9560c68d7b5e110037883e13d3b8b6c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Deriving a Product Model from Heterogeneous Processes Ghang Lee, Ph. D. Research Scientist, College of Architecture Georgia Institute of Technology ghang. lee@arch. gatech. edu NASA-ESA PDE 2005 Workshop Georgia Tech, April 22, 2005
Deriving a Product Model from Heterogeneous Processes Ghang Lee, Ph. D. Research Scientist, College of Architecture Georgia Institute of Technology ghang. lee@arch. gatech. edu NASA-ESA PDE 2005 Workshop Georgia Tech, April 22, 2005
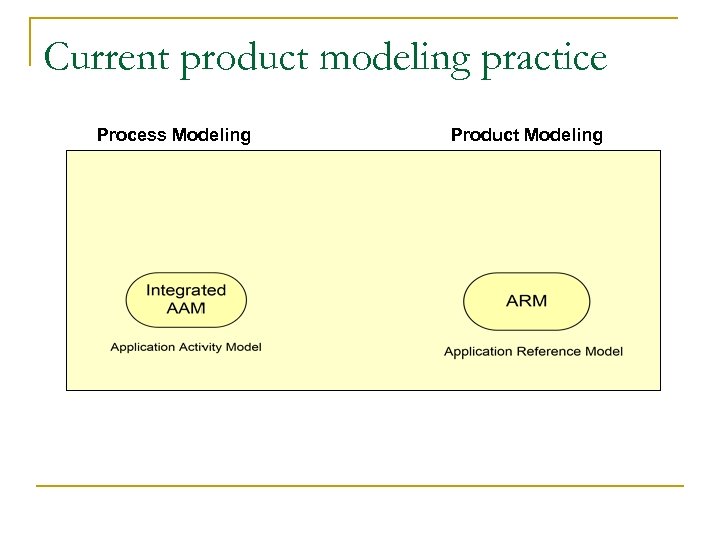 Current product modeling practice Process Modeling Product Modeling
Current product modeling practice Process Modeling Product Modeling
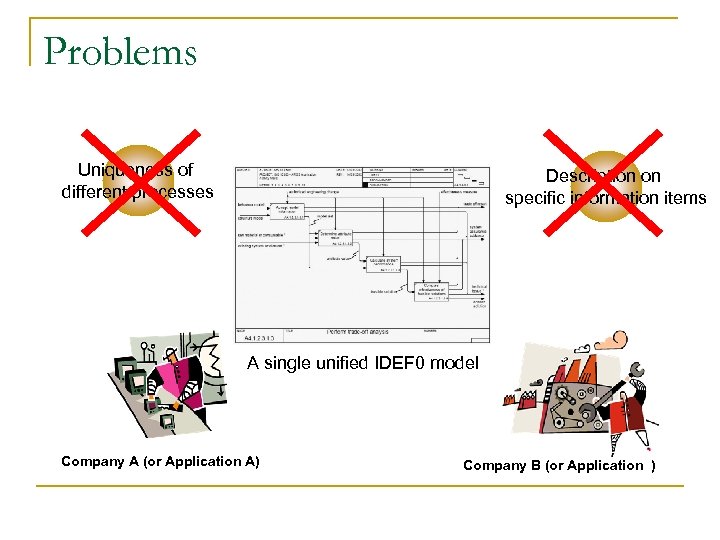 Problems Uniqueness of different processes Description on specific information items A single unified IDEF 0 model Company A (or Application A) Company B (or Application )
Problems Uniqueness of different processes Description on specific information items A single unified IDEF 0 model Company A (or Application A) Company B (or Application )
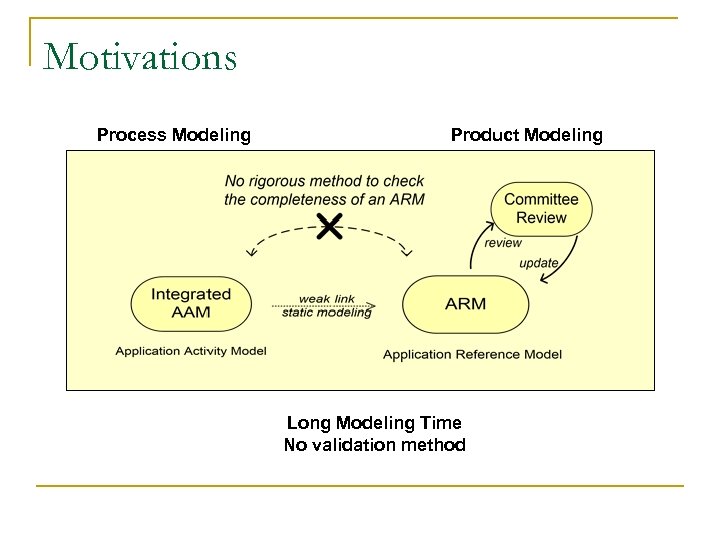 Motivations Process Modeling Product Modeling Long Modeling Time No validation method
