e77b2628f9a60774cb5eba52b2cb4e00.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Detection anomalies for decohering wavepackets I. E. Mazets Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia mazets@astro. ioffe. rssi. ru Collaboration with: G. Kurizki (WIS, Israel) C. A. Chatzidimitriou-Dreismmann (TU Berlin, Germany)
Detection anomalies for decohering wavepackets I. E. Mazets Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia mazets@astro. ioffe. rssi. ru Collaboration with: G. Kurizki (WIS, Israel) C. A. Chatzidimitriou-Dreismmann (TU Berlin, Germany)
 Stationary QM scattering theory vs. timedependent measurements. How is the signal formed? Entanglement, correlations, decoherence… Scattering of a particle on a localized target: 1) coherent CW regime 2) incoherent regime • Possible cause of the anomaly in NCS • Effects of very fast decoherence • Interference of entangled wavepackets •
Stationary QM scattering theory vs. timedependent measurements. How is the signal formed? Entanglement, correlations, decoherence… Scattering of a particle on a localized target: 1) coherent CW regime 2) incoherent regime • Possible cause of the anomaly in NCS • Effects of very fast decoherence • Interference of entangled wavepackets •
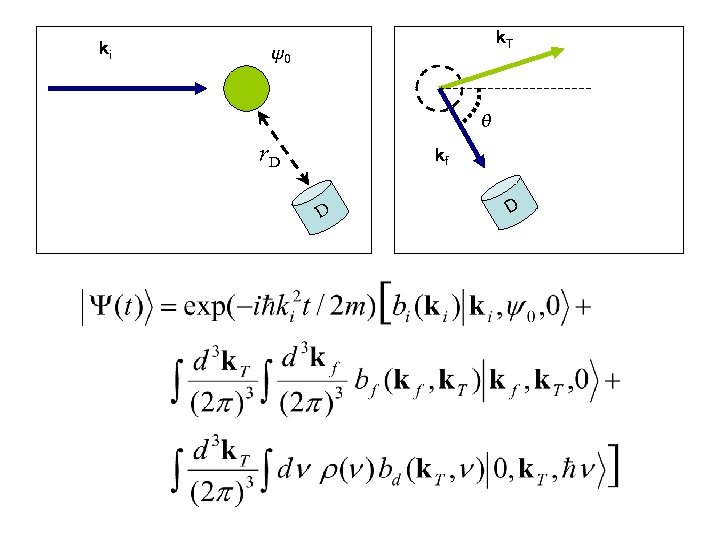 ki k. T ψ0 θ r. D kf D D
ki k. T ψ0 θ r. D kf D D
