0dca5b65cc4ac639a1950d23a21ddf21.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 DEPFET Readout and Control Electronics Ivan Peric, Peter Fischer, Christian Kreidl Heidelberg University 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
DEPFET Readout and Control Electronics Ivan Peric, Peter Fischer, Christian Kreidl Heidelberg University 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 Outline - Module Electronics - Introduction Principle of DEPFET readout Switcher with LV transistors (Switcher 3) Switcher with HV transistors DCD Chip Bumping technologies 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Outline - Module Electronics - Introduction Principle of DEPFET readout Switcher with LV transistors (Switcher 3) Switcher with HV transistors DCD Chip Bumping technologies 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 DEPFET readout and control-ASICS 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
DEPFET readout and control-ASICS 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
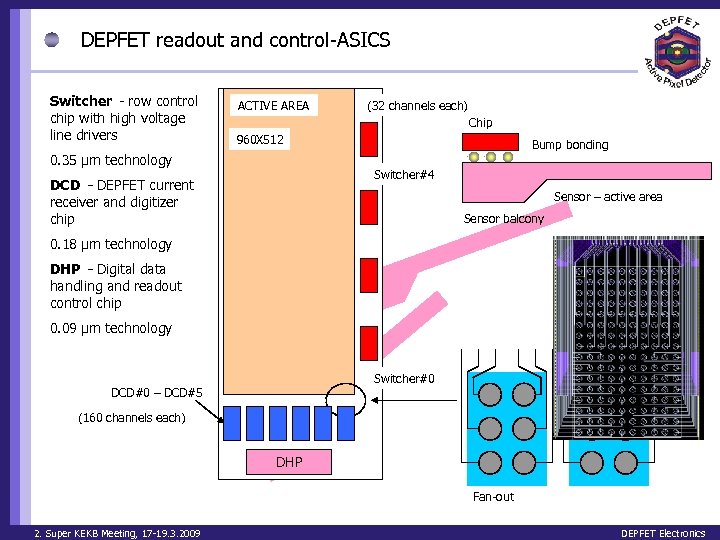 DEPFET readout and control-ASICS Switcher – row control chip with high voltage line drivers ACTIVE AREA (32 channels each) Chip 960 X 512 0. 35 μm technology Bump bonding Switcher#4 DCD – DEPFET current receiver and digitizer chip Sensor – active area Sensor balcony 0. 18 μm technology DHP – Digital data handling and readout control chip 0. 09 μm technology Switcher#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 (160 channels each) DHP Fan-out 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
DEPFET readout and control-ASICS Switcher – row control chip with high voltage line drivers ACTIVE AREA (32 channels each) Chip 960 X 512 0. 35 μm technology Bump bonding Switcher#4 DCD – DEPFET current receiver and digitizer chip Sensor – active area Sensor balcony 0. 18 μm technology DHP – Digital data handling and readout control chip 0. 09 μm technology Switcher#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 (160 channels each) DHP Fan-out 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
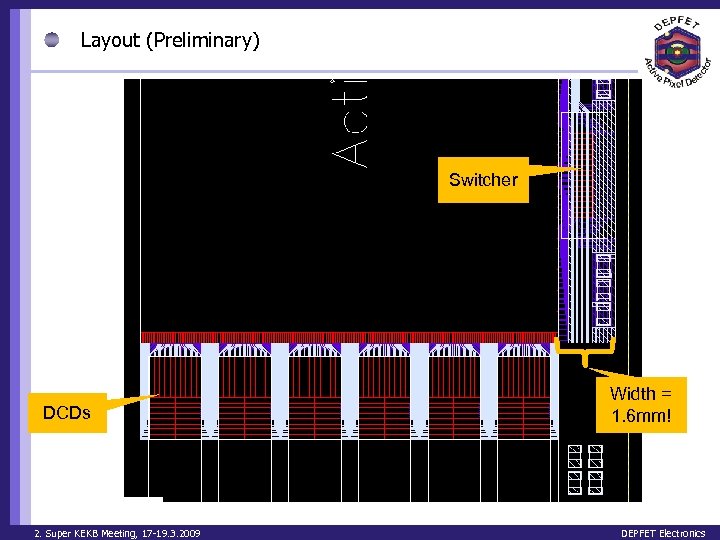 Layout (Preliminary) Switcher DCDs 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Width = 1. 6 mm! DEPFET Electronics
Layout (Preliminary) Switcher DCDs 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Width = 1. 6 mm! DEPFET Electronics
 Principle of DEPFET readout 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Principle of DEPFET readout 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
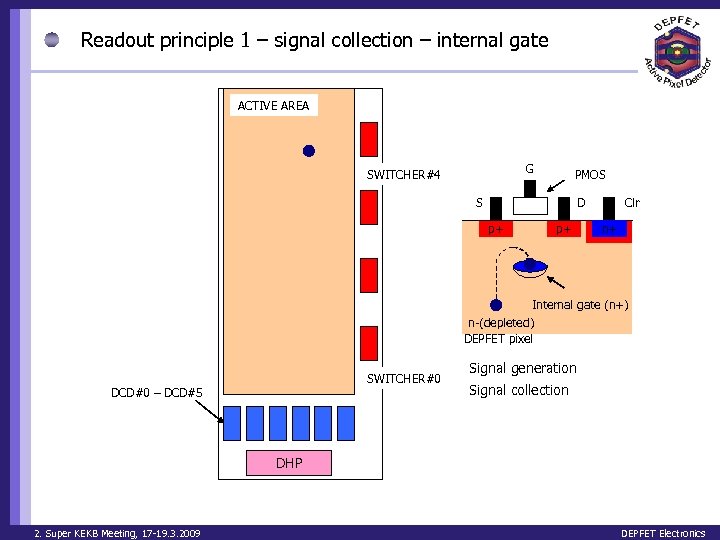 Readout principle 1 – signal collection – internal gate ACTIVE AREA G SWITCHER#4 PMOS S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Readout principle 1 – signal collection – internal gate ACTIVE AREA G SWITCHER#4 PMOS S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
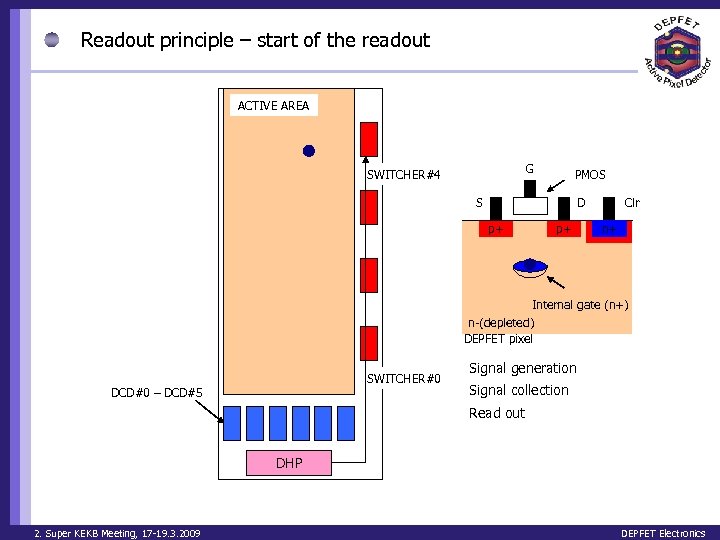 Readout principle – start of the readout ACTIVE AREA G SWITCHER#4 PMOS S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Readout principle – start of the readout ACTIVE AREA G SWITCHER#4 PMOS S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
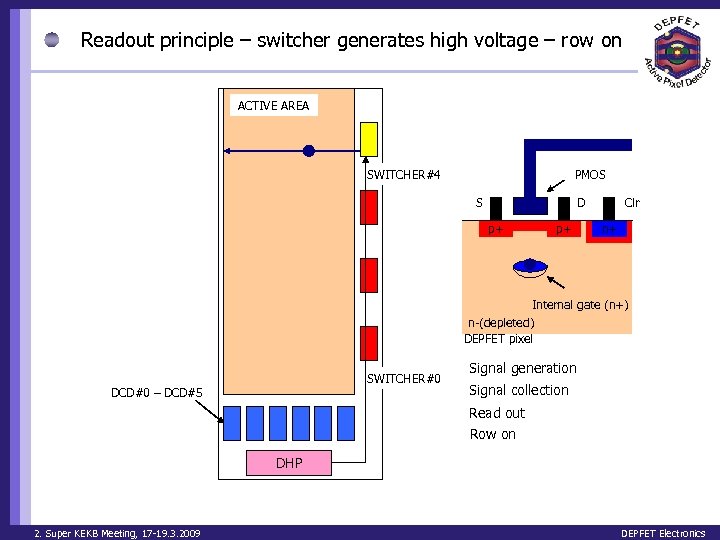 Readout principle – switcher generates high voltage – row on ACTIVE AREA G SWITCHER#4 PMOS S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Readout principle – switcher generates high voltage – row on ACTIVE AREA G SWITCHER#4 PMOS S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
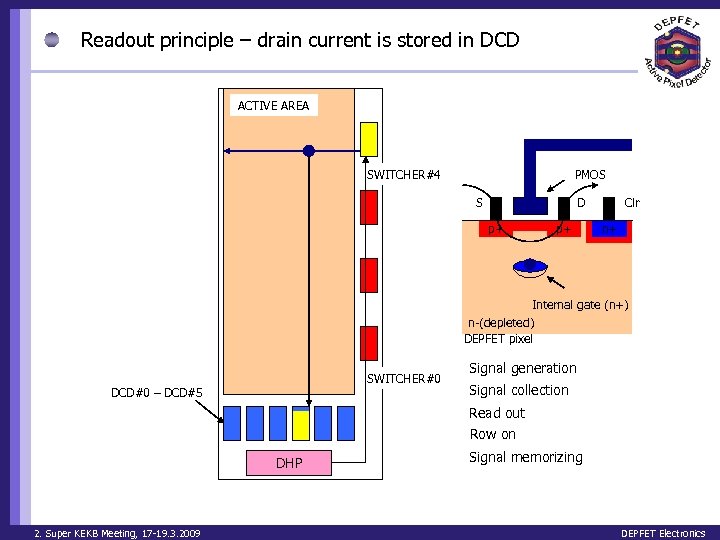 Readout principle – drain current is stored in DCD ACTIVE AREA PMOS SWITCHER#4 S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Signal memorizing DEPFET Electronics
