e1d3c609814360d27fc0ae782c9e69e0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Developing long acting agonists and antagonists of glycoprotein hormones using gene fusion and gene transfer: from bench to clinics Prof. Fuad Fares University of Haifa 2 nd International conference on Endocrinology Chicago October 2014
Developing long acting agonists and antagonists of glycoprotein hormones using gene fusion and gene transfer: from bench to clinics Prof. Fuad Fares University of Haifa 2 nd International conference on Endocrinology Chicago October 2014
 Structure-Function studies Using site-directed mutagenesis and gene transfer Development of new analogs
Structure-Function studies Using site-directed mutagenesis and gene transfer Development of new analogs
 Therapeutical Recombinant proteins n 1978 Human Growth Hormone n 1979 Human Insulin
Therapeutical Recombinant proteins n 1978 Human Growth Hormone n 1979 Human Insulin
 The Problem Most therapeutic proteins are <30 k. D and hence: • Are filtered out quickly by the kidneys Are taken up by the liver and cleaved enzymatically § § § Have to be injected frequently for optimal therapy Cause adverse effects due to peak dose injection
The Problem Most therapeutic proteins are <30 k. D and hence: • Are filtered out quickly by the kidneys Are taken up by the liver and cleaved enzymatically § § § Have to be injected frequently for optimal therapy Cause adverse effects due to peak dose injection
 Success of Long-Lasting Proteins § PEGylation - Interferon (SGP/Roche) § § § PEGylation - GCSF (Amgen) § § § PEGIntron/Pegasys $3. 2 billion in sales in 2006 Neulasta $2. 5 billion in sales in 2006 Hyper Glycosylation - EPO (Amgen) § § Aranesp (DNA Modifications) $3. 9 billion in sales in 2006
Success of Long-Lasting Proteins § PEGylation - Interferon (SGP/Roche) § § § PEGylation - GCSF (Amgen) § § § PEGIntron/Pegasys $3. 2 billion in sales in 2006 Neulasta $2. 5 billion in sales in 2006 Hyper Glycosylation - EPO (Amgen) § § Aranesp (DNA Modifications) $3. 9 billion in sales in 2006
 Structure-Function of Glycoprotein Hormones n FSH - Human Stimulating Hormone n LH - Luteinizing Hormone n h. CG - Human Chorionic Gonadotropin n TSH - Thyrotropin Hormone
Structure-Function of Glycoprotein Hormones n FSH - Human Stimulating Hormone n LH - Luteinizing Hormone n h. CG - Human Chorionic Gonadotropin n TSH - Thyrotropin Hormone
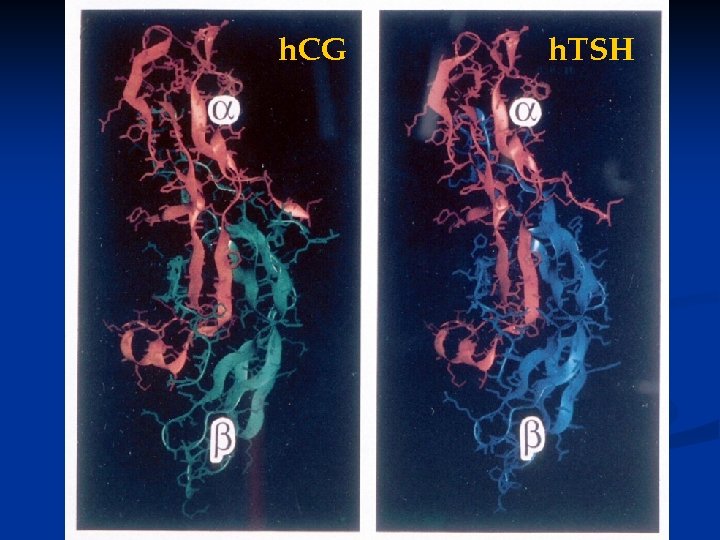 h. CG h. TSH
h. CG h. TSH
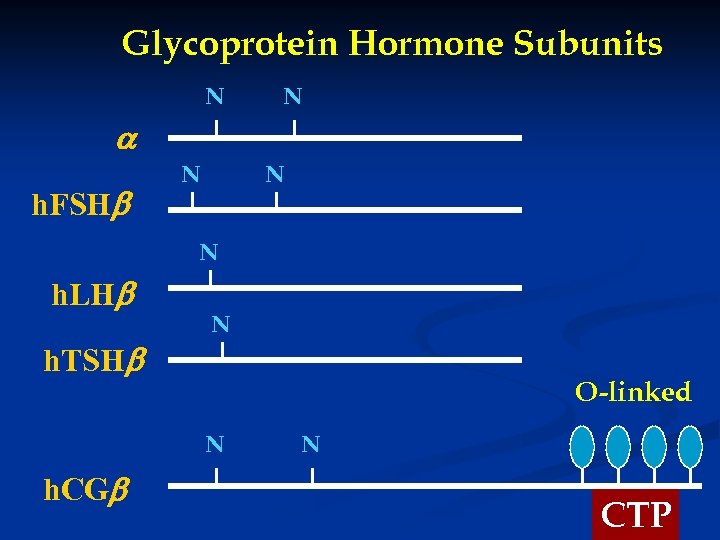 Glycoprotein Hormone Subunits N N h. FSH N N N h. LH h. TSH N O-linked N h. CG N CTP
Glycoprotein Hormone Subunits N N h. FSH N N N h. LH h. TSH N O-linked N h. CG N CTP
