4902a6d320b97f666882f5a1a09be4ef.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Developing Ethernet Services Offerings with MEF Specifications Dmitry Dergalov, Technical Director RAD Data Communications-Russia www. rad. ru Tel/Fax +7 (495) 231 -1239/1097 1
Developing Ethernet Services Offerings with MEF Specifications Dmitry Dergalov, Technical Director RAD Data Communications-Russia www. rad. ru Tel/Fax +7 (495) 231 -1239/1097 1
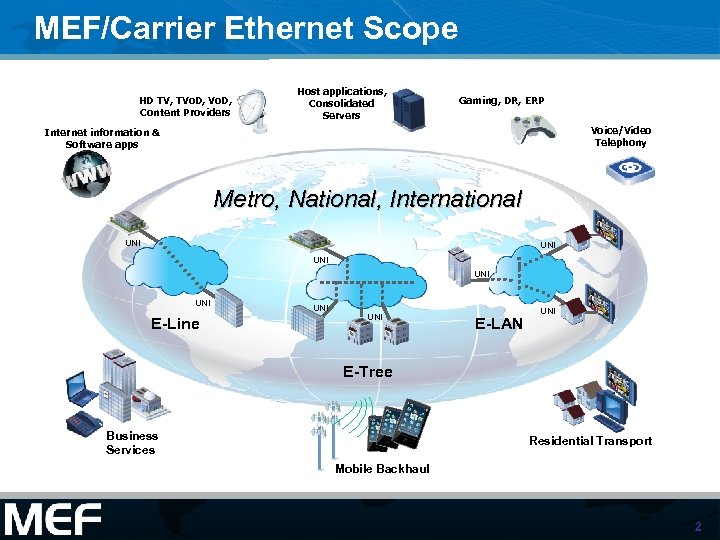 MEF/Carrier Ethernet Scope HD TV, TVo. D, Content Providers Host applications, Consolidated Servers Gaming, DR, ERP Voice/Video Telephony Internet information & Software apps Metro, National, International UNI UNI UNI E-Line UNI E-LAN UNI E-Tree Business Services Residential Transport Mobile Backhaul 2
MEF/Carrier Ethernet Scope HD TV, TVo. D, Content Providers Host applications, Consolidated Servers Gaming, DR, ERP Voice/Video Telephony Internet information & Software apps Metro, National, International UNI UNI UNI E-Line UNI E-LAN UNI E-Tree Business Services Residential Transport Mobile Backhaul 2
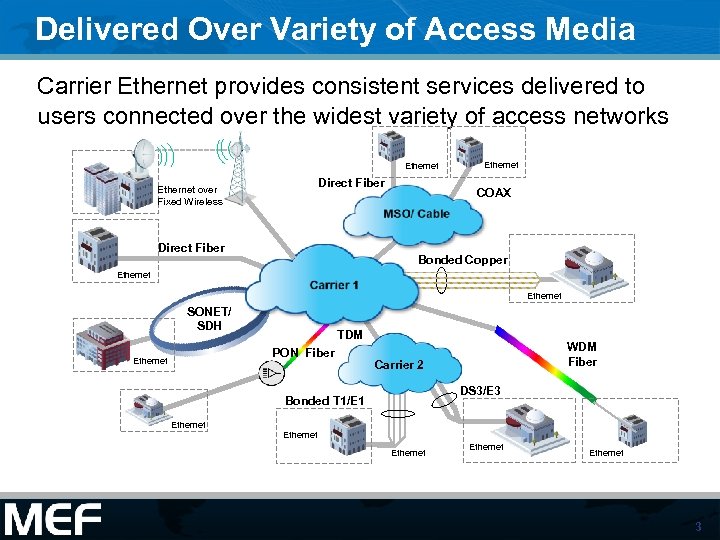 Delivered Over Variety of Access Media Carrier Ethernet provides consistent services delivered to users connected over the widest variety of access networks Ethernet Direct Fiber Ethernet over Fixed Wireless Direct Fiber Ethernet COAX Bonded Copper Ethernet SONET/ SDH TDM PON Fiber Ethernet Carrier 2 DS 3/E 3 Bonded T 1/E 1 Ethernet WDM Fiber Ethernet 3
Delivered Over Variety of Access Media Carrier Ethernet provides consistent services delivered to users connected over the widest variety of access networks Ethernet Direct Fiber Ethernet over Fixed Wireless Direct Fiber Ethernet COAX Bonded Copper Ethernet SONET/ SDH TDM PON Fiber Ethernet Carrier 2 DS 3/E 3 Bonded T 1/E 1 Ethernet WDM Fiber Ethernet 3
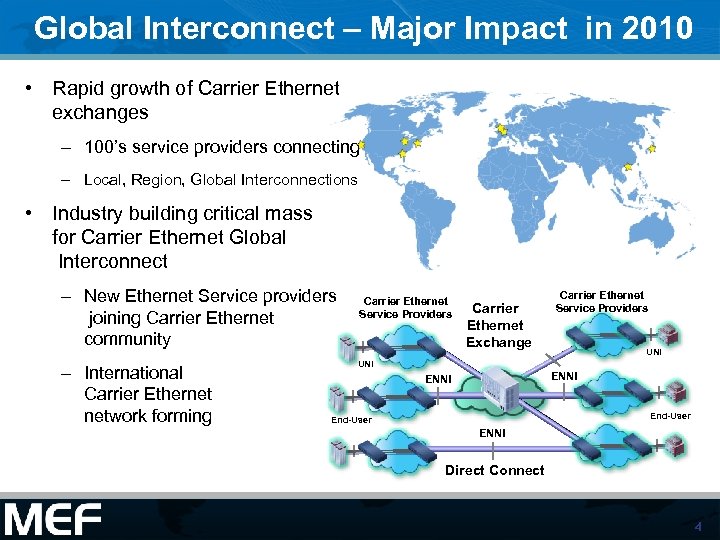 Global Interconnect – Major Impact in 2010 • Rapid growth of Carrier Ethernet exchanges – 100’s service providers connecting – Local, Region, Global Interconnections • Industry building critical mass for Carrier Ethernet Global Interconnect – New Ethernet Service providers joining Carrier Ethernet community – International Carrier Ethernet network forming Carrier Ethernet Service Providers Carrier Ethernet Exchange Carrier Ethernet Service Providers UNI ENNI End-User ENNI Direct Connect 4
Global Interconnect – Major Impact in 2010 • Rapid growth of Carrier Ethernet exchanges – 100’s service providers connecting – Local, Region, Global Interconnections • Industry building critical mass for Carrier Ethernet Global Interconnect – New Ethernet Service providers joining Carrier Ethernet community – International Carrier Ethernet network forming Carrier Ethernet Service Providers Carrier Ethernet Exchange Carrier Ethernet Service Providers UNI ENNI End-User ENNI Direct Connect 4
 MEF: Defining Body of Carrier Ethernet • 174 Member Companies • 78 Service Providers • Global Representation Standards Education Compliance Program Focus 2010 -2011: Global Interconnect 5
MEF: Defining Body of Carrier Ethernet • 174 Member Companies • 78 Service Providers • Global Representation Standards Education Compliance Program Focus 2010 -2011: Global Interconnect 5
