d3be8fdec70cadc12017f7b5a0ca62a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 115
 Demonstration Win. APRS Running with TNC
Demonstration Win. APRS Running with TNC
 Welcome FWARC APRS Clinic
Welcome FWARC APRS Clinic
 Why We Are Here APRS is a powerful tool for emergency management Readiness requires skilled cadre of Hams Federal Way is not an APRS hotspot
Why We Are Here APRS is a powerful tool for emergency management Readiness requires skilled cadre of Hams Federal Way is not an APRS hotspot
 Our Sponsor Weyerhaeuser Foundation Making WAVEs n Weyerhaeuser Active Volunteer Employees Grant to FWARC for this activity
Our Sponsor Weyerhaeuser Foundation Making WAVEs n Weyerhaeuser Active Volunteer Employees Grant to FWARC for this activity
 CD Win. APRS, UI View and APRS+SA programs AGWPE program Win. APRS map files Setup information APRS Spec Satellite tracker programs
CD Win. APRS, UI View and APRS+SA programs AGWPE program Win. APRS map files Setup information APRS Spec Satellite tracker programs
 Other Sources of Information Tucson Amateur Packet Radio (TAPR) – http: //www. tapr. org NWAPRS – http: //www. nwaprs. org http: //aprs. rutgers. edu Use Google to search Books – check what’s available from ARRL
Other Sources of Information Tucson Amateur Packet Radio (TAPR) – http: //www. tapr. org NWAPRS – http: //www. nwaprs. org http: //aprs. rutgers. edu Use Google to search Books – check what’s available from ARRL
 What is APRS Automatic Position Reporting System Packet communication protocol for sharing live data on a network in real time Realtime tactical communications and display system for emergencies and public service applications (APRS Spec)
What is APRS Automatic Position Reporting System Packet communication protocol for sharing live data on a network in real time Realtime tactical communications and display system for emergencies and public service applications (APRS Spec)
 APRS Features Maps Messaging Objects Bulletins and announcements Weather station reporting DX Cluster reporting Internet access Telemetry
APRS Features Maps Messaging Objects Bulletins and announcements Weather station reporting DX Cluster reporting Internet access Telemetry
 History Invented by Bob Bruninga, WB 4 APR in 1992 Devised to facilitate short haul, short duration data transfer – conventional packet was not suitable
History Invented by Bob Bruninga, WB 4 APR in 1992 Devised to facilitate short haul, short duration data transfer – conventional packet was not suitable
 History APRS for DOS was the first program Mac. APRS 1994 by Sproule brothers Win. APRS is recompiled from Mac. APRS Many other APRS apps since – runs on Windows 3. x, 9 x, NT and XP, Mac, Linux, Palm, CE and DOS GPS adjunct came afterwards
History APRS for DOS was the first program Mac. APRS 1994 by Sproule brothers Win. APRS is recompiled from Mac. APRS Many other APRS apps since – runs on Windows 3. x, 9 x, NT and XP, Mac, Linux, Palm, CE and DOS GPS adjunct came afterwards
 Uses Passive Fun n Watch the display of many stations Watch the ISS or PCsat fly by Watch emergencies in action Tracking n n n Find your buddies Track your teenager Balloons and rockets
Uses Passive Fun n Watch the display of many stations Watch the ISS or PCsat fly by Watch emergencies in action Tracking n n n Find your buddies Track your teenager Balloons and rockets
 Uses Telemetry n Balloons and rockets Post bulletins, event notices and venues Send email
Uses Telemetry n Balloons and rockets Post bulletins, event notices and venues Send email
 More Uses Events n n Track the parade Grand Marshal Track the last marathoner or bike racer Emergencies n n Search and rescue Disaster information EOC messaging Track the fire chief
More Uses Events n n Track the parade Grand Marshal Track the last marathoner or bike racer Emergencies n n Search and rescue Disaster information EOC messaging Track the fire chief
