1e0d9a416730bdfe56e07641efab846f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Design of Inverter Driven Induction Machines Daniel M. Saban, PE Ph. D saban@ieee. org
Design of Inverter Driven Induction Machines Daniel M. Saban, PE Ph. D saban@ieee. org
 Overview • The induction machine problem – Stakeholders & design drivers – Analysis & synthesis challenges – Design rules-of-thumb & constraints • Optimization and/or synthesis – Common tools – Selected approaches – Inverter system consideration • Opportunities 2
Overview • The induction machine problem – Stakeholders & design drivers – Analysis & synthesis challenges – Design rules-of-thumb & constraints • Optimization and/or synthesis – Common tools – Selected approaches – Inverter system consideration • Opportunities 2
 Induction machine • Stakeholders and their perspectives – – – Customers Sales & Marketing Manufacturing Engineering & Operations Application Engineering Product Development • Opportunities – Materials: improved and exotic – Manufacturing processes and process control – Design, analysis and optimization tools • Size & Topology 3
Induction machine • Stakeholders and their perspectives – – – Customers Sales & Marketing Manufacturing Engineering & Operations Application Engineering Product Development • Opportunities – Materials: improved and exotic – Manufacturing processes and process control – Design, analysis and optimization tools • Size & Topology 3
 Induction machine • Temperature “is everything” – Material limits (life) • Insulation system • Bearing system – Material dependencies (performance) – Cooling system – Rules-of-thumb in design • Cost “is everything” – Operating cost: efficiency, power factor – Initial cost: better material, more material • Quality “is everything” • Performance “is everything”? 4
Induction machine • Temperature “is everything” – Material limits (life) • Insulation system • Bearing system – Material dependencies (performance) – Cooling system – Rules-of-thumb in design • Cost “is everything” – Operating cost: efficiency, power factor – Initial cost: better material, more material • Quality “is everything” • Performance “is everything”? 4
 IM analysis challenges • • • Non-linear: saturation, core losses Winding harmonics Rotor/Stator slotting & skewing Material property variation (lot-to-lot) Dimensional variation & shift Manufacturing/assembly variation Rotor resistance End-leakage (consider frame) High-frequency impedance (bearing currents) 5
IM analysis challenges • • • Non-linear: saturation, core losses Winding harmonics Rotor/Stator slotting & skewing Material property variation (lot-to-lot) Dimensional variation & shift Manufacturing/assembly variation Rotor resistance End-leakage (consider frame) High-frequency impedance (bearing currents) 5
 Proximity & Skin Effect • Fundamental current injected into conductors • 1 turn per coil; 4. 0 k. W loss/pole • 4 turns per coil; 2. 5 k. W loss/pole 6
Proximity & Skin Effect • Fundamental current injected into conductors • 1 turn per coil; 4. 0 k. W loss/pole • 4 turns per coil; 2. 5 k. W loss/pole 6
