0f784f5171807393daea59a5456e02f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Destination: Differentiation (D 2) Megan Gates - English as a Second Language Susan Wouters - Extended Learning Program
Destination: Differentiation (D 2) Megan Gates - English as a Second Language Susan Wouters - Extended Learning Program
 Journey The bend in the road is not the end of the road, unless you refuse to take the turn.
Journey The bend in the road is not the end of the road, unless you refuse to take the turn.
 Consider the 3 questions guiding professional development What are students learning? Content How do you know they are learning? Formative Assessment What are we doing for those who struggle, those who excel, and those in the middle? Differentiation
Consider the 3 questions guiding professional development What are students learning? Content How do you know they are learning? Formative Assessment What are we doing for those who struggle, those who excel, and those in the middle? Differentiation
 Ways Individuals Differ Prior knowledge or Skill Expertise Learning Rate Cognitive Ability Learning Style Preference Motivation, Attitude, and Effort Interest, Strength, or Talent The National Research Center on the Gifted and Talented, 2002
Ways Individuals Differ Prior knowledge or Skill Expertise Learning Rate Cognitive Ability Learning Style Preference Motivation, Attitude, and Effort Interest, Strength, or Talent The National Research Center on the Gifted and Talented, 2002
 “There is nothing more unequal than the equal treatment of unequal people. ” Thomas Jefferson
“There is nothing more unequal than the equal treatment of unequal people. ” Thomas Jefferson
 What is differentiation?
What is differentiation?
 Differentiation is … “…shaking up what goes on in the classroom so it’s a better fit for everyone. It is not a pedagogical ‘bag of tricks. ’ It is a way of thinking about teaching and learning. ” Carol Tomlinson
Differentiation is … “…shaking up what goes on in the classroom so it’s a better fit for everyone. It is not a pedagogical ‘bag of tricks. ’ It is a way of thinking about teaching and learning. ” Carol Tomlinson
 Differentiation is … Differentiated instruction specifically responds to students’ progress on the learning continuum - what they already know and what they need to learn. Diane Heacox
Differentiation is … Differentiated instruction specifically responds to students’ progress on the learning continuum - what they already know and what they need to learn. Diane Heacox
 Differentiation means starting where the kids are! - Carol Ann Tomlinson
Differentiation means starting where the kids are! - Carol Ann Tomlinson
 What is Differentiated Instruction? Differentiated instruction is: Proactive Qualitative Rooted in assessment Multiple approaches to content, process, and product Student centered Blend of whole class, group, and individual instruction “Organic” - instruction is dynamic
What is Differentiated Instruction? Differentiated instruction is: Proactive Qualitative Rooted in assessment Multiple approaches to content, process, and product Student centered Blend of whole class, group, and individual instruction “Organic” - instruction is dynamic
 What Differentiated Instruction is NOT Differentiated instruction is not: individualized instruction chaotic another way of homogeneous grouping “tailoring the same suit of clothes” every subject, every student, every day!
What Differentiated Instruction is NOT Differentiated instruction is not: individualized instruction chaotic another way of homogeneous grouping “tailoring the same suit of clothes” every subject, every student, every day!
 Learning: Forward progress from the point of entry.
Learning: Forward progress from the point of entry.
