2982f6ee3dc0aae5aec6c34bebb0a725.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 79

Developed By Information Technology Services University Of Saskatchewan Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S

SPSS Introductory Course Topics • Windows XP Review (/Vista/7) • SPSS Version 17. 0 Introduction • SPSS Data Window • SPSS Analysis • SPSS Output Window • SPSS Advanced Topics Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 2

Windows XP (/Vista/7) Review • Desktop – Taskbar • Start Button • Toolbars • Mouse – – Left Mouse Click Right Mouse Click Double Clicking Dragging • Start Windows Applications – Start Button – Desktop Icons Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 3
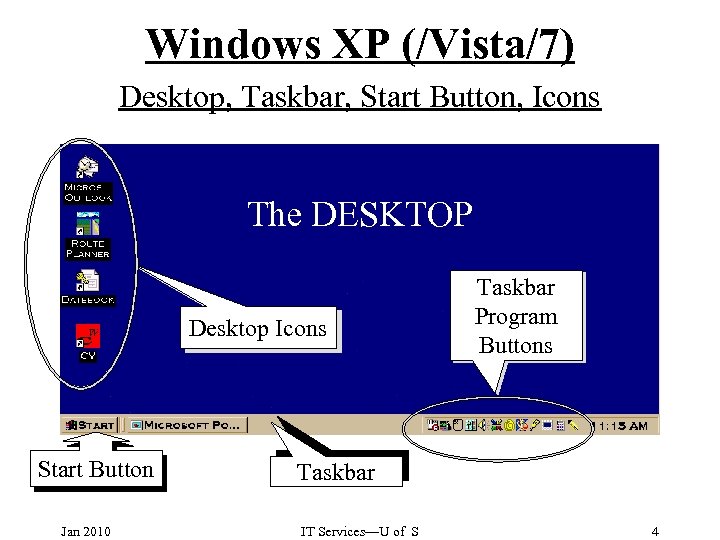
Windows XP (/Vista/7) Desktop, Taskbar, Start Button, Icons The DESKTOP Desktop Icons Start Button Jan 2010 Taskbar Program Buttons Taskbar IT Services—U of S 4
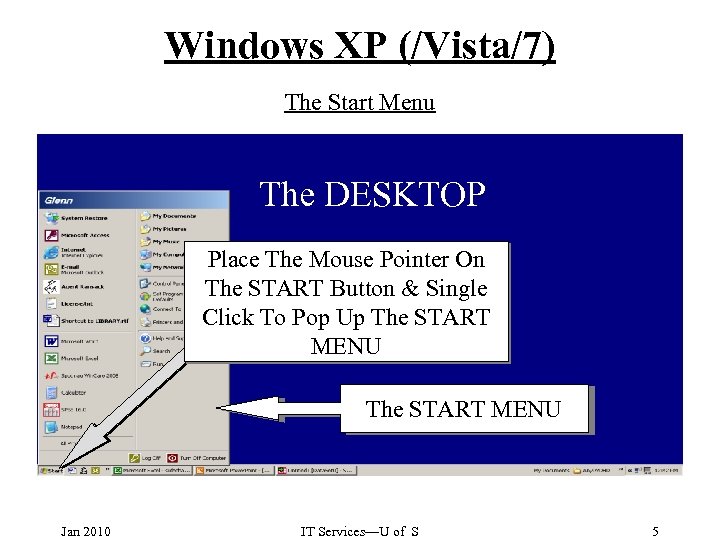
Windows XP (/Vista/7) The Start Menu The DESKTOP Place The Mouse Pointer On The START Button & Single Click To Pop Up The START MENU Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 5
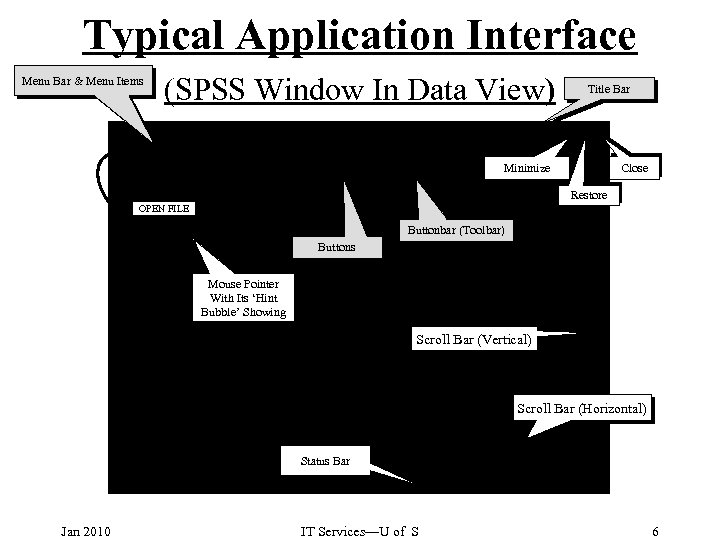
Typical Application Interface Menu Bar & Menu Items (SPSS Window In Data View) Title Bar Minimize Close Restore OPEN FILE Buttonbar (Toolbar) Buttons Mouse Pointer With Its ‘Hint Bubble’ Showing Scroll Bar (Vertical) Scroll Bar (Horizontal) Status Bar Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 6

SPSS Version 17. 0 Introduction • Starting SPSS – Minimize, Maximize, Restore & Close SPSS • • Open File Save & Save As File General Application Interface SPSS Windows – – Jan 2010 Data Editor Window Output Window Syntax Window Navigate the Windows IT Services—U of S 7
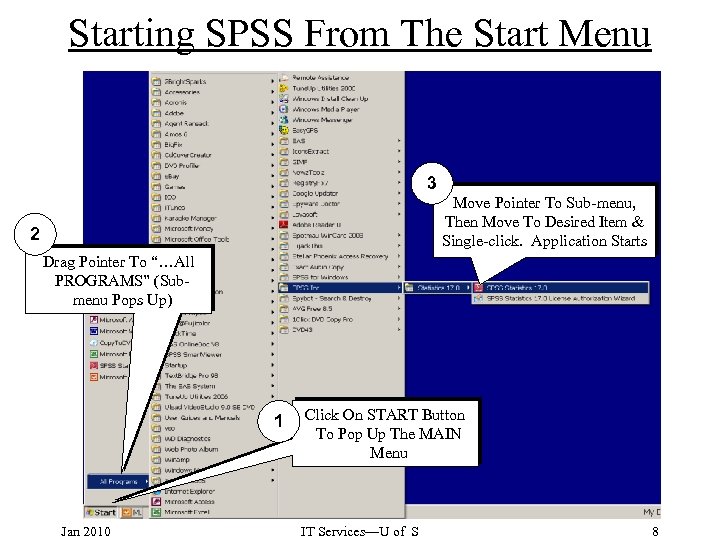
Starting SPSS From The Start Menu 3 Move Pointer To Sub-menu, Then Move To Desired Item & Single-click. Application Starts 2 Drag Pointer To “…All PROGRAMS” (Submenu Pops Up) 1 Jan 2010 Click On START Button To Pop Up The MAIN Menu IT Services—U of S 8

SPSS Start Screen Select Desired Option for: 1. Opening An Existing Dataset, Or 2. Creating A New Dataset, Or – 3. Running Tutorials Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 9
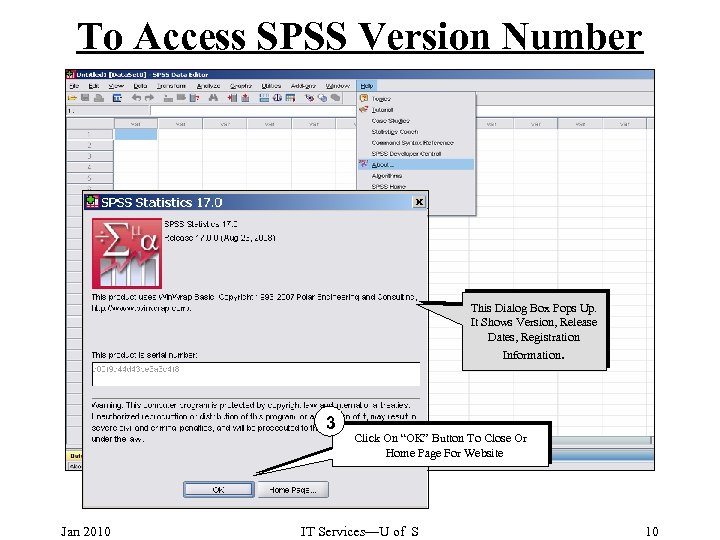
To Access SPSS Version Number 1 Click On Help 2 Move Pointer To About & Click This Dialog Box Pops Up. It Shows Version, Release Dates, Registration Information. 3 Jan 2010 Click On “OK” Button To Close Or Home Page For Website IT Services—U of S 10
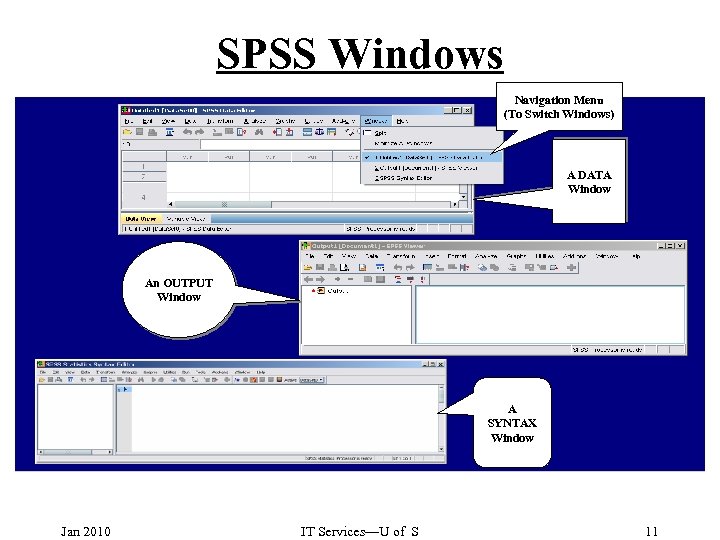
SPSS Windows Navigation Menu (To Switch Windows) A DATA Window An OUTPUT Window A SYNTAX Window Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 11
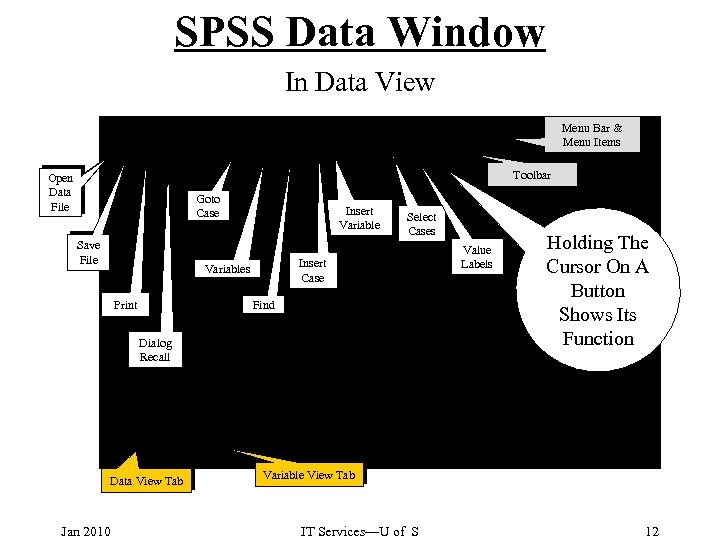
SPSS Data Window In Data View Menu Bar & Menu Items Toolbar Open Data File Goto Case Save File Insert Variable Select Cases Insert Case Variables Find Print Dialog Recall Data View Tab Jan 2010 Value Labels Holding The Cursor On A Button Shows Its Function Variable View Tab IT Services—U of S 12