Motivations Process Modeling Product Modeling Long Modeling Time No validation method
 Goals n n Provision of logical and scientific foundation and methods for constructing efficient and practical product models Reduction of the time and cost of developing and updating a data model from 3 -10 years to 1 -2 years
Goals n n Provision of logical and scientific foundation and methods for constructing efficient and practical product models Reduction of the time and cost of developing and updating a data model from 3 -10 years to 1 -2 years
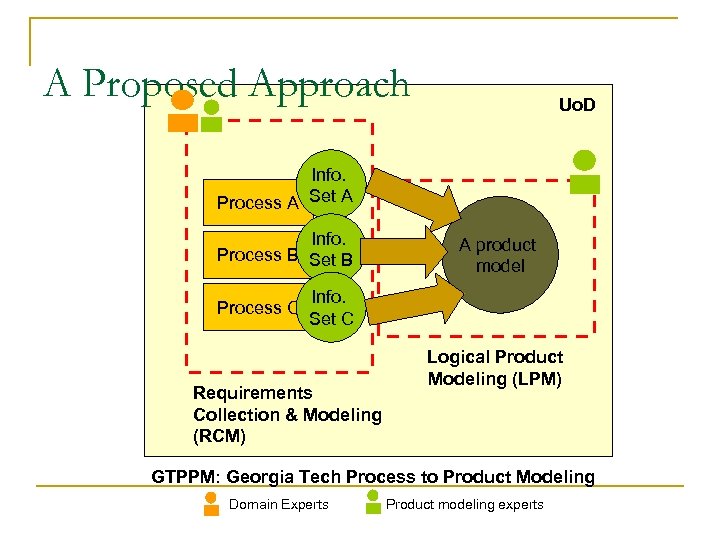 A Proposed Approach Uo. D Info. Process A Set A Info. Process B Set B Process C A product model Info. Set C Requirements Collection & Modeling (RCM) Logical Product Modeling (LPM) GTPPM: Georgia Tech Process to Product Modeling Domain Experts Product modeling experts
A Proposed Approach Uo. D Info. Process A Set A Info. Process B Set B Process C A product model Info. Set C Requirements Collection & Modeling (RCM) Logical Product Modeling (LPM) GTPPM: Georgia Tech Process to Product Modeling Domain Experts Product modeling experts
