3b3a7d85f02524b3b7372e6cd482f7c7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
Developing domain specific gateways based on the WSPGRADE/g. USE framework http: //www. sci-bus. eu Peter Kacsuk MTA SZTAKI Start date: 2011 -10 -01 Duration: 36 months SCI-BUS is supported by the FP 7 Capacities Programme under contract nr RI-283481 1

How to build a science gateway? 1. Build from scratch – If the gateway is not extremely simple, it requires long time to develop a robust gateway – Requires substantial manpower and development cost – It is very specialized and as users start to use it and come up with new requirements it is difficult to extend in a scalable way – Isolated development without belonging to an open source community => sustainability is difficult 2

How to build a science gateway? 2. Adapt and customize an existing gateway technology – Significantly reduces development time (e. g. Yuri Gordienko’s talk) – Requires limited manpower and development cost – Produces a robust and usable service – The open source community is driving force for further development and extensions SCI-BUS provides the required core gateway and customization technology 3
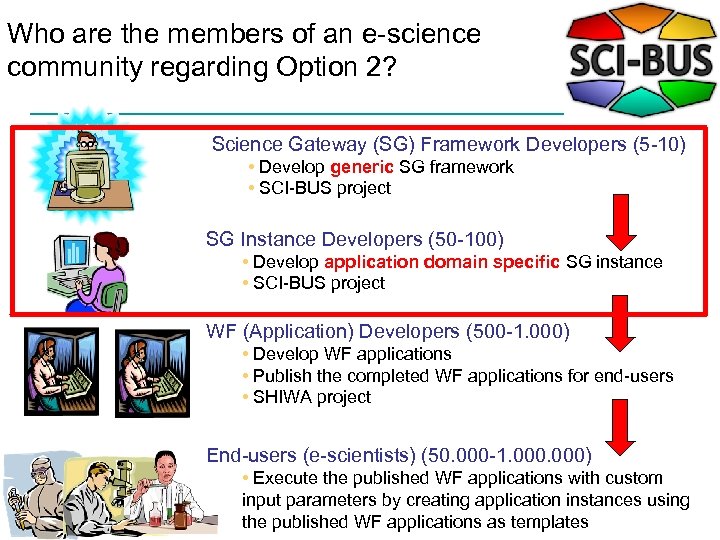
Who are the members of an e-science community regarding Option 2? Science Gateway (SG) Framework Developers (5 -10) • Develop generic SG framework • SCI-BUS project SG Instance Developers (50 -100) • Develop application domain specific SG instance • SCI-BUS project WF (Application) Developers (500 -1. 000) • Develop WF applications • Publish the completed WF applications for end-users • SHIWA project End-users (e-scientists) (50. 000 -1. 000) • Execute the published WF applications with custom input parameters by creating application instances using the published WF applications as templates
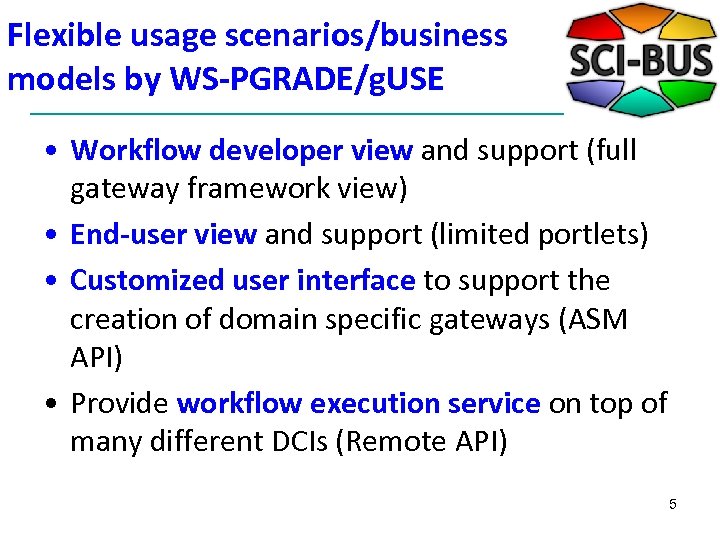
Flexible usage scenarios/business models by WS-PGRADE/g. USE • Workflow developer view and support (full gateway framework view) • End-user view and support (limited portlets) • Customized user interface to support the creation of domain specific gateways (ASM API) • Provide workflow execution service on top of many different DCIs (Remote API) 5
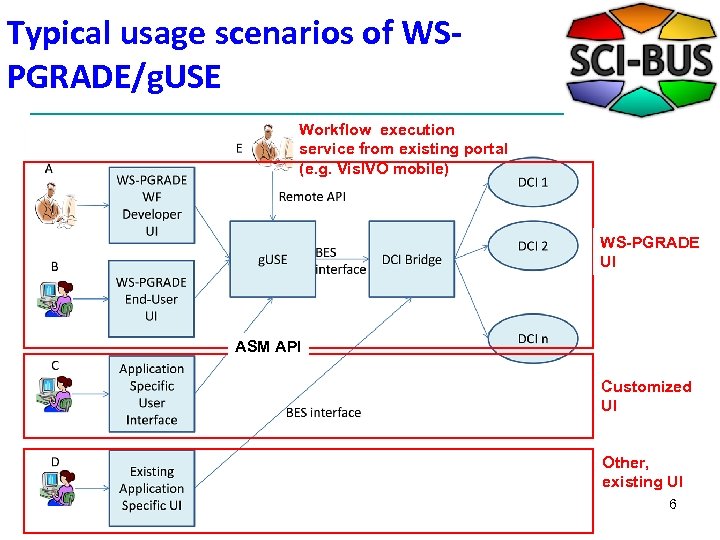
