0e7d8a634e322e7f0380138b1e79771a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Designing Architected SOA Solutions using the IBM Software Delivery Platform Ameeta Roy Technical Sales Manager – Rational India/SA

Topics • The Importance of the “A” in SOA • Keys to Success – Successful Alignment of IT and Business – Understanding and Enforcing your Best Practices and Architecture – Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets – Keep Design Assets and Code in sync/aligned/coordinated – Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC – Early Focus on Quality and Testing – Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets • Q&A

What is Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) ? SOA is different things to different people: – a set of services that a business wants to expose to their customers and partners, or other portions of the organization Business Executive, Analyst – an architectural style which requires a service provider, requestor and a service description – a set of architectural principles, patterns and criteria which address characteristics such as modularity, encapsulation, loose coupling, separation of concerns, reuse, composability Architect IT Architect – a programming model complete with standards, tools and technologies such as Web Services – A middleware solution optimized for service assembly, orchestration, monitoring, an management Software and Developer System Developer
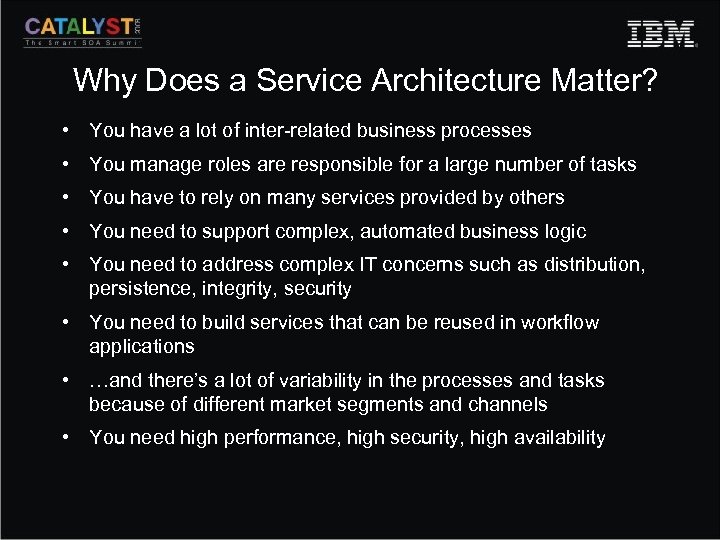
Why Does a Service Architecture Matter? • You have a lot of inter-related business processes • You manage roles are responsible for a large number of tasks • You have to rely on many services provided by others • You need to support complex, automated business logic • You need to address complex IT concerns such as distribution, persistence, integrity, security • You need to build services that can be reused in workflow applications • …and there’s a lot of variability in the processes and tasks because of different market segments and channels • You need high performance, high security, high availability
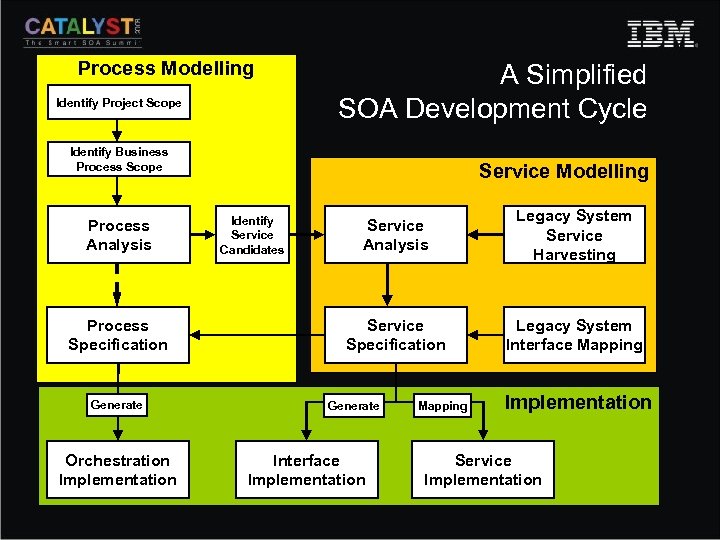
Process Modelling Identify Project Scope A Simplified SOA Development Cycle Identify Business Process Scope Process Analysis Process Specification Generate Orchestration Implementation Service Modelling Service Analysis Legacy System Service Harvesting Service Specification Identify Service Candidates Legacy System Interface Mapping Generate Interface Implementation Mapping Implementation Service Implementation
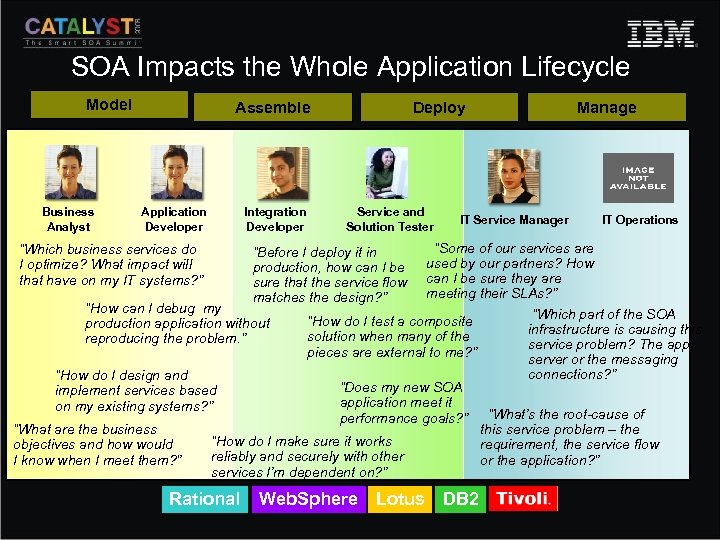
SOA Impacts the Whole Application Lifecycle Model Business Analyst Assemble Application Developer Integration Developer Deploy Service and Solution Tester IT Service Manager Manage IT Operations “Some of our services are used by our partners? How can I be sure they are meeting their SLAs? ” “How can I debug my “Which part of the SOA “How do I test a composite production application without infrastructure is causing this solution when many of the reproducing the problem. ” service problem? The app pieces are external to me? ” server or the messaging connections? ” “How do I design and “Does my new SOA implement services based application meet it on my existing systems? ” performance goals? ” “What’s the root-cause of this service problem – the “What are the business “How do I make sure it works requirement, the service flow objectives and how would reliably and securely with other or the application? ” I know when I meet them? ” services I’m dependent on? ” “Which business services do I optimize? What impact will that have on my IT systems? ” Rational “Before I deploy it in production, how can I be sure that the service flow matches the design? ” Web. Sphere Lotus DB 2
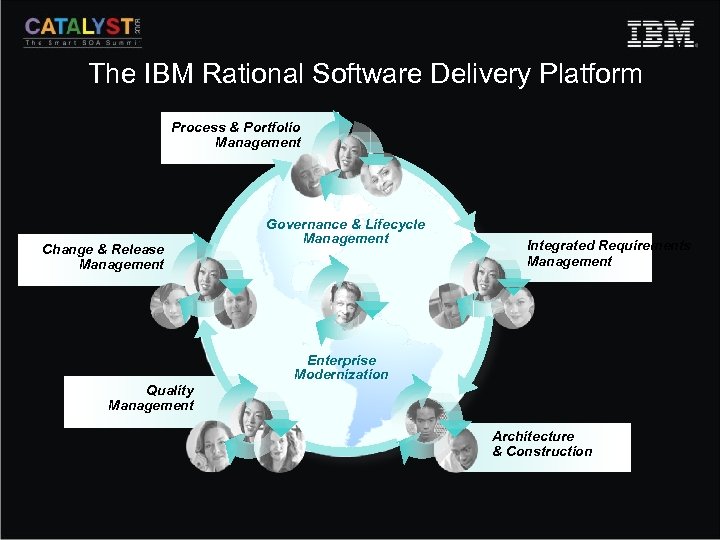
The IBM Rational Software Delivery Platform Process & Portfolio Management Change & Release Management Governance & Lifecycle Management Integrated Requirements Management Enterprise Modernization Quality Management Architecture & Construction

