ed75bb93ed1e7414c24fb816b68b9a8c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Detector and Optical Physics Group Click to edit Master title style Cavendish Laboratory Transition Edge Sensor Bolometers D. J. Goldie, M. D. Audley, D. M. Glowacka, V. N. Tsaneva, S. Withington. Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
Detector and Optical Physics Group Click to edit Master title style Cavendish Laboratory Transition Edge Sensor Bolometers D. J. Goldie, M. D. Audley, D. M. Glowacka, V. N. Tsaneva, S. Withington. Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
 DPG activities • DPG capabilities • Optical modelling • Electromagnetics • Thermal behaviour • Device modelling • Fabrication (Transition Edge Sensors (TESs), Kinetic Inductance Detectors, SIS tunnel junctions, SQUIDs. . • Characterization • Detector packaging • This talk • TESs for CMB polarization experiments Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
DPG activities • DPG capabilities • Optical modelling • Electromagnetics • Thermal behaviour • Device modelling • Fabrication (Transition Edge Sensors (TESs), Kinetic Inductance Detectors, SIS tunnel junctions, SQUIDs. . • Characterization • Detector packaging • This talk • TESs for CMB polarization experiments Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
 Cl. OVER TEAM • Cambridge – M. D. Audley, B. Barker, M. Brown, M. Crane, D. Glowacka, D. Goldie, K. Grainge, A. Lasenby, H. Stevenson, D. Titterington, V. Tsaneva, S. Withington • Cardiff – P. A. R Ade, P. G. Calisse, W. Gear, w. Grainger, P. Hargrave, J, House, K. Isaac, , B. Kiernan, P. Mauskopf, S. Parsley, G. Savini, R. V. Sudiwala, C. Tucker, R. Tucker, I. Walker, M. Whitehead, J. Zhang • Manchester – L. Piccirillo, P. Diamond, A. Galtress, V. Haynes, P. Leahy, S. Lewis, B. Maffei, L. Martinis, S. Melhuish, G. Pisano, R. Watson, • Oxford – M. Brock, P. Cabella, P. Ferreira, P. Grimes, B. Johnson, M. Jones, W. Lau, J. Leech, D. O’Dea, C. North, D. Sutton, A. Taylor, G. Yassin • NIST- K. D. Irwin • UBC- M. Halpern Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Cl. OVER TEAM • Cambridge – M. D. Audley, B. Barker, M. Brown, M. Crane, D. Glowacka, D. Goldie, K. Grainge, A. Lasenby, H. Stevenson, D. Titterington, V. Tsaneva, S. Withington • Cardiff – P. A. R Ade, P. G. Calisse, W. Gear, w. Grainger, P. Hargrave, J, House, K. Isaac, , B. Kiernan, P. Mauskopf, S. Parsley, G. Savini, R. V. Sudiwala, C. Tucker, R. Tucker, I. Walker, M. Whitehead, J. Zhang • Manchester – L. Piccirillo, P. Diamond, A. Galtress, V. Haynes, P. Leahy, S. Lewis, B. Maffei, L. Martinis, S. Melhuish, G. Pisano, R. Watson, • Oxford – M. Brock, P. Cabella, P. Ferreira, P. Grimes, B. Johnson, M. Jones, W. Lau, J. Leech, D. O’Dea, C. North, D. Sutton, A. Taylor, G. Yassin • NIST- K. D. Irwin • UBC- M. Halpern Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
 Key Features of CLOVER • Two telescopes measuring polarization of CMB: • LF: 97 GHz • HF: combined 150 and 220 GHz focal plane • Detectors: Bolometers with superconducting transition edge sensors (TES) • Sensitivity: limited by unavoidable photon noise (2. 2 x 10 -17 W/√Hz) • Operating Temperature: 100 m. K (active control of bath temperature) • Focal Plane: hexagonal array of horns, two polarizations per horn LF: 96 horns => 192 finline-coupled detectors at 97 GHz HF: 192 horns => 192 4 -probe OMTs in mixed 150/220 GHz focal plane • Readout: Time-division SQUID multiplexer (NIST, UBC) Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Key Features of CLOVER • Two telescopes measuring polarization of CMB: • LF: 97 GHz • HF: combined 150 and 220 GHz focal plane • Detectors: Bolometers with superconducting transition edge sensors (TES) • Sensitivity: limited by unavoidable photon noise (2. 