Typical usage scenarios of WSPGRADE/g. USE Workflow execution service from existing portal (e. g. Vis. IVO mobile) WS-PGRADE UI ASM API Customized UI Other, existing UI 6
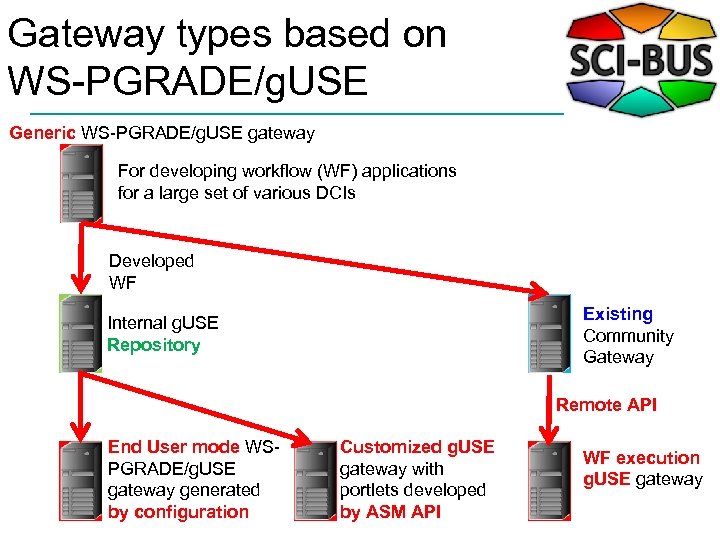
Gateway types based on WS-PGRADE/g. USE Generic WS-PGRADE/g. USE gateway For developing workflow (WF) applications for a large set of various DCIs Developed WF Existing Community Gateway Internal g. USE Repository Remote API End User mode WSPGRADE/g. USE gateway generated by configuration Customized g. USE gateway with portlets developed by ASM API WF execution g. USE gateway
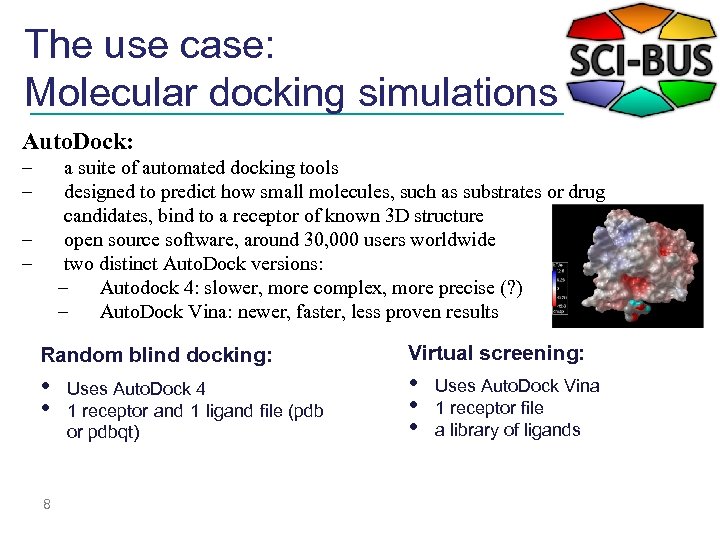
The use case: Molecular docking simulations Auto. Dock: – – a suite of automated docking tools designed to predict how small molecules, such as substrates or drug candidates, bind to a receptor of known 3 D structure open source software, around 30, 000 users worldwide two distinct Auto. Dock versions: – Autodock 4: slower, more complex, more precise (? ) – Auto. Dock Vina: newer, faster, less proven results – – Random blind docking: Virtual screening: • • • 8 Uses Auto. Dock 4 1 receptor and 1 ligand file (pdb or pdbqt) Uses Auto. Dock Vina 1 receptor file a library of ligands