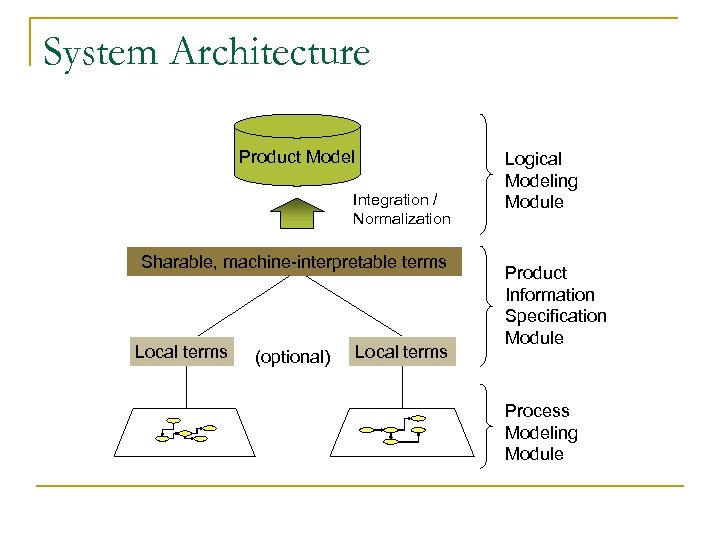 System Architecture Product Model Integration / Normalization Sharable, machine-interpretable terms Local terms (optional) Local terms Logical Modeling Module Product Information Specification Module Process Modeling Module
System Architecture Product Model Integration / Normalization Sharable, machine-interpretable terms Local terms (optional) Local terms Logical Modeling Module Product Information Specification Module Process Modeling Module
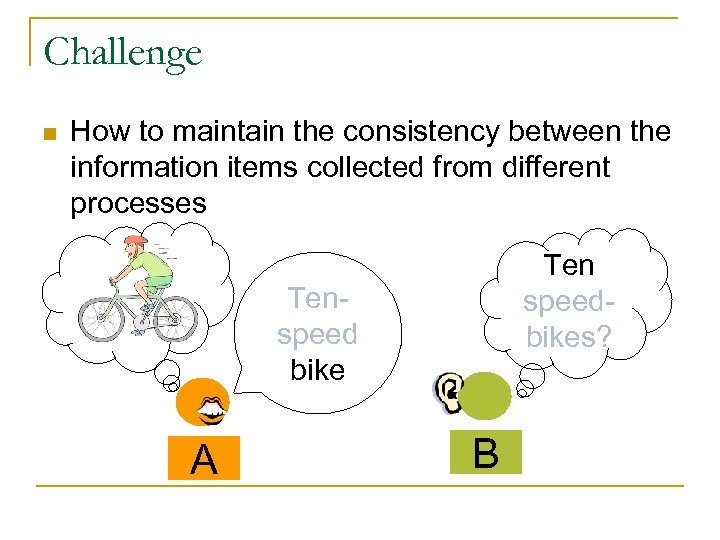 Challenge n How to maintain the consistency between the information items collected from different processes Ten speedbikes? Tenspeed bike A B
Challenge n How to maintain the consistency between the information items collected from different processes Ten speedbikes? Tenspeed bike A B
 Four-level consistency assurance methods n n Semantic level Syntactic level Information flow level Data model level
Four-level consistency assurance methods n n Semantic level Syntactic level Information flow level Data model level
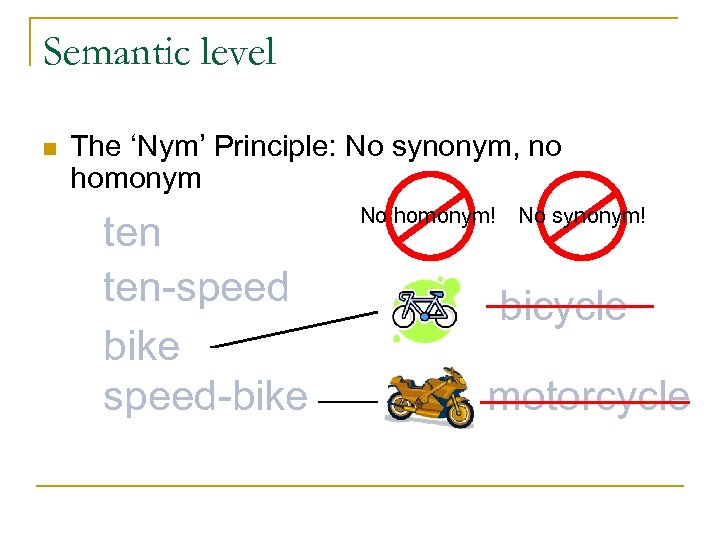 Semantic level n The ‘Nym’ Principle: No synonym, no homonym ten-speed bike speed-bike No homonym! No synonym! bicycle motorcycle
