347337bd365a5a0fdc30296eae184051.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Design Technology We all need Design technology as a part of life, its all about making things to help make life easier. In the next couple of weeks you will develop a better understanding of Design Technology
Design Technology We all need Design technology as a part of life, its all about making things to help make life easier. In the next couple of weeks you will develop a better understanding of Design Technology
 STRUCTURES • What are materials? Give some examples Materials are what we use to make things out of • What is meant by Technology? Technology is how things will work • What do we mean by Structures? A Structure is an arrangement of parts to create an end product, e. g. buildings, cars etc. We use materials and Technology to create more products • There are two types of structure. What are they? Man-made: these are generally made by us, e. g. Cars, toys etc Natural: These are generally made by nature, e. g. trees, grass etc
STRUCTURES • What are materials? Give some examples Materials are what we use to make things out of • What is meant by Technology? Technology is how things will work • What do we mean by Structures? A Structure is an arrangement of parts to create an end product, e. g. buildings, cars etc. We use materials and Technology to create more products • There are two types of structure. What are they? Man-made: these are generally made by us, e. g. Cars, toys etc Natural: These are generally made by nature, e. g. trees, grass etc
 STRUCTURES • In Design Technology we learn about Man-made structures, these can be put into two groups or types; 1. Shell Structures 2. Frame Structures A SHELL structure protects and contains something A FRAME structure is made up from a number of different parts that are joined together to support something • In your books write down 8 examples of Shell structures and 8 examples of Frame structures 1. Shell Structures: Bottles, Crash helmet, House, Car, Banana Skin, etc 2. Frame Structures: Human Skeleton, Bicycle, Crane, tennis racquet, etc
STRUCTURES • In Design Technology we learn about Man-made structures, these can be put into two groups or types; 1. Shell Structures 2. Frame Structures A SHELL structure protects and contains something A FRAME structure is made up from a number of different parts that are joined together to support something • In your books write down 8 examples of Shell structures and 8 examples of Frame structures 1. Shell Structures: Bottles, Crash helmet, House, Car, Banana Skin, etc 2. Frame Structures: Human Skeleton, Bicycle, Crane, tennis racquet, etc
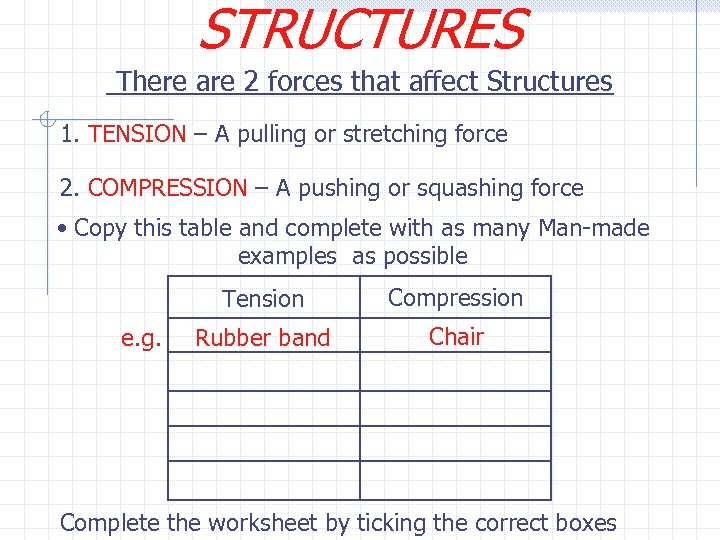 STRUCTURES There are 2 forces that affect Structures 1. TENSION – A pulling or stretching force 2. COMPRESSION – A pushing or squashing force • Copy this table and complete with as many Man-made examples as possible Tension e. g. Compression Rubber band Chair Complete the worksheet by ticking the correct boxes