 What keeps us going as learners? Success Effort Success
What keeps us going as learners? Success Effort Success
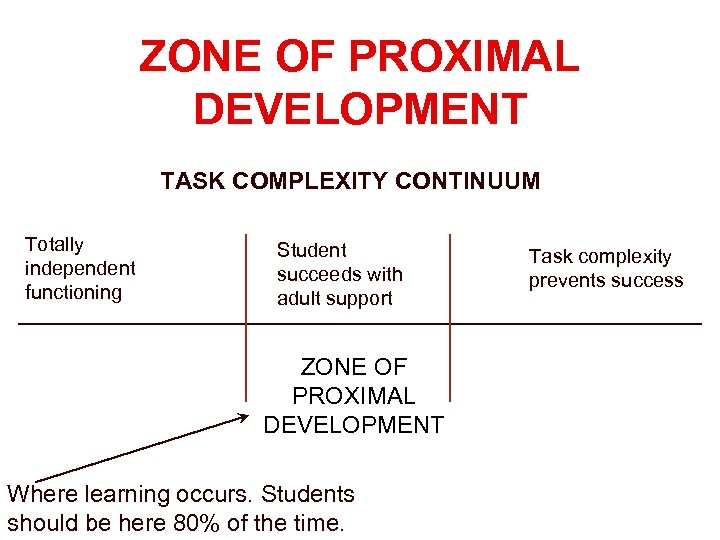 ZONE OF PROXIMAL DEVELOPMENT TASK COMPLEXITY CONTINUUM Totally independent functioning Student succeeds with adult support ZONE OF PROXIMAL DEVELOPMENT Where learning occurs. Students should be here 80% of the time. Task complexity prevents success
ZONE OF PROXIMAL DEVELOPMENT TASK COMPLEXITY CONTINUUM Totally independent functioning Student succeeds with adult support ZONE OF PROXIMAL DEVELOPMENT Where learning occurs. Students should be here 80% of the time. Task complexity prevents success
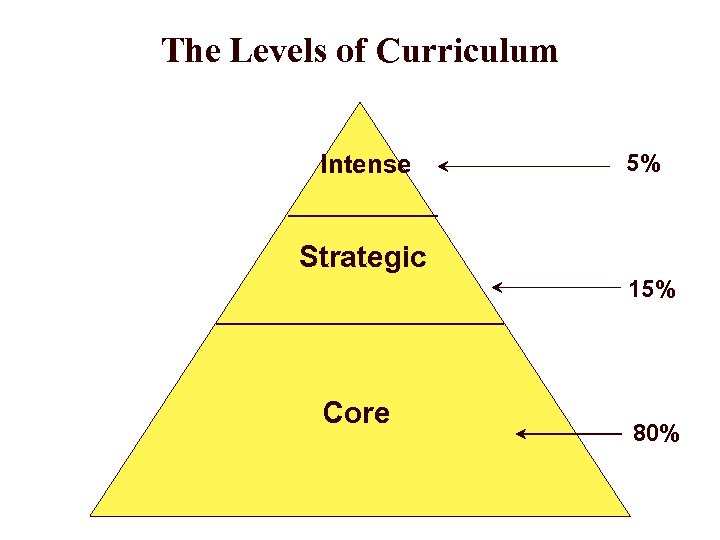 The Levels of Curriculum Intense 5% Strategic 15% Core 80%
The Levels of Curriculum Intense 5% Strategic 15% Core 80%
 “Not every child has an equal talent or an equal ability or equal motivation; but children have the equal right to develop their talent, their ability, and their motivation. ” John F. Kennedy
“Not every child has an equal talent or an equal ability or equal motivation; but children have the equal right to develop their talent, their ability, and their motivation. ” John F. Kennedy
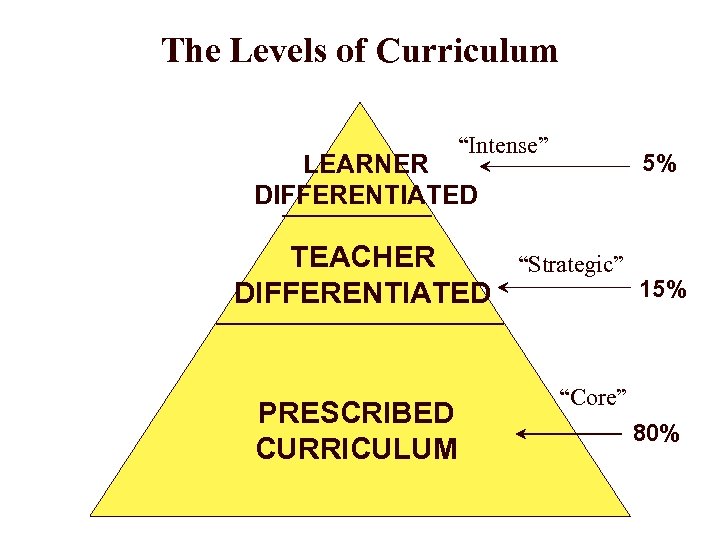 The Levels of Curriculum “Intense” 5% LEARNER DIFFERENTIATED TEACHER DIFFERENTIATED PRESCRIBED CURRICULUM “Strategic” 15% “Core” 80%
The Levels of Curriculum “Intense” 5% LEARNER DIFFERENTIATED TEACHER DIFFERENTIATED PRESCRIBED CURRICULUM “Strategic” 15% “Core” 80%
