translation6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
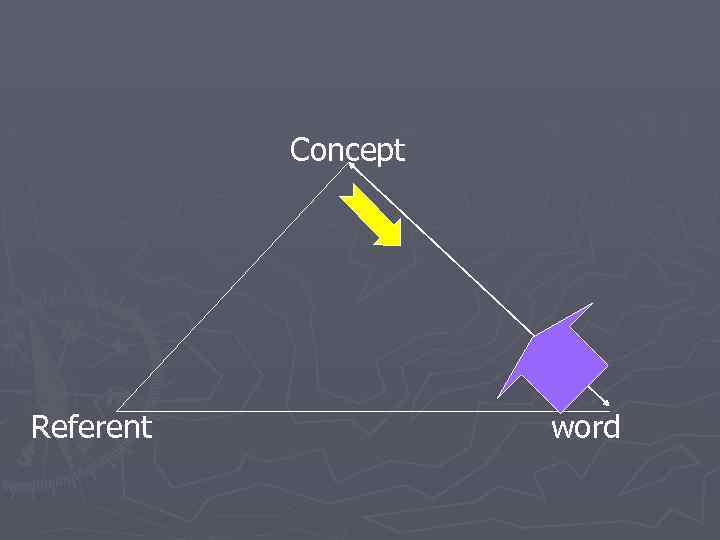
 Denotative Approach According to denotative approach (DA) the process of translation consists of the following steps: ► Translator reads (hears) a message in the source language ► Translator finds a denotatum and concept corresponding to the message ► Translator formulates a message in the target language relevant to the above denotatum and concept.
Denotative Approach According to denotative approach (DA) the process of translation consists of the following steps: ► Translator reads (hears) a message in the source language ► Translator finds a denotatum and concept corresponding to the message ► Translator formulates a message in the target language relevant to the above denotatum and concept.
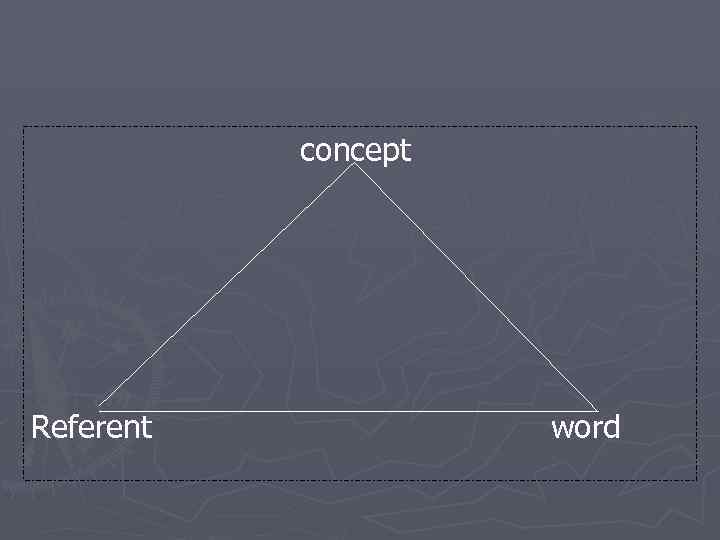 concept Referent word
concept Referent word
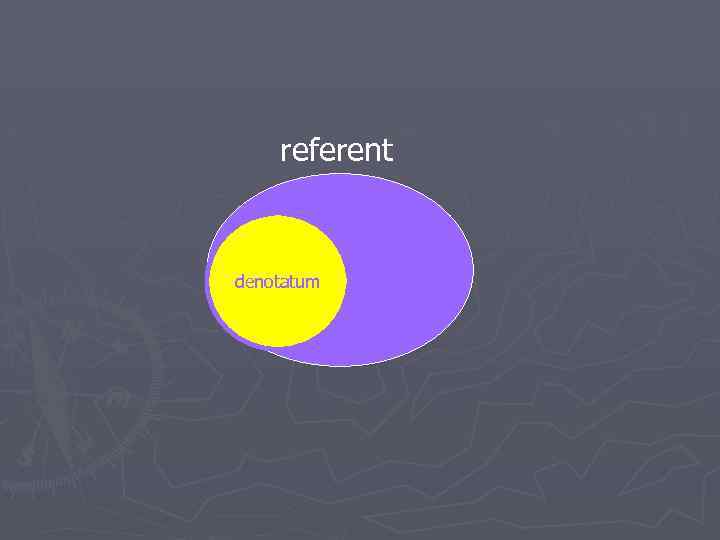 referent denotatum
referent denotatum
 Denotatum is the nominated part of the referent: Медведь, молодожены, Window, telephone, television, Halloween is a Scottish contraction of All Hallow’s Even or All Hallow’s Eve, a reference to All Saint’s Day which falls on the first of November. October 31 st is the day before, or eve
Denotatum is the nominated part of the referent: Медведь, молодожены, Window, telephone, television, Halloween is a Scottish contraction of All Hallow’s Even or All Hallow’s Eve, a reference to All Saint’s Day which falls on the first of November. October 31 st is the day before, or eve
 According to the DA the relationship between the source and the target word forms is occasional rather than regular.
According to the DA the relationship between the source and the target word forms is occasional rather than regular.