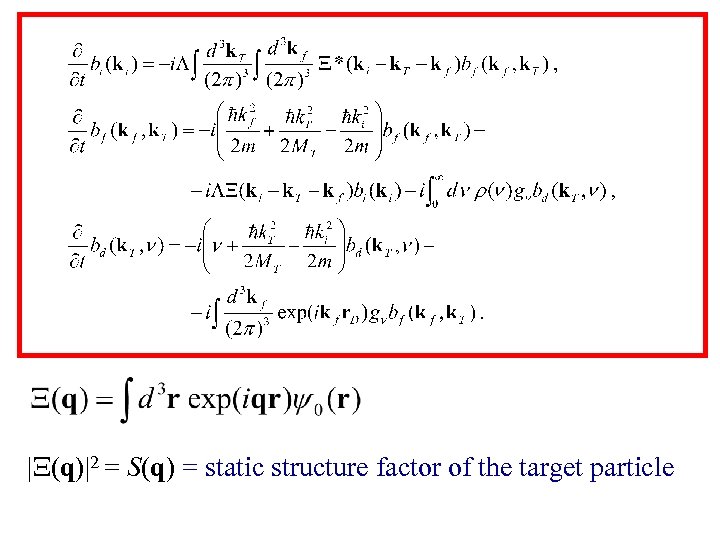 |Ξ(q)|2 = S(q) = static structure factor of the target particle
|Ξ(q)|2 = S(q) = static structure factor of the target particle
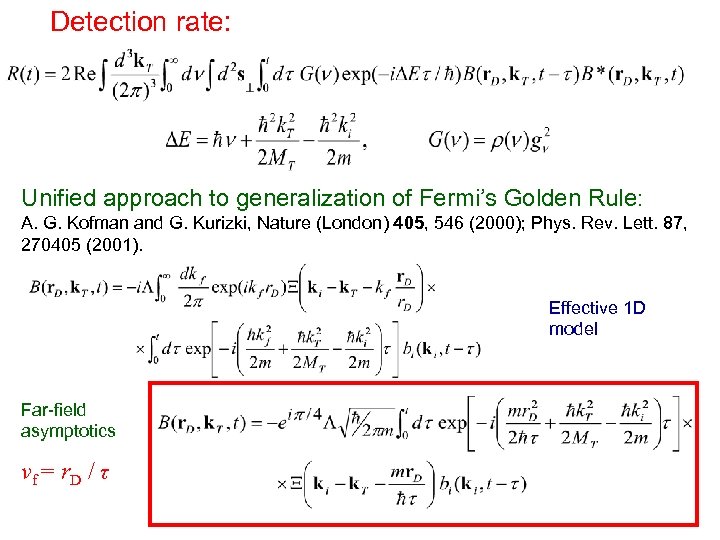 Detection rate: Unified approach to generalization of Fermi’s Golden Rule: A. G. Kofman and G. Kurizki, Nature (London) 405, 546 (2000); Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 270405 (2001). Effective 1 D model Far-field asymptotics v f = r. D / τ
Detection rate: Unified approach to generalization of Fermi’s Golden Rule: A. G. Kofman and G. Kurizki, Nature (London) 405, 546 (2000); Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 270405 (2001). Effective 1 D model Far-field asymptotics v f = r. D / τ
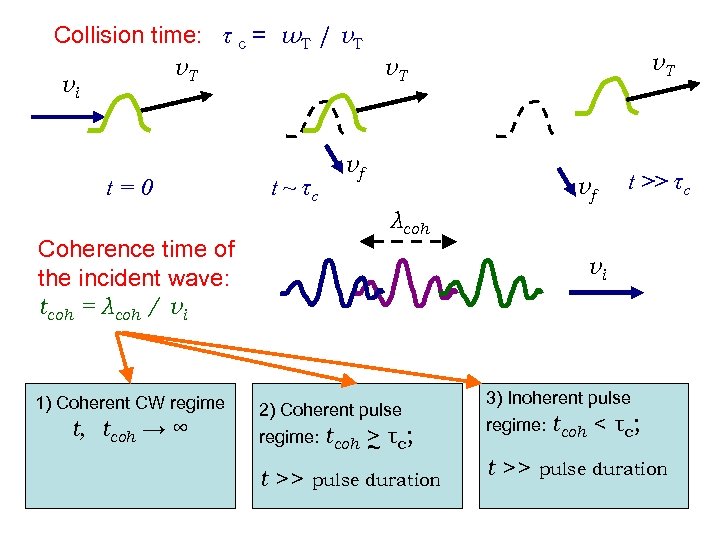 Collision time: τ c = w. T / v. T vi t=0 t ~ τc vf vf t, tcoh → ∞ t >> τc λcoh Coherence time of the incident wave: tcoh = λcoh / vi 1) Coherent CW regime v. T vi 2) Coherent pulse regime: tcoh > τc; ~ t >> pulse duration 3) Inoherent pulse regime: tcoh < τc; t >> pulse duration
Collision time: τ c = w. T / v. T vi t=0 t ~ τc vf vf t, tcoh → ∞ t >> τc λcoh Coherence time of the incident wave: tcoh = λcoh / vi 1) Coherent CW regime v. T vi 2) Coherent pulse regime: tcoh > τc; ~ t >> pulse duration 3) Inoherent pulse regime: tcoh < τc; t >> pulse duration