Semantic level n The ‘Nym’ Principle: No synonym, no homonym ten-speed bike speed-bike No homonym! No synonym! bicycle motorcycle
 Syntactic level ten-speed bike speed-bike
Syntactic level ten-speed bike speed-bike
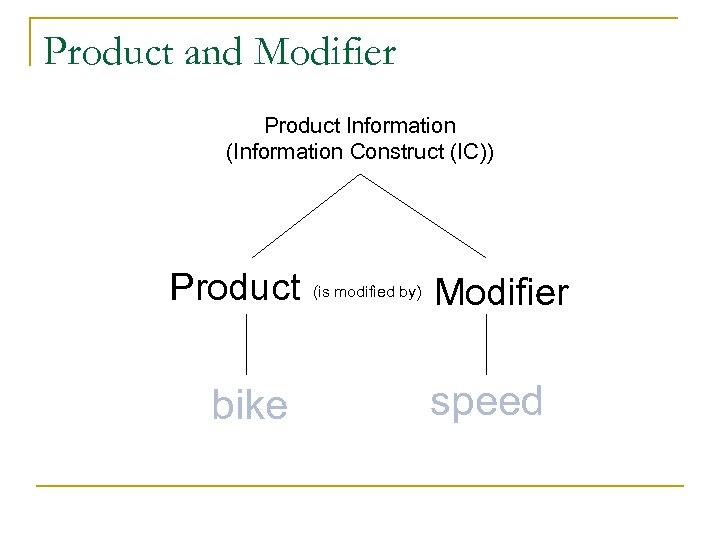 Product and Modifier Product Information (Information Construct (IC)) Product bike (is modified by) Modifier speed
Product and Modifier Product Information (Information Construct (IC)) Product bike (is modified by) Modifier speed
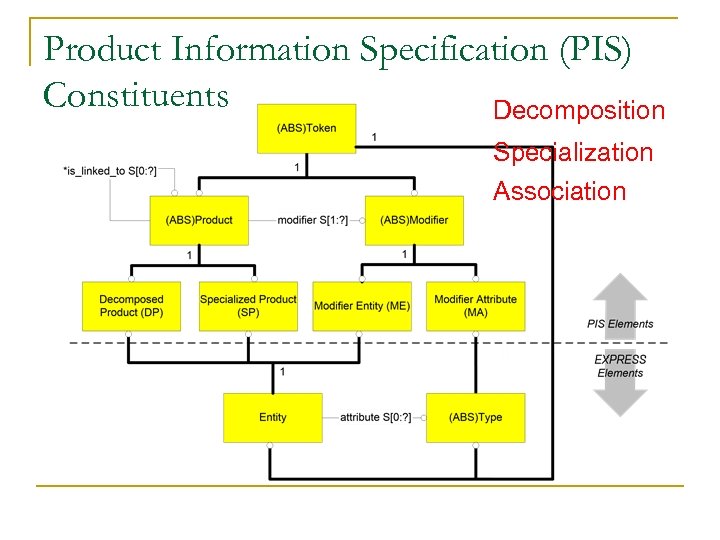 Product Information Specification (PIS) Constituents Decomposition Specialization Association
Product Information Specification (PIS) Constituents Decomposition Specialization Association
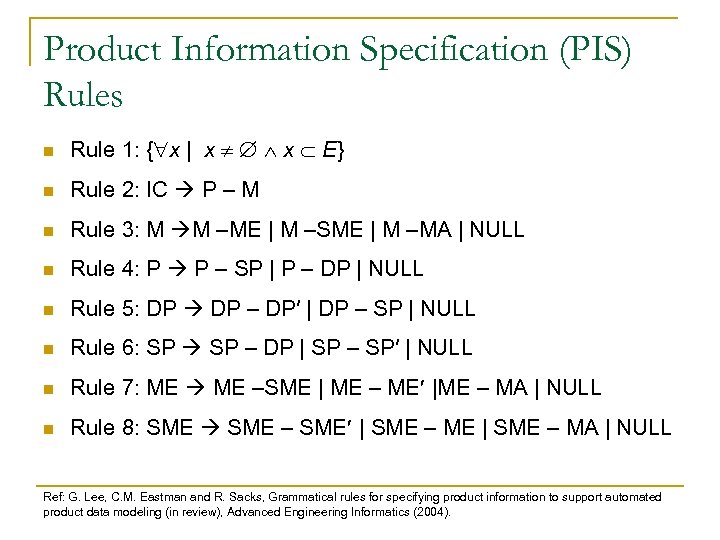 Product Information Specification (PIS) Rules n Rule 1: { x | x x E} n Rule 2: IC P – M n Rule 3: M M –ME | M –SME | M –MA | NULL n Rule 4: P P – SP | P – DP | NULL n Rule 5: DP – DP′ | DP – SP | NULL n Rule 6: SP – DP | SP – SP′ | NULL n Rule 7: ME –SME | ME – ME |ME – MA | NULL n Rule 8: SME – SME | SME – MA | NULL Ref: G. Lee, C. M. Eastman and R. Sacks, Grammatical rules for specifying product information to support automated product data modeling (in review), Advanced Engineering Informatics (2004).