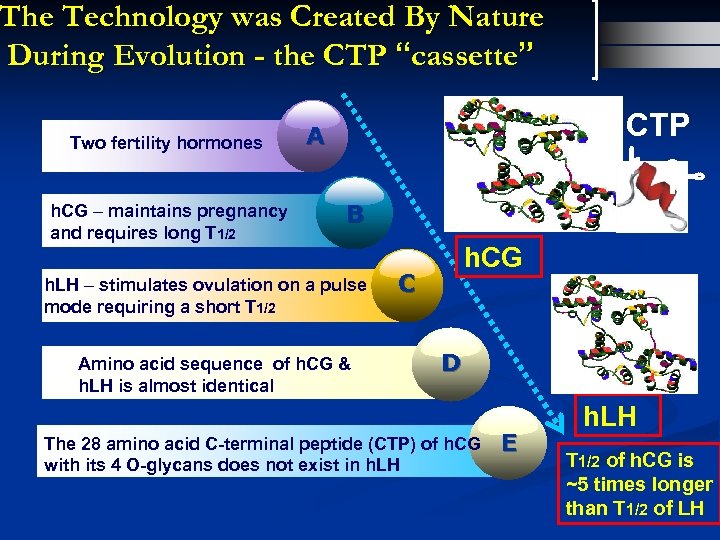 The Technology was Created By Nature During Evolution - the CTP “cassette” Two fertility hormones h. CG – maintains pregnancy and requires long T 1/2 CTP A B h. LH – stimulates ovulation on a pulse mode requiring a short T 1/2 Amino acid sequence of h. CG & h. LH is almost identical h. CG C D The 28 amino acid C-terminal peptide (CTP) of h. CG with its 4 O-glycans does not exist in h. LH E h. LH T 1/2 of h. CG is ~5 times longer than T 1/2 of LH
The Technology was Created By Nature During Evolution - the CTP “cassette” Two fertility hormones h. CG – maintains pregnancy and requires long T 1/2 CTP A B h. LH – stimulates ovulation on a pulse mode requiring a short T 1/2 Amino acid sequence of h. CG & h. LH is almost identical h. CG C D The 28 amino acid C-terminal peptide (CTP) of h. CG with its 4 O-glycans does not exist in h. LH E h. LH T 1/2 of h. CG is ~5 times longer than T 1/2 of LH
 O O O Ser. Lys. Ala. Pro. Ser. Leu. Pro. Ser. Arg. Leu O Pro Gly. Pro. Ser. Asp. Thr. Pro. Ile. Leu. Pro. Gln
O O O Ser. Lys. Ala. Pro. Ser. Leu. Pro. Ser. Arg. Leu O Pro Gly. Pro. Ser. Asp. Thr. Pro. Ile. Leu. Pro. Gln
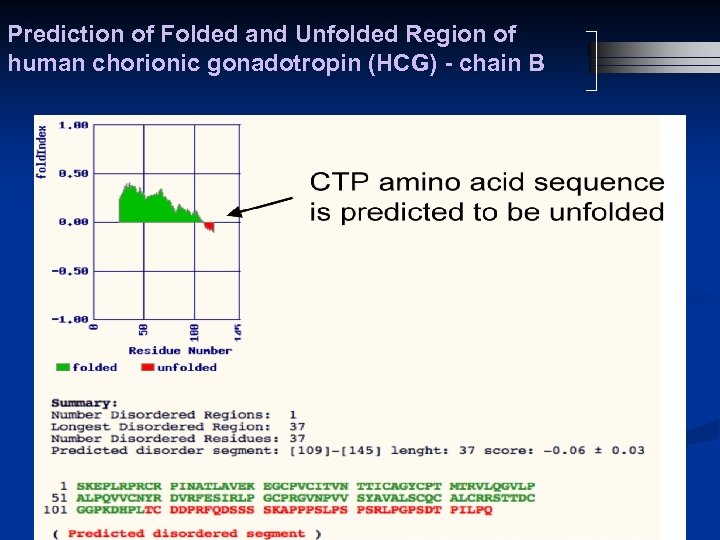 Prediction of Folded and Unfolded Region of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) - chain B
Prediction of Folded and Unfolded Region of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) - chain B
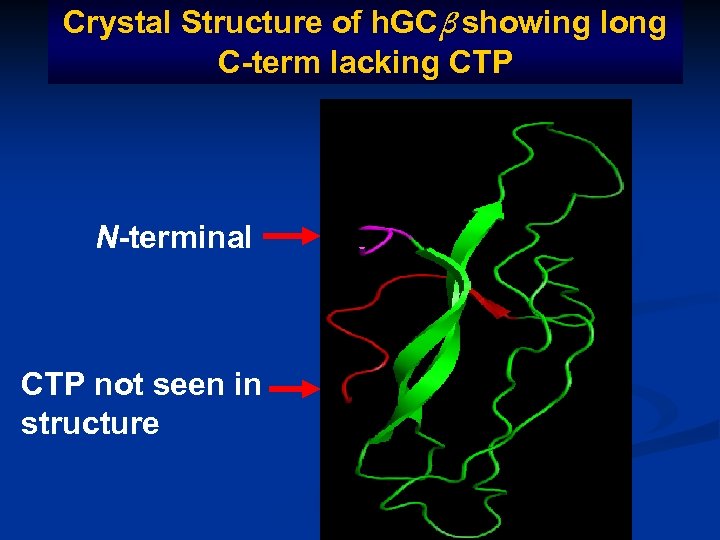 Crystal Structure of h. GCβ showing long C-term lacking CTP N-terminal CTP not seen in structure
Crystal Structure of h. GCβ showing long C-term lacking CTP N-terminal CTP not seen in structure
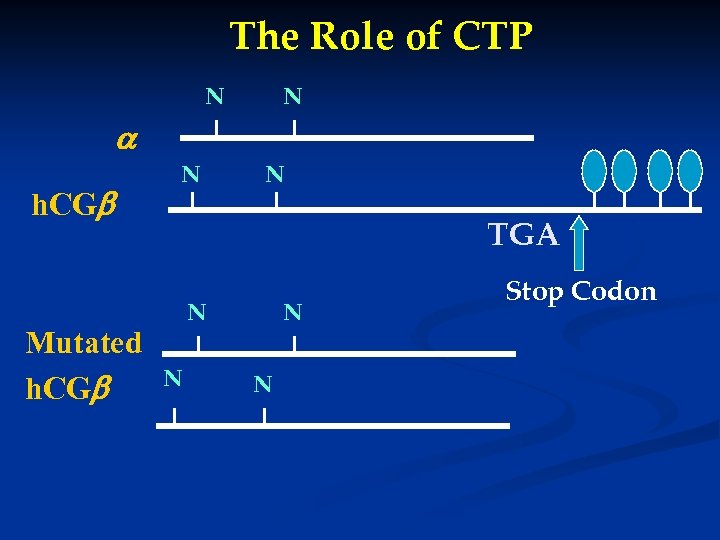 The Role of CTP N N h. CG Mutated h. CG N N TGA N N Stop Codon
The Role of CTP N N h. CG Mutated h. CG N N TGA N N Stop Codon
 Deletion of CTP from h. CG - No effect on the assembly of subunits - No effect on receptor binding - No effect on in vitro bioactivity - Significantly decreased the bioactivity in vivo
Deletion of CTP from h. CG - No effect on the assembly of subunits - No effect on receptor binding - No effect on in vitro bioactivity - Significantly decreased the bioactivity in vivo
 + Protein +CTP Half- Life
+ Protein +CTP Half- Life
 Designing New FSH Analog
Designing New FSH Analog
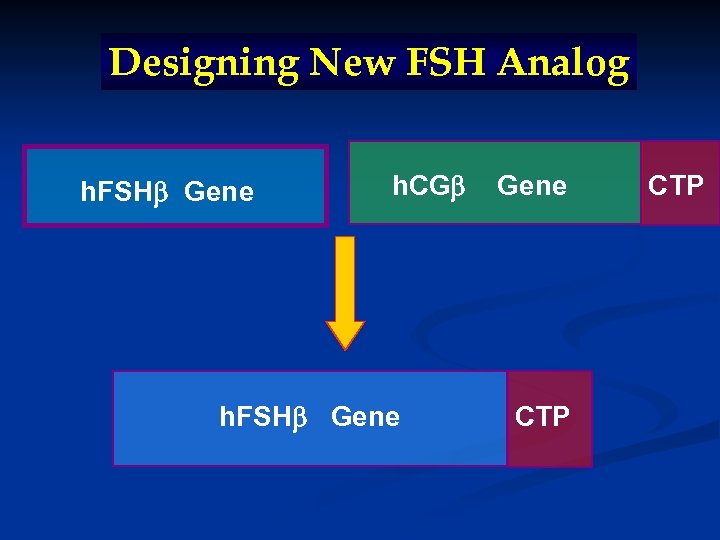 Designing New FSH Analog h. FSH Gene h. CG h. FSH Gene CTP
Designing New FSH Analog h. FSH Gene h. CG h. FSH Gene CTP
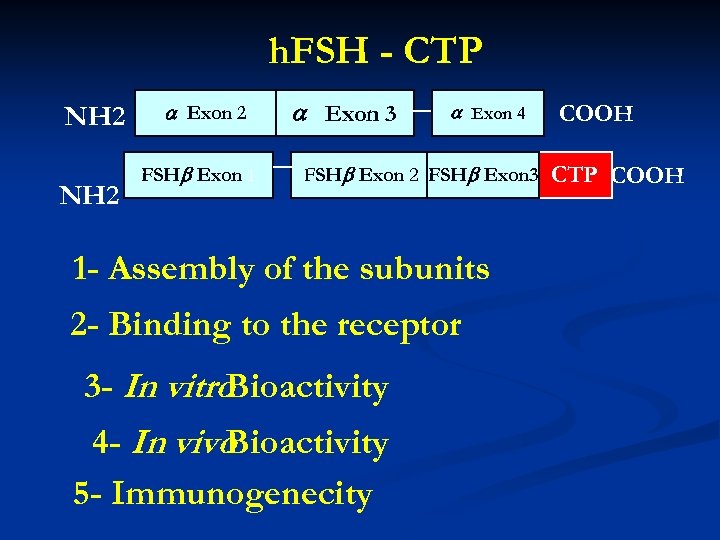 h. FSH - CTP NH 2 Exon 2 FSH Exon 1 Exon 3 Exon 4 FSH Exon 2 FSH Exon 3 1 - Assembly of the subunits 2 - Binding to the receptor 3 - In vitro Bioactivity 4 - In vivo Bioactivity 5 - Immunogenecity COOH CTP COOH
h. FSH - CTP NH 2 Exon 2 FSH Exon 1 Exon 3 Exon 4 FSH Exon 2 FSH Exon 3 1 - Assembly of the subunits 2 - Binding to the receptor 3 - In vitro Bioactivity 4 - In vivo Bioactivity 5 - Immunogenecity COOH CTP COOH