STRUCTURES There are 2 forces that affect Structures 1. TENSION – A pulling or stretching force 2. COMPRESSION – A pushing or squashing force • Copy this table and complete with as many Man-made examples as possible Tension e. g. Compression Rubber band Chair Complete the worksheet by ticking the correct boxes
 STRUCTURES Task 1 Using a sheet of A 4 paper only, Design and build a structure to support a load of 5 kg. It must be a minimum distance of 35 mm above base level. (use of scissors and PVA glue permitted) HOMEWORK Draw 2 different designs for your possible structure giving sizes and details of how to make them
STRUCTURES Task 1 Using a sheet of A 4 paper only, Design and build a structure to support a load of 5 kg. It must be a minimum distance of 35 mm above base level. (use of scissors and PVA glue permitted) HOMEWORK Draw 2 different designs for your possible structure giving sizes and details of how to make them
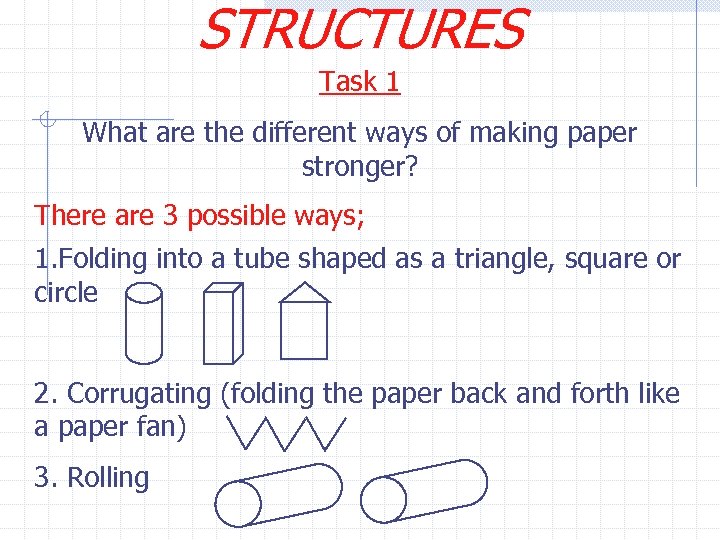 STRUCTURES Task 1 What are the different ways of making paper stronger? There are 3 possible ways; 1. Folding into a tube shaped as a triangle, square or circle 2. Corrugating (folding the paper back and forth like a paper fan) 3. Rolling
STRUCTURES Task 1 What are the different ways of making paper stronger? There are 3 possible ways; 1. Folding into a tube shaped as a triangle, square or circle 2. Corrugating (folding the paper back and forth like a paper fan) 3. Rolling
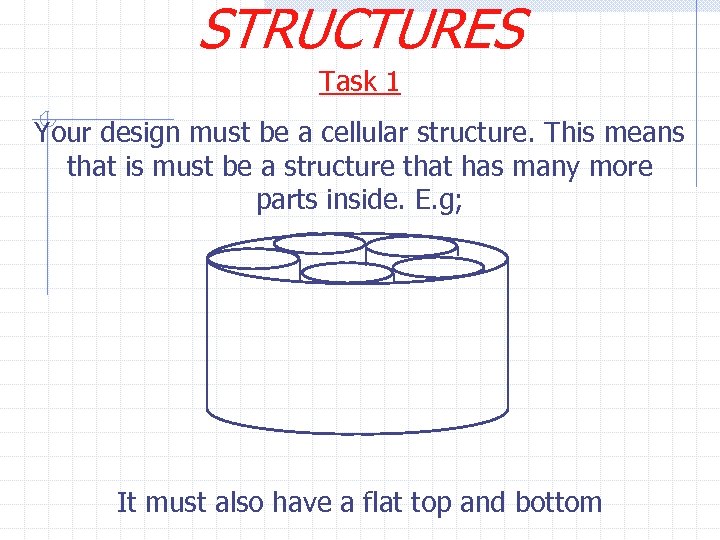 STRUCTURES Task 1 Your design must be a cellular structure. This means that is must be a structure that has many more parts inside. E. g; It must also have a flat top and bottom
STRUCTURES Task 1 Your design must be a cellular structure. This means that is must be a structure that has many more parts inside. E. g; It must also have a flat top and bottom
 Starter Write down a word related to Technology, each beginning with the letter from: e. g: Drawing T E E S C I H G N
Starter Write down a word related to Technology, each beginning with the letter from: e. g: Drawing T E E S C I H G N
 Starter Copy all questions into books first then answer. • What is the difference between Man-made and natural structures? • What is the force acting on a chair? • How do we know that this is the force acting on the chair? • Is a plastic chair a man-made or natural structure? • What are the shapes we can use to make paper stronger?
Starter Copy all questions into books first then answer. • What is the difference between Man-made and natural structures? • What is the force acting on a chair? • How do we know that this is the force acting on the chair? • Is a plastic chair a man-made or natural structure? • What are the shapes we can use to make paper stronger?