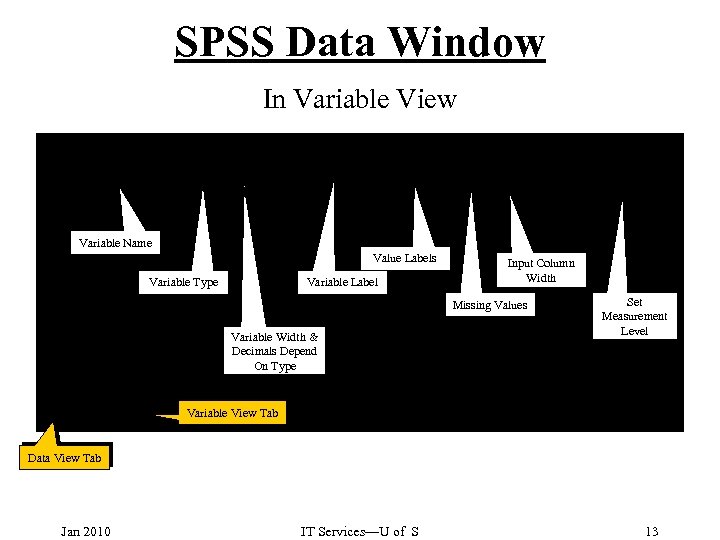
SPSS Data Window In Variable View Variable Name Value Labels Variable Type Variable Label Input Column Width Missing Values Variable Width & Decimals Depend On Type Set Measurement Level Variable View Tab Data View Tab Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 13
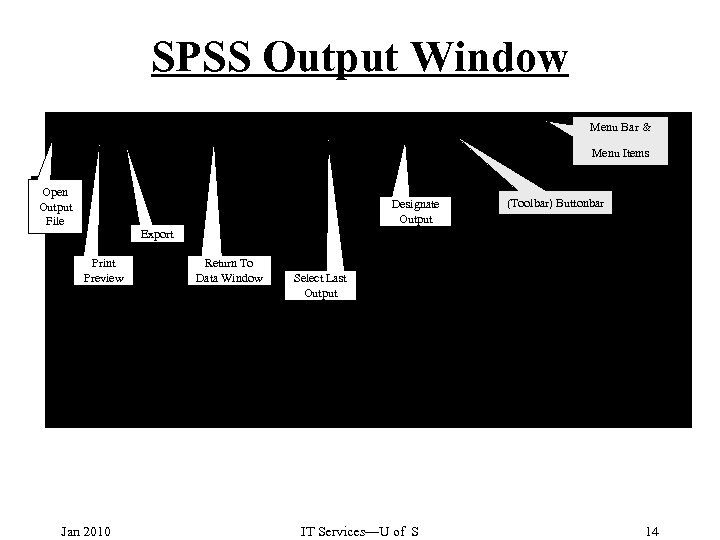
SPSS Output Window Menu Bar & Menu Items Open Output File Designate Output (Toolbar) Buttonbar Export Print Preview Jan 2010 Return To Data Window Select Last Output IT Services—U of S 14
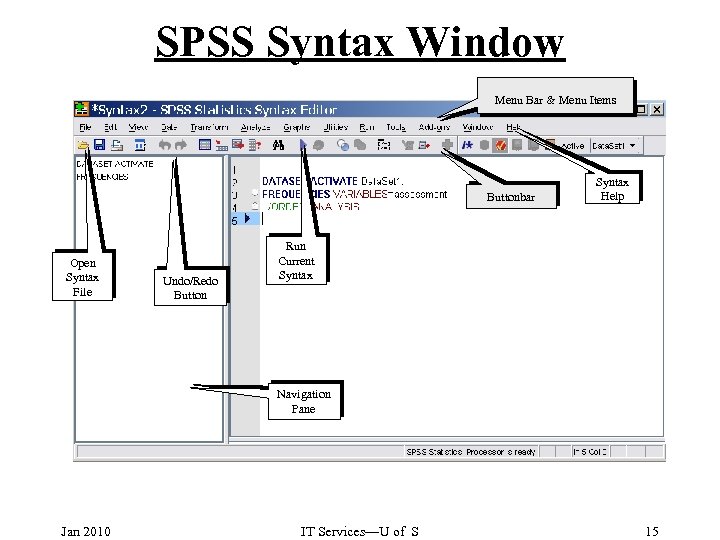
SPSS Syntax Window Menu Bar & Menu Items Buttonbar Open Syntax File Undo/Redo Button Syntax Help Run Current Syntax Navigation Pane Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 15
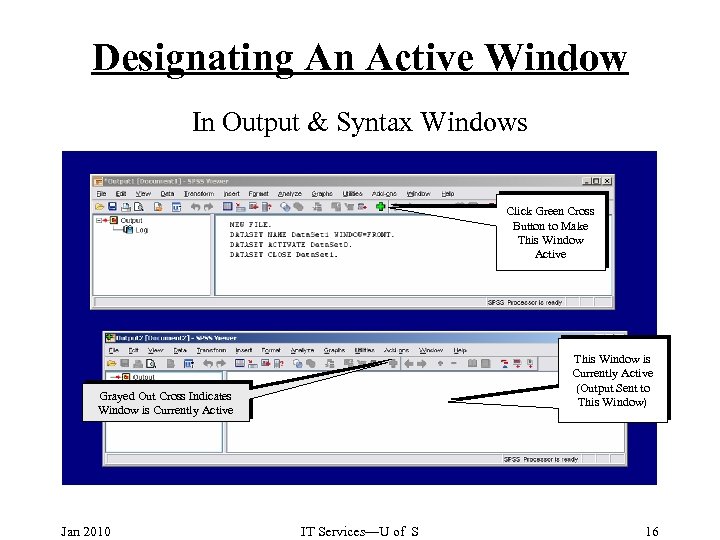
Designating An Active Window In Output & Syntax Windows Click Green Cross Button to Make This Window Active This Window is Currently Active (Output Sent to This Window) Grayed Out Cross Indicates Window is Currently Active Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 16
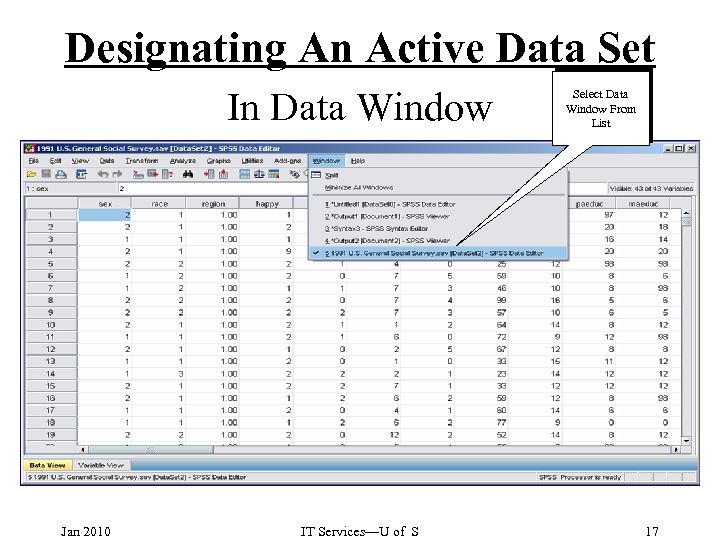
Designating An Active Data Set In Data Window Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S Select Data Window From List 17
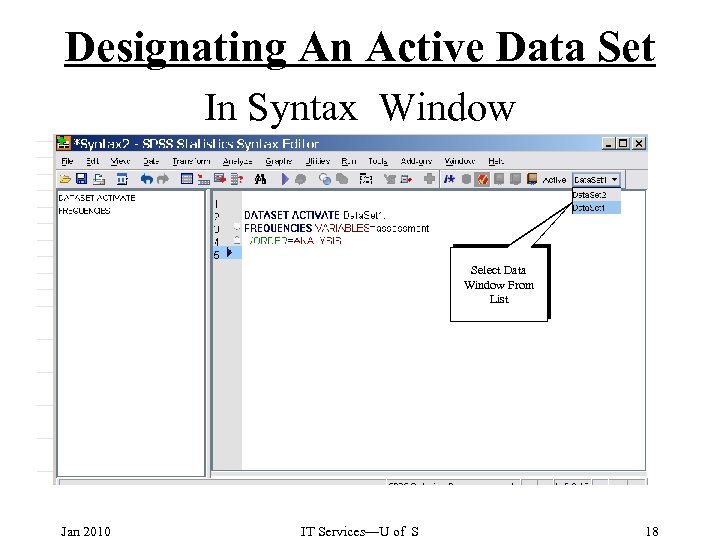
Designating An Active Data Set In Syntax Window Select Data Window From List Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 18

The Data Editor Window • Opening An Existing File • Navigating The Data Editor Window – Data view tab – Variable view tab • Modifying data • Creating A New Data File – – Create variables Copy variables Modify variables Move variables • Creating Variables • Saving Data Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 19
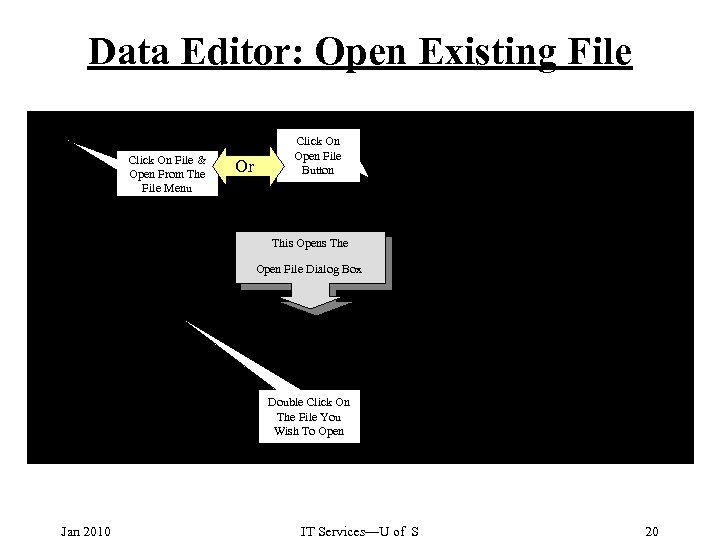
Data Editor: Open Existing File Click On File & Open From The File Menu Or Click On Open File Button This Opens The Open File Dialog Box Double Click On The File You Wish To Open Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 20

Modifying Data—Cell Address & Data Bar (Shows Value) Highlighted Cell Address Bar: When Cell Is Highlighted It Shows Row Number & Variable Name Jan 2010 To Change The Value In This Cell Type In New Value & Hit Return IT Services—U of S 21

Data Editor Keyboard Navigation Access Under HELP Menu, Topics, KEYBOARD NAVIGATION Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 22
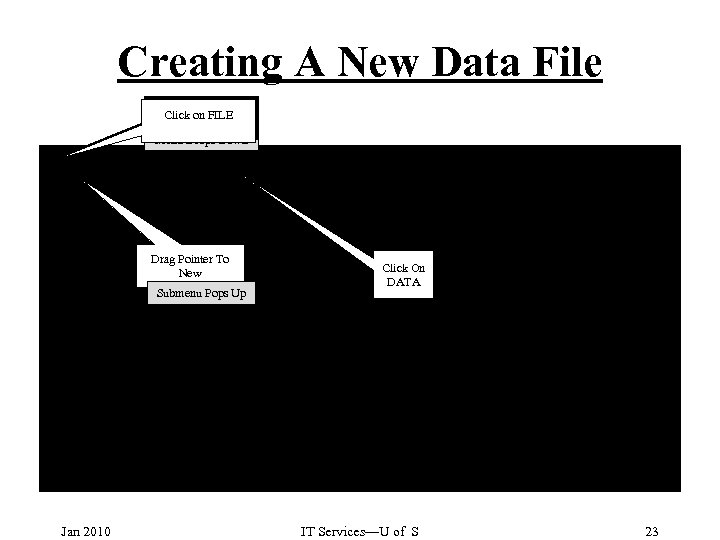
Creating A New Data File Click on FILE Menu Drops Down Drag Pointer To New Submenu Pops Up Jan 2010 Click On DATA IT Services—U of S 23
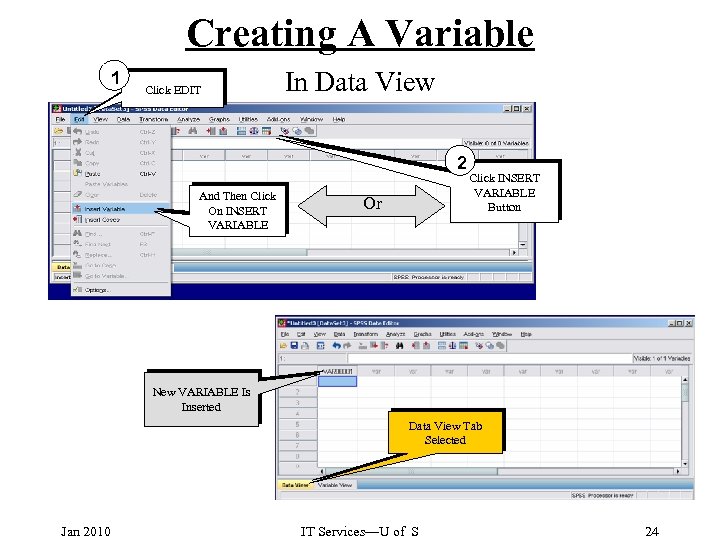
Creating A Variable 1 Click EDIT In Data View 2 And Then Click On INSERT VARIABLE Or Click INSERT VARIABLE Button New VARIABLE Is Inserted Data View Tab Selected Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 24
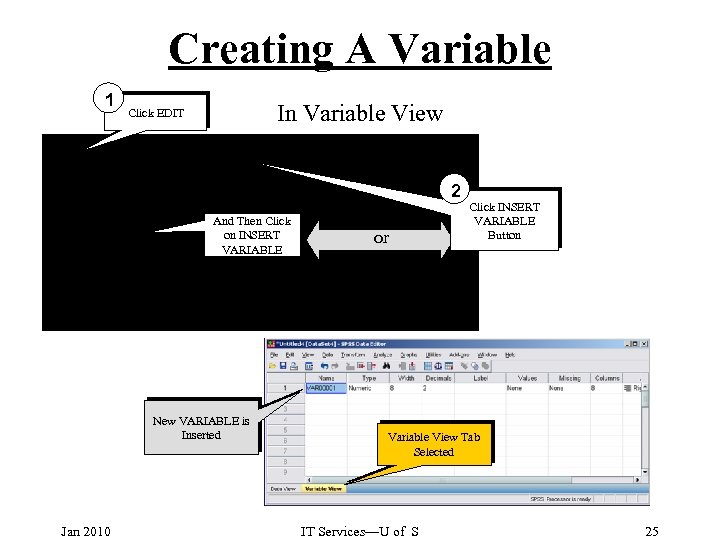
Creating A Variable 1 In Variable View Click EDIT 2 And Then Click on INSERT VARIABLE New VARIABLE is Inserted Jan 2010 or Click INSERT VARIABLE Button Variable View Tab Selected IT Services—U of S 25