Autodock gateway operated by SZTAKI

Autodock and rendering gateway operated by Univ. of Westminster
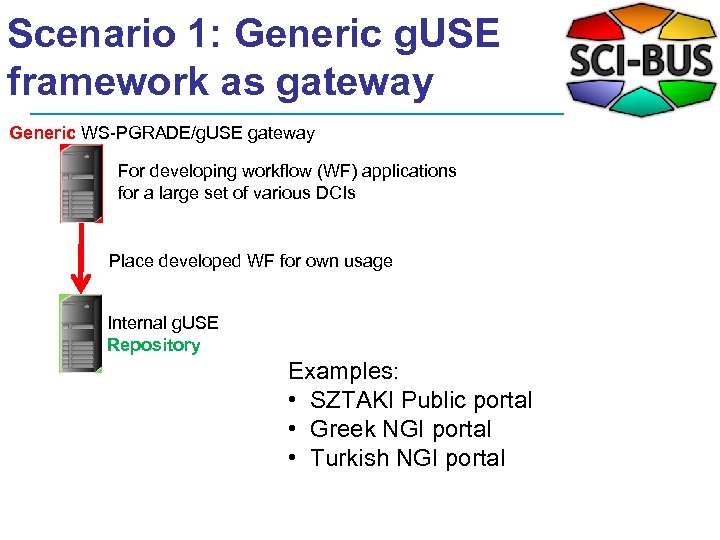
Scenario 1: Generic g. USE framework as gateway Generic WS-PGRADE/g. USE gateway For developing workflow (WF) applications for a large set of various DCIs Place developed WF for own usage Internal g. USE Repository Examples: • SZTAKI Public portal • Greek NGI portal • Turkish NGI portal
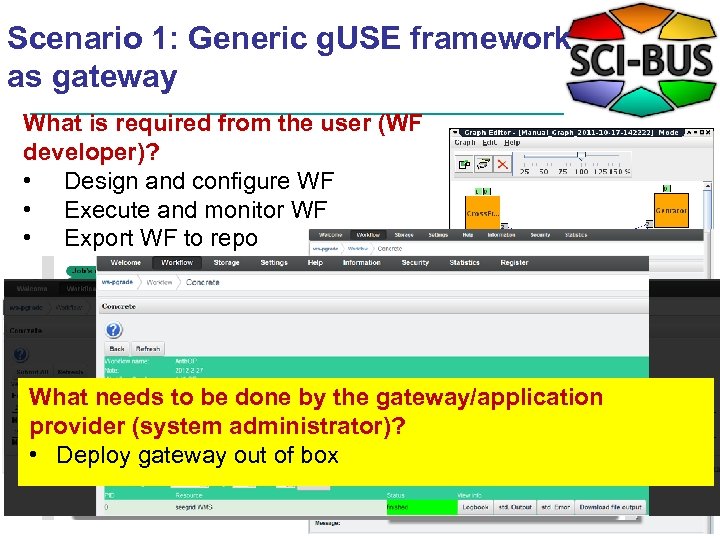
Scenario 1: Generic g. USE framework as gateway What is required from the user (WF developer)? • Design and configure WF • Execute and monitor WF • Export WF to repo What needs to be done by the gateway/application provider (system administrator)? • Deploy gateway out of box
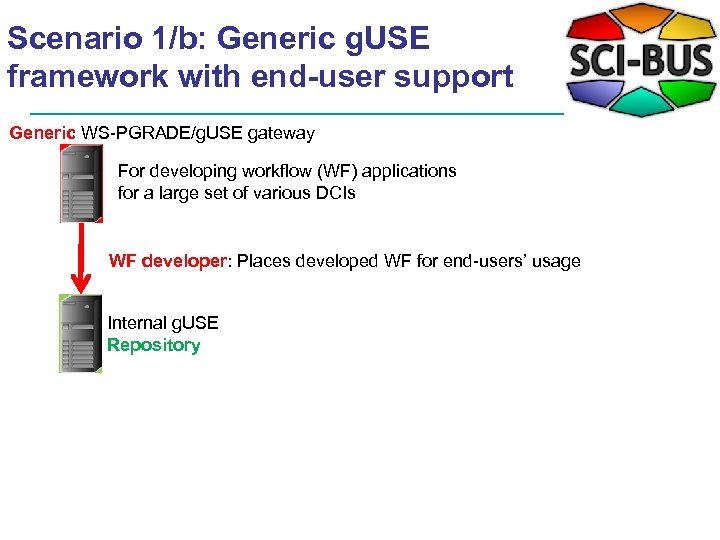
Scenario 1/b: Generic g. USE framework with end-user support Generic WS-PGRADE/g. USE gateway For developing workflow (WF) applications for a large set of various DCIs WF developer: Places developed WF for end-users’ usage Internal g. USE Repository
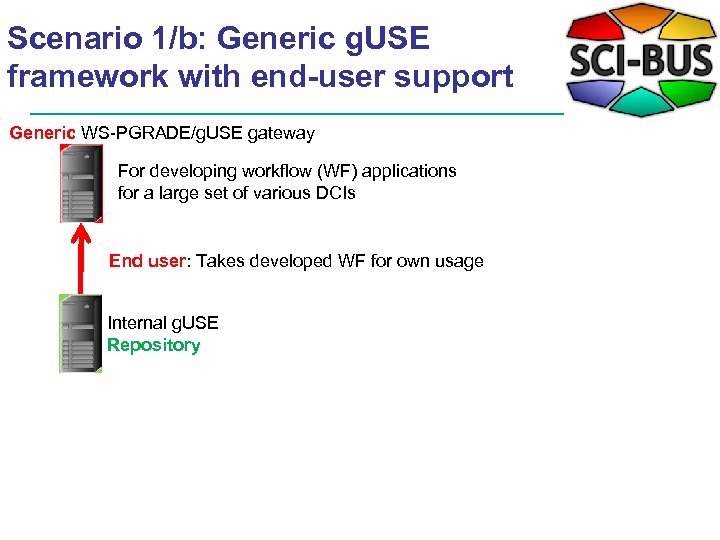