 STRUCTURES Task 1 Making your paper structure. 1. You will have 15 minutes to make you final plan on paper 2. You will then have 50 minutes to make and complete your structure Remember to use only a thin layer of Glue to stick the paper together. TAKE YOUR TIME WHEN PLANNING AND MAKING
STRUCTURES Task 1 Making your paper structure. 1. You will have 15 minutes to make you final plan on paper 2. You will then have 50 minutes to make and complete your structure Remember to use only a thin layer of Glue to stick the paper together. TAKE YOUR TIME WHEN PLANNING AND MAKING
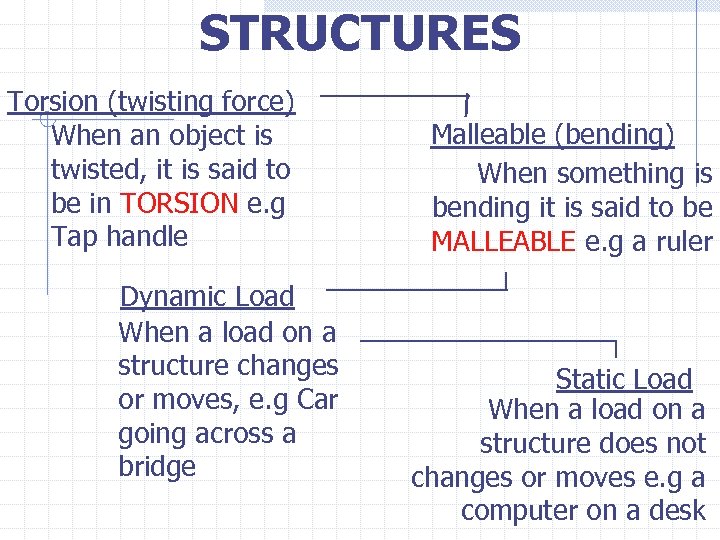 STRUCTURES Torsion (twisting force) When an object is twisted, it is said to be in TORSION e. g Tap handle Dynamic Load When a load on a structure changes or moves, e. g Car going across a bridge Malleable (bending) When something is bending it is said to be MALLEABLE e. g a ruler Static Load When a load on a structure does not changes or moves e. g a computer on a desk
STRUCTURES Torsion (twisting force) When an object is twisted, it is said to be in TORSION e. g Tap handle Dynamic Load When a load on a structure changes or moves, e. g Car going across a bridge Malleable (bending) When something is bending it is said to be MALLEABLE e. g a ruler Static Load When a load on a structure does not changes or moves e. g a computer on a desk
 STRUCTURES • Copy these tables and complete with Man-made examples Torsion Malleable Dynamic Static
STRUCTURES • Copy these tables and complete with Man-made examples Torsion Malleable Dynamic Static
 STRUCTURES HOMEWORK Complete exercise sheet. Do all your work on the sheet. To be handed in next lesson
STRUCTURES HOMEWORK Complete exercise sheet. Do all your work on the sheet. To be handed in next lesson
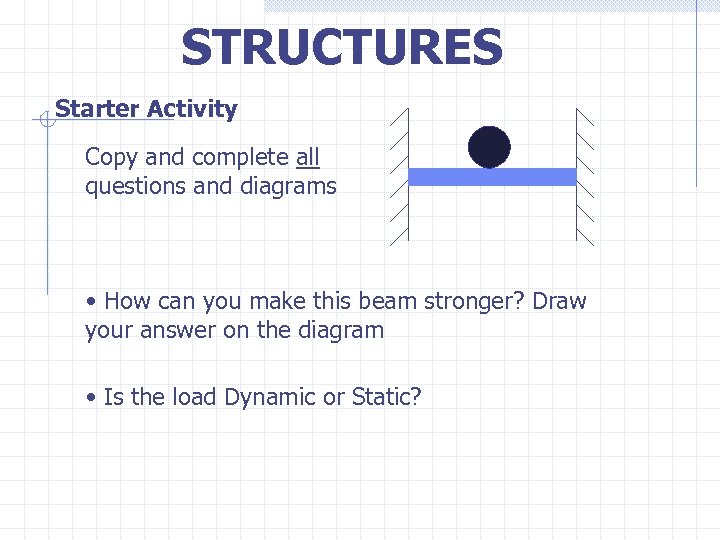 STRUCTURES Starter Activity Copy and complete all questions and diagrams • How can you make this beam stronger? Draw your answer on the diagram • Is the load Dynamic or Static?
STRUCTURES Starter Activity Copy and complete all questions and diagrams • How can you make this beam stronger? Draw your answer on the diagram • Is the load Dynamic or Static?