Product Information Specification (PIS) Rules n Rule 1: { x | x x E} n Rule 2: IC P – M n Rule 3: M M –ME | M –SME | M –MA | NULL n Rule 4: P P – SP | P – DP | NULL n Rule 5: DP – DP′ | DP – SP | NULL n Rule 6: SP – DP | SP – SP′ | NULL n Rule 7: ME –SME | ME – ME |ME – MA | NULL n Rule 8: SME – SME | SME – MA | NULL Ref: G. Lee, C. M. Eastman and R. Sacks, Grammatical rules for specifying product information to support automated product data modeling (in review), Advanced Engineering Informatics (2004).
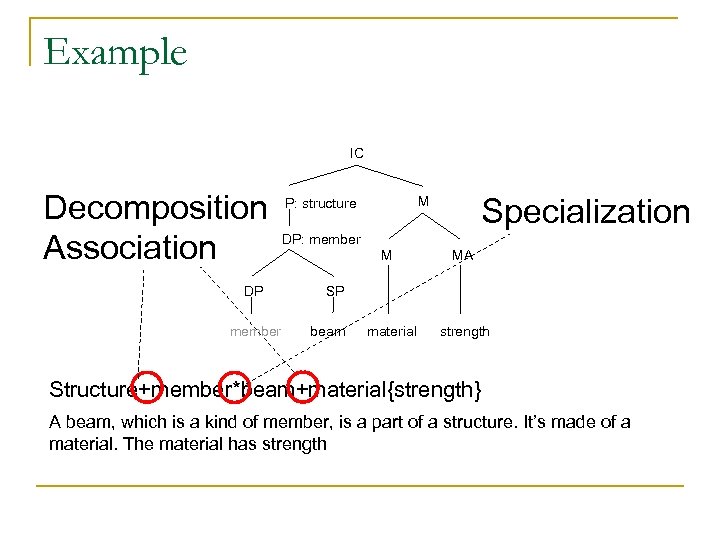 Example IC Decomposition Association DP member Specialization M P: structure DP: member M MA SP beam material strength Structure+member*beam+material{strength} A beam, which is a kind of member, is a part of a structure. It’s made of a material. The material has strength
Example IC Decomposition Association DP member Specialization M P: structure DP: member M MA SP beam material strength Structure+member*beam+material{strength} A beam, which is a kind of member, is a part of a structure. It’s made of a material. The material has strength
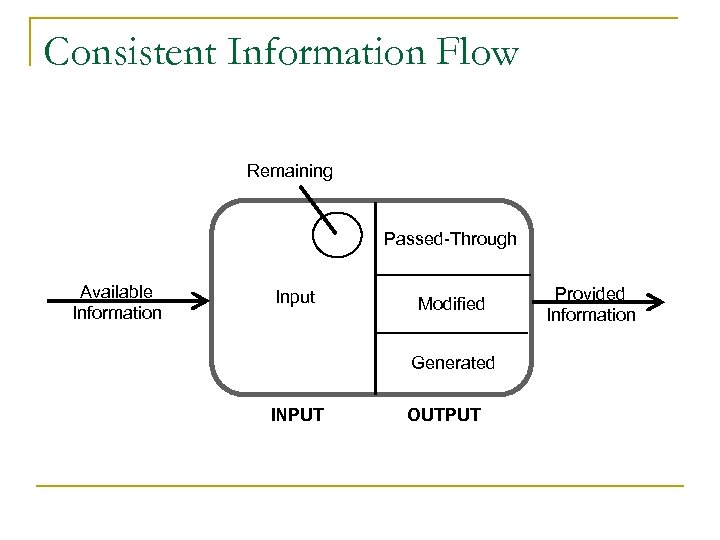 Consistent Information Flow Remaining Passed-Through Available Information Input Modified Generated INPUT OUTPUT Provided Information
Consistent Information Flow Remaining Passed-Through Available Information Input Modified Generated INPUT OUTPUT Provided Information
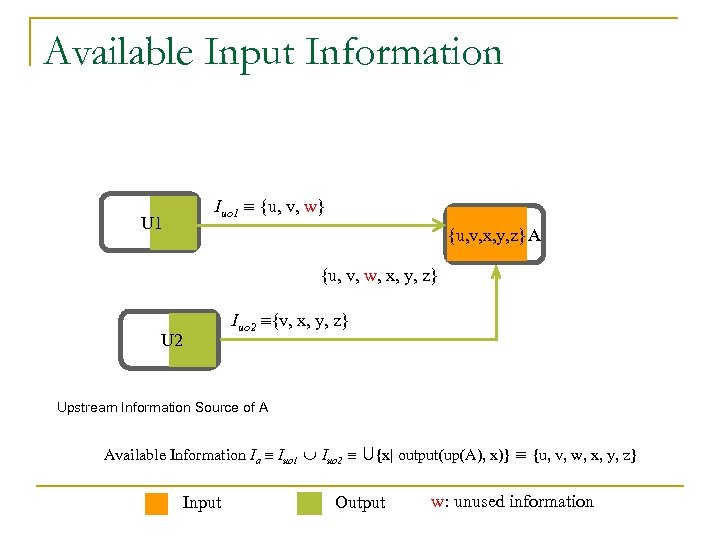 Available Input Information U 1 Iuo 1 {u, v, w} {u, v, x, y, z} A {u, v, w, x, y, z} Iuo 2 {v, x, y, z} U 2 Upstream Information Source of A Available Information Ia Iuo 1 Iuo 2 U{x| output(up(A), x)} {u, v, w, x, y, z} Input Output w: unused information
