89798cca1987b8c5cf0c54e68ab4e74c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 DESIR at SPIRAL 2 Désintégration, Excitation et Stockage des Ions Radioactifs Decay, excitation and storage of radioactive beams • DESIR: facility layout • DESIR: scientific objectives • BESTIOL • LUMIERE • DETRAP • Transfer beam lines • Context BARC/TIFR – DESIR: transfer beam lines Bertram Blank, CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan
DESIR at SPIRAL 2 Désintégration, Excitation et Stockage des Ions Radioactifs Decay, excitation and storage of radioactive beams • DESIR: facility layout • DESIR: scientific objectives • BESTIOL • LUMIERE • DETRAP • Transfer beam lines • Context BARC/TIFR – DESIR: transfer beam lines Bertram Blank, CEN Bordeaux-Gradignan
 DESIR in three parts… BESTIOL: BEta decay STudies at the SPIRAL 2 Is. OL facility LUMIERE: Laser Utilization for Measurement and Ionization of Exotic Radioactive Elements DETRAP: DESIR Trapping facilites
DESIR in three parts… BESTIOL: BEta decay STudies at the SPIRAL 2 Is. OL facility LUMIERE: Laser Utilization for Measurement and Ionization of Exotic Radioactive Elements DETRAP: DESIR Trapping facilites
 The BESTIOL facility BEta decay STudies at the SPIRAL 2 Is. OL facility M. J. G. Borge, B. Blank et al. , CSIC Madrid, CENBG Ø high-precision measurements of 0+-0+ and mirror b decays: quark mixing 21 Na, 23 Mg, 31 S, 39 Ca, 66 As, 70 Br Ø b-decay studies of neutron-rich and neutron-deficient nuclei -> lifetime and decay spectroscopy: magic numbers and astrophysics 81 Cu, 103 -106 Y, 81 Cu, 83 Zn, 86 Ga, 87 Ge, 88 As, 92 Se, 100 Kr, 130 Ag, 139 Sb, 142 Te -> delayed charged-particle correlations (b 2 p emission): pairing in nuclei 22 Al, 23 Si, 26 P, 27 S, 31 Ar, 35 Ca, 39 Ti -> 12 C cluster emission: 112, 114 Ba: from a decay to fission Ø Gamow-Teller strength distribution: shape coexistence, deformation 78 -80 Cu, 80 -82 Zn, 83 -85 Ga, 93 -100 Kr, 98, 99, 101 In, 101 Sn, 97 -99 Cd, 130 -132 In, 129 -132 Cd, 130 Ag Ø Neutron emission probabilities Pn, 2 n: reactor physics Ø b-decay properties of neutron rich nuclei: reactor decay heat
The BESTIOL facility BEta decay STudies at the SPIRAL 2 Is. OL facility M. J. G. Borge, B. Blank et al. , CSIC Madrid, CENBG Ø high-precision measurements of 0+-0+ and mirror b decays: quark mixing 21 Na, 23 Mg, 31 S, 39 Ca, 66 As, 70 Br Ø b-decay studies of neutron-rich and neutron-deficient nuclei -> lifetime and decay spectroscopy: magic numbers and astrophysics 81 Cu, 103 -106 Y, 81 Cu, 83 Zn, 86 Ga, 87 Ge, 88 As, 92 Se, 100 Kr, 130 Ag, 139 Sb, 142 Te -> delayed charged-particle correlations (b 2 p emission): pairing in nuclei 22 Al, 23 Si, 26 P, 27 S, 31 Ar, 35 Ca, 39 Ti -> 12 C cluster emission: 112, 114 Ba: from a decay to fission Ø Gamow-Teller strength distribution: shape coexistence, deformation 78 -80 Cu, 80 -82 Zn, 83 -85 Ga, 93 -100 Kr, 98, 99, 101 In, 101 Sn, 97 -99 Cd, 130 -132 In, 129 -132 Cd, 130 Ag Ø Neutron emission probabilities Pn, 2 n: reactor physics Ø b-decay properties of neutron rich nuclei: reactor decay heat
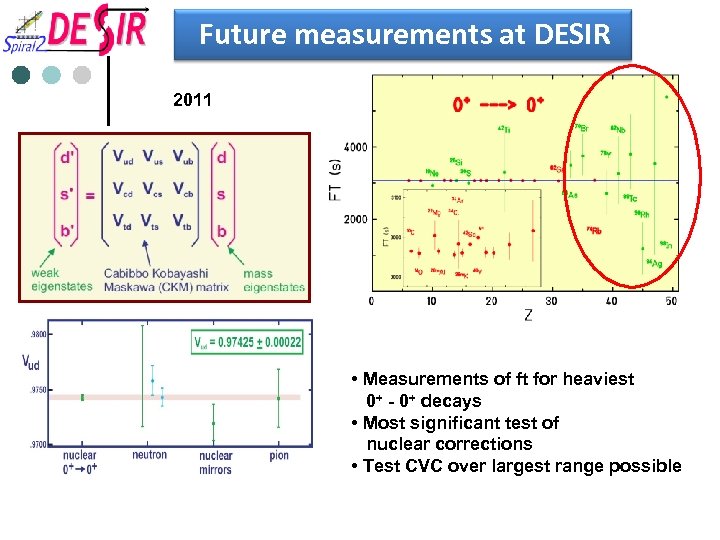 Future measurements at DESIR 2011 • Measurements of ft for heaviest 0+ - 0+ decays • Most significant test of nuclear corrections • Test CVC over largest range possible
Future measurements at DESIR 2011 • Measurements of ft for heaviest 0+ - 0+ decays • Most significant test of nuclear corrections • Test CVC over largest range possible