Readout principle – drain current is stored in DCD ACTIVE AREA PMOS SWITCHER#4 S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Signal memorizing DEPFET Electronics
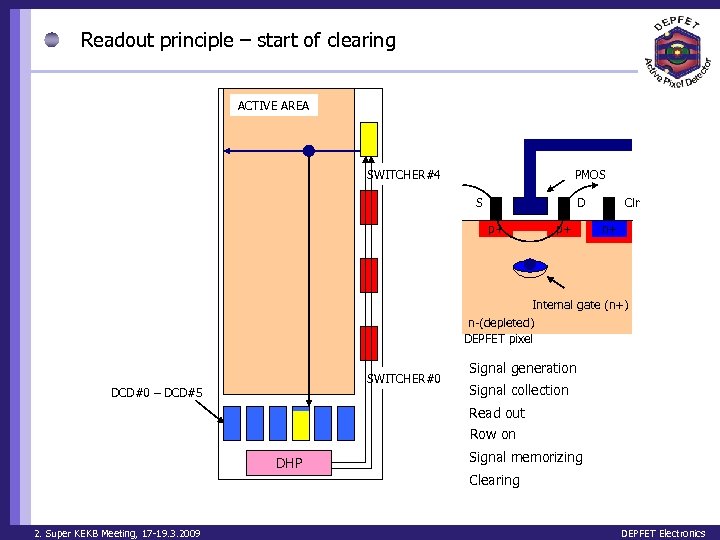 Readout principle – start of clearing ACTIVE AREA PMOS SWITCHER#4 S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Signal memorizing Clearing DEPFET Electronics
Readout principle – start of clearing ACTIVE AREA PMOS SWITCHER#4 S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Signal memorizing Clearing DEPFET Electronics
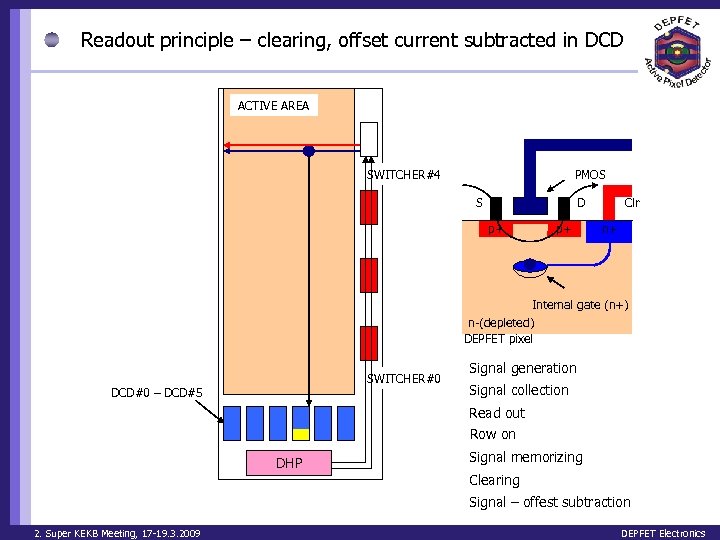 Readout principle – clearing, offset current subtracted in DCD ACTIVE AREA PMOS SWITCHER#4 S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP Signal memorizing Clearing Signal – offest subtraction 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Readout principle – clearing, offset current subtracted in DCD ACTIVE AREA PMOS SWITCHER#4 S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP Signal memorizing Clearing Signal – offest subtraction 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 Readout principle – A/D conversion ACTIVE AREA G SWITCHER#4 PMOS S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP 00110 A/D conversion 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Signal memorizing Clearing Signal – offest subtraction DEPFET Electronics
Readout principle – A/D conversion ACTIVE AREA G SWITCHER#4 PMOS S D p+ p+ Clr n+ Internal gate (n+) n-(depleted) DEPFET pixel SWITCHER#0 DCD#0 – DCD#5 Signal generation Signal collection Read out Row on DHP 00110 A/D conversion 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Signal memorizing Clearing Signal – offest subtraction DEPFET Electronics
 Row control “Switcher” chip 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Row control “Switcher” chip 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
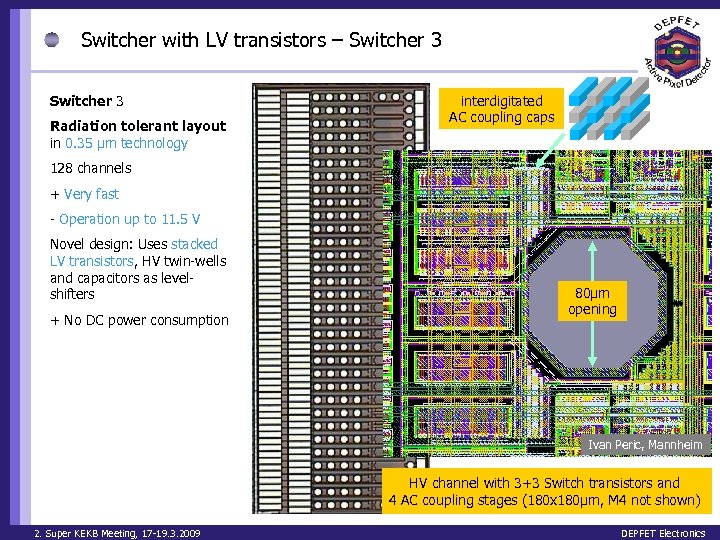 Switcher with LV transistors – Switcher 3 Radiation tolerant layout in 0. 35 μm technology interdigitated AC coupling caps 128 channels + Very fast - Operation up to 11. 5 V Novel design: Uses stacked LV transistors, HV twin-wells and capacitors as levelshifters + No DC power consumption 80µm opening Ivan Peric, Mannheim HV channel with 3+3 Switch transistors and 4 AC coupling stages (180 x 180µm, M 4 not shown) 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Switcher with LV transistors – Switcher 3 Radiation tolerant layout in 0. 35 μm technology interdigitated AC coupling caps 128 channels + Very fast - Operation up to 11. 5 V Novel design: Uses stacked LV transistors, HV twin-wells and capacitors as levelshifters + No DC power consumption 80µm opening Ivan Peric, Mannheim HV channel with 3+3 Switch transistors and 4 AC coupling stages (180 x 180µm, M 4 not shown) 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
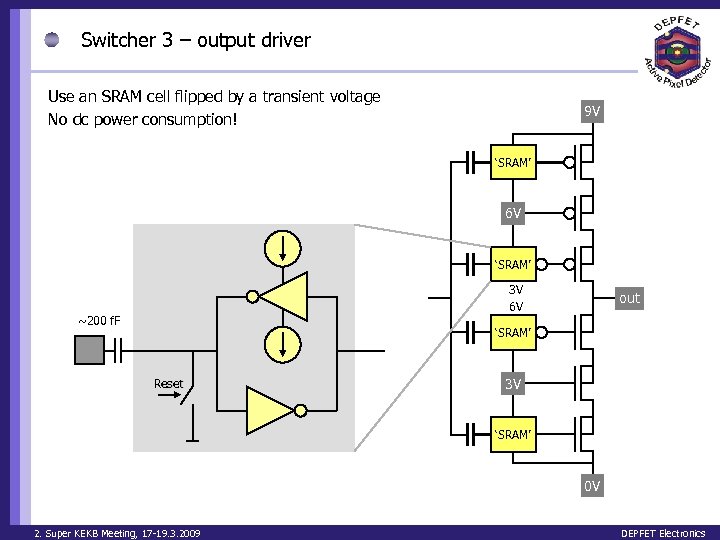 Switcher 3 – output driver Use an SRAM cell flipped by a transient voltage No dc power consumption! 9 V ‘SRAM’ 6 V ‘SRAM’ 3 V 6 V ~200 f. F out ‘SRAM’ Reset 3 V ‘SRAM’ 0 V 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Switcher 3 – output driver Use an SRAM cell flipped by a transient voltage No dc power consumption! 9 V ‘SRAM’ 6 V ‘SRAM’ 3 V 6 V ~200 f. F out ‘SRAM’ Reset 3 V ‘SRAM’ 0 V 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 Switcher with LV transistors – Switcher 3 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Switcher with LV transistors – Switcher 3 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
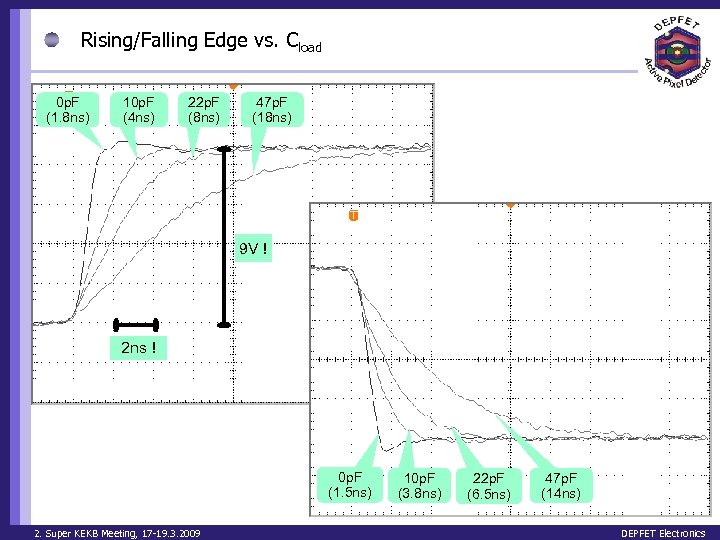 Rising/Falling Edge vs. Cload 0 p. F (1. 8 ns) 10 p. F (4 ns) 22 p. F (8 ns) 47 p. F (18 ns) 9 V ! 2 ns ! 0 p. F (1. 5 ns) 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 10 p. F (3. 8 ns) 22 p. F (6. 5 ns) 47 p. F (14 ns) DEPFET Electronics
