b92a04e685556456450df0fd080e1e5f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Developing and Rolling Out a Unified Training Program Tim Springer Mary Smith
Developing and Rolling Out a Unified Training Program Tim Springer Mary Smith
 Agenda • • • Introduction Key Concepts Training Plan Content Development Delivery
Agenda • • • Introduction Key Concepts Training Plan Content Development Delivery
 About SSB BART Group • • • Unmatched Experience Focus on Accessibility Solutions That Manage Risk Real-World Strategy Organizational Strength and Continuity • Dynamic, Forward-Thinking Intelligence • Fourteen hundred organizations (1445) • Fifteen hundred individual accessibility best practices (1595) • Twenty-two core technology platforms (22) • Fifty-five thousand audits (55, 930) • One hundred fifty million accessibility violations (152, 351, 725) • Three hundred sixty-six thousand human validated accessibility violations (366, 096)
About SSB BART Group • • • Unmatched Experience Focus on Accessibility Solutions That Manage Risk Real-World Strategy Organizational Strength and Continuity • Dynamic, Forward-Thinking Intelligence • Fourteen hundred organizations (1445) • Fifteen hundred individual accessibility best practices (1595) • Twenty-two core technology platforms (22) • Fifty-five thousand audits (55, 930) • One hundred fifty million accessibility violations (152, 351, 725) • Three hundred sixty-six thousand human validated accessibility violations (366, 096)
 Introduction
Introduction
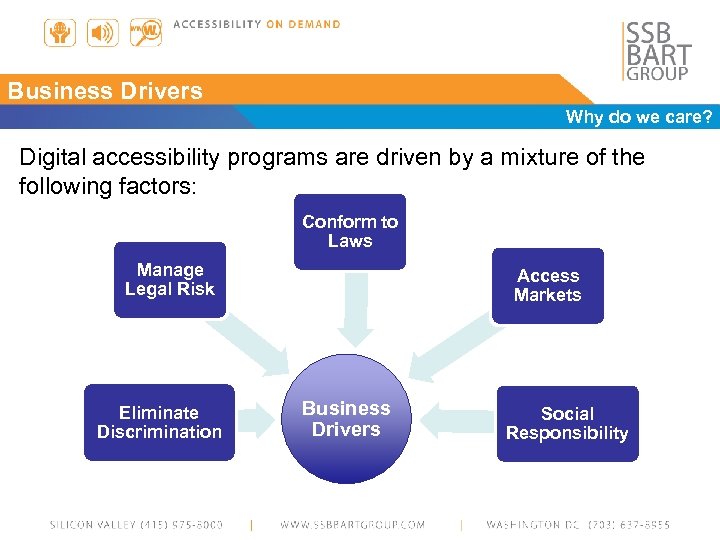 Business Drivers Why do we care? Digital accessibility programs are driven by a mixture of the following factors: Conform to Laws Manage Legal Risk Eliminate Discrimination Access Markets Business Drivers Social Responsibility
Business Drivers Why do we care? Digital accessibility programs are driven by a mixture of the following factors: Conform to Laws Manage Legal Risk Eliminate Discrimination Access Markets Business Drivers Social Responsibility
 Overarching Model Digital Accessibility Maturity Model (DAMM) High level areas of activity or competence needed for an effective digital accessibility program • Program maturity is measured along ten key dimensions: – – – – – Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance Communications Policy and Standards Legal and Regulatory Fiscal Management Development Lifecycle Testing and Validation Support and Documentation Procurement Training
Overarching Model Digital Accessibility Maturity Model (DAMM) High level areas of activity or competence needed for an effective digital accessibility program • Program maturity is measured along ten key dimensions: – – – – – Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance Communications Policy and Standards Legal and Regulatory Fiscal Management Development Lifecycle Testing and Validation Support and Documentation Procurement Training
 Phase 1: Training Plan
Phase 1: Training Plan
 Training Plan Goals • Have the knowledge in place to ensure sites and applications are compliant with accessibility policy • The ability to maintain that knowledge over time and staffing changes • The ability to certify knowledge transfer to key roles
Training Plan Goals • Have the knowledge in place to ensure sites and applications are compliant with accessibility policy • The ability to maintain that knowledge over time and staffing changes • The ability to certify knowledge transfer to key roles
 Target Roles Core Development Roles Procurement • • • Procurement • Contract Specialists • Vendors Designers Developers Quality Assurance Project and Product Managers Documentation Roles • Technical Writers • Communications and Marketing Other Roles • Customer Service Representatives • Human Resources