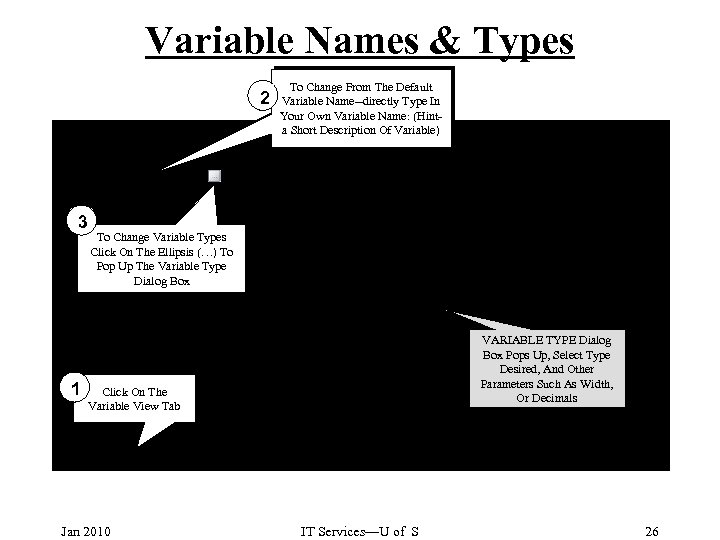
Variable Names & Types 2 3 1 To Change From The Default Variable Name--directly Type In Your Own Variable Name: (Hinta Short Description Of Variable) To Change Variable Types Click On The Ellipsis (…) To Pop Up The Variable Type Dialog Box VARIABLE TYPE Dialog Box Pops Up, Select Type Desired, And Other Parameters Such As Width, Or Decimals Click On The Variable View Tab Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 26
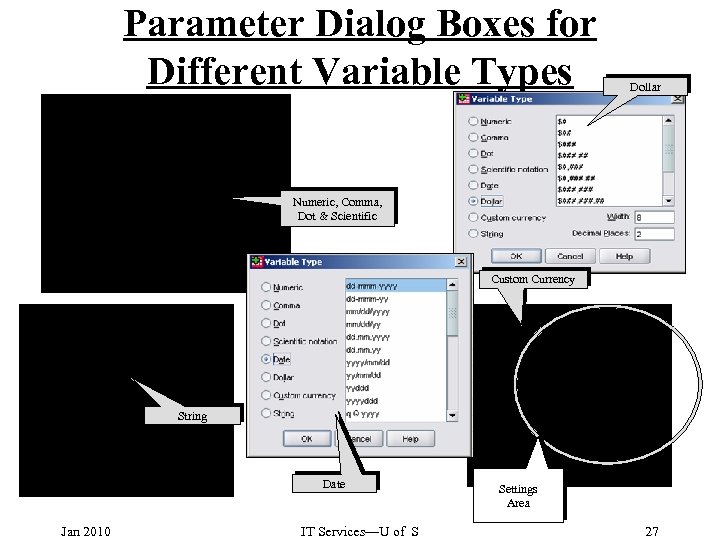
Parameter Dialog Boxes for Different Variable Types Dollar Numeric, Comma, Dot & Scientific Custom Currency String Date Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S Settings Area 27
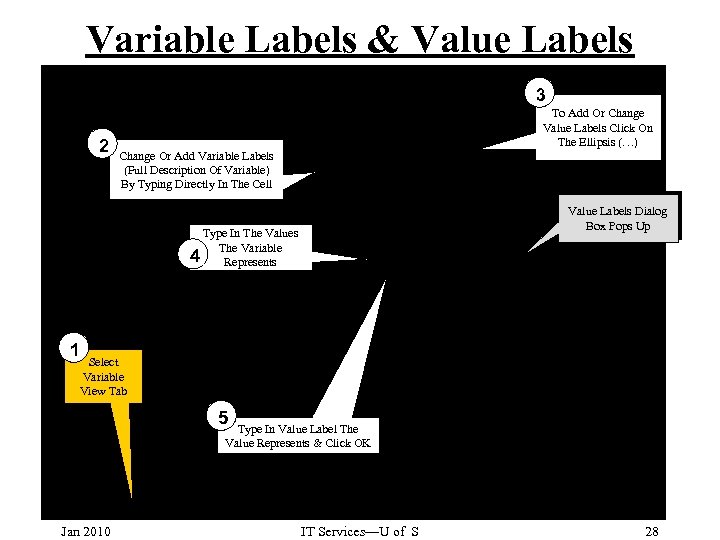
Variable Labels & Value Labels 3 2 To Add Or Change Value Labels Click On The Ellipsis (…) Change Or Add Variable Labels (Full Description Of Variable) By Typing Directly In The Cell Value Labels Dialog Box Pops Up Type In The Values The Variable 4 Represents 1 Select Variable View Tab 5 Type In Value Label The Value Represents & Click OK Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 28
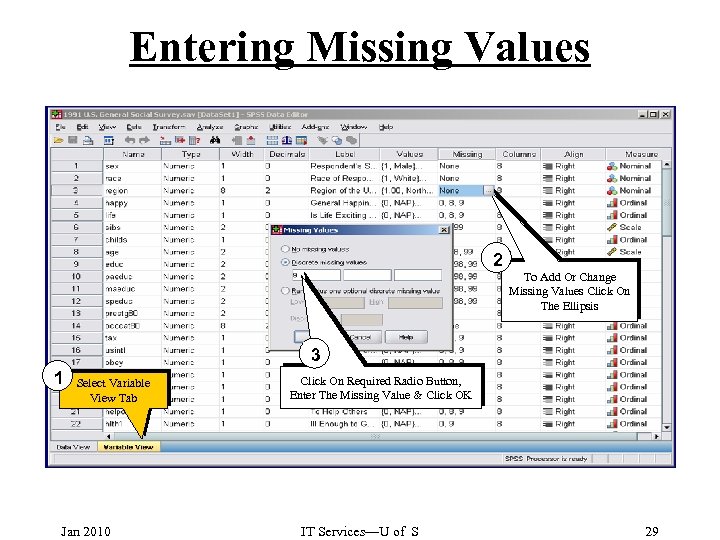
Entering Missing Values 2 To Add Or Change Missing Values Click On The Ellipsis 3 1 Select Variable View Tab Jan 2010 Click On Required Radio Button, Enter The Missing Value & Click OK IT Services—U of S 29
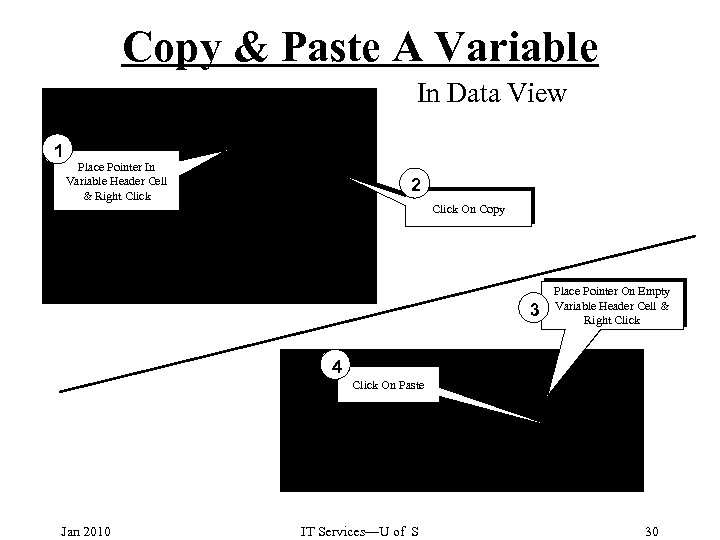
Copy & Paste A Variable In Data View 1 Place Pointer In Variable Header Cell & Right Click 2 Click On Copy 3 Place Pointer On Empty Variable Header Cell & Right Click 4 Click On Paste Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 30
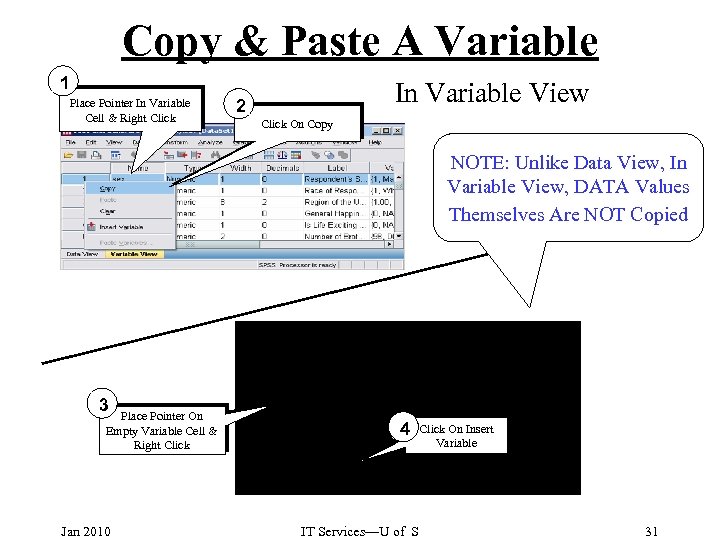
Copy & Paste A Variable 1 Place Pointer In Variable Cell & Right Click In Variable View 2 Click On Copy NOTE: Unlike Data View, In Variable View, DATA Values Themselves Are NOT Copied 3 Place Pointer On Empty Variable Cell & Right Click Jan 2010 4 IT Services—U of S Click On Insert Variable 31
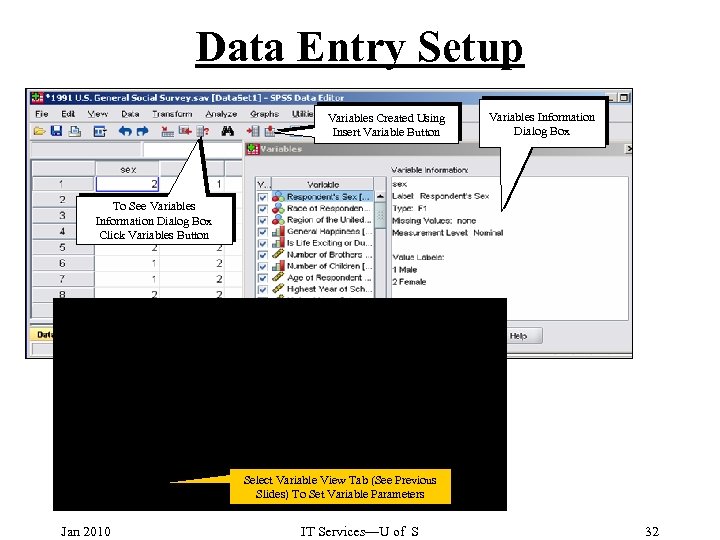
Data Entry Setup Variables Created Using Insert Variable Button Variables Information Dialog Box To See Variables Information Dialog Box Click Variables Button Select Variable View Tab (See Previous Slides) To Set Variable Parameters Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 32
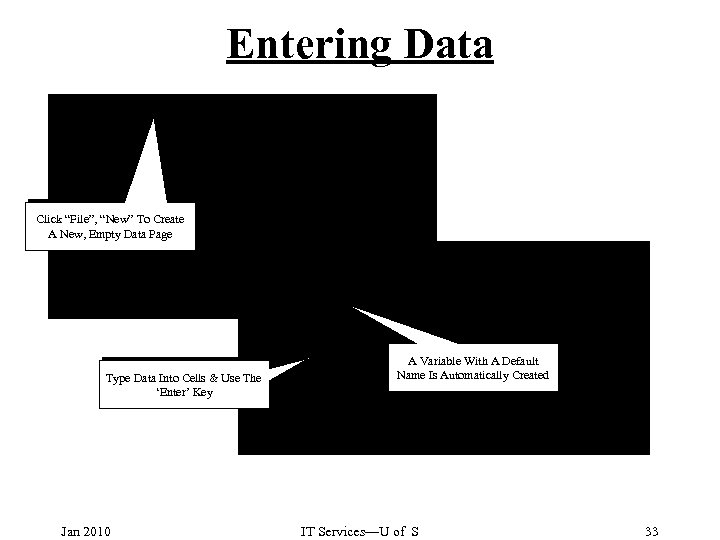
Entering Data Click “File”, “New” To Create A New, Empty Data Page Type Data Into Cells & Use The ‘Enter’ Key Jan 2010 A Variable With A Default Name Is Automatically Created IT Services—U of S 33
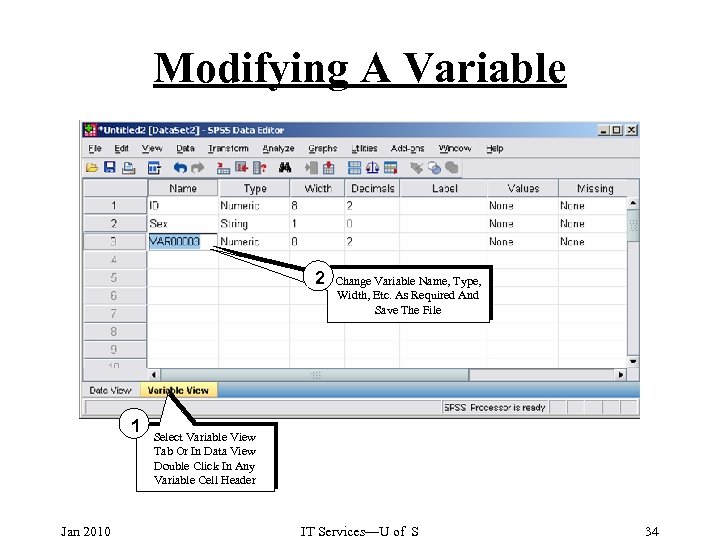
Modifying A Variable 2 1 Jan 2010 Change Variable Name, Type, Width, Etc. As Required And Save The File Select Variable View Tab Or In Data View Double Click In Any Variable Cell Header IT Services—U of S 34
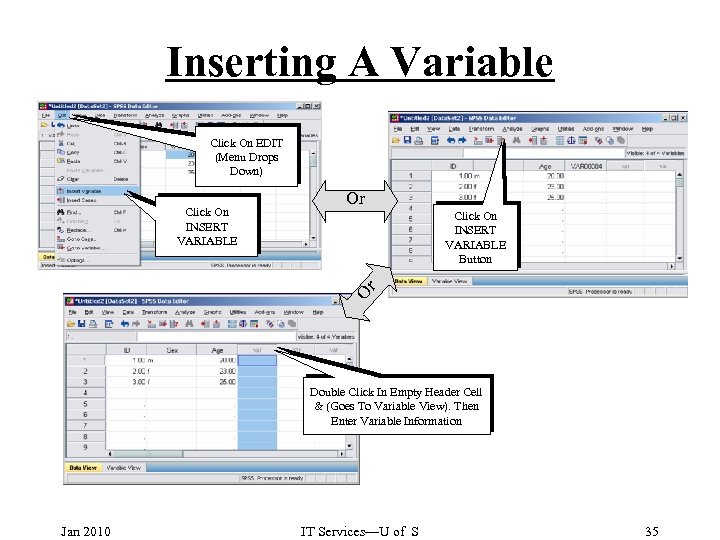