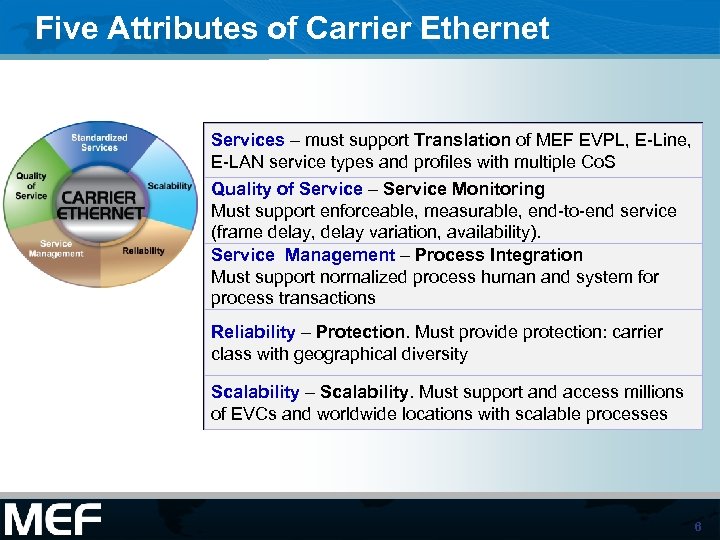 Five Attributes of Carrier Ethernet Services – must support Translation of MEF EVPL, E-Line, E-LAN service types and profiles with multiple Co. S Quality of Service – Service Monitoring Must support enforceable, measurable, end-to-end service (frame delay, delay variation, availability). Service Management – Process Integration Must support normalized process human and system for process transactions Reliability – Protection. Must provide protection: carrier class with geographical diversity Scalability – Scalability. Must support and access millions of EVCs and worldwide locations with scalable processes 6
Five Attributes of Carrier Ethernet Services – must support Translation of MEF EVPL, E-Line, E-LAN service types and profiles with multiple Co. S Quality of Service – Service Monitoring Must support enforceable, measurable, end-to-end service (frame delay, delay variation, availability). Service Management – Process Integration Must support normalized process human and system for process transactions Reliability – Protection. Must provide protection: carrier class with geographical diversity Scalability – Scalability. Must support and access millions of EVCs and worldwide locations with scalable processes 6
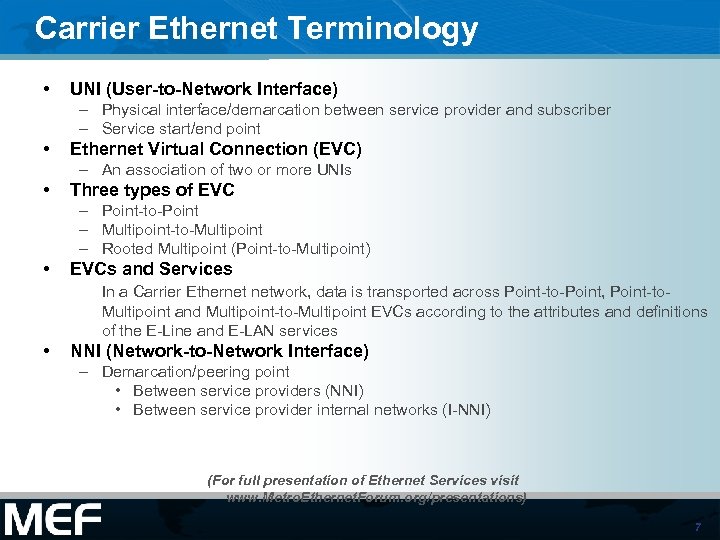 Carrier Ethernet Terminology • UNI (User-to-Network Interface) – Physical interface/demarcation between service provider and subscriber – Service start/end point • Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC) – An association of two or more UNIs • Three types of EVC – Point-to-Point – Multipoint-to-Multipoint – Rooted Multipoint (Point-to-Multipoint) • EVCs and Services In a Carrier Ethernet network, data is transported across Point-to-Point, Point-to. Multipoint and Multipoint-to-Multipoint EVCs according to the attributes and definitions of the E-Line and E-LAN services • NNI (Network-to-Network Interface) – Demarcation/peering point • Between service providers (NNI) • Between service provider internal networks (I-NNI) (For full presentation of Ethernet Services visit www. Metro. Ethernet. Forum. org/presentations) 7
Carrier Ethernet Terminology • UNI (User-to-Network Interface) – Physical interface/demarcation between service provider and subscriber – Service start/end point • Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC) – An association of two or more UNIs • Three types of EVC – Point-to-Point – Multipoint-to-Multipoint – Rooted Multipoint (Point-to-Multipoint) • EVCs and Services In a Carrier Ethernet network, data is transported across Point-to-Point, Point-to. Multipoint and Multipoint-to-Multipoint EVCs according to the attributes and definitions of the E-Line and E-LAN services • NNI (Network-to-Network Interface) – Demarcation/peering point • Between service providers (NNI) • Between service provider internal networks (I-NNI) (For full presentation of Ethernet Services visit www. Metro. Ethernet. Forum. org/presentations) 7
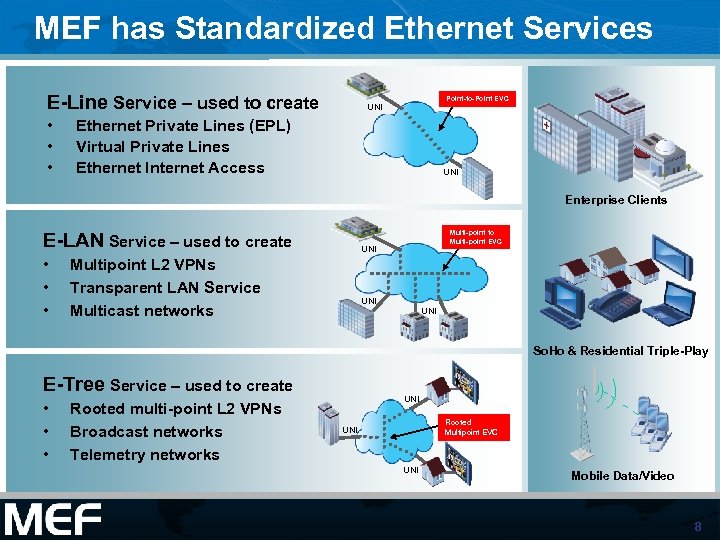 MEF has Standardized Ethernet Services E-Line Service – used to create • • • Point-to-Point EVC UNI Ethernet Private Lines (EPL) Virtual Private Lines Ethernet Internet Access UNI Enterprise Clients E-LAN Service – used to create • • • Multi-point to Multi-point EVC UNI Multipoint L 2 VPNs Transparent LAN Service Multicast networks UNI So. Ho & Residential Triple-Play E-Tree Service – used to create • • • Rooted multi-point L 2 VPNs Broadcast networks Telemetry networks UNI Rooted Multipoint EVC UNI Mobile Data/Video 8