2 x 10 -17 W/√Hz) • Operating Temperature: 100 m. K (active control of bath temperature) • Focal Plane: hexagonal array of horns, two polarizations per horn LF: 96 horns => 192 finline-coupled detectors at 97 GHz HF: 192 horns => 192 4 -probe OMTs in mixed 150/220 GHz focal plane • Readout: Time-division SQUID multiplexer (NIST, UBC) Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
 Why Microstrip-coupled TESs? • CLOVER needs high-performance polarimetry • Flexibility: RF absorption is separated from the bolometer • TES design can be optimised separately and doesn’t have to change if the array architecture changes • Calibration • Can include planar band-pass filters, phase shifters, modulators etc. => simple detector becomes multi-function integrated circuit Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Why Microstrip-coupled TESs? • CLOVER needs high-performance polarimetry • Flexibility: RF absorption is separated from the bolometer • TES design can be optimised separately and doesn’t have to change if the array architecture changes • Calibration • Can include planar band-pass filters, phase shifters, modulators etc. => simple detector becomes multi-function integrated circuit Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
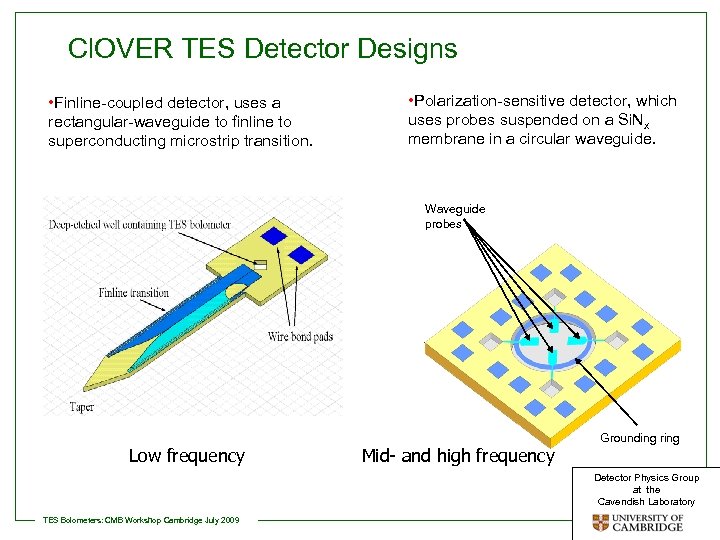 Cl. OVER TES Detector Designs • Finline-coupled detector, uses a rectangular-waveguide to finline to superconducting microstrip transition. • Polarization-sensitive detector, which uses probes suspended on a Si. Nx membrane in a circular waveguide. Waveguide probes Low frequency Mid- and high frequency Grounding ring Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Cl. OVER TES Detector Designs • Finline-coupled detector, uses a rectangular-waveguide to finline to superconducting microstrip transition. • Polarization-sensitive detector, which uses probes suspended on a Si. Nx membrane in a circular waveguide. Waveguide probes Low frequency Mid- and high frequency Grounding ring Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
 TESs for Cl. OVER • Mo-Cu TESs • 500 nm Si. Nx support and thermal isolation • Tc 200 m. K • Tbath 100 m. K Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
TESs for Cl. OVER • Mo-Cu TESs • 500 nm Si. Nx support and thermal isolation • Tc 200 m. K • Tbath 100 m. K Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
 Cl. OVER Science-Grade Detectors 30 chips per wafer Tc: 190 m. K Power handling: 11 p. W Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Cl. OVER Science-Grade Detectors 30 chips per wafer Tc: 190 m. K Power handling: 11 p. W Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
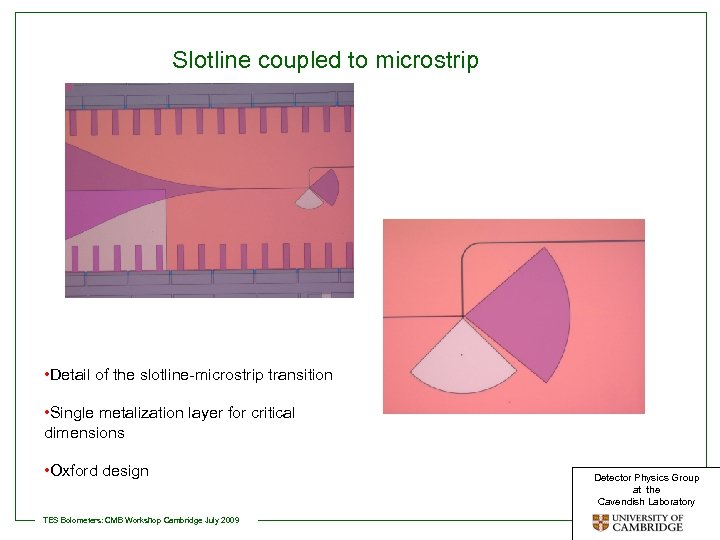 Slotline coupled to microstrip • Detail of the slotline-microstrip transition • Single metalization layer for critical dimensions • Oxford design TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
Slotline coupled to microstrip • Detail of the slotline-microstrip transition • Single metalization layer for critical dimensions • Oxford design TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