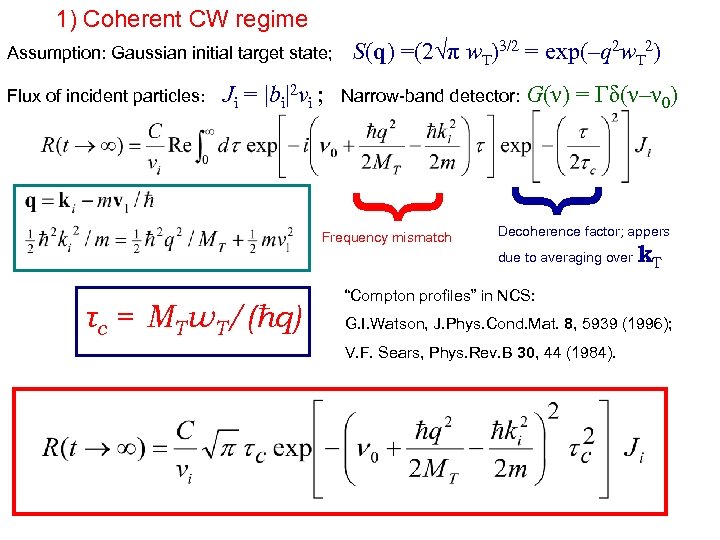 1) Coherent CW regime Ji = |bi|2 vi ; Narrow-band detector: G(ν) { Flux of incident particles: S(q) =(2√π w. T)3/2 = exp(–q 2 w. T 2) Frequency mismatch = Γδ(ν–ν 0) { Assumption: Gaussian initial target state; Decoherence factor; appers due to averaging over τc = MTw. T/(ħq) k. T “Compton profiles” in NCS: G. I. Watson, J. Phys. Cond. Mat. 8, 5939 (1996); V. F. Sears, Phys. Rev. B 30, 44 (1984).
1) Coherent CW regime Ji = |bi|2 vi ; Narrow-band detector: G(ν) { Flux of incident particles: S(q) =(2√π w. T)3/2 = exp(–q 2 w. T 2) Frequency mismatch = Γδ(ν–ν 0) { Assumption: Gaussian initial target state; Decoherence factor; appers due to averaging over τc = MTw. T/(ħq) k. T “Compton profiles” in NCS: G. I. Watson, J. Phys. Cond. Mat. 8, 5939 (1996); V. F. Sears, Phys. Rev. B 30, 44 (1984).
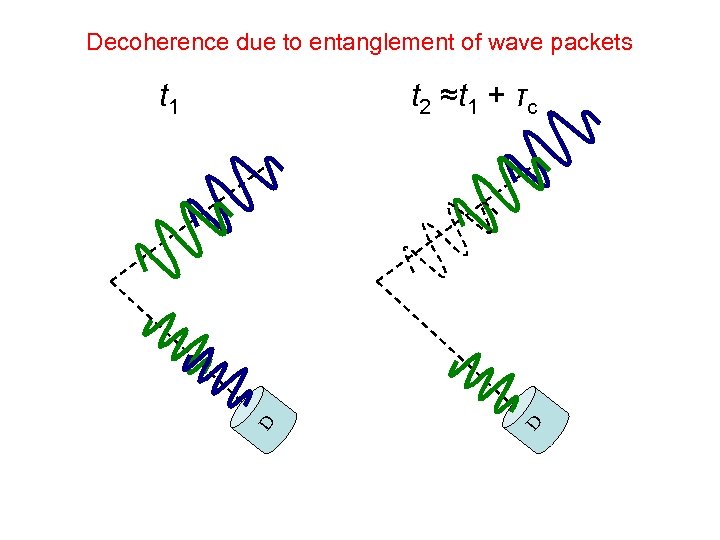 Decoherence due to entanglement of wave packets D t 2 ≈t 1 + τc D t 1
Decoherence due to entanglement of wave packets D t 2 ≈t 1 + τc D t 1
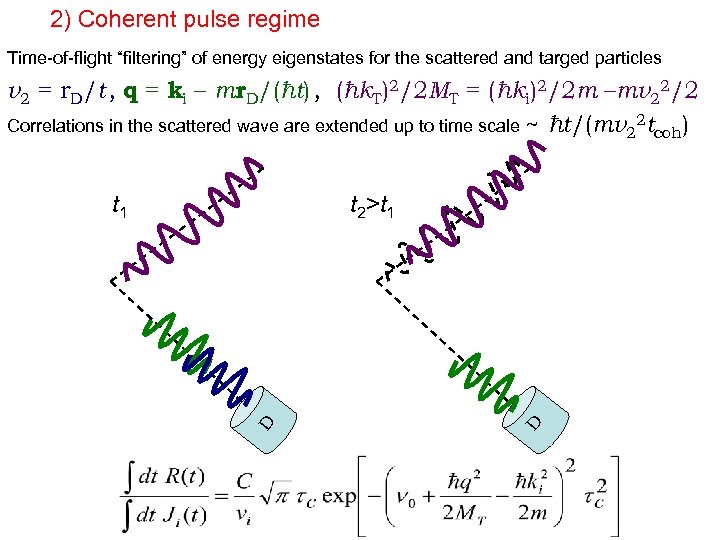 2) Coherent pulse regime Time-of-flight “filtering” of energy eigenstates for the scattered and targed particles v 2 = r. D/t , q = ki – mr. D/(ħt) , (ħk. T)2/2 MT = (ħki)2/2 m –mv 22/2 Correlations in the scattered wave are extended up to time scale ~ ħt/(mv 22 tcoh) D t 2>t 1 D t 1