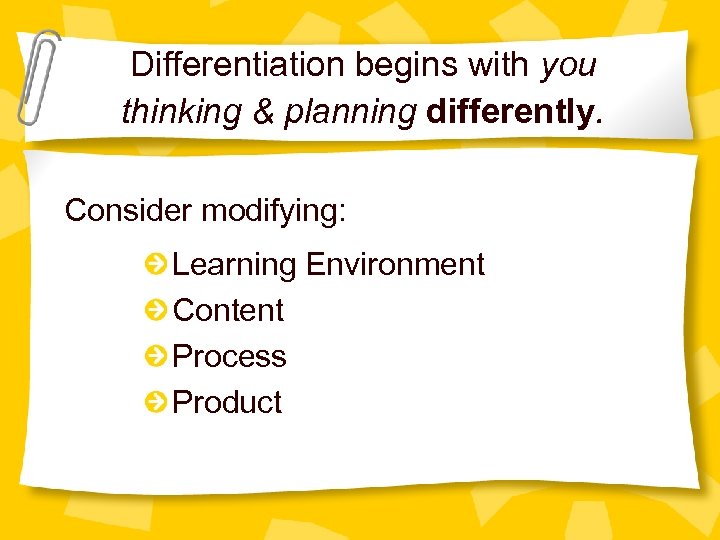 Differentiation begins with you thinking & planning differently. Consider modifying: Learning Environment Content Process Product
Differentiation begins with you thinking & planning differently. Consider modifying: Learning Environment Content Process Product
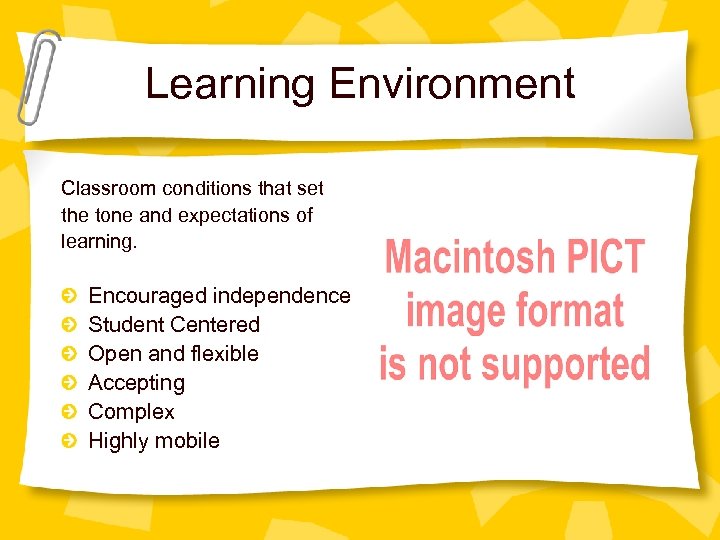 Learning Environment Classroom conditions that set the tone and expectations of learning. Encouraged independence Student Centered Open and flexible Accepting Complex Highly mobile
Learning Environment Classroom conditions that set the tone and expectations of learning. Encouraged independence Student Centered Open and flexible Accepting Complex Highly mobile
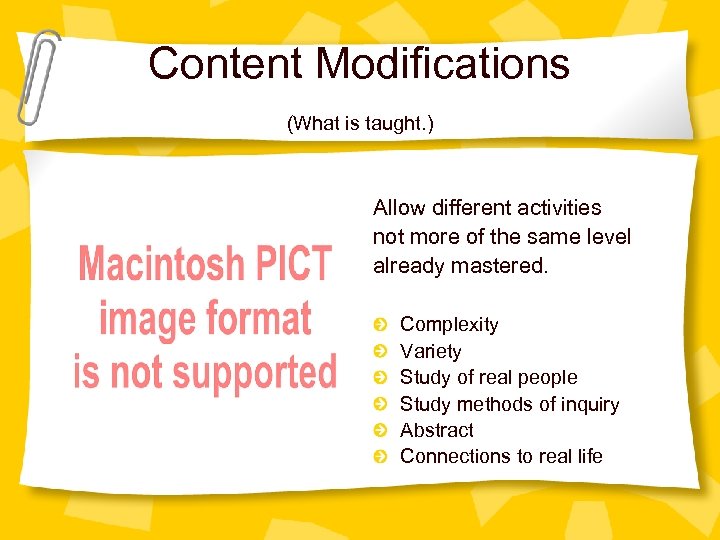 Content Modifications (What is taught. ) Allow different activities not more of the same level already mastered. Complexity Variety Study of real people Study methods of inquiry Abstract Connections to real life
Content Modifications (What is taught. ) Allow different activities not more of the same level already mastered. Complexity Variety Study of real people Study methods of inquiry Abstract Connections to real life
 Process Modifications (Instruction) The activities through which students make sense of key ideas using essential skills. Creative thinking Higher level thinking Discovery Open-ended Group interaction Variable Pacing Variety of learning processes Debriefing Freedom of choice Teamwork