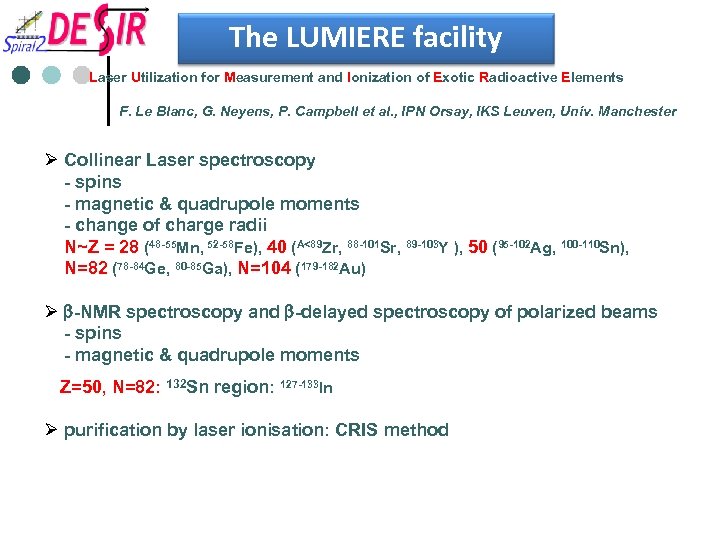 The LUMIERE facility Laser Utilization for Measurement and Ionization of Exotic Radioactive Elements F. Le Blanc, G. Neyens, P. Campbell et al. , IPN Orsay, IKS Leuven, Univ. Manchester Ø Collinear Laser spectroscopy - spins - magnetic & quadrupole moments - change of charge radii N~Z = 28 (48 -55 Mn, 52 -58 Fe), 40 (A<89 Zr, 88 -101 Sr, 89 -103 Y ), 50 (95 -102 Ag, 100 -110 Sn), N=82 (78 -84 Ge, 80 -85 Ga), N=104 (179 -182 Au) Ø b-NMR spectroscopy and b-delayed spectroscopy of polarized beams - spins - magnetic & quadrupole moments Z=50, N=82: 132 Sn region: 127 -133 In Ø purification by laser ionisation: CRIS method
The LUMIERE facility Laser Utilization for Measurement and Ionization of Exotic Radioactive Elements F. Le Blanc, G. Neyens, P. Campbell et al. , IPN Orsay, IKS Leuven, Univ. Manchester Ø Collinear Laser spectroscopy - spins - magnetic & quadrupole moments - change of charge radii N~Z = 28 (48 -55 Mn, 52 -58 Fe), 40 (A<89 Zr, 88 -101 Sr, 89 -103 Y ), 50 (95 -102 Ag, 100 -110 Sn), N=82 (78 -84 Ge, 80 -85 Ga), N=104 (179 -182 Au) Ø b-NMR spectroscopy and b-delayed spectroscopy of polarized beams - spins - magnetic & quadrupole moments Z=50, N=82: 132 Sn region: 127 -133 In Ø purification by laser ionisation: CRIS method
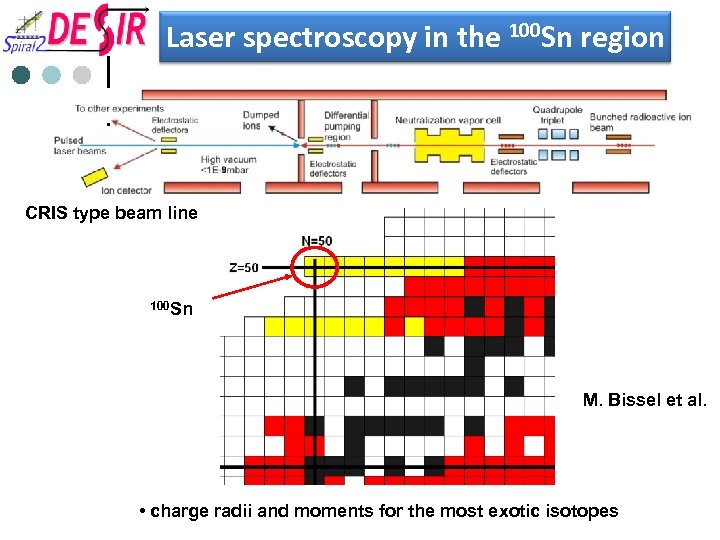 Laser spectroscopy in the 100 Sn region CRIS type beam line 100 Sn M. Bissel et al. • charge radii and moments for the most exotic isotopes
Laser spectroscopy in the 100 Sn region CRIS type beam line 100 Sn M. Bissel et al. • charge radii and moments for the most exotic isotopes
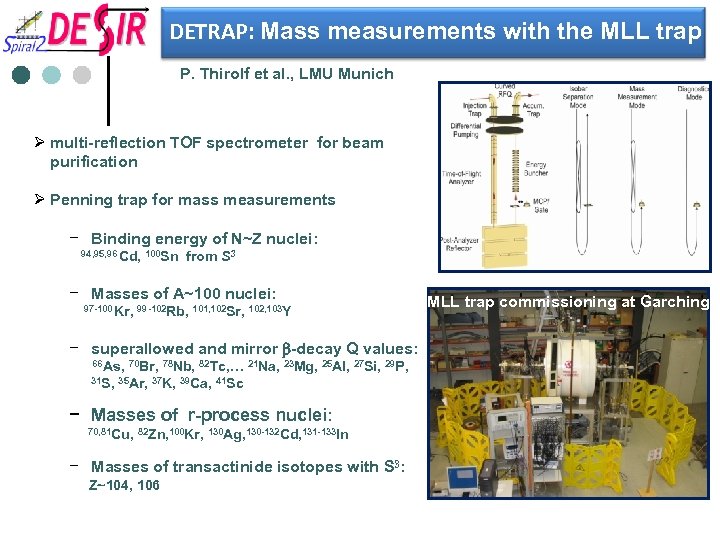 DETRAP: Mass measurements with the MLL trap P. Thirolf et al. , LMU Munich Ø multi-reflection TOF spectrometer for beam purification Ø Penning trap for mass measurements − Binding energy of N~Z nuclei: 94, 95, 96 Cd, 100 Sn from S 3 − Masses of A~100 nuclei: 97 -100 Kr, 99 -102 Rb, 101, 102 Sr, 102, 103 Y − superallowed and mirror b-decay Q values: 66 As, 70 Br, 78 Nb, 82 Tc, … 21 Na, 23 Mg, 25 Al, 27 Si, 29 P, 31 S, 35 Ar, 37 K, 39 Ca, 41 Sc − Masses of r-process nuclei: 70, 81 Cu, 82 Zn, 100 Kr, 130 Ag, 130 -132 Cd, 131 -133 In − Masses of transactinide isotopes with S 3: Z~104, 106 MLL trap commissioning at Garching
DETRAP: Mass measurements with the MLL trap P. Thirolf et al. , LMU Munich Ø multi-reflection TOF spectrometer for beam purification Ø Penning trap for mass measurements − Binding energy of N~Z nuclei: 94, 95, 96 Cd, 100 Sn from S 3 − Masses of A~100 nuclei: 97 -100 Kr, 99 -102 Rb, 101, 102 Sr, 102, 103 Y − superallowed and mirror b-decay Q values: 66 As, 70 Br, 78 Nb, 82 Tc, … 21 Na, 23 Mg, 25 Al, 27 Si, 29 P, 31 S, 35 Ar, 37 K, 39 Ca, 41 Sc − Masses of r-process nuclei: 70, 81 Cu, 82 Zn, 100 Kr, 130 Ag, 130 -132 Cd, 131 -133 In − Masses of transactinide isotopes with S 3: Z~104, 106 MLL trap commissioning at Garching
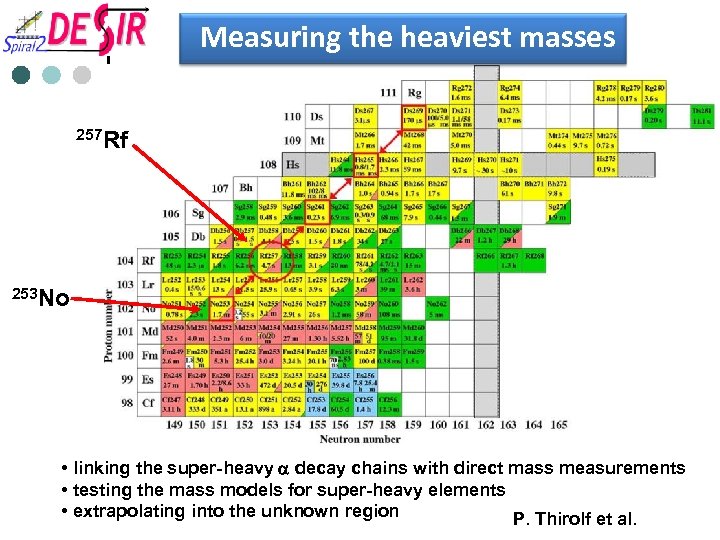 Measuring the heaviest masses 257 Rf 253 No • linking the super-heavy a decay chains with direct mass measurements • testing the mass models for super-heavy elements • extrapolating into the unknown region P. Thirolf et al.
Measuring the heaviest masses 257 Rf 253 No • linking the super-heavy a decay chains with direct mass measurements • testing the mass models for super-heavy elements • extrapolating into the unknown region P. Thirolf et al.