Inserting A Variable Click On EDIT (Menu Drops Down) Or Click On INSERT VARIABLE Button Variable is Inserted Or Click On INSERT VARIABLE Double Click In Empty Header Cell & (Goes To Variable View). Then Enter Variable Information Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 35

Create A Practice Data Set Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 36
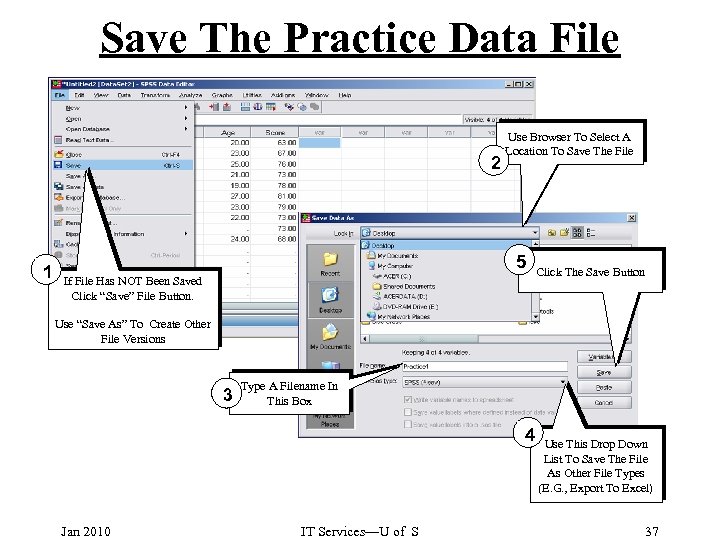
Save The Practice Data File 2 1 Use Browser To Select A Location To Save The File 5 If File Has NOT Been Saved Click “Save” File Button. Click The Save Button Use “Save As” To Create Other File Versions 3 Type A Filename In This Box 4 Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S Use This Drop Down List To Save The File As Other File Types (E. G. , Export To Excel) 37
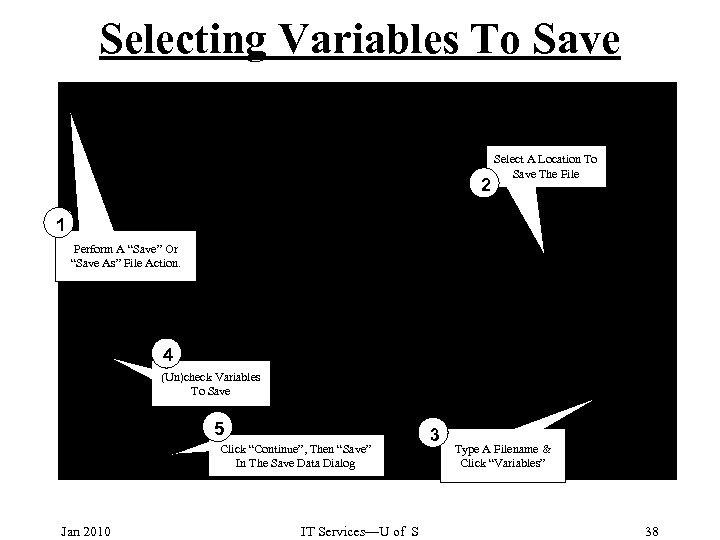
Selecting Variables To Save 2 Select A Location To Save The File 1 Perform A “Save” Or “Save As” File Action. 4 (Un)check Variables To Save 5 Click “Continue”, Then “Save” In The Save Data Dialog Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 3 Type A Filename & Click “Variables” 38
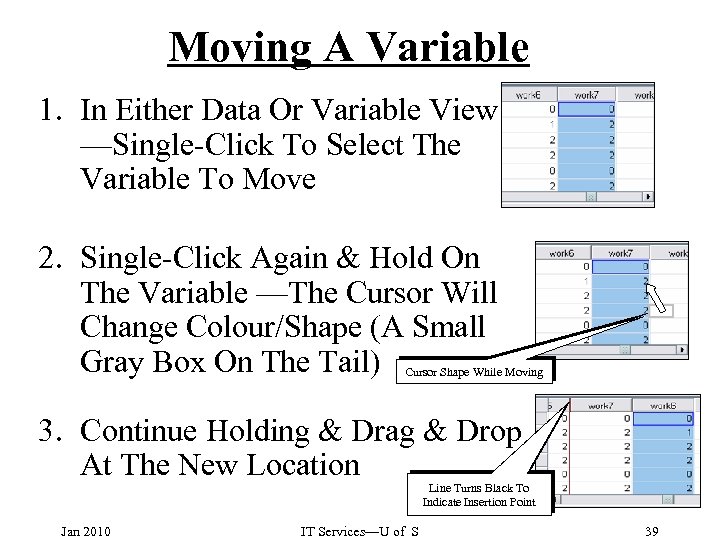
Moving A Variable 1. In Either Data Or Variable View —Single-Click To Select The Variable To Move 2. Single-Click Again & Hold On The Variable —The Cursor Will Change Colour/Shape (A Small Gray Box On The Tail) Cursor Shape While Moving 3. Continue Holding & Drag & Drop At The New Location Line Turns Black To Indicate Insertion Point Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 39
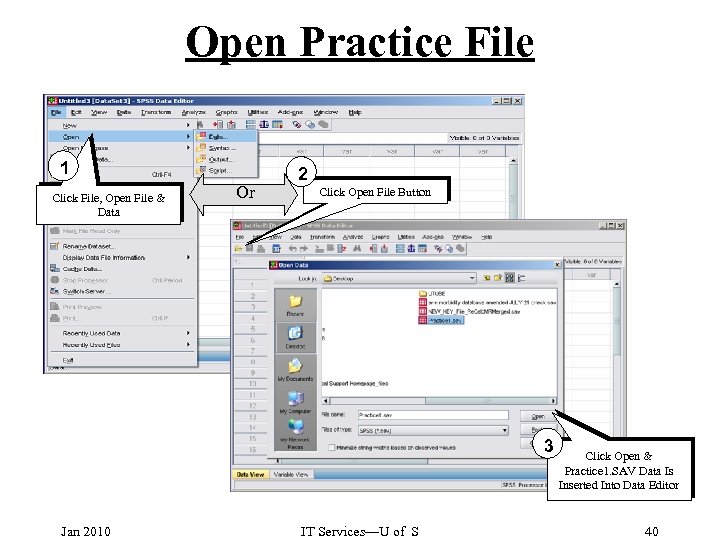
Open Practice File 1 Click File, Open File & Data Or 2 Click Open File Button 3 Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S Click Open & Practice 1. SAV Data Is Inserted Into Data Editor 40

SPSS Analysis • Open Sample Data File • Analysis 1 – Categorical Variables – Frequencies • Analysis 2 – Continuous Variables – Descriptives – Correlations • Analysis 3 – Graph Menu & Graph Categorical Variables – Scatter plot Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 41
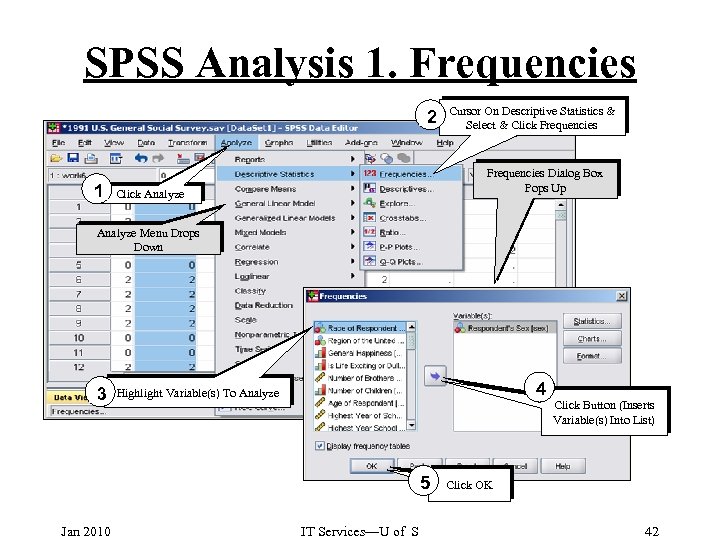
SPSS Analysis 1. Frequencies 2 1 Cursor On Descriptive Statistics & Select & Click Frequencies Dialog Box Pops Up Click Analyze Menu Drops Down 3 4 Highlight Variable(s) To Analyze 5 Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S Click Button (Inserts Variable(s) Into List) Click OK 42
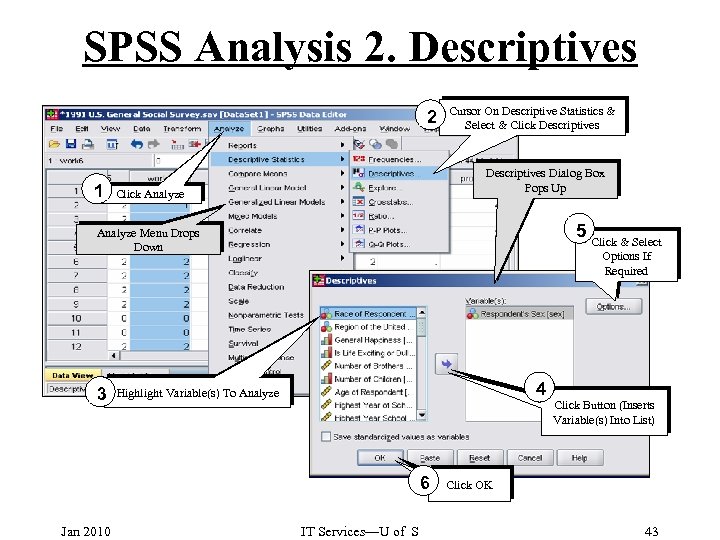
SPSS Analysis 2. Descriptives 2 1 Cursor On Descriptive Statistics & Select & Click Descriptives Dialog Box Pops Up Click Analyze 5 Analyze Menu Drops Down 3 4 Highlight Variable(s) To Analyze 6 Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S Click & Select Options If Required Click Button (Inserts Variable(s) Into List) Click OK 43
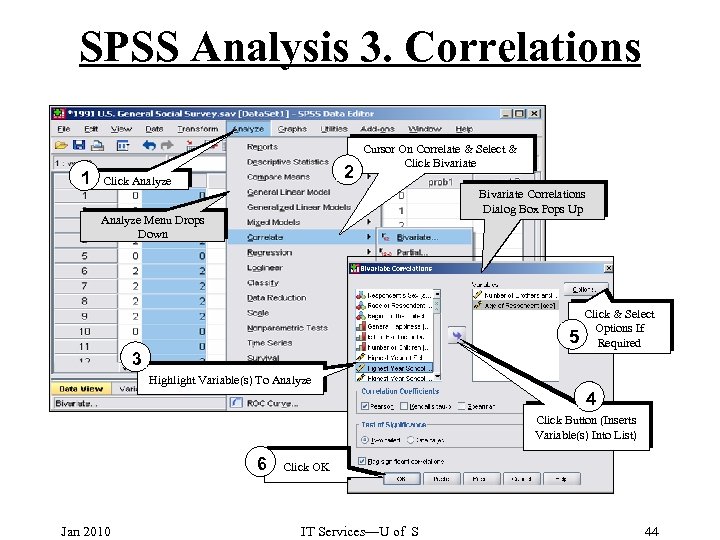
SPSS Analysis 3. Correlations 1 2 Click Analyze Cursor On Correlate & Select & Click Bivariate Correlations Dialog Box Pops Up Analyze Menu Drops Down 5 3 Click & Select Options If Required Highlight Variable(s) To Analyze 4 Click Button (Inserts Variable(s) Into List) 6 Jan 2010 Click OK IT Services—U of S 44