 The attendance was good yesterday Посещаемость была хорошая вчера
The attendance was good yesterday Посещаемость была хорошая вчера
 The equivalencies of the sentence are regular. The concept pertaining to the whole sentence may be divided into those relating to its individual components : attendance- посещаемость, was была, good - хорошая, yesterday - вчера)
The equivalencies of the sentence are regular. The concept pertaining to the whole sentence may be divided into those relating to its individual components : attendance- посещаемость, was была, good - хорошая, yesterday - вчера)
 ► East or West home is best - В гостях хорошо, а дома лучше. ► He went West – Он умер. ► Charity begins at home –Своя рубашка ближе к телу. ► Diamond cut diamond – Hашла коса на камень. ► A wonder lasts, but 9 days – Bсе приедается
► East or West home is best - В гостях хорошо, а дома лучше. ► He went West – Он умер. ► Charity begins at home –Своя рубашка ближе к телу. ► Diamond cut diamond – Hашла коса на камень. ► A wonder lasts, but 9 days – Bсе приедается
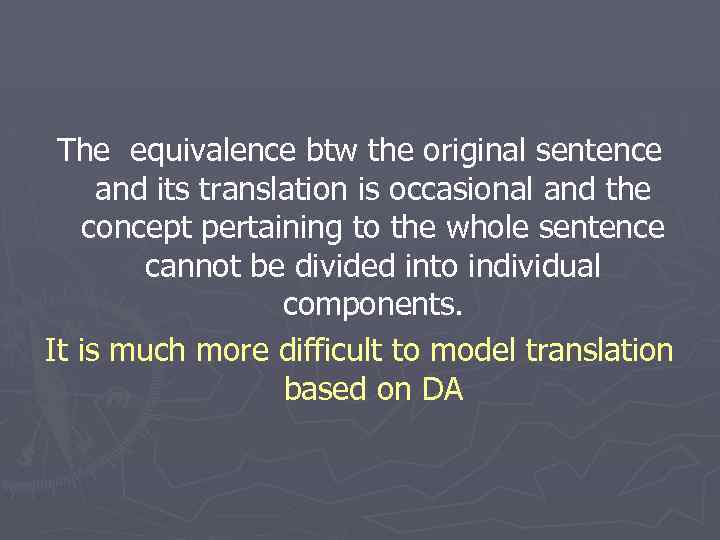 The equivalence btw the original sentence and its translation is occasional and the concept pertaining to the whole sentence cannot be divided into individual components. It is much more difficult to model translation based on DA
The equivalence btw the original sentence and its translation is occasional and the concept pertaining to the whole sentence cannot be divided into individual components. It is much more difficult to model translation based on DA
 Communicational approach suggested by O. Kade (Kommunikationswissenschaftliche Probleme der Translation//Grundfragen der Übersetzungswissenschaft. - Leipzig. - 1968) is based on the notions of communication and thesaurus.