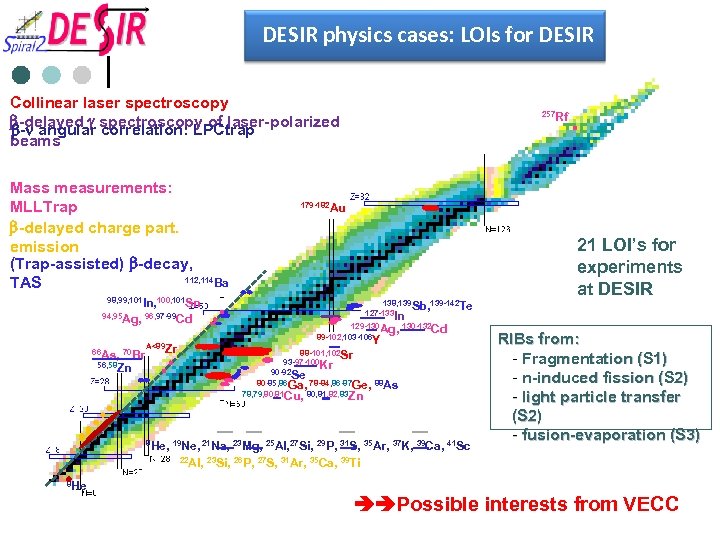 DESIR physics cases: LOIs for DESIR Collinear laser spectroscopy b-delayed g spectroscopy of laser-polarized b-n angular correlation: LPCtrap beams Mass measurements: MLLTrap b-delayed charge part. emission N=Z line (Trap-assisted) b-decay, 112, 114 Ba TAS 257 Rf 179 -182 Au 21 LOI’s for experiments at DESIR 98, 99, 101 In, 100, 101 Sn 94, 95 Ag, 96, 97 -99 Cd 66 As, 70 Br 56, 58 Zn A<89 Zr 138, 139 Sb, 139 -142 Te 127 -133 In 129 -130 Ag, 130 -132 Cd 89 -102, 103 -106 Y 88 -101, 102 Sr 93 -97 -100 Kr 90 -92 Se 80 -85, 86 Ga, 78 -84, 86 -87 Ge, 88 As 78, 79, 80, 81 Cu, 80, 81, 82, 83 Zn 8 He, 19 Ne, 21 Na, 23 Mg, 25 Al, 27 Si, 29 P, 31 S, 35 Ar, 37 K, 39 Ca, 41 Sc RIBs from: - Fragmentation (S 1) - n-induced fission (S 2) - light particle transfer (S 2) - fusion-evaporation (S 3) 22 Al, 23 Si, 26 P, 27 S, 31 Ar, 35 Ca, 39 Ti 8 He Possible interests from VECC
DESIR physics cases: LOIs for DESIR Collinear laser spectroscopy b-delayed g spectroscopy of laser-polarized b-n angular correlation: LPCtrap beams Mass measurements: MLLTrap b-delayed charge part. emission N=Z line (Trap-assisted) b-decay, 112, 114 Ba TAS 257 Rf 179 -182 Au 21 LOI’s for experiments at DESIR 98, 99, 101 In, 100, 101 Sn 94, 95 Ag, 96, 97 -99 Cd 66 As, 70 Br 56, 58 Zn A<89 Zr 138, 139 Sb, 139 -142 Te 127 -133 In 129 -130 Ag, 130 -132 Cd 89 -102, 103 -106 Y 88 -101, 102 Sr 93 -97 -100 Kr 90 -92 Se 80 -85, 86 Ga, 78 -84, 86 -87 Ge, 88 As 78, 79, 80, 81 Cu, 80, 81, 82, 83 Zn 8 He, 19 Ne, 21 Na, 23 Mg, 25 Al, 27 Si, 29 P, 31 S, 35 Ar, 37 K, 39 Ca, 41 Sc RIBs from: - Fragmentation (S 1) - n-induced fission (S 2) - light particle transfer (S 2) - fusion-evaporation (S 3) 22 Al, 23 Si, 26 P, 27 S, 31 Ar, 35 Ca, 39 Ti 8 He Possible interests from VECC
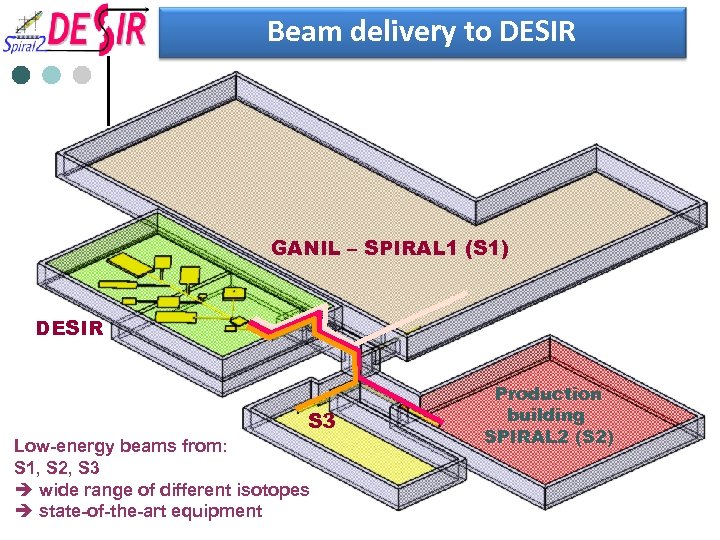 Beam delivery to DESIR GANIL – SPIRAL 1 (S 1) DESIR S 3 Low-energy beams from: S 1, S 2, S 3 è wide range of different isotopes è state-of-the-art equipment Production building SPIRAL 2 (S 2)
Beam delivery to DESIR GANIL – SPIRAL 1 (S 1) DESIR S 3 Low-energy beams from: S 1, S 2, S 3 è wide range of different isotopes è state-of-the-art equipment Production building SPIRAL 2 (S 2)
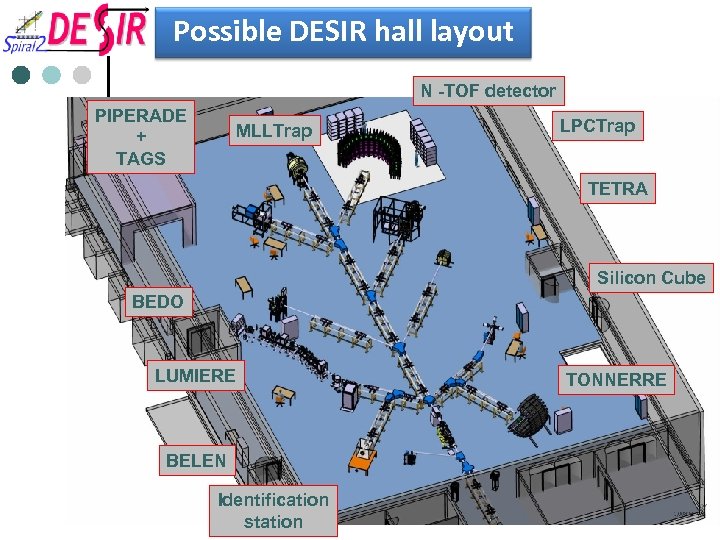 Possible DESIR hall layout N -TOF detector PIPERADE + TAGS MLLTrap LPCTrap TETRA Silicon Cube BEDO LUMIERE BELEN Identification station TONNERRE
Possible DESIR hall layout N -TOF detector PIPERADE + TAGS MLLTrap LPCTrap TETRA Silicon Cube BEDO LUMIERE BELEN Identification station TONNERRE