MEF has Standardized Ethernet Services E-Line Service – used to create • • • Point-to-Point EVC UNI Ethernet Private Lines (EPL) Virtual Private Lines Ethernet Internet Access UNI Enterprise Clients E-LAN Service – used to create • • • Multi-point to Multi-point EVC UNI Multipoint L 2 VPNs Transparent LAN Service Multicast networks UNI So. Ho & Residential Triple-Play E-Tree Service – used to create • • • Rooted multi-point L 2 VPNs Broadcast networks Telemetry networks UNI Rooted Multipoint EVC UNI Mobile Data/Video 8
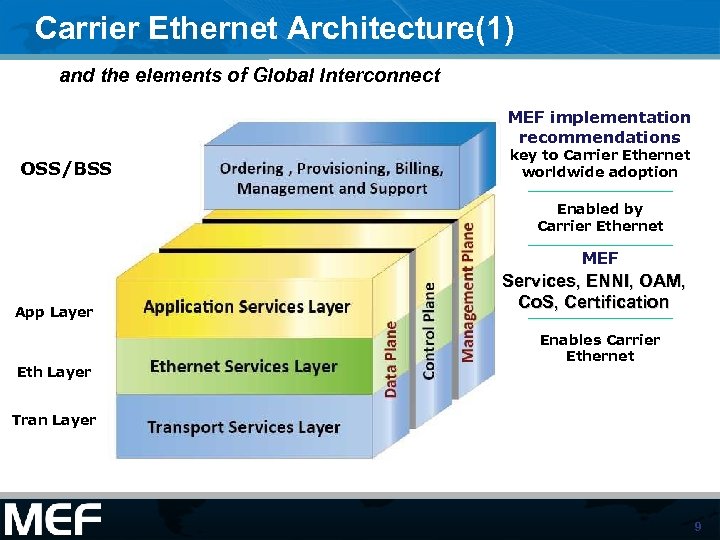 Carrier Ethernet Architecture(1) and the elements of Global Interconnect MEF implementation recommendations OSS/BSS key to Carrier Ethernet worldwide adoption Enabled by Carrier Ethernet MEF App Layer Eth Layer Services, ENNI, OAM, Co. S, Certification Enables Carrier Ethernet Tran Layer 9
Carrier Ethernet Architecture(1) and the elements of Global Interconnect MEF implementation recommendations OSS/BSS key to Carrier Ethernet worldwide adoption Enabled by Carrier Ethernet MEF App Layer Eth Layer Services, ENNI, OAM, Co. S, Certification Enables Carrier Ethernet Tran Layer 9
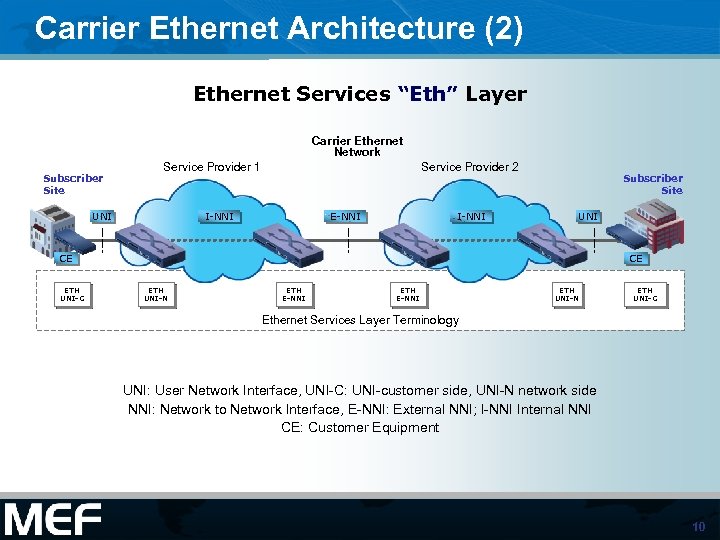 Carrier Ethernet Architecture (2) Ethernet Services “Eth” Layer Carrier Ethernet Network Subscriber Site Service Provider 1 UNI Service Provider 2 I-NNI E-NNI I-NNI Subscriber Site UNI CE ETH UNI-C CE ETH UNI-N ETH E-NNI ETH UNI-N ETH UNI-C Ethernet Services Layer Terminology UNI: User Network Interface, UNI-C: UNI-customer side, UNI-N network side NNI: Network to Network Interface, E-NNI: External NNI; I-NNI Internal NNI CE: Customer Equipment 10
Carrier Ethernet Architecture (2) Ethernet Services “Eth” Layer Carrier Ethernet Network Subscriber Site Service Provider 1 UNI Service Provider 2 I-NNI E-NNI I-NNI Subscriber Site UNI CE ETH UNI-C CE ETH UNI-N ETH E-NNI ETH UNI-N ETH UNI-C Ethernet Services Layer Terminology UNI: User Network Interface, UNI-C: UNI-customer side, UNI-N network side NNI: Network to Network Interface, E-NNI: External NNI; I-NNI Internal NNI CE: Customer Equipment 10
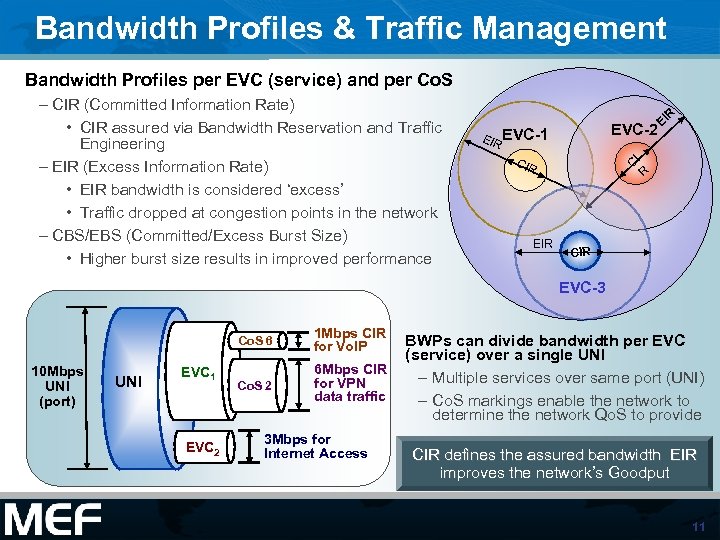 Bandwidth Profiles & Traffic Management Bandwidth Profiles per EVC (service) and per Co. S – CIR (Committed Information Rate) • CIR assured via Bandwidth Reservation and Traffic Engineering – EIR (Excess Information Rate) • EIR bandwidth is considered ‘excess’ • Traffic dropped at congestion points in the network – CBS/EBS (Committed/Excess Burst Size) • Higher burst size results in improved performance EVC-2 EIR EVC-1 CI CIR EIR R EI R CIR EVC-3 Co. S 6 10 Mbps UNI (port) UNI EVC 1 EVC 2 1 Mbps CIR for Vo. IP Co. S 2 6 Mbps CIR for VPN data traffic 3 Mbps for Internet Access BWPs can divide bandwidth per EVC (service) over a single UNI – Multiple services over same port (UNI) – Co. S markings enable the network to determine the network Qo. S to provide CIR defines the assured bandwidth EIR improves the network’s Goodput 11
