efa43a3dcfff4d454595cf2e7acc86d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
 Developing Assessment Literacy: A workshop on the relationship between instruction, assessment & evaluation Developed & Presented by Edward J. Caropreso, Ph. D Watson School of Education University of North Carolina Wilmington caropresoe@uncw. edu 910. 962. 7830 Director of Academics Marine Corps Combat Service Support Schools Camp Johnson, NC January, 2011
Developing Assessment Literacy: A workshop on the relationship between instruction, assessment & evaluation Developed & Presented by Edward J. Caropreso, Ph. D Watson School of Education University of North Carolina Wilmington caropresoe@uncw. edu 910. 962. 7830 Director of Academics Marine Corps Combat Service Support Schools Camp Johnson, NC January, 2011
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information 1. Describe validity; reliability 2. Explain the relationship between high quality assessment and validity/reliability 1. Recognize/value the role of instructors as student study supports 2. Recognize the relationship between test item types & specific study strategies
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information 1. Describe validity; reliability 2. Explain the relationship between high quality assessment and validity/reliability 1. Recognize/value the role of instructors as student study supports 2. Recognize the relationship between test item types & specific study strategies
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts)
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts)
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 5. 6. 7. 8. 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information 1. Describe validity; reliability 2. Explain the relationship between high quality assessment and validity/reliability 1. Recognize/value the role of instructors as student study supports 2. Recognize the relationship between test item types & specific study strategies
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 5. 6. 7. 8. 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information 1. Describe validity; reliability 2. Explain the relationship between high quality assessment and validity/reliability 1. Recognize/value the role of instructors as student study supports 2. Recognize the relationship between test item types & specific study strategies
 Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability Supporting Student Learning through Assessment KSU Study Strategies; Test Preps Improving Performance; MIT Test Strategies
Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability Supporting Student Learning through Assessment KSU Study Strategies; Test Preps Improving Performance; MIT Test Strategies
 Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc.
Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc.
 Workshop Contents 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability Supporting Student Learning through Assessment KSU Study Strategies; Test Preps Improving Performance; MIT Test Strategies
Workshop Contents 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability Supporting Student Learning through Assessment KSU Study Strategies; Test Preps Improving Performance; MIT Test Strategies
 Workshop Contents 1. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge-Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts
Workshop Contents 1. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge-Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary
 1. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model of Assessment & Evaluation Professional Vocabulary for Concepts
1. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model of Assessment & Evaluation Professional Vocabulary for Concepts
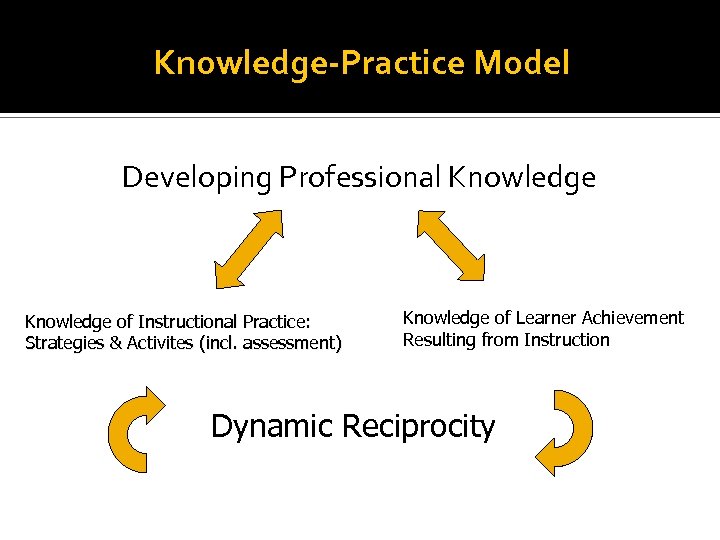 Knowledge-Practice Model Developing Professional Knowledge of Instructional Practice: Strategies & Activites (incl. assessment) Knowledge of Learner Achievement Resulting from Instruction Dynamic Reciprocity
Knowledge-Practice Model Developing Professional Knowledge of Instructional Practice: Strategies & Activites (incl. assessment) Knowledge of Learner Achievement Resulting from Instruction Dynamic Reciprocity
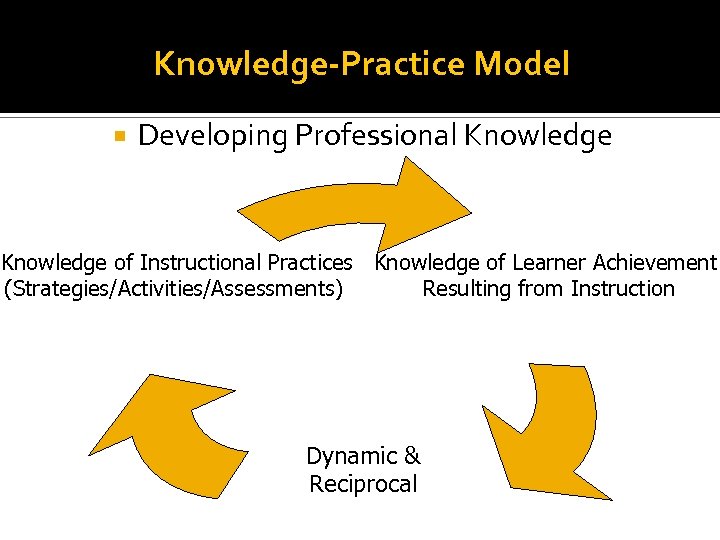 Knowledge-Practice Model Developing Professional Knowledge of Instructional Practices Knowledge of Learner Achievement (Strategies/Activities/Assessments) Resulting from Instruction Dynamic & Reciprocal
Knowledge-Practice Model Developing Professional Knowledge of Instructional Practices Knowledge of Learner Achievement (Strategies/Activities/Assessments) Resulting from Instruction Dynamic & Reciprocal
 Knowledge-Practice Model (Discussion Activity) What’s the current status of your professional knowledge? How have you developed your knowledge of instruction, assessment and evaluation? What are your expectations for developing your professional knowledge & practice? What are your professional development alternatives?