Keys to Success • Successful Alignment of IT and Business • Understanding and Enforcing your Best Practices and Architecture • Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets • Keep Design Assets and Code insync/aligned/coordinated • Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC • Early Focus on Quality and Testing • Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets

Keys to Success • Successful Alignment of IT and Business • Understanding and Enforcing your Best Practices and Architecture • Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets • Keep Design Assets and Code insync/aligned/coordinated • Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC • Early Focus on Quality and Testing • Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets
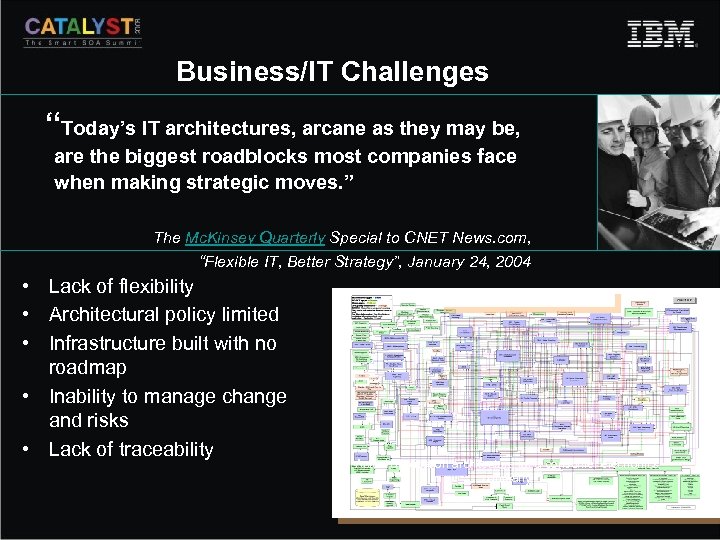
Business/IT Challenges “Today’s IT architectures, arcane as they may be, are the biggest roadblocks most companies face when making strategic moves. ” The Mc. Kinsey Quarterly Special to CNET News. com, “Flexible IT, Better Strategy”, January 24, 2004 • Lack of flexibility • Architectural policy limited • Infrastructure built with no roadmap • Inability to manage change and risks • Lack of traceability Actual application architecture for a consumer electronics company
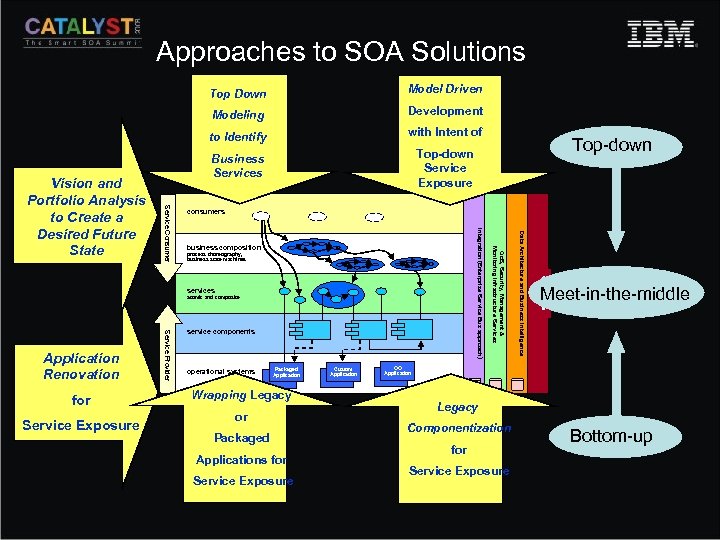
Approaches to SOA Solutions Top Down Modeling Development to Identify with Intent of Business Services Top-down Service Exposure Service Provider for service components operational systems Packaged Application Wrapping Legacy or Packaged Applications for Service Exposure Custom Application Governance atomic and composite Data Architecture and Business Intelligence process choreography, business state machines Qo. S, Security, Management & Monitoring Infrastructure Services business composition services Application Renovation Top-down consumers Integration (Enterprise Service Bus approach) Service Consumer Vision and Portfolio Analysis to Create a Desired Future State Model Driven Meet-in-the-middle OO Application Legacy Componentization for Service Exposure Bottom-up
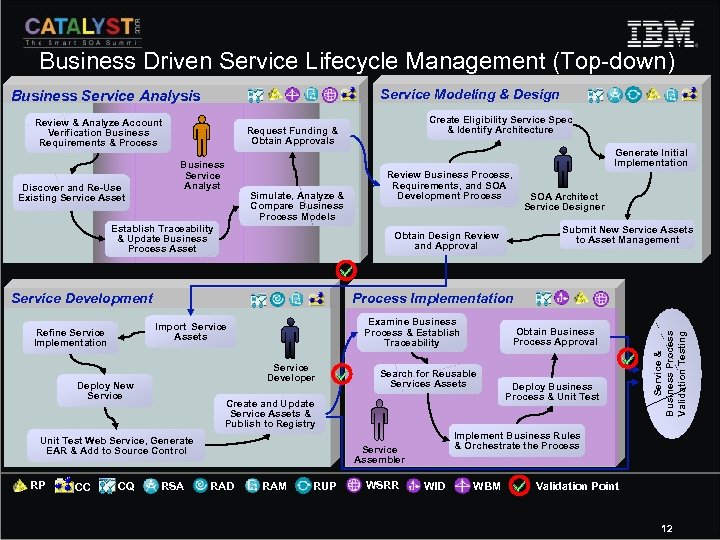
Business Driven Service Lifecycle Management (Top-down) Service Modeling & Design Business Service Analysis Review & Analyze Account Verification Business Requirements & Process Business Service Analyst Generate Initial Implementation Simulate, Analyze & Compare Business Process Models Establish Traceability & Update Business Process Asset Process Implementation Examine Business Process & Establish Traceability Import Service Assets Service Developer Deploy New Service CC CQ Obtain Business Process Approval Search for Reusable Services Assets Create and Update Service Assets & Publish to Registry Unit Test Web Service, Generate EAR & Add to Source Control RP SOA Architect Service Designer Submit New Service Assets to Asset Management Obtain Design Review and Approval Service Development Refine Service Implementation Review Business Process, Requirements, and SOA Development Process RSA Implement Business Rules & Orchestrate the Process Service Assembler RAD RAM RUP WSRR Deploy Business Process & Unit Test Service & Business Process Validation Testing Discover and Re-Use Existing Service Asset Create Eligibility Service Spec & Identify Architecture Request Funding & Obtain Approvals WID WBM Validation Point 12
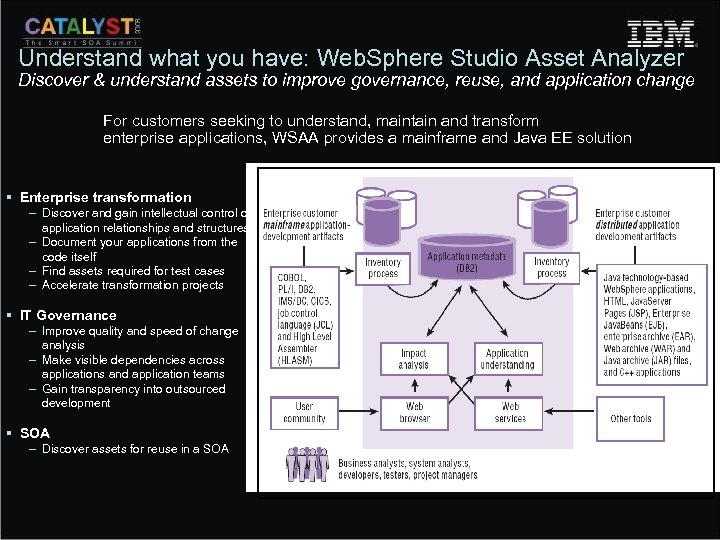
Understand what you have: Web. Sphere Studio Asset Analyzer Discover & understand assets to improve governance, reuse, and application change For customers seeking to understand, maintain and transform enterprise applications, WSAA provides a mainframe and Java EE solution § Enterprise transformation – Discover and gain intellectual control of application relationships and structures – Document your applications from the code itself – Find assets required for test cases – Accelerate transformation projects § IT Governance – Improve quality and speed of change analysis – Make visible dependencies across applications and application teams – Gain transparency into outsourced development § SOA – Discover assets for reuse in a SOA

Keys to Success • Successful Alignment of IT and Business • Understanding and Enforcing your Best Practices and Best Architecture • Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets • Keep Design Assets and Code insync/aligned/coordinated • Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC • Early Focus on Quality and Testing • Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets
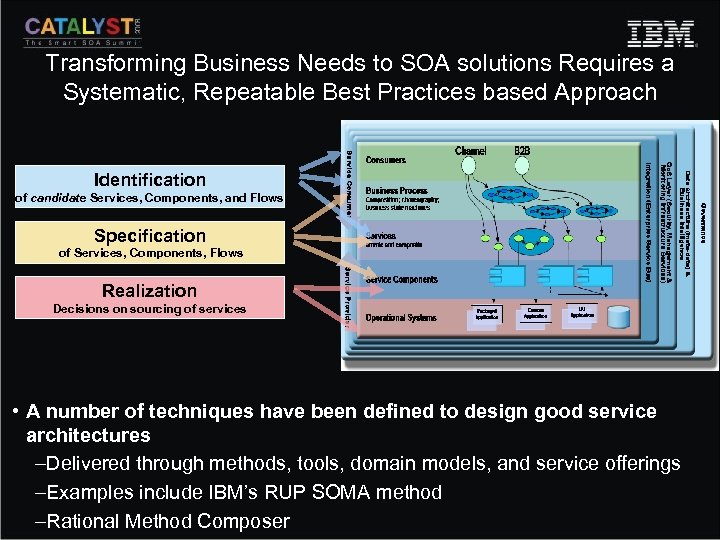
Transforming Business Needs to SOA solutions Requires a Systematic, Repeatable Best Practices based Approach Identification of candidate Services, Components, and Flows Specification of Services, Components, Flows Realization Decisions on sourcing of services • A number of techniques have been defined to design good service architectures –Delivered through methods, tools, domain models, and service offerings –Examples include IBM’s RUP SOMA method –Rational Method Composer