Target Roles Core Development Roles Procurement • • • Procurement • Contract Specialists • Vendors Designers Developers Quality Assurance Project and Product Managers Documentation Roles • Technical Writers • Communications and Marketing Other Roles • Customer Service Representatives • Human Resources
 Sample Curricula and Courses Accessibility Awareness Mobile Accessibility • Accessibility Concepts • Section 508, WCAG, ADA, CVAA, AODA • Overview, i. OS for Testers, i. OS for Developers Accessibility Testing and Evaluation • Overview, Basics and Advanced • Audit Methodology, Testing Tools Support Document Accessibility • Acrobat, In. Design, MS Office Web Accessibility • Handling Accessibility Issues
Sample Curricula and Courses Accessibility Awareness Mobile Accessibility • Accessibility Concepts • Section 508, WCAG, ADA, CVAA, AODA • Overview, i. OS for Testers, i. OS for Developers Accessibility Testing and Evaluation • Overview, Basics and Advanced • Audit Methodology, Testing Tools Support Document Accessibility • Acrobat, In. Design, MS Office Web Accessibility • Handling Accessibility Issues
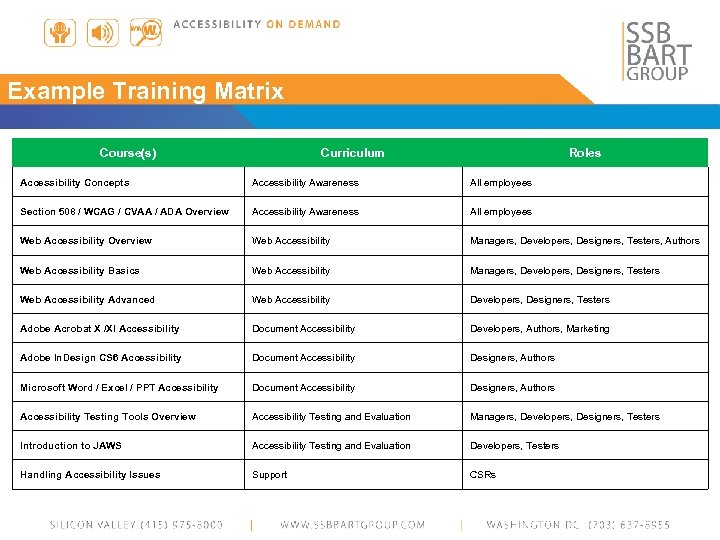 Example Training Matrix Course(s) Curriculum Roles Accessibility Concepts Accessibility Awareness All employees Section 508 / WCAG / CVAA / ADA Overview Accessibility Awareness All employees Web Accessibility Overview Web Accessibility Managers, Developers, Designers, Testers, Authors Web Accessibility Basics Web Accessibility Managers, Developers, Designers, Testers Web Accessibility Advanced Web Accessibility Developers, Designers, Testers Adobe Acrobat X /XI Accessibility Document Accessibility Developers, Authors, Marketing Adobe In. Design CS 6 Accessibility Document Accessibility Designers, Authors Microsoft Word / Excel / PPT Accessibility Document Accessibility Designers, Authors Accessibility Testing Tools Overview Accessibility Testing and Evaluation Managers, Developers, Designers, Testers Introduction to JAWS Accessibility Testing and Evaluation Developers, Testers Handling Accessibility Issues Support CSRs
Example Training Matrix Course(s) Curriculum Roles Accessibility Concepts Accessibility Awareness All employees Section 508 / WCAG / CVAA / ADA Overview Accessibility Awareness All employees Web Accessibility Overview Web Accessibility Managers, Developers, Designers, Testers, Authors Web Accessibility Basics Web Accessibility Managers, Developers, Designers, Testers Web Accessibility Advanced Web Accessibility Developers, Designers, Testers Adobe Acrobat X /XI Accessibility Document Accessibility Developers, Authors, Marketing Adobe In. Design CS 6 Accessibility Document Accessibility Designers, Authors Microsoft Word / Excel / PPT Accessibility Document Accessibility Designers, Authors Accessibility Testing Tools Overview Accessibility Testing and Evaluation Managers, Developers, Designers, Testers Introduction to JAWS Accessibility Testing and Evaluation Developers, Testers Handling Accessibility Issues Support CSRs
 Certification Process • Certification process for specific roles and groups • Courses that must be completed • Knowledge transfer that must be demonstrated – Ideal - Demonstrated ability to find (and resolve) issues in real world systems – Actual - Online multiple choice tests
Certification Process • Certification process for specific roles and groups • Courses that must be completed • Knowledge transfer that must be demonstrated – Ideal - Demonstrated ability to find (and resolve) issues in real world systems – Actual - Online multiple choice tests
 Training Rollout Plan Time based implementation of the training matrix • When do specific roles need to complete specific training? • What is the refresh period for training? • What triggers training needs to occur?