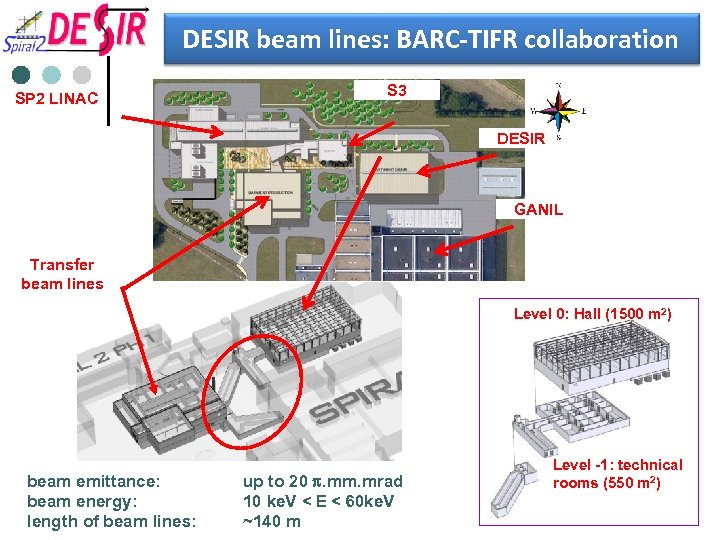 DESIR beam lines: BARC-TIFR collaboration SP 2 LINAC S 3 DESIR GANIL Production Transfer beam lines building Level 0: Hall (1500 m 2) beam emittance: beam energy: length of beam lines: up to 20 p. mm. mrad 10 ke. V < E < 60 ke. V ~140 m Level -1: technical rooms (550 m 2)
DESIR beam lines: BARC-TIFR collaboration SP 2 LINAC S 3 DESIR GANIL Production Transfer beam lines building Level 0: Hall (1500 m 2) beam emittance: beam energy: length of beam lines: up to 20 p. mm. mrad 10 ke. V < E < 60 ke. V ~140 m Level -1: technical rooms (550 m 2)
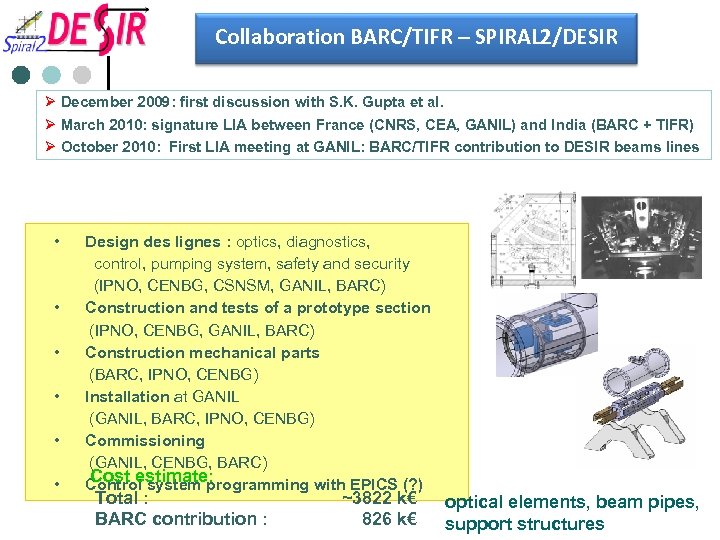 Collaboration BARC/TIFR – SPIRAL 2/DESIR Ø December 2009: first discussion with S. K. Gupta et al. Ø March 2010: signature LIA between France (CNRS, CEA, GANIL) and India (BARC + TIFR) Ø October 2010: First LIA meeting at GANIL: BARC/TIFR contribution to DESIR beams lines • • • Design des lignes : optics, diagnostics, control, pumping system, safety and security (IPNO, CENBG, CSNSM, GANIL, BARC) Construction and tests of a prototype section (IPNO, CENBG, GANIL, BARC) Construction mechanical parts (BARC, IPNO, CENBG) Installation at GANIL (GANIL, BARC, IPNO, CENBG) Commissioning (GANIL, CENBG, BARC) Cost estimate: Control system programming with EPICS (? ) Total : BARC contribution : ~3822 k€ 826 k€ optical elements, beam pipes, support structures
Collaboration BARC/TIFR – SPIRAL 2/DESIR Ø December 2009: first discussion with S. K. Gupta et al. Ø March 2010: signature LIA between France (CNRS, CEA, GANIL) and India (BARC + TIFR) Ø October 2010: First LIA meeting at GANIL: BARC/TIFR contribution to DESIR beams lines • • • Design des lignes : optics, diagnostics, control, pumping system, safety and security (IPNO, CENBG, CSNSM, GANIL, BARC) Construction and tests of a prototype section (IPNO, CENBG, GANIL, BARC) Construction mechanical parts (BARC, IPNO, CENBG) Installation at GANIL (GANIL, BARC, IPNO, CENBG) Commissioning (GANIL, CENBG, BARC) Cost estimate: Control system programming with EPICS (? ) Total : BARC contribution : ~3822 k€ 826 k€ optical elements, beam pipes, support structures
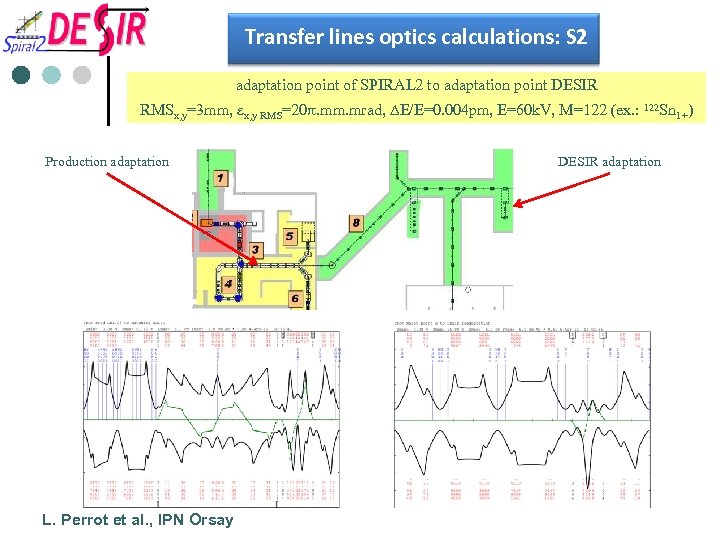 Transfer lines optics calculations: S 2 adaptation point of SPIRAL 2 to adaptation point DESIR RMSx, y=3 mm, ex, y RMS=20 p. mm. mrad, DE/E=0. 004 pm, E=60 k. V, M=122 (ex. : 122 Sn 1+) Production adaptation L. Perrot et al. , IPN Orsay DESIR adaptation