Example: Candidate Service Definition using SOMA Service Specification defines the dependencies, composition, exposure decisions, messages, quality of service constraints and decisions regarding the management of state within a service. Apply Service Litmus Tests & Document Exposure Decisions Use Service Litmus Tests to make service exposure decisions – “From my candidate services, which ones I choose to expose? ” Service Model Service Exposure Decisions Identify Service Dependencies Detailed review of the service may expose service dependencies on other services or applications that will be used to realize the functionality of the service. Identify Services Composition and Flow Review of functional areas and business processes will elaborate the composition of services from other services and their flow to enable the business function. (Service) Flow Specification describes the choreography between services. Identify Quality of Service Requirements Use non-functional requirements to specify the desired quality of service Quality Of Service Identify and specify the format and content of input and output messages of a service. Service Messages Specification Document State Management Decisions Sometimes the composition of services requires management of state. Document these decisions such as the answer to “What kind of persistence will be used and how will to be enabled? ” Service Dependencies Service Composition State Management Decisions
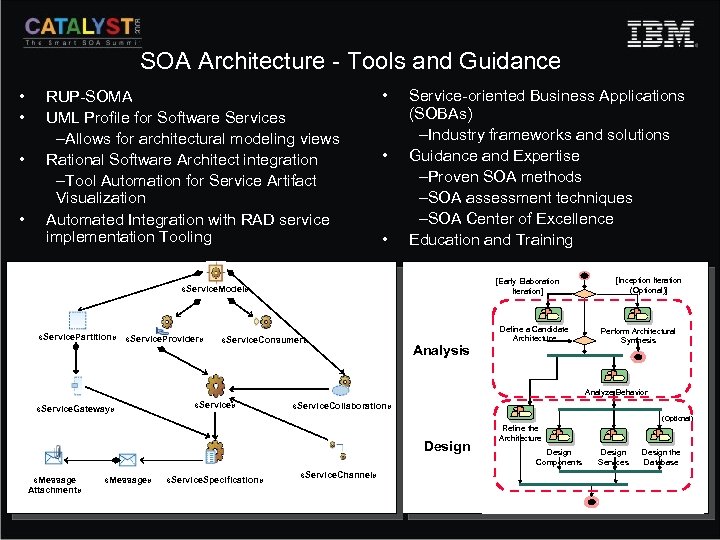
SOA Architecture - Tools and Guidance • • RUP-SOMA UML Profile for Software Services –Allows for architectural modeling views Rational Software Architect integration –Tool Automation for Service Artifact Visualization Automated Integration with RAD service implementation Tooling • • • Service-oriented Business Applications (SOBAs) –Industry frameworks and solutions Guidance and Expertise –Proven SOA methods –SOA assessment techniques –SOA Center of Excellence Education and Training [Early Elaboration Iteration] «Service. Model» «Service. Partition» «Service. Provider» «Service. Consumer» Analysis Define a Candidate Architecture [Inception Iteration (Optional)] Perform Architectural Synthesis Analyze Behavior «Service. Gateway» «Service. Collaboration» (Optional) Design «Message Attachment» «Message» «Service. Specification» «Service. Channel» Refine the Architecture Design Components Design Services Design the Database
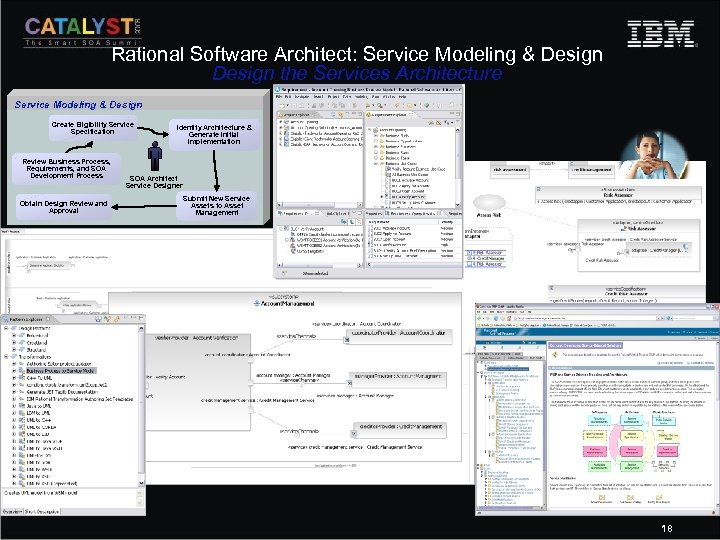
Rational Software Architect: Service Modeling & Design the Services Architecture Service Modeling & Design Create Eligibility Service Specification Review Business Process, Requirements, and SOA Development Process Obtain Design Review and Approval Identify Architecture & Generate Initial Implementation SOA Architect Service Designer Submit New Service Assets to Asset Management 18

Rational Application Developer: Web Services Development and Testing • Discover, create, build, test, deploy & publish Web services • Build new Web services or enable existing apps for WS-I compliance • Discover & consume existing Web services • Little to no coding to enable existing assets • Low learning curve • High productivity

