Design.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 1
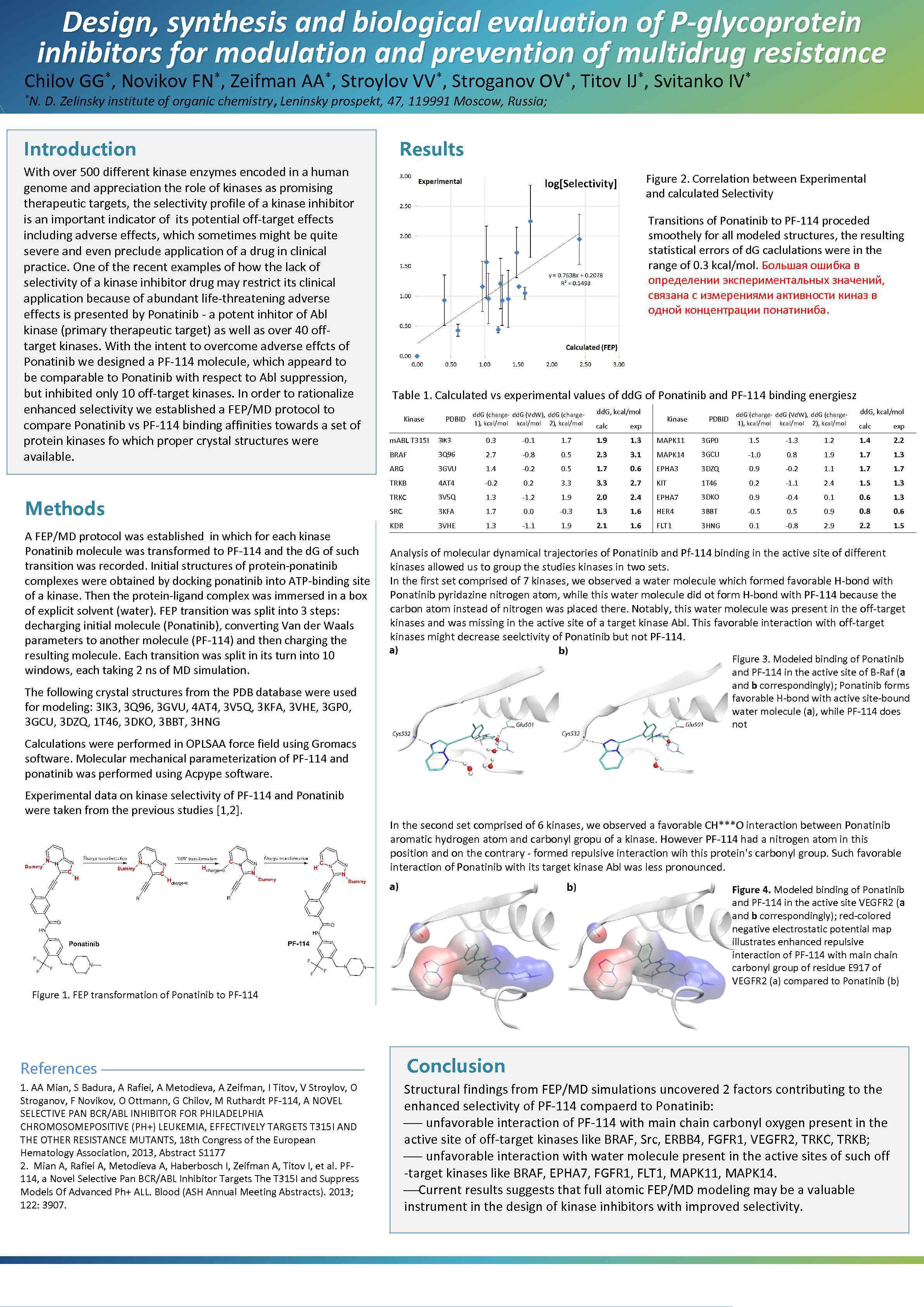
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of P-glycoprotein inhibitors for modulation and prevention of multidrug resistance Chilov *N. *, GG Novikov *, FN Zeifman *, AA Stroylov *, VV Stroganov *, OV D. Zelinsky institute of organic chemistry, Leninsky prospekt, 47, 119991 Moscow, Russia; Introduction With over 500 different kinase enzymes encoded in a human genome and appreciation the role of kinases as promising therapeutic targets, the selectivity profile of a kinase inhibitor is an important indicator of its potential off-target effects including adverse effects, which sometimes might be quite severe and even preclude application of a drug in clinical practice. One of the recent examples of how the lack of selectivity of a kinase inhibitor drug may restrict its clinical application because of abundant life-threatening adverse effects is presented by Ponatinib - a potent inhitor of Abl kinase (primary therapeutic target) as well as over 40 offtarget kinases. With the intent to overcome adverse effcts of Ponatinib we designed a PF-114 molecule, which appeard to be comparable to Ponatinib with respect to Abl suppression, but inhibited only 10 off-target kinases. In order to rationalize enhanced selectivity we established a FEP/MD protocol to compare Ponatinib vs PF-114 binding affinities towards a set of protein kinases fo which proper crystal structures were available. Titov *, IJ Svitanko * IV Results Figure 2. Correlation between Experimental and calculated Selectivity Transitions of Ponatinib to PF-114 proceded smoothely for all modeled structures, the resulting statistical errors of d. G caclulations were in the range of 0. 3 kcal/mol. Большая ошибка в определении экспериментальных значений, связана с измерениями активности киназ в одной концентрации понатиниба. Table 1. Calculated vs experimental values of dd. G of Ponatinib and PF-114 binding energiesz Kinase PDBID dd. G (charge- dd. G (Vd. W), dd. G (charge 1), kcal/mol 2), kcal/mol dd. G, kcal/mol calc Kinase exp PDBID dd. G (charge- dd. G (Vd. W), dd. G (charge 1), kcal/mol 2), kcal/mol dd. G, kcal/mol calc exp A FEP/MD protocol was established in which for each kinase Ponatinib molecule was transformed to PF-114 and the d. G of such transition was recorded. Initial structures of protein-ponatinib complexes were obtained by docking ponatinib into ATP-binding site of a kinase. Then the protein-ligand complex was immersed in a box of explicit solvent (water). FEP transition was split into 3 steps: decharging initial molecule (Ponatinib), converting Van der Waals parameters to another molecule (PF-114) and then charging the resulting molecule. Each transition was split in its turn into 10 windows, each taking 2 ns of MD simulation. 3 IK 3 0. 3 -0. 1 1. 7 1. 9 1. 3 MAPK 11 3 GP 0 1. 5 -1. 3 1. 2 1. 4 2. 2 BRAF 3 Q 96 2. 7 -0. 8 0. 5 2. 3 3. 1 MAPK 14 3 GCU -1. 0 0. 8 1. 9 1. 7 1. 3 ARG 3 GVU 1. 4 -0. 2 0. 5 1. 7 0. 6 EPHA 3 3 DZQ 0. 9 -0. 2 1. 1 1. 7 TRKB Methods m. ABL T 315 I 4 AT 4 -0. 2 3. 3 2. 7 KIT 1 T 46 0. 2 -1. 1 2. 4 1. 5 1. 3 TRKC 3 V 5 Q 1. 3 -1. 2 1. 9 2. 0 2. 4 EPHA 7 3 DKO 0. 9 -0. 4 0. 1 0. 6 1. 3 SRC 3 KFA 1. 7 0. 0 -0. 3 1. 6 HER 4 3 BBT -0. 5 0. 9 0. 8 0. 6 KDR 3 VHE 1. 3 -1. 1 1. 9 2. 1 1. 6 FLT 1 3 HNG 0. 1 -0. 8 2. 9 2. 