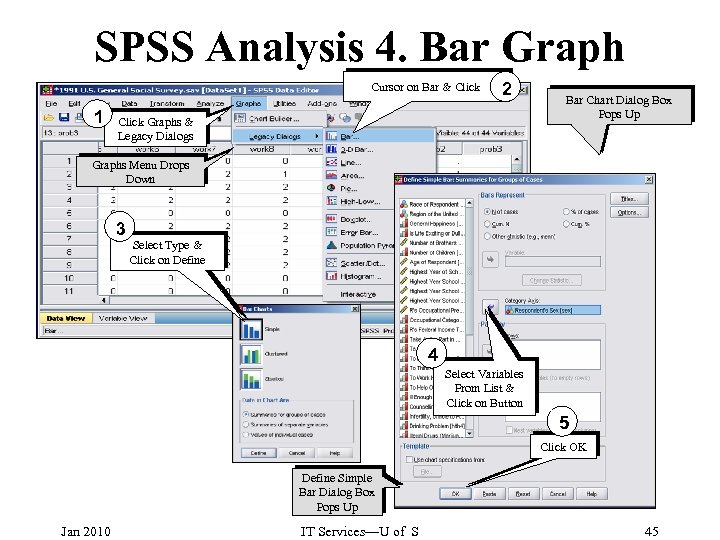
SPSS Analysis 4. Bar Graph Cursor on Bar & Click 1 2 Click Graphs & Legacy Dialogs Bar Chart Dialog Box Pops Up Graphs Menu Drops Down 3 Select Type & Click on Define 4 Select Variables From List & Click on Button 5 Click OK Define Simple Bar Dialog Box Pops Up Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 45
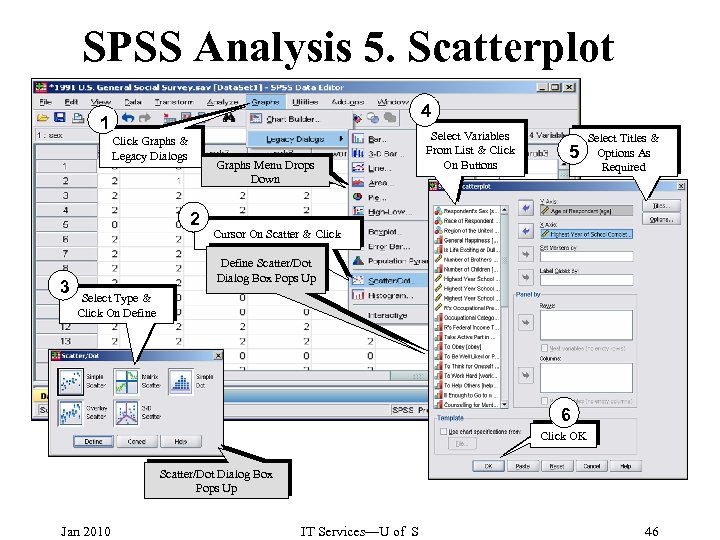
SPSS Analysis 5. Scatterplot 4 1 Click Graphs & Legacy Dialogs Graphs Menu Drops Down 2 3 Select Variables From List & Click On Buttons 5 Select Titles & Options As Required Cursor On Scatter & Click Define Scatter/Dot Dialog Box Pops Up Select Type & Click On Define 6 Click OK Scatter/Dot Dialog Box Pops Up Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 46

SPSS Output Window • Expanding Output Items • Selecting Output Items – Shift Key Continuous Selection – CTRL Key Specific Selection • Print Preview • Save Output • Open Output Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 47
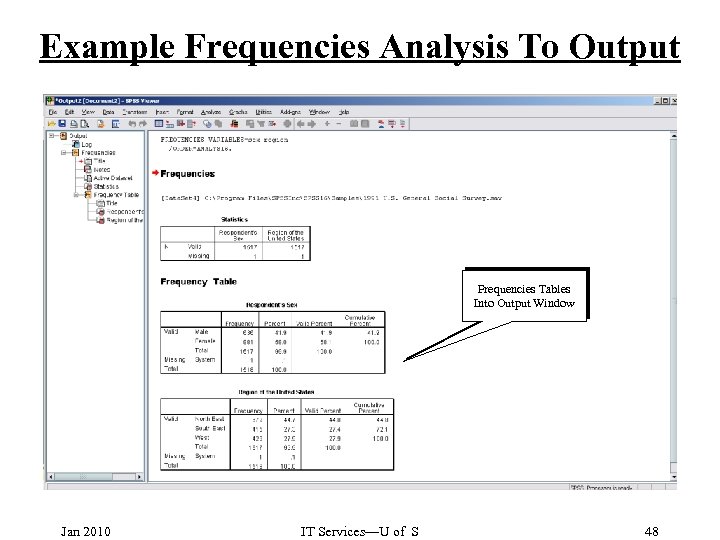
Example Frequencies Analysis To Output Frequencies Tables Into Output Window Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 48
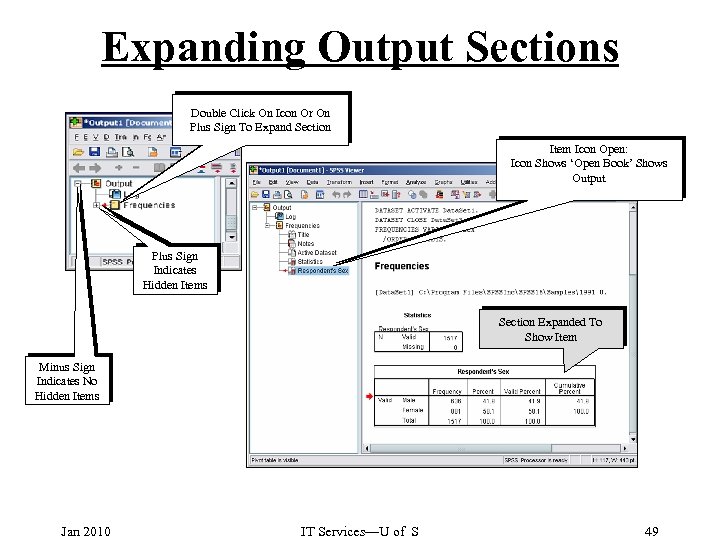
Expanding Output Sections Double Click On Icon Or On Plus Sign To Expand Section Item Icon Open: Icon Shows ‘Open Book’ Shows Output Plus Sign Indicates Hidden Items Section Expanded To Show Item Minus Sign Indicates No Hidden Items Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 49

Selecting Output Items • Click on Heading Icon to Select All Items Within that Section • Control-Click Selects Multiple Specific Items • Items May Be Moved By ‘Dragging & Dropping’ Icons Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 50
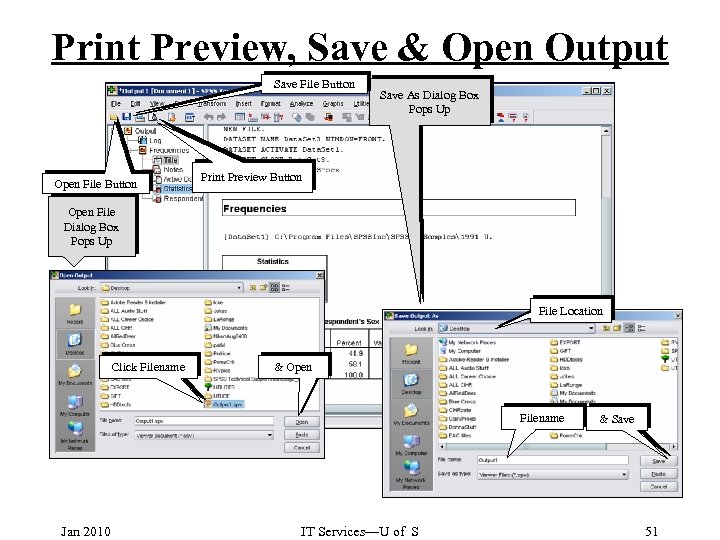
Print Preview, Save & Open Output Save File Button Open File Button Save As Dialog Box Pops Up Print Preview Button Open File Dialog Box Pops Up File Location Click Filename & Open Filename Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S & Save 51

SPSS Advanced Topics • • • Syntax Editor Computing New Variables Subsetting Data Setting Options Editing Output Pasting Output to a Word Processor • Advanced Graphics Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S • SPSS System File Commands • Import/Export Data • Production Facility • Advanced Statistics Discussion – Crosstabs – ANOVA – Regression 52
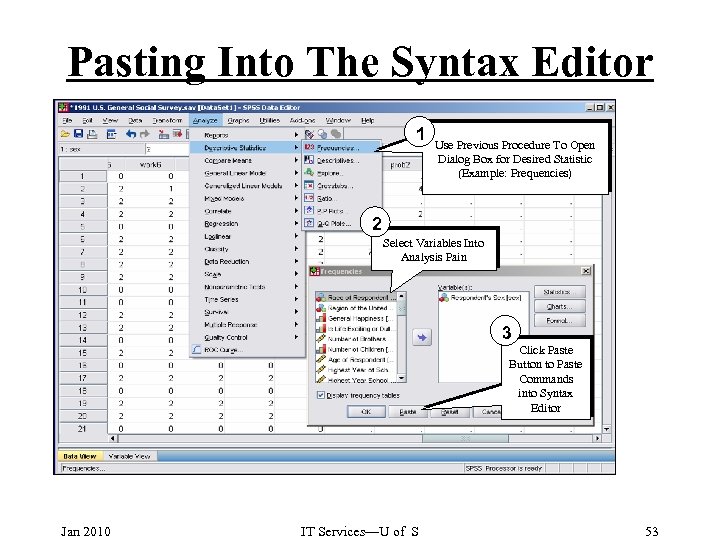
Pasting Into The Syntax Editor 1 Use Previous Procedure To Open Dialog Box for Desired Statistic (Example: Frequencies) 2 Select Variables Into Analysis Pain 3 Click Paste Button to Paste Commands into Syntax Editor Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 53
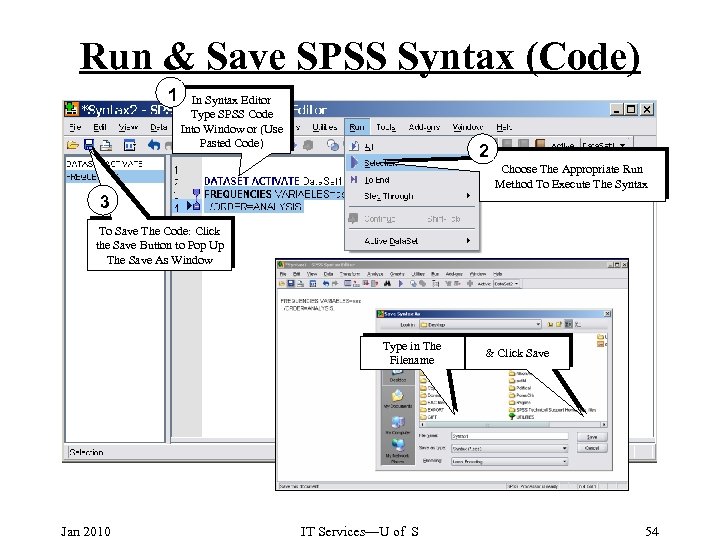
Run & Save SPSS Syntax (Code) 1 In Syntax Editor Type SPSS Code Into Window or (Use Pasted Code) 2 Choose The Appropriate Run Method To Execute The Syntax 3 To Save The Code: Click the Save Button to Pop Up The Save As Window Type in The Filename Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S & Click Save 54