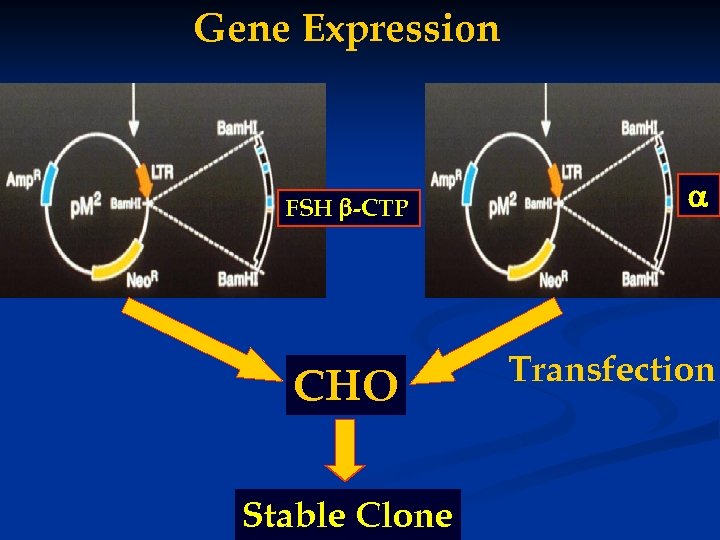 Gene Expression FSH -CTP CHO Stable Clone Transfection
Gene Expression FSH -CTP CHO Stable Clone Transfection
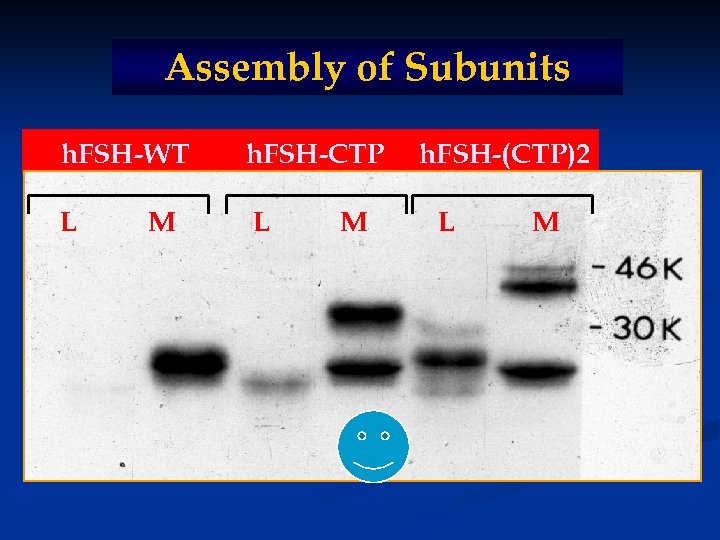 Assembly of Subunits h. FSH-WT h. FSH-CTP L L M M h. FSH-(CTP)2 L M
Assembly of Subunits h. FSH-WT h. FSH-CTP L L M M h. FSH-(CTP)2 L M
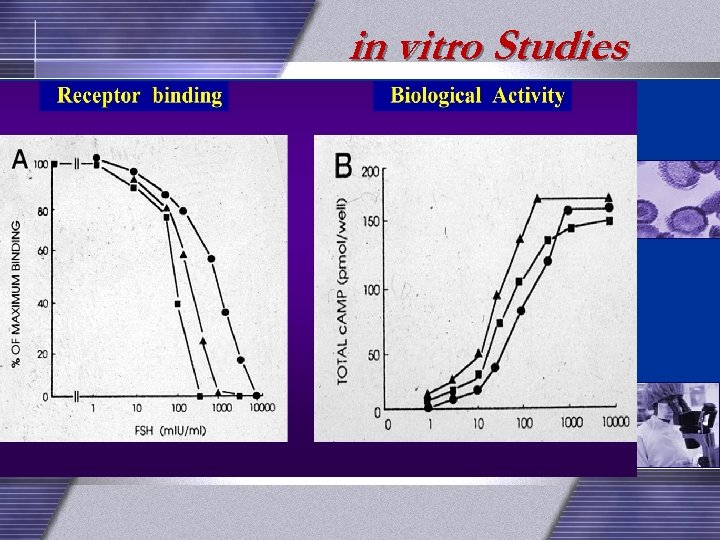 in vitro Studies
in vitro Studies
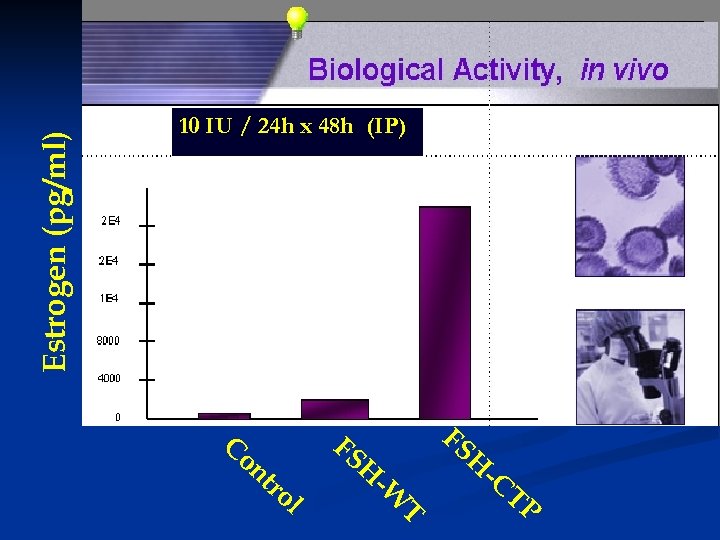 Estrogen (pg/ml) 10 IU / 24 h x 48 h (IP) C on tr ol FS FS H H -W T -C TP
Estrogen (pg/ml) 10 IU / 24 h x 48 h (IP) C on tr ol FS FS H H -W T -C TP
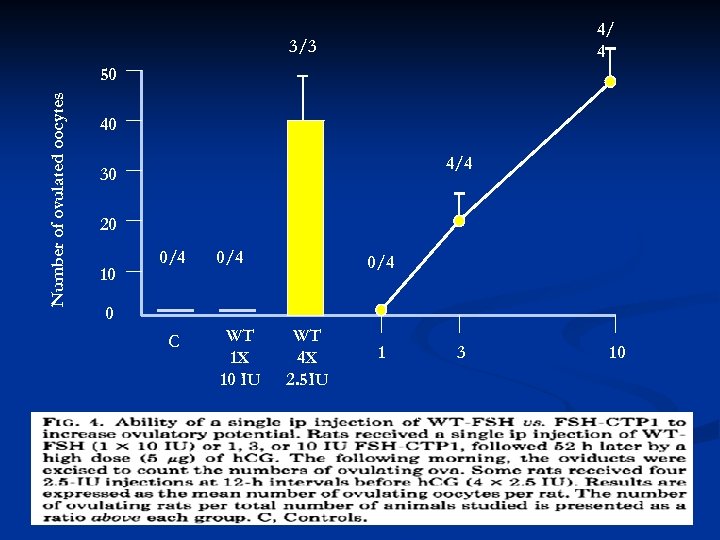 4/ 4 3/3 Number of ovulated oocytes 50 40 4/4 30 20 10 0/4 0/4 0 C WT 1 X 10 IU WT 4 X 2. 5 IU 1 3 10
4/ 4 3/3 Number of ovulated oocytes 50 40 4/4 30 20 10 0/4 0/4 0 C WT 1 X 10 IU WT 4 X 2. 5 IU 1 3 10
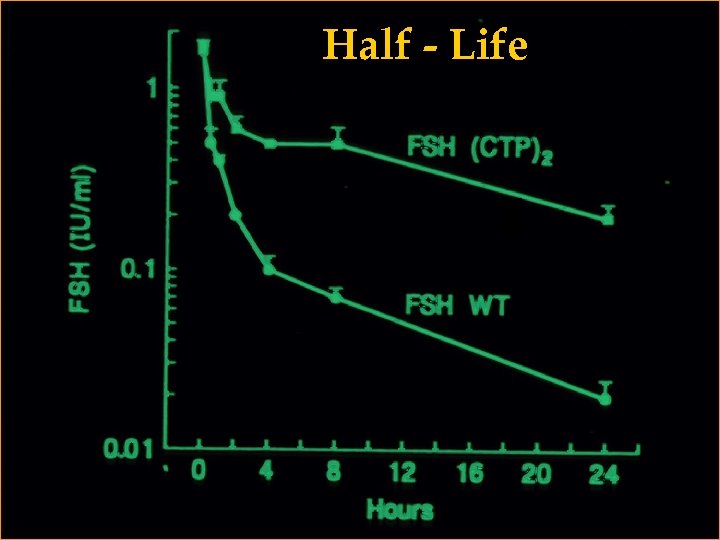 Half - Life
Half - Life
 O O O Ser. Lys. Ala. Pro. Ser. Leu. Pro. Ser. Arg. Leu O Pro Gly. Pro. Ser. Asp. Thr. Pro. Ile. Leu. Pro. Gln
O O O Ser. Lys. Ala. Pro. Ser. Leu. Pro. Ser. Arg. Leu O Pro Gly. Pro. Ser. Asp. Thr. Pro. Ile. Leu. Pro. Gln
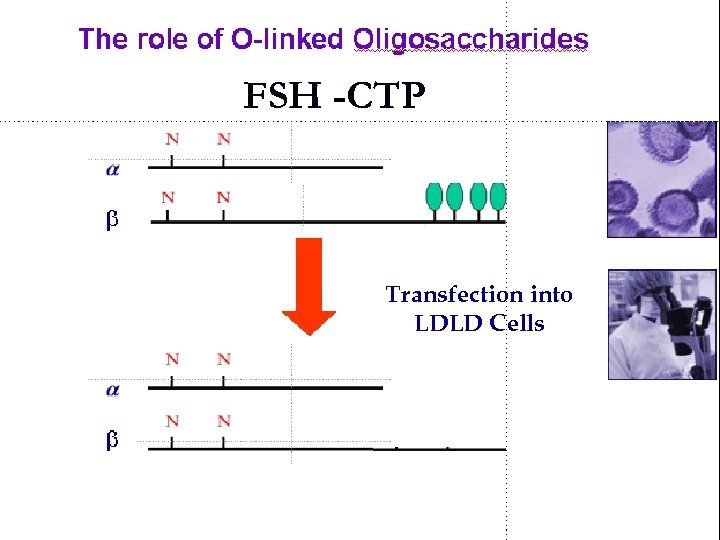 FSH -CTP Transfection into LDLD Cells
FSH -CTP Transfection into LDLD Cells
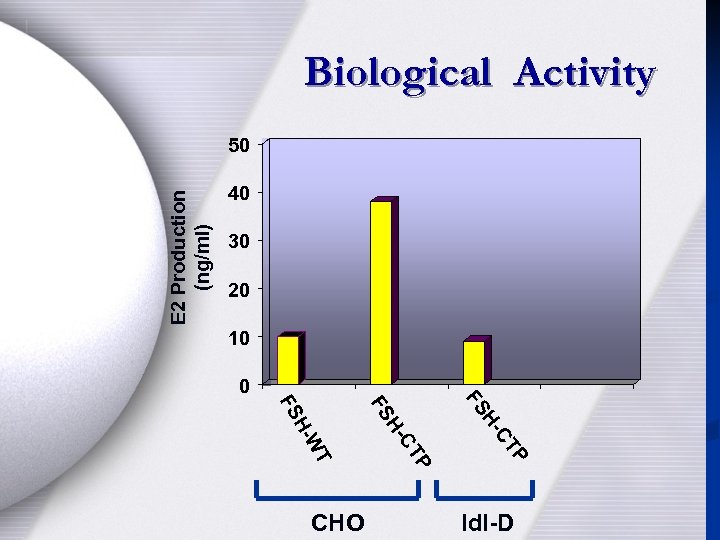 Biological Activity E 2 Production (ng/ml) 50 40 30 20 10 0 P CT HFS P CT H- FS WT HFS CHO Idl-D
Biological Activity E 2 Production (ng/ml) 50 40 30 20 10 0 P CT HFS P CT H- FS WT HFS CHO Idl-D
 O O O Ser. Lys. Ala. Pro. Ser. Leu. Pro. Ser. Arg. Leu O Pro Gly. Pro. Ser. Asp. Thr. Pro. Ile. Leu. Pro. Gln
O O O Ser. Lys. Ala. Pro. Ser. Leu. Pro. Ser. Arg. Leu O Pro Gly. Pro. Ser. Asp. Thr. Pro. Ile. Leu. Pro. Gln
 Organon - Merck • FSH – CTP is effective in follicular stimulation • FSH – CTP is safe • FSH – CTP is not immunogenic
Organon - Merck • FSH – CTP is effective in follicular stimulation • FSH – CTP is safe • FSH – CTP is not immunogenic
 February 2, 2010 — The European Commission (EC) has approved ELONVA (FSH-CTP) Merck Receives Positive Regulatory Opinion for European Marketing of Long-Acting CTPModified Fertility Treatment ELONVA
February 2, 2010 — The European Commission (EC) has approved ELONVA (FSH-CTP) Merck Receives Positive Regulatory Opinion for European Marketing of Long-Acting CTPModified Fertility Treatment ELONVA
 FSH – CTP (ELONVA) World – Wide Use
FSH – CTP (ELONVA) World – Wide Use
 Start Up Company CTP “Enhancing the potency and longevity of highly valuable proteins”
Start Up Company CTP “Enhancing the potency and longevity of highly valuable proteins”
 Start Up Company Public Company • NASDAQ, Stock Exchange, NY, USA. • Tel-Aviv Stock Exchange, Tel-Aviv, Israel.