Communicational approach suggested by O. Kade (Kommunikationswissenschaftliche Probleme der Translation//Grundfragen der Übersetzungswissenschaft. - Leipzig. - 1968) is based on the notions of communication and thesaurus.
 Communication is an act of sending and resending some information which is called a message. Information may be of any kind (gestures, looks, signs) but here we limit ourselves to verbal C only. In order to formulate a message we use our system of interrelated data, which is called thesaurus.
Communication is an act of sending and resending some information which is called a message. Information may be of any kind (gestures, looks, signs) but here we limit ourselves to verbal C only. In order to formulate a message we use our system of interrelated data, which is called thesaurus.
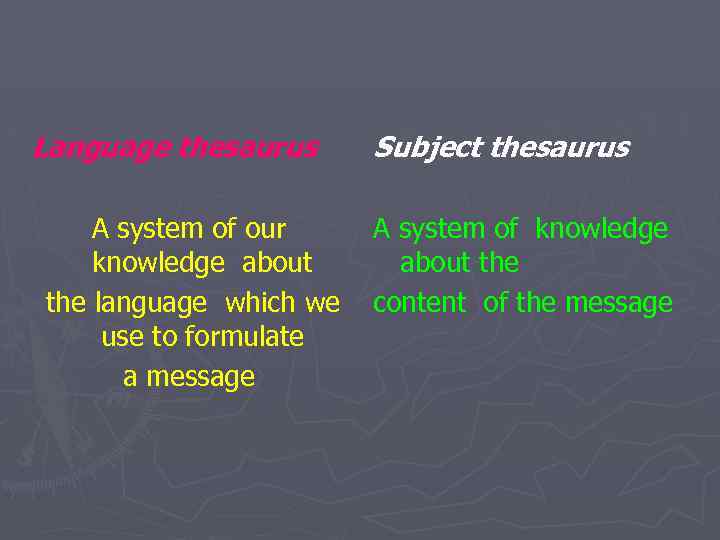 Language thesaurus A system of our knowledge about the language which we use to formulate a message Subject thesaurus A system of knowledge about the content of the message
Language thesaurus A system of our knowledge about the language which we use to formulate a message Subject thesaurus A system of knowledge about the content of the message
 So in order to communicate the message: ► the sender formulates the mental concept of the message using subject thesaurus, ► the sender encodes it using his language thesaurus ► the sender conveys it to the message recipient, ► the message recipient decodes the message using his language thesaurus ► the message recipient interprets the message using subject thesaurus.
So in order to communicate the message: ► the sender formulates the mental concept of the message using subject thesaurus, ► the sender encodes it using his language thesaurus ► the sender conveys it to the message recipient, ► the message recipient decodes the message using his language thesaurus ► the message recipient interprets the message using subject thesaurus.
 Concept Referent word
Concept Referent word
 This is a monolingual communication. Important: thesauruses of the sender and recipient may be different to a greater or lesser degree and that’s why we sometimes do not understand each other
This is a monolingual communication. Important: thesauruses of the sender and recipient may be different to a greater or lesser degree and that’s why we sometimes do not understand each other
 In bilingual communication, we have 3 actors: ►sender ►recipient ►intermediary (translator)
In bilingual communication, we have 3 actors: ►sender ►recipient ►intermediary (translator)
 The translator has 2 language thesauruses (source and target one) and performs 2 functions: decodes the source message and encodes the target one to be received by the recipient
The translator has 2 language thesauruses (source and target one) and performs 2 functions: decodes the source message and encodes the target one to be received by the recipient
 Communicational Theory describes the process of translation as an act of special bilingual communication in which the translator acts as a special communication intermediary, making it possible to understand a message sent in different languages.