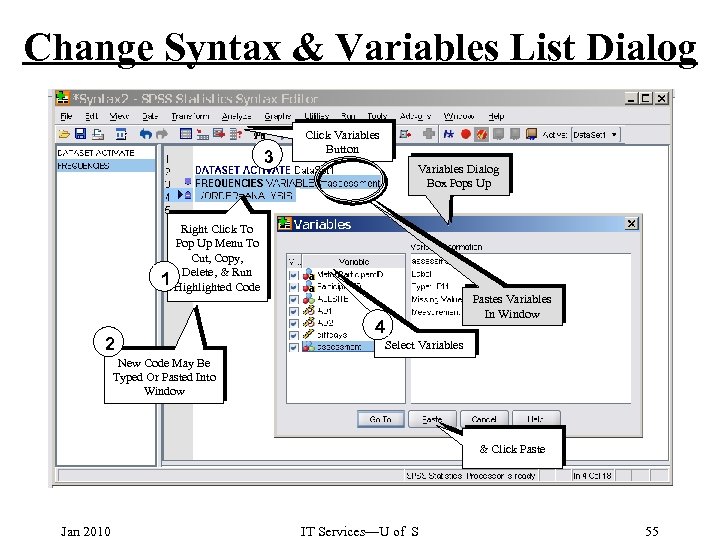
Change Syntax & Variables List Dialog 3 Click Variables Button Variables Dialog Box Pops Up Right Click To Pop Up Menu To Cut, Copy, Delete, & 1 Highlighted. Run Code 2 Pastes Variables In Window 4 Select Variables New Code May Be Typed Or Pasted Into Window & Click Paste Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 55
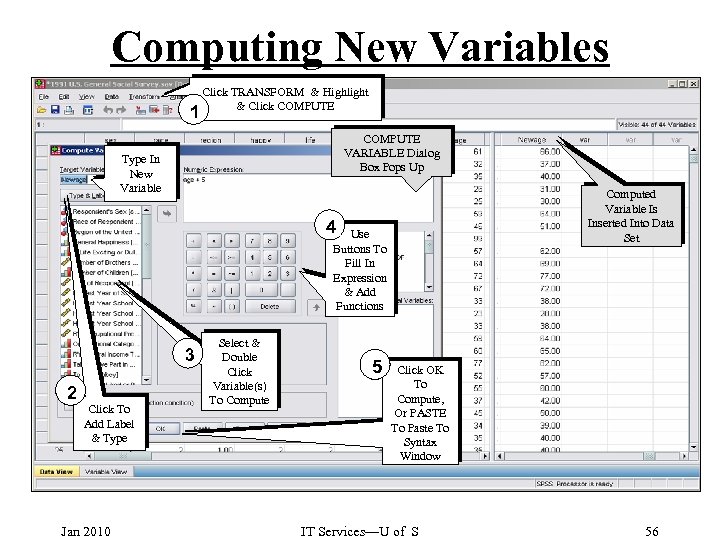
Computing New Variables 1 Click TRANSFORM & Highlight & Click COMPUTE VARIABLE Dialog Box Pops Up Type In New Variable Computed Variable Is Inserted Into Data Set 4 Use Buttons To Fill In Expression & Add Functions 3 2 Click To Add Label & Type Jan 2010 Select & Double Click Variable(s) To Compute 5 Click OK To Compute, Or PASTE To Paste To Syntax Window IT Services—U of S 56
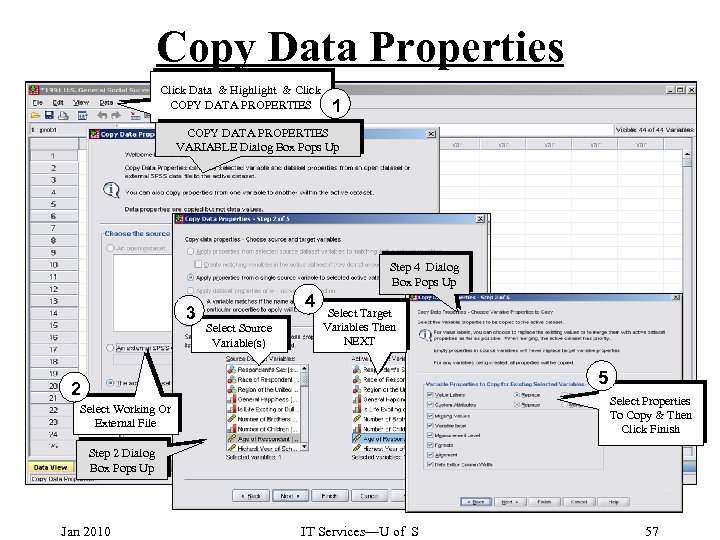
Copy Data Properties Click Data & Highlight & Click COPY DATA PROPERTIES 1 COPY DATA PROPERTIES VARIABLE Dialog Box Pops Up Step 4 Dialog Box Pops Up 3 4 Select Source Variable(s) Select Target Variables Then NEXT 5 2 Select Properties To Copy & Then Click Finish Select Working Or External File Step 2 Dialog Box Pops Up Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 57
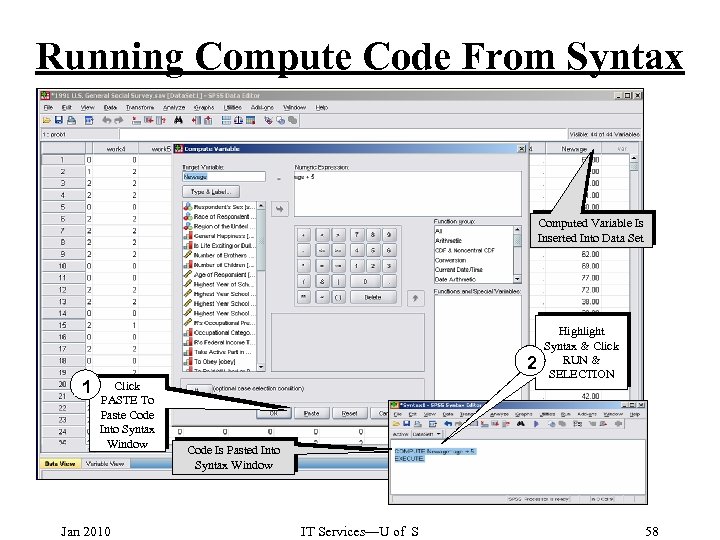
Running Compute Code From Syntax Computed Variable Is Inserted Into Data Set 2 1 Click PASTE To Paste Code Into Syntax Window Jan 2010 Highlight Syntax & Click RUN & SELECTION Code Is Pasted Into Syntax Window IT Services—U of S 58
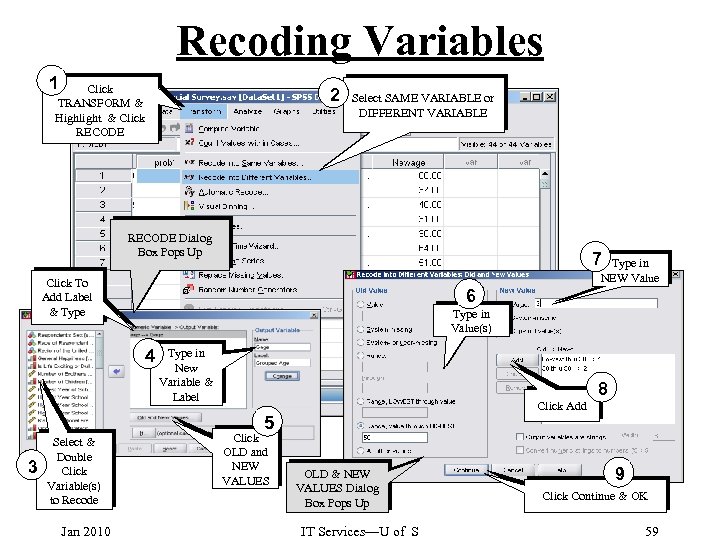
Recoding Variables 1 Click TRANSFORM & Highlight & Click RECODE 2 Select SAME VARIABLE or DIFFERENT VARIABLE RECODE Dialog Box Pops Up 7 Type in NEW Value Click To Add Label & Type 6 Type in Value(s) 4 Type in New Variable & Label Click Add 8 5 3 Select & Double Click Variable(s) to Recode Jan 2010 Click OLD and NEW VALUES OLD & NEW VALUES Dialog Box Pops Up IT Services—U of S 9 Click Continue & OK 59
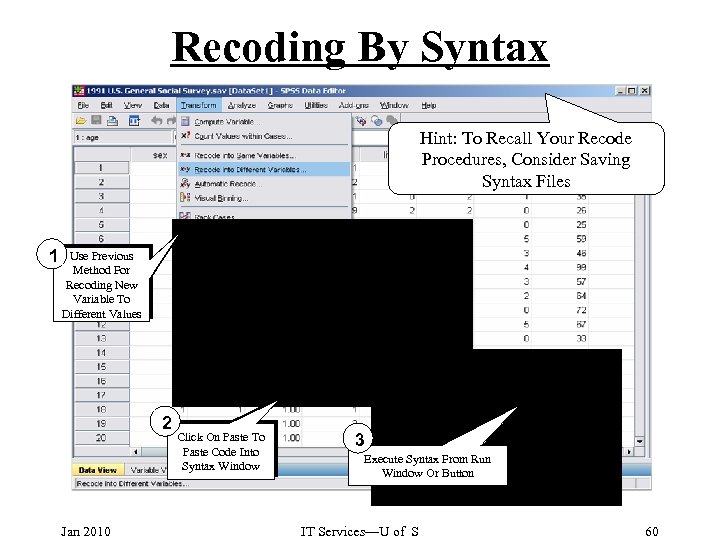
Recoding By Syntax Hint: To Recall Your Recode Procedures, Consider Saving Syntax Files 1 Use Previous Method For Recoding New Variable To Different Values 2 Jan 2010 Click On Paste To Paste Code Into Syntax Window 3 Execute Syntax From Run Window Or Button IT Services—U of S 60
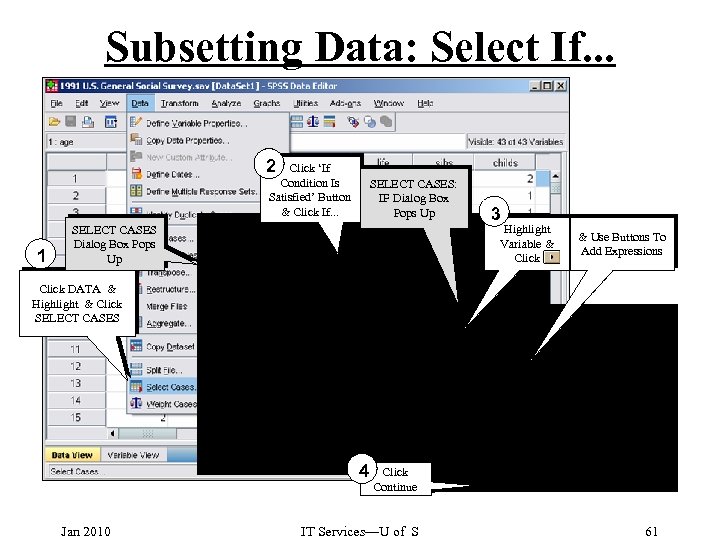
Subsetting Data: Select If. . . 2 Click ‘If Condition Is Satisfied’ Button & Click If. . . 1 SELECT CASES: IF Dialog Box Pops Up 3 Highlight Variable & Click SELECT CASES Dialog Box Pops Up & Use Buttons To Add Expressions Click DATA & Highlight & Click SELECT CASES 4 Jan 2010 Click Continue IT Services—U of S 61
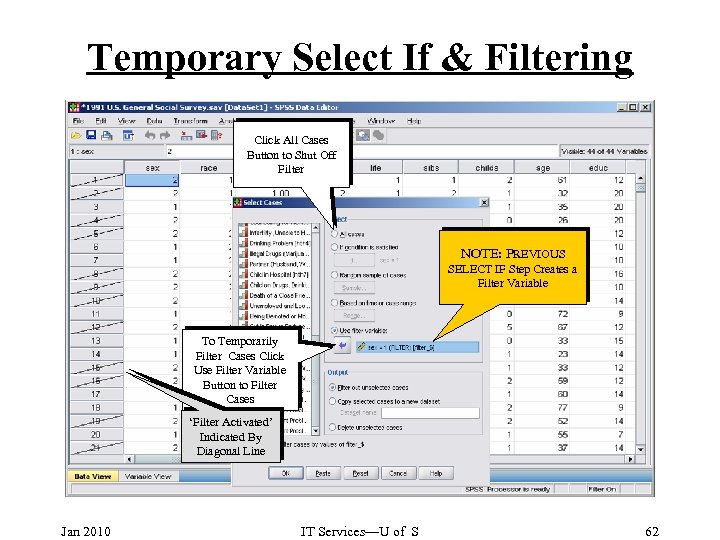
Temporary Select If & Filtering Click All Cases Button to Shut Off Filter NOTE: PREVIOUS SELECT IF Step Creates a Filter Variable To Temporarily Filter Cases Click Use Filter Variable Button to Filter Cases ‘Filter Activated’ Indicated By Diagonal Line Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 62