Start Up Company Public Company • NASDAQ, Stock Exchange, NY, USA. • Tel-Aviv Stock Exchange, Tel-Aviv, Israel.
 OPKO Health, Inc. a multinational biopharmaceutical and diagnostics company
OPKO Health, Inc. a multinational biopharmaceutical and diagnostics company
 Designing Long Acting Proteins n Erythropoietin n Growth Hormone n Interferon n Factors, XI & VII n Short Peptides
Designing Long Acting Proteins n Erythropoietin n Growth Hormone n Interferon n Factors, XI & VII n Short Peptides
 Erythropoietin (EPO) The most common use is in people with anemia (low blood count) related to kidney dysfunction.
Erythropoietin (EPO) The most common use is in people with anemia (low blood count) related to kidney dysfunction.
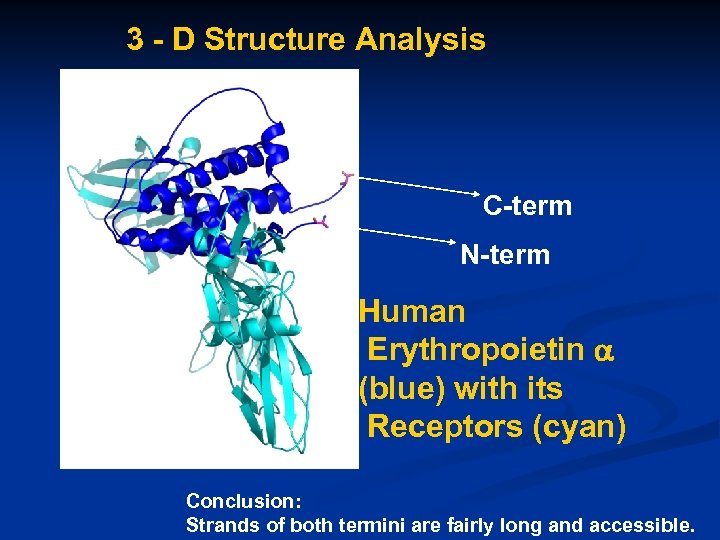 3 - D Structure Analysis C-term N-term Human Erythropoietin (blue) with its Receptors (cyan) Conclusion: Strands of both termini are fairly long and accessible.
3 - D Structure Analysis C-term N-term Human Erythropoietin (blue) with its Receptors (cyan) Conclusion: Strands of both termini are fairly long and accessible.
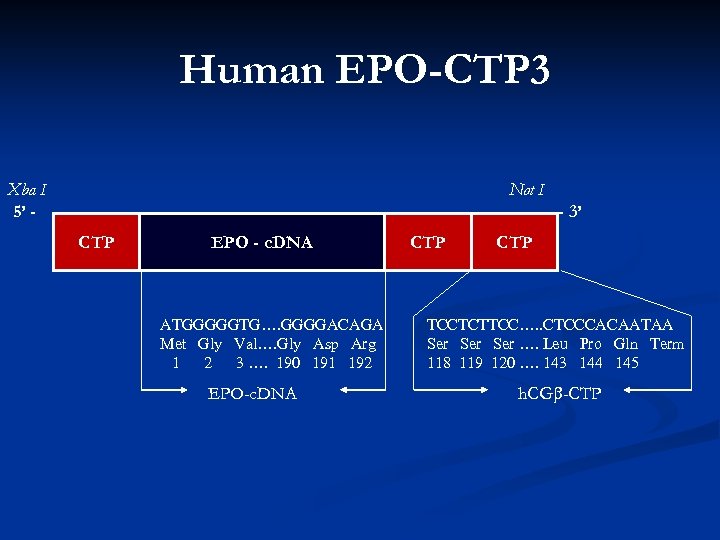 Human EPO-CTP 3 Xba I 5’ - Not I - 3’ CTP EPO - c. DNA ATGGGGGTG…. GGGGACAGA Met Gly Val…. Gly Asp Arg 1 2 3 …. 190 191 192 EPO-c. DNA CTP TCCTCTTCC…. . CTCCCACAATAA Ser …. Leu Pro Gln Term 118 119 120 …. 143 144 145 h. CG -CTP
Human EPO-CTP 3 Xba I 5’ - Not I - 3’ CTP EPO - c. DNA ATGGGGGTG…. GGGGACAGA Met Gly Val…. Gly Asp Arg 1 2 3 …. 190 191 192 EPO-c. DNA CTP TCCTCTTCC…. . CTCCCACAATAA Ser …. Leu Pro Gln Term 118 119 120 …. 143 144 145 h. CG -CTP
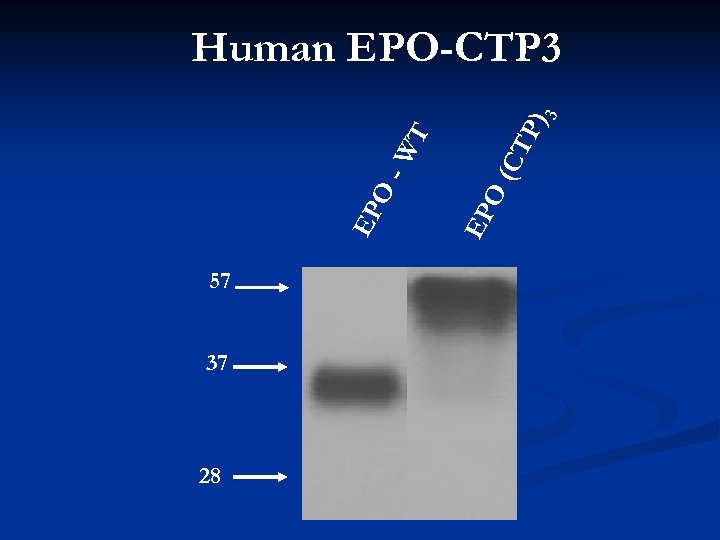 57 37 28 P) (CT O EP EP O -W T 3 Human EPO-CTP 3
57 37 28 P) (CT O EP EP O -W T 3 Human EPO-CTP 3
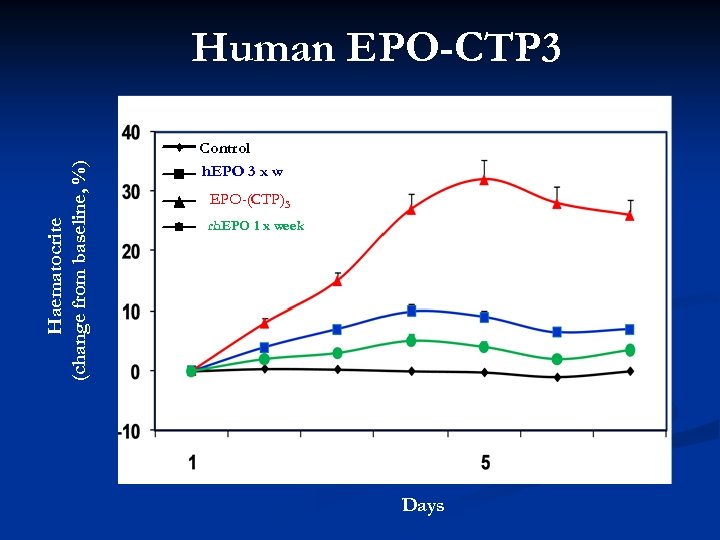 Human EPO-CTP 3 Haematocrite (change from baseline, %) 40 Control rh. EPO 3 x week 30 EPO-(CTP)3 rh. EPO 1 x week 20 10 Days
Human EPO-CTP 3 Haematocrite (change from baseline, %) 40 Control rh. EPO 3 x week 30 EPO-(CTP)3 rh. EPO 1 x week 20 10 Days
