a573fa60abc05d5c7af93ac37315a8b2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62

Design of UAV Systems Objectives Lesson objective - to discuss UAV Conceptual Design including… • What does it cover? • What are the issues? • Why are they important? Expectations • You will understand why early design phases are so important and what kinds of issues are addressed • By the end of the course, you will have enough understanding to be able to do your own conceptual UAV design studies c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -1
Design of UAV Systems Overview Pre-concept design • The very early work that establishes the general concept, what it should do and how it will be used • Previously done by customer organizations (e. g. the government) now done by customers and companies • The product is usually a set of initial requirements and estimates of cost and schedule Key technical issues addressed during this phase include: • Overall needs and objectives • Concepts of operations “Products” of • Potential design solutions the pre-concept • Initial cost and schedule design phase • Effectiveness estimates • Analysis of alternatives c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -2

Design of UAV Systems Overview Conceptual design • The next phase that starts with initial requirements and objectives and develops a preferred system concept and a plan to develop it • The product is usually a proposal for preliminary design with enough technical, cost and risk information to convince your customer to select your concept Key technical issues addressed during this phase include: • Substantiated needs and objectives • Refined concepts of operations “Products” of • Preferred design solution the conceptual • Refined cost and schedule design phase • Refined effectiveness estimates • Refined analysis of alternatives c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -3

Design of UAV Systems Needs and objectives How do customers know what they need? Does somebody tell them? If so, who? • Their boss? • The government? • The department of defense? • USAF? • Public documents? • Research institutes? • Contractors? • Think tanks? • Groups? • Individuals? • Others? c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -4
Design of UAV Systems The answer is not UAV unique How you find out what kind of UAVs your customers are interested in • Read their documents • Talk to them about their needs • Help them discover needs they might not even know about • Enabled by new technology • Enabled by new concepts • Enabled by new integration This is how the most successful design teams operate If you wait for a customer to tell you his needs in a specification or request for proposal it may be too late • Somebody else may have already sold them on their solution! c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -5
Design of UAV Systems Con. Ops Concept of operations (Con. Ops) definition(s) 1. How something is used or operated • Typically associated with military systems but also applicable to commercial systems. 2. The name of a document used to describe how a system should be operated, e. g. …describes the approach to deployment, employment, and operation of a new or upgraded system or capability being advocated to meet identified tasks or missions. CONOPS are not limited to single systems but can rely on other systems and organizations, as required. http: //www. fas. org/spp/military/docops/afspc/i 10_606. htm We will use the first definition – determining how something is used or operated vs. a Con. Ops document c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -6