Rising/Falling Edge vs. Cload 0 p. F (1. 8 ns) 10 p. F (4 ns) 22 p. F (8 ns) 47 p. F (18 ns) 9 V ! 2 ns ! 0 p. F (1. 5 ns) 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 10 p. F (3. 8 ns) 22 p. F (6. 5 ns) 47 p. F (14 ns) DEPFET Electronics
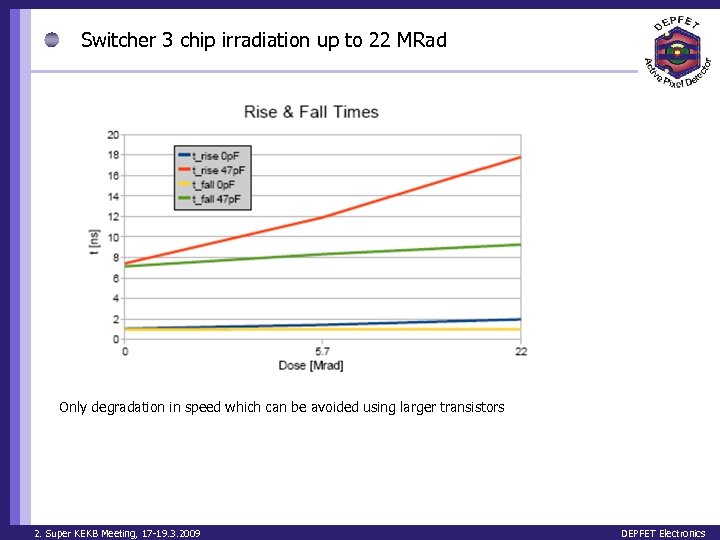 Switcher 3 chip irradiation up to 22 MRad Only degradation in speed which can be avoided using larger transistors 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Switcher 3 chip irradiation up to 22 MRad Only degradation in speed which can be avoided using larger transistors 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
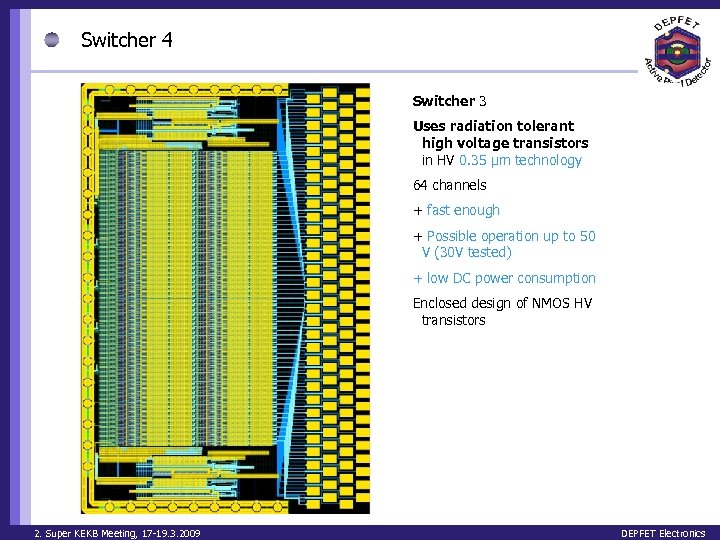 Switcher 4 Switcher 3 Uses radiation tolerant high voltage transistors in HV 0. 35 μm technology 64 channels + fast enough + Possible operation up to 50 V (30 V tested) + low DC power consumption Enclosed design of NMOS HV transistors 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Switcher 4 Switcher 3 Uses radiation tolerant high voltage transistors in HV 0. 35 μm technology 64 channels + fast enough + Possible operation up to 50 V (30 V tested) + low DC power consumption Enclosed design of NMOS HV transistors 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
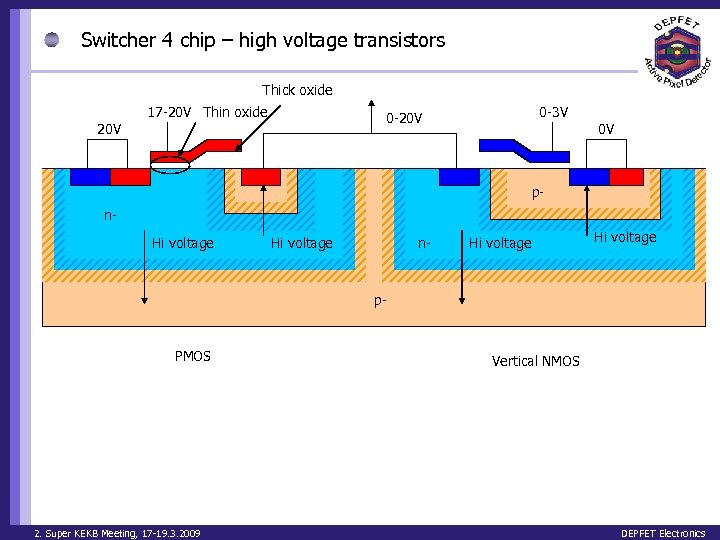 Switcher 4 chip – high voltage transistors Thick oxide 17 -20 V Thin oxide 0 -3 V 0 -20 V 0 V pn. Hi voltage n- Hi voltage p- PMOS 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Vertical NMOS DEPFET Electronics
Switcher 4 chip – high voltage transistors Thick oxide 17 -20 V Thin oxide 0 -3 V 0 -20 V 0 V pn. Hi voltage n- Hi voltage p- PMOS 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Vertical NMOS DEPFET Electronics
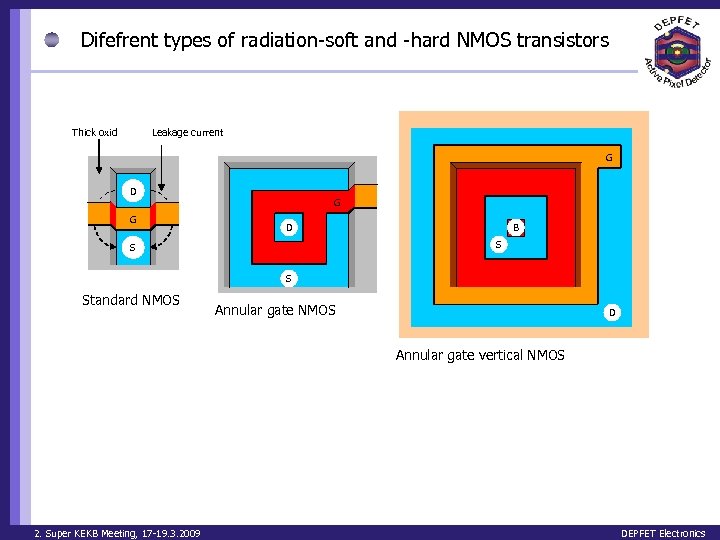 Difefrent types of radiation-soft and -hard NMOS transistors Thick oxid Leakage current G D G G D B S Standard NMOS Annular gate NMOS D Annular gate vertical NMOS 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Difefrent types of radiation-soft and -hard NMOS transistors Thick oxid Leakage current G D G G D B S Standard NMOS Annular gate NMOS D Annular gate vertical NMOS 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
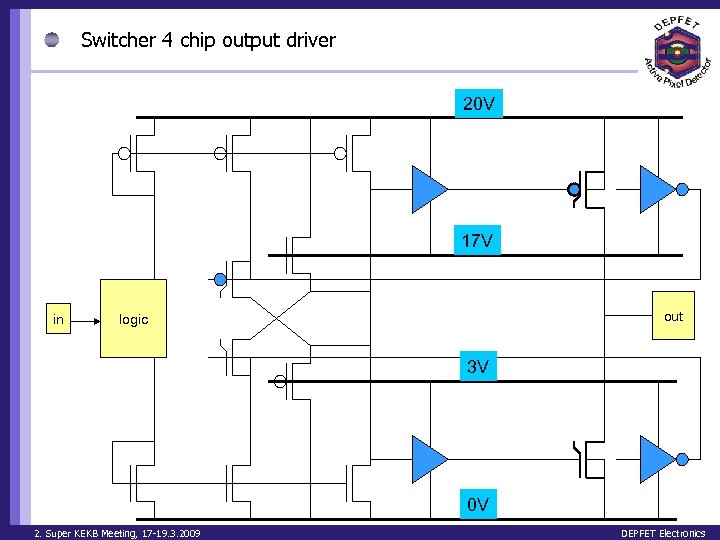 Switcher 4 chip output driver 20 V 17 V in out logic 3 V 0 V 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Switcher 4 chip output driver 20 V 17 V in out logic 3 V 0 V 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
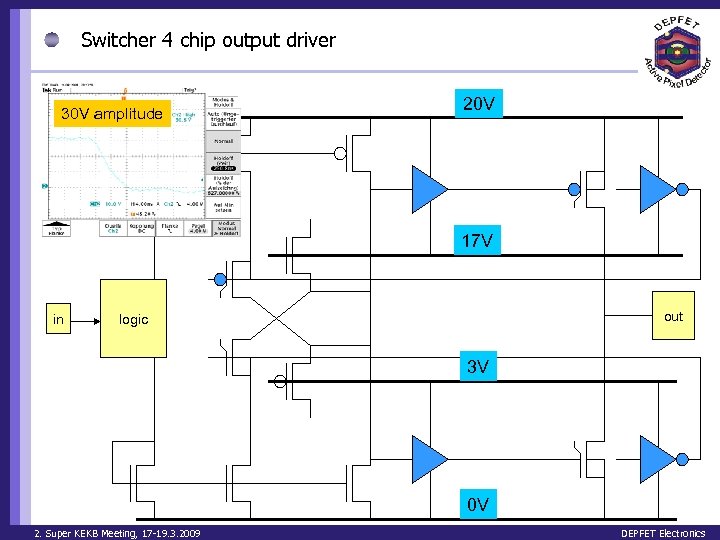 Switcher 4 chip output driver 30 V amplitude 20 V 17 V in out logic 3 V 0 V 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Switcher 4 chip output driver 30 V amplitude 20 V 17 V in out logic 3 V 0 V 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
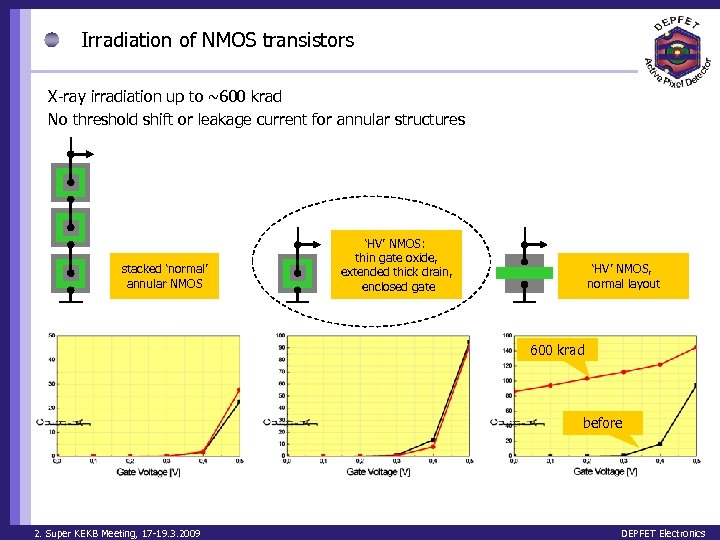 Irradiation of NMOS transistors X-ray irradiation up to ~600 krad No threshold shift or leakage current for annular structures stacked ‘normal’ annular NMOS ‘HV’ NMOS: thin gate oxide, extended thick drain, enclosed gate ‘HV’ NMOS, normal layout 600 krad before 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Irradiation of NMOS transistors X-ray irradiation up to ~600 krad No threshold shift or leakage current for annular structures stacked ‘normal’ annular NMOS ‘HV’ NMOS: thin gate oxide, extended thick drain, enclosed gate ‘HV’ NMOS, normal layout 600 krad before 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 DEPFET signal digitizer chip - DCD 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