Knowledge-Practice Model (Discussion Activity) What’s the current status of your professional knowledge? How have you developed your knowledge of instruction, assessment and evaluation? What are your expectations for developing your professional knowledge & practice? What are your professional development alternatives?
 Professional Vocabulary for Concepts Activity: Review/id concepts you know well; compare/contrast with colleagues’/groups’ Resources & Databases New Horizons for Learning http: //www. newhorizons. org/strategies/assess/terminology. htm Nat’l. Center for Research on Evaluation, Standards, & Student Testing (CRESST @ UCLA) http: //www. cse. ucla. edu/products/glossary. html Coalition of Essential Schools: Defining Assessment http: //www. essentialschools. org/cs/resources/view/ces_res/124 System of Adult Basic Education Supports http: //www. sabes. org/assessment/glossary. htm Beyond Confusion: An Assessment Glossary, by Andrea Leskes http: //ctl. stanford. edu/Tomprof/postings/448. html Continuous Assessment: Practical Guide for Teachers
Professional Vocabulary for Concepts Activity: Review/id concepts you know well; compare/contrast with colleagues’/groups’ Resources & Databases New Horizons for Learning http: //www. newhorizons. org/strategies/assess/terminology. htm Nat’l. Center for Research on Evaluation, Standards, & Student Testing (CRESST @ UCLA) http: //www. cse. ucla. edu/products/glossary. html Coalition of Essential Schools: Defining Assessment http: //www. essentialschools. org/cs/resources/view/ces_res/124 System of Adult Basic Education Supports http: //www. sabes. org/assessment/glossary. htm Beyond Confusion: An Assessment Glossary, by Andrea Leskes http: //ctl. stanford. edu/Tomprof/postings/448. html Continuous Assessment: Practical Guide for Teachers
 Professional Vocabulary (Activity) Review the glossaries Identify the terms & concepts you know Mark the ones you know & understand Compare your list to colleagues’/groups’ What’s the same; what’s different? Why are there differences? What are the implications for professional practice given inconsistencies in the knowledge base?
Professional Vocabulary (Activity) Review the glossaries Identify the terms & concepts you know Mark the ones you know & understand Compare your list to colleagues’/groups’ What’s the same; what’s different? Why are there differences? What are the implications for professional practice given inconsistencies in the knowledge base?
 Workshop Contents 2. Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives
Workshop Contents 2. Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 2. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 2. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system
 2. Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives
2. Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives
 Educational Goals & Objectives Educational Goals: “…those human activities which contribute to the functioning of a society (including the functioning of an individual in society), and which can be acquired through learning. ” (Gagne, Briggs, & Wagner, 1988, p. 39; cited in Nitko, 2001, p. 23) Goals are stated in broad terms that give direction and purpose to planning overall educational activities.
Educational Goals & Objectives Educational Goals: “…those human activities which contribute to the functioning of a society (including the functioning of an individual in society), and which can be acquired through learning. ” (Gagne, Briggs, & Wagner, 1988, p. 39; cited in Nitko, 2001, p. 23) Goals are stated in broad terms that give direction and purpose to planning overall educational activities.