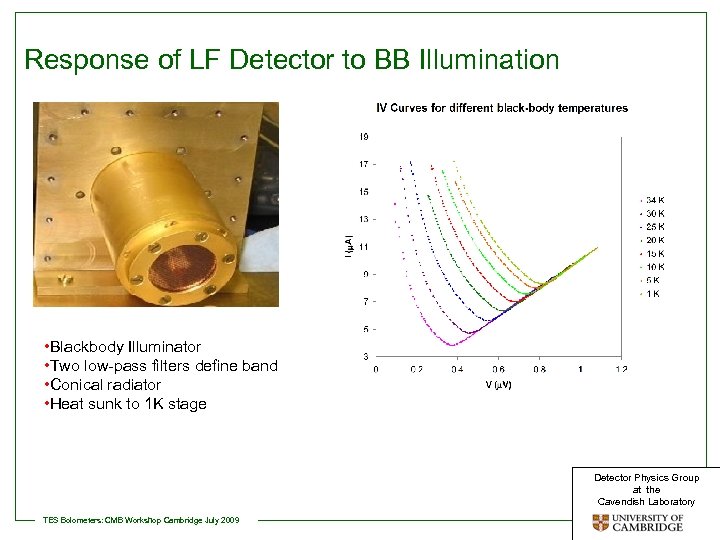 Response of LF Detector to BB Illumination • Blackbody Illuminator • Two low-pass filters define band • Conical radiator • Heat sunk to 1 K stage Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Response of LF Detector to BB Illumination • Blackbody Illuminator • Two low-pass filters define band • Conical radiator • Heat sunk to 1 K stage Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
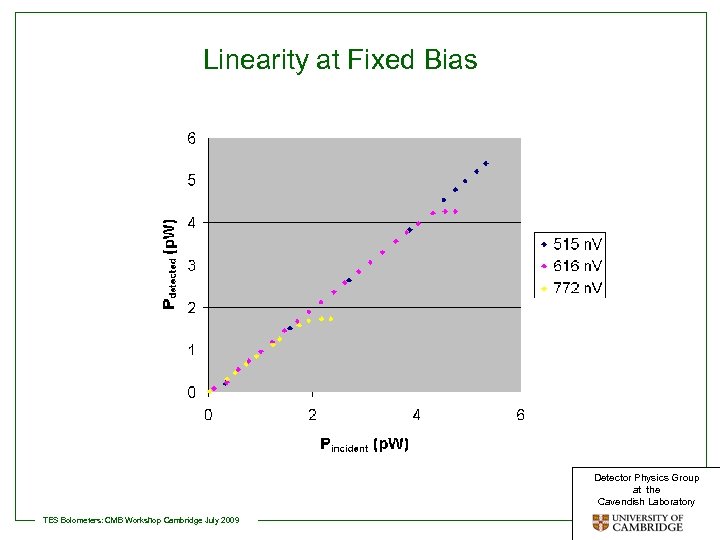 Linearity at Fixed Bias Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Linearity at Fixed Bias Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
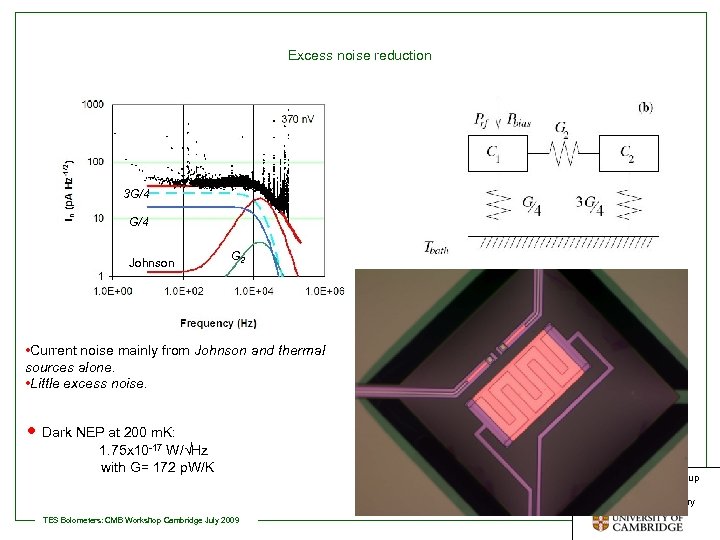 Excess noise reduction 3 G/4 Johnson G 2 • Current noise mainly from Johnson and thermal sources alone. • Little excess noise. • Dark NEP at 200 m. K: 1. 75 x 10 -17 W/√Hz with G= 172 p. W/K TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
Excess noise reduction 3 G/4 Johnson G 2 • Current noise mainly from Johnson and thermal sources alone. • Little excess noise. • Dark NEP at 200 m. K: 1. 75 x 10 -17 W/√Hz with G= 172 p. W/K TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
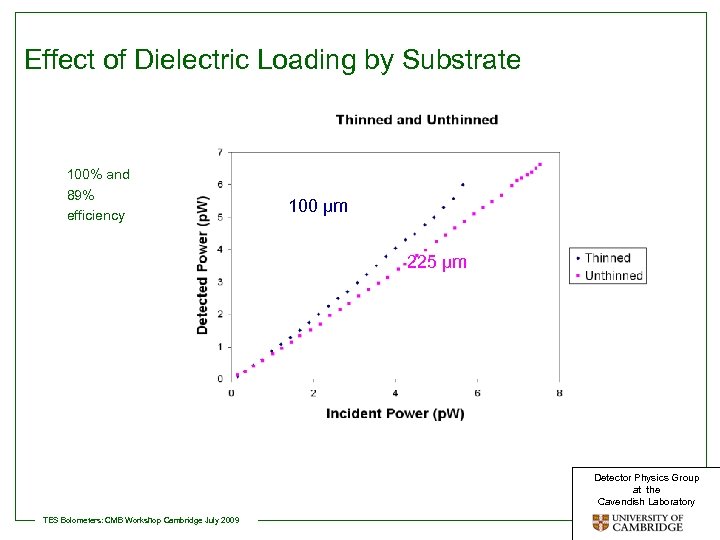 Effect of Dielectric Loading by Substrate 100% and 89% efficiency 100 μm 225 μm Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Effect of Dielectric Loading by Substrate 100% and 89% efficiency 100 μm 225 μm Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
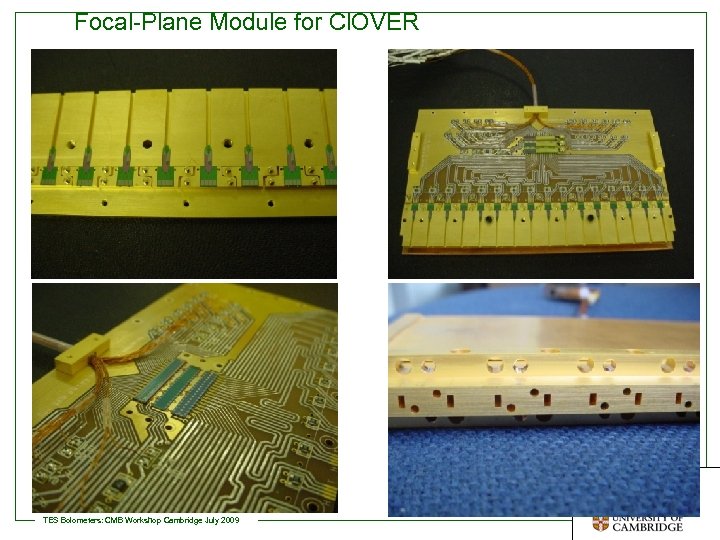 Focal-Plane Module for Cl. OVER Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Focal-Plane Module for Cl. OVER Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
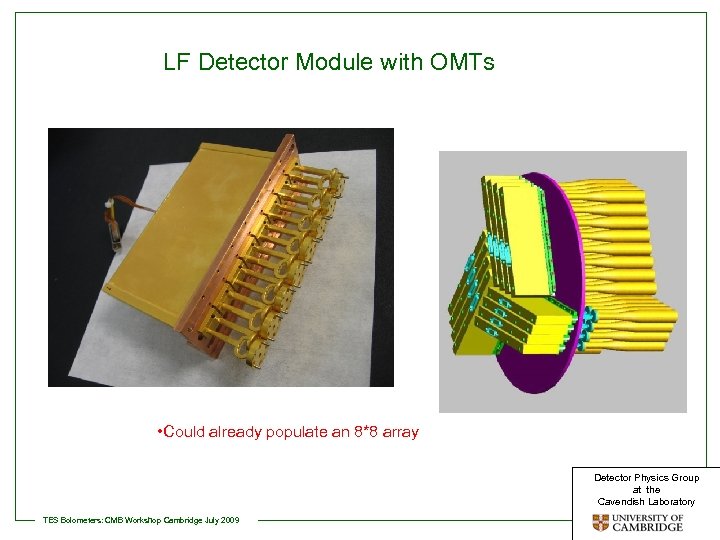 LF Detector Module with OMTs • Could already populate an 8*8 array Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
LF Detector Module with OMTs • Could already populate an 8*8 array Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
