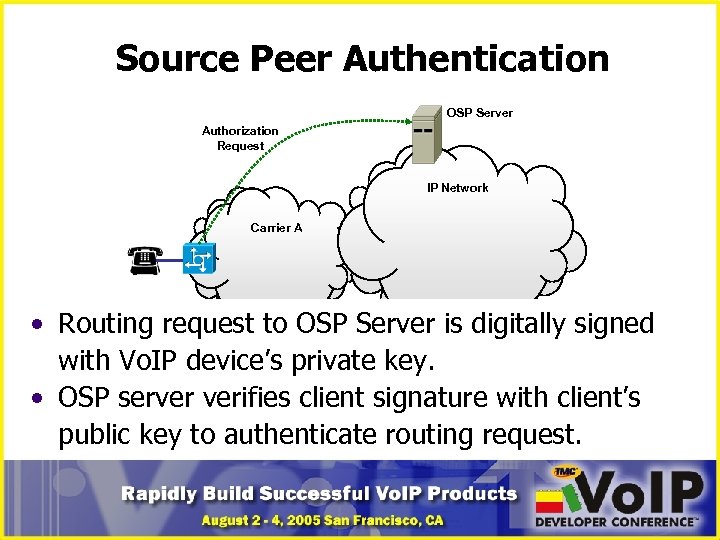 Source Peer Authentication OSP Server Authorization Request IP Network Carrier A • Routing request to OSP Server is digitally signed with Vo. IP device’s private key. • OSP server verifies client signature with client’s public key to authenticate routing request.
Source Peer Authentication OSP Server Authorization Request IP Network Carrier A • Routing request to OSP Server is digitally signed with Vo. IP device’s private key. • OSP server verifies client signature with client’s public key to authenticate routing request.
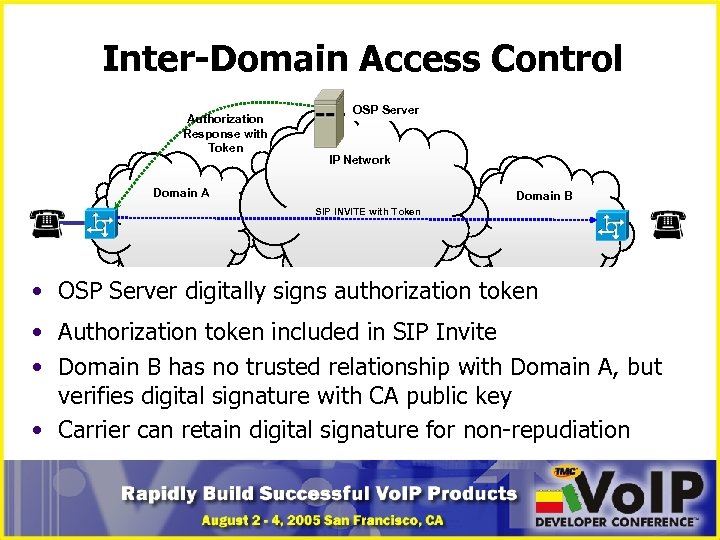 Inter-Domain Access Control Authorization Response with Token OSP Server IP Network Domain A Domain B SIP INVITE with Token • OSP Server digitally signs authorization token • Authorization token included in SIP Invite • Domain B has no trusted relationship with Domain A, but verifies digital signature with CA public key • Carrier can retain digital signature for non-repudiation
Inter-Domain Access Control Authorization Response with Token OSP Server IP Network Domain A Domain B SIP INVITE with Token • OSP Server digitally signs authorization token • Authorization token included in SIP Invite • Domain B has no trusted relationship with Domain A, but verifies digital signature with CA public key • Carrier can retain digital signature for non-repudiation
 Authorization Token • Destination o IP address, domain name, sip uri, tel uri, E 164, trunk group • Destination Protocol o • • • SIP, Q 931, H 323 -LRQ, IAX, other Transaction ID Service Type, Bandwidth, Number of Channels Call ID, Session ID, Multi. Session ID Valid after – Valid Until Authorized amount o Seconds, packets, bytes, pages, call, session, price, currency • Authority URL