Design of UAV Systems Example - Con. Ops document CONCEPT OF OPERATIONS FOR ENDURANCE UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLES 3 Dec 1996 - Version 2 This Concept of Operations (CONOPS) describes the operational employment of various classes of Endurance Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). This CONOPS will provide an overview of the principal endurance UAV components and organizations, the intended operational environment, and the primary command control relationships and responsibilities. It also provides a framework for the development of theater-specific concepts of employment and operations planning documents. www. fas. org/irp/doddir/usaf/conops_uav/index. html c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -7
Design of UAV Systems Another way to think about it Generally here are two ways to describe a product: 1. Physical description - what something looks like, a drawing or words that describe physical features such as lengths, weights, shapes, etc. 2. Functional description - how something operates, a block diagram, pictures or words that tell the reader how a product works and how it fits in with other products A UAV Con. Ops is a functional description of the overall UAV system c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -8
Design of UAV Systems Design solutions During the pre-concept design, there is no need to develop a preferred design solution. • This is what we do during conceptual design During pre-concept design, it is only necessary to develop a reasonable design solution. • It must be good enough to support technology readiness, cost, risk and schedule estimates Customers should avoid the temptation to specify the design solution during pre-concept design • Customers usually get what they ask for • It may not be the best answer c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -9
Design of UAV Systems Cost and schedule The technical work done during pre-concept and conceptual design establishes the initial cost and schedule estimate that the project will have to live with for the rest of its life c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -10
Design of UAV Systems Effectiveness • A quantified measure of how well something works • Typically associated with the field of Operations Analysis • Example This analysis was conducted to determine which of the systems concepts showed the greatest potential for enhancing space operations, and which of their embedded technologies have the highest leverage. The analytical expertise was provided by the Department of Operational Sciences at the Air Force Institute of Technology (AFIT); technology assessments were done by the 2020 Technology Team and practical operational judgments were provided by Air War College and Air Command Staff College faculty and students. A Value Model was developed based on Joint Space Doctrine to quantify and compare different systems' contributions to various space capabilities. The overall goal of operational analysis was to rank systems and their technologies in a way that was traceable. Thus, the model functioned as an aid to decision makers. www. fas. org/spp/military/docops/usaf/2020/ops-anal. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -11