Available Input Information U 1 Iuo 1 {u, v, w} {u, v, x, y, z} A {u, v, w, x, y, z} Iuo 2 {v, x, y, z} U 2 Upstream Information Source of A Available Information Ia Iuo 1 Iuo 2 U{x| output(up(A), x)} {u, v, w, x, y, z} Input Output w: unused information
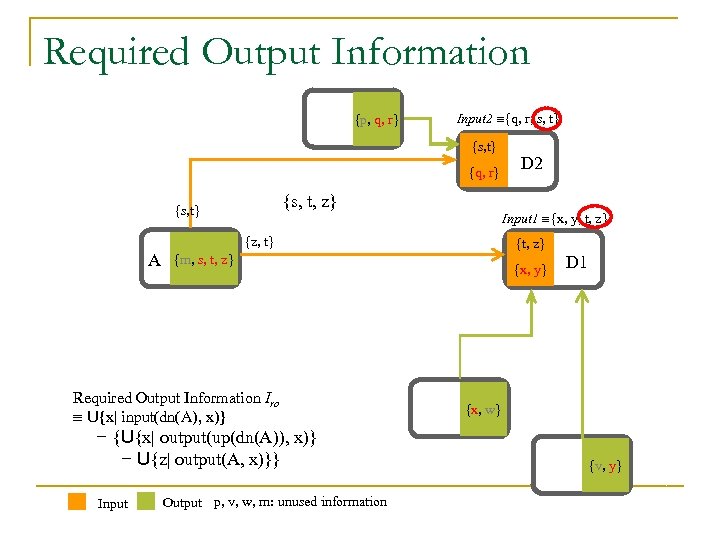 Required Output Information {p, q, r} Input 2 {q, r, s, t} {s, t} D 2 {q, r} {s, t, z} {s, t} Input 1 {x, y, t, z} {z, t} A {t, z} {m, s, t, z} {x, y} D 1 Downstream Information Source of A Required Output Information Iro U{x| input(dn(A), x)} – {U{x| output(up(dn(A)), x)} - U{z| output(A, x)}} Input Output p, v, w, m: unused information {x, w} {v, y}
Required Output Information {p, q, r} Input 2 {q, r, s, t} {s, t} D 2 {q, r} {s, t, z} {s, t} Input 1 {x, y, t, z} {z, t} A {t, z} {m, s, t, z} {x, y} D 1 Downstream Information Source of A Required Output Information Iro U{x| input(dn(A), x)} – {U{x| output(up(dn(A)), x)} - U{z| output(A, x)}} Input Output p, v, w, m: unused information {x, w} {v, y}
 Remedies n n n Adjustment of information items Adjustment of flows Adjustment of activities
Remedies n n n Adjustment of information items Adjustment of flows Adjustment of activities
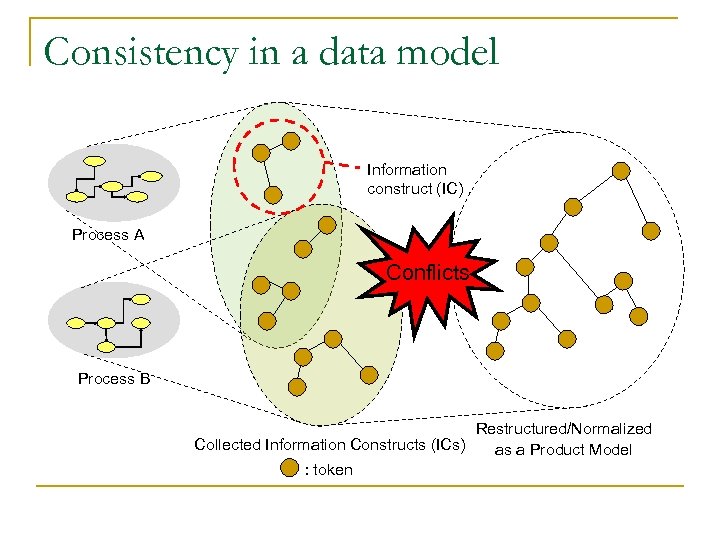 Consistency in a data model Information construct (IC) Process A Conflicts Process B Restructured/Normalized Collected Information Constructs (ICs) as a Product Model : token
Consistency in a data model Information construct (IC) Process A Conflicts Process B Restructured/Normalized Collected Information Constructs (ICs) as a Product Model : token