Scenario 1/b: Generic g. USE framework with end-user support Generic WS-PGRADE/g. USE gateway For developing workflow (WF) applications for a large set of various DCIs End user: Takes developed WF for own usage Internal g. USE Repository

Scenario 1/b: Generic g. USE framework with end-user support What is required from the end-user? • Import workflow from repository • Customise, execute and monitor workflow What needs to be done by the gateway/application provider (system administrator + workflow developer)? • Deploy gateway out of box • Develop and configure workflows • Export workflows to repository
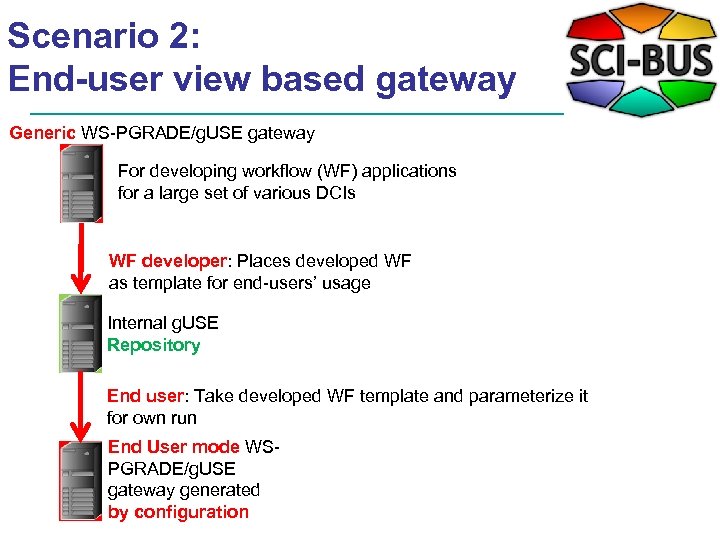
Scenario 2: End-user view based gateway Generic WS-PGRADE/g. USE gateway For developing workflow (WF) applications for a large set of various DCIs WF developer: Places developed WF as template for end-users’ usage Internal g. USE Repository End user: Take developed WF template and parameterize it for own run End User mode WSPGRADE/g. USE gateway generated by configuration
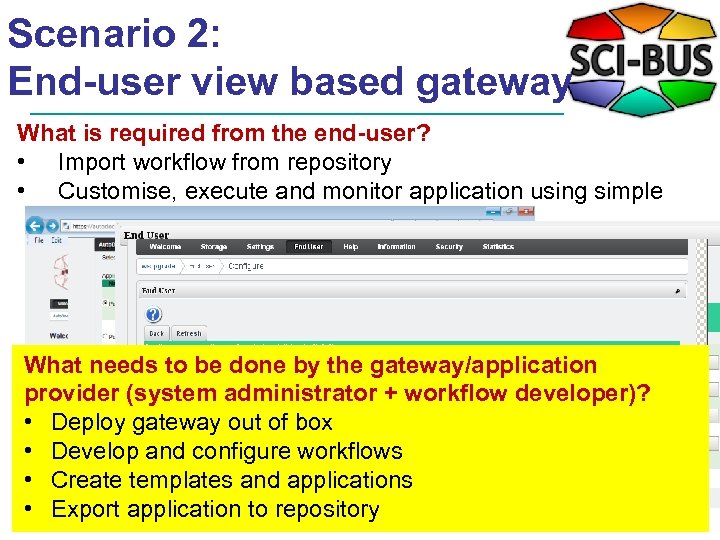