 Educational Goals & Objectives Educational Goals (or global objectives) : Broad, complex learning outcomes that require substantial time and instruction to accomplish Typically encompassing many specific learning objectives which require learner success on most/all to reach the general goal (from Airasian, 2001)
Educational Goals & Objectives Educational Goals (or global objectives) : Broad, complex learning outcomes that require substantial time and instruction to accomplish Typically encompassing many specific learning objectives which require learner success on most/all to reach the general goal (from Airasian, 2001)
 Educational Goals & Objectives Educational Goals UT Examples of Goals vs Objectives More Examples of Goals vs Objectives Airasian’s 3 Level Model
Educational Goals & Objectives Educational Goals UT Examples of Goals vs Objectives More Examples of Goals vs Objectives Airasian’s 3 Level Model
 Models of Objectives Two Common Models: Mager & Gronlund Mager Tips Gagne & Briggs & ABCD Models A Comparison of Models Greenberg’s 6 Keys to Successful Performance Objectives
Models of Objectives Two Common Models: Mager & Gronlund Mager Tips Gagne & Briggs & ABCD Models A Comparison of Models Greenberg’s 6 Keys to Successful Performance Objectives
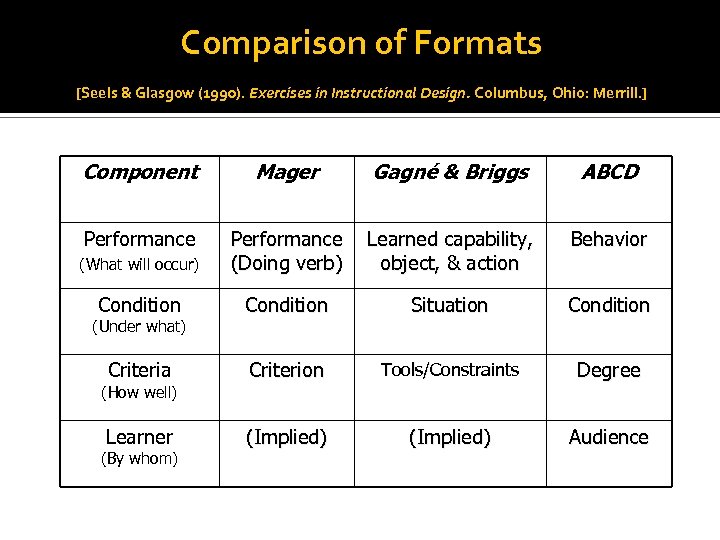 Comparison of Formats [Seels & Glasgow (1990). Exercises in Instructional Design. Columbus, Ohio: Merrill. ] Component Mager Gagné & Briggs ABCD Performance Learned capability, object, & action Behavior (What will occur) Performance (Doing verb) Condition Situation Condition Criteria Criterion Tools/Constraints Degree Learner (Implied) Audience (Under what) (How well) (By whom)
Comparison of Formats [Seels & Glasgow (1990). Exercises in Instructional Design. Columbus, Ohio: Merrill. ] Component Mager Gagné & Briggs ABCD Performance Learned capability, object, & action Behavior (What will occur) Performance (Doing verb) Condition Situation Condition Criteria Criterion Tools/Constraints Degree Learner (Implied) Audience (Under what) (How well) (By whom)
 Working with Objectives Understanding the Context of Learning How do you make sense of learning? How do you identify/describe expectations? Putting Bloom’s Taxonomy to Work Three Types of Learning What Drives Statements of Learning: Active Verbs
Working with Objectives Understanding the Context of Learning How do you make sense of learning? How do you identify/describe expectations? Putting Bloom’s Taxonomy to Work Three Types of Learning What Drives Statements of Learning: Active Verbs
 Working with Objectives: Activity Identify & State 1 3 TLOs (goals; in your area) For each TLO (goal), using the course materials, identify & state 1 2 knowledge & 1 2 performance objectives (ELOs) in at least two models we’ve reviewed Compare your objectives with a colleague’s Using Greenberg’s Criteria to review your objectives, how do they hold up? What’s similar to your colleague? What’s different? Keep your objectives for later; we’ll use them again!
Working with Objectives: Activity Identify & State 1 3 TLOs (goals; in your area) For each TLO (goal), using the course materials, identify & state 1 2 knowledge & 1 2 performance objectives (ELOs) in at least two models we’ve reviewed Compare your objectives with a colleague’s Using Greenberg’s Criteria to review your objectives, how do they hold up? What’s similar to your colleague? What’s different? Keep your objectives for later; we’ll use them again!
 Workshop Contents 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision-making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc.
Workshop Contents 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision-making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc.