Bandwidth Profiles & Traffic Management Bandwidth Profiles per EVC (service) and per Co. S – CIR (Committed Information Rate) • CIR assured via Bandwidth Reservation and Traffic Engineering – EIR (Excess Information Rate) • EIR bandwidth is considered ‘excess’ • Traffic dropped at congestion points in the network – CBS/EBS (Committed/Excess Burst Size) • Higher burst size results in improved performance EVC-2 EIR EVC-1 CI CIR EIR R EI R CIR EVC-3 Co. S 6 10 Mbps UNI (port) UNI EVC 1 EVC 2 1 Mbps CIR for Vo. IP Co. S 2 6 Mbps CIR for VPN data traffic 3 Mbps for Internet Access BWPs can divide bandwidth per EVC (service) over a single UNI – Multiple services over same port (UNI) – Co. S markings enable the network to determine the network Qo. S to provide CIR defines the assured bandwidth EIR improves the network’s Goodput 11
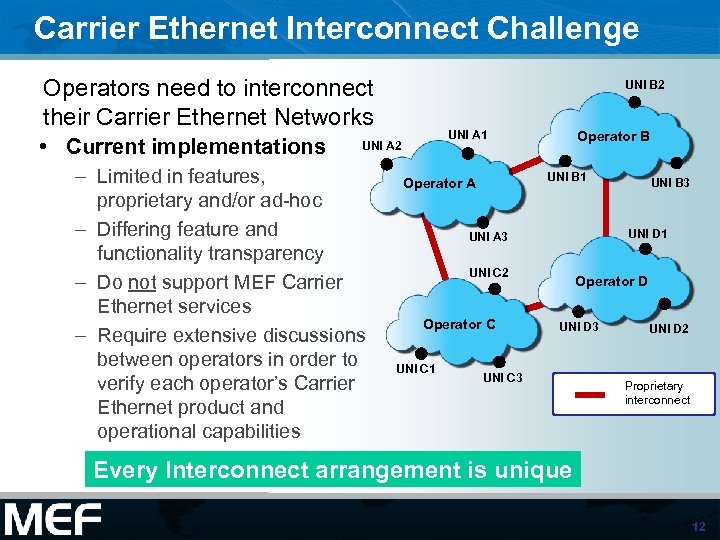 Carrier Ethernet Interconnect Challenge Operators need to interconnect their Carrier Ethernet Networks • Current implementations UNI B 2 – Limited in features, proprietary and/or ad-hoc – Differing feature and functionality transparency – Do not support MEF Carrier Ethernet services – Require extensive discussions between operators in order to verify each operator’s Carrier Ethernet product and operational capabilities Operator B UNI A 1 UNI A 2 UNI B 1 Operator A UNI D 1 UNI A 3 UNI C 2 Operator C UNI C 1 UNI B 3 Operator D UNI D 3 UNI C 3 UNI D 2 Proprietary interconnect Every Interconnect arrangement is unique 12
Carrier Ethernet Interconnect Challenge Operators need to interconnect their Carrier Ethernet Networks • Current implementations UNI B 2 – Limited in features, proprietary and/or ad-hoc – Differing feature and functionality transparency – Do not support MEF Carrier Ethernet services – Require extensive discussions between operators in order to verify each operator’s Carrier Ethernet product and operational capabilities Operator B UNI A 1 UNI A 2 UNI B 1 Operator A UNI D 1 UNI A 3 UNI C 2 Operator C UNI C 1 UNI B 3 Operator D UNI D 3 UNI C 3 UNI D 2 Proprietary interconnect Every Interconnect arrangement is unique 12
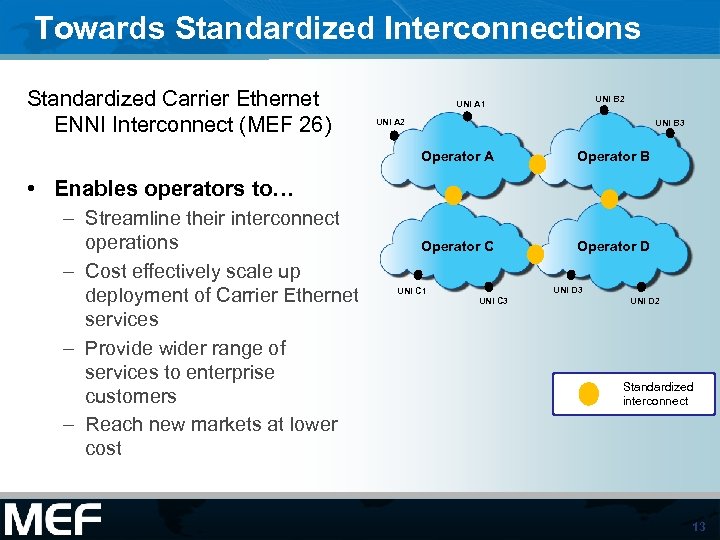 Towards Standardized Interconnections Standardized Carrier Ethernet ENNI Interconnect (MEF 26) UNI B 2 UNI A 1 UNI A 2 UNI B 3 Operator A Operator B Operator C Operator D • Enables operators to… – Streamline their interconnect operations – Cost effectively scale up deployment of Carrier Ethernet services – Provide wider range of services to enterprise customers – Reach new markets at lower cost UNI C 1 UNI D 3 UNI C 3 UNI D 2 Standardized interconnect 13
Towards Standardized Interconnections Standardized Carrier Ethernet ENNI Interconnect (MEF 26) UNI B 2 UNI A 1 UNI A 2 UNI B 3 Operator A Operator B Operator C Operator D • Enables operators to… – Streamline their interconnect operations – Cost effectively scale up deployment of Carrier Ethernet services – Provide wider range of services to enterprise customers – Reach new markets at lower cost UNI C 1 UNI D 3 UNI C 3 UNI D 2 Standardized interconnect 13
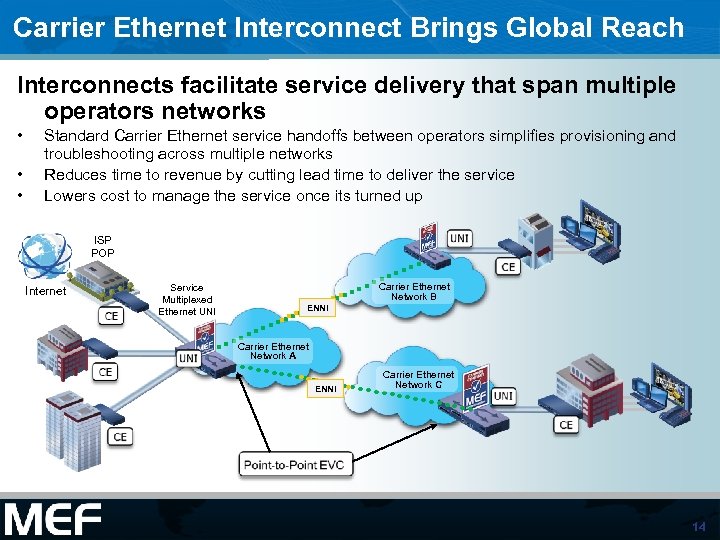 Carrier Ethernet Interconnect Brings Global Reach Interconnects facilitate service delivery that span multiple operators networks • • • Standard Carrier Ethernet service handoffs between operators simplifies provisioning and troubleshooting across multiple networks Reduces time to revenue by cutting lead time to deliver the service Lowers cost to manage the service once its turned up ISP POP Internet Service Multiplexed Ethernet UNI Carrier Ethernet Network B ENNI Carrier Ethernet Network A ENNI Carrier Ethernet Network C 14