Keys to Success • Successful Alignment of IT and Business • Understanding and Enforcing your Best Practices and Architecture • Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets • Keep Design Assets and Code insync/aligned/coordinated • Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC • Early Focus on Quality and Testing • Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets
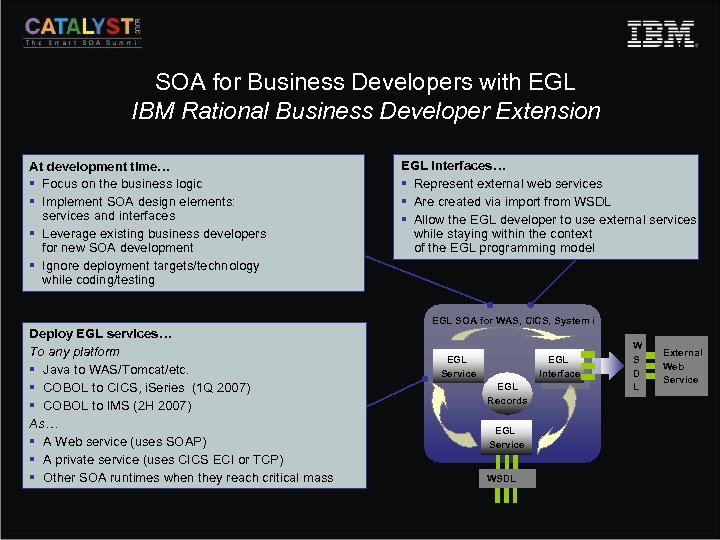
SOA for Business Developers with EGL IBM Rational Business Developer Extension At development time… § Focus on the business logic § Implement SOA design elements: services and interfaces § Leverage existing business developers for new SOA development § Ignore deployment targets/technology while coding/testing EGL interfaces… § Represent external web services § Are created via import from WSDL § Allow the EGL developer to use external services while staying within the context of the EGL programming model EGL SOA for WAS, CICS, System i Deploy EGL services… To any platform § Java to WAS/Tomcat/etc. § COBOL to CICS, i. Series (1 Q 2007) § COBOL to IMS (2 H 2007) As… § A Web service (uses SOAP) § A private service (uses CICS ECI or TCP) § Other SOA runtimes when they reach critical mass EGL Service EGL Interface EGL Records EGL Service WSDL W S D L External Web Service

Keys to Success • Successful Alignment of IT and Business • Understanding and Enforcing your Best Practices and Architecture • Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets • Keep Design Assets and Code insync/aligned/coordinated • Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC • Early Focus on Quality and Testing • Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets

Challenges to Understanding and Enforcing Architecture • Achieve Architecture Consistency • Enforce Architectural Decisions • Ensure consistent use of best practices for re-occurring problems – Apply best practices for functional and non-functional requirements • Harness existing Architectural specifications often gathered only in mindshare or text • Alleviate issues related to completely hand coded solutions (unnecessary time consumed, lack of consistency, etc)
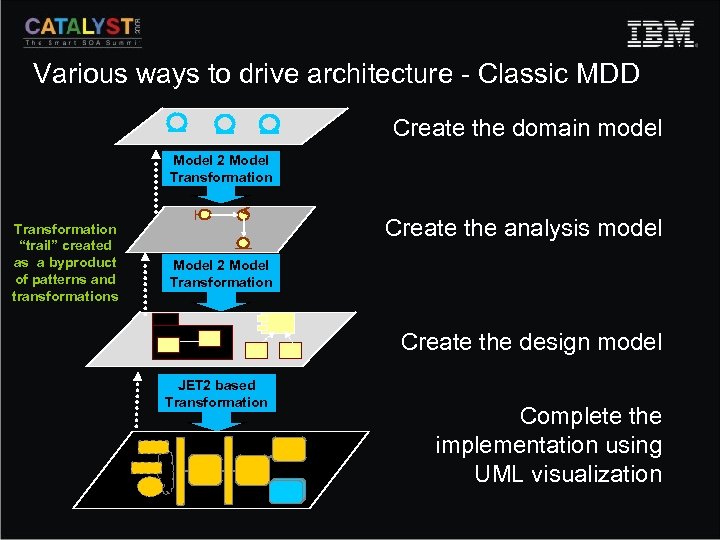
Various ways to drive architecture - Classic MDD Create the domain model Model 2 Model Transformation “trail” created as a byproduct of patterns and transformations Create the analysis model Model 2 Model Transformation Create the design model JET 2 based Transformation Complete the implementation using UML visualization
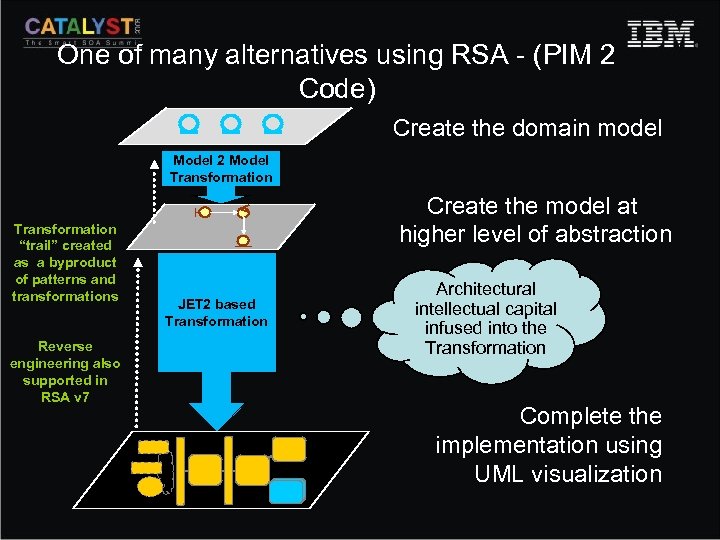
One of many alternatives using RSA - (PIM 2 Code) Create the domain model Model 2 Model Transformation “trail” created as a byproduct of patterns and transformations Reverse engineering also supported in RSA v 7 Create the model at higher level of abstraction JET 2 based Transformation Architectural intellectual capital infused into the Transformation Complete the implementation using UML visualization