Authorization Token • Destination o IP address, domain name, sip uri, tel uri, E 164, trunk group • Destination Protocol o • • • SIP, Q 931, H 323 -LRQ, IAX, other Transaction ID Service Type, Bandwidth, Number of Channels Call ID, Session ID, Multi. Session ID Valid after – Valid Until Authorized amount o Seconds, packets, bytes, pages, call, session, price, currency • Authority URL
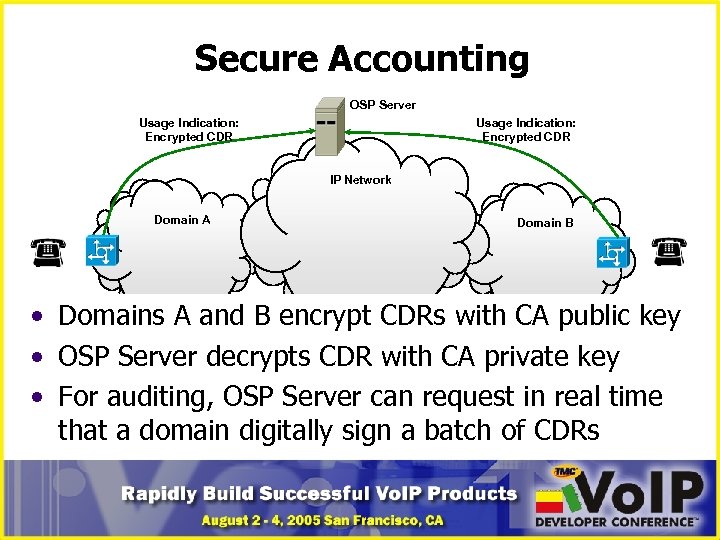 Secure Accounting OSP Server Usage Indication: Encrypted CDR IP Network Domain A Domain B • Domains A and B encrypt CDRs with CA public key • OSP Server decrypts CDR with CA private key • For auditing, OSP Server can request in real time that a domain digitally sign a batch of CDRs
Secure Accounting OSP Server Usage Indication: Encrypted CDR IP Network Domain A Domain B • Domains A and B encrypt CDRs with CA public key • OSP Server decrypts CDR with CA private key • For auditing, OSP Server can request in real time that a domain digitally sign a batch of CDRs
 Capabilities & Pricing Messages • OSP enables clients to update OSP server database in real time. • Capabilities Exchange messages can be used o o o To indicate service features available To indicate bandwidth or channel available To indicate presence • Pricing Indication is used to provide rate changes o o for services (voice, fax, message, video …) based on seconds, pages, bytes, packets and currency