 STRUCTURES Starter Activity Copy this diagram • How can you make this beam stronger? Draw your answer on the diagram • Is the load Dynamic or Static? Static, as it is not moving
STRUCTURES Starter Activity Copy this diagram • How can you make this beam stronger? Draw your answer on the diagram • Is the load Dynamic or Static? Static, as it is not moving
 STRUCTURES Evaluation Now that you’ve tested your Paper structures, you need to evaluate them. Think about: 1. Why did it fail? 2. How could you strengthen your structure further? 3. What would you have done differently? 4. What other improvements could you have done? 5. Draw your new plan and a sketch of what it would have looked like if you were to redo the structure. 6. Think of more questions you could ask yourself to help understand how you would do things differently if you were to make it again
STRUCTURES Evaluation Now that you’ve tested your Paper structures, you need to evaluate them. Think about: 1. Why did it fail? 2. How could you strengthen your structure further? 3. What would you have done differently? 4. What other improvements could you have done? 5. Draw your new plan and a sketch of what it would have looked like if you were to redo the structure. 6. Think of more questions you could ask yourself to help understand how you would do things differently if you were to make it again
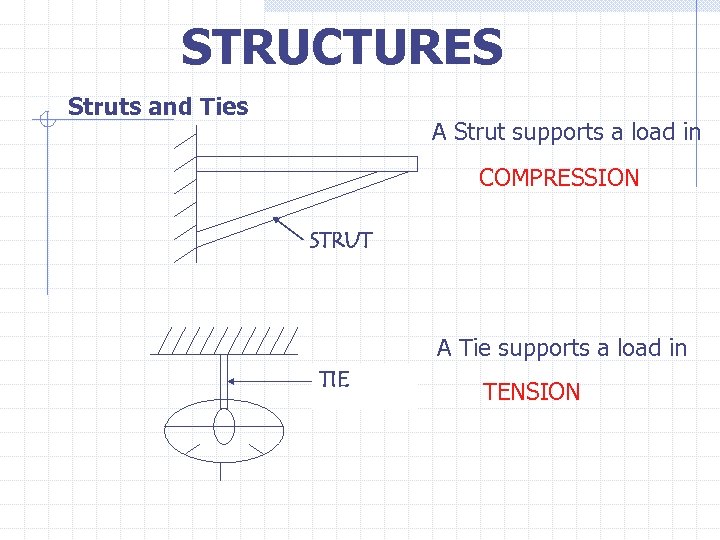 STRUCTURES Struts and Ties A Strut supports a load in COMPRESSION STRUT A Tie supports a load in TIE TENSION
STRUCTURES Struts and Ties A Strut supports a load in COMPRESSION STRUT A Tie supports a load in TIE TENSION
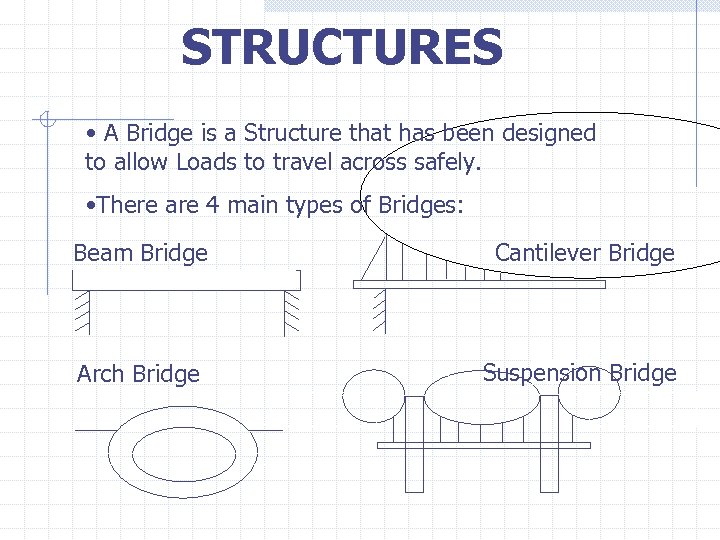 STRUCTURES • A Bridge is a Structure that has been designed to allow Loads to travel across safely. • There are 4 main types of Bridges: Beam Bridge Cantilever Bridge Arch Bridge Suspension Bridge
STRUCTURES • A Bridge is a Structure that has been designed to allow Loads to travel across safely. • There are 4 main types of Bridges: Beam Bridge Cantilever Bridge Arch Bridge Suspension Bridge
 STRUCTURES Bridges – Girder Truss types Bowstring Lattice Truss Howe Truss Warren Girder What is the most common shape you can see in all of these Trusses? Triangles. Using Triangles to strengthen a structure is called TRIANGULATION
STRUCTURES Bridges – Girder Truss types Bowstring Lattice Truss Howe Truss Warren Girder What is the most common shape you can see in all of these Trusses? Triangles. Using Triangles to strengthen a structure is called TRIANGULATION
 Name 4 types of Bridge Write down 5 different types of forces that act upon structures Draw a diagram for each force that you have named in the last question How do you think that this may help you when designing a bridge?