DEPFET signal digitizer chip - DCD 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 DCD 3 chip - 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Technology 0. 18 μm 72 Channels 2 ADCs and regulated cascode/channel 6 channels multiplexed to one digital LVDS output ADC sampling period 160 ns (8 bits) Channel sampling period 80 ns LVDS output: 600 M bits/s Chip: 7. 2 G bits/s (12 outputs) Radiation tolerant design ~ 1 m. W/ADC DEPFET Electronics
DCD 3 chip - 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Technology 0. 18 μm 72 Channels 2 ADCs and regulated cascode/channel 6 channels multiplexed to one digital LVDS output ADC sampling period 160 ns (8 bits) Channel sampling period 80 ns LVDS output: 600 M bits/s Chip: 7. 2 G bits/s (12 outputs) Radiation tolerant design ~ 1 m. W/ADC DEPFET Electronics
 DCD 3 chip 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 3 chip 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
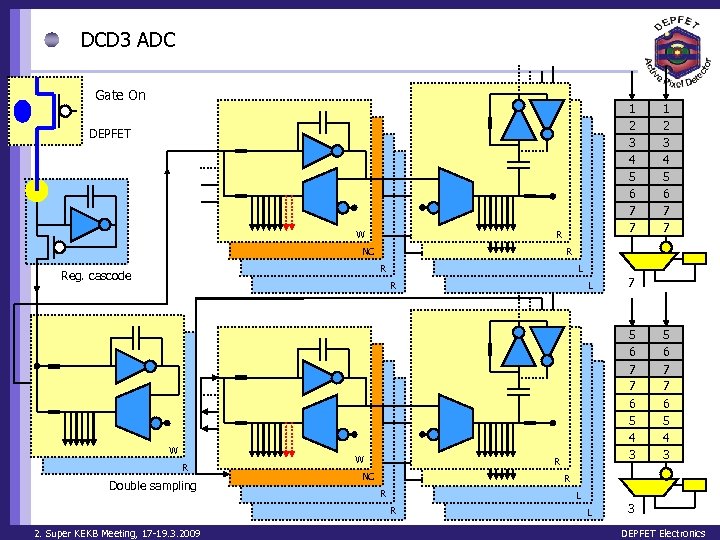 DCD 3 ADC Gate On 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling W L 7 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R NC 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L 3 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 3 ADC Gate On 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling W L 7 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R NC 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L 3 DEPFET Electronics
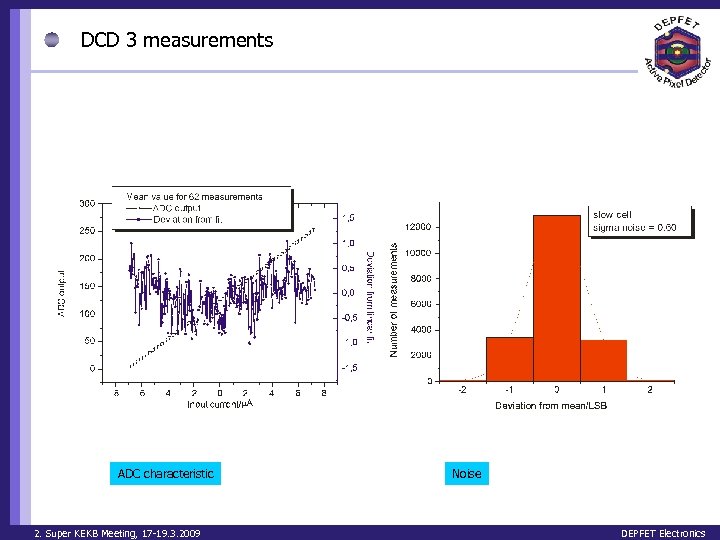 DCD 3 measurements ADC characteristic 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Noise DEPFET Electronics
DCD 3 measurements ADC characteristic 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Noise DEPFET Electronics
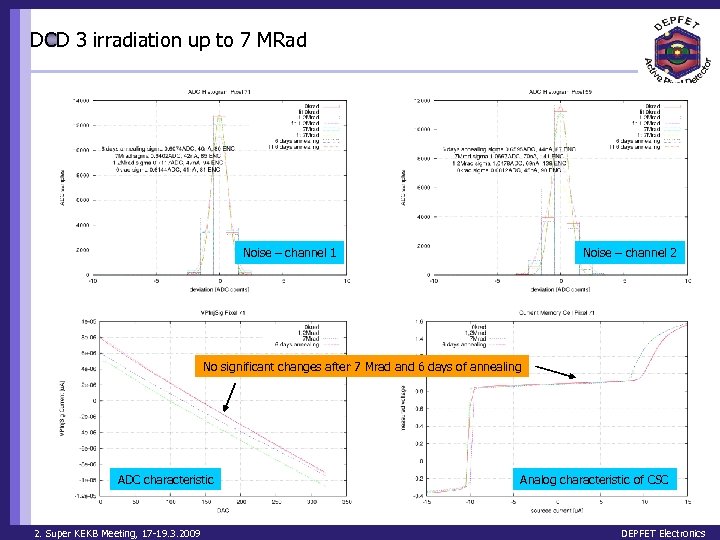 DCD 3 irradiation up to 7 MRad Noise – channel 1 Noise – channel 2 No significant changes after 7 Mrad and 6 days of annealing ADC characteristic 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Analog characteristic of CSC DEPFET Electronics
DCD 3 irradiation up to 7 MRad Noise – channel 1 Noise – channel 2 No significant changes after 7 Mrad and 6 days of annealing ADC characteristic 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Analog characteristic of CSC DEPFET Electronics
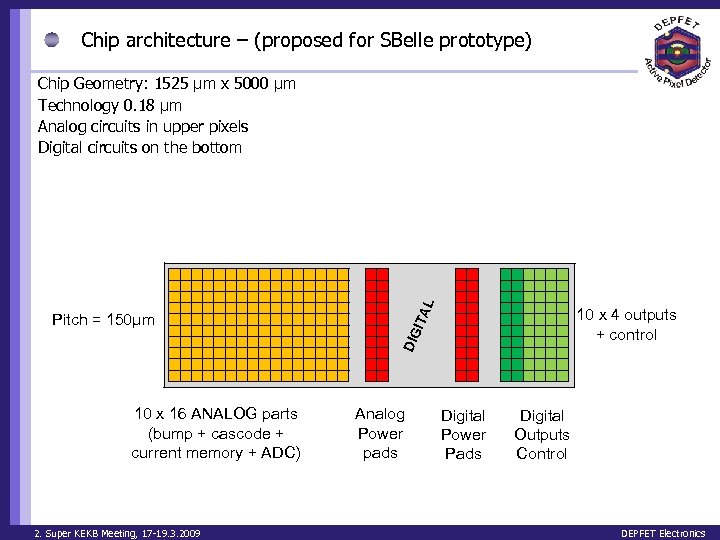 Chip architecture – (proposed for SBelle prototype) L Chip Geometry: 1525 µm x 5000 µm Technology 0. 18 μm Analog circuits in upper pixels Digital circuits on the bottom ITA 10 x 4 outputs + control DIG Pitch = 150µm 10 x 16 ANALOG parts (bump + cascode + current memory + ADC) 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Analog Power pads Digital Power Pads Digital Outputs Control DEPFET Electronics
Chip architecture – (proposed for SBelle prototype) L Chip Geometry: 1525 µm x 5000 µm Technology 0. 18 μm Analog circuits in upper pixels Digital circuits on the bottom ITA 10 x 4 outputs + control DIG Pitch = 150µm 10 x 16 ANALOG parts (bump + cascode + current memory + ADC) 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 Analog Power pads Digital Power Pads Digital Outputs Control DEPFET Electronics
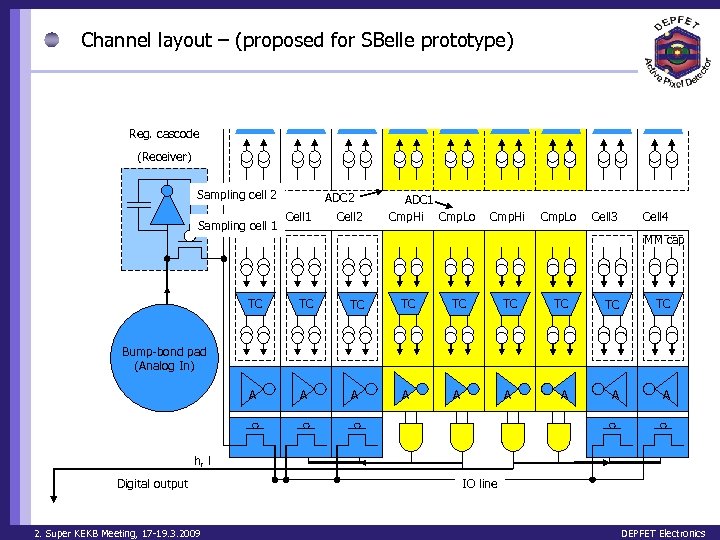 Channel layout – (proposed for SBelle prototype) Reg. cascode (Receiver) Sampling cell 2 Sampling cell 1 ADC 2 Cell 1 Cell 2 ADC 1 Cmp. Hi Cmp. Lo Cell 3 Cell 4 MM cap TC TC TC A A A A A Bump-bond pad (Analog In) h, l Digital output 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 IO line DEPFET Electronics
Channel layout – (proposed for SBelle prototype) Reg. cascode (Receiver) Sampling cell 2 Sampling cell 1 ADC 2 Cell 1 Cell 2 ADC 1 Cmp. Hi Cmp. Lo Cell 3 Cell 4 MM cap TC TC TC A A A A A Bump-bond pad (Analog In) h, l Digital output 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 IO line DEPFET Electronics
 Data handling processor - DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Data handling processor - DHP 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
