ae39ba6cd7e4742e21aa8a2692a73107.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Detectors and Analog Electronics Bill Crain The Aerospace Corporation 310 -336 -8530 Bill. Crain@aero. org Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 28 September 2005

Introduction • • • Design Overview Requirements Flowdown Detector Specification Signals, Noise, and Processing Board Descriptions Interface Diagram Power Consumption Trade Studies Summary Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 2 28 September 2005
Detector Electronics Design Overview • Electronic Board Designs – Telescope Board – Analog Processing Board (APB) in E-box • Heritage approach from Polar CEPPAD/IPS unchanged from proposal – Linear pulse processing system with Amptek front-end – Circuits designed specifically for CRa. TER requirements • Functional requirements summary – – Measure LET of high LET particles in thin detectors Measure LET of low LET particles in thick detectors Provide good resolution for TEP effects Robust to temperature drift and environments Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 3 28 September 2005
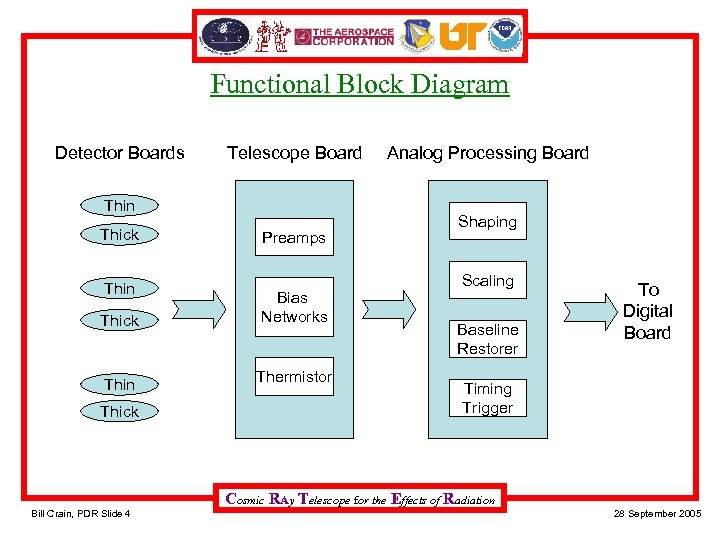
Functional Block Diagram Detector Boards Telescope Board Thin Thick Preamps Bias Networks Thermistor Analog Processing Board Shaping Scaling Baseline Restorer To Digital Board Timing Trigger Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 4 28 September 2005

Analog Signal Flow Diagram • Single fixed gain, linear transfer function • All detector channels use same topology Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 5 28 September 2005
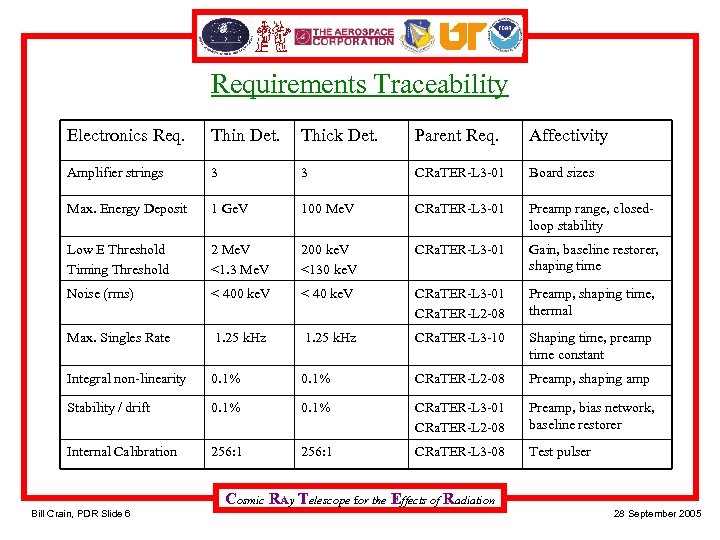