 Still More Uses Weather monitoring n n n See wind speeds and temperatures in the area Report wind damage Track tornados
Still More Uses Weather monitoring n n n See wind speeds and temperatures in the area Report wind damage Track tornados
 Theory Assumptions Packet radio Digipeaters APRS Protocol Frequencies GPS
Theory Assumptions Packet radio Digipeaters APRS Protocol Frequencies GPS
 Assumptions Radios Antennas PC Skills
Assumptions Radios Antennas PC Skills
 How does APRS Work? Some details…
How does APRS Work? Some details…
 Packet Radio History n n n AX. 25 protocol was approved by ARRL in 1984 Came from X. 25 protocol (the A is for Amateur) Primary difference from X. 25 is allowance for call signs and for unconnected packets
Packet Radio History n n n AX. 25 protocol was approved by ARRL in 1984 Came from X. 25 protocol (the A is for Amateur) Primary difference from X. 25 is allowance for call signs and for unconnected packets
 Packet Radio Packets n n Strings of data bytes called frames 3 kinds of frames in ordinary packet Information (I frame) Supervisory (S frame) Unnumbered (U frame) n n 6 kinds of U frames, one is Unnumbered Information frame UI frames are used for transmitting data in an unconnected mode
Packet Radio Packets n n Strings of data bytes called frames 3 kinds of frames in ordinary packet Information (I frame) Supervisory (S frame) Unnumbered (U frame) n n 6 kinds of U frames, one is Unnumbered Information frame UI frames are used for transmitting data in an unconnected mode
 Packet Radio In packet radio, qso’s are always between ‘connected’ stations Several qso’s can take place simultaneously on the same frequency Packet qso’s may be digipeated but by specific stations
Packet Radio In packet radio, qso’s are always between ‘connected’ stations Several qso’s can take place simultaneously on the same frequency Packet qso’s may be digipeated but by specific stations
 How is APRS different from Packet Radio? Communication is ‘one to many’ Uses generic digipeating with well-known aliases Supports intelligent digipeating to reduce network flooding Uses UI frames for messaging, bulletins and announcements Provides maps and other features
How is APRS different from Packet Radio? Communication is ‘one to many’ Uses generic digipeating with well-known aliases Supports intelligent digipeating to reduce network flooding Uses UI frames for messaging, bulletins and announcements Provides maps and other features
 How APRS uses Packets Uses the same AX. 25 protocol but only a part of it Uses Unnumbered Information (UI) frames exclusively Always runs in connectionless mode
How APRS uses Packets Uses the same AX. 25 protocol but only a part of it Uses Unnumbered Information (UI) frames exclusively Always runs in connectionless mode
 How APRS uses Packets Frames are transmitted without expecting any response Reception is not guaranteed Messages work same way but use an ‘ack’ technique
How APRS uses Packets Frames are transmitted without expecting any response Reception is not guaranteed Messages work same way but use an ‘ack’ technique
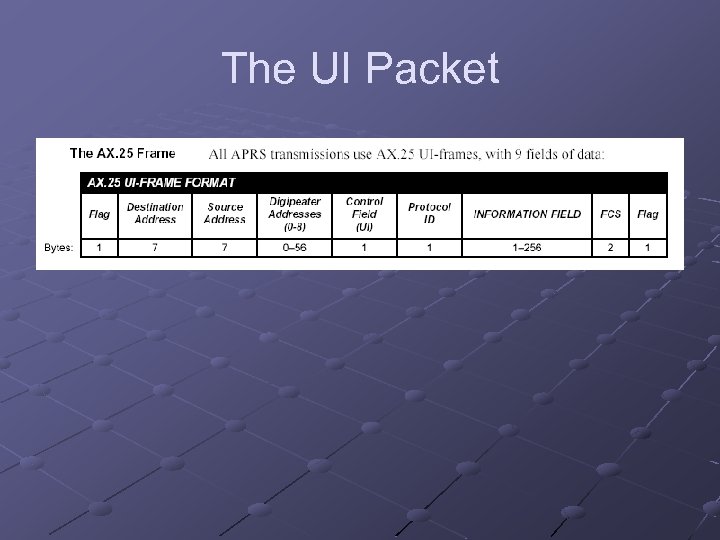 The UI Packet
The UI Packet
 Destination Address From the APRS spec…
Destination Address From the APRS spec…
 Destination Address The adr ‘SPCL’ is to be used for special events. APRS s/w should provide for only showing stations with this adr (but it doesn’t). Usually just shows the software version. Win. APRS v 2. 6. 1 sets this to APW 261
Destination Address The adr ‘SPCL’ is to be used for special events. APRS s/w should provide for only showing stations with this adr (but it doesn’t). Usually just shows the software version. Win. APRS v 2. 6. 1 sets this to APW 261
 Destination Address May also contain n n MIC-E encoded data Other unique encoded data No reason to change this since s/w can’t cope
Destination Address May also contain n n MIC-E encoded data Other unique encoded data No reason to change this since s/w can’t cope
 Source Address My station call sign