2) Coherent pulse regime Time-of-flight “filtering” of energy eigenstates for the scattered and targed particles v 2 = r. D/t , q = ki – mr. D/(ħt) , (ħk. T)2/2 MT = (ħki)2/2 m –mv 22/2 Correlations in the scattered wave are extended up to time scale ~ ħt/(mv 22 tcoh) D t 2>t 1 D t 1
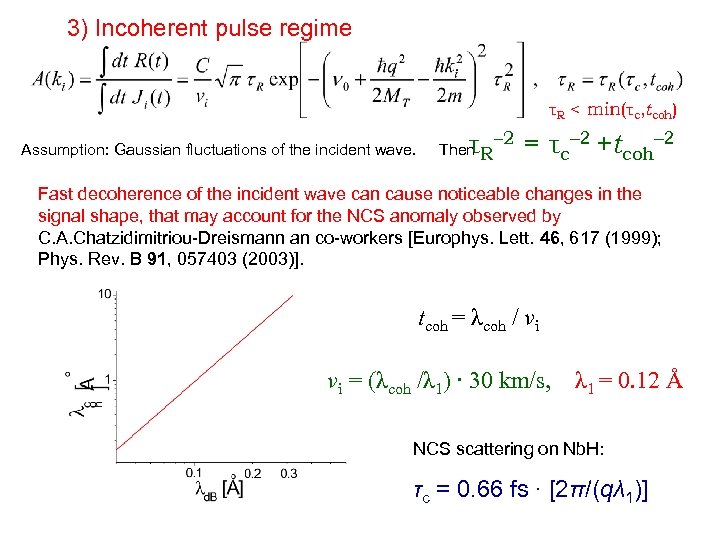 3) Incoherent pulse regime τR < min(τc, tcoh) Assumption: Gaussian fluctuations of the incident wave. τ Then R – 2 = τc– 2 +tcoh– 2 Fast decoherence of the incident wave can cause noticeable changes in the signal shape, that may account for the NCS anomaly observed by C. A. Chatzidimitriou-Dreismann an co-workers [Europhys. Lett. 46, 617 (1999); Phys. Rev. B 91, 057403 (2003)]. tcoh = λcoh / vi vi = (λcoh /λ 1) ∙ 30 km/s, λ 1 = 0. 12 Å NCS scattering on Nb. H: τc = 0. 66 fs ∙ [2π/(qλ 1)]
3) Incoherent pulse regime τR < min(τc, tcoh) Assumption: Gaussian fluctuations of the incident wave. τ Then R – 2 = τc– 2 +tcoh– 2 Fast decoherence of the incident wave can cause noticeable changes in the signal shape, that may account for the NCS anomaly observed by C. A. Chatzidimitriou-Dreismann an co-workers [Europhys. Lett. 46, 617 (1999); Phys. Rev. B 91, 057403 (2003)]. tcoh = λcoh / vi vi = (λcoh /λ 1) ∙ 30 km/s, λ 1 = 0. 12 Å NCS scattering on Nb. H: τc = 0. 66 fs ∙ [2π/(qλ 1)]