Name 4 types of Bridge Write down 5 different types of forces that act upon structures Draw a diagram for each force that you have named in the last question How do you think that this may help you when designing a bridge?
 What shape is the most common in some bridges? what is the special name for this? Draw a diagram for Tension What product might be in Tension What force is the opposite to tension?
What shape is the most common in some bridges? what is the special name for this? Draw a diagram for Tension What product might be in Tension What force is the opposite to tension?
 Name 4 types of forces that act upon a structure Name 3 shapes that help make a paper structure stronger Draw a diagram for each shape that makes a structure stronger with labels How do you think that this may help you when designing a bridge?
Name 4 types of forces that act upon a structure Name 3 shapes that help make a paper structure stronger Draw a diagram for each shape that makes a structure stronger with labels How do you think that this may help you when designing a bridge?
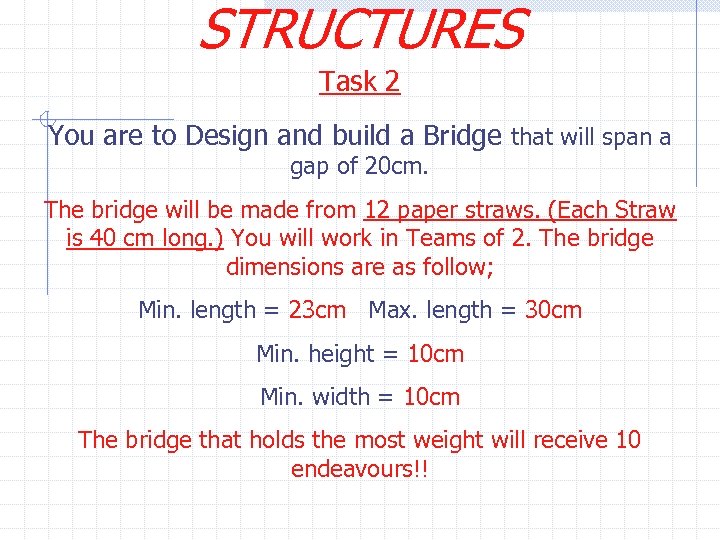 STRUCTURES Task 2 You are to Design and build a Bridge that will span a gap of 20 cm. The bridge will be made from 12 paper straws. (Each Straw is 40 cm long. ) You will work in Teams of 2. The bridge dimensions are as follow; Min. length = 23 cm Max. length = 30 cm Min. height = 10 cm Min. width = 10 cm The bridge that holds the most weight will receive 10 endeavours!!
STRUCTURES Task 2 You are to Design and build a Bridge that will span a gap of 20 cm. The bridge will be made from 12 paper straws. (Each Straw is 40 cm long. ) You will work in Teams of 2. The bridge dimensions are as follow; Min. length = 23 cm Max. length = 30 cm Min. height = 10 cm Min. width = 10 cm The bridge that holds the most weight will receive 10 endeavours!!