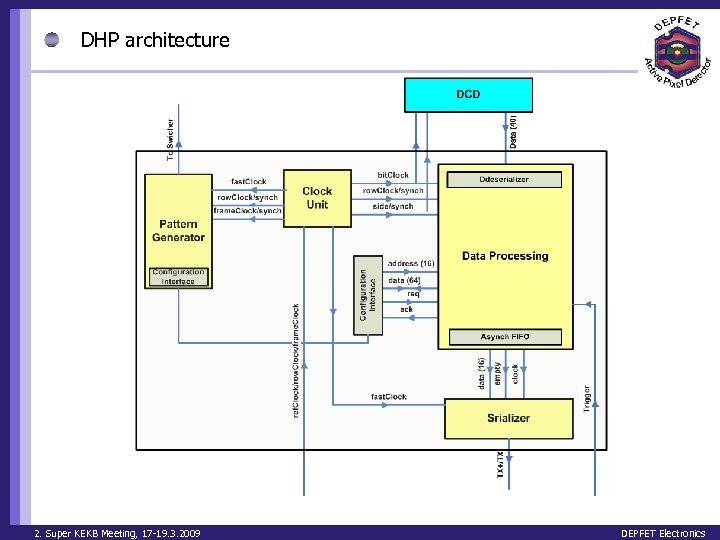 DHP architecture 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
DHP architecture 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
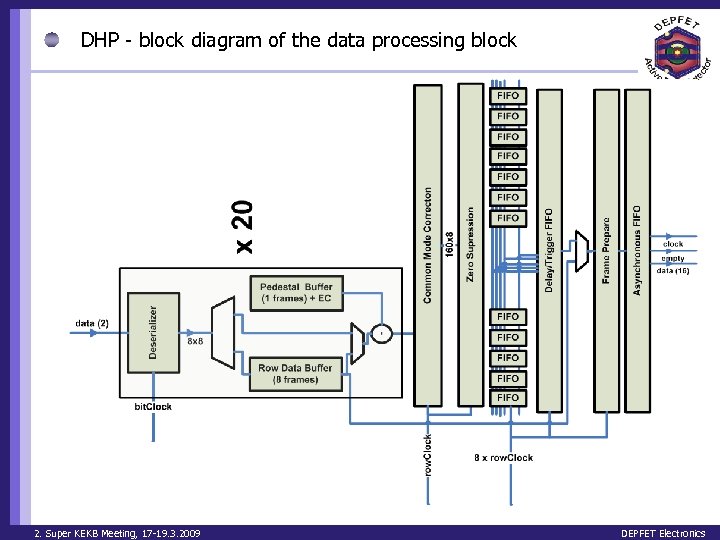 DHP - block diagram of the data processing block 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
DHP - block diagram of the data processing block 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 Bumping 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Bumping 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 Base technology – chip with gold stuts 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Base technology – chip with gold stuts 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
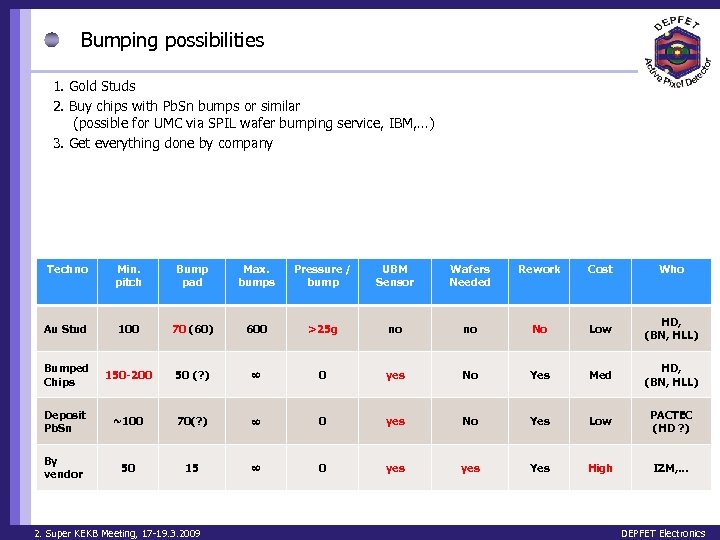 Bumping possibilities 1. Gold Studs 2. Buy chips with Pb. Sn bumps or similar (possible for UMC via SPIL wafer bumping service, IBM, …) 3. Get everything done by company Techno Min. pitch Bump pad Max. bumps Pressure / bump UBM Sensor Wafers Needed Rework Cost Who Au Stud 100 70 (60) 600 >25 g no no No Low HD, (BN, HLL) Bumped Chips 150 -200 50 (? ) 0 yes No Yes Med HD, (BN, HLL) Deposit Pb. Sn ~100 70(? ) 0 yes No Yes Low PACTEC (HD ? ) By vendor 50 15 0 yes Yes High IZM, … 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Bumping possibilities 1. Gold Studs 2. Buy chips with Pb. Sn bumps or similar (possible for UMC via SPIL wafer bumping service, IBM, …) 3. Get everything done by company Techno Min. pitch Bump pad Max. bumps Pressure / bump UBM Sensor Wafers Needed Rework Cost Who Au Stud 100 70 (60) 600 >25 g no no No Low HD, (BN, HLL) Bumped Chips 150 -200 50 (? ) 0 yes No Yes Med HD, (BN, HLL) Deposit Pb. Sn ~100 70(? ) 0 yes No Yes Low PACTEC (HD ? ) By vendor 50 15 0 yes Yes High IZM, … 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 Conclusions - DCD prototype chip has been tested with test signals that correspond to DEPFET currents and irradiated up to 7 Mrad. The chip works fine and has high enough conversion speed. Operation with matrices still to be tested – we do not expect problems. Only „fine tuning“ of the design for the super KEKB operation is necessary. - Switcher prototype with LV transistors has been tested and irradiated up to 22 MRad. The chip works fine and has adequate speed for SBelle operation. - Another prototype with HV transistors has been designed and tested. - The irradiation of the chip still has to be done but the basic and most critical part (high-voltage NMOS) has been irradiated up to 600 KRad and no damage has been observed. - DHP chip will be designed using digital design tools in intrinsically radiation hard 90 nm technology. - Choice between 4 different bumping technologies – advantages and disadvantages still to be evaluated… 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Conclusions - DCD prototype chip has been tested with test signals that correspond to DEPFET currents and irradiated up to 7 Mrad. The chip works fine and has high enough conversion speed. Operation with matrices still to be tested – we do not expect problems. Only „fine tuning“ of the design for the super KEKB operation is necessary. - Switcher prototype with LV transistors has been tested and irradiated up to 22 MRad. The chip works fine and has adequate speed for SBelle operation. - Another prototype with HV transistors has been designed and tested. - The irradiation of the chip still has to be done but the basic and most critical part (high-voltage NMOS) has been irradiated up to 600 KRad and no damage has been observed. - DHP chip will be designed using digital design tools in intrinsically radiation hard 90 nm technology. - Choice between 4 different bumping technologies – advantages and disadvantages still to be evaluated… 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