Transfer lines optics calculations: S 2 adaptation point of SPIRAL 2 to adaptation point DESIR RMSx, y=3 mm, ex, y RMS=20 p. mm. mrad, DE/E=0. 004 pm, E=60 k. V, M=122 (ex. : 122 Sn 1+) Production adaptation L. Perrot et al. , IPN Orsay DESIR adaptation
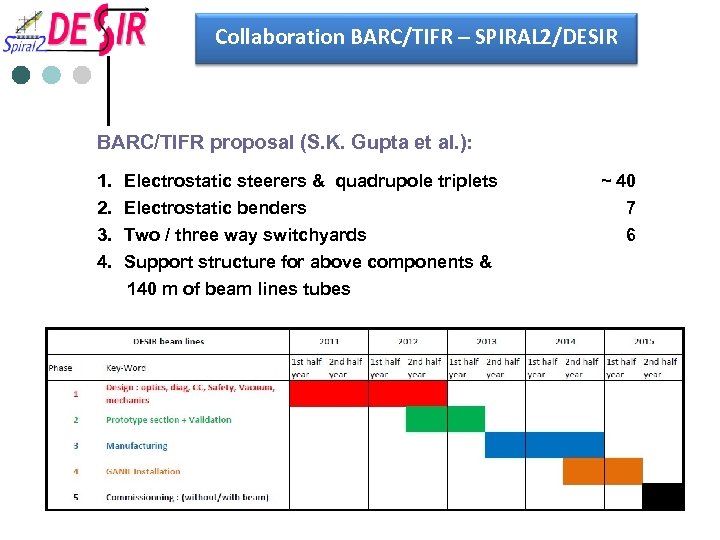 Collaboration BARC/TIFR – SPIRAL 2/DESIR BARC/TIFR proposal (S. K. Gupta et al. ): 1. Electrostatic steerers & quadrupole triplets 2. Electrostatic benders 3. Two / three way switchyards 4. Support structure for above components & 140 m of beam lines tubes ~ 40 7 6
Collaboration BARC/TIFR – SPIRAL 2/DESIR BARC/TIFR proposal (S. K. Gupta et al. ): 1. Electrostatic steerers & quadrupole triplets 2. Electrostatic benders 3. Two / three way switchyards 4. Support structure for above components & 140 m of beam lines tubes ~ 40 7 6
 DESIR: • exciting physics opportunities: • Laser spectroscopy • Decay studies • Trap (assisted) measurement • large variety of beams due to different production schemes • state of the art equipment… possibilities for equipemnt from India • large international collaboration • DESIR letter of intent (Oct. 2006): 97 scientists • DESIR technical design report (Jan. 2010): 111 scientists • DESIR related LOIs for SPIRAL 2 (Jan. 2011): 132 scientists • collaboration with and contribution from BARC/TIFR, VECC and others is must welcome
DESIR: • exciting physics opportunities: • Laser spectroscopy • Decay studies • Trap (assisted) measurement • large variety of beams due to different production schemes • state of the art equipment… possibilities for equipemnt from India • large international collaboration • DESIR letter of intent (Oct. 2006): 97 scientists • DESIR technical design report (Jan. 2010): 111 scientists • DESIR related LOIs for SPIRAL 2 (Jan. 2011): 132 scientists • collaboration with and contribution from BARC/TIFR, VECC and others is must welcome

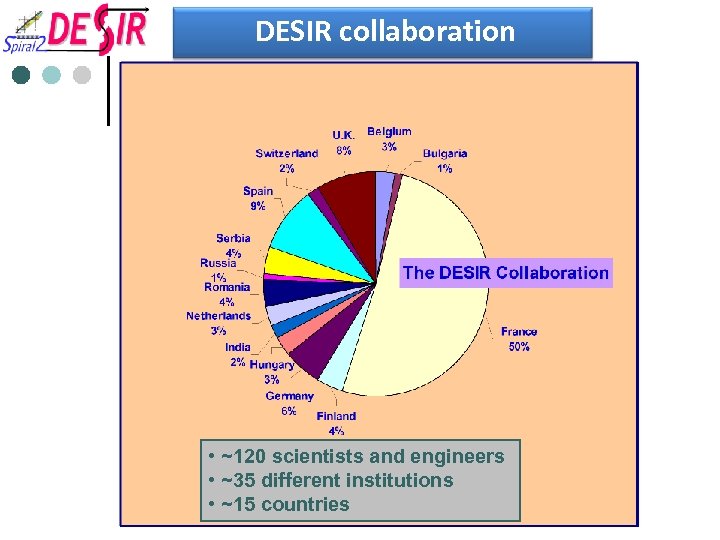 DESIR collaboration • ~120 scientists and engineers • ~35 different institutions • ~15 countries
DESIR collaboration • ~120 scientists and engineers • ~35 different institutions • ~15 countries
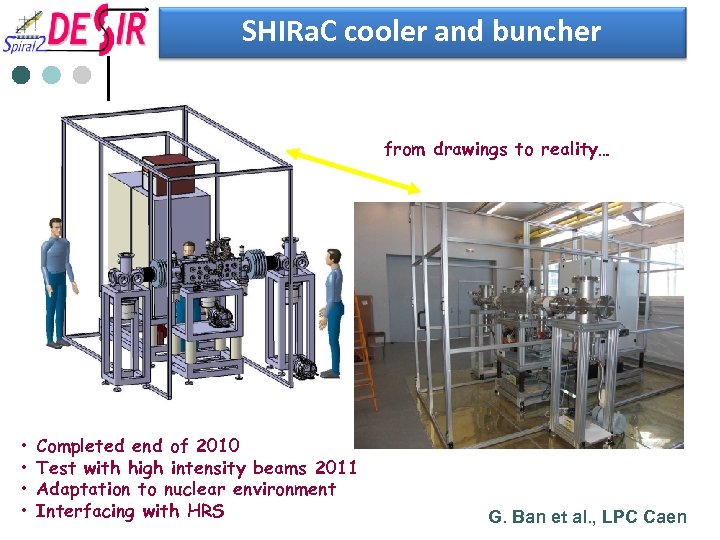 SHIRa. C cooler and buncher from drawings to reality… • • Completed end of 2010 Test with high intensity beams 2011 Adaptation to nuclear environment Interfacing with HRS G. Ban et al. , LPC Caen
SHIRa. C cooler and buncher from drawings to reality… • • Completed end of 2010 Test with high intensity beams 2011 Adaptation to nuclear environment Interfacing with HRS G. Ban et al. , LPC Caen