Design of UAV Systems A way think about effectiveness • Most engineers never even hear about “effectiveness” or “Operations Analysis” until their first day on the job. • Then they find out how important it is and how it is used to make key technical and program decisions. • Some engineers respond by finding out more about it and become successful systems engineers. • Others conclude it is “black magic” or “funny numbers” and/or accept the results without challenge and never develop a system level perspective. • Operational effectiveness assessments are key technical products produced during every design phase. • Every good system level design engineer should understand know how to apply them. c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -12
Design of UAV Systems Analysis of alternatives An objective assessment of other ways to do something besides the one you are proposing • An analysis of the estimated costs and operational effectiveness of alternative systems to meet a mission need and the associated program for acquiring each alternative. • Formerly known as cost and operational effectiveness analysis. A study conducted to provide support for acquisition decisions in the acquisition cycle. http: //www. fas. org/news/reference/lexicon/dea. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -13

Design of UAV Systems UAV Alternatives Do UAVs always provide the best solution to meet customer needs for……? • Intelligence collection • Surveillance • Reconnaissance • Communication relay • Strike • Combat support Are they better than other ways of doing the job? • Satellites • Manned aircraft • Expendable systems Careful analysis is required to answer the question c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -14
Design of UAV Systems Next subject Lesson objective - to discuss UAV Conceptual Design including… • How is it different? • What are the issues? • Why are they important? Expectations • You will understand why early design phases are so important and what kinds of issues are addressed • By the end of the course, you will have enough understanding to be able to do your own conceptual UAV design studies c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -15
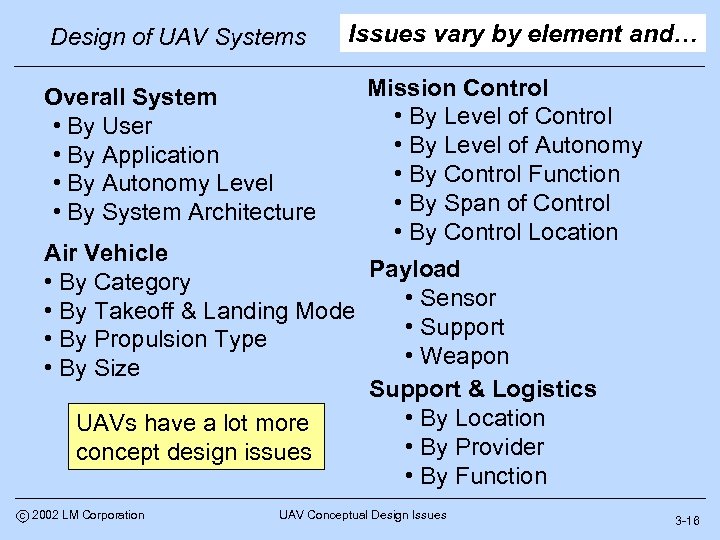
Design of UAV Systems Overall System • By User • By Application • By Autonomy Level • By System Architecture Issues vary by element and… Mission Control • By Level of Autonomy • By Control Function • By Span of Control • By Control Location Air Vehicle Payload • By Category • Sensor • By Takeoff & Landing Mode • Support • By Propulsion Type • Weapon • By Size Support & Logistics • By Location UAVs have a lot more • By Provider concept design issues • By Function c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -16
Design of UAV Systems User categories Civil Military Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -17

Design of UAV Systems Military Applications Attack Predator (Tier II) Reconnaissance http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/predator. htm http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/uav. htm Combat Support http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/global_hawk. htm • Signals intelligence collection • Communications relay • Etc. c 2002 LM Corporation Flight Research UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -18

Design of UAV Systems Military (cont’d) And target drones… http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/uav. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -19
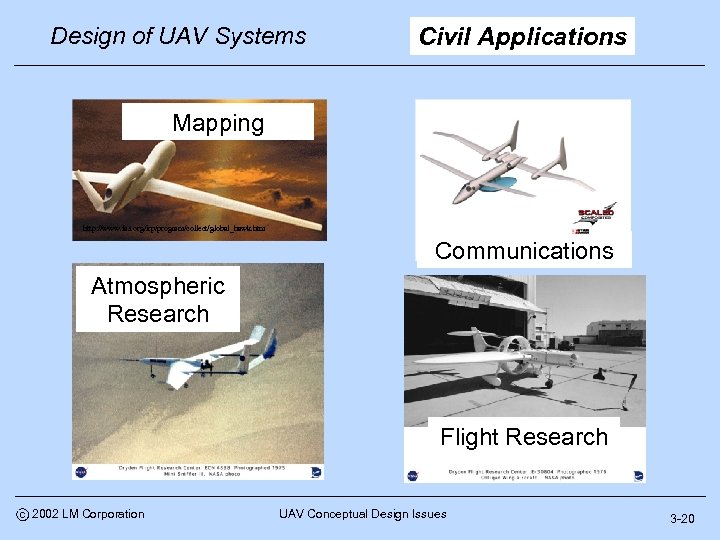