High level business benefits • Improve time to market – Automatically generate infrastructure (CRUD, Transactional Logic, etc) • Automatically infuse best practices into applications – Functional – Non-Functional • Minimize risk and increase productivity around Globally Distributed Development (GDD) • Automatic traceability from requirements, thru model, into code (Compliance) • Automatic generation of J-Unit and other test code
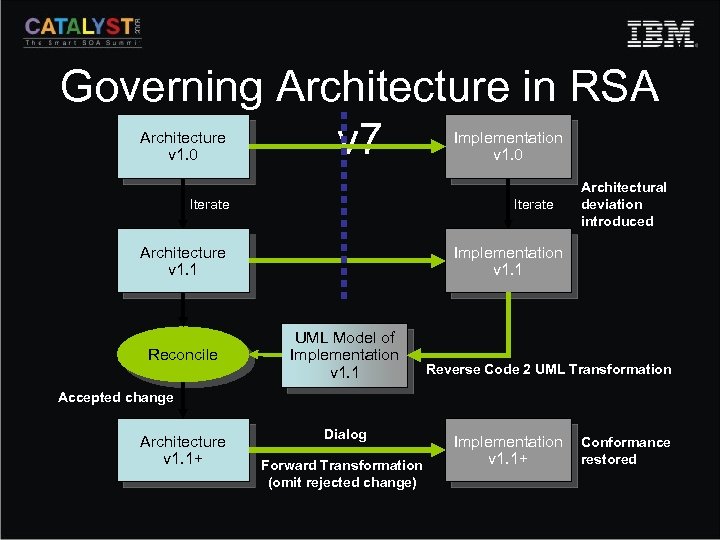
Governing Architecture in RSA v 7 Architecture v 1. 0 Implementation v 1. 0 Iterate Architecture v 1. 1 Reconcile Architectural deviation introduced Implementation v 1. 1 UML Model of Implementation v 1. 1 Reverse Code 2 UML Transformation Accepted change Architecture v 1. 1+ Dialog Forward Transformation (omit rejected change) Implementation v 1. 1+ Conformance restored

Keys to Success • Successful Alignment of IT and Business • Understanding and Enforcing your Best Practices and Architecture • Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets • Keep Design Assets and Code insync/aligned/coordinated • Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC • Early Focus on Quality and Testing • Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets

Rational Tester for SOA Quality Code free test of GUI-less web services • Simplify testing of GUI-less services – Automated generation of web service test client • Eliminate need for manual coding Test log details – Automated data correlation and data driven testing through a code-free test environment – Supporting wide variety of users on a broad range of platforms • Simplify service integration testing – Automated test creation from Web Services BPEL resources (from WBM) Test creation WS-BPEL Create, comprehend, modify, and execute a functional or performance test – Graphical test editor enables both high-level and deeper detail views – Supports Web services standards (e. g. SOAP, HTTP(S), JMS, WS-Security, UDDI) Targeted at developers and the QA Team – Supports testing secure web services by means of using XML Signatures.

Rational Tester for SOA Quality Products target higher service reuse and improved business flexibility Enable quality management throughout the lifecycle A common, integrated platform for building, managing, deploying and testing projects across the entire delivery and deployment team Reduce cost and improve credibility with early detection of defects and an integrated lifecycle approach Ensure business flexibility Enhance organizational efficiencies Functional and performance testing of SOA applications complimented with automated workflows and services best practices Integrations between operations and pre-production. Ability to manage and automate quality across business processes Ensure compliance and customer satisfaction through predictability and high quality SOA implementations Improve return on investment of software delivery by streamlining business processes across the lifecycle Connecting software results to business objectives
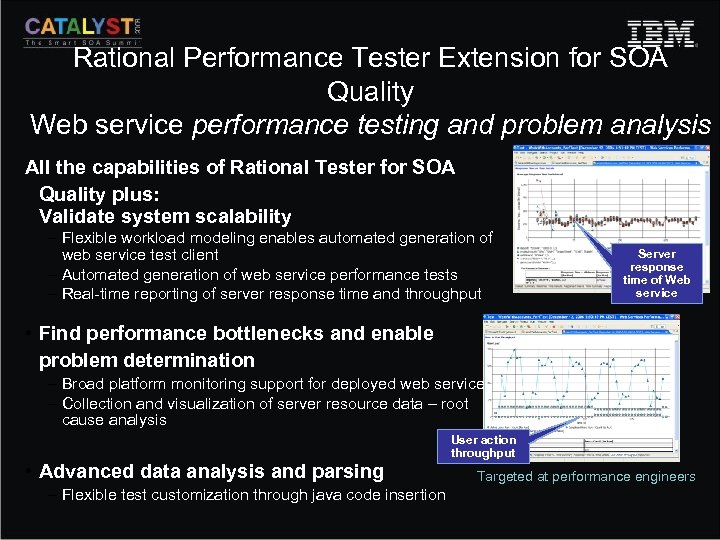
Rational Performance Tester Extension for SOA Quality Web service performance testing and problem analysis All the capabilities of Rational Tester for SOA Quality plus: Validate system scalability – Flexible workload modeling enables automated generation of web service test client – Automated generation of web service performance tests – Real-time reporting of server response time and throughput Server response time of Web service • Find performance bottlenecks and enable problem determination – Broad platform monitoring support for deployed web services – Collection and visualization of server resource data – root cause analysis • Advanced data analysis and parsing – Flexible test customization through java code insertion User action throughput Targeted at performance engineers