2 1. 5 Analysis of molecular dynamical trajectories of Ponatinib and Pf-114 binding in the active site of different kinases allowed us to group the studies kinases in two sets. In the first set comprised of 7 kinases, we observed a water molecule which formed favorable H-bond with Ponatinib pyridazine nitrogen atom, while this water molecule did ot form H-bond with PF-114 because the carbon atom instead of nitrogen was placed there. Notably, this water molecule was present in the off-target kinases and was missing in the active site of a target kinase Abl. This favorable interaction with off-target kinases might decrease seelctivity of Ponatinib but not PF-114. Figure 3. Modeled binding of Ponatinib and PF-114 in the active site of B-Raf (a and b correspondingly); Ponatinib forms favorable H-bond with active site-bound water molecule (a), while PF-114 does not The following crystal structures from the PDB database were used for modeling: 3 IK 3, 3 Q 96, 3 GVU, 4 AT 4, 3 V 5 Q, 3 KFA, 3 VHE, 3 GP 0, 3 GCU, 3 DZQ, 1 T 46, 3 DKO, 3 BBT, 3 HNG Calculations were performed in OPLSAA force field using Gromacs software. Molecular mechanical parameterization of PF-114 and ponatinib was performed using Acpype software. Experimental data on kinase selectivity of PF-114 and Ponatinib were taken from the previous studies [1, 2]. In the second set comprised of 6 kinases, we observed a favorable CH***O interaction between Ponatinib aromatic hydrogen atom and carbonyl gropu of a kinase. However PF-114 had a nitrogen atom in this position and on the contrary - formed repulsive interaction wih this protein's carbonyl group. Such favorable interaction of Ponatinib with its target kinase Abl was less pronounced. Figure 4. Modeled binding of Ponatinib and PF-114 in the active site VEGFR 2 (a and b correspondingly); red-colored negative electrostatic potential map illustrates enhanced repulsive interaction of PF-114 with main chain carbonyl group of residue E 917 of VEGFR 2 (a) compared to Ponatinib (b) Figure 1. FEP transformation of Ponatinib to PF-114 References Conclusion 1. AA Mian, S Badura, A Rafiei, A Metodieva, A Zeifman, I Titov, V Stroylov, O Stroganov, F Novikov, O Ottmann, G Chilov, M Ruthardt PF-114, A NOVEL SELECTIVE PAN BCR/ABL INHIBITOR FOR PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOMEPOSITIVE (PH+) LEUKEMIA, EFFECTIVELY TARGETS T 315 I AND THE OTHER RESISTANCE MUTANTS, 18 th Congress of the European Hematology Association, 2013, Abstract S 1177 2. Mian A, Rafiei A, Metodieva A, Haberbosch I, Zeifman A, Titov I, et al. PF 114, a Novel Selective Pan BCR/ABL Inhibitor Targets The T 315 I and Suppress Models Of Advanced Ph+ ALL. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts). 2013; 122: 3907. Structural findings from FEP/MD simulations uncovered 2 factors contributing to the enhanced selectivity of PF-114 compaerd to Ponatinib: ¾- unfavorable interaction of PF-114 with main chain carbonyl oxygen present in the active site of off-target kinases like BRAF, Src, ERBB 4, FGFR 1, VEGFR 2, TRKC, TRKB; ¾- unfavorable interaction with water molecule present in the active sites of such off -target kinases like BRAF, EPHA 7, FGFR 1, FLT 1, MAPK 14. ¾Current results suggests that full atomic FEP/MD modeling may be a valuable instrument in the design of kinase inhibitors with improved selectivity.
Design.pptx