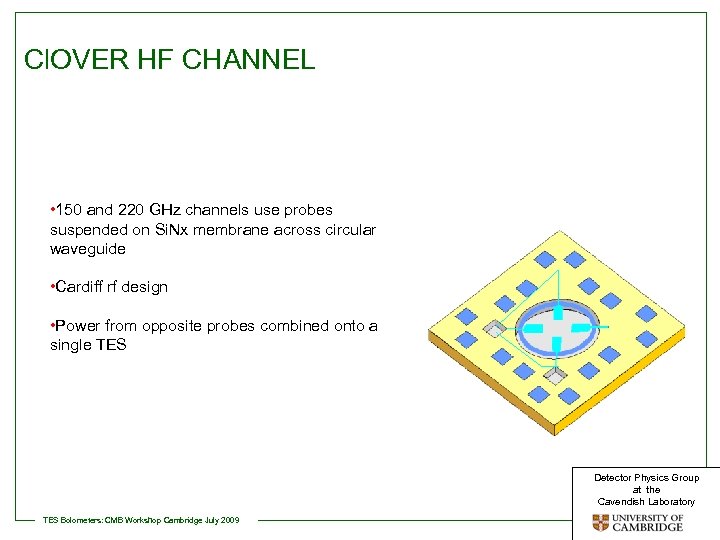 Cl. OVER HF CHANNEL • 150 and 220 GHz channels use probes suspended on Si. Nx membrane across circular waveguide • Cardiff rf design • Power from opposite probes combined onto a single TES Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Cl. OVER HF CHANNEL • 150 and 220 GHz channels use probes suspended on Si. Nx membrane across circular waveguide • Cardiff rf design • Power from opposite probes combined onto a single TES Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
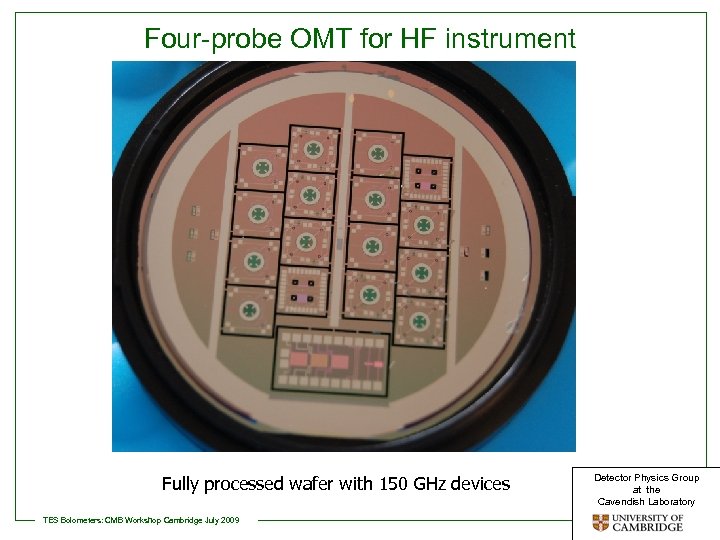 Four-probe OMT for HF instrument Fully processed wafer with 150 GHz devices TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
Four-probe OMT for HF instrument Fully processed wafer with 150 GHz devices TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
 Four-probe OMT for HF instrument Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Four-probe OMT for HF instrument Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
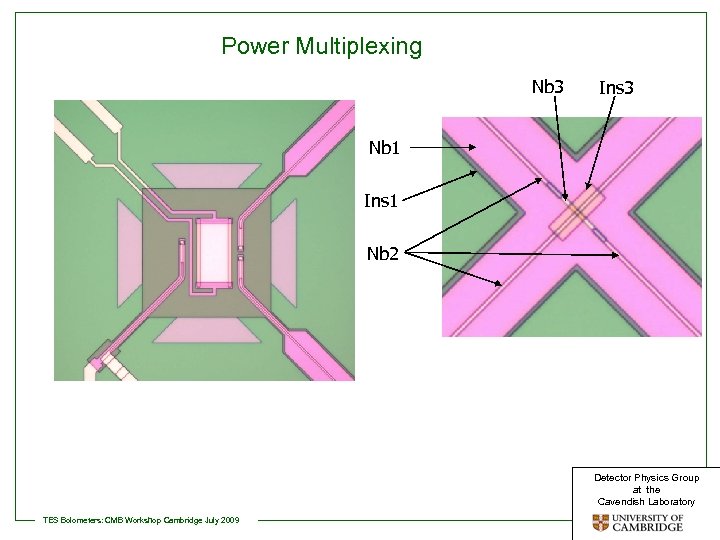 Power Multiplexing Nb 3 Ins 3 Nb 1 Ins 1 Nb 2 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Power Multiplexing Nb 3 Ins 3 Nb 1 Ins 1 Nb 2 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
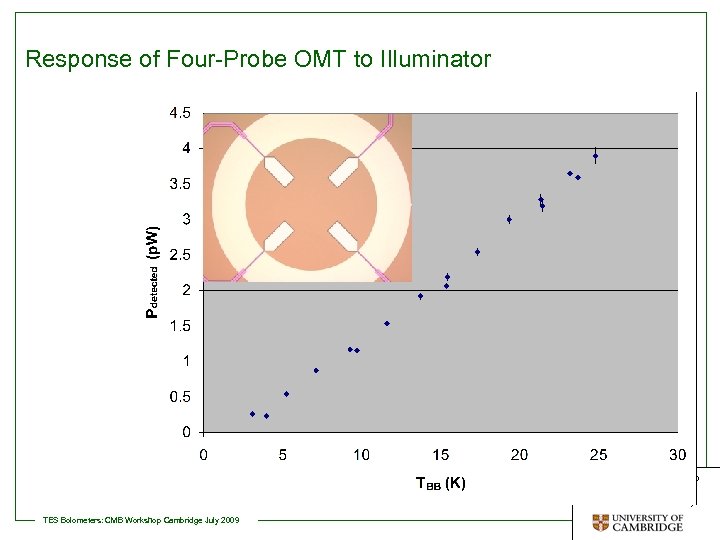 Response of Four-Probe OMT to Illuminator Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Response of Four-Probe OMT to Illuminator Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
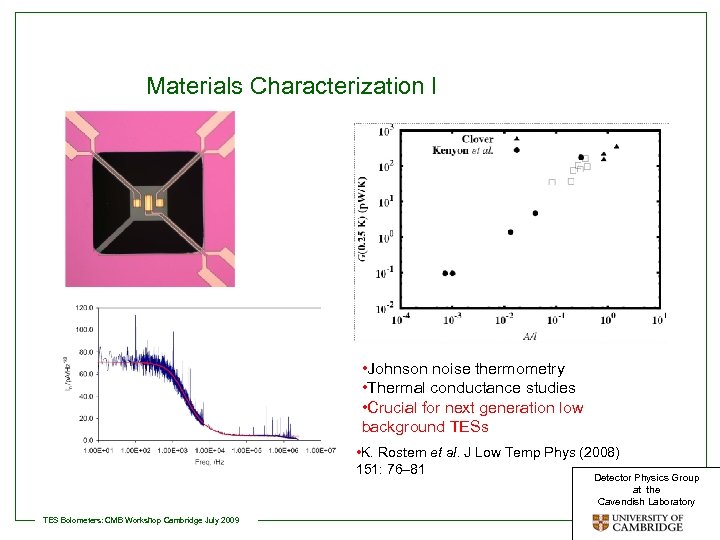 Materials Characterization I • Johnson noise thermometry • Thermal conductance studies • Crucial for next generation low background TESs • K. Rostem et al. J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 76– 81 