Carrier Ethernet Interconnect Brings Global Reach Interconnects facilitate service delivery that span multiple operators networks • • • Standard Carrier Ethernet service handoffs between operators simplifies provisioning and troubleshooting across multiple networks Reduces time to revenue by cutting lead time to deliver the service Lowers cost to manage the service once its turned up ISP POP Internet Service Multiplexed Ethernet UNI Carrier Ethernet Network B ENNI Carrier Ethernet Network A ENNI Carrier Ethernet Network C 14
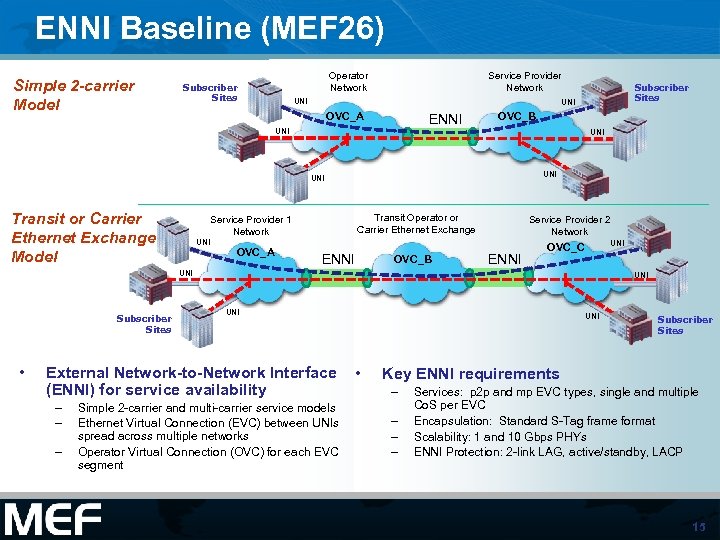 ENNI Baseline (MEF 26) Simple 2 -carrier Model Service Provider Network Operator Network Subscriber Sites UNI OVC_A ENNI OVC_B UNI UNI Transit or Carrier Ethernet Exchange Model Transit Operator or Carrier Ethernet Exchange Service Provider 1 Network UNI OVC_A Subscriber Sites ENNI OVC_B Service Provider 2 Network ENNI UNI OVC_C UNI Subscriber Sites • UNI External Network-to-Network Interface (ENNI) for service availability – – – Simple 2 -carrier and multi-carrier service models Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC) between UNIs spread across multiple networks Operator Virtual Connection (OVC) for each EVC segment UNI • Subscriber Sites Key ENNI requirements – – Services: p 2 p and mp EVC types, single and multiple Co. S per EVC Encapsulation: Standard S-Tag frame format Scalability: 1 and 10 Gbps PHYs ENNI Protection: 2 -link LAG, active/standby, LACP 15
ENNI Baseline (MEF 26) Simple 2 -carrier Model Service Provider Network Operator Network Subscriber Sites UNI OVC_A ENNI OVC_B UNI UNI Transit or Carrier Ethernet Exchange Model Transit Operator or Carrier Ethernet Exchange Service Provider 1 Network UNI OVC_A Subscriber Sites ENNI OVC_B Service Provider 2 Network ENNI UNI OVC_C UNI Subscriber Sites • UNI External Network-to-Network Interface (ENNI) for service availability – – – Simple 2 -carrier and multi-carrier service models Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC) between UNIs spread across multiple networks Operator Virtual Connection (OVC) for each EVC segment UNI • Subscriber Sites Key ENNI requirements – – Services: p 2 p and mp EVC types, single and multiple Co. S per EVC Encapsulation: Standard S-Tag frame format Scalability: 1 and 10 Gbps PHYs ENNI Protection: 2 -link LAG, active/standby, LACP 15
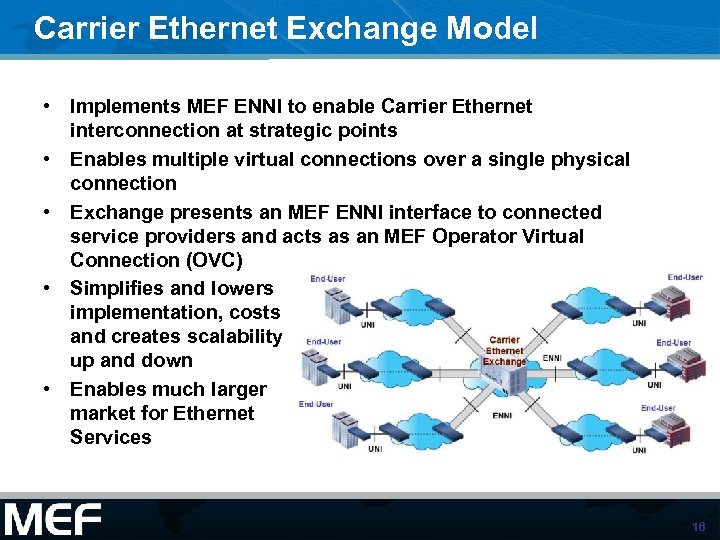 Carrier Ethernet Exchange Model • Implements MEF ENNI to enable Carrier Ethernet interconnection at strategic points • Enables multiple virtual connections over a single physical connection • Exchange presents an MEF ENNI interface to connected service providers and acts as an MEF Operator Virtual Connection (OVC) • Simplifies and lowers implementation, costs and creates scalability up and down • Enables much larger market for Ethernet Services 16
Carrier Ethernet Exchange Model • Implements MEF ENNI to enable Carrier Ethernet interconnection at strategic points • Enables multiple virtual connections over a single physical connection • Exchange presents an MEF ENNI interface to connected service providers and acts as an MEF Operator Virtual Connection (OVC) • Simplifies and lowers implementation, costs and creates scalability up and down • Enables much larger market for Ethernet Services 16