Design of UAV Systems Civil Applications Mapping http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/global_hawk. htm Communications Atmospheric Research Flight Research c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -20
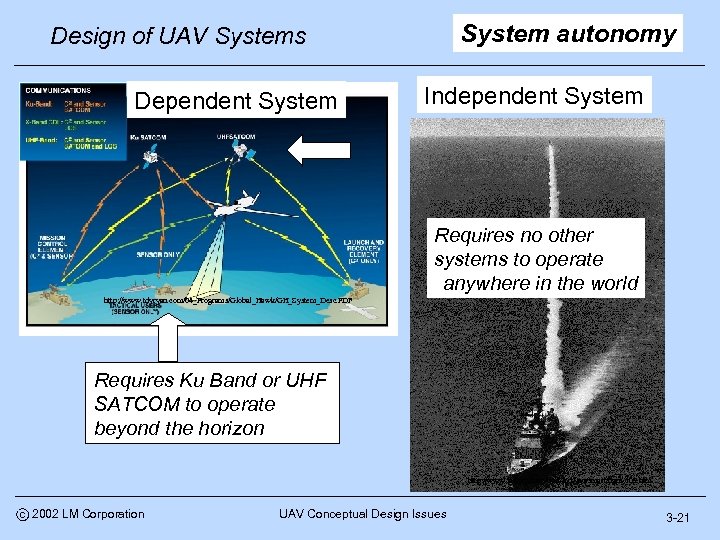
System autonomy Design of UAV Systems Dependent System Independent System Requires no other systems to operate anywhere in the world http: //www. tdyryan. com/04_Programs/Global_Hawk/GH_System_Desc. PDF Requires Ku Band or UHF SATCOM to operate beyond the horizon http: //www. fas. org/man/dod-101/sys/smart/bgm-109. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -21
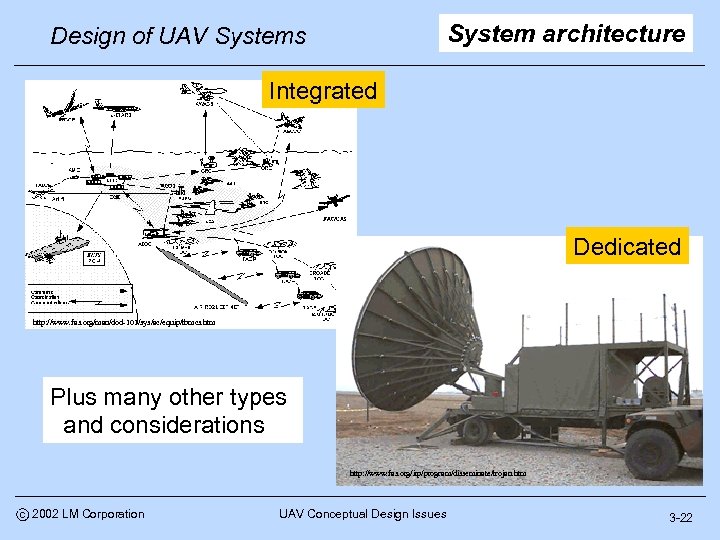
System architecture Design of UAV Systems Integrated Dedicated http: //www. fas. org/man/dod-101/sys/ac/equip/tbmcs. htm Plus many other types and considerations http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/disseminate/trojan. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -22
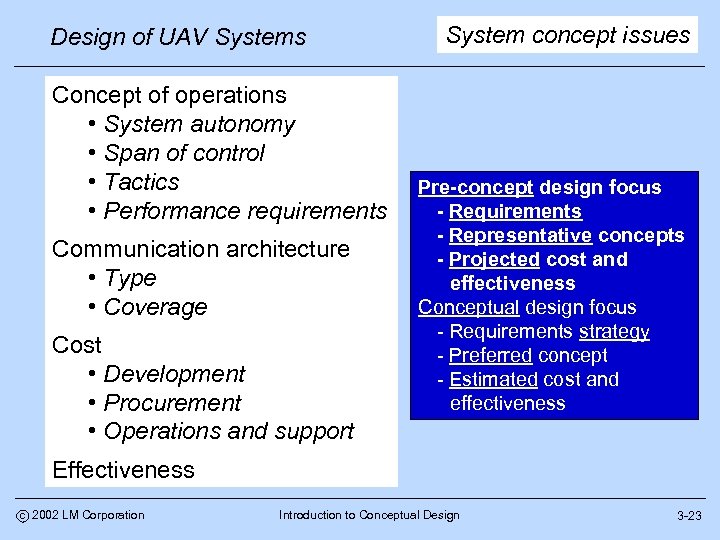
Design of UAV Systems Concept of operations • System autonomy • Span of control • Tactics • Performance requirements Communication architecture • Type • Coverage Cost • Development • Procurement • Operations and support System concept issues Pre-concept design focus - Requirements - Representative concepts - Projected cost and effectiveness Conceptual design focus - Requirements strategy - Preferred concept - Estimated cost and effectiveness Effectiveness c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -23
Design of UAV Systems System autonomy During early design phases winning teams work with customers to understand customer system autonomy requirements and rationale c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -24
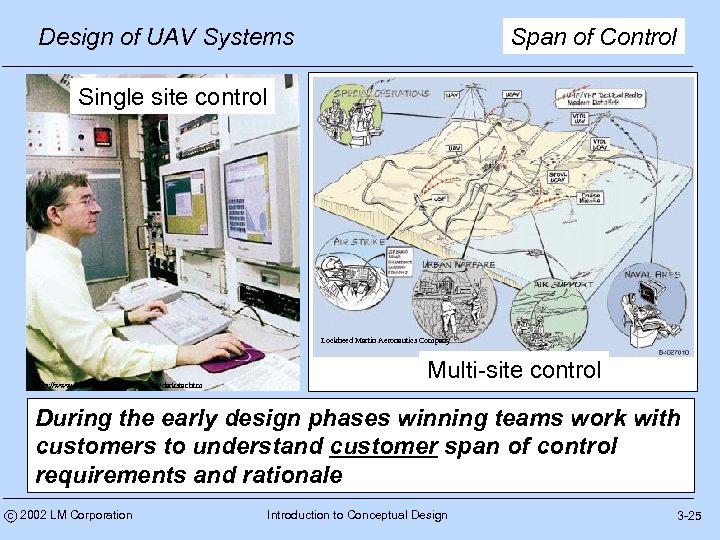
Design of UAV Systems Span of Control Single site control Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/darkstar. htm Multi-site control During the early design phases winning teams work with customers to understand customer span of control requirements and rationale c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -25

Design of UAV Systems Tactics Example - Global Hawk tactics for survivability http: //www. tdyryan. com/04_Programs/Global_Hawk/GH_System_Desc. PDF During the early design phases winning teams work with customers to understand develop tactics that take advantage of the inherent characteristics of their preferred design approach c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -26
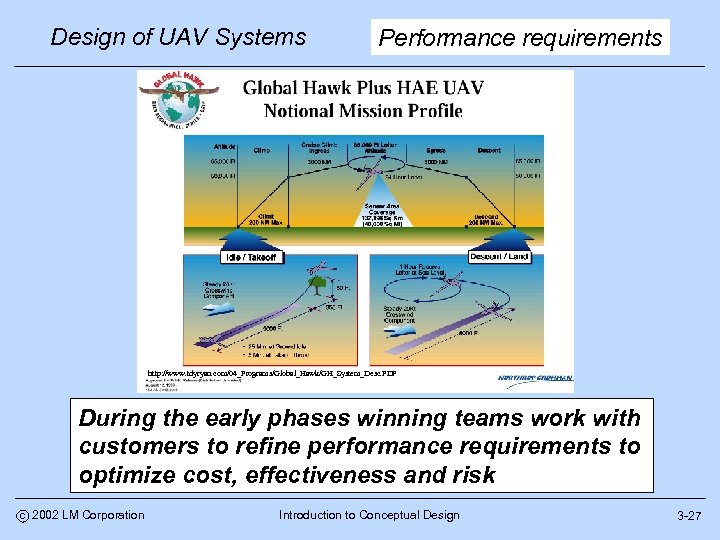
Design of UAV Systems Performance requirements http: //www. tdyryan. com/04_Programs/Global_Hawk/GH_System_Desc. PDF During the early phases winning teams work with customers to refine performance requirements to optimize cost, effectiveness and risk c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -27
Design of UAV Systems Type of communications • Military • Dedicated • Shared • Relayed • Commercial • Terrestrial • SATCOM Frequency • HF • UHF • VHF • Ku band • Ka band Covered in detail in Lesson 9 c 2002 LM Corporation Communications issues Format • Analog Not covered • Digital Bandwidth • Narrow • Wide • Continuous • On demand Area coverage • Local • Line of sight • Over the horizon Survivability • Probability of intercept • Redundancy Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -28
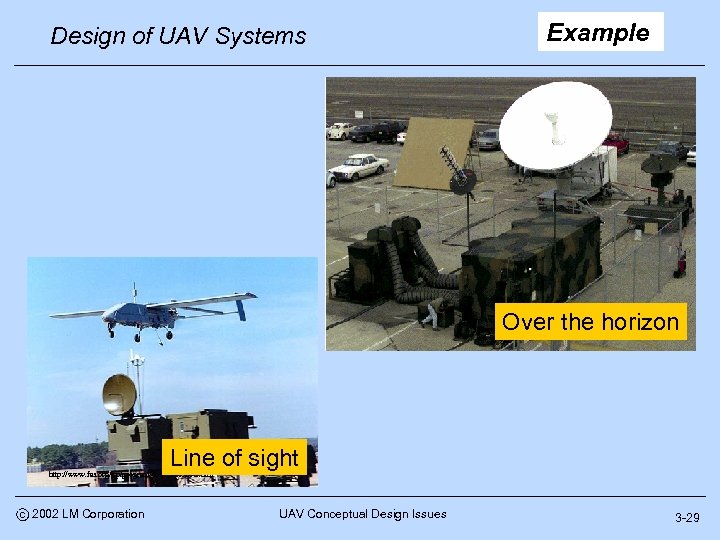
Design of UAV Systems Example Over the horizon Line of sight http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/pioneer. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -29