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 3. 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 3. 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment
 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation Establishing vocabulary & conceptual framework Assessment and Evaluation: What do they mean? Relationship between assessment, evaluation and decision making: The role of time What about instructional outcomes? Instruction, assessment and evaluation Developing Criteria
3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation Establishing vocabulary & conceptual framework Assessment and Evaluation: What do they mean? Relationship between assessment, evaluation and decision making: The role of time What about instructional outcomes? Instruction, assessment and evaluation Developing Criteria
 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation Model of Assessment Identifying & applying appropriate strategies to gather information for specific purposes &/or decisions Determining appropriate assessment strategies Appropriately applying strategies
3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation Model of Assessment Identifying & applying appropriate strategies to gather information for specific purposes &/or decisions Determining appropriate assessment strategies Appropriately applying strategies
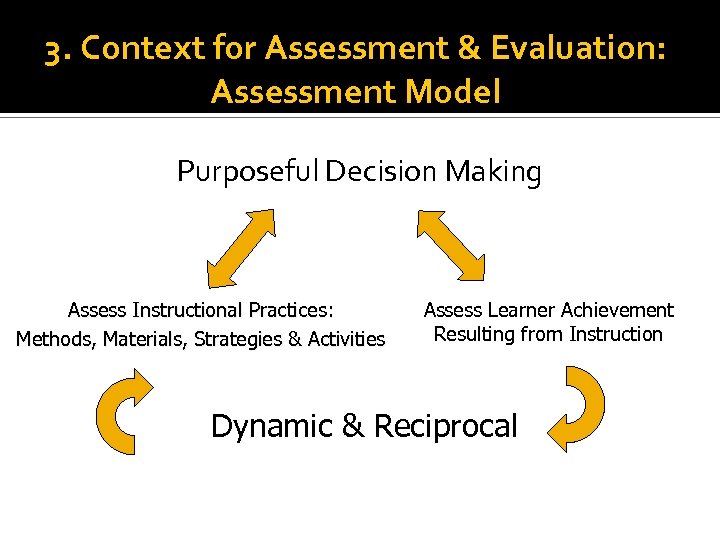 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation: Assessment Model Purposeful Decision Making Assess Instructional Practices: Methods, Materials, Strategies & Activities Assess Learner Achievement Resulting from Instruction Dynamic & Reciprocal
3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation: Assessment Model Purposeful Decision Making Assess Instructional Practices: Methods, Materials, Strategies & Activities Assess Learner Achievement Resulting from Instruction Dynamic & Reciprocal
 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation Types of Assessments by Purpose Bloom’s Taxonomy as Context Aim High Objective Assessment Selected vs Constructed Response Subjective (Non Objective) Assessment Writing/Generating Responses Role & Control of Subjectivity in Assessment Alternative Assessment Authentic Assessment Performance Assessment
3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation Types of Assessments by Purpose Bloom’s Taxonomy as Context Aim High Objective Assessment Selected vs Constructed Response Subjective (Non Objective) Assessment Writing/Generating Responses Role & Control of Subjectivity in Assessment Alternative Assessment Authentic Assessment Performance Assessment
![3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation [http: //vudat. msu. edu/assessment/] Objective Assessment Objective assessments 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation [http: //vudat. msu. edu/assessment/] Objective Assessment Objective assessments](https://present5.com/presentation/efa43a3dcfff4d454595cf2e7acc86d8/image-32.jpg) 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation [http: //vudat. msu. edu/assessment/] Objective Assessment Objective assessments (usually multiple choice, true false, matching, short answer) have correct answers. These are good for testing recall of facts and can be automated. Objective tests assume that there are true answers and assume that all students should learn the same things.
3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation [http: //vudat. msu. edu/assessment/] Objective Assessment Objective assessments (usually multiple choice, true false, matching, short answer) have correct answers. These are good for testing recall of facts and can be automated. Objective tests assume that there are true answers and assume that all students should learn the same things.
![3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation [http: //vudat. msu. edu/assessment/] Subjective (Non Objective) Assessment 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation [http: //vudat. msu. edu/assessment/] Subjective (Non Objective) Assessment](https://present5.com/presentation/efa43a3dcfff4d454595cf2e7acc86d8/image-33.jpg) 3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation [http: //vudat. msu. edu/assessment/] Subjective (Non Objective) Assessment With subjective assessments, teacher's judgment determines the grade These include essay tests. Essay tests take longer to answer and they take longer to grade than objective questions and therefore only include a small number of questions, focusing on complex concepts. Writing/Generating Responses Role & Control of Subjectivity: Criteria &/or Rubrics
3. Context for Assessment & Evaluation [http: //vudat. msu. edu/assessment/] Subjective (Non Objective) Assessment With subjective assessments, teacher's judgment determines the grade These include essay tests. Essay tests take longer to answer and they take longer to grade than objective questions and therefore only include a small number of questions, focusing on complex concepts. Writing/Generating Responses Role & Control of Subjectivity: Criteria &/or Rubrics
 Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment
Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 4. 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts)
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 4. 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts)
 4. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Alternative To what? Portfolio Assessment: An example Authentic With respect to what? Performance What types?
4. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Alternative To what? Portfolio Assessment: An example Authentic With respect to what? Performance What types?
 4. Alternative Assessment : Activity Alternative Possible examples? Portfolio Assessment: Possible examples? Authentic Possible examples? Performance Possible examples?