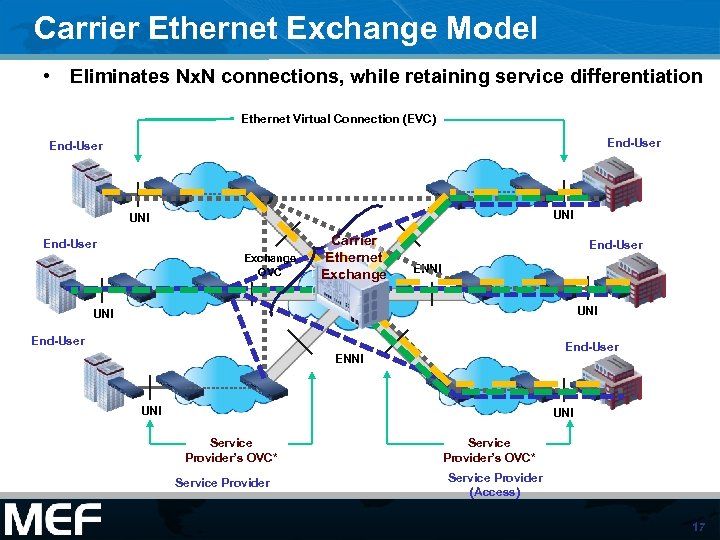 Carrier Ethernet Exchange Model • Eliminates Nx. N connections, while retaining service differentiation Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC) End-User UNI End-User Exchange OVC Carrier Ethernet Exchange End-User ENNI UNI Service Provider’s OVC* Service Provider (Access) 17
Carrier Ethernet Exchange Model • Eliminates Nx. N connections, while retaining service differentiation Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC) End-User UNI End-User Exchange OVC Carrier Ethernet Exchange End-User ENNI UNI Service Provider’s OVC* Service Provider (Access) 17
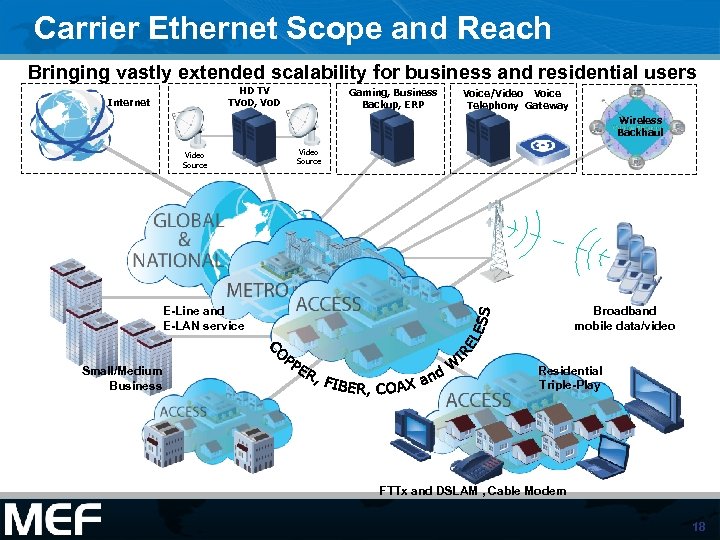 Carrier Ethernet Scope and Reach Bringing vastly extended scalability for business and residential users HD TV TVo. D, Vo. D Internet Gaming, Business Backup, ERP Voice/Video Voice Telephony Gateway Wireless Backhaul Video Source E-Line and E-LAN service Small/Medium Business Broadband mobile data/video Residential Triple-Play FTTx and DSLAM , Cable Modem 18
Carrier Ethernet Scope and Reach Bringing vastly extended scalability for business and residential users HD TV TVo. D, Vo. D Internet Gaming, Business Backup, ERP Voice/Video Voice Telephony Gateway Wireless Backhaul Video Source E-Line and E-LAN service Small/Medium Business Broadband mobile data/video Residential Triple-Play FTTx and DSLAM , Cable Modem 18
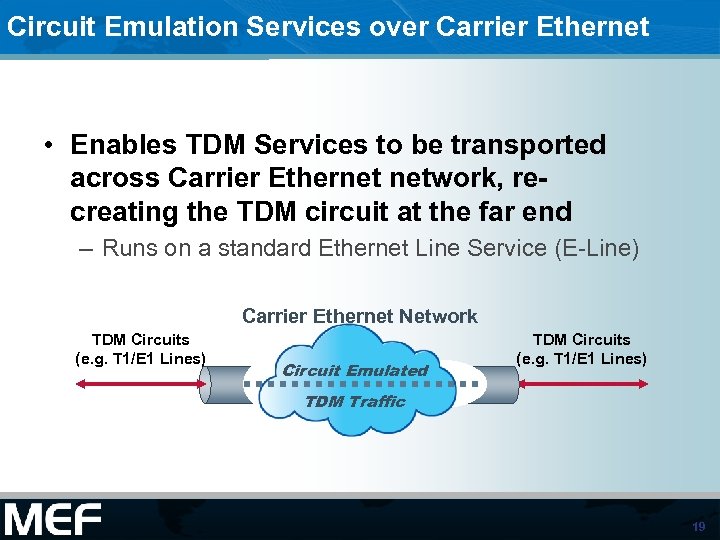 Circuit Emulation Services over Carrier Ethernet • Enables TDM Services to be transported across Carrier Ethernet network, recreating the TDM circuit at the far end – Runs on a standard Ethernet Line Service (E-Line) Carrier Ethernet Network TDM Circuits (e. g. T 1/E 1 Lines) Circuit Emulated TDM Circuits (e. g. T 1/E 1 Lines) TDM Traffic 19
Circuit Emulation Services over Carrier Ethernet • Enables TDM Services to be transported across Carrier Ethernet network, recreating the TDM circuit at the far end – Runs on a standard Ethernet Line Service (E-Line) Carrier Ethernet Network TDM Circuits (e. g. T 1/E 1 Lines) Circuit Emulated TDM Circuits (e. g. T 1/E 1 Lines) TDM Traffic 19
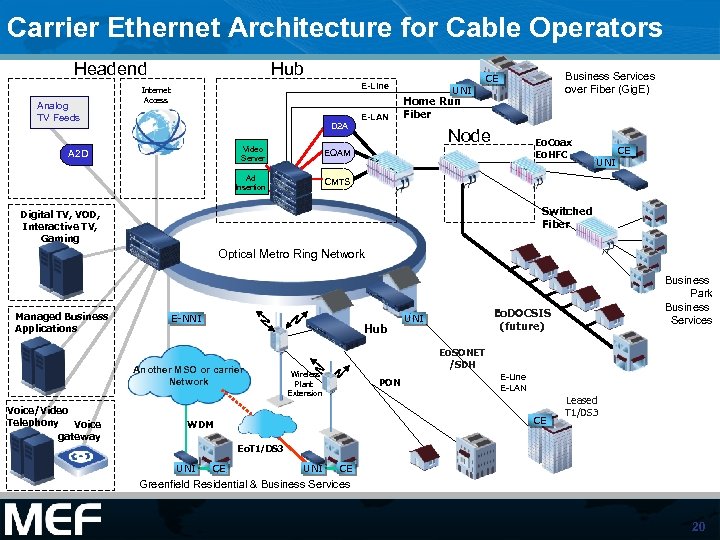 Carrier Ethernet Architecture for Cable Operators Headend Analog TV Feeds Hub D 2 A Video Server UNI Home Run Fiber Node Eo. Coax Eo. HFC EQAM Ad Insertion A 2 D E-LAN Business Services over Fiber (Gig. E) CE E-Line Internet Access CE CMTS UNI Switched Fiber Digital TV, VOD, Interactive TV, Gaming Optical Metro Ring Network Managed Business Applications E-NNI Hub Another MSO or carrier Network Voice/Video Telephony Voice gateway Business Park Business Services Eo. DOCSIS (future) UNI Eo. SONET /SDH Wireless Plant Extension PON E-Line E-LAN CE WDM Leased T 1/DS 3 Eo. T 1/DS 3 UNI CE Greenfield Residential & Business Services 20
Carrier Ethernet Architecture for Cable Operators Headend Analog TV Feeds Hub D 2 A Video Server UNI Home Run Fiber Node Eo. Coax Eo. HFC EQAM Ad Insertion A 2 D E-LAN Business Services over Fiber (Gig. E) CE E-Line Internet Access CE CMTS UNI Switched Fiber Digital TV, VOD, Interactive TV, Gaming Optical Metro Ring Network Managed Business Applications E-NNI Hub Another MSO or carrier Network Voice/Video Telephony Voice gateway Business Park Business Services Eo. DOCSIS (future) UNI Eo. SONET /SDH Wireless Plant Extension PON E-Line E-LAN CE WDM Leased T 1/DS 3 Eo. T 1/DS 3 UNI CE Greenfield Residential & Business Services 20