Capabilities & Pricing Messages • OSP enables clients to update OSP server database in real time. • Capabilities Exchange messages can be used o o o To indicate service features available To indicate bandwidth or channel available To indicate presence • Pricing Indication is used to provide rate changes o o for services (voice, fax, message, video …) based on seconds, pages, bytes, packets and currency
 Examples of OSP Peering • • Enterprise Vo. IP VPN Wholesale Inter-Carrier Vo. IP Services Tiered Peering Dundi Settlement Clearinghouse
Examples of OSP Peering • • Enterprise Vo. IP VPN Wholesale Inter-Carrier Vo. IP Services Tiered Peering Dundi Settlement Clearinghouse
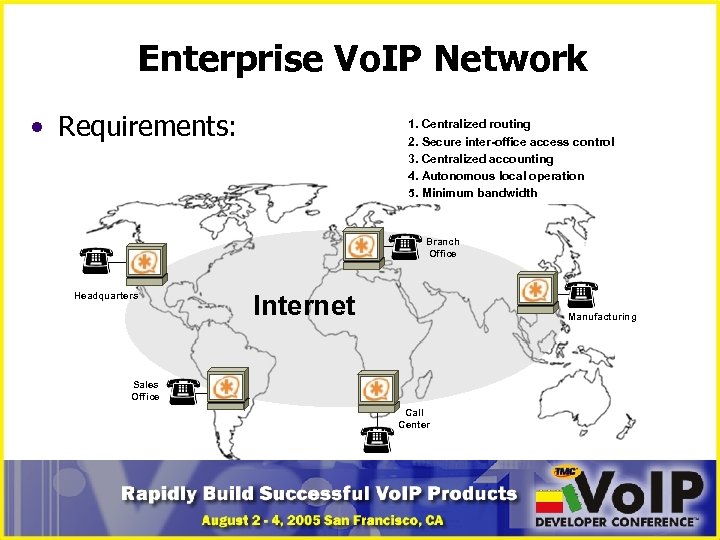 Enterprise Vo. IP Network • Requirements: 1. Centralized routing 2. Secure inter-office access control 3. Centralized accounting 4. Autonomous local operation 5. Minimum bandwidth 2. 4. Autonomous local operation 5. Minimum bandwidth 3. Centralized accounting 1. Secure inter-office access control routing Branch Office Headquarters Internet Manufacturing Sales Office Call Center
Enterprise Vo. IP Network • Requirements: 1. Centralized routing 2. Secure inter-office access control 3. Centralized accounting 4. Autonomous local operation 5. Minimum bandwidth 2. 4. Autonomous local operation 5. Minimum bandwidth 3. Centralized accounting 1. Secure inter-office access control routing Branch Office Headquarters Internet Manufacturing Sales Office Call Center
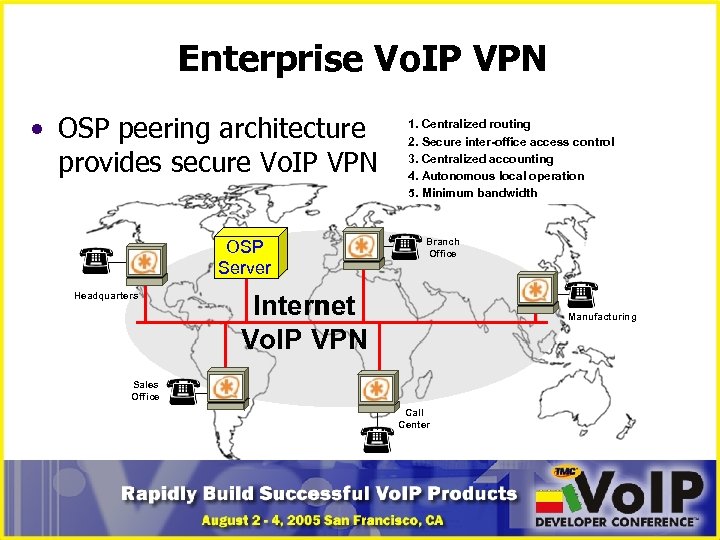 Enterprise Vo. IP VPN • OSP peering architecture provides secure Vo. IP VPN OSP Server Headquarters 1. Centralized routing 2. Secure inter-office access control 3. Centralized accounting 4. Autonomous local operation 5. Minimum bandwidth Branch Office Internet Vo. IP VPN Manufacturing Sales Office Call Center