4. Alternative Assessment : Activity Alternative Possible examples? Portfolio Assessment: Possible examples? Authentic Possible examples? Performance Possible examples?
 4. Alternative Assessment: Alternative Methods to Document Learning 3 Formal Models of Assessment: Holistic: Applying all criteria as a single judgment Modified Holistic: Adding levels of judgment Analytical: Judgment by criteria; weighting factors; scaling Valid decision making: Matching the “tool” and the instructional outcome Examples of Rubrics: Rubric Primer Information Skills Oral Presentation Creating Rubrics
4. Alternative Assessment: Alternative Methods to Document Learning 3 Formal Models of Assessment: Holistic: Applying all criteria as a single judgment Modified Holistic: Adding levels of judgment Analytical: Judgment by criteria; weighting factors; scaling Valid decision making: Matching the “tool” and the instructional outcome Examples of Rubrics: Rubric Primer Information Skills Oral Presentation Creating Rubrics
 Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction
Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 5. 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 5. 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s
 5. Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Formative Assessment Types of Formative Assessment Objective assessments ▪ Forms/versions of summative assessments that will be implemented for final evaluation of students Alternative assessments ▪ Forms/versions of summative assessments that could be implemented for final evaluation of students Used to provide feedback on developing learning ▪ Should not contribute to final grades May or may not be “graded” assessments ▪ Limited direct impact on final evaluation of student
5. Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Formative Assessment Types of Formative Assessment Objective assessments ▪ Forms/versions of summative assessments that will be implemented for final evaluation of students Alternative assessments ▪ Forms/versions of summative assessments that could be implemented for final evaluation of students Used to provide feedback on developing learning ▪ Should not contribute to final grades May or may not be “graded” assessments ▪ Limited direct impact on final evaluation of student
 5. Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Observation Strategies Using explicit formal tools Informal observations Questioning Strategies Taba Tables Self & Peer Assessment Strategies
5. Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Observation Strategies Using explicit formal tools Informal observations Questioning Strategies Taba Tables Self & Peer Assessment Strategies
 5. Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Alternative assessments Used to provide feedback on developing learning Examples: Formative Evaluation Form Summary Evaluation Form Observation Record Form Observation Guide Form Observation Assessment Form Open ended Questions
5. Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Alternative assessments Used to provide feedback on developing learning Examples: Formative Evaluation Form Summary Evaluation Form Observation Record Form Observation Guide Form Observation Assessment Form Open ended Questions
 Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context
Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 6. 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 6. 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information
 6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies (within local work context) Writing assessment plans Who’s responsible for developing plans? What’s the basis for developing plans? Developing assessment tools & items Who develops summative assessments? ▪ Who implements summative assessments? ▪ Who interprets data from summative assessments? Formative assessments Who develops formative assessments? ▪ Who implements formative assessments? ▪ Who interprets data from formative assessments?
6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies (within local work context) Writing assessment plans Who’s responsible for developing plans? What’s the basis for developing plans? Developing assessment tools & items Who develops summative assessments? ▪ Who implements summative assessments? ▪ Who interprets data from summative assessments? Formative assessments Who develops formative assessments? ▪ Who implements formative assessments? ▪ Who interprets data from formative assessments?
 6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Objective Tests & Assessments Planning Assessments Types of Objective Assessments Sample Table of Specifications Judging Assessments
6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Objective Tests & Assessments Planning Assessments Types of Objective Assessments Sample Table of Specifications Judging Assessments
 6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Objective Tests & Assessments Resources online @ Writing Test Items Testing Primer Matching Items to Objectives
6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Objective Tests & Assessments Resources online @ Writing Test Items Testing Primer Matching Items to Objectives
 6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Objective Tests & Assessments Test Construction Activity (online @ http: //people. uncw. edu/caropresoe/)
6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Objective Tests & Assessments Test Construction Activity (online @ http: //people. uncw. edu/caropresoe/)
 6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Subjective (Non objective) Tests & Assessments See Test Primer materials (online @ http: //people. uncw. edu/caropresoe/)