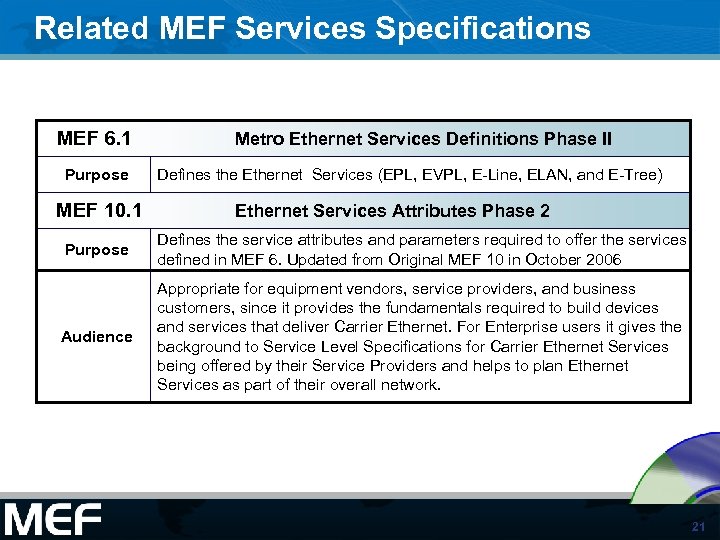 Related MEF Services Specifications MEF 6. 1 Purpose MEF 10. 1 Metro Ethernet Services Definitions Phase II Defines the Ethernet Services (EPL, EVPL, E-Line, ELAN, and E-Tree) Ethernet Services Attributes Phase 2 Purpose Defines the service attributes and parameters required to offer the services defined in MEF 6. Updated from Original MEF 10 in October 2006 Audience Appropriate for equipment vendors, service providers, and business customers, since it provides the fundamentals required to build devices and services that deliver Carrier Ethernet. For Enterprise users it gives the background to Service Level Specifications for Carrier Ethernet Services being offered by their Service Providers and helps to plan Ethernet Services as part of their overall network. 21
Related MEF Services Specifications MEF 6. 1 Purpose MEF 10. 1 Metro Ethernet Services Definitions Phase II Defines the Ethernet Services (EPL, EVPL, E-Line, ELAN, and E-Tree) Ethernet Services Attributes Phase 2 Purpose Defines the service attributes and parameters required to offer the services defined in MEF 6. Updated from Original MEF 10 in October 2006 Audience Appropriate for equipment vendors, service providers, and business customers, since it provides the fundamentals required to build devices and services that deliver Carrier Ethernet. For Enterprise users it gives the background to Service Level Specifications for Carrier Ethernet Services being offered by their Service Providers and helps to plan Ethernet Services as part of their overall network. 21
 Buyer Benefits • • • Reduce operating costs – Through aggregation and inter-operability of multiple Carrier Ethernet services over a single standards-based physical connection Reduce capital costs – Through use of logical connections instead of capital intensive physical assets (e. g. POPs, circuits, etc. ) Increase footprint and reach larger and/or new markets – Geographic (e. g. emerging markets, regional markets) – Capacity (e. g. 1 Gb. E, 10 Gb. E) – Capability to address new market segments (e. g. residential, enterprise, etc. ) Reduce time to market and improve financial benefits – Building a standardized ENNI is faster than building out proprietary infrastructure – Quicker recognition of internal SP infrastructure projects’ financial benefits Increase business efficiencies – Lower management costs through proven inter-operability processes (ordering, implementation, operations, billing) 22
Buyer Benefits • • • Reduce operating costs – Through aggregation and inter-operability of multiple Carrier Ethernet services over a single standards-based physical connection Reduce capital costs – Through use of logical connections instead of capital intensive physical assets (e. g. POPs, circuits, etc. ) Increase footprint and reach larger and/or new markets – Geographic (e. g. emerging markets, regional markets) – Capacity (e. g. 1 Gb. E, 10 Gb. E) – Capability to address new market segments (e. g. residential, enterprise, etc. ) Reduce time to market and improve financial benefits – Building a standardized ENNI is faster than building out proprietary infrastructure – Quicker recognition of internal SP infrastructure projects’ financial benefits Increase business efficiencies – Lower management costs through proven inter-operability processes (ordering, implementation, operations, billing) 22