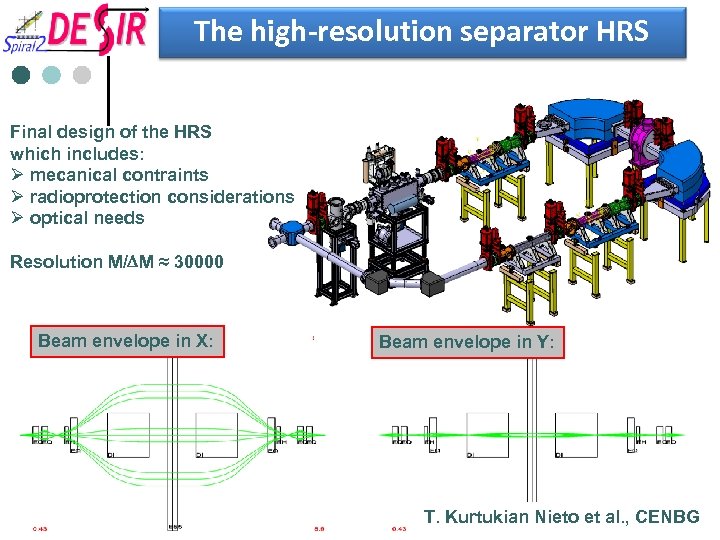 The high-resolution separator HRS Final design of the HRS which includes: Ø mecanical contraints Ø radioprotection considerations Ø optical needs Resolution M/DM ≈ 30000 Beam envelope in X: Beam envelope in Y: T. Kurtukian Nieto et al. , CENBG
The high-resolution separator HRS Final design of the HRS which includes: Ø mecanical contraints Ø radioprotection considerations Ø optical needs Resolution M/DM ≈ 30000 Beam envelope in X: Beam envelope in Y: T. Kurtukian Nieto et al. , CENBG
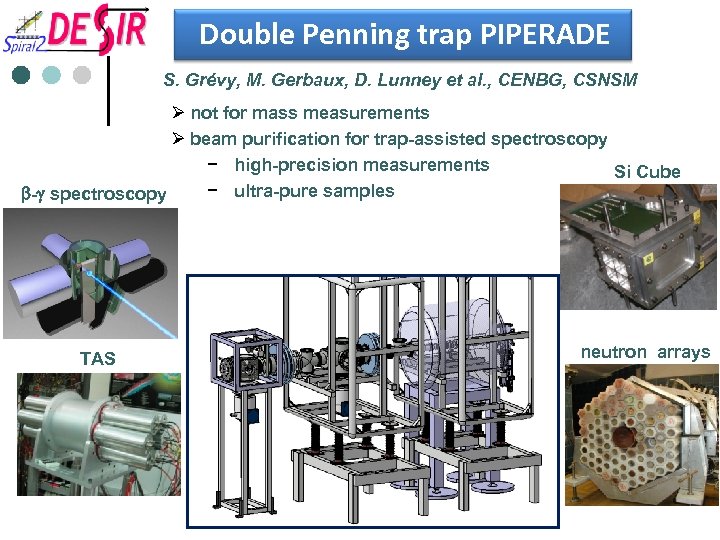 Double Penning trap PIPERADE S. Grévy, M. Gerbaux, D. Lunney et al. , CENBG, CSNSM Ø not for mass measurements Ø beam purification for trap-assisted spectroscopy − high-precision measurements Si Cube − ultra-pure samples b-g spectroscopy TAS neutron arrays
Double Penning trap PIPERADE S. Grévy, M. Gerbaux, D. Lunney et al. , CENBG, CSNSM Ø not for mass measurements Ø beam purification for trap-assisted spectroscopy − high-precision measurements Si Cube − ultra-pure samples b-g spectroscopy TAS neutron arrays
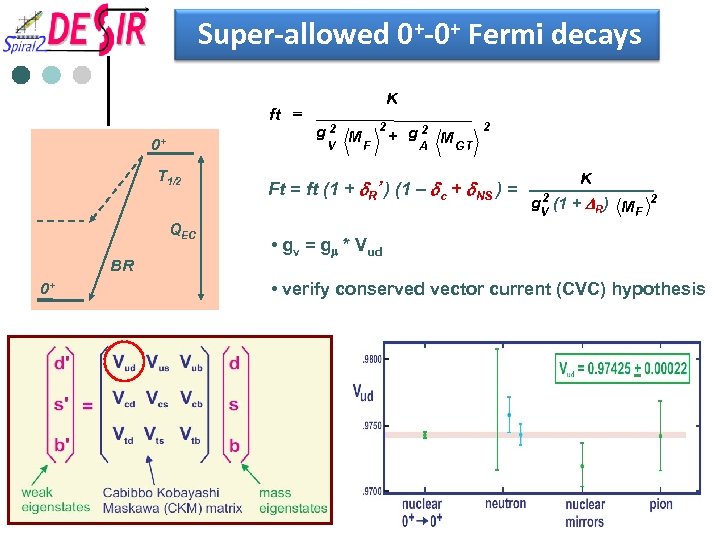 Super-allowed 0+-0+ Fermi decays ft = 0+ T 1/2 QEC BR 0+ K g 2 M V F 2 + g 2 M A GT 2 Ft = ft (1 + d. R’ ) (1 – dc + d. NS ) = K 2 g. V (1 + DR) M F 2 • gv = gm * Vud • verify conserved vector current (CVC) hypothesis
Super-allowed 0+-0+ Fermi decays ft = 0+ T 1/2 QEC BR 0+ K g 2 M V F 2 + g 2 M A GT 2 Ft = ft (1 + d. R’ ) (1 – dc + d. NS ) = K 2 g. V (1 + DR) M F 2 • gv = gm * Vud • verify conserved vector current (CVC) hypothesis
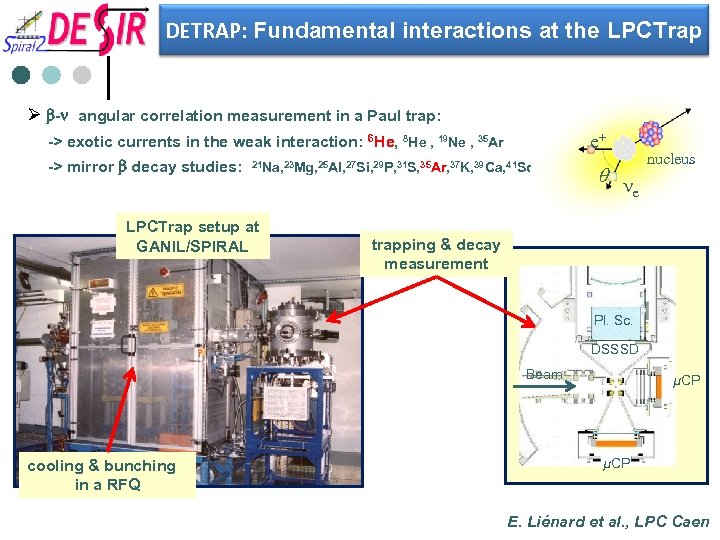 DETRAP: Fundamental interactions at the LPCTrap Ø b-n angular correlation measurement in a Paul trap: e+ -> exotic currents in the weak interaction: 6 He, 8 He , 19 Ne , 35 Ar -> mirror b decay studies: 21 Na, 23 Mg, 25 Al, 27 Si, 29 P, 31 S, 35 Ar, 37 K, 39 Ca, 41 Sc LPCTrap setup at GANIL/SPIRAL q n e nucleus trapping & decay measurement Pl. Sc. DSSSD Beam cooling & bunching in a RFQ µCP E. Liénard et al. , LPC Caen
DETRAP: Fundamental interactions at the LPCTrap Ø b-n angular correlation measurement in a Paul trap: e+ -> exotic currents in the weak interaction: 6 He, 8 He , 19 Ne , 35 Ar -> mirror b decay studies: 21 Na, 23 Mg, 25 Al, 27 Si, 29 P, 31 S, 35 Ar, 37 K, 39 Ca, 41 Sc LPCTrap setup at GANIL/SPIRAL q n e nucleus trapping & decay measurement Pl. Sc. DSSSD Beam cooling & bunching in a RFQ µCP E. Liénard et al. , LPC Caen