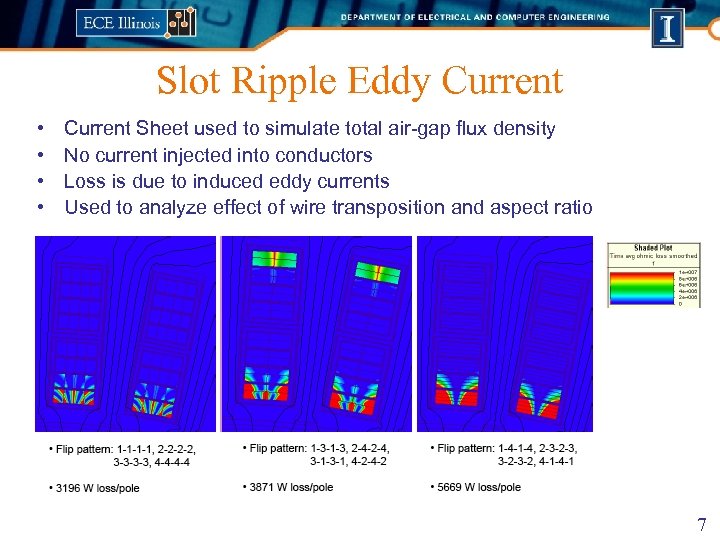 Slot Ripple Eddy Current • • Current Sheet used to simulate total air-gap flux density No current injected into conductors Loss is due to induced eddy currents Used to analyze effect of wire transposition and aspect ratio 7
Slot Ripple Eddy Current • • Current Sheet used to simulate total air-gap flux density No current injected into conductors Loss is due to induced eddy currents Used to analyze effect of wire transposition and aspect ratio 7
 IM design synthesis • Clean sheet – Single application – Product family • Existing laminations • Brute Hp vs. finesse 8
IM design synthesis • Clean sheet – Single application – Product family • Existing laminations • Brute Hp vs. finesse 8
 IM design synthesis challenges • Knowns – Full stator slots – High conductivity conductors – Small gap? • Unknowns – Rotor & stator aspect ratios – Slot shape details – Discrete values only • • • Pole count Discrete wire sizes, non-linear cost function Winding details: number of turns, coils, pitch Integral numbers of slots, rotor/stator Lamination material, grade, thickness 9
IM design synthesis challenges • Knowns – Full stator slots – High conductivity conductors – Small gap? • Unknowns – Rotor & stator aspect ratios – Slot shape details – Discrete values only • • • Pole count Discrete wire sizes, non-linear cost function Winding details: number of turns, coils, pitch Integral numbers of slots, rotor/stator Lamination material, grade, thickness 9
 Rules-of-thumb • Stator current density – 620 A/cm 2 to 1 k. A/cm 2 – Highly dependant on cooling system – Revise after thermal modeling • Peak flux density of stator teeth, yoke – ~1. 7 T, ~1. 6 T – Revise upward for more power density – Revise lower for higher efficiency • Rotor current density • Gap flux density: 0. 5 T to 0. 8 T 10
Rules-of-thumb • Stator current density – 620 A/cm 2 to 1 k. A/cm 2 – Highly dependant on cooling system – Revise after thermal modeling • Peak flux density of stator teeth, yoke – ~1. 7 T, ~1. 6 T – Revise upward for more power density – Revise lower for higher efficiency • Rotor current density • Gap flux density: 0. 5 T to 0. 8 T 10
 Common Design Constraints • • • Rotor OD Stack length Machine construction Cooling system 11
Common Design Constraints • • • Rotor OD Stack length Machine construction Cooling system 11
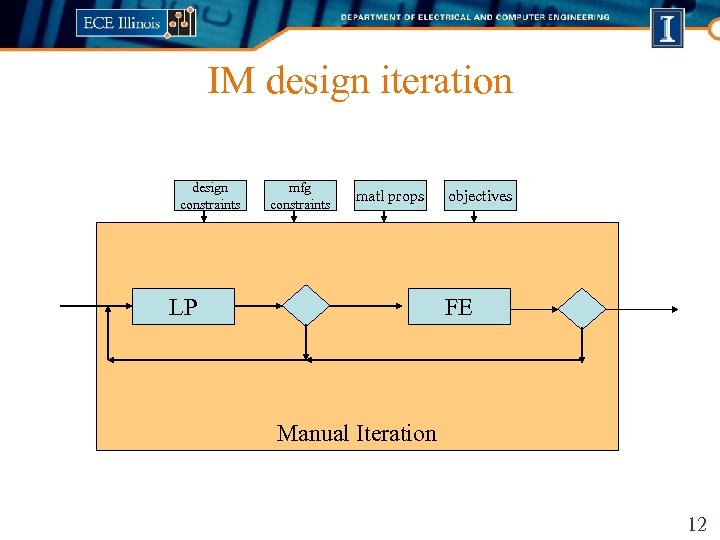 IM design iteration design constraints mfg constraints matl props LP objectives FE Manual Iteration 12
IM design iteration design constraints mfg constraints matl props LP objectives FE Manual Iteration 12
 IM design tools • In-house – Typically only lumped parameter (LP) – May be tied to manufacturing or operations – Some “special” versions of commercial software • Commercial – – – LP: PC-IMD (SPEED), VICA (support? ) LP+FE: PC-IMD/FEA (SPEED), RMxprt (Ansoft) MCM: ? ? FE: Magnet (Infolytica), (Flux, Maxwell) Ansys/Ansoft System simulation: Matlab/Simulink, Simplorer (Ansoft), Easy 5 13
IM design tools • In-house – Typically only lumped parameter (LP) – May be tied to manufacturing or operations – Some “special” versions of commercial software • Commercial – – – LP: PC-IMD (SPEED), VICA (support? ) LP+FE: PC-IMD/FEA (SPEED), RMxprt (Ansoft) MCM: ? ? FE: Magnet (Infolytica), (Flux, Maxwell) Ansys/Ansoft System simulation: Matlab/Simulink, Simplorer (Ansoft), Easy 5 13