Source Address My station call sign
 An Intervening Word about Digipeaters Why do we need them? n Increase coverage Digipeater versus repeater n n n Voice repeaters operate in duplex mode Digipeaters operate in simplex mode Digipeaters use store and forward technique
An Intervening Word about Digipeaters Why do we need them? n Increase coverage Digipeater versus repeater n n n Voice repeaters operate in duplex mode Digipeaters operate in simplex mode Digipeaters use store and forward technique
 Digipeaters Wide area digipeaters n n In this area are usually on a mountaintop Have good antennas and more power Operate automatically Operate all the time
Digipeaters Wide area digipeaters n n In this area are usually on a mountaintop Have good antennas and more power Operate automatically Operate all the time
 Digipeaters Relay digipeater n n n Usually somebody’s home station Should be able to communicate with a WIDE station Purpose is to help low powered stations get to the WIDE
Digipeaters Relay digipeater n n n Usually somebody’s home station Should be able to communicate with a WIDE station Purpose is to help low powered stations get to the WIDE
 Digipeaters Wide area digipeaters may be known by an alias n Examples: SOMTN, KOPEAK, SEATAC …or not n Examples: N 7 OEP-10, K 7 NWS-10
Digipeaters Wide area digipeaters may be known by an alias n Examples: SOMTN, KOPEAK, SEATAC …or not n Examples: N 7 OEP-10, K 7 NWS-10
 Digipeaters respond to certain generic aliases n n n Relay, used by any station to relay mobiles to a wide Echo, HF only, same function as Relay Wide, all high digipeaters Trace, use call sign substitution to indicate path the packet took Wide. N-N, wide digipeating limited to N hops Gate, HF to VHF connection
Digipeaters respond to certain generic aliases n n n Relay, used by any station to relay mobiles to a wide Echo, HF only, same function as Relay Wide, all high digipeaters Trace, use call sign substitution to indicate path the packet took Wide. N-N, wide digipeating limited to N hops Gate, HF to VHF connection
 Digipeaters only repeat if their call sign, their unique alias, or a generic alias is in the digi path
Digipeaters only repeat if their call sign, their unique alias, or a generic alias is in the digi path
 Back to the UI Packet -Digipeater Addresses Also known as the ‘unproto path’ Up to 9 addresses Specific or generic aliases Specified in s/w configuration Represents the route you want your packet to follow
Back to the UI Packet -Digipeater Addresses Also known as the ‘unproto path’ Up to 9 addresses Specific or generic aliases Specified in s/w configuration Represents the route you want your packet to follow
 Digipeater Addresses Rules of thumb (see Win. APRS help file) n n n Don’t use RELAY unless you are a mobile If you can hit a wide, then include it as the first digi in the string If you want wide coverage then use WIDE 22 or WIDE 3 -3 after a specific WIDE Example: SOMTN, WIDE 2 -2
Digipeater Addresses Rules of thumb (see Win. APRS help file) n n n Don’t use RELAY unless you are a mobile If you can hit a wide, then include it as the first digi in the string If you want wide coverage then use WIDE 22 or WIDE 3 -3 after a specific WIDE Example: SOMTN, WIDE 2 -2
 Digipeater Addresses n You can be really specific about the path Example: SOMTN, KOPEAK, MEGLER would route you down to Seaside, OR area and nowhere else
Digipeater Addresses n You can be really specific about the path Example: SOMTN, KOPEAK, MEGLER would route you down to Seaside, OR area and nowhere else
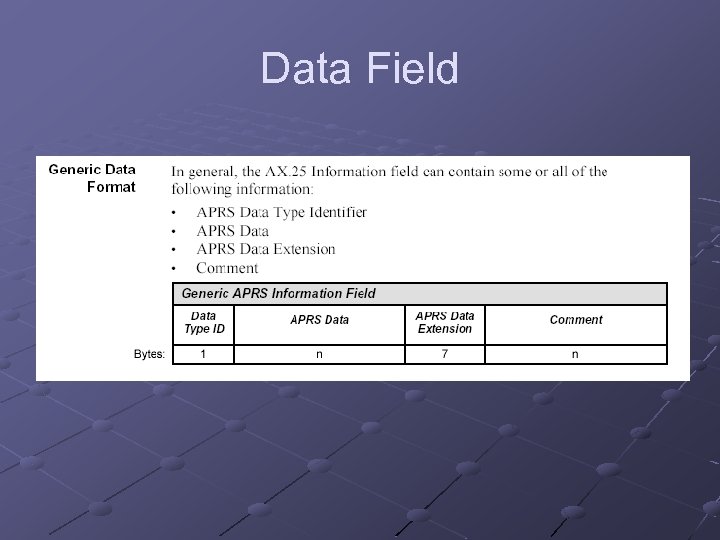 Data Field
Data Field
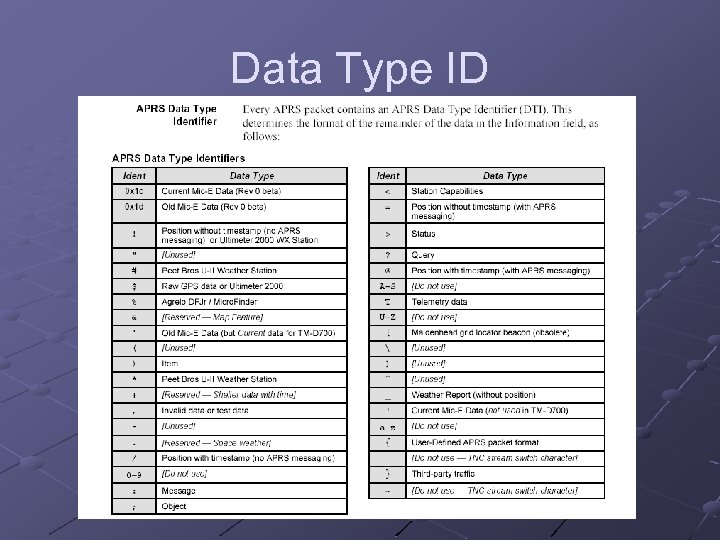 Data Type ID
Data Type ID
 Types of Data There are ten main types of APRS Data: n n n Position Direction Finding Objects and Items Weather Telemetry
Types of Data There are ten main types of APRS Data: n n n Position Direction Finding Objects and Items Weather Telemetry