Design of UAV Systems Life cycle cost Development cost • The cost of developing a system • Considered a “non-recurring” cost • Occurs only once (hopefully) + Procurement cost • The cost to buy a system once it is developed • Includes a lot of “recurring” cost • Costs incurred every time a system is produced + Operations and support cost • The cost to maintain and operate a system after purchase • Includes the cost of maintaining crew proficiency • Excludes the cost of combat operations c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -30

Design of UAV Systems Cost issues Development cost • Customers want this to be as small as possible • New systems are expensive • Most of the cost is associated with risk reduction, engineering and test • Programs need “margin” to cover uncertainty Procurement cost • This cost is sensitive to procurement quantity • Repetitive tasks become more efficient • Also sensitive to the size and complexity • Aircraft empty weight, speed and capability are the major cost drivers Operations and support cost • Most of the life cycle cost of an aircraft is the “O&S” • O&S cost can be reduced by good up-front design c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -31
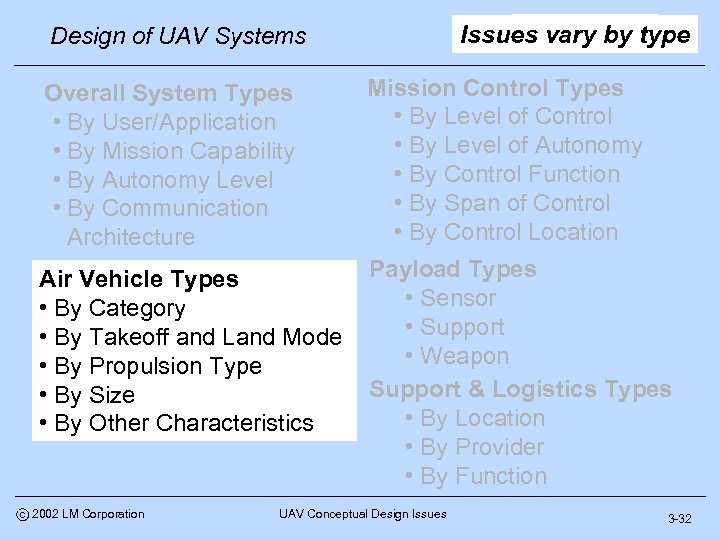
UAV Types Issues vary by type Design of UAV Systems Overall System Types • By User/Application • By Mission Capability • By Autonomy Level • By Communication Architecture Mission Control Types • By Level of Control • By Level of Autonomy • By Control Function • By Span of Control • By Control Location Air Vehicle Types • By Category • By Takeoff and Land Mode • By Propulsion Type • By Size • By Other Characteristics Payload Types • Sensor • Support • Weapon Support & Logistics Types • By Location • By Provider • By Function c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -32
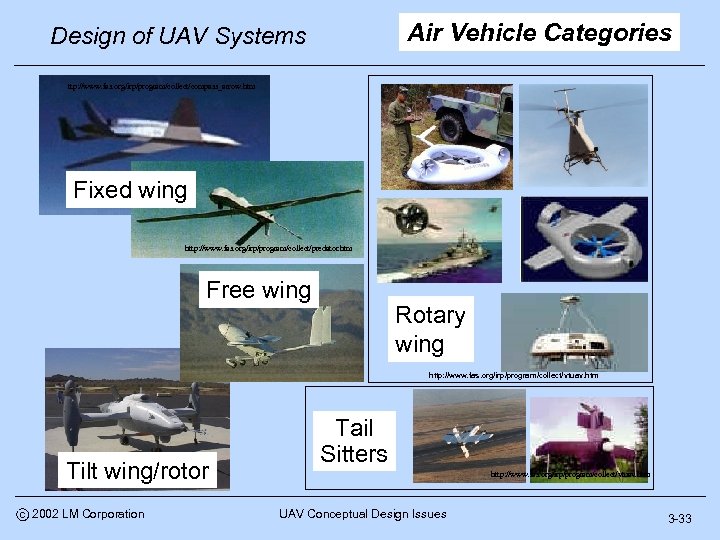
Air Vehicle Categories Design of UAV Systems ttp: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/compass_arrow. htm Fixed wing http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/predator. htm Free wing Rotary wing http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/vtuav. htm Tilt wing/rotor c 2002 LM Corporation Tail Sitters http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/vtuav. htm UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -33
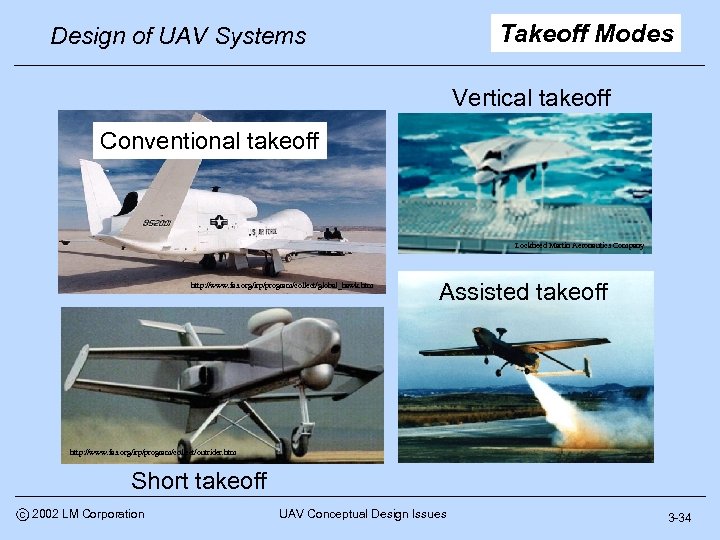
Takeoff Modes Design of UAV Systems Vertical takeoff Conventional takeoff Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/global_hawk. htm Assisted takeoff http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/outrider. htm http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/pioneer. htm Short takeoff c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -34
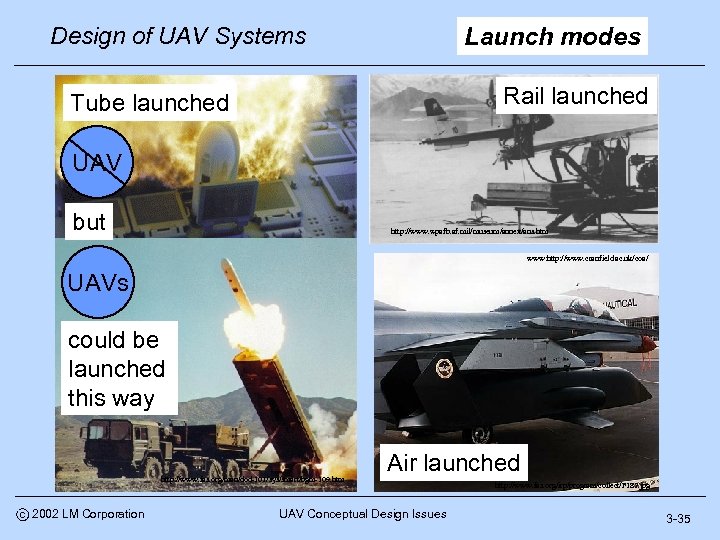
Design of UAV Systems Launch modes Rail launched Tube launched UAV but http: //www. wpafb. af. mil/museum/annex/ans. htm www: http: //www. cranfield. ac. uk/coa/ UAVs could be launched this way http: //www. fas. org/man/dod-101/sys/smart/bgm-109. htm c 2002 LM Corporation Air launched UAV Conceptual Design Issues http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/F 182. jpg 3 -35
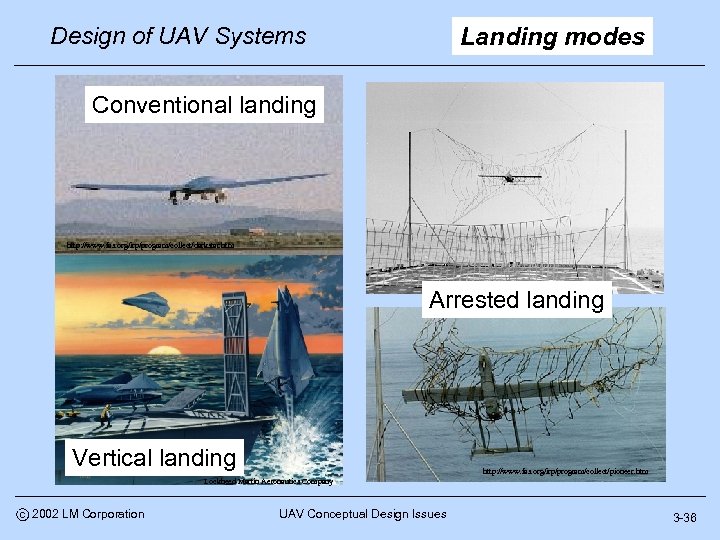
Design of UAV Systems Landing modes Conventional landing http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/darkstar. htm Arrested landing Vertical landing http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/pioneer. htm Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -36