Requirements Traceability Electronics Req. Thin Det. Thick Det. Parent Req. Affectivity Amplifier strings 3 3 CRa. TER-L 3 -01 Board sizes Max. Energy Deposit 1 Ge. V 100 Me. V CRa. TER-L 3 -01 Preamp range, closedloop stability Low E Threshold Timing Threshold 2 Me. V <1. 3 Me. V 200 ke. V <130 ke. V CRa. TER-L 3 -01 Gain, baseline restorer, shaping time Noise (rms) < 400 ke. V < 40 ke. V CRa. TER-L 3 -01 CRa. TER-L 2 -08 Preamp, shaping time, thermal Max. Singles Rate 1. 25 k. Hz CRa. TER-L 3 -10 Shaping time, preamp time constant Integral non-linearity 0. 1% CRa. TER-L 2 -08 Preamp, shaping amp Stability / drift 0. 1% CRa. TER-L 3 -01 CRa. TER-L 2 -08 Preamp, bias network, baseline restorer Internal Calibration 256: 1 CRa. TER-L 3 -08 Test pulser Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 6 28 September 2005

Detector Specification (1) • Document 32 -05001 released rev 02 August 1, 2005 • Micron Semiconductor Limited – Lancing Sussex, UK • 20 years experience in supplying detectors for space physics – CEPPAD, CRRES, WIND, CLUSTER, ACE, IMAGE, STEREO, and more… • Detector Type – Ion-implanted doping to form P+ junction on N-type silicon – Very stable technology – Advantages to science include good carrier lifetime, stable to environmental conditions, and thin entrance windows Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 7 28 September 2005
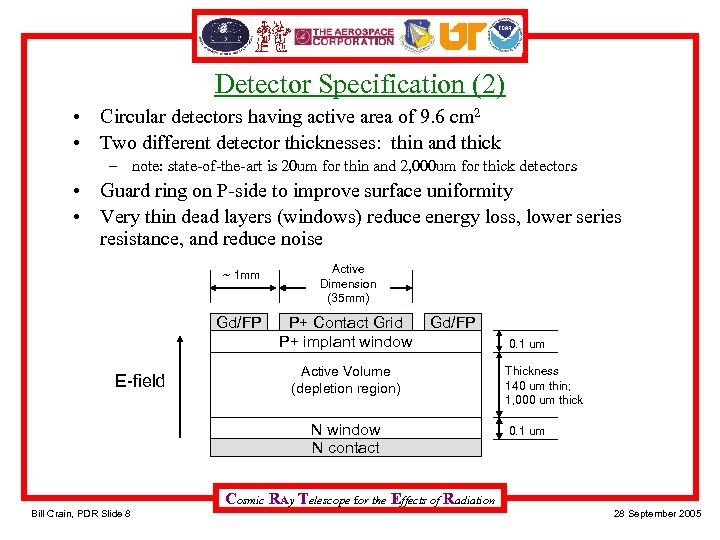
Detector Specification (2) • Circular detectors having active area of 9. 6 cm 2 • Two different detector thicknesses: thin and thick – note: state-of-the-art is 20 um for thin and 2, 000 um for thick detectors • Guard ring on P-side to improve surface uniformity • Very thin dead layers (windows) reduce energy loss, lower series resistance, and reduce noise ~ 1 mm Gd/FP E-field Active Dimension (35 mm) P+ Contact Grid P+ implant window Gd/FP Active Volume (depletion region) N window N contact 0. 1 um Thickness 140 um thin; 1, 000 um thick 0. 1 um Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 8 28 September 2005
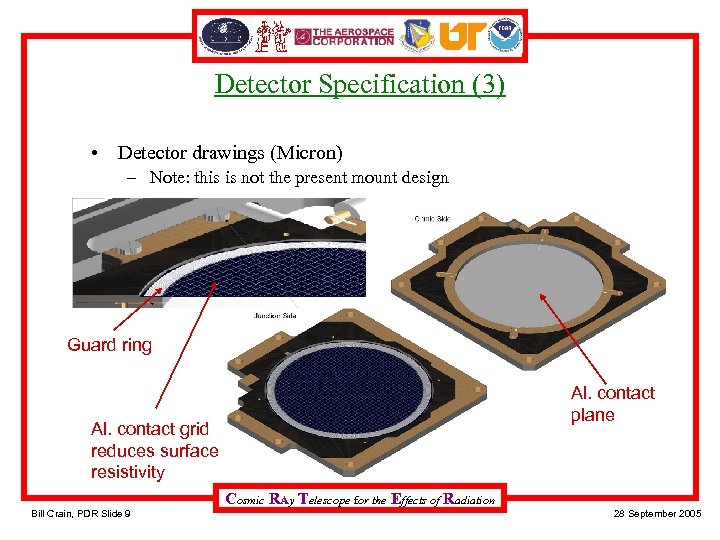
Detector Specification (3) • Detector drawings (Micron) – Note: this is not the present mount design Guard ring Al. contact plane Al. contact grid reduces surface resistivity Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 9 28 September 2005