 Types of Data n n n Messages, Bulletins and Announcements Queries Responses Status Other
Types of Data n n n Messages, Bulletins and Announcements Queries Responses Status Other
 Data Example Position data
Data Example Position data
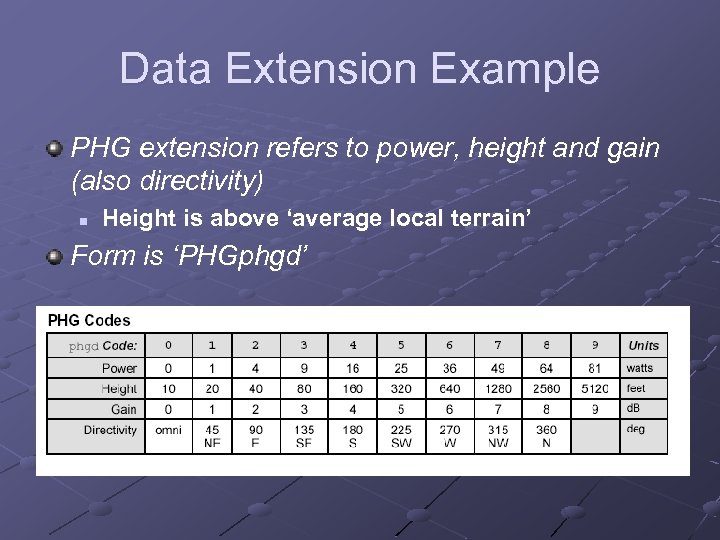 Data Extension Example PHG extension refers to power, height and gain (also directivity) n Height is above ‘average local terrain’ Form is ‘PHGphgd’
Data Extension Example PHG extension refers to power, height and gain (also directivity) n Height is above ‘average local terrain’ Form is ‘PHGphgd’
 Frequencies VHF 144. 39 n 1200 baud HF 10. 15151 LSB n 300 baud Satellite n n n ISS Downlink 145. 800, uplink 145. 990 PCsat simplex 145. 828 1200 baud
Frequencies VHF 144. 39 n 1200 baud HF 10. 15151 LSB n 300 baud Satellite n n n ISS Downlink 145. 800, uplink 145. 990 PCsat simplex 145. 828 1200 baud
 Getting on the Air with APRS – What to Buy/Scrounge Details…
Getting on the Air with APRS – What to Buy/Scrounge Details…
 Hardware Home station requirements n n n 2 meter radio and antenna Desktop computer TNC or soundcard/interface Mobile station requirements n n 2 meter radio and antenna Variables
Hardware Home station requirements n n n 2 meter radio and antenna Desktop computer TNC or soundcard/interface Mobile station requirements n n 2 meter radio and antenna Variables
 Hardware Mobile variables – the Full Meal Deal n n n GPS Laptop TNC or soundcard/interface or Baycom modem
Hardware Mobile variables – the Full Meal Deal n n n GPS Laptop TNC or soundcard/interface or Baycom modem
 Hardware Mobile variables – minimal functionality n n n No GPS Laptop TNC or soundcard/interface
Hardware Mobile variables – minimal functionality n n n No GPS Laptop TNC or soundcard/interface
 Hardware Mobile variables – tracking n n GPS No computer Tracker interface device Power source for portability
Hardware Mobile variables – tracking n n GPS No computer Tracker interface device Power source for portability
 Hardware What is a sound card interface? n n n Connects the computer’s sound card i/o to the radio mike and speaker terminals Provides isolation and attenuation May provide a VOX capability
Hardware What is a sound card interface? n n n Connects the computer’s sound card i/o to the radio mike and speaker terminals Provides isolation and attenuation May provide a VOX capability
 Hardware West Mountain Radio Rigblaster n See http: //www. westmountainradio. com/
Hardware West Mountain Radio Rigblaster n See http: //www. westmountainradio. com/
 Hardware Tigertronics Signal. Link ($50) n See http: //www. tigertronics. com
Hardware Tigertronics Signal. Link ($50) n See http: //www. tigertronics. com
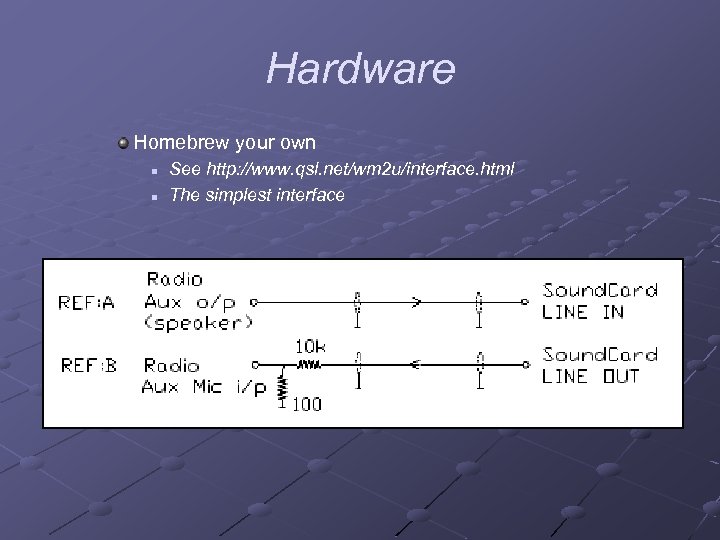 Hardware Homebrew your own n n See http: //www. qsl. net/wm 2 u/interface. html The simplest interface
Hardware Homebrew your own n n See http: //www. qsl. net/wm 2 u/interface. html The simplest interface
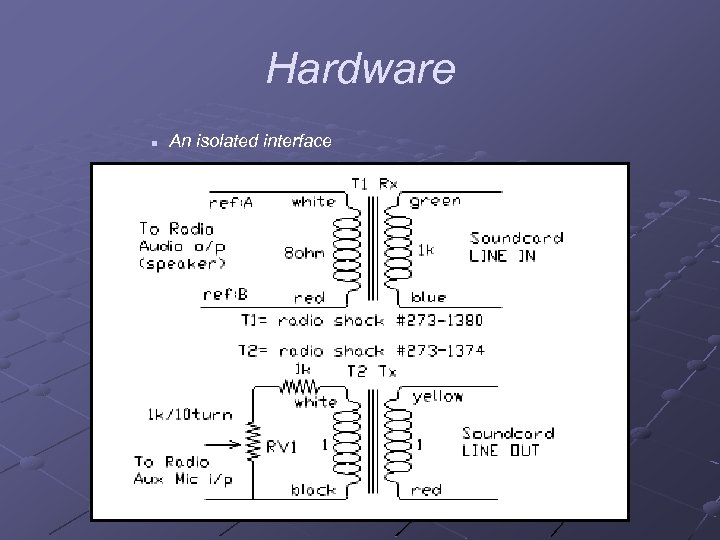 Hardware n An isolated interface
Hardware n An isolated interface
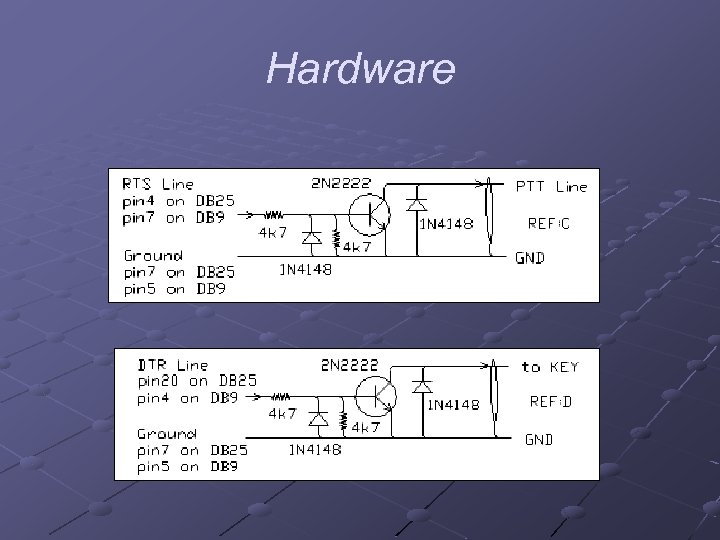 Hardware n PTT circuits
Hardware n PTT circuits
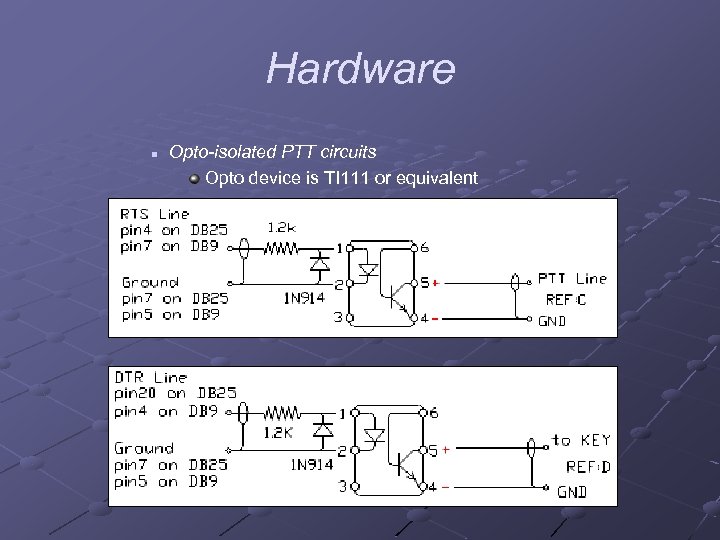 Hardware n Opto-isolated PTT circuits Opto device is TI 111 or equivalent
Hardware n Opto-isolated PTT circuits Opto device is TI 111 or equivalent
 Hardware What is a tracker interface device? n A mike encoder – TAPR Mic-E (kit discontinued) Tigertronics Tiger. Trak TM-1 ($90) n Also functions as a full function tracking and telemetry module
Hardware What is a tracker interface device? n A mike encoder – TAPR Mic-E (kit discontinued) Tigertronics Tiger. Trak TM-1 ($90) n Also functions as a full function tracking and telemetry module
 Hardware n A self-contained tracking/telemetry module Tigertronics Tiger. Trak TM-1 Tiny Trak II kit ($30) n See http: //www. byonics. com/tinytrak. html
Hardware n A self-contained tracking/telemetry module Tigertronics Tiger. Trak TM-1 Tiny Trak II kit ($30) n See http: //www. byonics. com/tinytrak. html