Keys to Success • Successful Alignment of IT and Business • Understanding and Enforcing your Best Practices and Architecture • Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets • Keep Design Assets and Code insync/aligned/coordinated • Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC • Early Focus on Quality and Testing • Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets
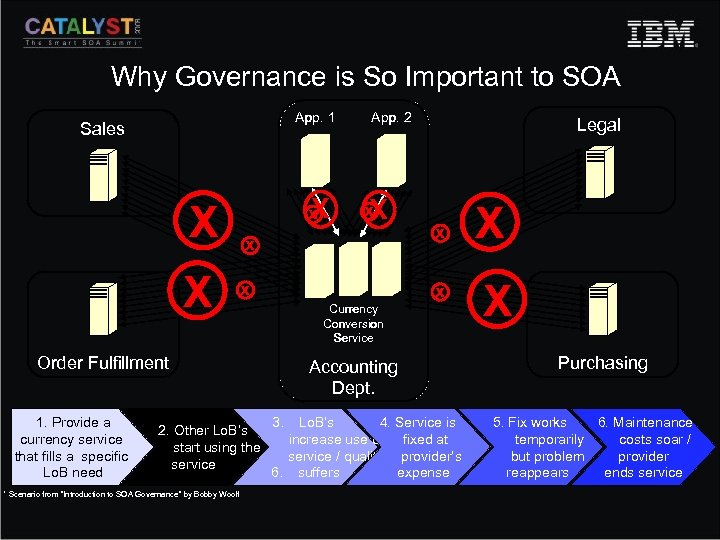
Why Governance is So Important to SOA App. 1 Sales X X X x x 2. Other Lo. B’s 4. start using the 5. service * Scenario from “Introduction to SOA Governance” by Bobby Woolf x X x Legal x x Currency Conversion Service Order Fulfillment 1. Provide a currency service that fills a specific Lo. B need App. 2 Accounting Dept. 3. 4. Service is Lo. B’s increase use of fixed at service / quality provider’s 6. suffers expense X X Purchasing 5. Fix works 6. Maintenance temporarily costs soar / but problem provider reappears ends service

What is SOA Governance? Governance: Establishing chains of responsibility, authority and communication to empower people (decision rights) Establishing measurement, policy and control mechanisms to enable people to carry out their roles and responsibilities IT Governance: Establishing decision making rights associated with IT Establishing mechanisms and policies used to measure and control the way IT decisions are made and carried out SOA Governance: Intersection of Business and IT governance focused on the lifecycle of services to ensure the business value of SOA Business Governance SOA Governance IT Governance SOA Governance is a catalyst for improving overall IT governance