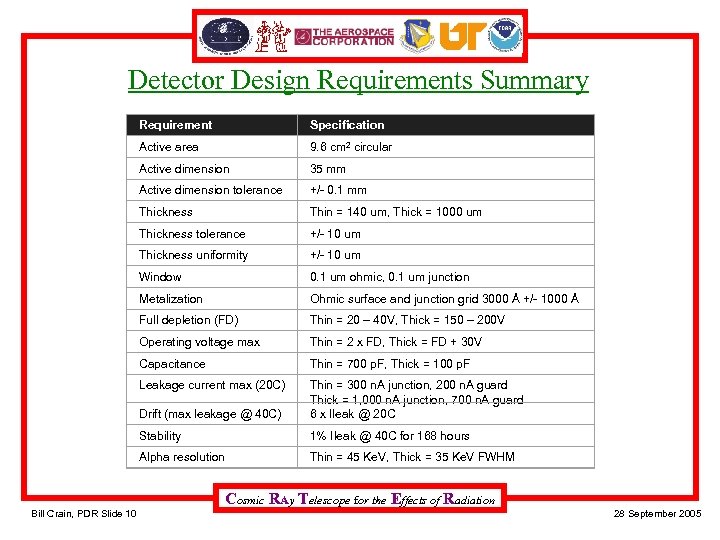
Detector Design Requirements Summary Requirement Specification Active area 9. 6 cm 2 circular Active dimension 35 mm Active dimension tolerance +/- 0. 1 mm Thickness Thin = 140 um, Thick = 1000 um Thickness tolerance +/- 10 um Thickness uniformity +/- 10 um Window 0. 1 um ohmic, 0. 1 um junction Metalization Ohmic surface and junction grid 3000 Å +/- 1000 Å Full depletion (FD) Thin = 20 – 40 V, Thick = 150 – 200 V Operating voltage max Thin = 2 x FD, Thick = FD + 30 V Capacitance Thin = 700 p. F, Thick = 100 p. F Leakage current max (20 C) Drift (max leakage @ 40 C) Thin = 300 n. A junction, 200 n. A guard Thick = 1, 000 n. A junction, 700 n. A guard 6 x Ileak @ 20 C Stability 1% Ileak @ 40 C for 168 hours Alpha resolution Thin = 45 Ke. V, Thick = 35 Ke. V FWHM Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 10 28 September 2005

Detector Specification (4) • ISO 9001 – Full traceability and serialization – Travelers maintained • Qualification tests prior to flight detector shipment – – Bond pull test Random vibration test Thermal cycling Stability • Verification matrix specifies test criteria – – Leakage current Capacitance I-V characteristic Alpha resolution / pulser noise measurement Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 11 28 September 2005
Detector Verification Matrix Eye Chart From 32 -05001 Rev 02 Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 12 28 September 2005
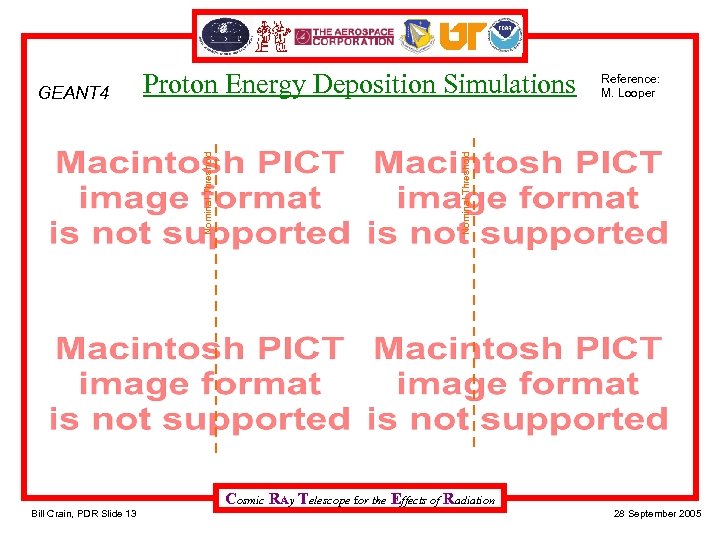
Proton Energy Deposition Simulations GEANT 4 Thick 150 Me. V incident E Nominal Threshold Thin 150 Me. V incident E Reference: M. Looper Thin 1000 Me. V incident E Thick 1000 Me. V incident E Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 13 28 September 2005
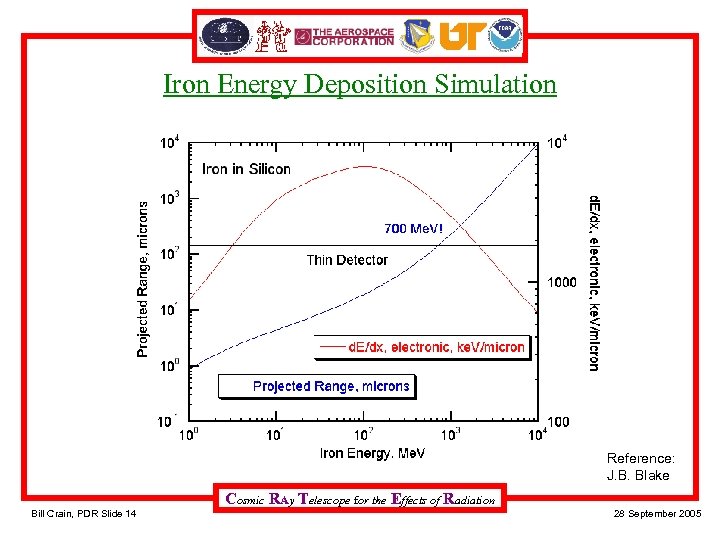