 Hardware TAPR PIC-E
Hardware TAPR PIC-E
 Hardware Another approach n Tigertronics Bay. Pac modem ($50) Accompanying software creates the packets in the computer Replaces the modem found in a TNC No sound card required
Hardware Another approach n Tigertronics Bay. Pac modem ($50) Accompanying software creates the packets in the computer Replaces the modem found in a TNC No sound card required
 Hardware Computers n Running with a TNC doesn’t require a fast computer or recent O/S A slow machine means your maps will refresh very slo-o-o-oly n n Running AGWPE requires a little horsepower, maybe 100 MHz, Win 98, 32 MB As with all apps, more memory is better
Hardware Computers n Running with a TNC doesn’t require a fast computer or recent O/S A slow machine means your maps will refresh very slo-o-o-oly n n Running AGWPE requires a little horsepower, maybe 100 MHz, Win 98, 32 MB As with all apps, more memory is better
 Hardware TNCs n n Any TNC will do when a computer is attached. Old style TNCs may not be GPS aware, but they work for base stations
Hardware TNCs n n Any TNC will do when a computer is attached. Old style TNCs may not be GPS aware, but they work for base stations
 Hardware Cables n Sources MFJ http: //www. mfjenterprises. com
Hardware Cables n Sources MFJ http: //www. mfjenterprises. com
 Hardware n TNC cables Computer serial port to TNC n Unique to your TNC to radio mike connector n Unique to your TNC and radio
Hardware n TNC cables Computer serial port to TNC n Unique to your TNC to radio mike connector n Unique to your TNC and radio
 Hardware n Sound card interface cables Computer sound card to interface box n May need Y connector to retain external speaker function Interface box to radio mike connector n n n Unique to your radio Buy a unique cable or have a way to configure the connectivity Sources for cables, MFJ or Buxcom May need a cable from speaker out to interface box if no speaker audio in mike connector
Hardware n Sound card interface cables Computer sound card to interface box n May need Y connector to retain external speaker function Interface box to radio mike connector n n n Unique to your radio Buy a unique cable or have a way to configure the connectivity Sources for cables, MFJ or Buxcom May need a cable from speaker out to interface box if no speaker audio in mike connector
 Hardware n Bay. Pac cable Bay. Pac plugs right onto the serial port connector on computer Bay. Pac to radio mike connector n n Unique to your radio Buy the right cable from Tigertronics
Hardware n Bay. Pac cable Bay. Pac plugs right onto the serial port connector on computer Bay. Pac to radio mike connector n n Unique to your radio Buy the right cable from Tigertronics
 Hardware Consideration for GPS with TNC n n 2 serial ports are needed If only 1 serial port is available, can use a “Port sharing” device
Hardware Consideration for GPS with TNC n n 2 serial ports are needed If only 1 serial port is available, can use a “Port sharing” device
 Hardware GPS Receivers n n n Must have PC interface port Must output NMEA messages on the PC port Good to have an external antenna for the GPS
Hardware GPS Receivers n n n Must have PC interface port Must output NMEA messages on the PC port Good to have an external antenna for the GPS
 Software Win. APRS n Pros Everybody knows about it Free maps Can use high quality Precision Maps Unregistered version has full functionality
Software Win. APRS n Pros Everybody knows about it Free maps Can use high quality Precision Maps Unregistered version has full functionality
 Software n Cons Help function is bad Not totally stable Not everything works Maps aren’t so good Expensive to register Somewhat limited in scope
Software n Cons Help function is bad Not totally stable Not everything works Maps aren’t so good Expensive to register Somewhat limited in scope
 Software APRS+SA n Pros Comprehensive functionality High quality Street Atlas maps