 Thank you 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
Thank you 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 DEPFET Electronics
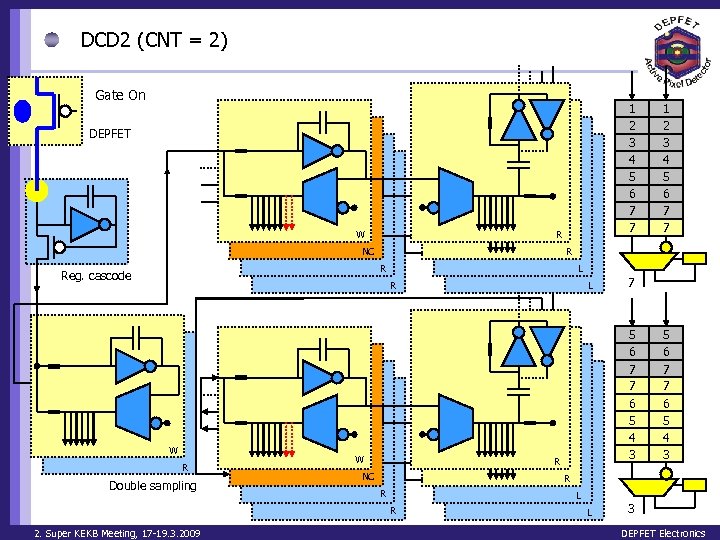 DCD 2 (CNT = 2) Gate On 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling W L 7 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R NC 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L 3 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 2) Gate On 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling W L 7 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R NC 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L 3 DEPFET Electronics
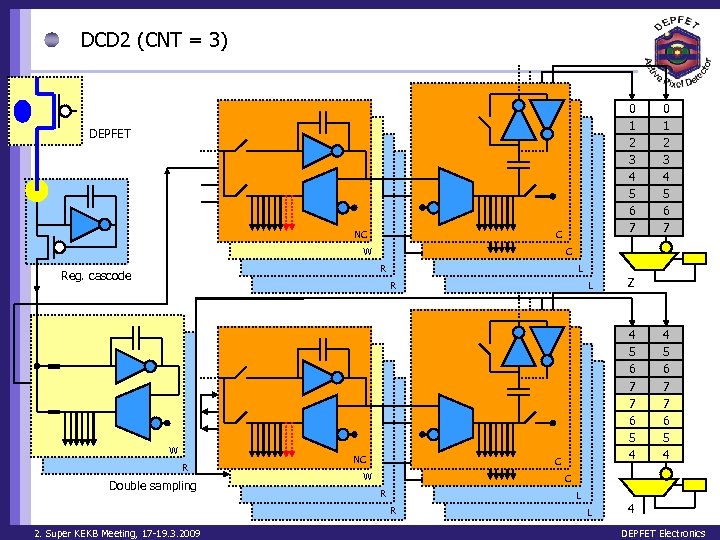 DCD 2 (CNT = 3) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling NC L Z 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 C W 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 L 4 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 3) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling NC L Z 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 C W 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 L 4 DEPFET Electronics
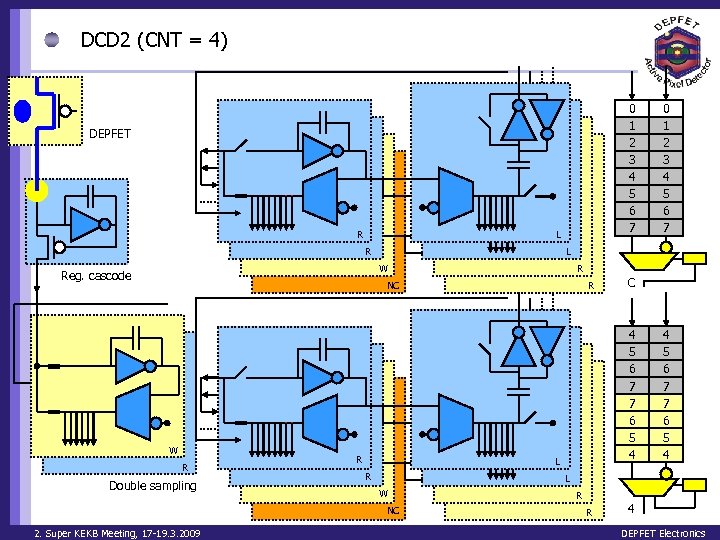 DCD 2 (CNT = 4) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DEPFET R L W Reg. cascode R NC W R Double sampling R R C 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 L R 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 L W NC 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 R R 4 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 4) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DEPFET R L W Reg. cascode R NC W R Double sampling R R C 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 L R 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 L W NC 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 R R 4 DEPFET Electronics
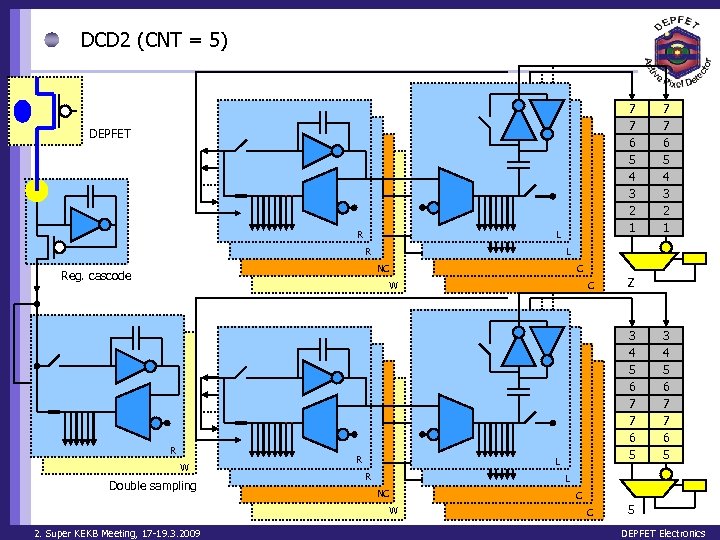 DCD 2 (CNT = 5) Clear On 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DEPFET R L NC Reg. cascode C W R W Double sampling R C Z 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 L R 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 L NC W 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 C C 5 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 5) Clear On 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DEPFET R L NC Reg. cascode C W R W Double sampling R C Z 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 L R 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 L NC W 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 C C 5 DEPFET Electronics
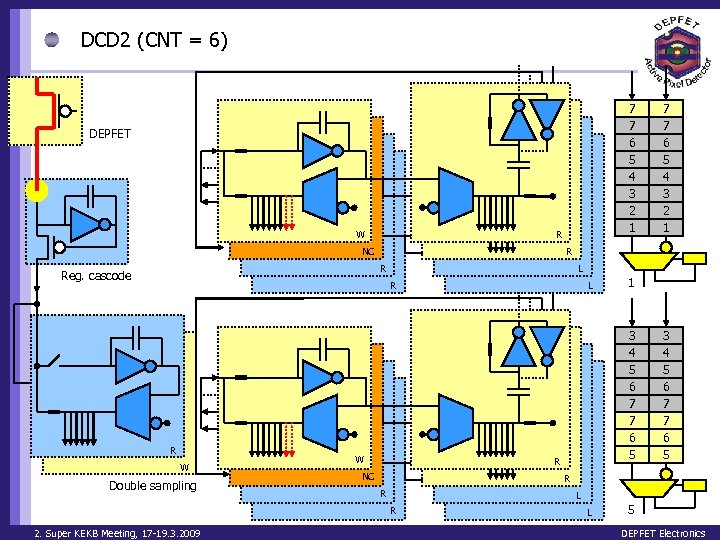 DCD 2 (CNT = 6) 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R R W Double sampling W L 1 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 R NC 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 L 5 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 6) 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R R W Double sampling W L 1 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 R NC 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 L 5 DEPFET Electronics
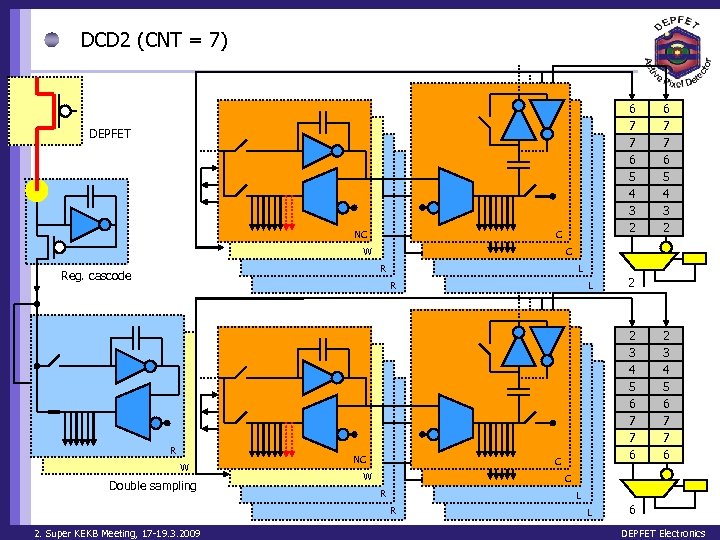 DCD 2 (CNT = 7) 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R R W Double sampling NC L 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 C W 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 L 6 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 7) 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R R W Double sampling NC L 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 C W 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 L 6 DEPFET Electronics