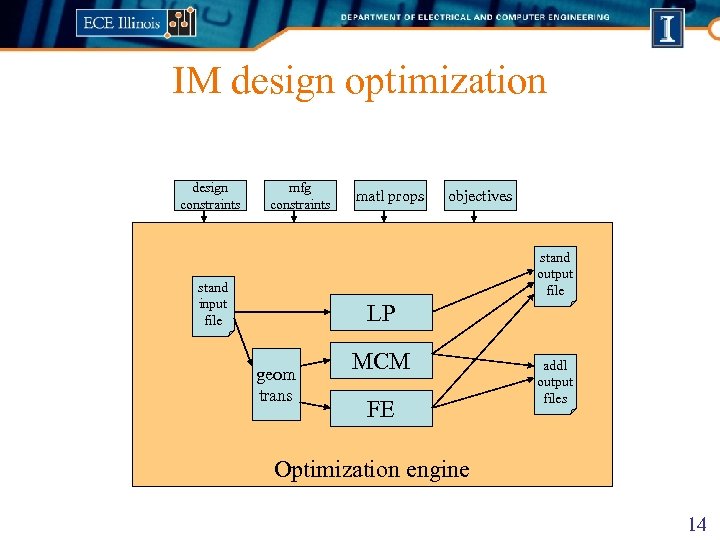 IM design optimization design constraints mfg constraints matl props objectives stand output file stand input file LP geom trans MCM FE addl output files Optimization engine 14
IM design optimization design constraints mfg constraints matl props objectives stand output file stand input file LP geom trans MCM FE addl output files Optimization engine 14
 IM design optimization • Inverter driven machines – Pole count is now a free variable – Stator & Rotor lamination design optimization can be decoupled – Skewing penalizes machine • Finesse approach – – – Size machine, ignore details & discrete values Create response surface & narrow search space Optimize rotor and stator separately Second pass takes into account discrete values Requires dedicated code • Key design points: torque corner point, max speed, max torque • Best motor will deliver maximum torque for maximum drive current 15
IM design optimization • Inverter driven machines – Pole count is now a free variable – Stator & Rotor lamination design optimization can be decoupled – Skewing penalizes machine • Finesse approach – – – Size machine, ignore details & discrete values Create response surface & narrow search space Optimize rotor and stator separately Second pass takes into account discrete values Requires dedicated code • Key design points: torque corner point, max speed, max torque • Best motor will deliver maximum torque for maximum drive current 15
 IM-Inverter system optimization • Max torque-speed envelope (output) – different than constant torque/power/slip – power factor and efficiency variations • Optimal motor leakage – Harmonic ripple current – Chopping frequency – Fundamental AC current – Peak transistor frequency 16
IM-Inverter system optimization • Max torque-speed envelope (output) – different than constant torque/power/slip – power factor and efficiency variations • Optimal motor leakage – Harmonic ripple current – Chopping frequency – Fundamental AC current – Peak transistor frequency 16
 Opportunity • Simple tools – When to apply vs. other technologies (IM vs. PM) – Rough sizing: stack length, stator od, rotor od – Fit of test data for lamination family, or single design • Models of different manufacturing techniques/defects • Stray load loss - rotor/stator harmonic interaction • Stator conductor eddy currents; large copper crosssection, high frequency • Vehicle to adapt academic work into industrial setting – Open source – Widespread use – Extensible framework 17
Opportunity • Simple tools – When to apply vs. other technologies (IM vs. PM) – Rough sizing: stack length, stator od, rotor od – Fit of test data for lamination family, or single design • Models of different manufacturing techniques/defects • Stray load loss - rotor/stator harmonic interaction • Stator conductor eddy currents; large copper crosssection, high frequency • Vehicle to adapt academic work into industrial setting – Open source – Widespread use – Extensible framework 17