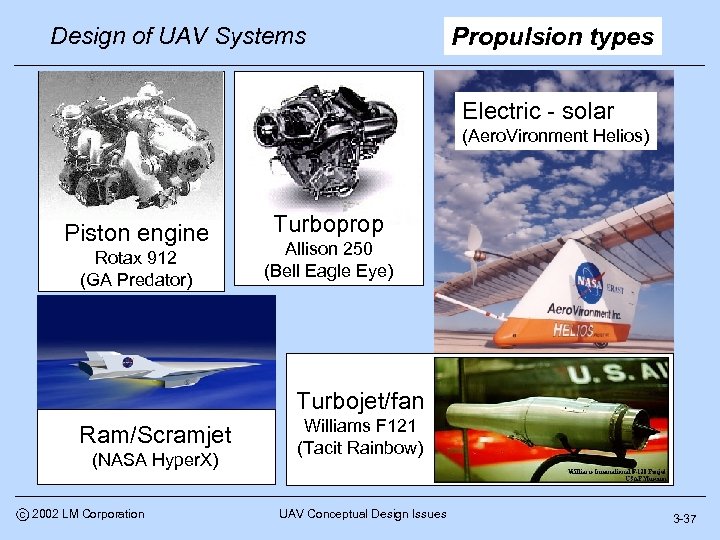
Design of UAV Systems Propulsion types Electric - solar (Aero. Vironment Helios) Piston engine Rotax 912 (GA Predator) Turboprop Allison 250 (Bell Eagle Eye) Turbojet/fan Ram/Scramjet (NASA Hyper. X) c 2002 LM Corporation Williams F 121 (Tacit Rainbow) UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -37
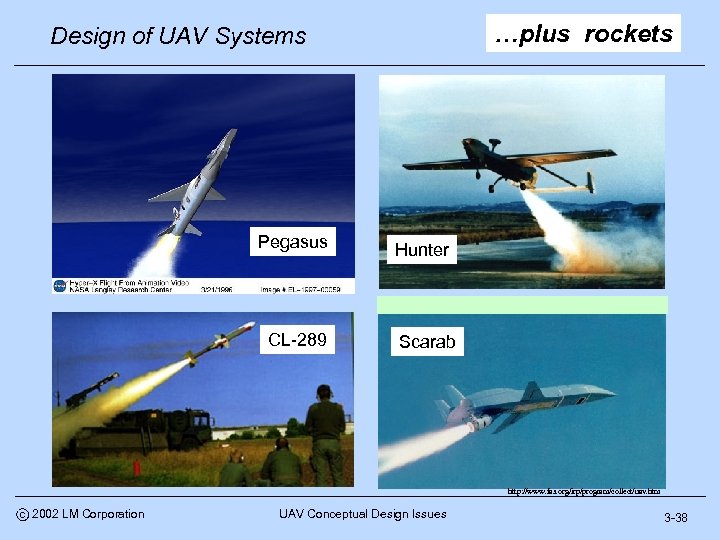
…plus rockets Design of UAV Systems Pegasus CL-289 Hunter Scarab http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/uav. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -38
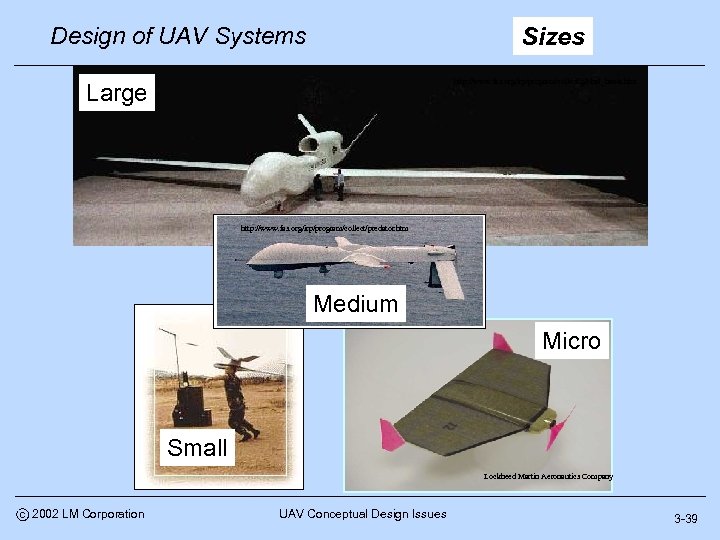
Design of UAV Systems Sizes http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/global_hawk. htm Large http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/predator. htm Medium Micro Small Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -39
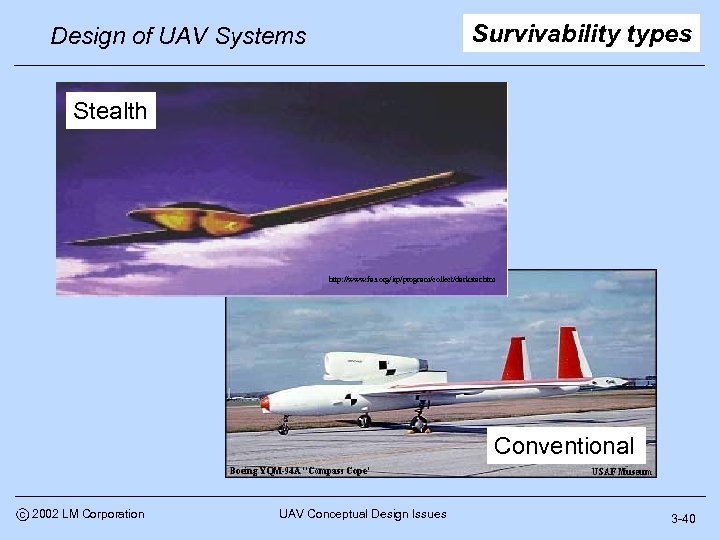
Survivability types Design of UAV Systems Stealth http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/darkstar. htm Conventional c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -40
Design of UAV Systems Air vehicle concept issues Configuration Manufacturing concept Size Subsystems concept Weight Signature level More on this subject in lessons 13 through 21 c 2002 LM Corporation Pre-concept design focus - Requirements - Representative concepts - Projected cost and effectiveness Conceptual design focus - Requirements strategy - Preferred concept - Estimated cost and effectiveness Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -41
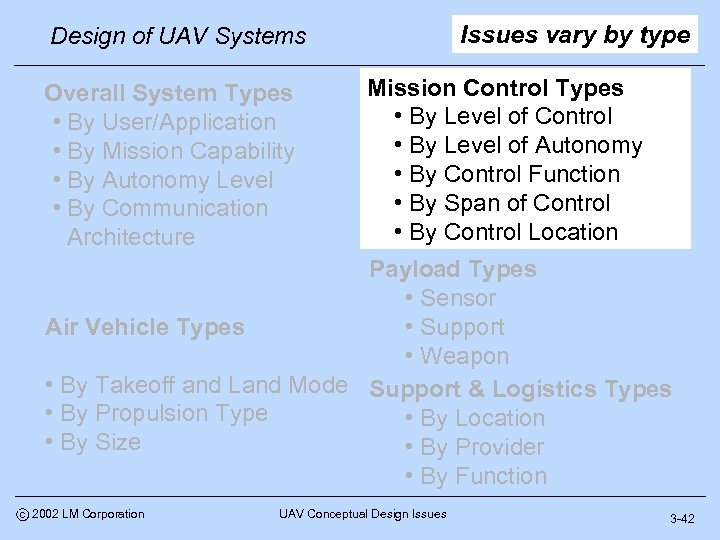
Issues vary by type Design of UAV Systems Overall System Types • By User/Application • By Mission Capability • By Autonomy Level • By Communication Architecture Mission Control Types • By Level of Control • By Level of Autonomy • By Control Function • By Span of Control • By Control Location Payload Types • Sensor Air Vehicle Types • Support • Weapon • By Takeoff and Land Mode Support & Logistics Types • By Propulsion Type • By Location • By Size • By Provider • By Function c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -42
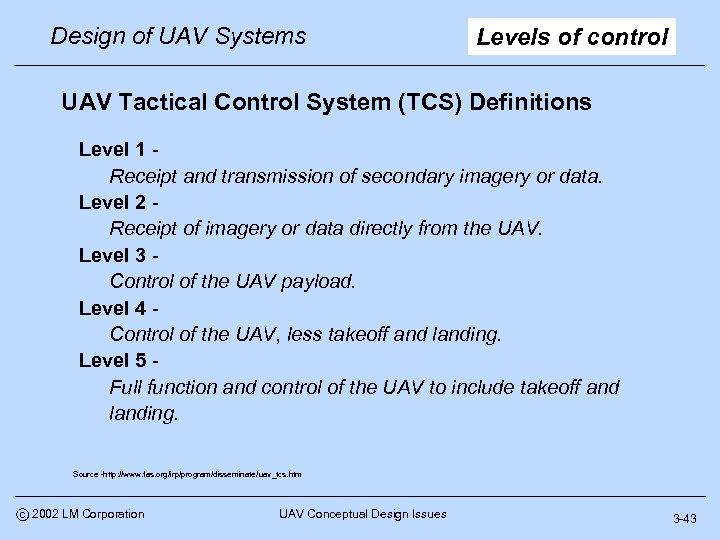
Design of UAV Systems Levels of control UAV Tactical Control System (TCS) Definitions Level 1 Receipt and transmission of secondary imagery or data. Level 2 Receipt of imagery or data directly from the UAV. Level 3 Control of the UAV payload. Level 4 Control of the UAV, less takeoff and landing. Level 5 Full function and control of the UAV to include takeoff and landing. Source -http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/disseminate/uav_tcs. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -43
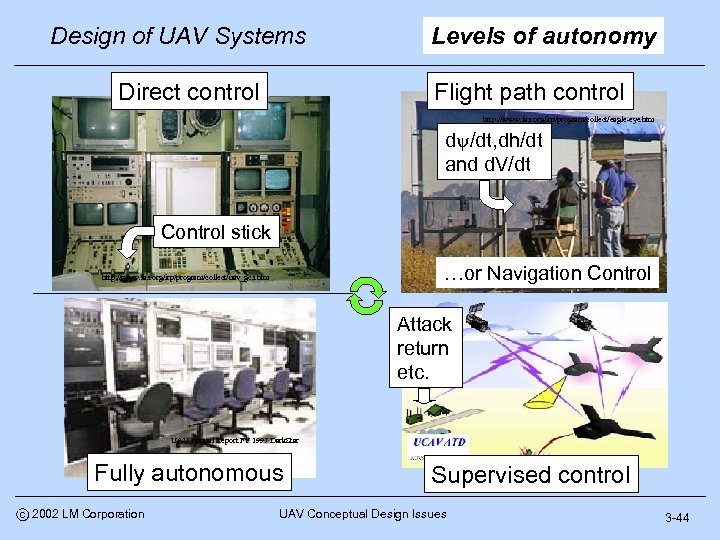
Design of UAV Systems Direct control Levels of autonomy Flight path control http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/eagle-eye. htm d /dt, dh/dt and d. V/dt Control stick …or Navigation Control http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/uav_gcs. htm Attack return etc. UAV Annual Report FY 1997 Dark. Star Fully autonomous c 2002 LM Corporation Supervised control UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -44