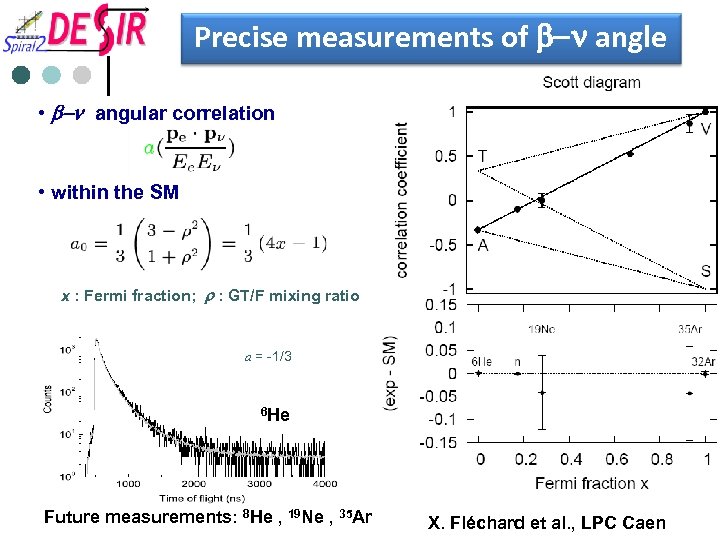 Precise measurements of b-n angle • b-n angular correlation • within the SM x : Fermi fraction; r : GT/F mixing ratio a = -1/3 6 He Future measurements: 8 He , 19 Ne , 35 Ar X. Fléchard et al. , LPC Caen
Precise measurements of b-n angle • b-n angular correlation • within the SM x : Fermi fraction; r : GT/F mixing ratio a = -1/3 6 He Future measurements: 8 He , 19 Ne , 35 Ar X. Fléchard et al. , LPC Caen
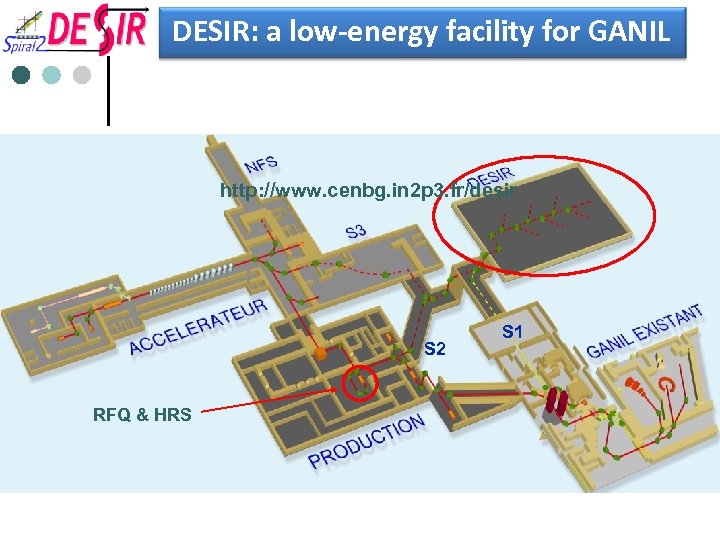 DESIR: a low-energy facility for GANIL http: //www. cenbg. in 2 p 3. fr/desir S 2 RFQ & HRS S 1
DESIR: a low-energy facility for GANIL http: //www. cenbg. in 2 p 3. fr/desir S 2 RFQ & HRS S 1
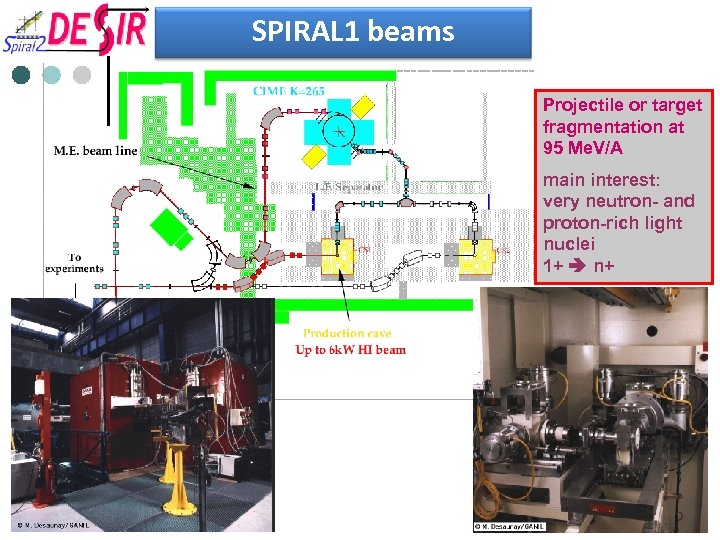 SPIRAL 1 beams Projectile or target fragmentation at 95 Me. V/A main interest: very neutron- and proton-rich light nuclei 1+ n+
SPIRAL 1 beams Projectile or target fragmentation at 95 Me. V/A main interest: very neutron- and proton-rich light nuclei 1+ n+
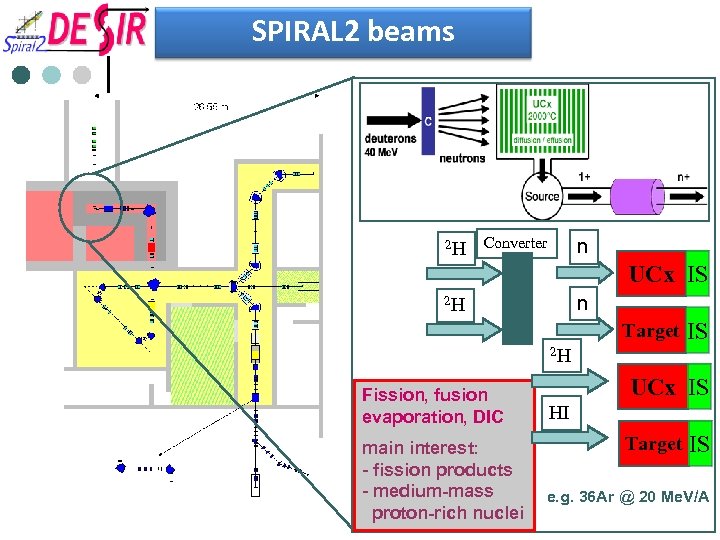 SPIRAL 2 beams 2 H Converter n UCx IS n 2 H Target IS 2 H Fission, fusion evaporation, DIC main interest: - fission products - medium-mass proton-rich nuclei UCx IS HI Target IS e. g. 36 Ar @ 20 Me. V/A
SPIRAL 2 beams 2 H Converter n UCx IS n 2 H Target IS 2 H Fission, fusion evaporation, DIC main interest: - fission products - medium-mass proton-rich nuclei UCx IS HI Target IS e. g. 36 Ar @ 20 Me. V/A
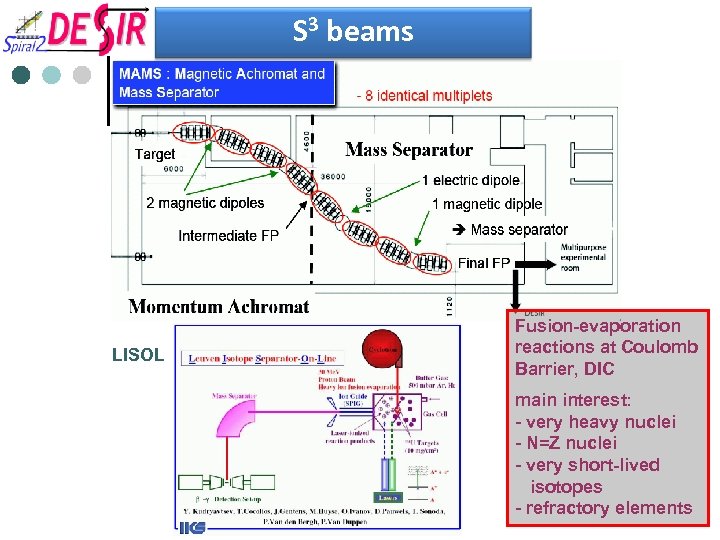 S 3 beams LISOL Fusion-evaporation reactions at Coulomb Barrier, DIC main interest: - very heavy nuclei - N=Z nuclei - very short-lived isotopes - refractory elements
S 3 beams LISOL Fusion-evaporation reactions at Coulomb Barrier, DIC main interest: - very heavy nuclei - N=Z nuclei - very short-lived isotopes - refractory elements
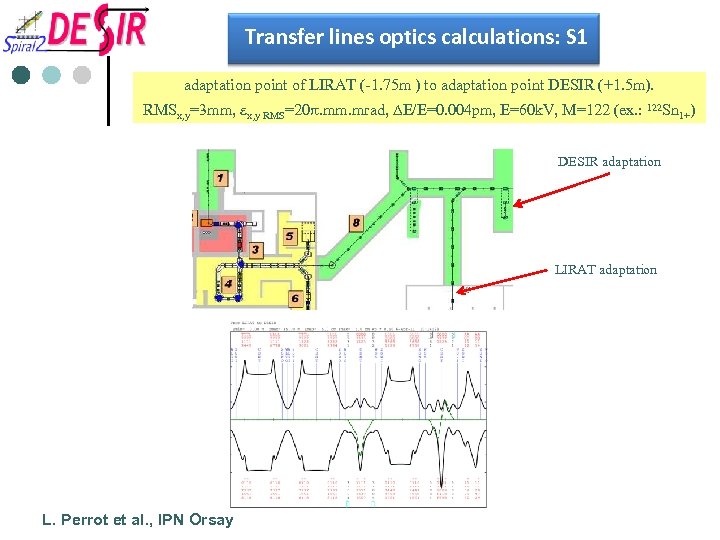 Transfer lines optics calculations: S 1 adaptation point of LIRAT (-1. 75 m ) to adaptation point DESIR (+1. 5 m). RMSx, y=3 mm, ex, y RMS=20 p. mm. mrad, DE/E=0. 004 pm, E=60 k. V, M=122 (ex. : 122 Sn 1+) DESIR adaptation LIRAT adaptation L. Perrot et al. , IPN Orsay
Transfer lines optics calculations: S 1 adaptation point of LIRAT (-1. 75 m ) to adaptation point DESIR (+1. 5 m). RMSx, y=3 mm, ex, y RMS=20 p. mm. mrad, DE/E=0. 004 pm, E=60 k. V, M=122 (ex. : 122 Sn 1+) DESIR adaptation LIRAT adaptation L. Perrot et al. , IPN Orsay