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Materials Characterization I • Johnson noise thermometry • Thermal conductance studies • Crucial for next generation low background TESs • K. Rostem et al. J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 76– 81 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
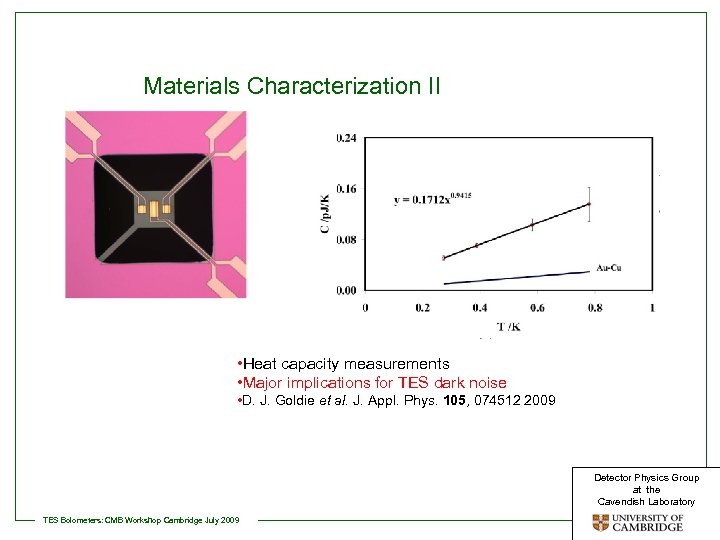 Materials Characterization II • Heat capacity measurements • Major implications for TES dark noise • D. J. Goldie et al. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 074512 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Materials Characterization II • Heat capacity measurements • Major implications for TES dark noise • D. J. Goldie et al. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 074512 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
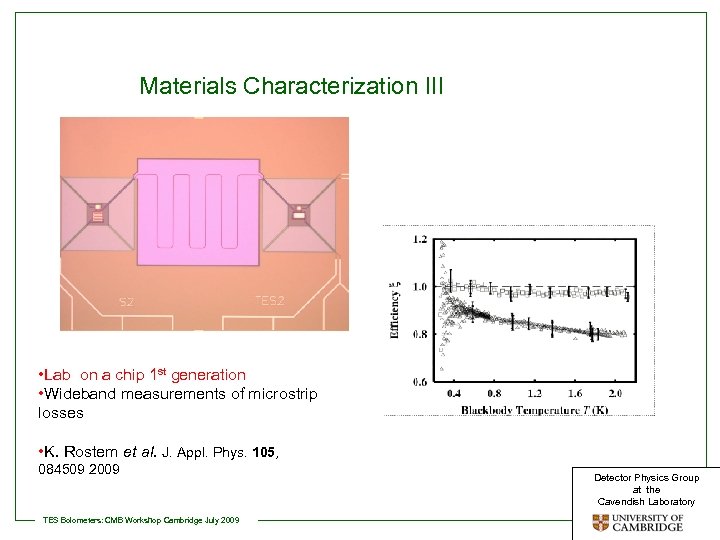 Materials Characterization III • Lab on a chip 1 st generation • Wideband measurements of microstrip losses • K. Rostem et al. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 084509 2009 TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
Materials Characterization III • Lab on a chip 1 st generation • Wideband measurements of microstrip losses • K. Rostem et al. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 084509 2009 TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009 Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory
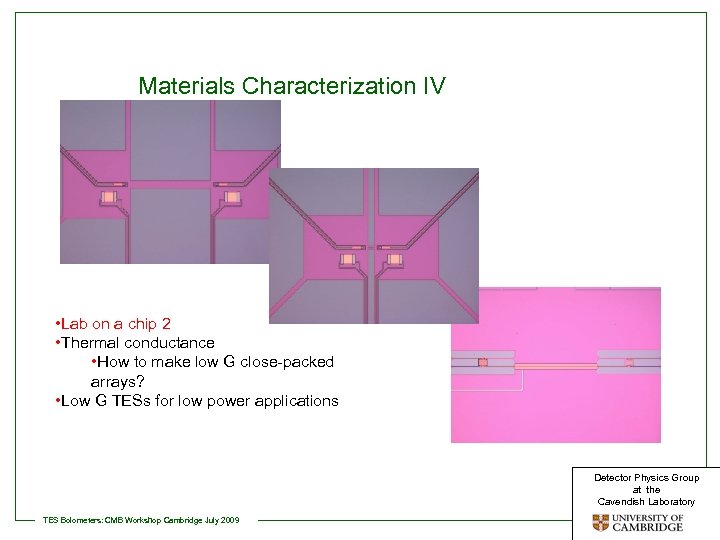 Materials Characterization IV • Lab on a chip 2 • Thermal conductance • How to make low G close-packed arrays? • Low G TESs for low power applications Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Materials Characterization IV • Lab on a chip 2 • Thermal conductance • How to make low G close-packed arrays? • Low G TESs for low power applications Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