Design of UAV Systems Control Functions http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/pioneer. htm http: //www. fas. org/man/dod-101/sys/ac/equip/afmss. htm Launch and Recovery Mission Planning http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/pioneer. htm http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/disseminate/uav_tcs. htm Mission and Payload Management c 2002 LM Corporation Information Processing and Dissemination UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -45
Span of control Design of UAV Systems http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/disseminate/uav_tcs. htm http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/eagle-eye. htm System Unique c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues Multi-System 3 -46
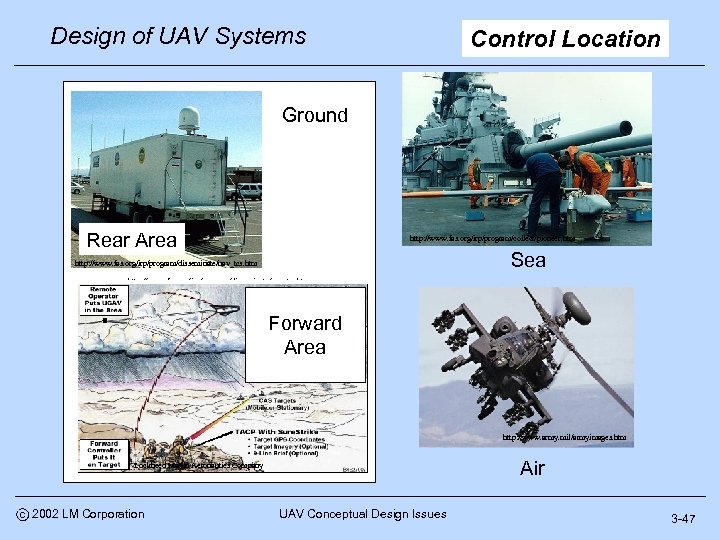
Design of UAV Systems Control Location Ground Rear Area http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/pioneer. htm Sea http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/disseminate/uav_tcs. htm Forward Area http: //www. army. mil/armyimages. htm Air Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -47
Design of UAV Systems Vehicle control concept Site requirements Manpower requirements Payload control concept Overall size Weapon control concept Product exploitation concept More on this subject in lesson 10 c 2002 LM Corporation Mission control concept issues Pre-concept design focus - Requirements - Representative concepts - Projected cost and effectiveness Conceptual design focus - Requirements strategy - Preferred concept - Estimated cost and effectiveness Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -48
Issues vary by type Design of UAV Systems Overall System Types • By User/Application • By Mission Capability • By Autonomy Level • By Communication Architecture Air Vehicle Types Mission Control Types • By Level of Control • By Level of Autonomy • By Control Function • By Span of Control • By Control Location Payload Types • Sensor • Support • Weapon • By Takeoff and Land Mode Support & Logistics Types • By Propulsion Type • By Location • By Size • By Provider • By Function c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -49
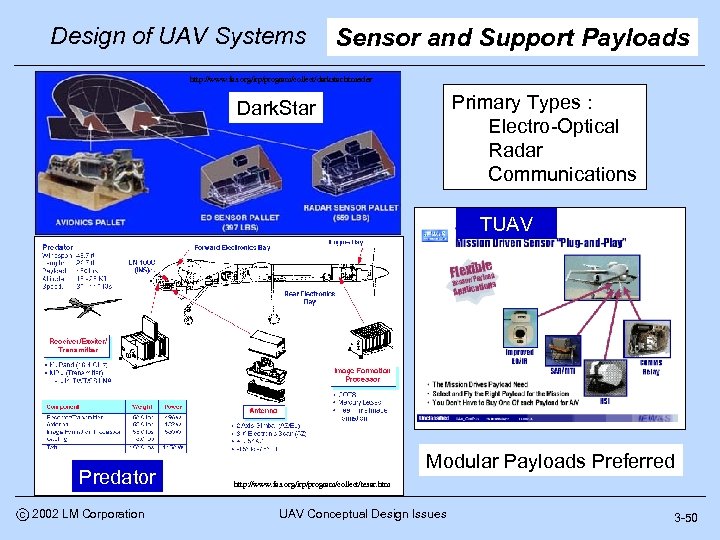
Design of UAV Systems Sensor and Support Payloads http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/darkstar. htmadar Primary Types : Electro-Optical Radar Communications Dark. Star TUAV Predator c 2002 LM Corporation Modular Payloads Preferred http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/tesar. htm UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -50
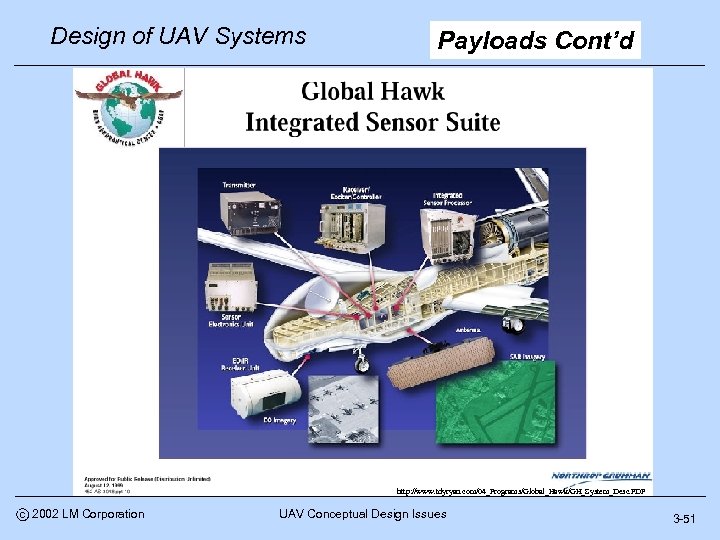
Design of UAV Systems Payloads Cont’d http: //www. tdyryan. com/04_Programs/Global_Hawk/GH_System_Desc. PDF c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -51
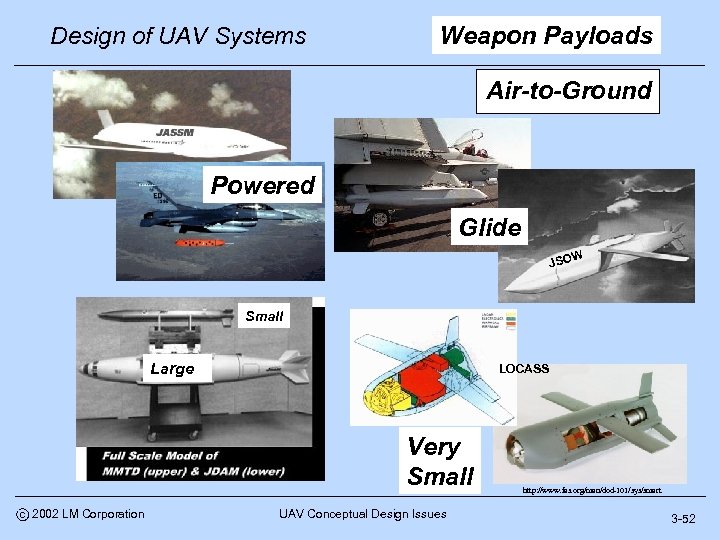
Design of UAV Systems Weapon Payloads Air-to-Ground Powered Glide W JSO Small Large LOCASS Very Small c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues http: //www. fas. org/man/dod-101/sys/smart 3 -52

Design of UAV Systems Weapons Payloads Air-to-Air Possible but not planned http: //www. fas. org/spp/military/docops/usaf/vistas. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -53
Design of UAV Systems Payload concept issues Sensor type(s) • Wide area • Spot • Targeting • Weather effects Weapon type(s) • Unguided • Platform guided • Off board guided • Self guided Overall sizes Pre-concept design focus - Requirements - Representative concepts - Projected cost and effectiveness Conceptual design focus - Requirements strategy - Preferred concept - Estimated cost and effectiveness Aperture requirements Power and cooling requirements More on this subject in lesson 11 c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -54