Enterprise Vo. IP VPN • OSP peering architecture provides secure Vo. IP VPN OSP Server Headquarters 1. Centralized routing 2. Secure inter-office access control 3. Centralized accounting 4. Autonomous local operation 5. Minimum bandwidth Branch Office Internet Vo. IP VPN Manufacturing Sales Office Call Center
 Wholesale Inter-Carrier Services • Challenge: How to manage interconnect access and billing among thousands of ITSP peers Internet
Wholesale Inter-Carrier Services • Challenge: How to manage interconnect access and billing among thousands of ITSP peers Internet
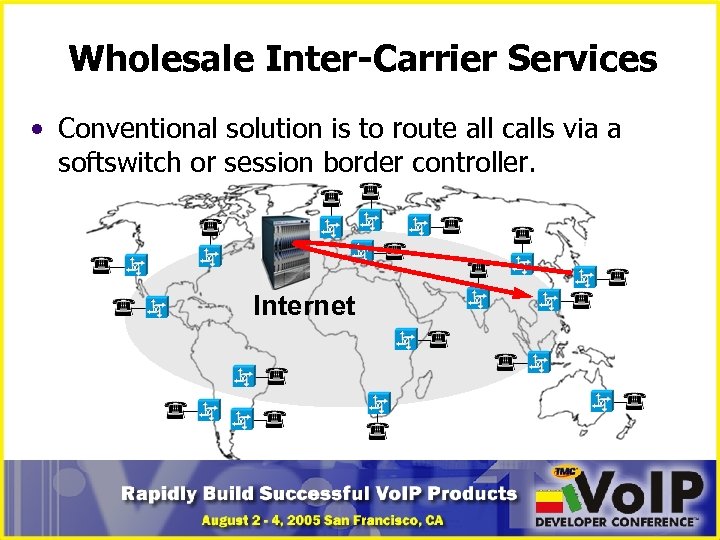 Wholesale Inter-Carrier Services • Conventional solution is to route all calls via a softswitch or session border controller. Internet
Wholesale Inter-Carrier Services • Conventional solution is to route all calls via a softswitch or session border controller. Internet
 Wholesale Inter-Carrier Services • Direct peering with OSP is more scalable, more reliable, better Qo. S, less bandwidth, lower cost. OSP OSP Server Internet Route Lookup
Wholesale Inter-Carrier Services • Direct peering with OSP is more scalable, more reliable, better Qo. S, less bandwidth, lower cost. OSP OSP Server Internet Route Lookup
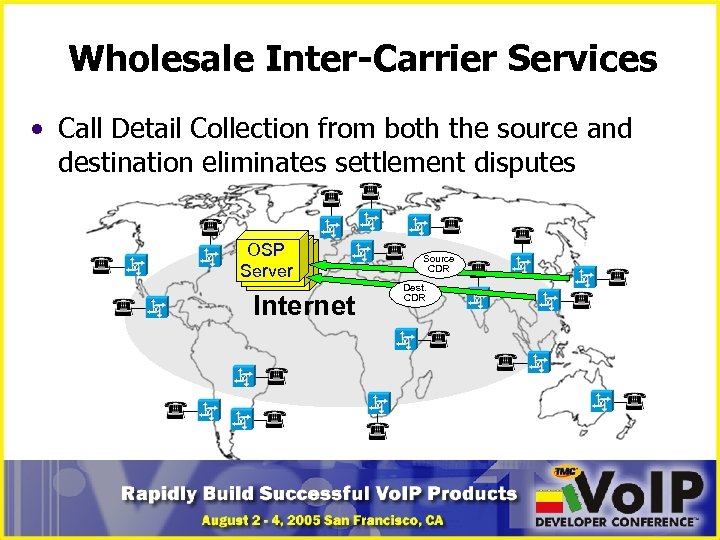 Wholesale Inter-Carrier Services • Call Detail Collection from both the source and destination eliminates settlement disputes OSP OSP Server Internet Source CDR Dest. CDR
Wholesale Inter-Carrier Services • Call Detail Collection from both the source and destination eliminates settlement disputes OSP OSP Server Internet Source CDR Dest. CDR