Iron Energy Deposition Simulation Reference: J. B. Blake Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 14 28 September 2005
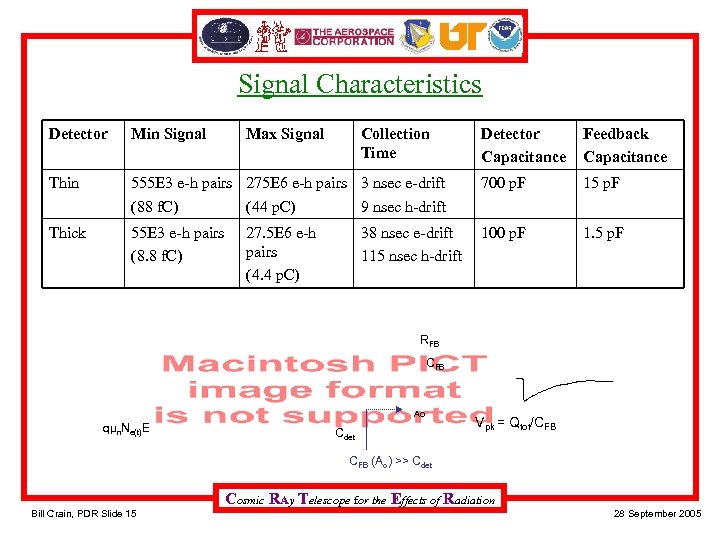
Signal Characteristics Detector Min Signal Thin Thick Max Signal Collection Time Detector Capacitance Feedback Capacitance 555 E 3 e-h pairs 275 E 6 e-h pairs 3 nsec e-drift (88 f. C) (44 p. C) 9 nsec h-drift 700 p. F 15 p. F 55 E 3 e-h pairs (8. 8 f. C) 100 p. F 1. 5 p. F 27. 5 E 6 e-h pairs (4. 4 p. C) 38 nsec e-drift 115 nsec h-drift RFB CFB Ao qμn. Ne(t)E qμp. Nh(t)E Cdet Vpk = Qtot/CFB (Ao) >> Cdet Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 15 28 September 2005
Signal Processing (1) • Combined dynamic range of thin/thick pair is 5, 000 • Thin threshold to provide overlap with thick range • Thin Detector Signal – Preamp input stage designed for 97% charge collection • High gain input j. FET for large dynamic input capacitance • 4% drift in operating point will result in 0. 1% in output peak – Large feedback capacitance needed to handle Fe deposit • Preamp compensation to maintain closed-loop stability • Thick Detector Signal – Not as sensitive to detector capacitance – Designed for low noise to maintain reliable 200 Ke. V low threshold and meet resolution requirement Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 16 28 September 2005
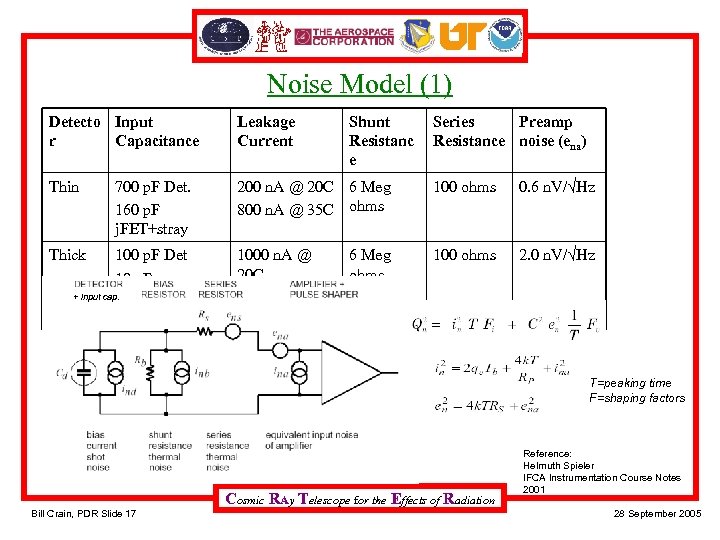
Noise Model (1) Detecto Input r Capacitance Leakage Current Thin 200 n. A @ 20 C 6 Meg 800 n. A @ 35 C ohms 100 ohms 0. 6 n. V/√Hz 1000 n. A @ 20 C 4000 n. A @ 35 C 100 ohms 2. 0 n. V/√Hz 700 p. F Det. 160 p. F j. FET+stray Thick 100 p. F Det 10 p. F + input cap. j. FET+stray Shunt Resistanc e 6 Meg ohms Series Preamp Resistance noise (ena) T=peaking time F=shaping factors Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 17 Reference: Helmuth Spieler IFCA Instrumentation Course Notes 2001 28 September 2005
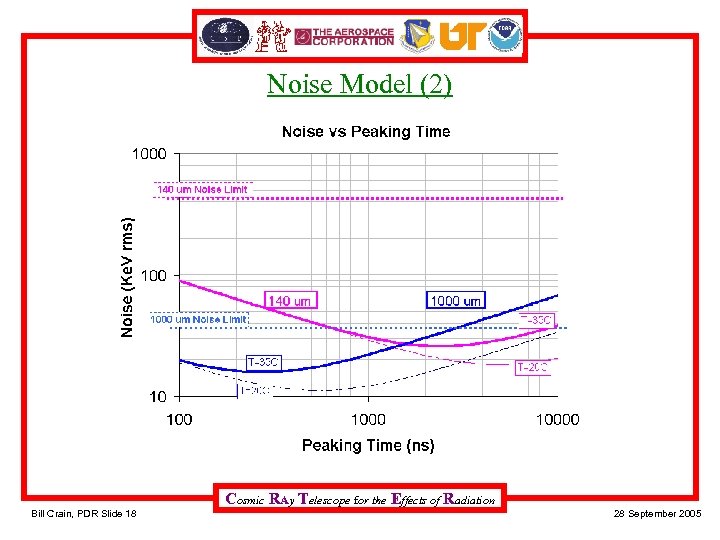
Noise Model (2) Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 18 28 September 2005