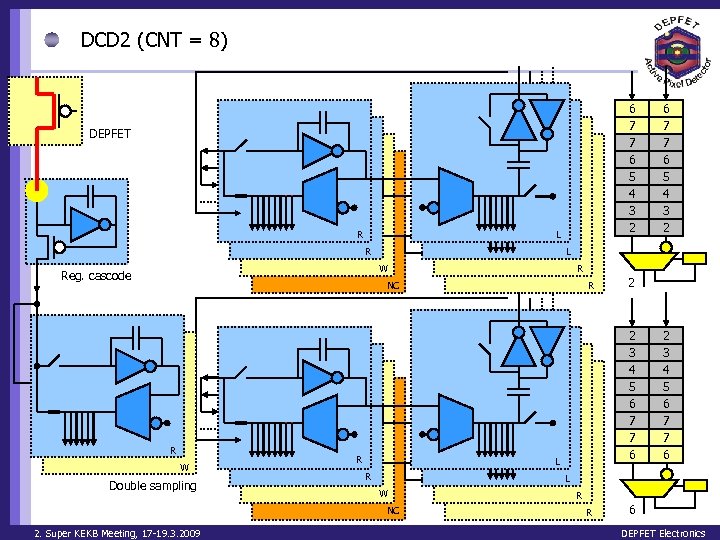 DCD 2 (CNT = 8) 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 DEPFET R L W Reg. cascode R NC R W Double sampling R R 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 L R 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 L W NC 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 R R 6 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 8) 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 DEPFET R L W Reg. cascode R NC R W Double sampling R R 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 L R 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 L W NC 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 R R 6 DEPFET Electronics
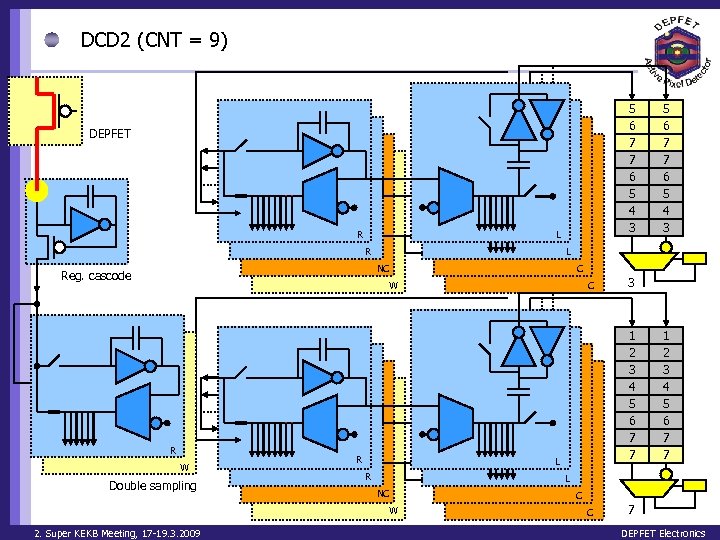 DCD 2 (CNT = 9) 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 DEPFET R L NC Reg. cascode C W R W Double sampling R C 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L R 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L NC W 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 C C 7 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 9) 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 DEPFET R L NC Reg. cascode C W R W Double sampling R C 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L R 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L NC W 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 C C 7 DEPFET Electronics
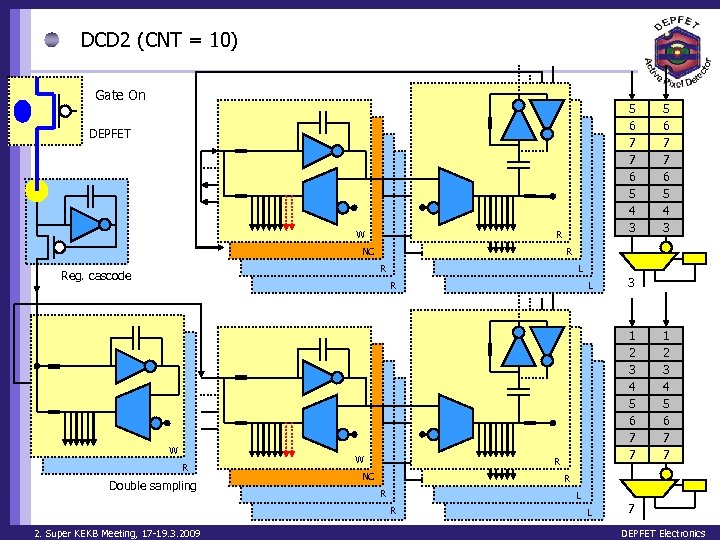 DCD 2 (CNT = 10) Gate On 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling W L 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 R NC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 L 7 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 10) Gate On 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling W L 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 R NC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 L 7 DEPFET Electronics
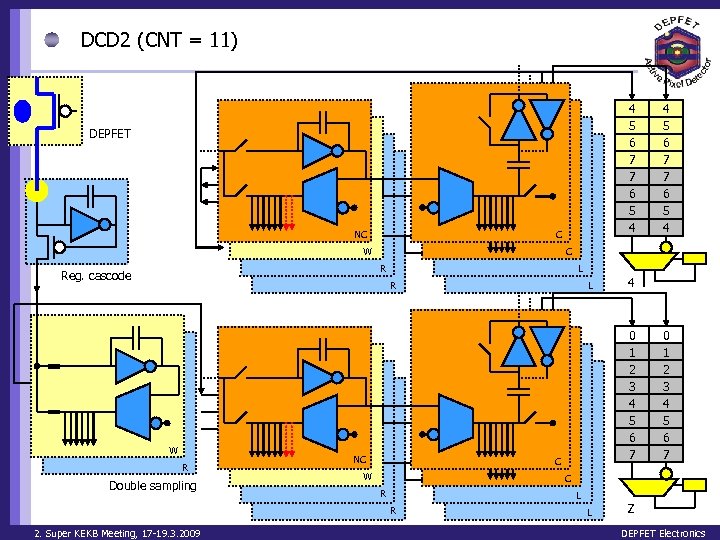 DCD 2 (CNT = 11) 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling NC L 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 C W 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 L Z DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 11) 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling NC L 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 C W 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 L Z DEPFET Electronics
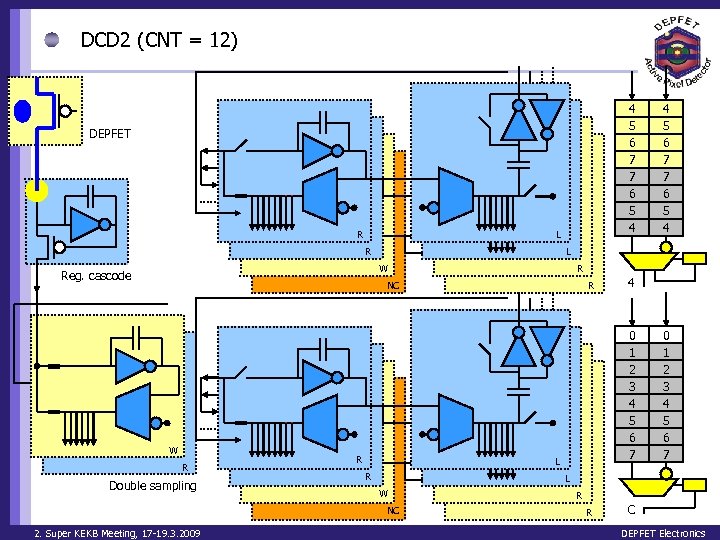 DCD 2 (CNT = 12) 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 DEPFET R L W Reg. cascode R NC W R Double sampling R R 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 L R 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 L W NC 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 R R C DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 12) 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 DEPFET R L W Reg. cascode R NC W R Double sampling R R 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 L R 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 L W NC 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 R R C DEPFET Electronics
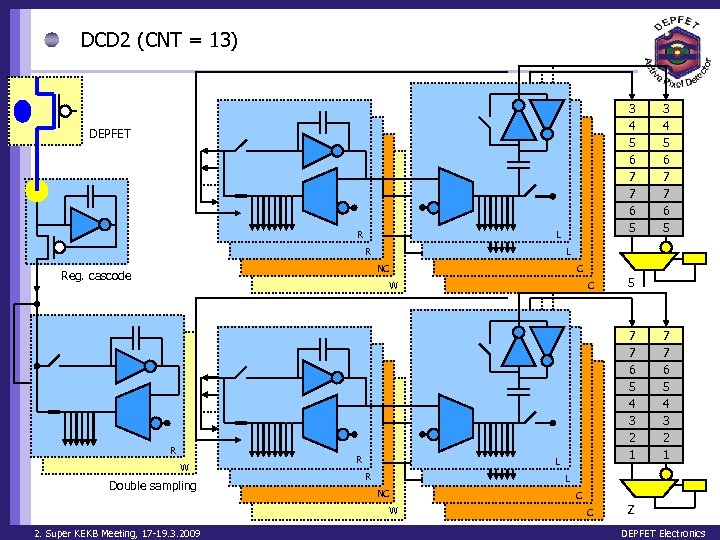 DCD 2 (CNT = 13) Clear On 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 DEPFET R L NC Reg. cascode C W R W Double sampling R C 5 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 L R 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 L NC W 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 C C Z DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 13) Clear On 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 DEPFET R L NC Reg. cascode C W R W Double sampling R C 5 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 L R 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 L NC W 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 C C Z DEPFET Electronics