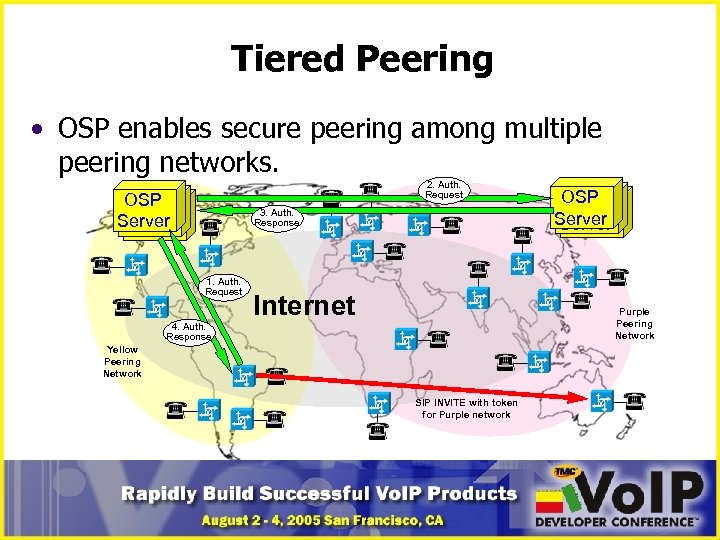 Tiered Peering • OSP enables secure peering among multiple peering networks. 2. Auth. Request OSP OSP Server 3. Auth. Response 1. Auth. Request Internet OSP OSP Server Purple Peering Network 4. Auth. Response Yellow Peering Network SIP INVITE with token for Purple network
Tiered Peering • OSP enables secure peering among multiple peering networks. 2. Auth. Request OSP OSP Server 3. Auth. Response 1. Auth. Request Internet OSP OSP Server Purple Peering Network 4. Auth. Response Yellow Peering Network SIP INVITE with token for Purple network
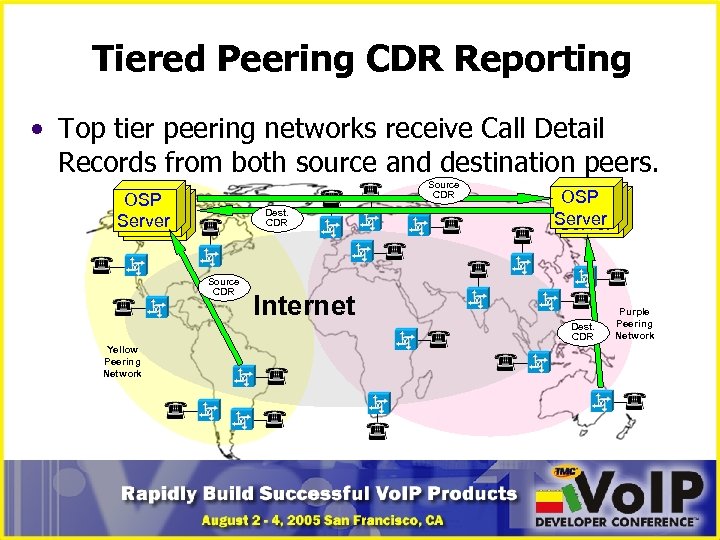 Tiered Peering CDR Reporting • Top tier peering networks receive Call Detail Records from both source and destination peers. Source CDR OSP OSP Server Dest. CDR Source CDR OSP OSP Server Internet Dest. CDR Yellow Peering Network Purple Peering Network
Tiered Peering CDR Reporting • Top tier peering networks receive Call Detail Records from both source and destination peers. Source CDR OSP OSP Server Dest. CDR Source CDR OSP OSP Server Internet Dest. CDR Yellow Peering Network Purple Peering Network
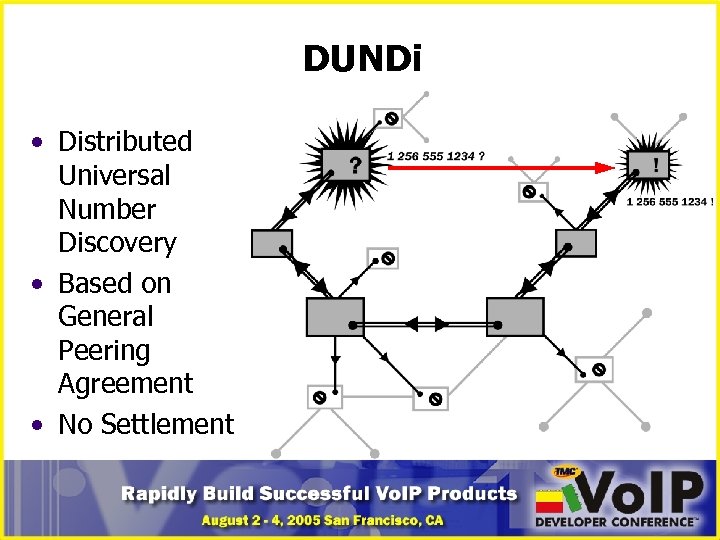 DUNDi • Distributed Universal Number Discovery • Based on General Peering Agreement • No Settlement
DUNDi • Distributed Universal Number Discovery • Based on General Peering Agreement • No Settlement
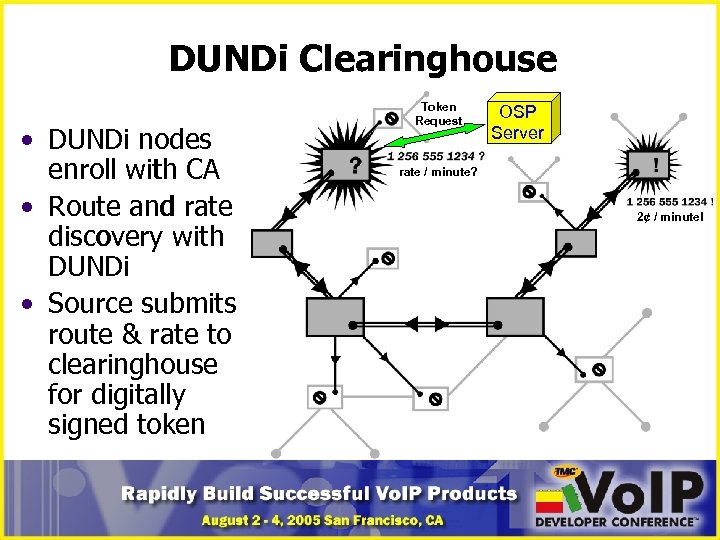 DUNDi Clearinghouse • DUNDi nodes enroll with CA • Route and rate discovery with DUNDi • Source submits route & rate to clearinghouse for digitally signed token Token Request OSP Server rate / minute? 2¢ / minute!