Process Modifications (Instruction) The activities through which students make sense of key ideas using essential skills. Creative thinking Higher level thinking Discovery Open-ended Group interaction Variable Pacing Variety of learning processes Debriefing Freedom of choice Teamwork
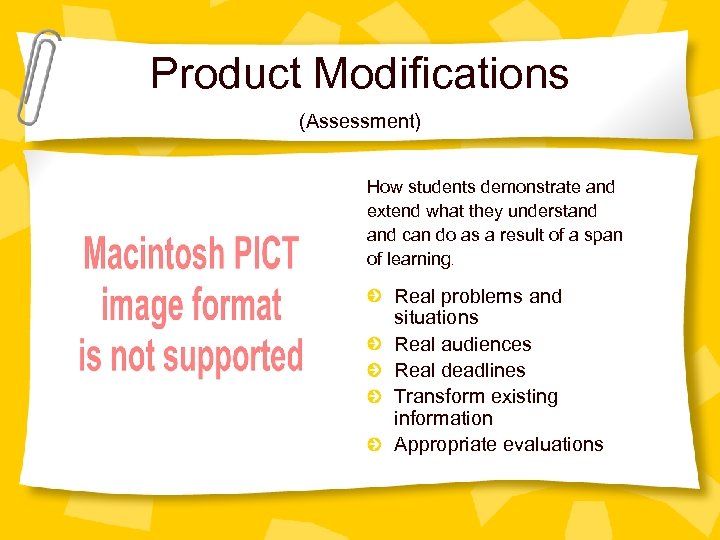 Product Modifications (Assessment) How students demonstrate and extend what they understand can do as a result of a span of learning. Real problems and situations Real audiences Real deadlines Transform existing information Appropriate evaluations
Product Modifications (Assessment) How students demonstrate and extend what they understand can do as a result of a span of learning. Real problems and situations Real audiences Real deadlines Transform existing information Appropriate evaluations
 When thinking differently about learners, consider … Readiness – Information, concepts, and skills students demonstrate at entry point of learning experience Interests – Topics, problems, and processes of personal relevance to students (passion learning) Learning Profile – Combination of students’ emotions, cultures, modality preferences, and intelligences that affect learning
When thinking differently about learners, consider … Readiness – Information, concepts, and skills students demonstrate at entry point of learning experience Interests – Topics, problems, and processes of personal relevance to students (passion learning) Learning Profile – Combination of students’ emotions, cultures, modality preferences, and intelligences that affect learning