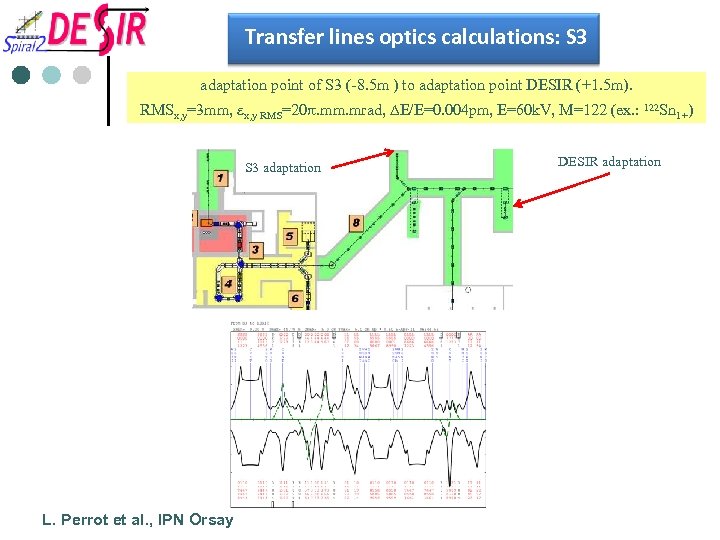 Transfer lines optics calculations: S 3 adaptation point of S 3 (-8. 5 m ) to adaptation point DESIR (+1. 5 m). RMSx, y=3 mm, ex, y RMS=20 p. mm. mrad, DE/E=0. 004 pm, E=60 k. V, M=122 (ex. : 122 Sn 1+) S 3 adaptation L. Perrot et al. , IPN Orsay DESIR adaptation
Transfer lines optics calculations: S 3 adaptation point of S 3 (-8. 5 m ) to adaptation point DESIR (+1. 5 m). RMSx, y=3 mm, ex, y RMS=20 p. mm. mrad, DE/E=0. 004 pm, E=60 k. V, M=122 (ex. : 122 Sn 1+) S 3 adaptation L. Perrot et al. , IPN Orsay DESIR adaptation
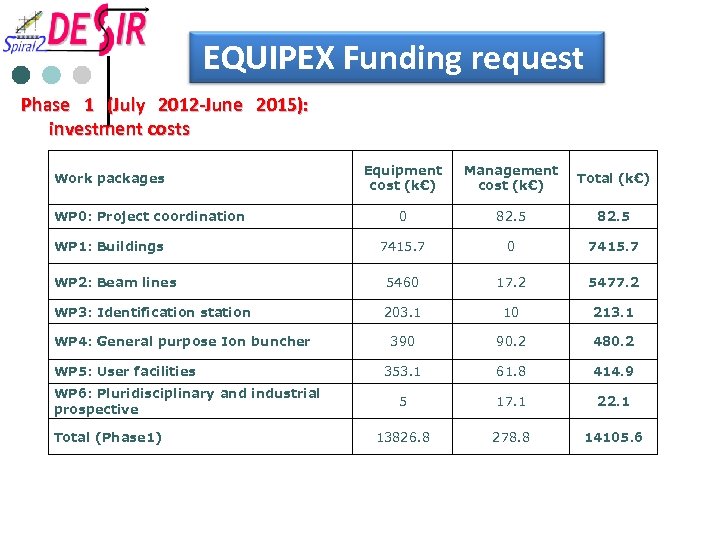 EQUIPEX Funding request Phase 1 (July 2012 -June 2015): investment costs Equipment cost (k€) Management cost (k€) Total (k€) 0 82. 5 7415. 7 0 7415. 7 WP 2: Beam lines 5460 17. 2 5477. 2 WP 3: Identification station 203. 1 10 213. 1 390 90. 2 480. 2 353. 1 61. 8 414. 9 5 17. 1 22. 1 13826. 8 278. 8 14105. 6 Work packages WP 0: Project coordination WP 1: Buildings WP 4: General purpose Ion buncher WP 5: User facilities WP 6: Pluridisciplinary and industrial prospective Total (Phase 1)
EQUIPEX Funding request Phase 1 (July 2012 -June 2015): investment costs Equipment cost (k€) Management cost (k€) Total (k€) 0 82. 5 7415. 7 0 7415. 7 WP 2: Beam lines 5460 17. 2 5477. 2 WP 3: Identification station 203. 1 10 213. 1 390 90. 2 480. 2 353. 1 61. 8 414. 9 5 17. 1 22. 1 13826. 8 278. 8 14105. 6 Work packages WP 0: Project coordination WP 1: Buildings WP 4: General purpose Ion buncher WP 5: User facilities WP 6: Pluridisciplinary and industrial prospective Total (Phase 1)
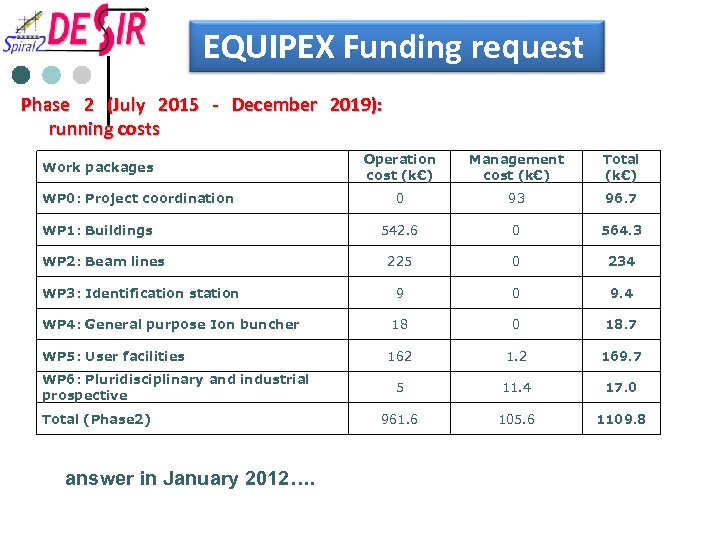 EQUIPEX Funding request Phase 2 (July 2015 - December 2019): running costs Work packages WP 0: Project coordination WP 1: Buildings WP 2: Beam lines WP 3: Identification station WP 4: General purpose Ion buncher WP 5: User facilities WP 6: Pluridisciplinary and industrial prospective Total (Phase 2) answer in January 2012…. Operation cost (k€) Management cost (k€) Total (k€) 0 93 96. 7 542. 6 0 564. 3 225 0 234 9 0 9. 4 18 0 18. 7 162 1. 2 169. 7 5 11. 4 17. 0 961. 6 105. 6 1109. 8
EQUIPEX Funding request Phase 2 (July 2015 - December 2019): running costs Work packages WP 0: Project coordination WP 1: Buildings WP 2: Beam lines WP 3: Identification station WP 4: General purpose Ion buncher WP 5: User facilities WP 6: Pluridisciplinary and industrial prospective Total (Phase 2) answer in January 2012…. Operation cost (k€) Management cost (k€) Total (k€) 0 93 96. 7 542. 6 0 564. 3 225 0 234 9 0 9. 4 18 0 18. 7 162 1. 2 169. 7 5 11. 4 17. 0 961. 6 105. 6 1109. 8