6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Subjective (Non objective) Tests & Assessments See Test Primer materials (online @ http: //people. uncw. edu/caropresoe/)
 6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Alternative Assessments See Test Primer materials (online @ http: //people. uncw. edu/caropresoe/)
6. Working with Assessment Tools & Strategies Developing Alternative Assessments See Test Primer materials (online @ http: //people. uncw. edu/caropresoe/)
 Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability
Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information 7. 1. Describe validity; reliability 2. Explain the relationship between high quality assessment and validity/reliability
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information 7. 1. Describe validity; reliability 2. Explain the relationship between high quality assessment and validity/reliability
 7. Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability
7. Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability
 Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability Difficulty & Discrimination Supporting Student Learning through Assessment ▪ KSU Study Strategies; Test Preps ▪ Improving Performance; MIT Testing Strategies
Workshop Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction & Context for Training Knowledge Practice Model Professional Vocabulary & Concepts Context for Instruction Educational Goals & Objectives Models of Objectives Working with Objectives Context for Assessment & Evaluation Role of Information for Decision making ▪ Types of data related to types of decisions Assessment Model Types of Assessments ▪ Objective vs Subjective, Etc. Alternative Assessment: Performance Strategies Complementing Paper Assessment Formative Assessment: Information about Teaching & Learning to Improve Instruction Working with Assessment Tools/Strategies: Writing assessment plans; developing assessment items within local work context Assessment & Test Construction: Technical Features & “Quality” Tools Validity Reliability Difficulty & Discrimination Supporting Student Learning through Assessment ▪ KSU Study Strategies; Test Preps ▪ Improving Performance; MIT Testing Strategies
 Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information 1. Describe validity; reliability 2. Explain the relationship between high quality assessment and validity/reliability 8. 1. Recognize/value the role of instructors as student study supports 2. Recognize the relationship between test item types & specific study strategies
Developing Assessment Literacy: Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 1. Recognize/value the relationship between components of professional practice (Inst; Asmt; Eval) 2. Recognize/value the relationship between professional vocabulary and practice 3. Recognize/value the use of professional vocabulary 1. Recognize/value the relationship between goals/objectives, instruction & assessment/evaluation 2. Recognize differences between objectives models 3. Write objectives using a specific model 4. Critique objectives using a specified evaluation system 1. Recognize/value the role of appropriate information in decision making 2. Recognize/value the relationship between types of assessment & resulting information 3. State the difference between objective & subjective (non objective) assessment 1. State the difference between traditional & alternative assessment models 2. State the difference between models of alternative assessment 3. State the purpose/s for rubrics in assessment 4. Identify appropriate applications of rubrics (in specific assessment settings/contexts) 1. Describe formative assessment strategies 2. State appropriate applications formative assessment/s 1. Recognize/value the need for systematic planning for assessment 2. Evaluate item types for given applications/purposes 3. Construct items to meet specific Los in given learning domains 4. Evaluate items/tests as to purpose/use of assessment information 1. Describe validity; reliability 2. Explain the relationship between high quality assessment and validity/reliability 8. 1. Recognize/value the role of instructors as student study supports 2. Recognize the relationship between test item types & specific study strategies
 8. Supporting Student Learning through Assessment Improving Student Performance on Assessments KSU Study Strategies Test Preps Improving Performance MIT Testing Strategies
8. Supporting Student Learning through Assessment Improving Student Performance on Assessments KSU Study Strategies Test Preps Improving Performance MIT Testing Strategies
 Developing Assessment Literacy The END!!! Hopefully, a beginning of improved professional practice!!!
Developing Assessment Literacy The END!!! Hopefully, a beginning of improved professional practice!!!
 Decision-making for learning: The role of assessment and evaluation Edward J. Caropreso, Ph. D Watson School of Education University of North Carolina Wilmington Assessment Workshop: Part 1 (June, 2007) Revised
Decision-making for learning: The role of assessment and evaluation Edward J. Caropreso, Ph. D Watson School of Education University of North Carolina Wilmington Assessment Workshop: Part 1 (June, 2007) Revised
 A Conversation with 3 Components A context for instructional decision making Establishing vocabulary and a conceptual framework Performance assessment as a model Developing and applying criteria Exploring formal models of performance assessment: ▪ Holistic; Modified Holistic; Analytical assessment Planning: Instruction to assessment Expectations, outcomes, tasks & assessments Developing tasks and assessments ▪ Review of current assignments, tasks, tools ▪ Development: Revisions and new constructions