Software APRS+SA n Pros Comprehensive functionality High quality Street Atlas maps
 Software n Cons No (I said no) help Hard to manipulate maps Confusing Only works with Street Atlas Have to register to use AGWPE Expensive to register
Software n Cons No (I said no) help Hard to manipulate maps Confusing Only works with Street Atlas Have to register to use AGWPE Expensive to register
 Software UIView n Pros 16 bit version is free, 32 bit version is inexpensive Quality coding Extensive help files Any GIF or bitmap file can be a map Works with Street Atlas and others
Software UIView n Pros 16 bit version is free, 32 bit version is inexpensive Quality coding Extensive help files Any GIF or bitmap file can be a map Works with Street Atlas and others
 Software n Cons Map zooming is a problem Somewhat limited in scope
Software n Cons Map zooming is a problem Somewhat limited in scope
 Software Xastir n Pros Works on Linux Good map capability n Cons Not a Windows program
Software Xastir n Pros Works on Linux Good map capability n Cons Not a Windows program
 Software Mac. APRS n Shares same code with Win. APRS
Software Mac. APRS n Shares same code with Win. APRS
 Software APRSPoint n Pros High quality MS Map. Point maps n Cons Program is expensive and maps are more expensive
Software APRSPoint n Pros High quality MS Map. Point maps n Cons Program is expensive and maps are more expensive
 Software My recommendation n n Use Win. APRS until you get your feet wet. Spend 20 bucks on Street Atlas and switch to UI View
Software My recommendation n n Use Win. APRS until you get your feet wet. Spend 20 bucks on Street Atlas and switch to UI View
 Satellites ISS n Excellent signal PCsat n Built by Bruninga’s students at Annapolis Find the satellite’s position n n http: //liftoff. msfc. nasa. gov/realtime/JTrack/ Spacecraft. html PCSAT Telemetry Decoder program on CD
Satellites ISS n Excellent signal PCsat n Built by Bruninga’s students at Annapolis Find the satellite’s position n n http: //liftoff. msfc. nasa. gov/realtime/JTrack/ Spacecraft. html PCSAT Telemetry Decoder program on CD
 Another way to view APRS Internet FINDU http: //map. findu. com/callsign (substitute your call for callsign)
Another way to view APRS Internet FINDU http: //map. findu. com/callsign (substitute your call for callsign)
 Lunch Break Brainstorm the Exercise
Lunch Break Brainstorm the Exercise
 Demo of Other APRS S/W APRS+SA UI View
Demo of Other APRS S/W APRS+SA UI View
 Win. APRS Installation Find the file w 261 updt. zip in the Win. APRS folder on the CD Unzip the contents to a folder of your choice In the folder in which you placed the Win. APRS files, create a maps subfolder Copy all of the files from the maps folder on the CD to the maps folder on the PC
Win. APRS Installation Find the file w 261 updt. zip in the Win. APRS folder on the CD Unzip the contents to a folder of your choice In the folder in which you placed the Win. APRS files, create a maps subfolder Copy all of the files from the maps folder on the CD to the maps folder on the PC
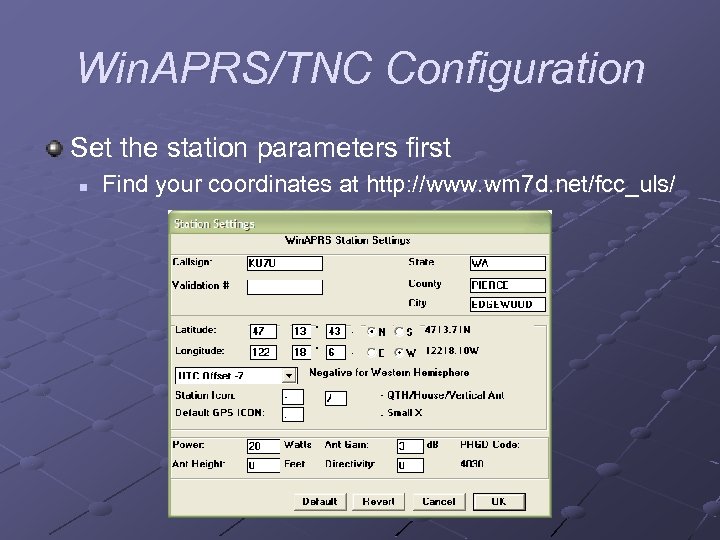 Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the station parameters first n Find your coordinates at http: //www. wm 7 d. net/fcc_uls/
Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the station parameters first n Find your coordinates at http: //www. wm 7 d. net/fcc_uls/
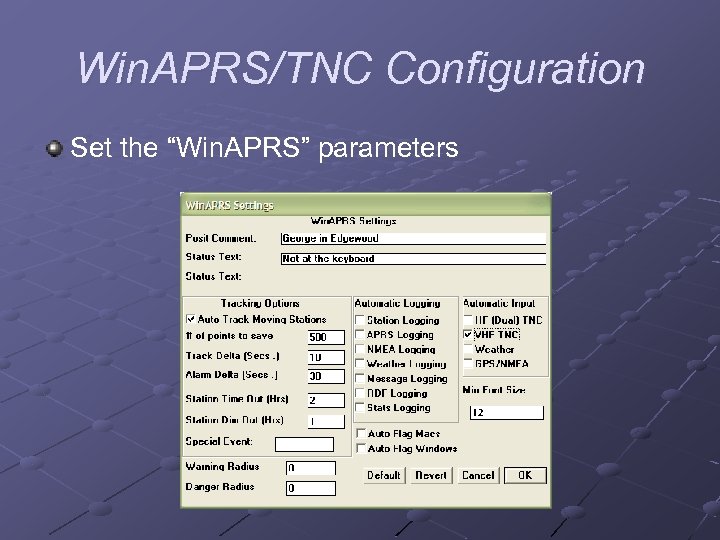 Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the “Win. APRS” parameters
Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the “Win. APRS” parameters
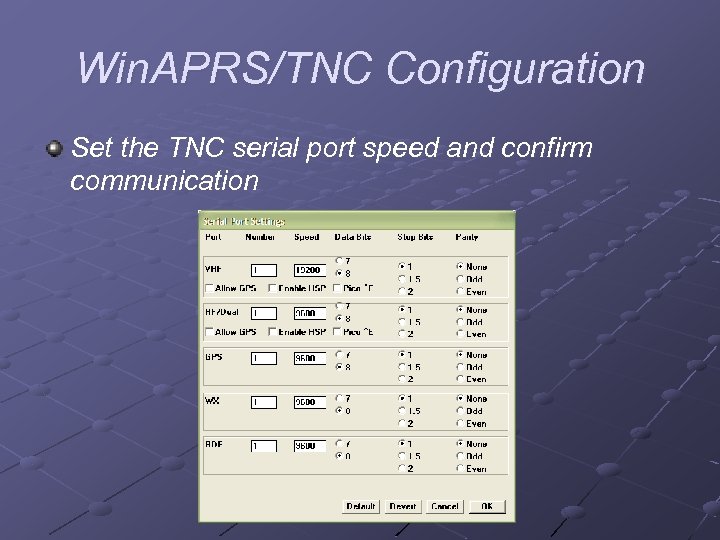 Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the TNC serial port speed and confirm communication
Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the TNC serial port speed and confirm communication
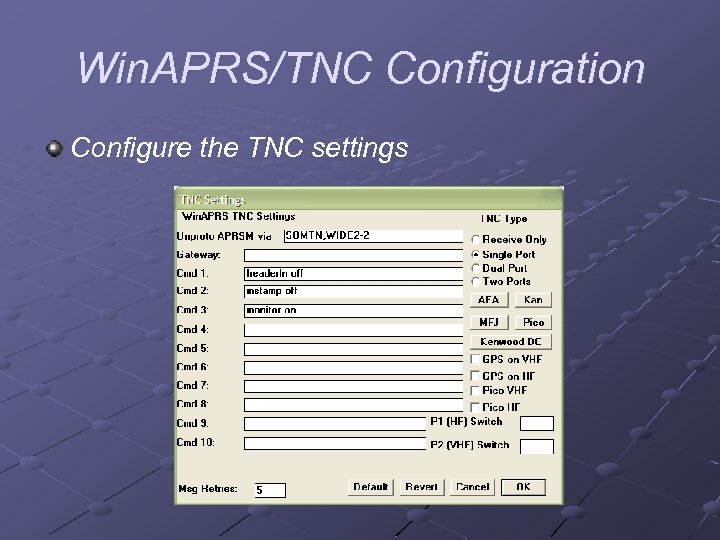 Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Configure the TNC settings
Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Configure the TNC settings
 Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the TNC radio port speed to 1200 for VHF, 300 for HF
Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the TNC radio port speed to 1200 for VHF, 300 for HF
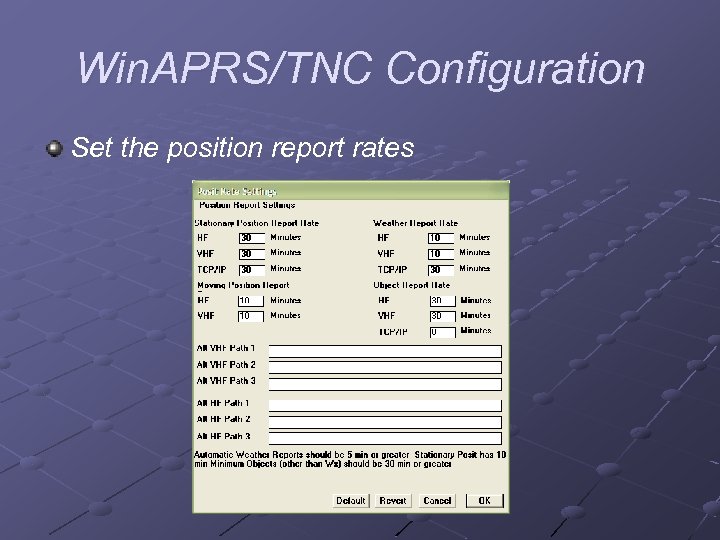 Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the position report rates
Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Set the position report rates
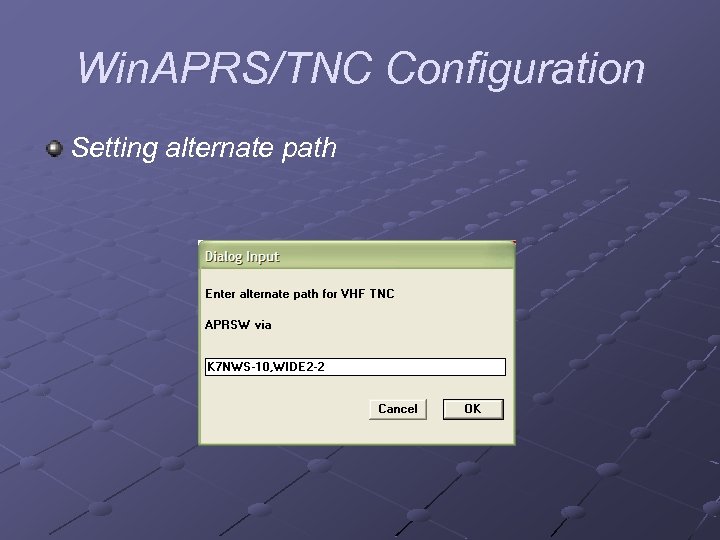 Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Setting alternate path
Win. APRS/TNC Configuration Setting alternate path
 Win. APRS/TNC Configuration n n Create file ALTPATHS. TXT in Win. APRS folder Edit this file to include your preferred alternate paths K 7 NWS-10, WIDE 2 -2 SOMTN, KOPEAK
Win. APRS/TNC Configuration n n Create file ALTPATHS. TXT in Win. APRS folder Edit this file to include your preferred alternate paths K 7 NWS-10, WIDE 2 -2 SOMTN, KOPEAK
 Running Win. APRS Enter station information n Until you register you must reenter all of your station information: Callsign State, county, city Position Station icon UTC offset Comments for position and status messag
Running Win. APRS Enter station information n Until you register you must reenter all of your station information: Callsign State, county, city Position Station icon UTC offset Comments for position and status messag
 Running Win. APRS n You must reconfigure the TNC or soundcard settings as well
Running Win. APRS n You must reconfigure the TNC or soundcard settings as well
 Running Win. APRS Maps n n n The program defaults to the USA map when started, pick ‘Sea. Tac Area Detail’ or ‘Northwest’ from the Maps menu to show a large scale view of our area Use zoom buttons from the toolbar on the right to zoom in and out Or hold down right mouse button and drag an area to be enlarged
Running Win. APRS Maps n n n The program defaults to the USA map when started, pick ‘Sea. Tac Area Detail’ or ‘Northwest’ from the Maps menu to show a large scale view of our area Use zoom buttons from the toolbar on the right to zoom in and out Or hold down right mouse button and drag an area to be enlarged
 Running Win. APRS n n n Click the ‘Home’ button to zoom all the way out Click anywhere in the map to center it at that point Page Up and Dn keys also zoom out and in respectively Use arrow keys to scroll Deselect menu item Display|Map Labels to get rid of annoying labels
Running Win. APRS n n n Click the ‘Home’ button to zoom all the way out Click anywhere in the map to center it at that point Page Up and Dn keys also zoom out and in respectively Use arrow keys to scroll Deselect menu item Display|Map Labels to get rid of annoying labels
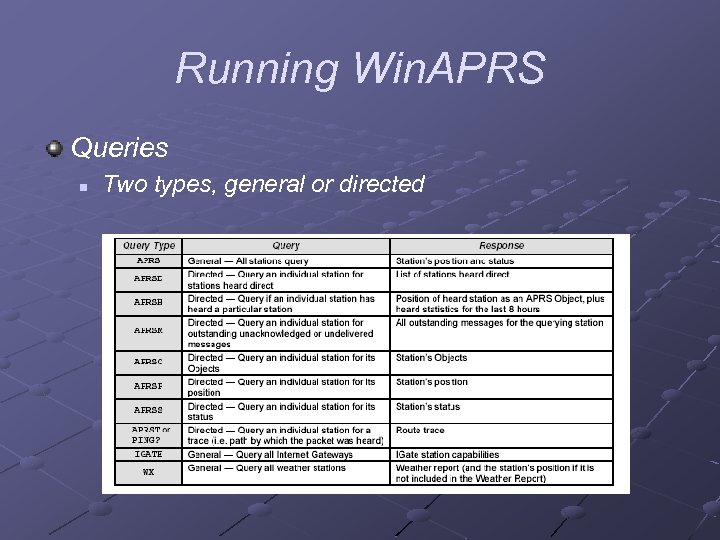 Running Win. APRS Queries n Two types, general or directed
Running Win. APRS Queries n Two types, general or directed
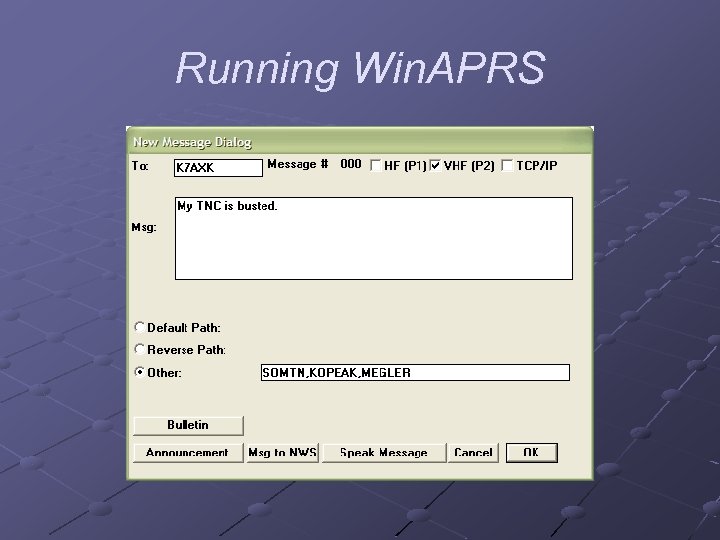
 Running Win. APRS Sending Messages n n n Easiest way is to select a station by double -clicking one on the map In the resulting window, click the message button (has envelope icon) In the New Message Dialog window, type the message and press OK
Running Win. APRS Sending Messages n n n Easiest way is to select a station by double -clicking one on the map In the resulting window, click the message button (has envelope icon) In the New Message Dialog window, type the message and press OK
 Running Win. APRS
Running Win. APRS
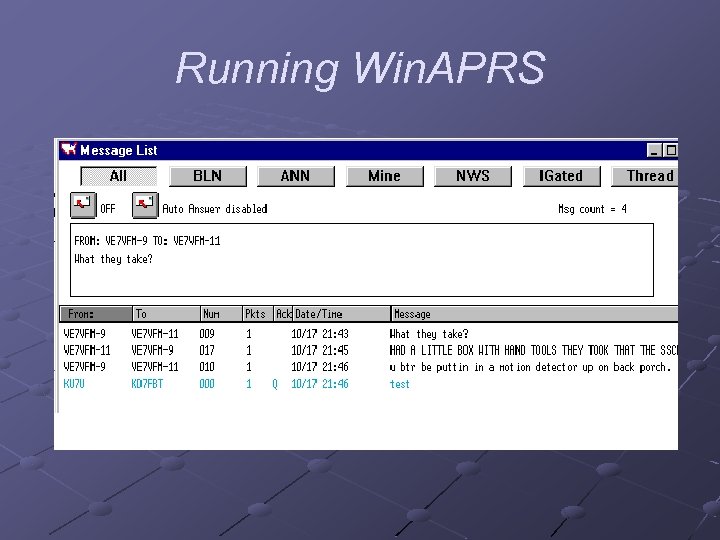
 Running Win. APRS n n n Click the Lists|Message List menu item In the Message List window monitor the progress of your message If you want to kill the message select it then press Backspace
Running Win. APRS n n n Click the Lists|Message List menu item In the Message List window monitor the progress of your message If you want to kill the message select it then press Backspace