Scenario 2: End-user view based gateway What is required from the end-user? • Import workflow from repository • Customise, execute and monitor application using simple web forms What needs to be done by the gateway/application provider (system administrator + workflow developer)? • Deploy gateway out of box • Develop and configure workflows • Create templates and applications • Export application to repository
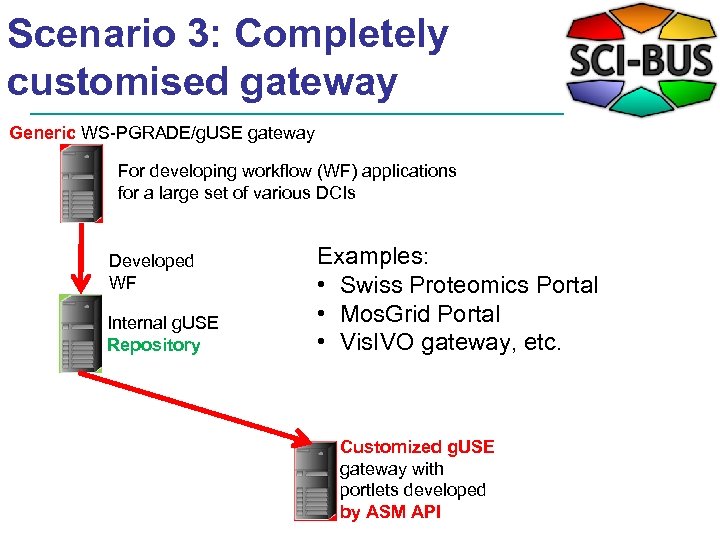
Scenario 3: Completely customised gateway Generic WS-PGRADE/g. USE gateway For developing workflow (WF) applications for a large set of various DCIs Developed WF Internal g. USE Repository Examples: • Swiss Proteomics Portal • Mos. Grid Portal • Vis. IVO gateway, etc. Customized g. USE gateway with portlets developed by ASM API

Scenario 3: Completely customised gateway What is required from the end-user? • Execute and monitor application using completely customised GUI What needs to be done by the gateway/application provider (system administrator + workflow developer + SG instance developer)? • Deploy gateway out of box • Develop and configure workflows • Export workflows to repository • Develop custom GUI using the Application Specific Module (ASM) API accessing g. USE services
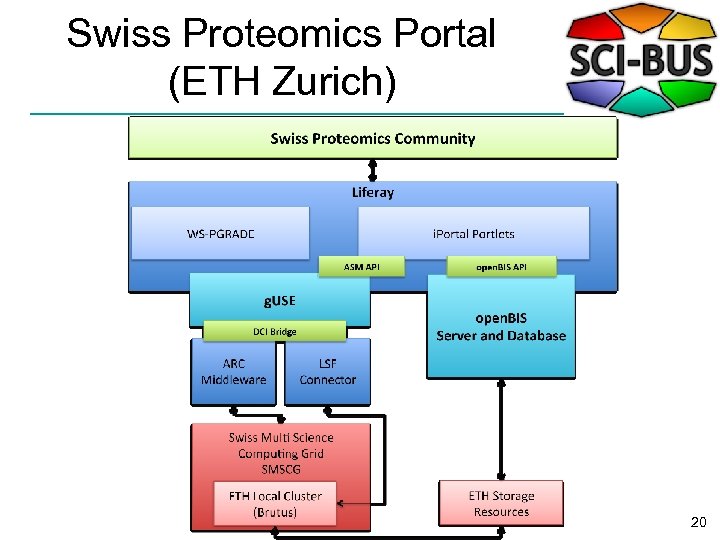