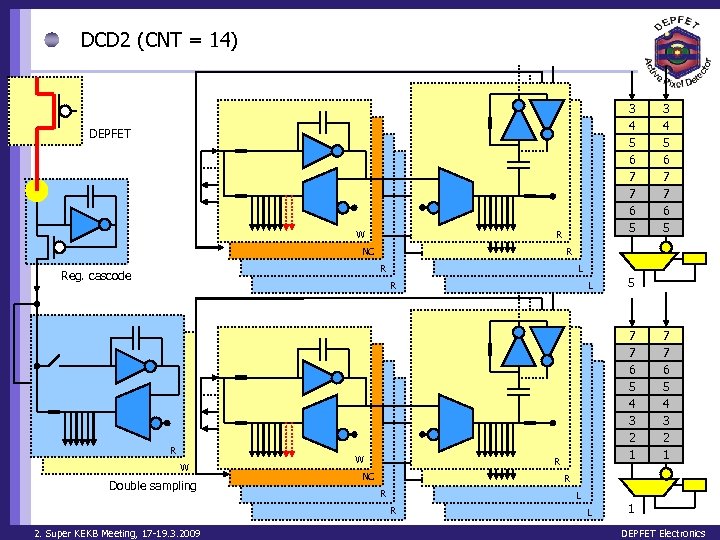 DCD 2 (CNT = 14) 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R R W Double sampling W L 5 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 R NC 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 L 1 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 14) 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R R W Double sampling W L 5 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 R NC 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 L 1 DEPFET Electronics
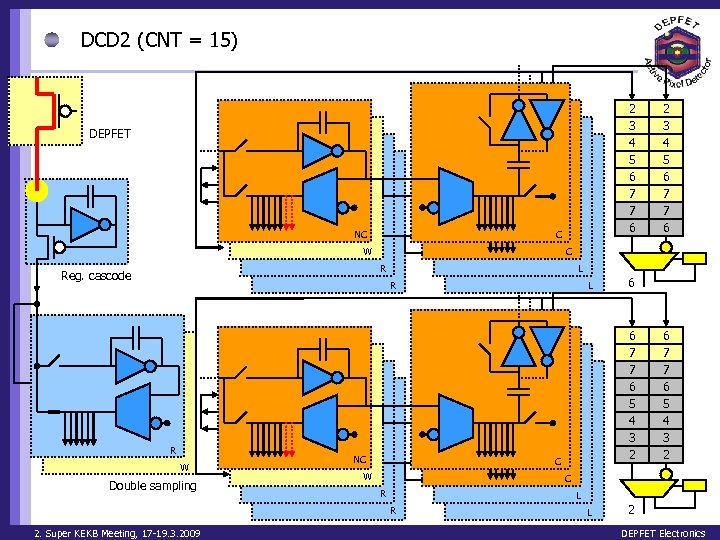 DCD 2 (CNT = 15) 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R R W Double sampling NC L 6 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 C W 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 L 2 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 15) 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R R W Double sampling NC L 6 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 C W 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 L 2 DEPFET Electronics
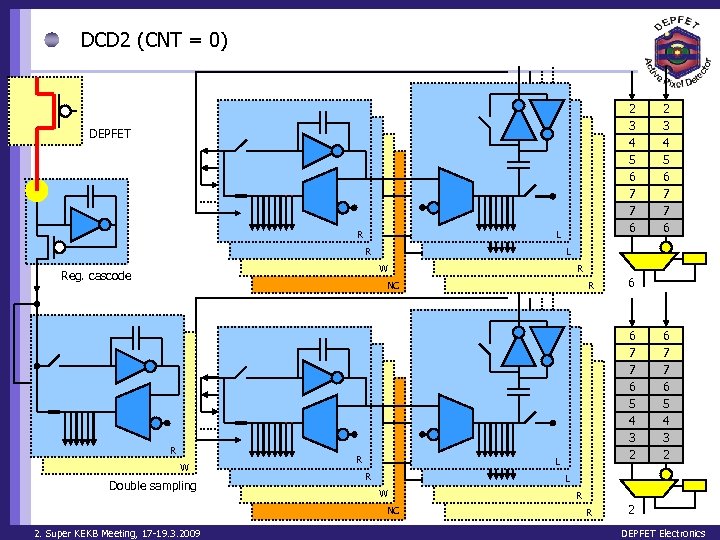 DCD 2 (CNT = 0) 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 DEPFET R L W Reg. cascode R NC R W Double sampling R R 6 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 L R 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 L W NC 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 R R 2 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 0) 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 DEPFET R L W Reg. cascode R NC R W Double sampling R R 6 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 L R 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 2 L W NC 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 6 R R 2 DEPFET Electronics
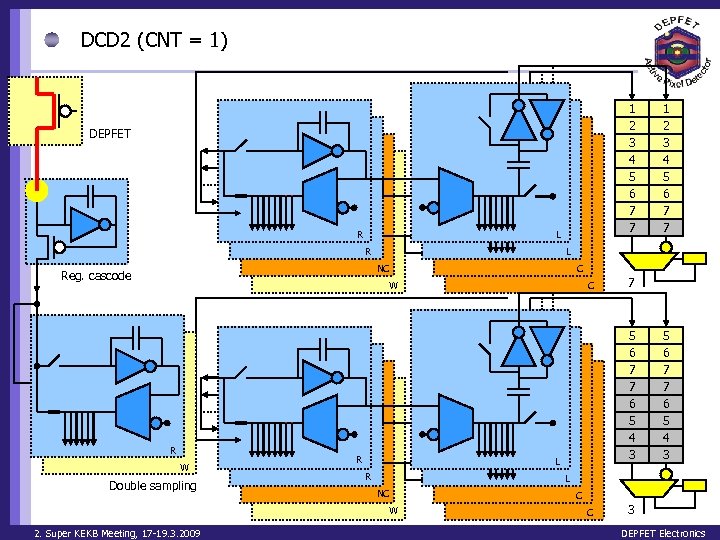 DCD 2 (CNT = 1) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 DEPFET R L NC Reg. cascode C W R W Double sampling R C 7 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 L R 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 L NC W 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 C C 3 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 1) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 DEPFET R L NC Reg. cascode C W R W Double sampling R C 7 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 L R 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 L NC W 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 C C 3 DEPFET Electronics
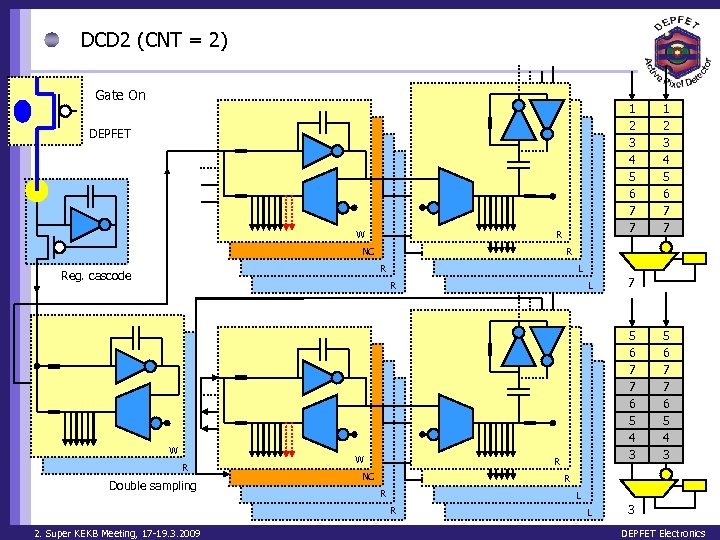 DCD 2 (CNT = 2) Gate On 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling W L 7 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R NC 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L 3 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 2) Gate On 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 DEPFET W R NC R R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling W L 7 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R NC 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 3 R R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 L 3 DEPFET Electronics
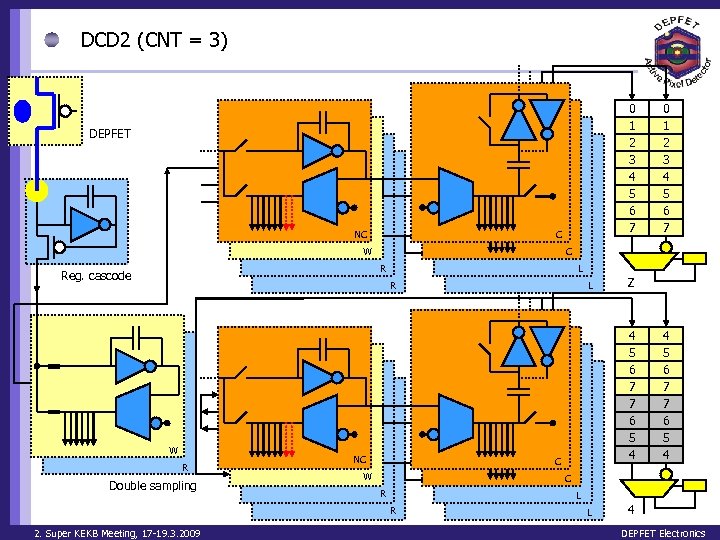 DCD 2 (CNT = 3) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling NC L Z 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 C W 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 L 4 DEPFET Electronics
DCD 2 (CNT = 3) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DEPFET NC C W C R Reg. cascode L R W R Double sampling NC L Z 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 C W 4 5 6 7 7 6 5 4 C R L R 2. Super KEKB Meeting, 17 -19. 3. 2009 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 L 4 DEPFET Electronics