SOA Governance with Rational Method Composer • IBM SOA Governance & Management Method – Defines Roles, Responsibilities, Tasks, and – Policies for SOA governance based on best practices and real-world experience • Tools can be used to help automate the governance process – Method content can be customized content based customer requirements • Manage SOA projects – Build project plans and allocate resources Best Practices Domain Experts Skills & Experience SOA Governance & Management Method Roles, responsibilities, tasks, policies Process Engineer Customize process templates based on company requirements Process templates Project Planning Project Manager Detailed project plan Resource allocation
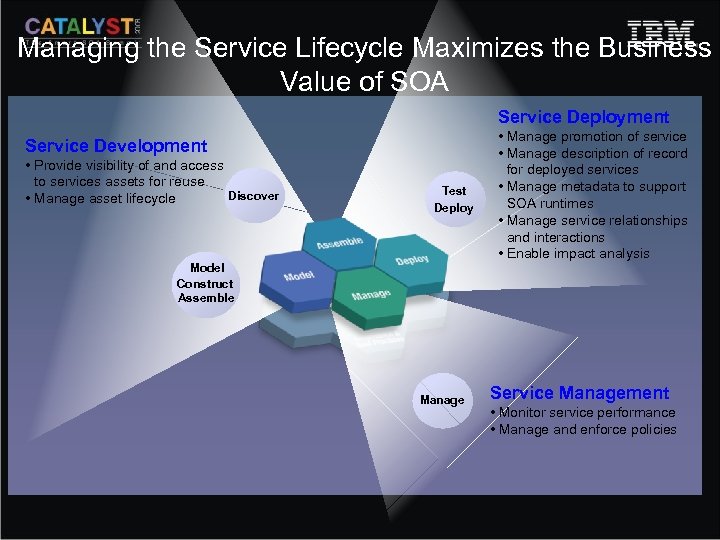
Managing the Service Lifecycle Maximizes the Business Value of SOA Service Deployment Service Development • Provide visibility of and access to services assets for reuse Discover • Manage asset lifecycle Test Deploy • Manage promotion of service • Manage description of record for deployed services • Manage metadata to support SOA runtimes • Manage service relationships and interactions • Enable impact analysis Model Construct Assemble Manage Service Management • Monitor service performance • Manage and enforce policies
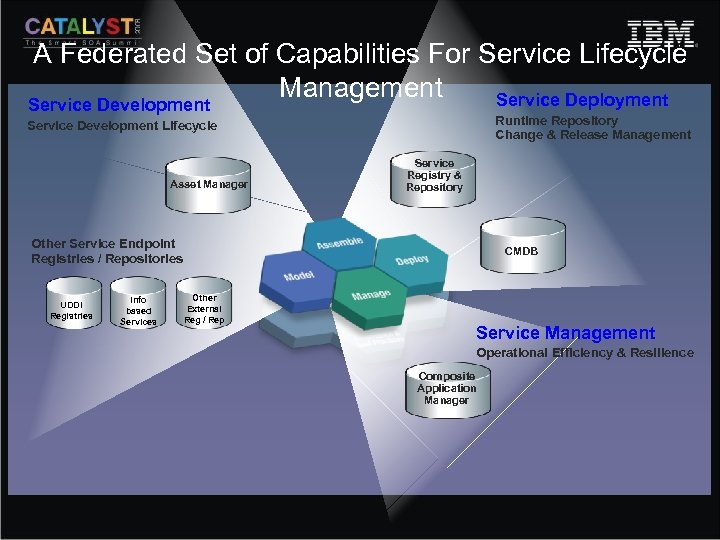
A Federated Set of Capabilities For Service Lifecycle Management Service Deployment Service Development Runtime Repository Change & Release Management Service Development Lifecycle Asset Manager Service Registry & Repository Other Service Endpoint Registries / Repositories UDDI Registries Info based Services CMDB Other External Reg / Rep Service Management Operational Efficiency & Resilience Composite Application Manager
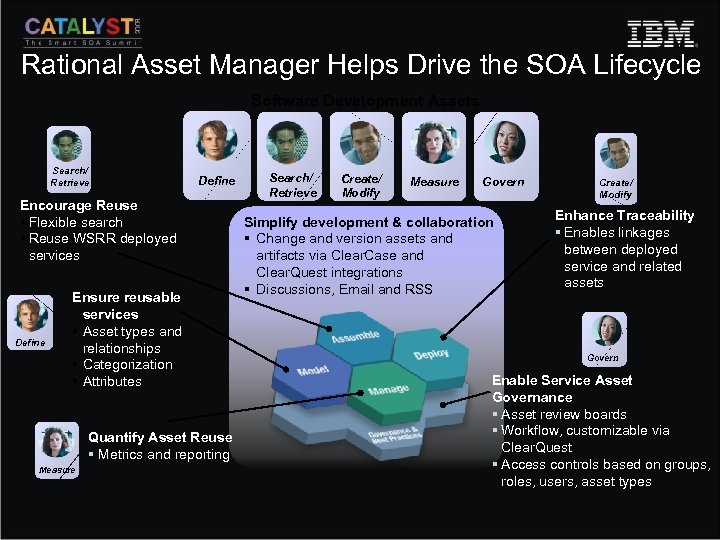
Rational Asset Manager Helps Drive the SOA Lifecycle Software Development Assets Search/ Retrieve Define Encourage Reuse § Flexible search § Reuse WSRR deployed services Define Ensure reusable services § Asset types and relationships § Categorization § Attributes Quantify Asset Reuse § Metrics and reporting Measure Search/ Retrieve Create/ Modify Measure Govern Simplify development & collaboration § Change and version assets and artifacts via Clear. Case and Clear. Quest integrations § Discussions, Email and RSS Create/ Modify Enhance Traceability § Enables linkages between deployed service and related assets Govern Enable Service Asset Governance § Asset review boards § Workflow, customizable via Clear. Quest § Access controls based on groups, roles, users, asset types