Training Rollout Plan Time based implementation of the training matrix • When do specific roles need to complete specific training? • What is the refresh period for training? • What triggers training needs to occur?
 Basic and Expert Tracks • Training internal accessibility experts is expensive • Easy fix - split up the tracks • Procedurally tier out accessibility development issues – Front line employees – Internal experts – External experts
Basic and Expert Tracks • Training internal accessibility experts is expensive • Easy fix - split up the tracks • Procedurally tier out accessibility development issues – Front line employees – Internal experts – External experts
 Basic and Expert Tracks The right class for the right person • Attendance roles that best match the course content • Tracks are broken up into specific areas so that attendees get the most out of the time
Basic and Expert Tracks The right class for the right person • Attendance roles that best match the course content • Tracks are broken up into specific areas so that attendees get the most out of the time
 Assistive Technology Training • Do not recommend organizations train developers or QA to perform functional or user acceptance testing in AT • Focus on performing normative testing against best practices • Supplement with functional testing by individuals with disabilities that use the assistive technology on a daily basis • Sighted users testing with AT results in radically inaccurate results
Assistive Technology Training • Do not recommend organizations train developers or QA to perform functional or user acceptance testing in AT • Focus on performing normative testing against best practices • Supplement with functional testing by individuals with disabilities that use the assistive technology on a daily basis • Sighted users testing with AT results in radically inaccurate results
 Coaching Support • Provide coaching support for trainees – Recurring, scheduled sessions – Help Desk support • Allows trainees to bring issues to an expert • Keeps the issue fresh in individuals minds • Let’s us track what issues are unclear in training
Coaching Support • Provide coaching support for trainees – Recurring, scheduled sessions – Help Desk support • Allows trainees to bring issues to an expert • Keeps the issue fresh in individuals minds • Let’s us track what issues are unclear in training
 Please(!), not just Power. Point Slides • Power. Point driven training is boring • Video training is better – 2 -3 minute videos • Simulation training is best • Practical reality is a mix is what we will get
Please(!), not just Power. Point Slides • Power. Point driven training is boring • Video training is better – 2 -3 minute videos • Simulation training is best • Practical reality is a mix is what we will get
 Phase 2: Content Development
Phase 2: Content Development
 Course Development Overview • • Create a series of courses implementing the training matrix Defining the content Defining the knowledge checks Defining a certification process
Course Development Overview • • Create a series of courses implementing the training matrix Defining the content Defining the knowledge checks Defining a certification process
 Course Development Methodology • Kickoff • Design Document – – – Delivery Approach Technical Specifications Goals Objectives Outlines Specific Best Practices • Storyboard – – – Introduction Goals and Objectives Modules Exercises Assessments Demonstrations • Review Cycles • Development • Deploy
Course Development Methodology • Kickoff • Design Document – – – Delivery Approach Technical Specifications Goals Objectives Outlines Specific Best Practices • Storyboard – – – Introduction Goals and Objectives Modules Exercises Assessments Demonstrations • Review Cycles • Development • Deploy
 Module Content • Grouped by media types (Images, Data Tables, Forms) • Content: – – – Description of relevant accessibility issues Compliant and non-compliant examples How to fix How to unit test Speaker notes or narration transcript
Module Content • Grouped by media types (Images, Data Tables, Forms) • Content: – – – Description of relevant accessibility issues Compliant and non-compliant examples How to fix How to unit test Speaker notes or narration transcript