 STRUCTURES Task 2 1. You need to start sketching some possible ideas in your books individually. (approx 30 mins) 2. When you have done this you must pair up and develop your ideas so that your team will have 2 possible solutions. Make sure you sketch these and have plenty of notes 3. Accurately draw out your chosen ideas, with measurements, as plans for making on A 3 4. Experiment different methods of joining the straws together using glue (hint: use strips of paper as ‘plasters’ to join at different angles)
STRUCTURES Task 2 1. You need to start sketching some possible ideas in your books individually. (approx 30 mins) 2. When you have done this you must pair up and develop your ideas so that your team will have 2 possible solutions. Make sure you sketch these and have plenty of notes 3. Accurately draw out your chosen ideas, with measurements, as plans for making on A 3 4. Experiment different methods of joining the straws together using glue (hint: use strips of paper as ‘plasters’ to join at different angles)
 STRUCTURES Task 2 1. Once you have chosen your two favourite designs and have experimented different methods of joining the straws together, make your two models half the size of the final one. 2. Choose your favourite out of the two and make the full size version with the correct measurements 3. ALWAYS REMEMBER TO TAKE YOUR TIME AND MEASURE ACCURATELY WHEN DESIGNING AND MAKING
STRUCTURES Task 2 1. Once you have chosen your two favourite designs and have experimented different methods of joining the straws together, make your two models half the size of the final one. 2. Choose your favourite out of the two and make the full size version with the correct measurements 3. ALWAYS REMEMBER TO TAKE YOUR TIME AND MEASURE ACCURATELY WHEN DESIGNING AND MAKING
 STRUCTURES Task 2 You are to Design and build a Bridge that will span a gap of 20 cm. The bridge will be made from 12 paper straws. You will work in Teams of 2. The bridge dimensions are as follow; Min. length = 23 cm Max. length = 30 cm Min. height = 10 cm Min. width = 10 cm The bridge that holds the most weight will receive 8 endeavours!!
STRUCTURES Task 2 You are to Design and build a Bridge that will span a gap of 20 cm. The bridge will be made from 12 paper straws. You will work in Teams of 2. The bridge dimensions are as follow; Min. length = 23 cm Max. length = 30 cm Min. height = 10 cm Min. width = 10 cm The bridge that holds the most weight will receive 8 endeavours!!
 Evaluation Evaluate your work. The questions are only a guide, you should write in full sentence answers 1. What did you find difficult whilst making your structure? 2. What parts of your structure do you feel did not come out as planned? 3. What would you do to improve the design of your structure. Describe and draw your answer 4. If you were to make your structure again with less straws, how would you do it? Draw a diagram with notes and measurements to explain your answer 5. What have you learnt about Structures? You should have many more details to add to your Evaluation
Evaluation Evaluate your work. The questions are only a guide, you should write in full sentence answers 1. What did you find difficult whilst making your structure? 2. What parts of your structure do you feel did not come out as planned? 3. What would you do to improve the design of your structure. Describe and draw your answer 4. If you were to make your structure again with less straws, how would you do it? Draw a diagram with notes and measurements to explain your answer 5. What have you learnt about Structures? You should have many more details to add to your Evaluation


 WORKSHOP SAFETY NEVER use a tool or machine in the workshop unless you’ve been shown how to One person at a time allowed in the yellow box areas ALWAYS wear an apron during a practical ALWAYS tie long hair or any loose clothing up Eye Protection must be worn when using Machinery No Running in Workshops at ANY time IF IN DOUBT ALWAYS ASK
WORKSHOP SAFETY NEVER use a tool or machine in the workshop unless you’ve been shown how to One person at a time allowed in the yellow box areas ALWAYS wear an apron during a practical ALWAYS tie long hair or any loose clothing up Eye Protection must be worn when using Machinery No Running in Workshops at ANY time IF IN DOUBT ALWAYS ASK
 MAKING YOUR STRUCTURE Lay tools that are to be used on the centre of your desk - DO NOT PLACE ON THE EDGE OF THE TABLE!! Collect 3 horizontal pieces from the front. 3 per pair/ group Place bench hook in the vice Measure the two end vertical uprights on your plan Place the marked piece on the bench hook and make an initial cut Continue cutting at an angle Once your two vertical end pieces are cut put your hands up
MAKING YOUR STRUCTURE Lay tools that are to be used on the centre of your desk - DO NOT PLACE ON THE EDGE OF THE TABLE!! Collect 3 horizontal pieces from the front. 3 per pair/ group Place bench hook in the vice Measure the two end vertical uprights on your plan Place the marked piece on the bench hook and make an initial cut Continue cutting at an angle Once your two vertical end pieces are cut put your hands up
 MAKING YOUR STRUCTURE Gluing your Structures Glue pieces of wood to each other. NOT to the paper Once the vertical uprights have been glued to the Horizontal rails, measure & cut the remaining pieces Make sure your names are on your work Use masking tape to attach structures to paper plan Place work in the tray at the front of the room Return tools to their correct places and tidy desk areas up
MAKING YOUR STRUCTURE Gluing your Structures Glue pieces of wood to each other. NOT to the paper Once the vertical uprights have been glued to the Horizontal rails, measure & cut the remaining pieces Make sure your names are on your work Use masking tape to attach structures to paper plan Place work in the tray at the front of the room Return tools to their correct places and tidy desk areas up