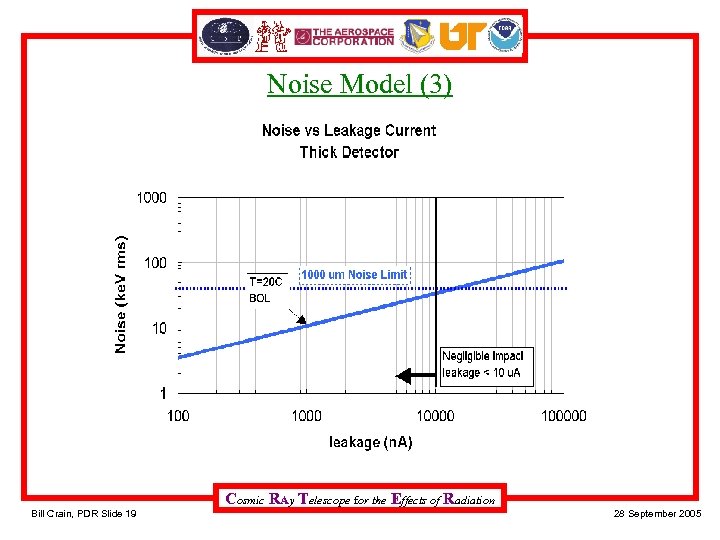
Noise Model (3) 20 C BOL Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 19 28 September 2005
Signal Processing (2) • Noise dominated by thick detector leakage current • Shaping time same for both thin and thick detectors – ~1 usec for comfortable PHA input timing – 3 -pole gaussian shaping improves symmetry – 2 -complex poles shortens tail • Coincidence Timing – Noise occupancy in 1 -usec coincidence window < 0. 1% – Threshold to noise ratio (T/N) ~ 3. 2 for timing discriminator – Timing discriminator threshold ~ 130 ke. V • Anticipated BOL T/N ratio is ~ 10 • Allows margin for leakage current drift up to 10 u. A Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 20 28 September 2005

Signal Processing (3) • Other factors affecting noise performance – Bias resistor on thin detector sized to minimize voltage drop – Bias resistor on thick detector sized to minimize noise – Detector shot noise doubles every 8 C • Beneficial to operate cold; preferably below 20 C Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 21 28 September 2005
Signal Processing (4) • Pileup is rare due to low event rate and relatively short shaping time – Exception: occasional periods of high ESP flux • Coincidence timing uncertainty from leading edge trigger is small – Amplified timing discriminator reduces time walk to acceptable 10% uncertainty • Ballistic deficit is not an issue due to short collection times relative to peaking time of shaper • Output voltage scaled for PHA input specifications Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 22 28 September 2005

Telescope Board Details • Thin/thick detector pair use same design topology • Signal collected on P-contact • Guard signal shunted to ground • No guard leakage noise • AC coupling to isolate DC detector leakage current • Low noise / high gain JFET input stage (Inter. FET) with Amptek A 250 hybrid • MIL-STD-5510 polyimide 8 layer construction Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 23 28 September 2005