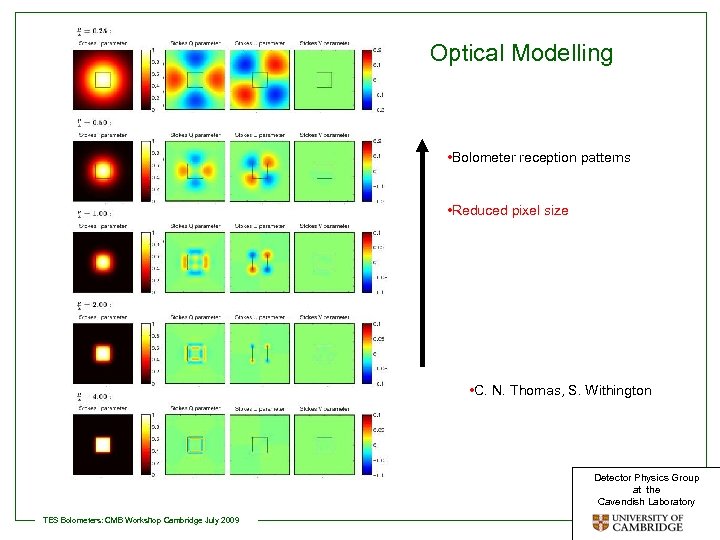 Optical Modelling • Bolometer reception patterns • Reduced pixel size • C. N. Thomas, S. Withington Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Optical Modelling • Bolometer reception patterns • Reduced pixel size • C. N. Thomas, S. Withington Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
 Summary Cl. OVER TESs • Highly developed process route for microstrip coupled TESs • High optical detection efficiency for both finline and probe-coupled designs • Satisfy Cl. OVER requirements for dark NEP, power handling and response time • Packaging-shielding complete • Integrated with time division MUX Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
Summary Cl. OVER TESs • Highly developed process route for microstrip coupled TESs • High optical detection efficiency for both finline and probe-coupled designs • Satisfy Cl. OVER requirements for dark NEP, power handling and response time • Packaging-shielding complete • Integrated with time division MUX Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
 The FUTURE • Recently kicked-off ESA TRP Cardiff/SRON/Maynooth/RAL • Next generation TESs for space missions • Far-IR TES detectors • Ultra-low noise CMB B-mode detectors • Cl. OVER a significant legacy a significant opportunity Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009
The FUTURE • Recently kicked-off ESA TRP Cardiff/SRON/Maynooth/RAL • Next generation TESs for space missions • Far-IR TES detectors • Ultra-low noise CMB B-mode detectors • Cl. OVER a significant legacy a significant opportunity Detector Physics Group at the Cavendish Laboratory TES Bolometers: CMB Workshop Cambridge July 2009