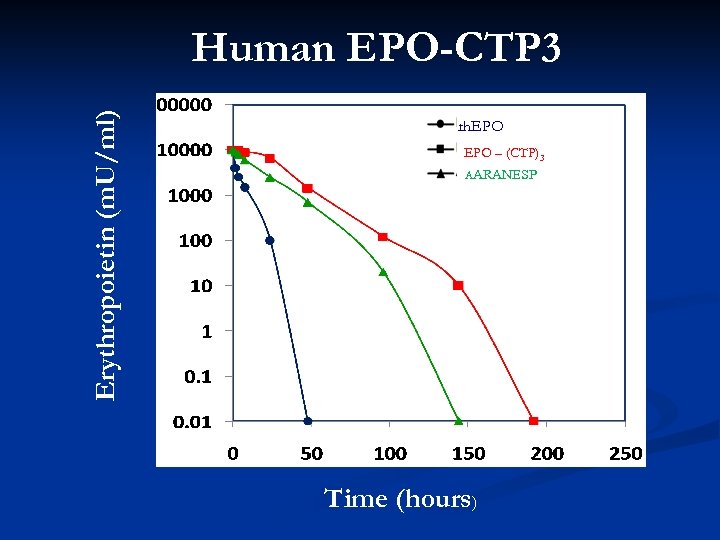 Erythropoietin (m. U/ml) Human EPO-CTP 3 rh. EPO – (CTP)3 AARANESP Time (hours)
Erythropoietin (m. U/ml) Human EPO-CTP 3 rh. EPO – (CTP)3 AARANESP Time (hours)
 Human Growth Hormone
Human Growth Hormone
 Pituitary
Pituitary
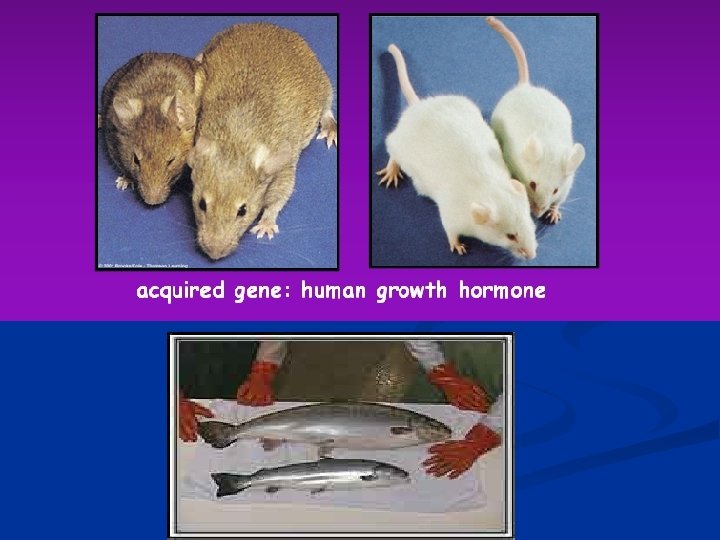
 Pharmaceutical and Biotechnological Uses of Growth Hormone To treat children of pathologically short stature
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnological Uses of Growth Hormone To treat children of pathologically short stature
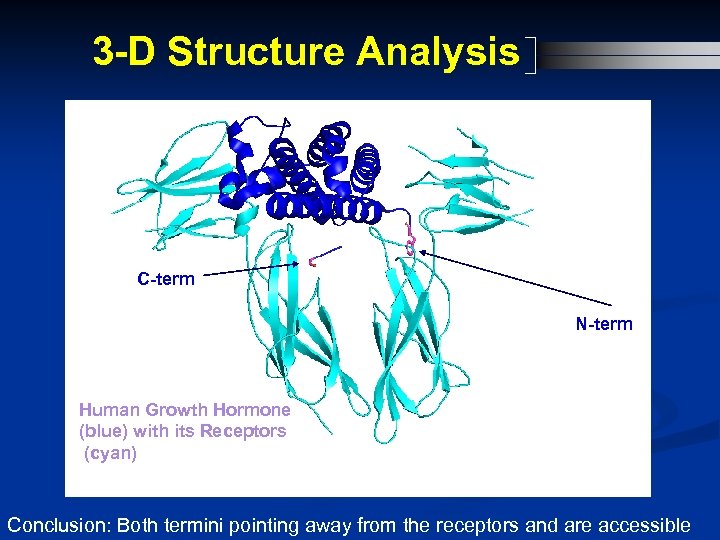 3 -D Structure Analysis C-term N-term Human Growth Hormone (blue) with its Receptors (cyan) Conclusion: Both termini pointing away from the receptors and are accessible
3 -D Structure Analysis C-term N-term Human Growth Hormone (blue) with its Receptors (cyan) Conclusion: Both termini pointing away from the receptors and are accessible
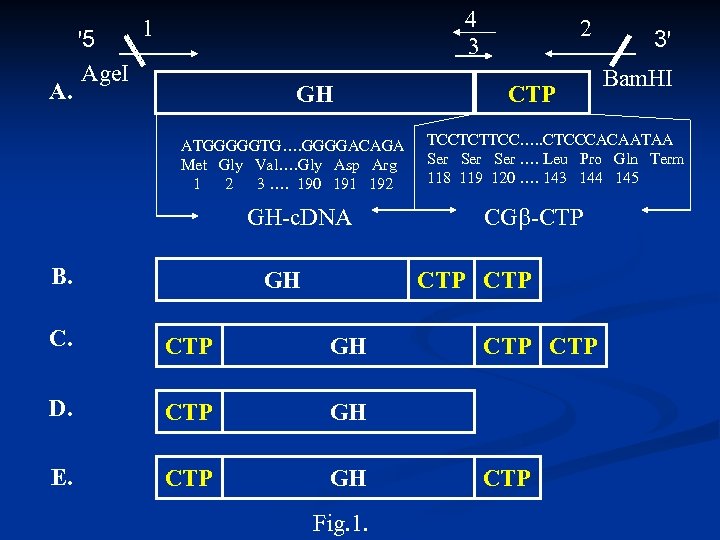 A. '5 Age. I 4 3 1 GH ATGGGGGTG…. GGGGACAGA Met Gly Val…. Gly Asp Arg 1 2 3 …. 190 191 192 2 CTP GH CTP C. CTP GH D. CTP GH E. CTP GH Fig. 1. Bam. HI TCCTCTTCC…. . CTCCCACAATAA Ser …. Leu Pro Gln Term 118 119 120 …. 143 144 145 GH-c. DNA CG -CTP B. 3' CTP CTP
A. '5 Age. I 4 3 1 GH ATGGGGGTG…. GGGGACAGA Met Gly Val…. Gly Asp Arg 1 2 3 …. 190 191 192 2 CTP GH CTP C. CTP GH D. CTP GH E. CTP GH Fig. 1. Bam. HI TCCTCTTCC…. . CTCCCACAATAA Ser …. Leu Pro Gln Term 118 119 120 …. 143 144 145 GH-c. DNA CG -CTP B. 3' CTP CTP
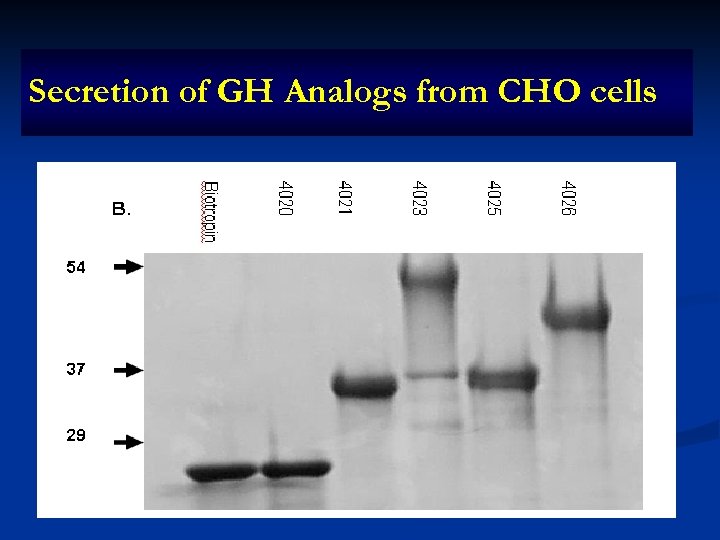 Secretion of GH Analogs from CHO cells
Secretion of GH Analogs from CHO cells
 GH – (CTP)3 CTP GH CTP
GH – (CTP)3 CTP GH CTP
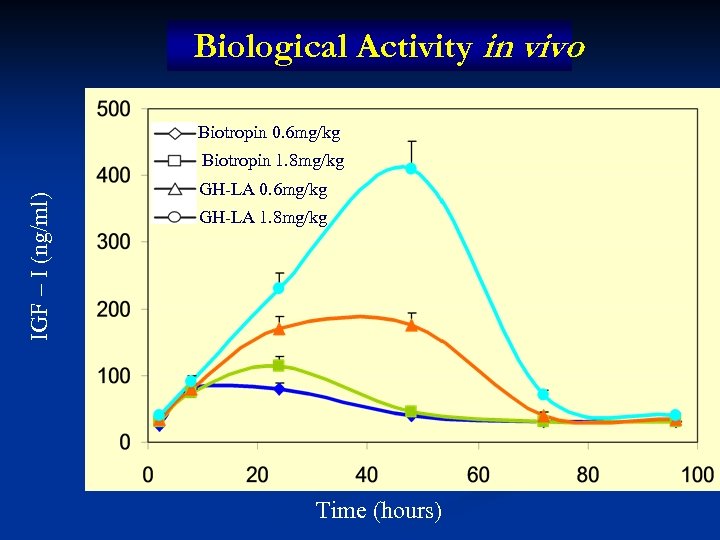 Biological Activity in vivo Biotropin 0. 6 mg/kg IGF – I (ng/ml) Biotropin 1. 8 mg/kg GH-LA 0. 6 mg/kg GH-LA 1. 8 mg/kg Time (hours)
Biological Activity in vivo Biotropin 0. 6 mg/kg IGF – I (ng/ml) Biotropin 1. 8 mg/kg GH-LA 0. 6 mg/kg GH-LA 1. 8 mg/kg Time (hours)
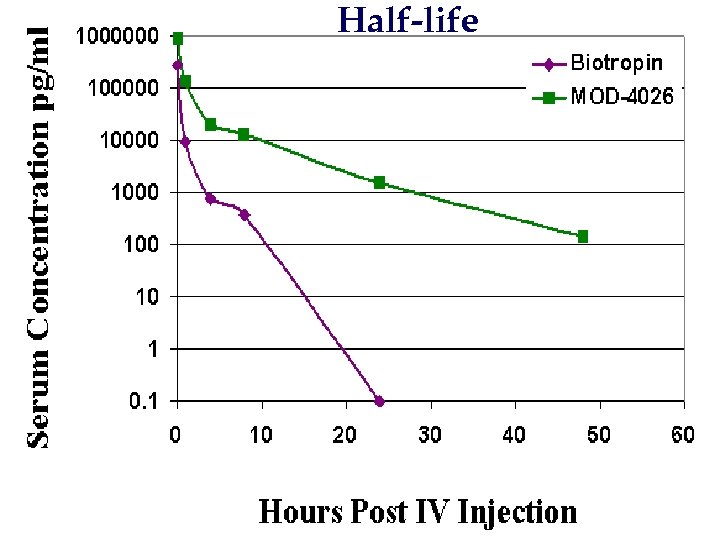 Half-life
Half-life