A Conversation with 3 Components A context for instructional decision making Establishing vocabulary and a conceptual framework Performance assessment as a model Developing and applying criteria Exploring formal models of performance assessment: ▪ Holistic; Modified Holistic; Analytical assessment Planning: Instruction to assessment Expectations, outcomes, tasks & assessments Developing tasks and assessments ▪ Review of current assignments, tasks, tools ▪ Development: Revisions and new constructions
 Instructional Decision-making 1: Establishing vocabulary and a conceptual framework What about instructional outcomes? Intent, expectation and instruction Two models of instructional objectives ▪ Gronlund: From the general to the specific ▪ Mager: From the specific to the general What’s the relationship between teaching and learning? Instruction and assessment? Some web sites of interest http: //www. ncrel. org/sdrs/areas/misc/glossary. htm http: //ctl. stanford. edu/Tomprof/postings/448. html http: //www. ericdigests. org/pre 9213/terms. htm http: //www. ericdigests. org/pre 9213/
Instructional Decision-making 1: Establishing vocabulary and a conceptual framework What about instructional outcomes? Intent, expectation and instruction Two models of instructional objectives ▪ Gronlund: From the general to the specific ▪ Mager: From the specific to the general What’s the relationship between teaching and learning? Instruction and assessment? Some web sites of interest http: //www. ncrel. org/sdrs/areas/misc/glossary. htm http: //ctl. stanford. edu/Tomprof/postings/448. html http: //www. ericdigests. org/pre 9213/terms. htm http: //www. ericdigests. org/pre 9213/
 What about instructional outcomes? Two models Gronlund's General and Specific Objectives Mager's Instructional Objectives
What about instructional outcomes? Two models Gronlund's General and Specific Objectives Mager's Instructional Objectives
 What about instructional outcomes? Gronlund's General and Specific Objectives Gronlund’s claim: Performance oriented objectives are effective with simple skills, but Complex cognitive behaviors require another approach Proposes that main objectives be expressed as general instructional outcomes Each main objective should be elaborated in terms of specific objectives; linking general, abstract level with specific, concrete performances
What about instructional outcomes? Gronlund's General and Specific Objectives Gronlund’s claim: Performance oriented objectives are effective with simple skills, but Complex cognitive behaviors require another approach Proposes that main objectives be expressed as general instructional outcomes Each main objective should be elaborated in terms of specific objectives; linking general, abstract level with specific, concrete performances
 What about instructional outcomes? Mager's Instructional Objectives Must specify clearly what the learner should be able to do following instruction. ▪ Uses behavioral terms the actual, observable performance of the student Specifies exactly what students must do to demonstrate that they have reached the course goal Provides teacher with specific guidelines for determining whether course goals have been reached; Uses specific, behavioral terms as opposed to general terms (general or vague terms include: student will understand, appreciate, know, etc. )
What about instructional outcomes? Mager's Instructional Objectives Must specify clearly what the learner should be able to do following instruction. ▪ Uses behavioral terms the actual, observable performance of the student Specifies exactly what students must do to demonstrate that they have reached the course goal Provides teacher with specific guidelines for determining whether course goals have been reached; Uses specific, behavioral terms as opposed to general terms (general or vague terms include: student will understand, appreciate, know, etc. )
 More about instructional outcomes Some useful websites on learning outcomes http: //web. bsu. edu/IRAA/AA/WB/chapter 2. h tm http: //chiron. valdosta. edu/whuitt/col/plan/pl an. html http: //www. harding. edu/USER/dlee/WWW/o bjectives. doc http: //www. e learningguru. com/articles/art 3_4. htm http: //www. nbii. gov/datainfo/metadata/trai ning/ttt/skills/pdf/objectives. pdf
More about instructional outcomes Some useful websites on learning outcomes http: //web. bsu. edu/IRAA/AA/WB/chapter 2. h tm http: //chiron. valdosta. edu/whuitt/col/plan/pl an. html http: //www. harding. edu/USER/dlee/WWW/o bjectives. doc http: //www. e learningguru. com/articles/art 3_4. htm http: //www. nbii. gov/datainfo/metadata/trai ning/ttt/skills/pdf/objectives. pdf
 Instructional Decision-making 2: Establishing vocabulary and a conceptual framework Assessment and Evaluation: What do they mean? Relationship between assessment, evaluation and decision making: The role of time What about instructional outcomes? Instruction, assessment and evaluation Developing Criteria
Instructional Decision-making 2: Establishing vocabulary and a conceptual framework Assessment and Evaluation: What do they mean? Relationship between assessment, evaluation and decision making: The role of time What about instructional outcomes? Instruction, assessment and evaluation Developing Criteria
 A Working Model 1: Developing Criteria Using a T chart: Instructional intent/expectation vs. Student performance (and its assessment) The task and the assessment: Not the same but necessarily related Expanding the chart beyond the “T”: Identifying assessment criteria Assessment and Evidence of Learning