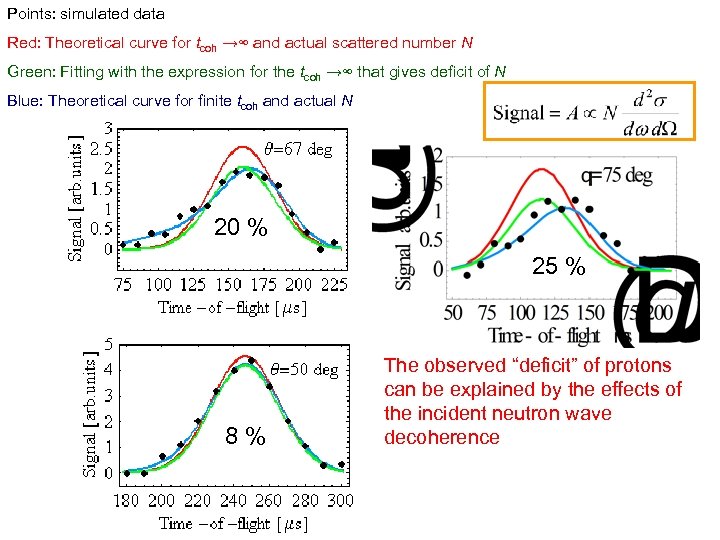 Points: simulated data Red: Theoretical curve for tcoh →∞ and actual scattered number N Green: Fitting with the expression for the tcoh →∞ that gives deficit of N Blue: Theoretical curve for finite tcoh and actual N 20 % 25 % 8% The observed “deficit” of protons can be explained by the effects of the incident neutron wave decoherence
Points: simulated data Red: Theoretical curve for tcoh →∞ and actual scattered number N Green: Fitting with the expression for the tcoh →∞ that gives deficit of N Blue: Theoretical curve for finite tcoh and actual N 20 % 25 % 8% The observed “deficit” of protons can be explained by the effects of the incident neutron wave decoherence
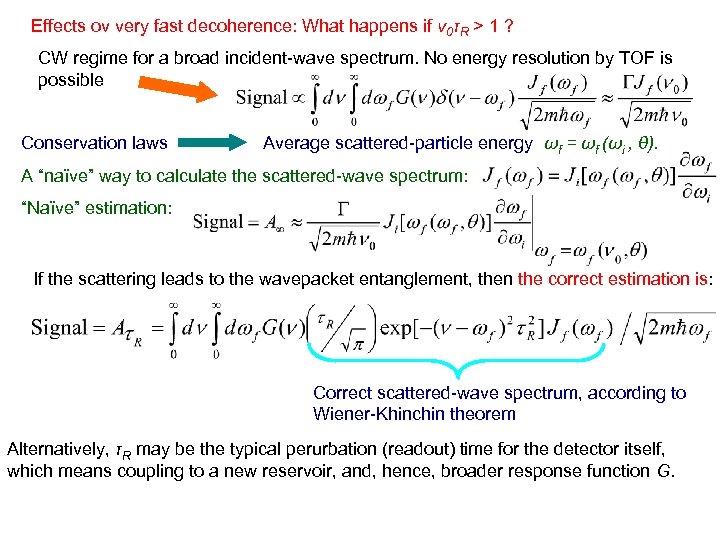 Effects ov very fast decoherence: What happens if ν 0τR > 1 ? CW regime for a broad incident-wave spectrum. No energy resolution by TOF is possible Conservation laws Average scattered-particle energy ωf = ωf (ωi , θ). A “naïve” way to calculate the scattered-wave spectrum: “Naïve” estimation: If the scattering leads to the wavepacket entanglement, then the correct estimation is: Correct scattered-wave spectrum, according to Wiener-Khinchin theorem Alternatively, τR may be the typical perurbation (readout) time for the detector itself, which means coupling to a new reservoir, and, hence, broader response function G.