 GH – (CTP)3 n Expeiments in Rehsus Monkeys and human clinical trials phase I that GHLong- acting is safe and not immunogenic n GH-(CTP)3 is in human clinical trials phase III
GH – (CTP)3 n Expeiments in Rehsus Monkeys and human clinical trials phase I that GHLong- acting is safe and not immunogenic n GH-(CTP)3 is in human clinical trials phase III
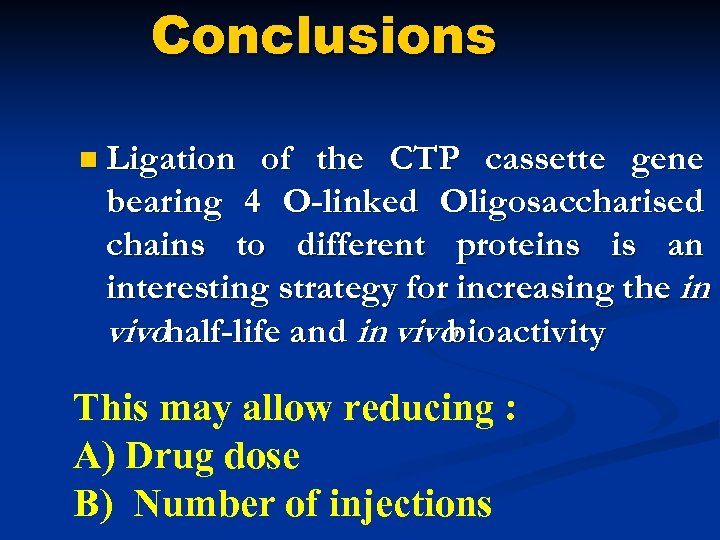 Conclusions n Ligation of the CTP cassette gene bearing 4 O-linked Oligosaccharised chains to different proteins is an interesting strategy for increasing the in vivohalf-life and in vivo bioactivity This may allow reducing : A) Drug dose B) Number of injections
Conclusions n Ligation of the CTP cassette gene bearing 4 O-linked Oligosaccharised chains to different proteins is an interesting strategy for increasing the in vivohalf-life and in vivo bioactivity This may allow reducing : A) Drug dose B) Number of injections
 TSH Studies
TSH Studies
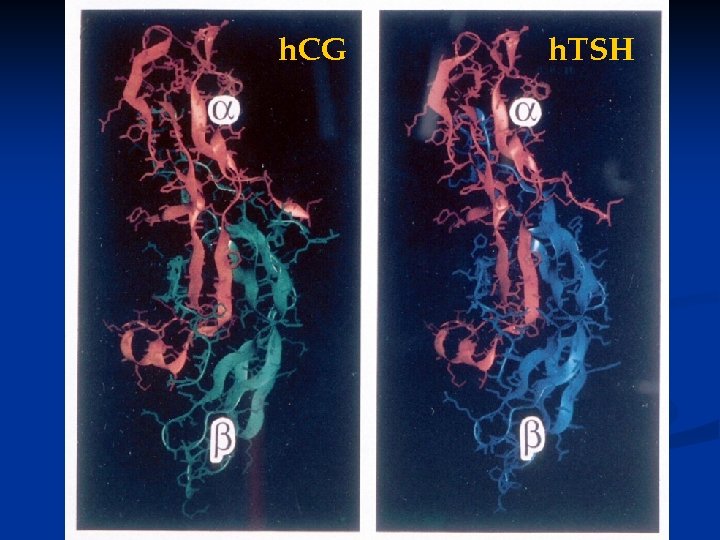 h. CG h. TSH
h. CG h. TSH
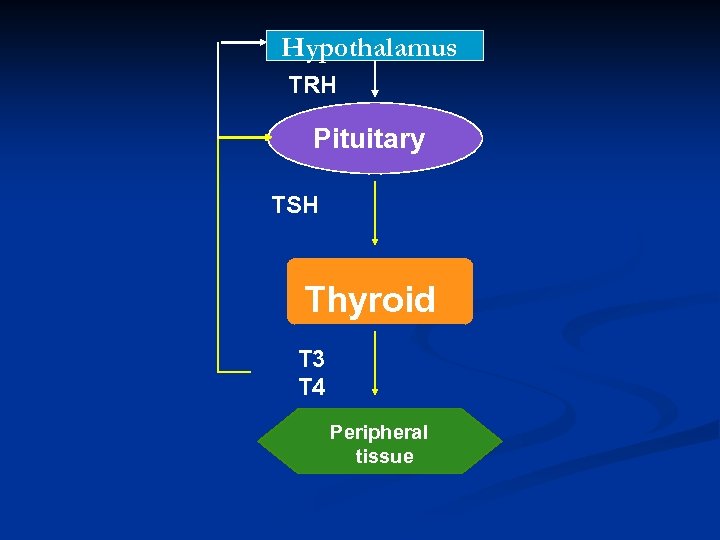 Hypothalamus TRH Pituitary TSH Thyroid T 3 T 4 Peripheral tissue
Hypothalamus TRH Pituitary TSH Thyroid T 3 T 4 Peripheral tissue
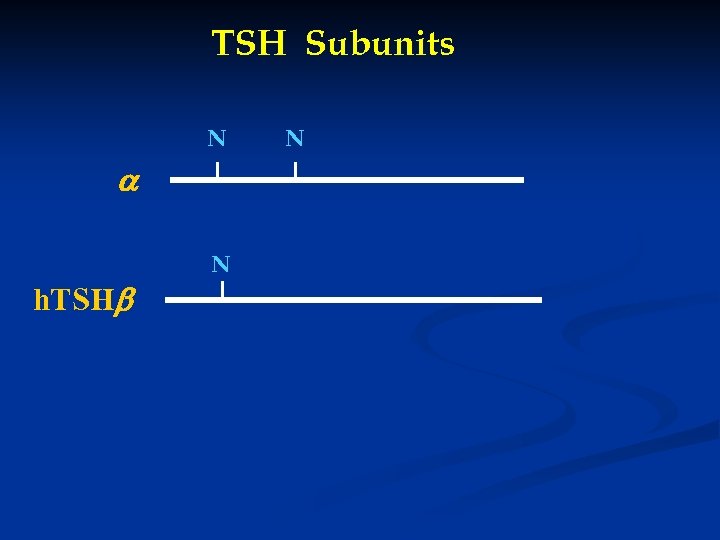 TSH Subunits N h. TSH N N
TSH Subunits N h. TSH N N
 h. TSH Variants
h. TSH Variants
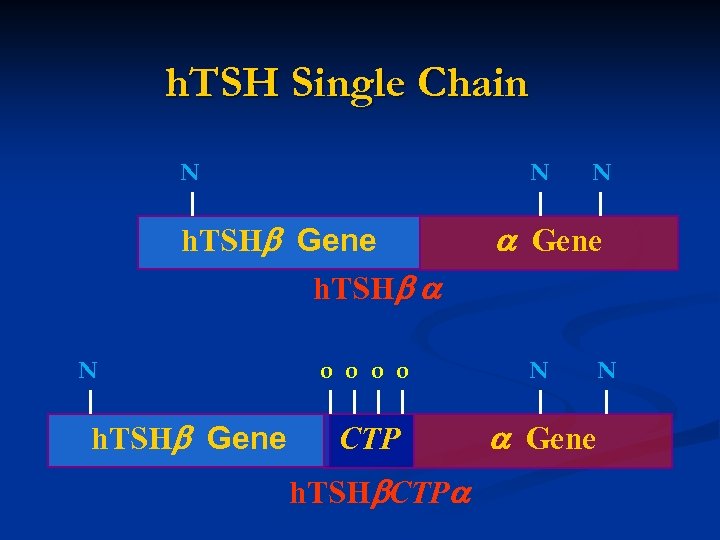 h. TSH Single Chain N N h. TSH Gene h. TSH N h. TSH Gene N Gene o o N CTP Gene h. TSH CTP N
h. TSH Single Chain N N h. TSH Gene h. TSH N h. TSH Gene N Gene o o N CTP Gene h. TSH CTP N
 h. TSH Single Chain u. Expressed in CHO cells u. Binds to TSH Receptor in high affinity as will as the TSH-WT u. Biologically active
h. TSH Single Chain u. Expressed in CHO cells u. Binds to TSH Receptor in high affinity as will as the TSH-WT u. Biologically active
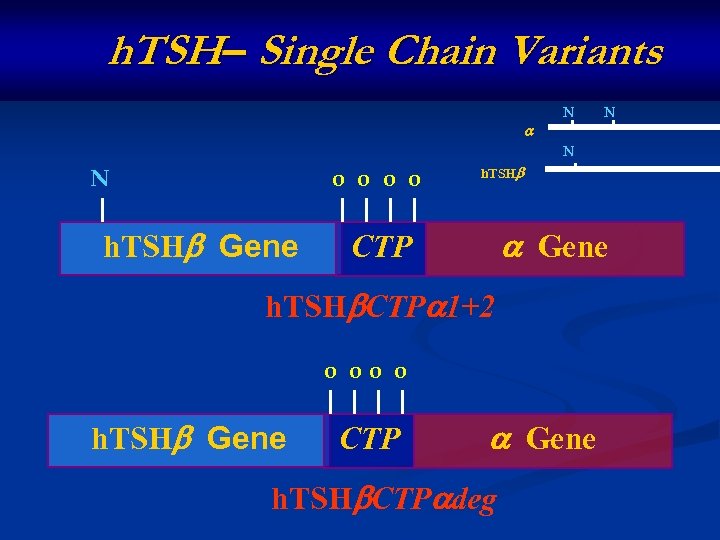 h. TSH– Single Chain Variants N N o o h. TSH Gene CTP h. TSH CTP 1+2 o oo o h. TSH Gene CTP Gene h. TSH CTP deg
h. TSH– Single Chain Variants N N o o h. TSH Gene CTP h. TSH CTP 1+2 o oo o h. TSH Gene CTP Gene h. TSH CTP deg