 Build vs. Buy Building courses Common Practice • Cheap if we don’t account for time • Custom by definition • Takes a lot of time • License base courses • Customize a subset Buying courses • The more frequently a course is taken, the more critical it is to customize it • In large organizations seat time is the dominant cost • Expensive if we don’t account for time • Not custom by default • Quick
Build vs. Buy Building courses Common Practice • Cheap if we don’t account for time • Custom by definition • Takes a lot of time • License base courses • Customize a subset Buying courses • The more frequently a course is taken, the more critical it is to customize it • In large organizations seat time is the dominant cost • Expensive if we don’t account for time • Not custom by default • Quick
 Phase 3 – Delivery
Phase 3 – Delivery
 Delivery Options On-site Instructor-Led Training • Classic classroom based training Web-based Instructor-Led Training • Remote training Online Self-Paced Training • Deploy courses via Saa. S or to the organization’s learning management system
Delivery Options On-site Instructor-Led Training • Classic classroom based training Web-based Instructor-Led Training • Remote training Online Self-Paced Training • Deploy courses via Saa. S or to the organization’s learning management system
 On-site Instructor-Led Training • Organizations typically see highest satisfaction ratings and knowledge retention with this method of delivery • More engagement from students • However, most expensive option
On-site Instructor-Led Training • Organizations typically see highest satisfaction ratings and knowledge retention with this method of delivery • More engagement from students • However, most expensive option
 Mixed Delivery Models • Basic courses often benefit from live demonstrations and examples of AT – Allows team members to experience accessibility challenges firsthand – Communicating the human impact • Advanced courses available online in a self-paced fashion • Provides the benefits of classroom and online training
Mixed Delivery Models • Basic courses often benefit from live demonstrations and examples of AT – Allows team members to experience accessibility challenges firsthand – Communicating the human impact • Advanced courses available online in a self-paced fashion • Provides the benefits of classroom and online training
 Accessibility Summits A Shotgun approach to kicking off a program Methodology: • Offsite assessment work • Onsite, hands-on intensive, custom training • Onsite consulting work with relevant groups • Offsite, ongoing coaching support for teams
Accessibility Summits A Shotgun approach to kicking off a program Methodology: • Offsite assessment work • Onsite, hands-on intensive, custom training • Onsite consulting work with relevant groups • Offsite, ongoing coaching support for teams
 Questions?
Questions?
 Thank You Contact Us Tim Springer Follow Us @SSBBARTGroup tim. springer@ssbbartgroup. com Mary Smith linkedin. com/company/ SSB-BART-Group mary. smith@ssbbartgroup. com facebook. com/ SSBBARTGroup. com/blog
Thank You Contact Us Tim Springer Follow Us @SSBBARTGroup tim. springer@ssbbartgroup. com Mary Smith linkedin. com/company/ SSB-BART-Group mary. smith@ssbbartgroup. com facebook. com/ SSBBARTGroup. com/blog
 About SSB BART Group • • • Unmatched Experience Focus on Accessibility Solutions That Manage Risk Real-World Strategy Organizational Strength and Continuity • Dynamic, Forward-Thinking Intelligence • Fourteen hundred organizations (1445) • Fifteen hundred individual accessibility best practices (1595) • Twenty-two core technology platforms (22) • Fifty-five thousand audits (55, 930) • One hundred fifty million accessibility violations (152, 351, 725) • Three hundred sixty-six thousand human validated accessibility violations (366, 096)
About SSB BART Group • • • Unmatched Experience Focus on Accessibility Solutions That Manage Risk Real-World Strategy Organizational Strength and Continuity • Dynamic, Forward-Thinking Intelligence • Fourteen hundred organizations (1445) • Fifteen hundred individual accessibility best practices (1595) • Twenty-two core technology platforms (22) • Fifty-five thousand audits (55, 930) • One hundred fifty million accessibility violations (152, 351, 725) • Three hundred sixty-six thousand human validated accessibility violations (366, 096)