Effects ov very fast decoherence: What happens if ν 0τR > 1 ? CW regime for a broad incident-wave spectrum. No energy resolution by TOF is possible Conservation laws Average scattered-particle energy ωf = ωf (ωi , θ). A “naïve” way to calculate the scattered-wave spectrum: “Naïve” estimation: If the scattering leads to the wavepacket entanglement, then the correct estimation is: Correct scattered-wave spectrum, according to Wiener-Khinchin theorem Alternatively, τR may be the typical perurbation (readout) time for the detector itself, which means coupling to a new reservoir, and, hence, broader response function G.
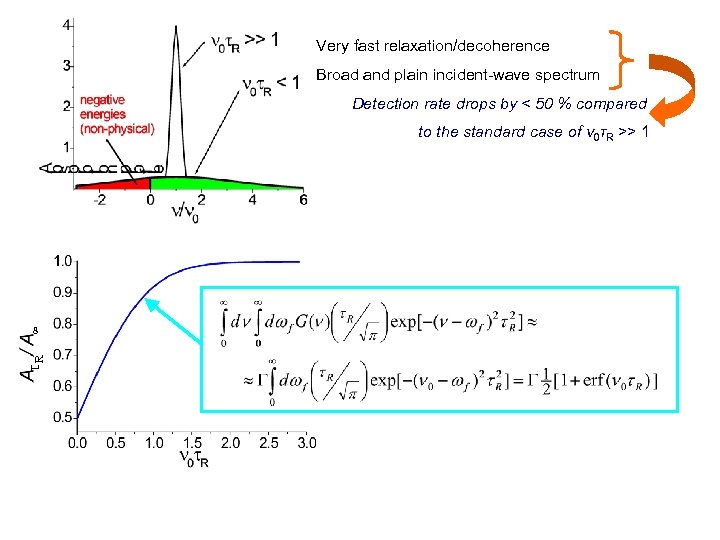 Very fast relaxation/decoherence Broad and plain incident-wave spectrum Detection rate drops by < 50 % compared to the standard case of ν 0τR >> 1 τR 8
Very fast relaxation/decoherence Broad and plain incident-wave spectrum Detection rate drops by < 50 % compared to the standard case of ν 0τR >> 1 τR 8
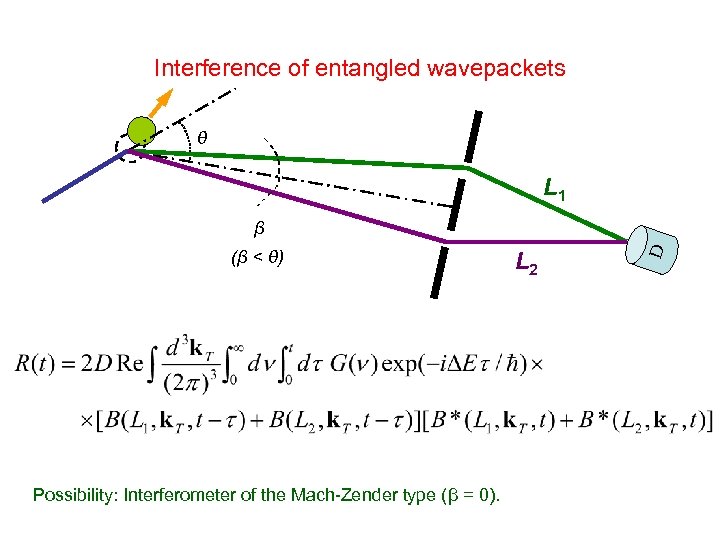 Interference of entangled wavepackets θ L 1 (β < θ) Possibility: Interferometer of the Mach-Zender type (β = 0). L 2 D β
Interference of entangled wavepackets θ L 1 (β < θ) Possibility: Interferometer of the Mach-Zender type (β = 0). L 2 D β
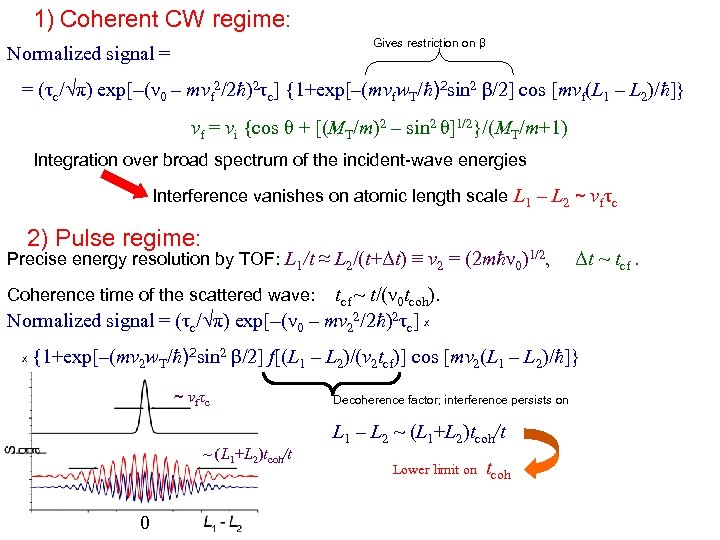 1) Coherent CW regime: Gives restriction on β Normalized signal = = (τc/√π) exp[–(ν 0 – mvf 2/2ħ)2τc] {1+exp[–(mvfw. T/ħ)2 sin 2 β/2] cos [mvf(L 1 – L 2)/ħ]} vf = vi {cos θ + [(MT/m)2 – sin 2 θ]1/2}/(MT/m+1) Integration over broad spectrum of the incident-wave energies Interference vanishes on atomic length scale L 1 – L 2 ~ vfτc 2) Pulse regime: Precise energy resolution by TOF: L 1/t ≈ L 2/(t+Δt) ≡ v 2 = (2 mħν 0)1/2, Δt ~ tcf ~ t/(ν 0 tcoh). Normalized signal = (τc/√π) exp[–(ν 0 – mv 22/2ħ)2τc] x Coherence time of the scattered wave: x {1+exp[–(mv 2 w. T/ħ)2 sin 2 β/2] f[(L 1 – L 2)/(v 2 tcf)] cos [mv 2(L 1 – L 2)/ħ]} ~ vfτc ~ (L 1+L 2)tcoh/t 0 Decoherence factor; interference persists on L 1 – L 2 ~ (L 1+L 2)tcoh/t Lower limit on tcoh