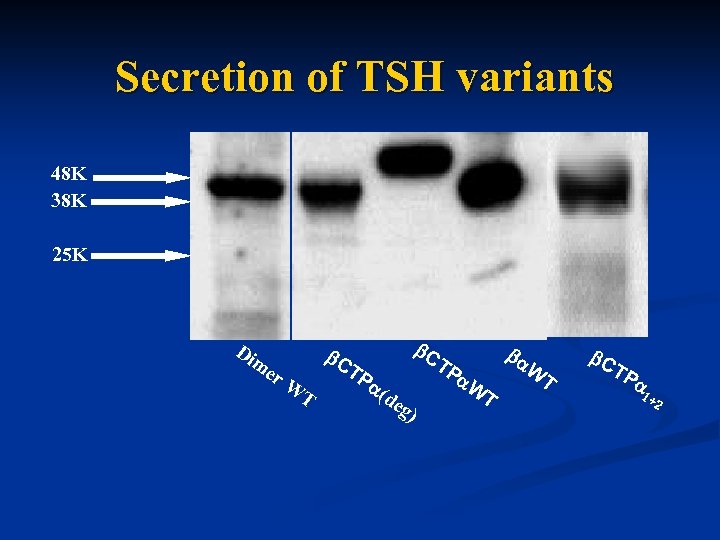 Secretion of TSH variants 48 K 38 K 25 K Di me r. W C T TP C ( de g TP ) W T C TP 1+ 2
Secretion of TSH variants 48 K 38 K 25 K Di me r. W C T TP C ( de g TP ) W T C TP 1+ 2
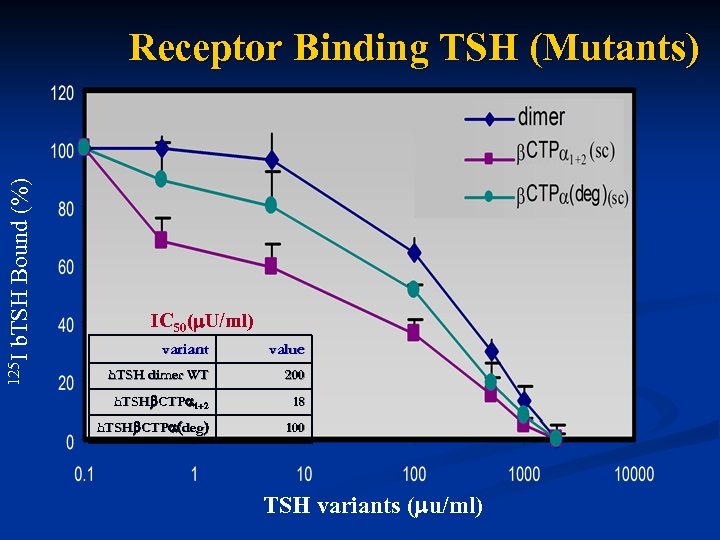 125 I b. TSH Bound (%) Receptor Binding TSH (Mutants) IC 50( U/ml) variant value h. TSH dimer WT 200 h. TSH CTP 1+2 18 h. TSH CTP (deg) 100 TSH variants ( u/ml)
125 I b. TSH Bound (%) Receptor Binding TSH (Mutants) IC 50( U/ml) variant value h. TSH dimer WT 200 h. TSH CTP 1+2 18 h. TSH CTP (deg) 100 TSH variants ( u/ml)
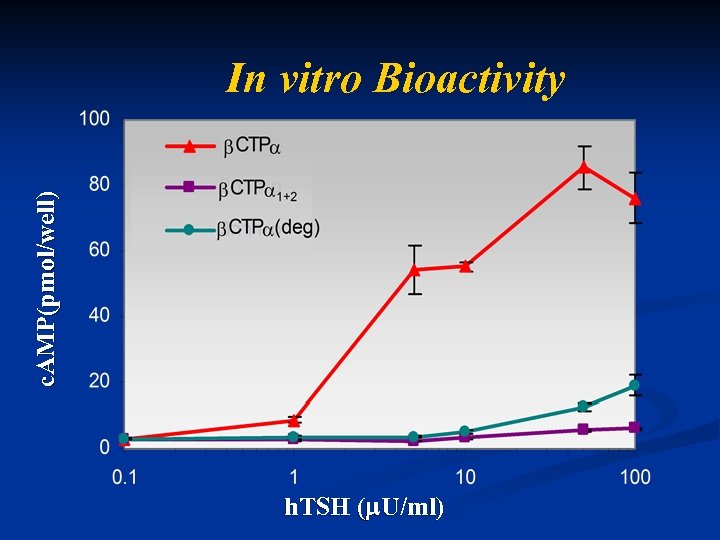 c. AMP(pmol/well) In vitro Bioactivity h. TSH ( U/ml)
c. AMP(pmol/well) In vitro Bioactivity h. TSH ( U/ml)
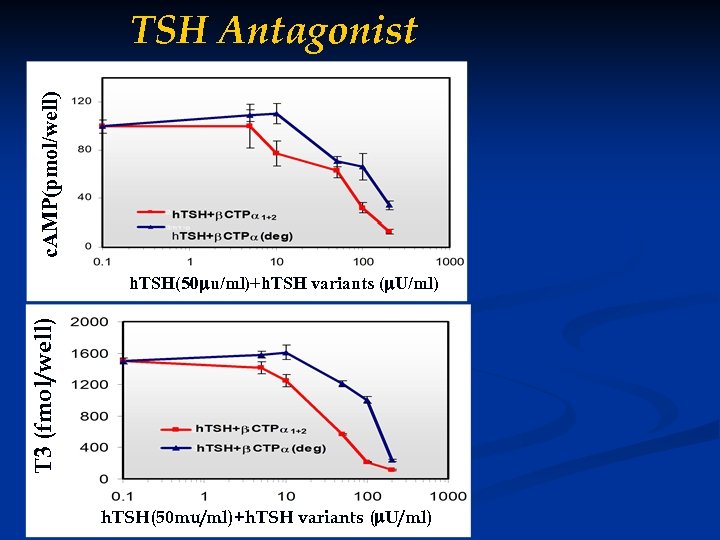 c. AMP(pmol/well) TSH Antagonist T 3 (fmol/well) T 3 (fmo/well) h. TSH(50 u/ml)+h. TSH variants ( U/ml) h. TSH(50 mu/ml)+h. TSH variants ( u/ml) h. TSH(50 u/ml)+h. TSH variants ( U/ml)
c. AMP(pmol/well) TSH Antagonist T 3 (fmol/well) T 3 (fmo/well) h. TSH(50 u/ml)+h. TSH variants ( U/ml) h. TSH(50 mu/ml)+h. TSH variants ( u/ml) h. TSH(50 u/ml)+h. TSH variants ( U/ml)
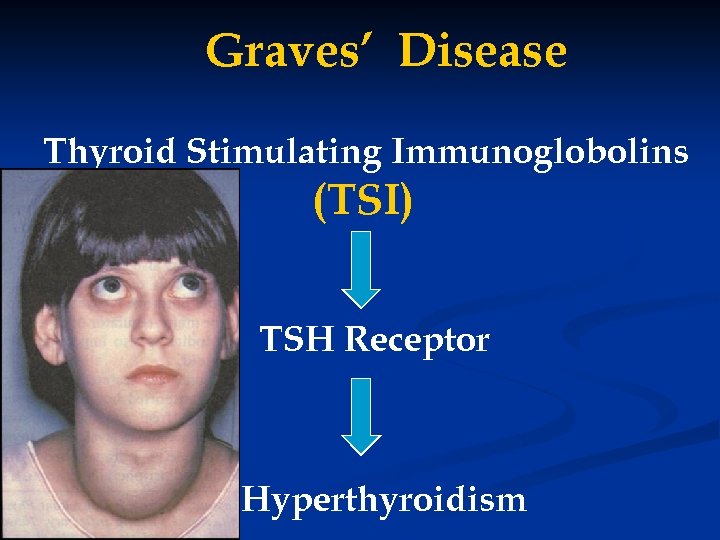 Graves’ Disease Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobolins (TSI) TSH Receptor Hyperthyroidism
Graves’ Disease Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobolins (TSI) TSH Receptor Hyperthyroidism
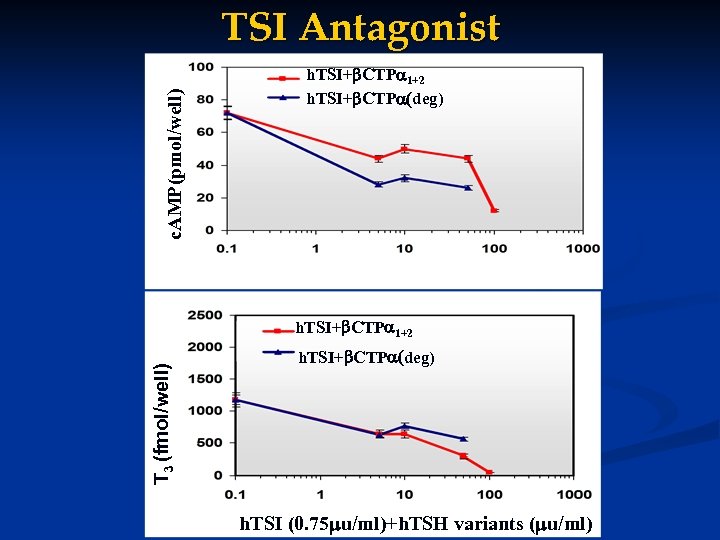 c. AMP(pmol/well) TSI Antagonist h. TSI+ CTP 1+2 h. TSI+ CTP (deg) h. TSI (0. 75 u/ml)+h. TSH variants ( u/ml) T 3 (fmol/well) h. TSI+ CTP 1+2 h. TSI+ CTP (deg) h. TSI (0. 75 u/ml)+h. TSH variants ( u/ml)
c. AMP(pmol/well) TSI Antagonist h. TSI+ CTP 1+2 h. TSI+ CTP (deg) h. TSI (0. 75 u/ml)+h. TSH variants ( u/ml) T 3 (fmol/well) h. TSI+ CTP 1+2 h. TSI+ CTP (deg) h. TSI (0. 75 u/ml)+h. TSH variants ( u/ml)
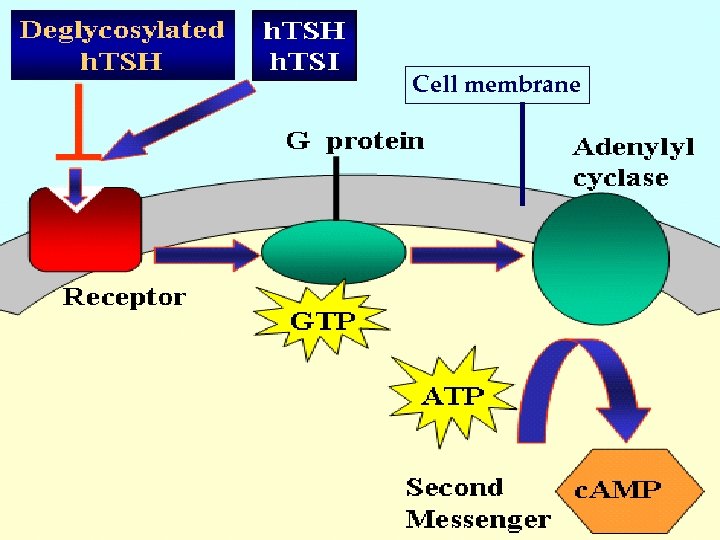 Cell membrane
Cell membrane