 Seller Benefits • Reduce operating costs – Spreading fixed operating costs over a large number of inter-operable, standardsbased virtual connections • Reduce capital costs – Faster amortization of initial investment through larger number of virtual connections • Defend footprint – By providing efficient access to seller’s footprint under seller SP commercial terms • Reduce time to market and improve financial benefits – More efficient sales distribution channel using ENNIs instead of multiple EPLs – Enables faster revenue recognition from retail customers • Increase business efficiencies – Through standardized ENNI fulfillment and repair processes 23
Seller Benefits • Reduce operating costs – Spreading fixed operating costs over a large number of inter-operable, standardsbased virtual connections • Reduce capital costs – Faster amortization of initial investment through larger number of virtual connections • Defend footprint – By providing efficient access to seller’s footprint under seller SP commercial terms • Reduce time to market and improve financial benefits – More efficient sales distribution channel using ENNIs instead of multiple EPLs – Enables faster revenue recognition from retail customers • Increase business efficiencies – Through standardized ENNI fulfillment and repair processes 23
 Summary • Implementation of Carrier Ethernet Global Interconnects worldwide with continued acceleration in 2011 and beyond • MEF Global Interconnect Program, consisting of MEF Specifications, Certification and Connect, provides a common and standard framework for the industry • Collectively, Global Interconnect exists to enable standardized and streamlined delivery of MEF-certified Carrier Ethernet services to scale locally and globally: – For end users the worldwide connection is transparent and seamless. – For service providers it unlocks new revenue opportunities: expanding the numbers of locations that can be reached economically 24
Summary • Implementation of Carrier Ethernet Global Interconnects worldwide with continued acceleration in 2011 and beyond • MEF Global Interconnect Program, consisting of MEF Specifications, Certification and Connect, provides a common and standard framework for the industry • Collectively, Global Interconnect exists to enable standardized and streamlined delivery of MEF-certified Carrier Ethernet services to scale locally and globally: – For end users the worldwide connection is transparent and seamless. – For service providers it unlocks new revenue opportunities: expanding the numbers of locations that can be reached economically 24
 MEF Global Interconnect Summary • Totality of interconnected autonomous Carrier Ethernet networks worldwide • Enabling – Standardized and streamlined delivery of MEFcertified Carrier Ethernet services – End-to-end Class of Service, management and protection Standards Education Compliance 25
MEF Global Interconnect Summary • Totality of interconnected autonomous Carrier Ethernet networks worldwide • Enabling – Standardized and streamlined delivery of MEFcertified Carrier Ethernet services – End-to-end Class of Service, management and protection Standards Education Compliance 25
 Thank you! Visit the following MEF Web sites for more details: www. metroethernetforum. org and www. ethernetacademy. net 26
Thank you! Visit the following MEF Web sites for more details: www. metroethernetforum. org and www. ethernetacademy. net 26