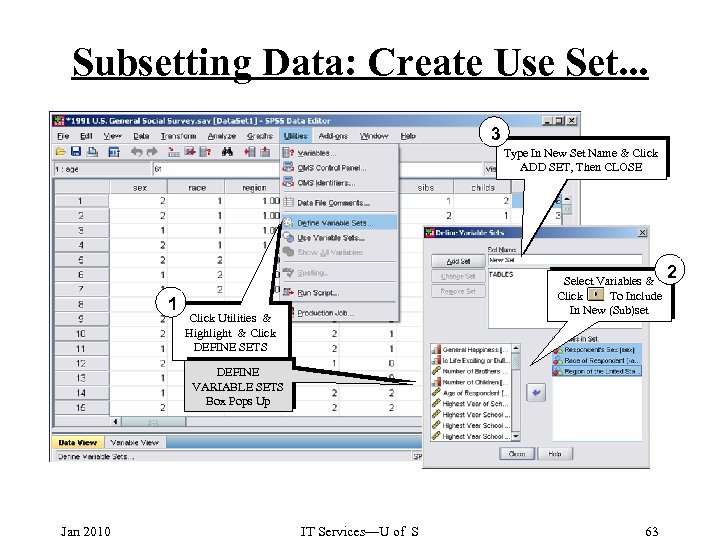
Subsetting Data: Create Use Set. . . 3 Type In New Set Name & Click ADD SET, Then CLOSE 1 Select Variables & Click To Include In New (Sub)set Click Utilities & Highlight & Click DEFINE SETS DEFINE VARIABLE SETS Box Pops Up Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 63 2
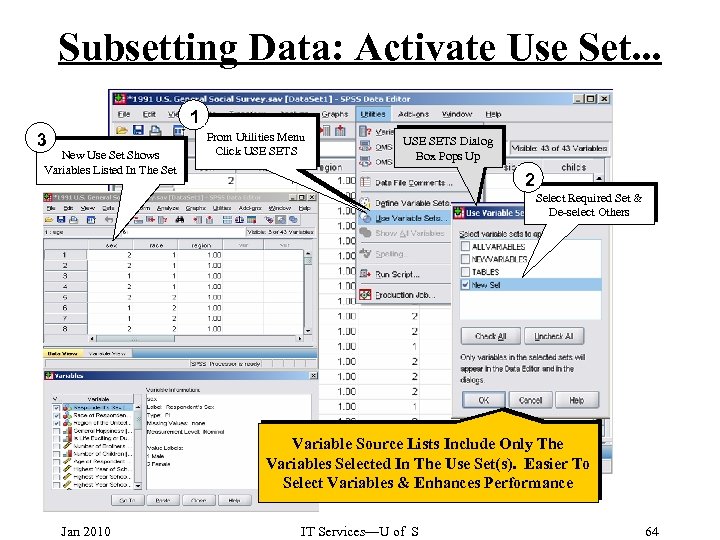
Subsetting Data: Activate Use Set. . . 1 3 New Use Set Shows Variables Listed In The Set From Utilities Menu Click USE SETS Dialog Box Pops Up 2 Select Required Set & De-select Others Variable Source Lists Include Only The Variables Selected In The Use Set(s). Easier To Select Variables & Enhances Performance Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 64
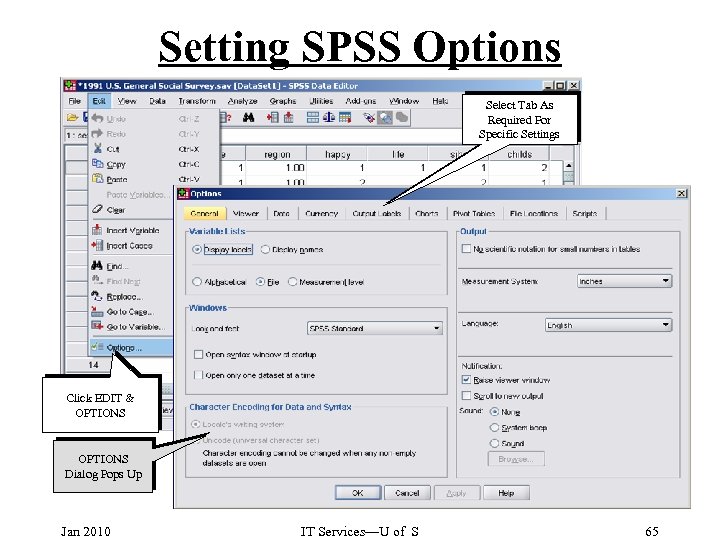
Setting SPSS Options Select Tab As Required For Specific Settings Click EDIT & OPTIONS Dialog Pops Up Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 65
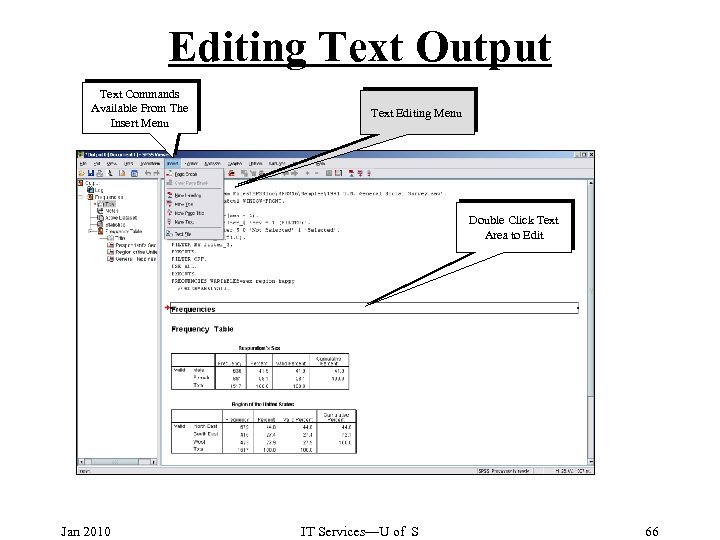
Editing Text Output Text Commands Available From The Insert Menu Text Editing Menu Double Click Text Area to Edit Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 66
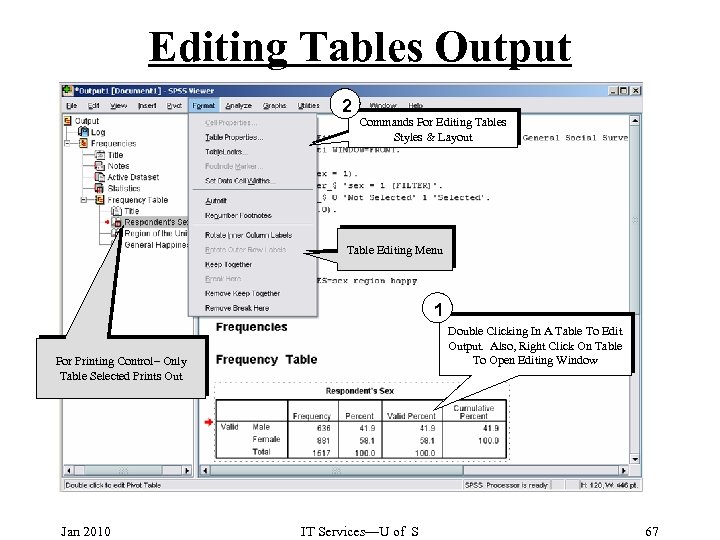
Editing Tables Output 2 Commands For Editing Tables Styles & Layout Table Editing Menu 1 Double Clicking In A Table To Edit Output. Also, Right Click On Table To Open Editing Window For Printing Control– Only Table Selected Prints Out Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 67
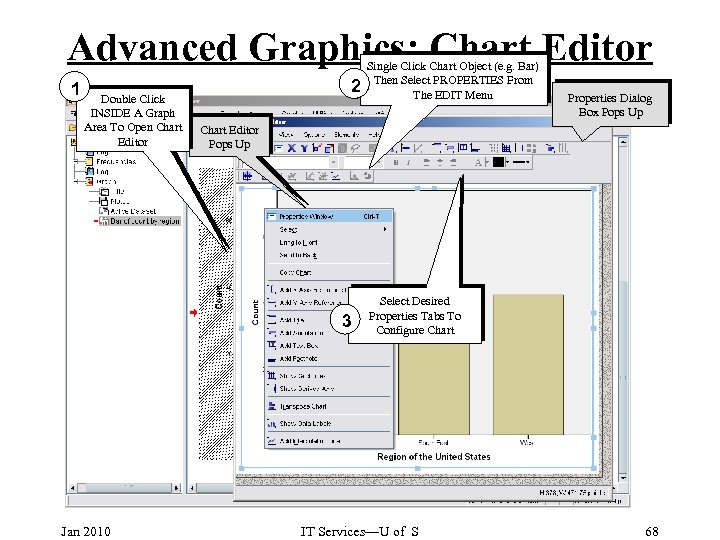
Advanced Graphics: Chart Editor 1 Double Click INSIDE A Graph Area To Open Chart Editor 2 Properties Dialog Box Pops Up Chart Editor Pops Up 3 Jan 2010 Single Click Chart Object (e. g. Bar) Then Select PROPERTIES From The EDIT Menu Select Desired Properties Tabs To Configure Chart IT Services—U of S 68
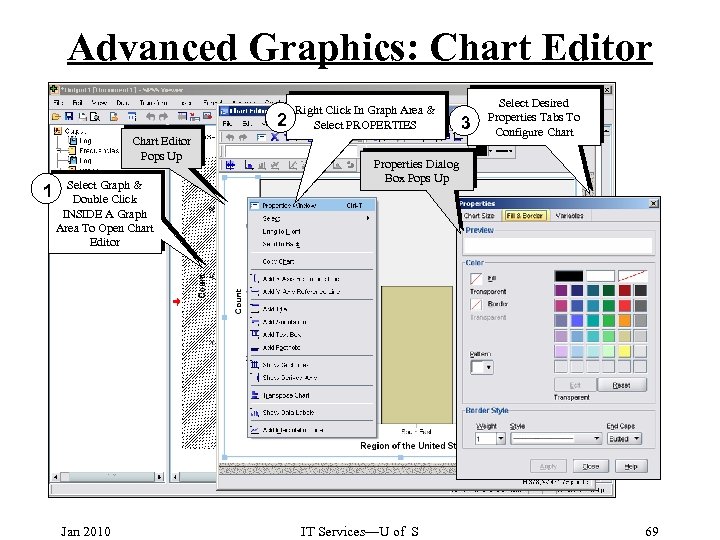
Advanced Graphics: Chart Editor 2 Chart Editor Pops Up 1 Select Graph & Double Click INSIDE A Graph Area To Open Chart Editor Jan 2010 Right Click In Graph Area & Select PROPERTIES 3 Select Desired Properties Tabs To Configure Chart Properties Dialog Box Pops Up IT Services—U of S 69
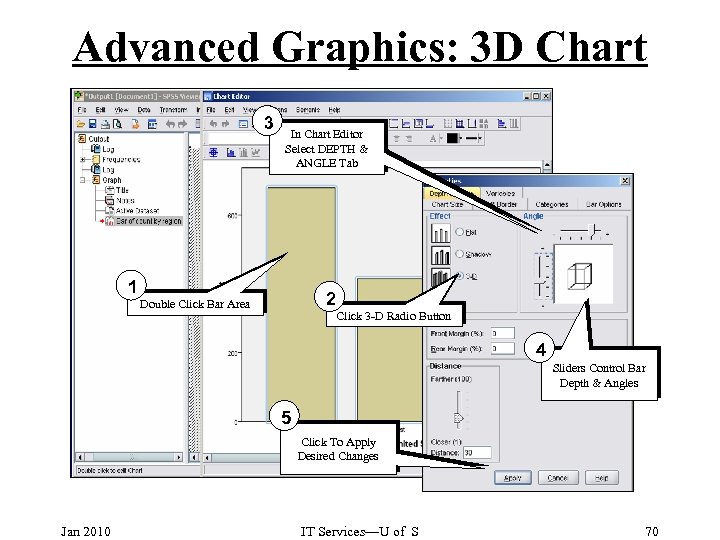
Advanced Graphics: 3 D Chart 3 In Chart Editor Select DEPTH & ANGLE Tab 1 2 Double Click Bar Area Click 3 -D Radio Button 4 Sliders Control Bar Depth & Angles 5 Click To Apply Desired Changes Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 70
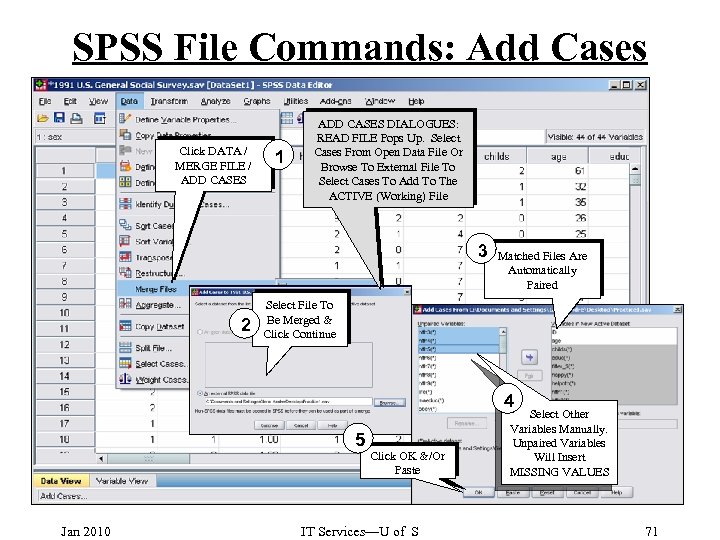
SPSS File Commands: Add Cases Click DATA / MERGE FILE / ADD CASES 1 ADD CASES DIALOGUES: READ FILE Pops Up. Select Cases From Open Data File Or Browse To External File To Select Cases To Add To The ACTIVE (Working) File 3 2 Matched Files Are Automatically Paired Select File To Be Merged & Click Continue 4 5 Jan 2010 Click OK &/Or Paste IT Services—U of S Select Other Variables Manually. Unpaired Variables Will Insert MISSING VALUES 71
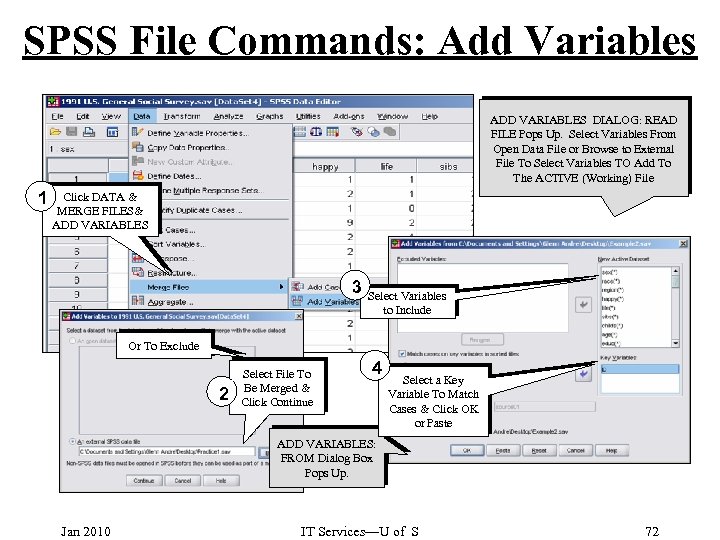