Swiss Proteomics Portal (ETH Zurich) 20
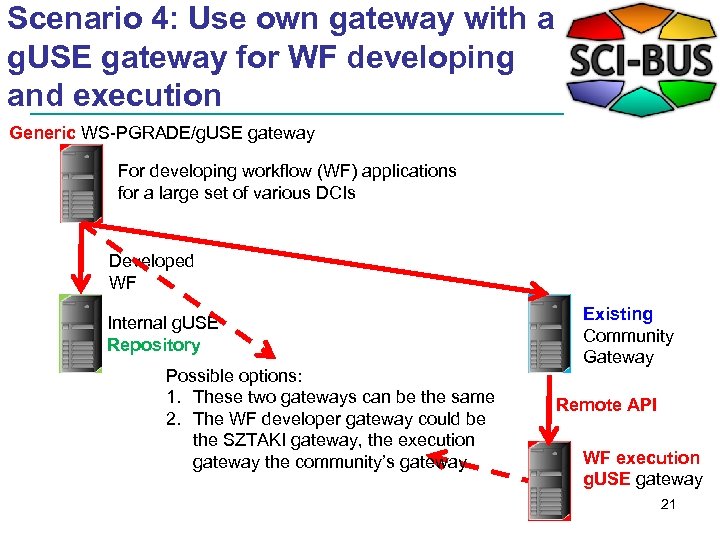
Scenario 4: Use own gateway with a g. USE gateway for WF developing and execution Generic WS-PGRADE/g. USE gateway For developing workflow (WF) applications for a large set of various DCIs Developed WF Internal g. USE Repository Possible options: 1. These two gateways can be the same 2. The WF developer gateway could be the SZTAKI gateway, the execution gateway the community’s gateway Existing Community Gateway Remote API WF execution g. USE gateway 21

Scenario 4: Use own gateway with a g. USE gateway for WF developing and execution • See the AEGIS CMPC Scientific Gateway poster as an example • Further examples: – 4 D Soft portal – e-Group portal – Vis. IVO Mobile 22
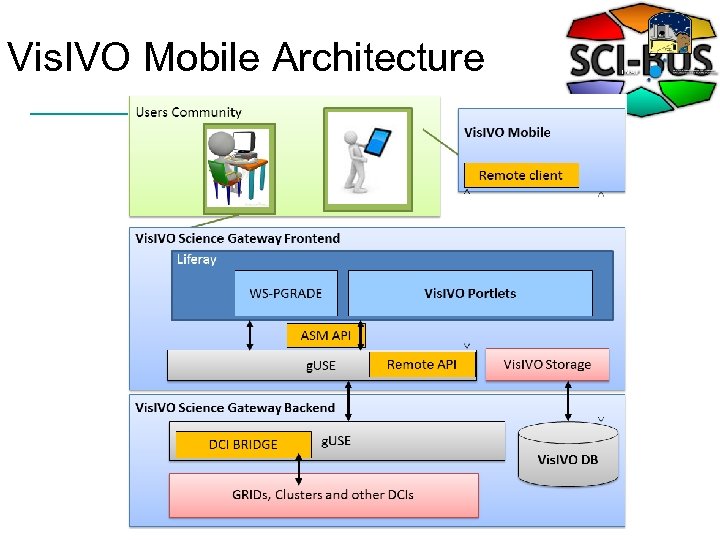
Vis. IVO Mobile Architecture
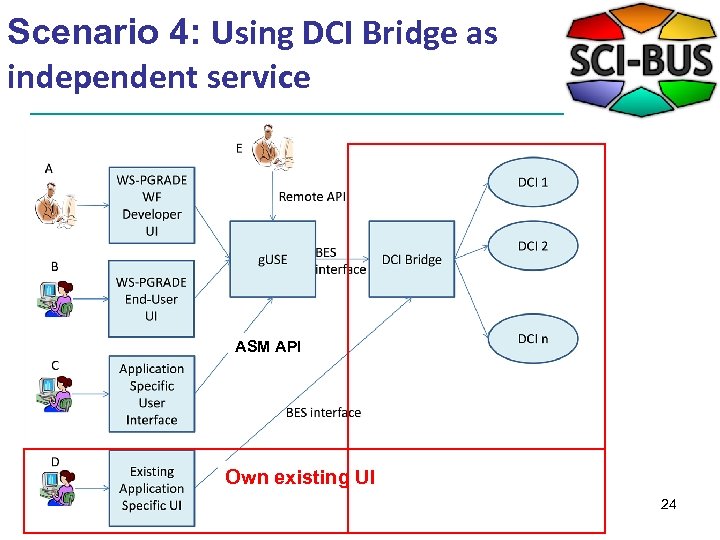
Scenario 4: Using DCI Bridge as independent service ASM API Own existing UI 24

Conclusions • There is a rich set of options on how to use WS-p. GRADE/g. USE technology • Think over how you would like to support your community and choose the most suitable option 25
3b3a7d85f02524b3b7372e6cd482f7c7.ppt