 Running Win. APRS
Running Win. APRS
 Running Win. APRS Creating an Object n n Click on the map where you want the object created Select menu item Edit|Edit/Add Station/Object
Running Win. APRS Creating an Object n n Click on the map where you want the object created Select menu item Edit|Edit/Add Station/Object
 Running Win. APRS
Running Win. APRS
 Running Win. APRS n n In the Edit/Add Station window type a name for the object in the ‘Call or Name’ field The lat/lon fields should show the value where you clicked
Running Win. APRS n n In the Edit/Add Station window type a name for the object in the ‘Call or Name’ field The lat/lon fields should show the value where you clicked
 Running Win. APRS n n Select an icon in the ‘Station Type’ box Click the ‘Active’ radio button to transmit the object To move the object, click on object and while pressing Alt, drag to new location To delete the object, delete from station list window
Running Win. APRS n n Select an icon in the ‘Station Type’ box Click the ‘Active’ radio button to transmit the object To move the object, click on object and while pressing Alt, drag to new location To delete the object, delete from station list window
 Running Win. APRS Sending Email n n In the New Message Dialog window, enter ‘EMAIL’ in the ‘To’ box. Enter the email address in the ‘Msg’ box followed by a space and then the message.
Running Win. APRS Sending Email n n In the New Message Dialog window, enter ‘EMAIL’ in the ‘To’ box. Enter the email address in the ‘Msg’ box followed by a space and then the message.
 Running Win. APRS Lists n Station list Use it to determine who your digipeaters are
Running Win. APRS Lists n Station list Use it to determine who your digipeaters are
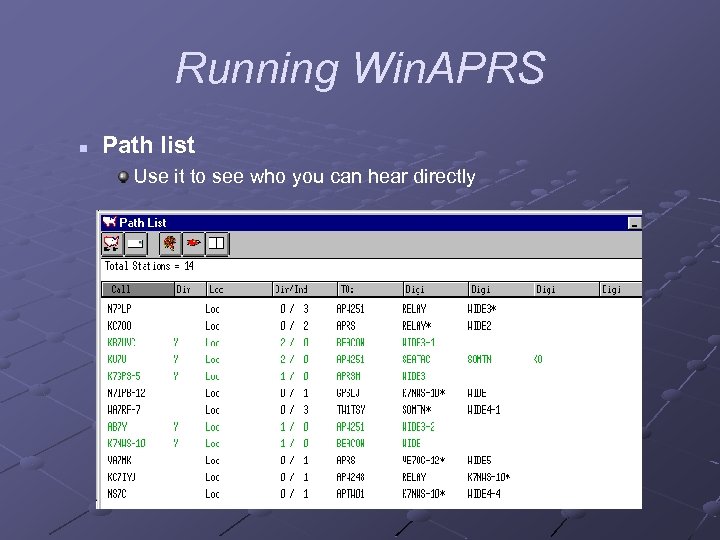 Running Win. APRS n Path list Use it to see who you can hear directly
Running Win. APRS n Path list Use it to see who you can hear directly
 AGWPE Installation Find the file agwpe. zip in the AGWPE folder on the CD Unzip the contents to a folder of your choice
AGWPE Installation Find the file agwpe. zip in the AGWPE folder on the CD Unzip the contents to a folder of your choice
 AGWPE Configuration Double click the file agwpe. exe on the PC Right click the agwpe icon in the systray (near the clock) Select ‘properties’ from the popup menu
AGWPE Configuration Double click the file agwpe. exe on the PC Right click the agwpe icon in the systray (near the clock) Select ‘properties’ from the popup menu
 AGWPE Configuration
AGWPE Configuration
 AGWPE Configuration In the Radio. Port Selection window select ‘New Port’ In the Properties for Port window, set TNC Type to ‘Soundcard’
AGWPE Configuration In the Radio. Port Selection window select ‘New Port’ In the Properties for Port window, set TNC Type to ‘Soundcard’
 AGWPE Configuration In the Sound. Card Modem/TNC Setup window, make no changes In the Properties for Port window, select ‘Single. Port’ Exit program and restart Sound card settings n n Set sliders to about 2/3 of max Set recording slider as well
AGWPE Configuration In the Sound. Card Modem/TNC Setup window, make no changes In the Properties for Port window, select ‘Single. Port’ Exit program and restart Sound card settings n n Set sliders to about 2/3 of max Set recording slider as well
 Win. APRS/AGWPE Configuration Start AGWPE first, then start Win. APRS Set Station settings as for TNC configuration Select ‘Ports list’ from Settings menu In Port Definitions window, select ‘AGWPE on Local’ and click Open Check that Comment field shows the installed version of AGWPE, then close the window
Win. APRS/AGWPE Configuration Start AGWPE first, then start Win. APRS Set Station settings as for TNC configuration Select ‘Ports list’ from Settings menu In Port Definitions window, select ‘AGWPE on Local’ and click Open Check that Comment field shows the installed version of AGWPE, then close the window
 Questions ? ?
Questions ? ?
 Student Installs
Student Installs