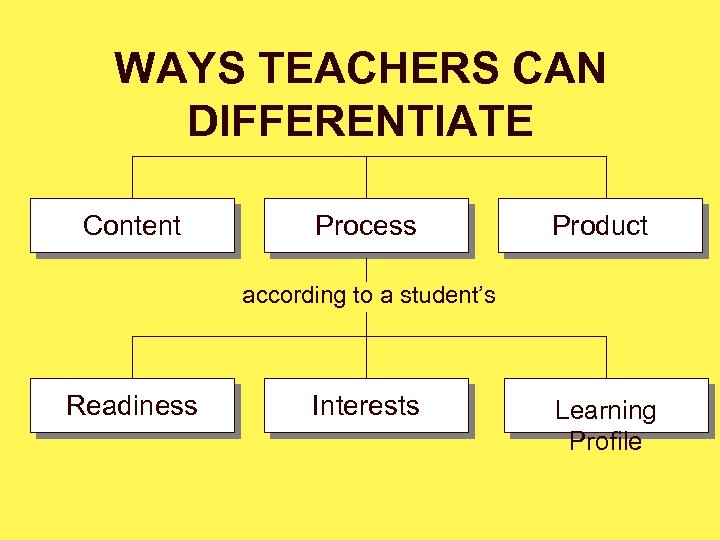 WAYS TEACHERS CAN DIFFERENTIATE Content Process Product according to a student’s Readiness Interests Learning Profile
WAYS TEACHERS CAN DIFFERENTIATE Content Process Product according to a student’s Readiness Interests Learning Profile
 A FRAMEWORK FOR THINKING ABOUT DIFFERENTIATION
A FRAMEWORK FOR THINKING ABOUT DIFFERENTIATION
 Differentiated Instruction is … Rigorous - Provide challenging instruction to motivate students to push themselves. The bar is set to balance effort and success. Relevant - Focus on essential learning. Not more of the same but challenging problems. Flexible and varied - Not “one size fits all” but designed to best meet the learners’ needs. Complex - Challenge students’ thinking and actively engage students in content that conveys depth and breadth.
Differentiated Instruction is … Rigorous - Provide challenging instruction to motivate students to push themselves. The bar is set to balance effort and success. Relevant - Focus on essential learning. Not more of the same but challenging problems. Flexible and varied - Not “one size fits all” but designed to best meet the learners’ needs. Complex - Challenge students’ thinking and actively engage students in content that conveys depth and breadth.