UAV Types Design of UAV Systems Overall System Types • By User/Application • By Mission Capability • By Autonomy Level • By Communication Architecture Air Vehicle Types Mission Control Types • By Level of Control • By Level of Autonomy • By Control Function • By Span of Control • By Control Location Payload Types • Sensor • Support • Weapon • By Takeoff and Land Mode Support & Logistics Types • By Propulsion Type • By Location • By Size • By Provider • By Function c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -55
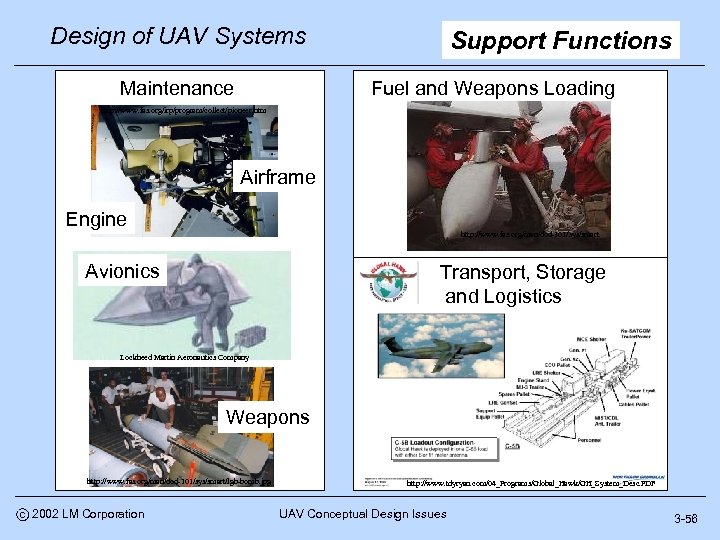
Design of UAV Systems Maintenance Support Functions Fuel and Weapons Loading http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/pioneer. htm Airframe Engine http: //www. fas. org/man/dod-101/sys/smart Avionics Transport, Storage and Logistics Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company Weapons http: //www. fas. org/man/dod-101/sys/smart/lgb-bomb. jpg c 2002 LM Corporation http: //www. tdyryan. com/04_Programs/Global_Hawk/GH_System_Desc. PDF UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -56

Design of UAV Systems Support Locations Main Base Forward Base Emergency Base c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -57
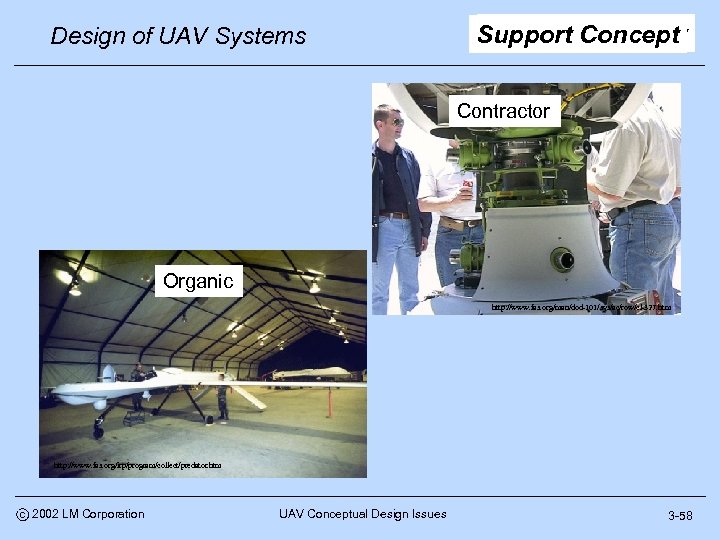
Design of UAV Systems Support Concept Contractor Organic http: //www. fas. org/man/dod-101/sys/ac/row/cl-327. htm http: //www. fas. org/irp/program/collect/predator. htm c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -58
Design of UAV Systems Maintenance concept • Repair vs. replace • Organic vs. contractor • Active duty vs. reserve Support equipment requirements Manpower requirements Peacetime Usage • Flown • Stored • Pre-positioned More on this subject in lesson 12 c 2002 LM Corporation Support concept issues Deployability • Self deploy • Air transport • Surface transport Pre-concept design focus - Requirements - Representative concepts - Projected cost and effectiveness Conceptual design focus - Requirements strategy - Preferred concept - Estimated cost and effectiveness Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -59
Design of UAV Systems Why early phases are so important Pre-concept design • The product of this phase is a set of initial requirements and projected cost, risk and schedule Key technical issues addressed during this phase include: • Overall needs and objectives • Concepts of operation • Representative design concepts • Initial cost and schedule • Effectiveness estimates • Analysis of alternatives The technical work done during the pre-concept design phase establishes the initial cost and schedule estimate that the project will have to live with for the rest of its life c 2002 LM Corporation Introduction to Conceptual Design 3 -60

Design of UAV Systems Recommended reading Raymer - Aircraft Design - A Conceptual Approach • Chapter 1 (2 pages) : Design - A Separate Discipline 1. 1 - What is Design 1. 2 - Introduction to the Book • Chapter 2 (11 pages) : Overview of the Design Process 2. 1 - Introduction 2. 2 - Phases of Aircraft Design 2. 3 - Aircraft Conceptual Design Process 2. 4 - Integrated Product Development and Aircraft Design c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues 3 -61
Design of UAV Systems c 2002 LM Corporation UAV Conceptual Design Issues Intermission 3 -62
a573fa60abc05d5c7af93ac37315a8b2.ppt