a799d12c919a33db2020a8257984fd37.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Developing an approach for Learning Design Players Patrick Mc. Andrew, Rob Nadolski & Alex Little Open University UK and Open University NL Paper available at http: //jime. open. ac. uk/2005/14
Developing an approach for Learning Design Players Patrick Mc. Andrew, Rob Nadolski & Alex Little Open University UK and Open University NL Paper available at http: //jime. open. ac. uk/2005/14
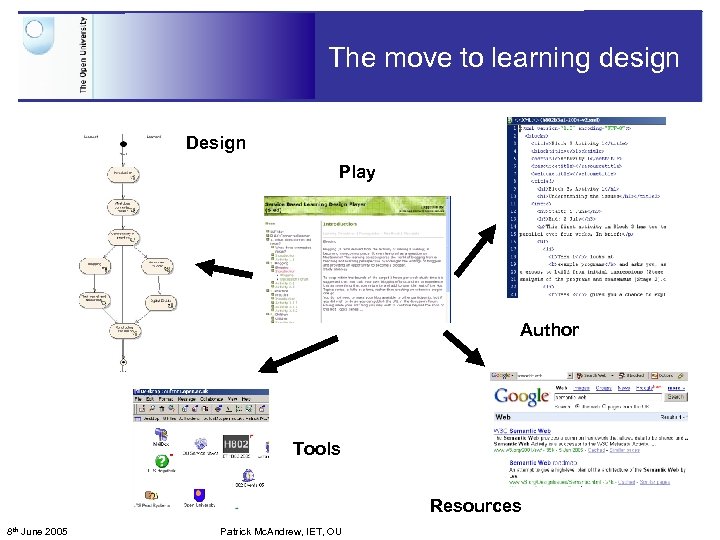 The move to learning design Design Play Author Tools Resources 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
The move to learning design Design Play Author Tools Resources 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 Copper. Core Reference LD Player Aims for the reference player: 1. a good test-bed for the developers of the Copper. Core Engine 2. a way to prove the API design for a thin client. 3. a good demonstrator for using the engine. 4. web technology/XML based 5. able to play all LD constructs during runtime of a certain run, 6. able to show all LD constructs during runtime of a certain run, 7. able to show the runtime behaviour for all users and roles, 8. able to show the LD content (mainly (X)HTML) in a legible format, 9. pedagogically neutral, 10. conformance to the common GUI guidelines No Performance, Scalability or End-user requirements 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Copper. Core Reference LD Player Aims for the reference player: 1. a good test-bed for the developers of the Copper. Core Engine 2. a way to prove the API design for a thin client. 3. a good demonstrator for using the engine. 4. web technology/XML based 5. able to play all LD constructs during runtime of a certain run, 6. able to show all LD constructs during runtime of a certain run, 7. able to show the runtime behaviour for all users and roles, 8. able to show the LD content (mainly (X)HTML) in a legible format, 9. pedagogically neutral, 10. conformance to the common GUI guidelines No Performance, Scalability or End-user requirements 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 Initial Copper. Core release Part of installation Level A 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Initial Copper. Core release Part of installation Level A 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 Issues from Copper. Core Player Three key issues a) The integration of services b) Management of units of learning. c) Player improvements: response, UI and security. 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Issues from Copper. Core Player Three key issues a) The integration of services b) Management of units of learning. c) Player improvements: response, UI and security. 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 SLe. D: Service-based Learning Design system 1. Overall aim to support and investigate the transfer and representation of learning using IMS Learning Design • • Validation of designs Generating variations in design Representing generic ways to use tools Modular architecture 2. Demonstrate that how the player can support existing designs 3. Produce a method for integrating tools tested on QTI, forum service and e. Portfolio 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