 Differentiation provides rigor, relevance, flexibility and complexity. Curriculum Compacting Tiered Activities / Assignments Learning Contracts Interest Centers or Interest Groups Group Investigations Independent Study Choice Boards Flexible Skill Grouping Adjusting Questions / High-Level Questions Mentorships
Differentiation provides rigor, relevance, flexibility and complexity. Curriculum Compacting Tiered Activities / Assignments Learning Contracts Interest Centers or Interest Groups Group Investigations Independent Study Choice Boards Flexible Skill Grouping Adjusting Questions / High-Level Questions Mentorships
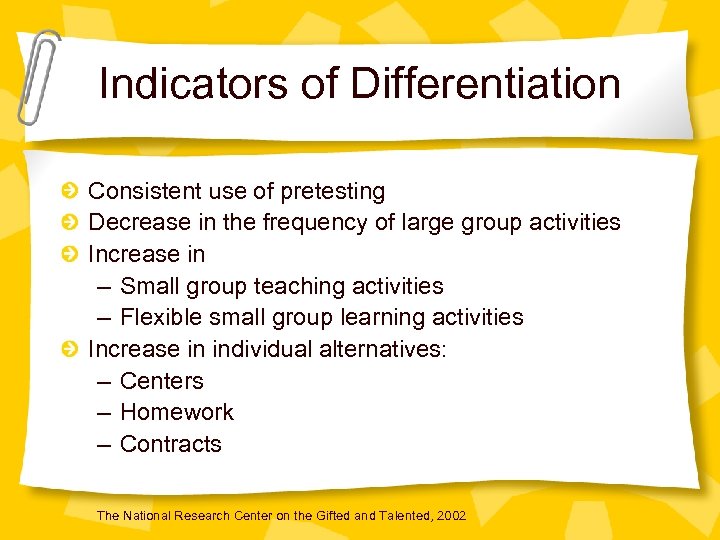 Indicators of Differentiation Consistent use of pretesting Decrease in the frequency of large group activities Increase in – Small group teaching activities – Flexible small group learning activities Increase in individual alternatives: – Centers – Homework – Contracts The National Research Center on the Gifted and Talented, 2002
Indicators of Differentiation Consistent use of pretesting Decrease in the frequency of large group activities Increase in – Small group teaching activities – Flexible small group learning activities Increase in individual alternatives: – Centers – Homework – Contracts The National Research Center on the Gifted and Talented, 2002
 Incorporating Differentiation Within the Curriculum Introduction Initial Teaching Determine Pretest Format Pre-testing Analyze results Planning Grouping Differentiated teaching and learning The National Research Center on the Gifted and Talented, 2002
Incorporating Differentiation Within the Curriculum Introduction Initial Teaching Determine Pretest Format Pre-testing Analyze results Planning Grouping Differentiated teaching and learning The National Research Center on the Gifted and Talented, 2002
 To Differentiate a Lesson Consider Adjusting These Curriculum: – Objective (vary the depth or breadth). – Introduction (use community resources, graphic organizers, or pretesting: demonstrate relevance; add intriguing twist). – Grouping ( involve individuals, pairs, small groups, choose homogeneous or heterogeneous groups). – Instruction (vary the teaching methods; use inductive, deductive, or hands-on strategies; alter the pace). – Learning Activities (choose from concrete to abstract, visual to tactile). – Resources (vary in depth, complexity, format, or nature). – Products (assign or create options, alternatives, or openended formats). The National Research Center on the Gifted and Talented, 2002
To Differentiate a Lesson Consider Adjusting These Curriculum: – Objective (vary the depth or breadth). – Introduction (use community resources, graphic organizers, or pretesting: demonstrate relevance; add intriguing twist). – Grouping ( involve individuals, pairs, small groups, choose homogeneous or heterogeneous groups). – Instruction (vary the teaching methods; use inductive, deductive, or hands-on strategies; alter the pace). – Learning Activities (choose from concrete to abstract, visual to tactile). – Resources (vary in depth, complexity, format, or nature). – Products (assign or create options, alternatives, or openended formats). The National Research Center on the Gifted and Talented, 2002
 Learning is like rowing upstream, not to advance is to drop back. ~ Chinese Proverb
Learning is like rowing upstream, not to advance is to drop back. ~ Chinese Proverb
