 Designing for Human Control
Designing for Human Control
 Operator Error: Traditional View
Operator Error: Traditional View
 Typical Problems with IT
Typical Problems with IT
 Cognitive Consequences of Computers
Cognitive Consequences of Computers
 Human-Centered Design
Human-Centered Design
 Advantages of Humans
Advantages of Humans
 Role of Humans in Automated Systems
Role of Humans in Automated Systems
 Role of Humans in Automated Systems (2)
Role of Humans in Automated Systems (2)
 Role of Humans in Automated Systems (3)
Role of Humans in Automated Systems (3)
 Consequences of Computers
Consequences of Computers
 Mixing Humans and Computers
Mixing Humans and Computers
 Typical Problems with IT
Typical Problems with IT
 Cognitive Consequences of Computers
Cognitive Consequences of Computers
 Designing for Human Control
Designing for Human Control
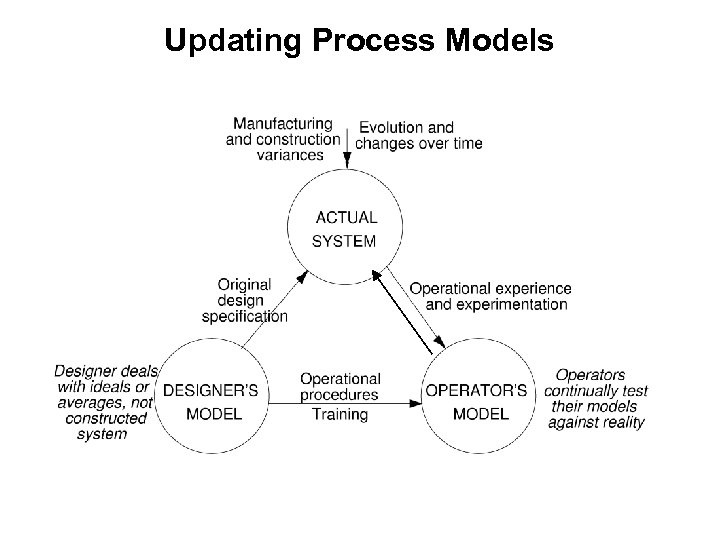 Updating Process Models
Updating Process Models
 Human Error Fundamentals
Human Error Fundamentals
 Human Factors in Accidents (4)
Human Factors in Accidents (4)
 General Design Principles
General Design Principles
 Inconsistent Behavior
Inconsistent Behavior
 Unintended Side Effects
Unintended Side Effects
 Providing Control Options
Providing Control Options
 Providing Control Options
Providing Control Options
 Design for Error Tolerance
Design for Error Tolerance
 Design for Error Tolerance (2)
Design for Error Tolerance (2)
 Matching Tasks to Human Characteristics
Matching Tasks to Human Characteristics
 Matching Tasks to Human Characteristics (2)
Matching Tasks to Human Characteristics (2)
 Reducing Human Errors
Reducing Human Errors
 Reducing Human Errors (2)
Reducing Human Errors (2)
 Reducing Human Errors (3)
Reducing Human Errors (3)
 Modes
Modes
 Mode Confusion
Mode Confusion
 Mode Confusion (2)
Mode Confusion (2)
 Mode Confusion (3)
Mode Confusion (3)
 Interface Interpretation Errors
Interface Interpretation Errors
 Interface Interpretation Errors (2)
Interface Interpretation Errors (2)
 Indirect Mode Changes
Indirect Mode Changes
 Indirect Mode Changes (2)
Indirect Mode Changes (2)
 Providing Information and Feedback
Providing Information and Feedback
 Updating Mental Models
Updating Mental Models
 Updating Mental Models (2)
Updating Mental Models (2)
 Updating Process Models (3)
Updating Process Models (3)
 Detecting Faults and Failures
Detecting Faults and Failures
 Example Accident
Example Accident
 Alarms
Alarms
 Alarms (2)
Alarms (2)
 Displaying Feedback to Human Controllers
Displaying Feedback to Human Controllers
 Displaying Feedback to Human Controllers
Displaying Feedback to Human Controllers
 Training and Maintaining Skills
Training and Maintaining Skills
 Training and Maintaining Skills
Training and Maintaining Skills