DUNDi Clearinghouse • DUNDi nodes enroll with CA • Route and rate discovery with DUNDi • Source submits route & rate to clearinghouse for digitally signed token Token Request OSP Server rate / minute? 2¢ / minute!
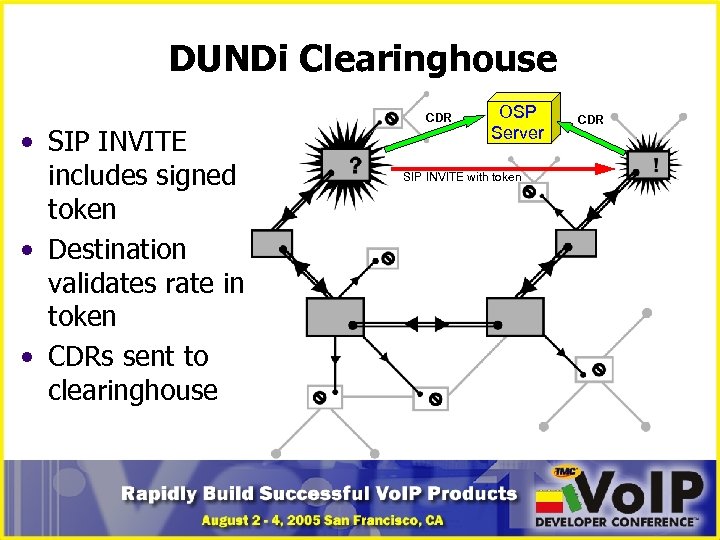 DUNDi Clearinghouse • SIP INVITE includes signed token • Destination validates rate in token • CDRs sent to clearinghouse CDR OSP Server SIP INVITE with token CDR
DUNDi Clearinghouse • SIP INVITE includes signed token • Destination validates rate in token • CDRs sent to clearinghouse CDR OSP Server SIP INVITE with token CDR
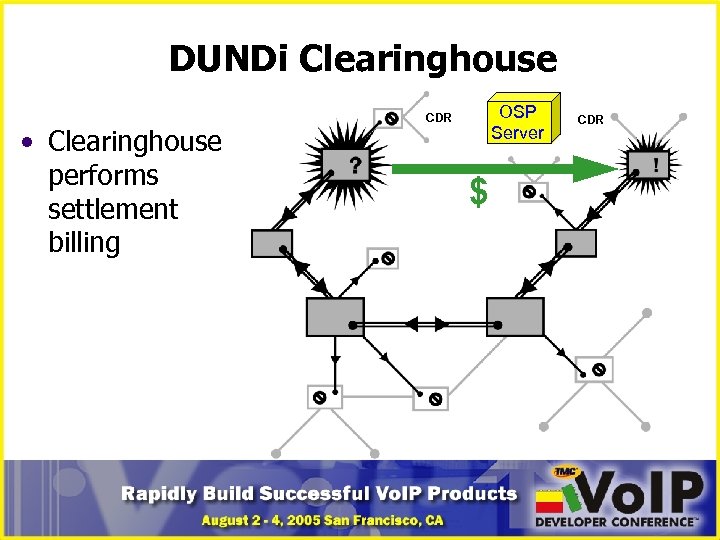 DUNDi Clearinghouse • Clearinghouse performs settlement billing OSP Server CDR $ CDR
DUNDi Clearinghouse • Clearinghouse performs settlement billing OSP Server CDR $ CDR
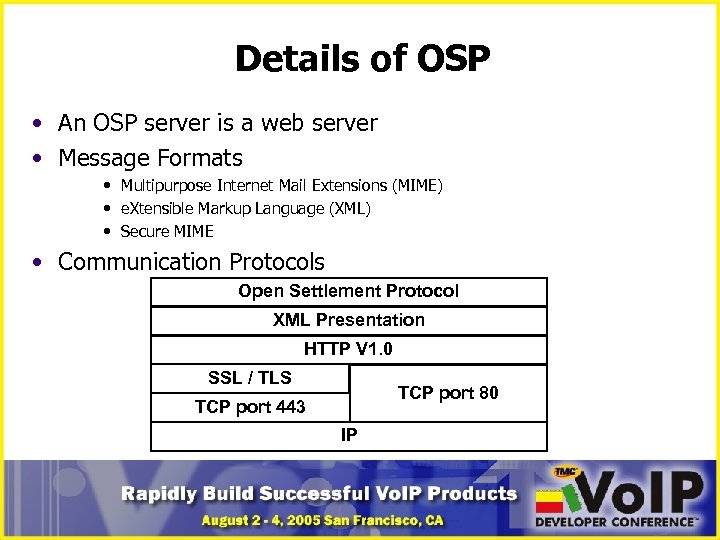 Details of OSP • An OSP server is a web server • Message Formats • Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) • e. Xtensible Markup Language (XML) • Secure MIME • Communication Protocols Open Settlement Protocol XML Presentation HTTP V 1. 0 SSL / TLS TCP port 80 TCP port 443 IP
Details of OSP • An OSP server is a web server • Message Formats • Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) • e. Xtensible Markup Language (XML) • Secure MIME • Communication Protocols Open Settlement Protocol XML Presentation HTTP V 1. 0 SSL / TLS TCP port 80 TCP port 443 IP