 A Basic Principle for conflict resolution “More semantics”
A Basic Principle for conflict resolution “More semantics”
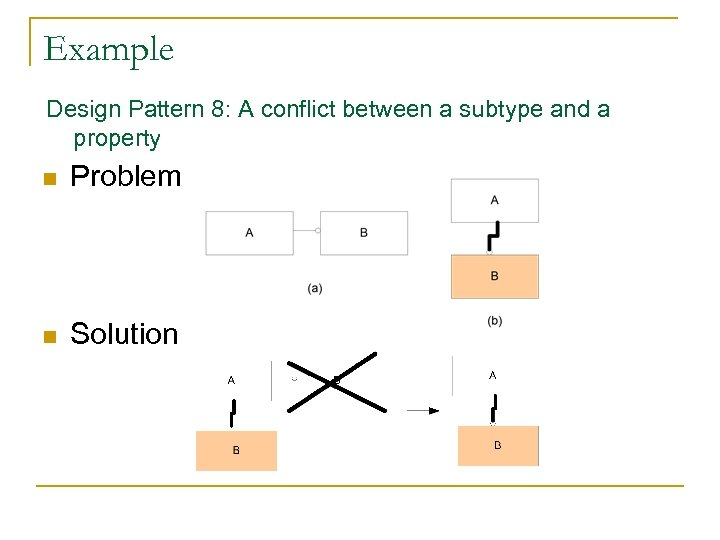 Example Design Pattern 8: A conflict between a subtype and a property n Problem n Solution
Example Design Pattern 8: A conflict between a subtype and a property n Problem n Solution
 Implementation n EXPRESS MS Visio Add-on GTPPM®
Implementation n EXPRESS MS Visio Add-on GTPPM®
 Current Status n n Experimentation with the fourteen North American precast concrete companies Deployment in several construction IT-related research projects at CMU, Purdue, U. Florida, and Teeside Univ. (UK), Israel Institute of Technology
Current Status n n Experimentation with the fourteen North American precast concrete companies Deployment in several construction IT-related research projects at CMU, Purdue, U. Florida, and Teeside Univ. (UK), Israel Institute of Technology
 Future Work & Possible Extension n n Further development with the ISO STEP committees Possible extensions q q q Project/Product lifecycle management (PLM) Workflow management Business process reengineering Conformance class development Product model update Automated data translator development
Future Work & Possible Extension n n Further development with the ISO STEP committees Possible extensions q q q Project/Product lifecycle management (PLM) Workflow management Business process reengineering Conformance class development Product model update Automated data translator development
 Questions? http: //dcom. arch. gatech. edu/glee/gtppm ghang. lee@arch. gatech. edu
Questions? http: //dcom. arch. gatech. edu/glee/gtppm ghang. lee@arch. gatech. edu