A Working Model 1: Developing Criteria Using a T chart: Instructional intent/expectation vs. Student performance (and its assessment) The task and the assessment: Not the same but necessarily related Expanding the chart beyond the “T”: Identifying assessment criteria Assessment and Evidence of Learning
 Using a T-chart T charts in education http: //www. enchantedlearning. com/graphicor ganizers/tchart/ http: //www. myread. org/organisation. htm http: //www 97. intel. com/en/Project. Design/Inst ructional. Strategies/Graphic. Organizers/T_Char ts. htm T charts in law http: //carbon. cudenver. edu/~econry/law 2. doc
Using a T-chart T charts in education http: //www. enchantedlearning. com/graphicor ganizers/tchart/ http: //www. myread. org/organisation. htm http: //www 97. intel. com/en/Project. Design/Inst ructional. Strategies/Graphic. Organizers/T_Char ts. htm T charts in law http: //carbon. cudenver. edu/~econry/law 2. doc
 A Working Model 2: Applying Criteria From criteria as evidence to a “tool” for assessment and evaluation: Checklists vs. Rating Scales Whose tool is it anyway? : What teachers and students should know to ensure learning occurs Evaluation decisions and “grading” student performance
A Working Model 2: Applying Criteria From criteria as evidence to a “tool” for assessment and evaluation: Checklists vs. Rating Scales Whose tool is it anyway? : What teachers and students should know to ensure learning occurs Evaluation decisions and “grading” student performance
 Performance Assessment: 3 Formal Models Holistic: Applying all criteria as a single judgment Modified Holistic: Adding levels of judgment Analytical: Judgment by criteria; weighting factors; scaling http: //www. teachervision. fen. com/teaching methods/rubrics/4524. html? detoured=1 Valid decision making: Matching the “tool” and the instructional outcome Examples of Rubrics http: //www. teachervision. fen. com/teaching methods/rubrics/4524. html http: //www. tcet. unt. edu/START/instruct/general/rubrics. htm
Performance Assessment: 3 Formal Models Holistic: Applying all criteria as a single judgment Modified Holistic: Adding levels of judgment Analytical: Judgment by criteria; weighting factors; scaling http: //www. teachervision. fen. com/teaching methods/rubrics/4524. html? detoured=1 Valid decision making: Matching the “tool” and the instructional outcome Examples of Rubrics http: //www. teachervision. fen. com/teaching methods/rubrics/4524. html http: //www. tcet. unt. edu/START/instruct/general/rubrics. htm
 Planning: Instruction to assessment Your expectations, outcomes, tasks & assessments Developing tasks and assessments Review: Current assignments, tasks, tools Development: ▪ Revisions and reconstructions ▪ New constructions
Planning: Instruction to assessment Your expectations, outcomes, tasks & assessments Developing tasks and assessments Review: Current assignments, tasks, tools Development: ▪ Revisions and reconstructions ▪ New constructions
 Examples of Instruction and Assessment Tools Rubrics and other assessment tools http: //www. teachervision. fen. com/teaching methods/rubrics/4521. html? detoured=1 http: //www. tcet. unt. edu/START/instruct/general/rubrics. htm http: //www. curriculum. org/csc/library/profiles/10/html/ELDBOP 5. htm http: //www. inmotionaame. org/education/lesson. cfm; jsessionid=f 8303421051 155499527848? migration=&id=6_003 LP&bhcp=1 http: //school. discovery. com/schrockguide/assess. html http: //www. ncsu. edu/midlink/ho. html http: //www. uwstout. edu/soe/profdev/rubrics. shtml
Examples of Instruction and Assessment Tools Rubrics and other assessment tools http: //www. teachervision. fen. com/teaching methods/rubrics/4521. html? detoured=1 http: //www. tcet. unt. edu/START/instruct/general/rubrics. htm http: //www. curriculum. org/csc/library/profiles/10/html/ELDBOP 5. htm http: //www. inmotionaame. org/education/lesson. cfm; jsessionid=f 8303421051 155499527848? migration=&id=6_003 LP&bhcp=1 http: //school. discovery. com/schrockguide/assess. html http: //www. ncsu. edu/midlink/ho. html http: //www. uwstout. edu/soe/profdev/rubrics. shtml
 Bloom’s Taxonomy Introduction & Major Categories http: //www. officeport. com/edu/blooms. htm http: //faculty. washington. edu/krumme/guides/bloom 1. html Applying Taxonomy (Cognitive Domain/Action Verbs) http: //www. coun. uvic. ca/learn/program/hndouts/bloom. html http: //chiron. valdosta. edu/whuitt/col/cogsys/bloom. html http: //www. teachers. ash. org. au/researchskills/dalton. htm Across the Domains http: //www. nwlink. com/~donclark/hrd/bloom. html http: //www. tedi. uq. edu. au/downloads/Bloom. pd Psychomotor Domain http: //www. olemiss. edu/depts/educ_school 2/docs/stai_manual/manual 10. htm http: //coe. sdsu. edu/eet/articles/Blooms. LD/index. htm http: //academic. udayton. edu/health/syllabi/health/lesson 01 b. htm
Bloom’s Taxonomy Introduction & Major Categories http: //www. officeport. com/edu/blooms. htm http: //faculty. washington. edu/krumme/guides/bloom 1. html Applying Taxonomy (Cognitive Domain/Action Verbs) http: //www. coun. uvic. ca/learn/program/hndouts/bloom. html http: //chiron. valdosta. edu/whuitt/col/cogsys/bloom. html http: //www. teachers. ash. org. au/researchskills/dalton. htm Across the Domains http: //www. nwlink. com/~donclark/hrd/bloom. html http: //www. tedi. uq. edu. au/downloads/Bloom. pd Psychomotor Domain http: //www. olemiss. edu/depts/educ_school 2/docs/stai_manual/manual 10. htm http: //coe. sdsu. edu/eet/articles/Blooms. LD/index. htm http: //academic. udayton. edu/health/syllabi/health/lesson 01 b. htm