SPSS File Commands: Add Variables ADD VARIABLES DIALOG: READ FILE Pops Up. Select Variables From Open Data File or Browse to External File To Select Variables TO Add To The ACTIVE (Working) File 1 Click DATA & MERGE FILES& ADD VARIABLES 3 Select Variables to Include Or To Exclude 2 Select File To Be Merged & Click Continue 4 Select a Key Variable To Match Cases & Click OK or Paste ADD VARIABLES: FROM Dialog Box Pops Up. Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 72
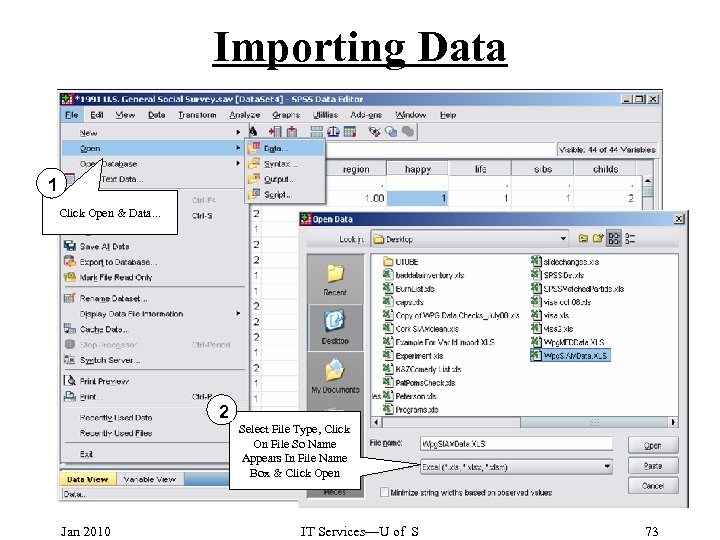
Importing Data 1 Click Open & Data. . . 2 Select File Type, Click On File So Name Appears In File Name Box & Click Open Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 73
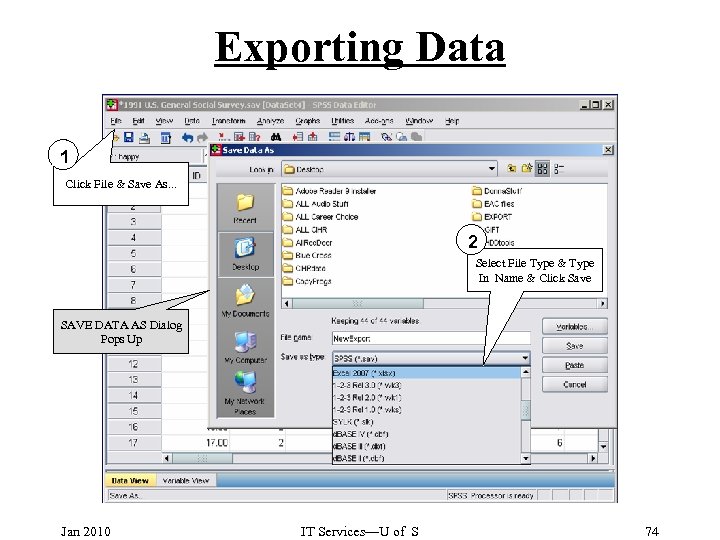
Exporting Data 1 Click File & Save As. . . 2 Select File Type & Type In Name & Click Save SAVE DATA AS Dialog Pops Up Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 74
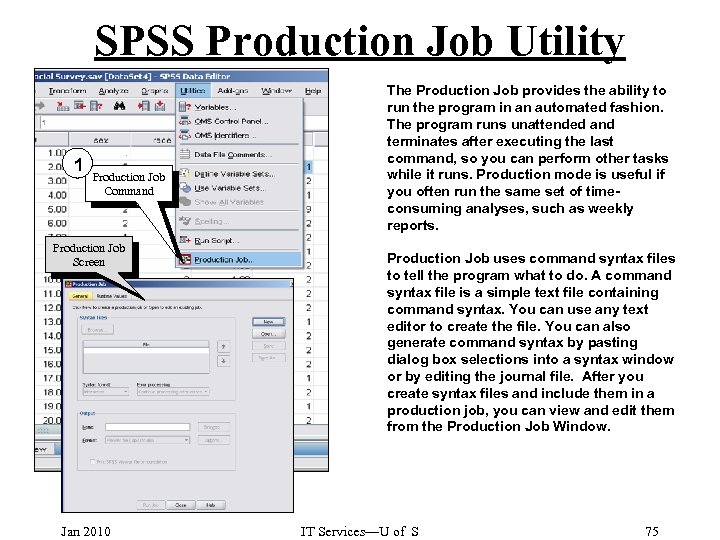
SPSS Production Job Utility 1 Production Job Command Production Job Screen Jan 2010 The Production Job provides the ability to run the program in an automated fashion. The program runs unattended and terminates after executing the last command, so you can perform other tasks while it runs. Production mode is useful if you often run the same set of timeconsuming analyses, such as weekly reports. Production Job uses command syntax files to tell the program what to do. A command syntax file is a simple text file containing command syntax. You can use any text editor to create the file. You can also generate command syntax by pasting dialog box selections into a syntax window or by editing the journal file. After you create syntax files and include them in a production job, you can view and edit them from the Production Job Window. IT Services—U of S 75
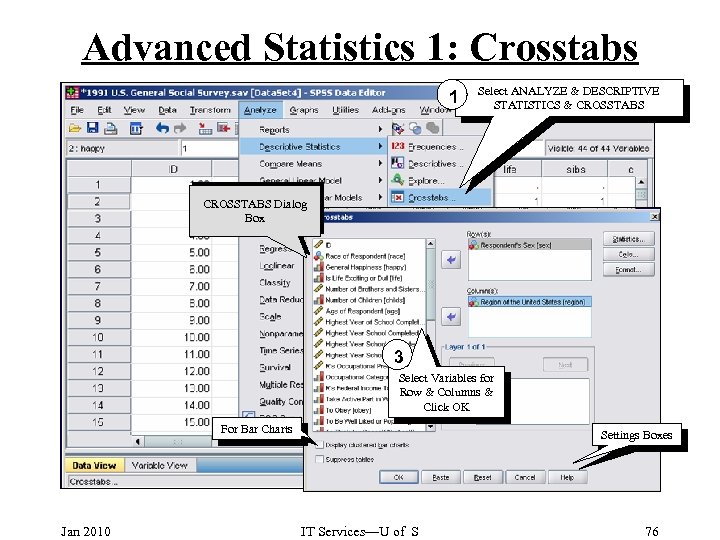
Advanced Statistics 1: Crosstabs 1 Select ANALYZE & DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS & CROSSTABS Dialog Box 3 Select Variables for Row & Columns & Click OK For Bar Charts Jan 2010 Settings Boxes IT Services—U of S 76
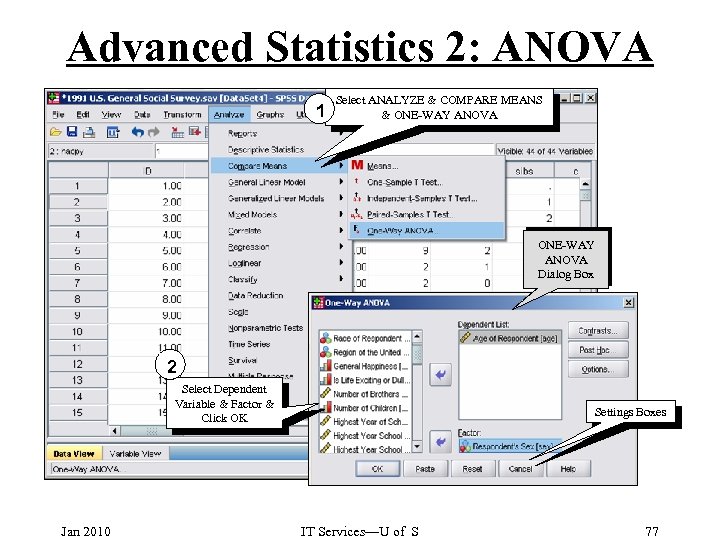
Advanced Statistics 2: ANOVA 1 Select ANALYZE & COMPARE MEANS & ONE-WAY ANOVA Dialog Box 2 Select Dependent Variable & Factor & Click OK Jan 2010 Settings Boxes IT Services—U of S 77
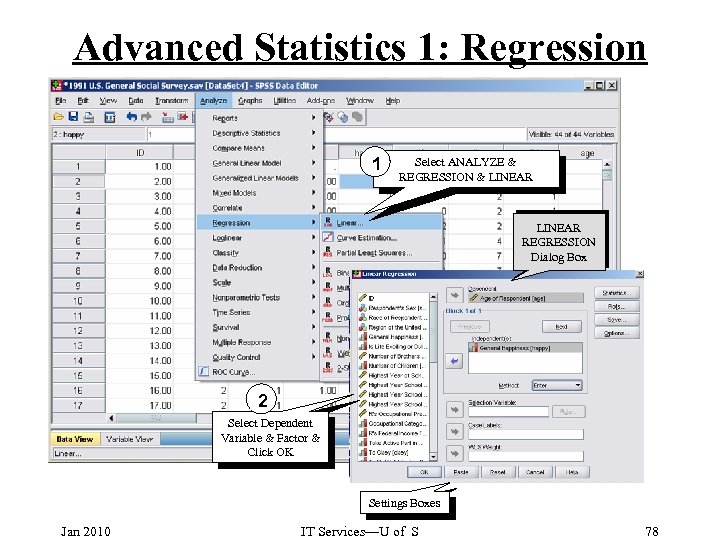
Advanced Statistics 1: Regression 1 Select ANALYZE & REGRESSION & LINEAR REGRESSION Dialog Box 2 Select Dependent Variable & Factor & Click OK Settings Boxes Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 78

For More Information • The SPSS Application Contains an Extensive Help System Including Tutorials, Syntax Guide, Statistics Coach & Other Assistance • Contact SPSS on the Internet at http: //www. spss. com/ • This Course Outline & SPSS Assistance Is Available From U of S Information Technology Services Help Desk At Arts 70, Phone 966 -4817 • For information on other workshops available, please see our web site at http: //training. usask. ca courses & click on the Statistical Software link Jan 2010 IT Services—U of S 79
2982f6ee3dc0aae5aec6c34bebb0a725.ppt