Communicational Theory describes the process of translation as an act of special bilingual communication in which the translator acts as a special communication intermediary, making it possible to understand a message sent in different languages.
 Distributional Approach rests on distribution: Linguistic ability of language units (parts of word, words and collocations) to occur together
Distributional Approach rests on distribution: Linguistic ability of language units (parts of word, words and collocations) to occur together
 Distribution pattern reflects meaning and combinatorial potential of lexical units Distribution of lexical units in the text reflects the fragmentation of the real word in human mind
Distribution pattern reflects meaning and combinatorial potential of lexical units Distribution of lexical units in the text reflects the fragmentation of the real word in human mind
 The valency/distributional set of the word may be ► Big скоропостижная ► Small get, fix, it
The valency/distributional set of the word may be ► Big скоропостижная ► Small get, fix, it
 According to the distributional approach, translation is a process of matching the distributional patterns of the source and target language units.
According to the distributional approach, translation is a process of matching the distributional patterns of the source and target language units.
 We should distinguish between regular and occasional distribution patterns. ► Regular pattern is characteristic of linguistic units which occur together on regular basis, as members of common distribution determined by grammar rules and the lexico -semantic structure of a language.
We should distinguish between regular and occasional distribution patterns. ► Regular pattern is characteristic of linguistic units which occur together on regular basis, as members of common distribution determined by grammar rules and the lexico -semantic structure of a language.
 ► Will + Inf → будешь, будет ► Shall Regular distribution patterns form the structural basis of any language and the “anchors” of any translation ► According to, In spite of that
► Will + Inf → будешь, будет ► Shall Regular distribution patterns form the structural basis of any language and the “anchors” of any translation ► According to, In spite of that
 They cover the majority of word combinations and it is possible to model both the combination rules of a particular language and the rules used to match the combination rules of different languages using regular distribution patterns.
They cover the majority of word combinations and it is possible to model both the combination rules of a particular language and the rules used to match the combination rules of different languages using regular distribution patterns.
 The occasional distribution pattern is characteristic of linguistic units which occur together occasionally being members of different paradigms, determined by grammar rules and the lexicosemantic structure of a language.
The occasional distribution pattern is characteristic of linguistic units which occur together occasionally being members of different paradigms, determined by grammar rules and the lexicosemantic structure of a language.
 Linguistic units occurring together occasionally form a single indivisible concept e. g. cold start - запуск двигателя на холоде red alert – повышенная боеготовность
Linguistic units occurring together occasionally form a single indivisible concept e. g. cold start - запуск двигателя на холоде red alert – повышенная боеготовность
 ► Blue boy – ► Blue bell – ► Blue back – ► Bluebeard ► Bluebottle – ► Blue discharge ► Blue John – ► Blue Low – ► ► ► – баловень, всеобщий любимец мороженое, колокольчик норка красная Трупная муха увольнение из армии без положительной аттестации ► жидкое снятое молоко ► пуританский закон в Англии ► ►
► Blue boy – ► Blue bell – ► Blue back – ► Bluebeard ► Bluebottle – ► Blue discharge ► Blue John – ► Blue Low – ► ► ► – баловень, всеобщий любимец мороженое, колокольчик норка красная Трупная муха увольнение из армии без положительной аттестации ► жидкое снятое молоко ► пуританский закон в Англии ► ►
 So according to the distributional approach the T. process takes one of the 2: ► word combinations within a regular pattern are translated by parts using the rules and matching distributional patterns of the 2 languages ► word combinations with an occasional distribution pattern in each case are translated as a conceptual whole, in a unique way which is true only for that given occasion
So according to the distributional approach the T. process takes one of the 2: ► word combinations within a regular pattern are translated by parts using the rules and matching distributional patterns of the 2 languages ► word combinations with an occasional distribution pattern in each case are translated as a conceptual whole, in a unique way which is true only for that given occasion
 This approach provides a fairly productive basis for machine translation design.
This approach provides a fairly productive basis for machine translation design.