1) Coherent CW regime: Gives restriction on β Normalized signal = = (τc/√π) exp[–(ν 0 – mvf 2/2ħ)2τc] {1+exp[–(mvfw. T/ħ)2 sin 2 β/2] cos [mvf(L 1 – L 2)/ħ]} vf = vi {cos θ + [(MT/m)2 – sin 2 θ]1/2}/(MT/m+1) Integration over broad spectrum of the incident-wave energies Interference vanishes on atomic length scale L 1 – L 2 ~ vfτc 2) Pulse regime: Precise energy resolution by TOF: L 1/t ≈ L 2/(t+Δt) ≡ v 2 = (2 mħν 0)1/2, Δt ~ tcf ~ t/(ν 0 tcoh). Normalized signal = (τc/√π) exp[–(ν 0 – mv 22/2ħ)2τc] x Coherence time of the scattered wave: x {1+exp[–(mv 2 w. T/ħ)2 sin 2 β/2] f[(L 1 – L 2)/(v 2 tcf)] cos [mv 2(L 1 – L 2)/ħ]} ~ vfτc ~ (L 1+L 2)tcoh/t 0 Decoherence factor; interference persists on L 1 – L 2 ~ (L 1+L 2)tcoh/t Lower limit on tcoh
 Conclusions ● Entanglement between the target and scattered-particle wavepackets determines the detection dynamics in CW regime. ● In the pulse (TOF-measurement) regime – entanglement between nearly-plane-wave states. ● Different interference properties of entangled matter waves in the CW and pulse regimes. ● Rapid decoherence of the incident matter wave may account for the observed anomaly in NCS.
Conclusions ● Entanglement between the target and scattered-particle wavepackets determines the detection dynamics in CW regime. ● In the pulse (TOF-measurement) regime – entanglement between nearly-plane-wave states. ● Different interference properties of entangled matter waves in the CW and pulse regimes. ● Rapid decoherence of the incident matter wave may account for the observed anomaly in NCS.