 OSP Message Example HTTP/1. 1 200 OK Server: IP address of OSP server Date: Thu, 12 May 2005 18: 32: 59 GMT Connection: Keep-Alive: timeout=3600, max=5000 Content-Length: 1996 Content-Type: text/plain HTTP Header
OSP Message Example HTTP/1. 1 200 OK Server: IP address of OSP server Date: Thu, 12 May 2005 18: 32: 59 GMT Connection: Keep-Alive: timeout=3600, max=5000 Content-Length: 1996 Content-Type: text/plain HTTP Header
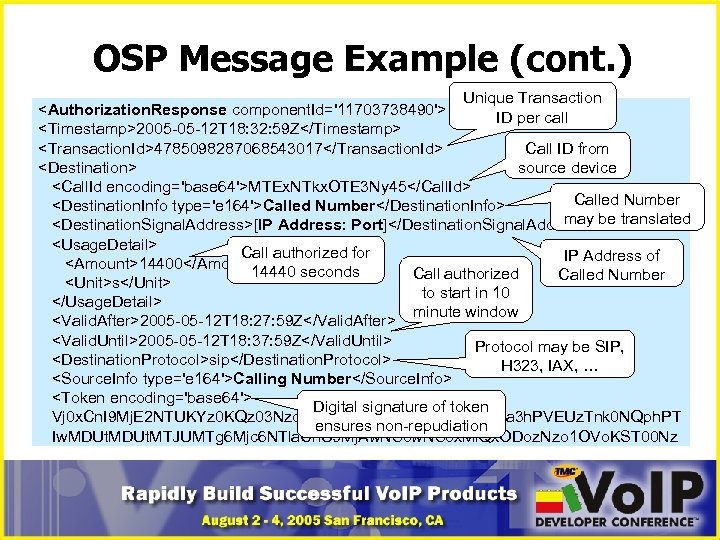 OSP Message Example (cont. ) Unique Transaction
OSP Message Example (cont. ) Unique Transaction
 Open Source Tools • www. SIPfoundry. org o o o OSP Toolkit (client) Open. OSP Server (based on Apache) RAMS OSP Server • www. Asterisk. org o Asterisk includes OSP client • OSP Module for SIP Express Router o http: //osp-module. berlios. de • www. voxgratia. org o OSP enabled H 323 proxy (future support for SIP) • www. Trans. Nexus. com o OSPrey – free OSP server
Open Source Tools • www. SIPfoundry. org o o o OSP Toolkit (client) Open. OSP Server (based on Apache) RAMS OSP Server • www. Asterisk. org o Asterisk includes OSP client • OSP Module for SIP Express Router o http: //osp-module. berlios. de • www. voxgratia. org o OSP enabled H 323 proxy (future support for SIP) • www. Trans. Nexus. com o OSPrey – free OSP server