Analog Processing Board Details • Single board in E-box contains 3 thin and 3 thick detector processing channels – Polyimide laminate, MIL-STD-55110, 8 -layers, 0. 062 in. – Interfaces to digital board in same box • Components – Linear Technology radiation tolerant opamps for shaping stages, BLR, and comparators – Analog Devices rad tolerant op-amp for test pulser interface and bias monitoring (see trade study chart) • Pole-zero cancellation circuit included to prevent undershoot Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 24 28 September 2005
Analog Interface Block Diagram • • ICD 32 -02052 rev 01 +/- 6 V power, 5 V Thin and thick bias voltages Unipolar gaussian signals input to peak-hold circuits • Low-level triggers for coincidence timing • Test pulser level and clocking signals Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 25 28 September 2005

Power Estimate Total estimated power dissipation is < 1 Watt Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 26 28 September 2005

Trade Studies • Considering detector bias current monitor – Housekeeping item to provide leakage current for each detector – No impact on noise or failure modes – Useful for diagnostic purposes especially during environmental testing of flight units Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 27 28 September 2005

Summary • Detectors are well-established technology from experienced supplier • Detector specification and Analog/Digital ICD documents have been released • Electronics design meets requirements of instrument requirements document 32 -01205 Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 28 28 September 2005
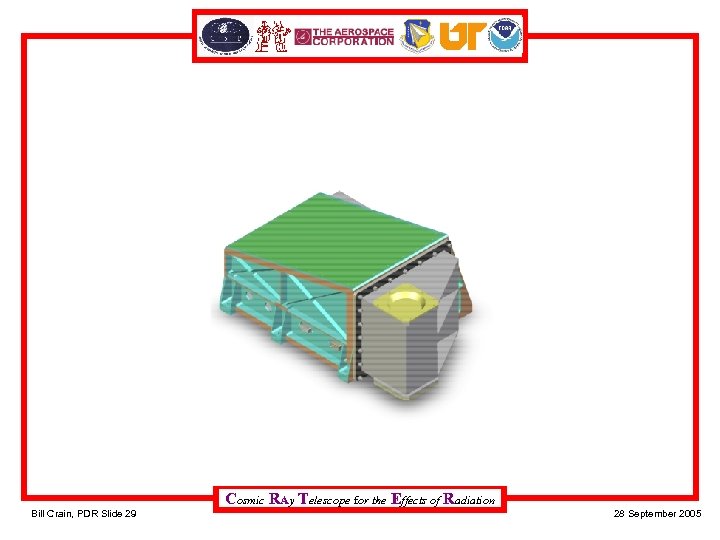
Cosmic RAy Telescope for the Effects of Radiation Bill Crain, PDR Slide 29 28 September 2005
ae39ba6cd7e4742e21aa8a2692a73107.ppt