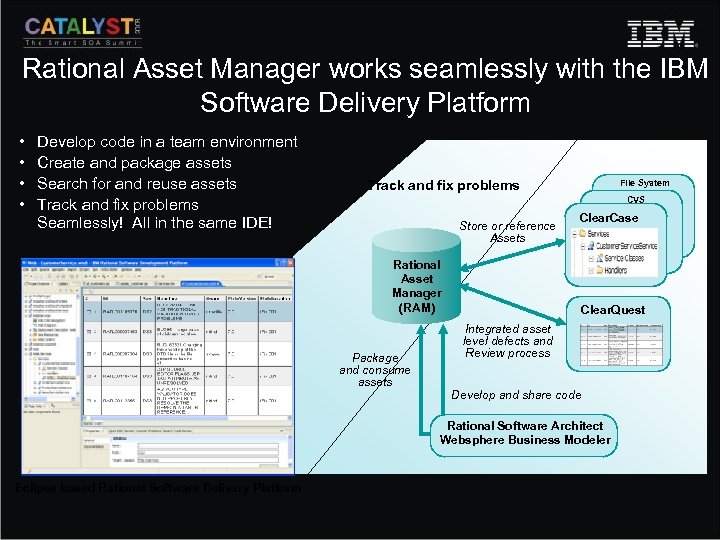
Rational Asset Manager works seamlessly with the IBM Software Delivery Platform • • Develop code in a team environment Create and package assets Search for and reuse assets Track and fix problems Seamlessly! All in the same IDE! Track and fix problems File System CVS Store or reference Assets Rational Asset Manager (RAM) Package and consume assets Clear. Case Clear. Quest Integrated asset level defects and Review process Develop and share code Rational Software Architect Websphere Business Modeler Eclipse based Rational Software Delivery Platform
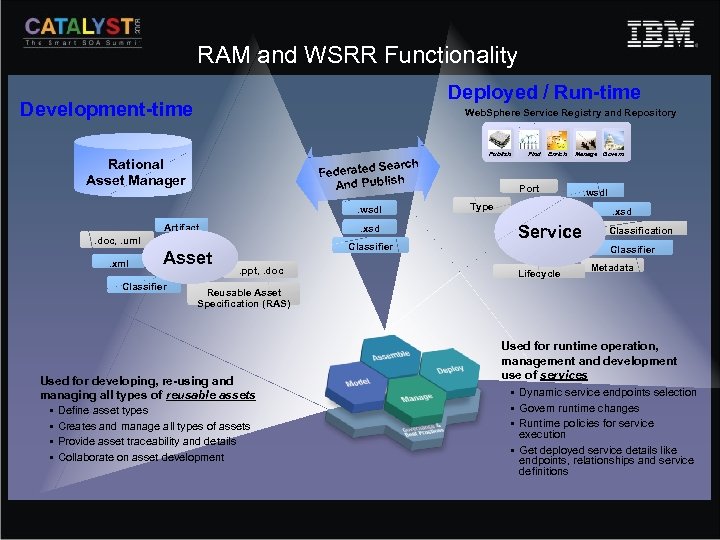
RAM and WSRR Functionality Deployed / Run-time Development-time Web. Sphere Service Registry and Repository Rational Asset Manager Search Federated h And Publis. wsdl Artifact . xsd . doc, . uml. xml Asset Classifier. ppt, . doc Publish Find Enrich Manage Govern Port Type . wsdl. xsd Service Classification Classifier Lifecycle Metadata Reusable Asset Specification (RAS) Used for developing, re-using and managing all types of reusable assets § Define asset types § Creates and manage all types of assets § Provide asset traceability and details § Collaborate on asset development Used for runtime operation, management and development use of services § Dynamic service endpoints selection § Govern runtime changes § Runtime policies for service execution § Get deployed service details like endpoints, relationships and service definitions

Summary • Focus of Enterprise Solutions Today – Service-oriented architecture – Model driven development – Business, domain, system, application…. . – Business innovation and optimization • Keys to Successful SOA – Successful Alignment of IT and Business – Understanding and Enforcing your Architecture – Taking Advantage of "heritage"/Mainframe/Core Assets – Keep Design Assets and Code in-sync/aligned/coordinated – Capture and Reuse of Architectural IC – Early Focus on Quality and Testing – Govern and Manage Effectively across E 2 E Assets

Thank you
0e7d8a634e322e7f0380138b1e79771a.ppt