 Conclusions Deletion of the N-linked oligosaccharides from TSH resulted in partial antagonists of TSH and TSI at the level of the receptor binding site. n n TSH variants may offer a novel therapeutic strategy in the treatment of hyperthyroidism and Graves’ disease.
Conclusions Deletion of the N-linked oligosaccharides from TSH resulted in partial antagonists of TSH and TSI at the level of the receptor binding site. n n TSH variants may offer a novel therapeutic strategy in the treatment of hyperthyroidism and Graves’ disease.
 Prof. Zaki Kraiem Dr. Naeil Azam Orit Sadeh Flonia Levi Rinat Alenberg Dr. Sharif Ganim Dr. Taleb Hajoj Prof. Irving Boime Prof. Aaron Hsueh Dr. Avri Havron Dr. Eyal Fima Mr. Shai Novik
Prof. Zaki Kraiem Dr. Naeil Azam Orit Sadeh Flonia Levi Rinat Alenberg Dr. Sharif Ganim Dr. Taleb Hajoj Prof. Irving Boime Prof. Aaron Hsueh Dr. Avri Havron Dr. Eyal Fima Mr. Shai Novik
 Clinical Advisory Panels World Known Opinion Leaders n n n h. GH n Rosenfeld, MD, Stanford n Barry Sherman, MD, Genentech, Bi. Par n Zvi Zadik, MD, Hebrew University EPO n Allen Nissenson, MD, UCLA n Anatole Besarab, MD, Henry Ford, Detroit Interferon-beta n William Mobley, MD, Stanford n Hillel Panitch, MD, Vermont n Ron Milo, MD, Israel
Clinical Advisory Panels World Known Opinion Leaders n n n h. GH n Rosenfeld, MD, Stanford n Barry Sherman, MD, Genentech, Bi. Par n Zvi Zadik, MD, Hebrew University EPO n Allen Nissenson, MD, UCLA n Anatole Besarab, MD, Henry Ford, Detroit Interferon-beta n William Mobley, MD, Stanford n Hillel Panitch, MD, Vermont n Ron Milo, MD, Israel
 • National Institutes of Health (NIH) • The Rockefeller Foundation • United States - Israel Binational Science Foundation (BSF) • Israel Science Foundation (ISF) • The Israel Ministry of Science • The Israel Ministry of Industry and Trade • Private Investors
• National Institutes of Health (NIH) • The Rockefeller Foundation • United States - Israel Binational Science Foundation (BSF) • Israel Science Foundation (ISF) • The Israel Ministry of Science • The Israel Ministry of Industry and Trade • Private Investors
 ifa Ha
ifa Ha