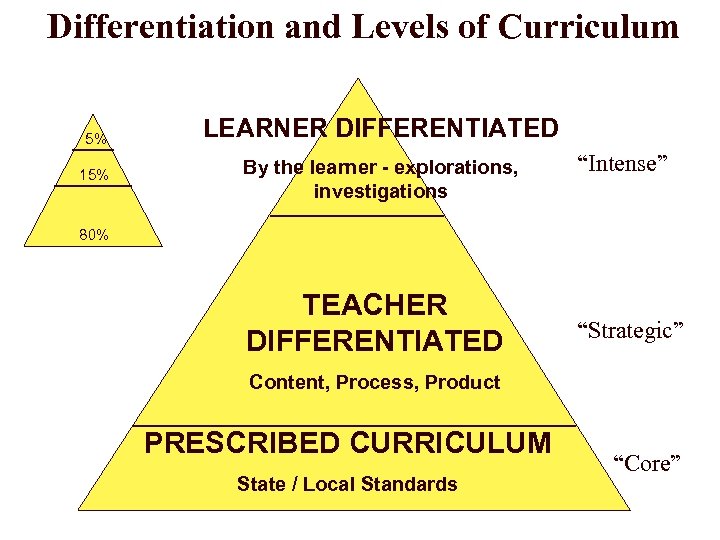 Differentiation and Levels of Curriculum 5% 15% LEARNER DIFFERENTIATED By the learner - explorations, investigations “Intense” 80% TEACHER DIFFERENTIATED “Strategic” Content, Process, Product PRESCRIBED CURRICULUM State / Local Standards “Core”
Differentiation and Levels of Curriculum 5% 15% LEARNER DIFFERENTIATED By the learner - explorations, investigations “Intense” 80% TEACHER DIFFERENTIATED “Strategic” Content, Process, Product PRESCRIBED CURRICULUM State / Local Standards “Core”
 How do I begin? There is no one “right way” to create an effectively differentiated classroom: teachers craft responsive learning places in ways that are a good match for their teaching styles as well as for learners’ needs. – Carol Ann Tomlinson
How do I begin? There is no one “right way” to create an effectively differentiated classroom: teachers craft responsive learning places in ways that are a good match for their teaching styles as well as for learners’ needs. – Carol Ann Tomlinson
 There are many ways to go forward but only one way of standing still. Franklin D. Roosevelt
There are many ways to go forward but only one way of standing still. Franklin D. Roosevelt
 Resources Burns, D. , Gubbins, E. J. , Reis, S. , Westberg, K. L. , Dinnocenti, S. T. & Tieso, C. L. (2002). Applying gifted education pedagogy in the general education classroom: Professional development module. National research center on the gifted and talented, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT. Eidson, C. , Iseminger, B. , & Taibbi, C (2007). Demystifying differentiation in middle school. Pieces of Learning. Heacox, D. (2007). Differentiating instruction in the regular classroom. Minneapolis, MN: Free Spirit. Kaufeldt, M. (2005). Teachers, change your bait! Brain compatible differentiated instruction. Bethel, PA: Crown House.
Resources Burns, D. , Gubbins, E. J. , Reis, S. , Westberg, K. L. , Dinnocenti, S. T. & Tieso, C. L. (2002). Applying gifted education pedagogy in the general education classroom: Professional development module. National research center on the gifted and talented, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT. Eidson, C. , Iseminger, B. , & Taibbi, C (2007). Demystifying differentiation in middle school. Pieces of Learning. Heacox, D. (2007). Differentiating instruction in the regular classroom. Minneapolis, MN: Free Spirit. Kaufeldt, M. (2005). Teachers, change your bait! Brain compatible differentiated instruction. Bethel, PA: Crown House.
 Resources, Cont’d. Kingore, B. (2007). Reaching all learners: Making differentiation work. Austin, TX: Professional Associates. Kingore, B. (2004). Differentiation: Simplified, realistic, and effective. How to challenge advanced potentials in mixed ability classrooms. Austin, TX: Professional Associates. Tomlinson, C. A. (2001). How to differentiate instruction in mixedability classrooms. Alexandria, VA: ASCD. Tomlinson, C. A. (1999). The differentiated classroom: Responding to the needs of all learners. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
Resources, Cont’d. Kingore, B. (2007). Reaching all learners: Making differentiation work. Austin, TX: Professional Associates. Kingore, B. (2004). Differentiation: Simplified, realistic, and effective. How to challenge advanced potentials in mixed ability classrooms. Austin, TX: Professional Associates. Tomlinson, C. A. (2001). How to differentiate instruction in mixedability classrooms. Alexandria, VA: ASCD. Tomlinson, C. A. (1999). The differentiated classroom: Responding to the needs of all learners. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.