SLe. D: Service-based Learning Design system 1. Overall aim to support and investigate the transfer and representation of learning using IMS Learning Design • • Validation of designs Generating variations in design Representing generic ways to use tools Modular architecture 2. Demonstrate that how the player can support existing designs 3. Produce a method for integrating tools tested on QTI, forum service and e. Portfolio 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
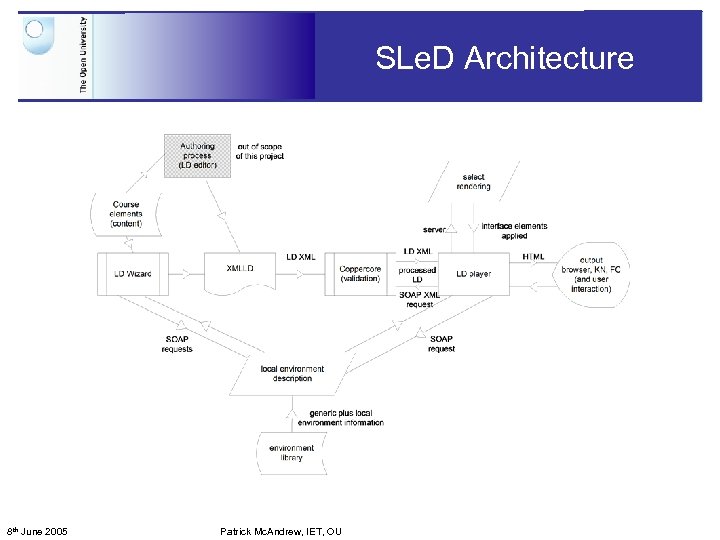 SLe. D Architecture 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
SLe. D Architecture 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
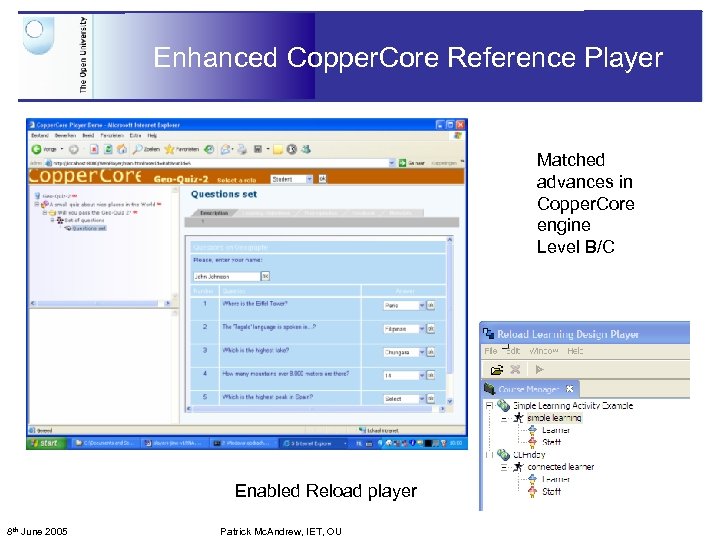 Enhanced Copper. Core Reference Player Matched advances in Copper. Core engine Level B/C Enabled Reload player 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Enhanced Copper. Core Reference Player Matched advances in Copper. Core engine Level B/C Enabled Reload player 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
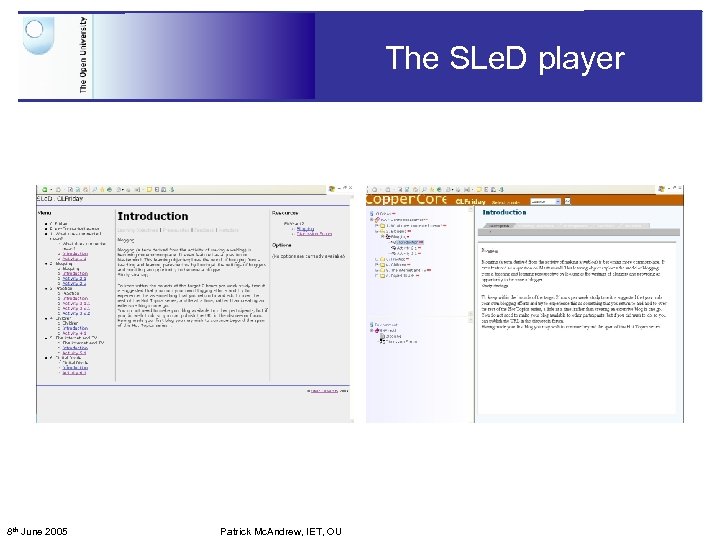 The SLe. D player 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
The SLe. D player 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
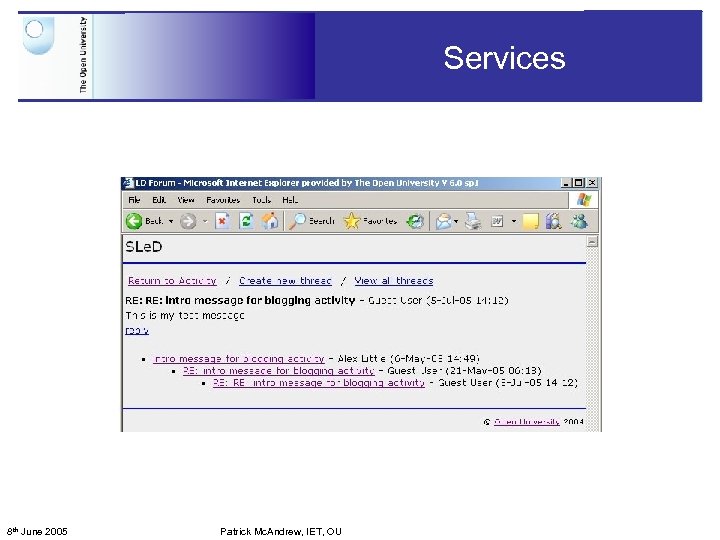 Services 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Services 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 Demonstrator site • Initial aims – – – Lower barrier of installation Remove need for command line interaction Allow exploration of collaboration and roles Build on UNFOLD success Provide information about units Communicate with Moodle • Site established – http: //sled. open. ac. uk/ 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Demonstrator site • Initial aims – – – Lower barrier of installation Remove need for command line interaction Allow exploration of collaboration and roles Build on UNFOLD success Provide information about units Communicate with Moodle • Site established – http: //sled. open. ac. uk/ 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 Initial limited evaluation • Appreciation for targeted scenarios • Brief features summary useful • Engagement in Units of Learning • Own view emerges • Demonstrator role is unclear – seen as real system • Concerns about materials – are designs “good” • More support needed during using the system • User interface can confuse 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Initial limited evaluation • Appreciation for targeted scenarios • Brief features summary useful • Engagement in Units of Learning • Own view emerges • Demonstrator role is unclear – seen as real system • Concerns about materials – are designs “good” • More support needed during using the system • User interface can confuse 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 Representing Design • Patterns – Textual descriptions – Building up a collection – pattern language – Needs interpretation before reuse • Activity tools – Software models – Engage people – Need to move towards transferability and standards • IMS Learning Design – XML description – Computer managed – Can be reused automatically 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Representing Design • Patterns – Textual descriptions – Building up a collection – pattern language – Needs interpretation before reuse • Activity tools – Software models – Engage people – Need to move towards transferability and standards • IMS Learning Design – XML description – Computer managed – Can be reused automatically 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 James Dalziel – reuse principles • Suggested new principles for fostering re-use and sharing: – – – – – Learning Designs/Learning Activities focus, rather than simply content Community focus, rather than repository focus Search based on free-text searching, not metadata searching Automated usage tracking/rating systems, not complex peer review/approval systems (and nothing on usage) Small set of simple licenses, not complex licenses (and nothing) Learning software and learning content are free - no payment required Resources can be easily adapted by others, not just fixed/static Close integration of Learning Platform and the Community for sharing Easy to share own work – short submission process, automated MD James Dalziel, 20 th September 2005. Presentation to appear: http: //www. cetis. ac. uk/members/pedagogy/articles/Metadata. Pedagogy. Meeting 200905 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
James Dalziel – reuse principles • Suggested new principles for fostering re-use and sharing: – – – – – Learning Designs/Learning Activities focus, rather than simply content Community focus, rather than repository focus Search based on free-text searching, not metadata searching Automated usage tracking/rating systems, not complex peer review/approval systems (and nothing on usage) Small set of simple licenses, not complex licenses (and nothing) Learning software and learning content are free - no payment required Resources can be easily adapted by others, not just fixed/static Close integration of Learning Platform and the Community for sharing Easy to share own work – short submission process, automated MD James Dalziel, 20 th September 2005. Presentation to appear: http: //www. cetis. ac. uk/members/pedagogy/articles/Metadata. Pedagogy. Meeting 200905 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
 Issues in Demonstrating Difficult choices • • • How to handle different user/different roles? User interface changes in Uo. Ls or in player? Overall design for the Player? What are the features of Units of Learning? How best to work with Moodle? • What should we demonstrate? 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU
Issues in Demonstrating Difficult choices • • • How to handle different user/different roles? User interface changes in Uo. Ls or in player? Overall design for the Player? What are the features of Units of Learning? How best to work with Moodle? • What should we demonstrate? 8 th June 2005 Patrick Mc. Andrew, IET, OU


