253c65873328ca202854f8df6e684ea6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Demonstrating Business Benefit By Maturing the Security Program John Pescatore Notes accompany this presentation. Please select Notes Page view. These materials can be reproduced only with written approval from Gartner. Such approvals must be requested via e-mail: vendor. relations@gartner. com. Gartner is a registered trademark of Gartner, Inc. or its affiliates.

Getting to Security 3. 0 Moving From

Getting to Security 3. 0 To

Security 3. 0 Security 1. 0 – the mainframe era: RACF, Top Secret: • Gurus in the basement know best • Restrict the user Security 2. 0 – the Internet era: worms and identity theft: • New threat hits, buy new point solutions • Catch up to the user Security 3. 0 – staying ahead of the threat: • Adaptive/integrated security processes, architecture, controls • Keep up with the user by building security in

The Last Year in Review • May 2006 — CIO and CISO fired at Ohio University; 137, 000 accounts compromised • May 2006 — laptop with 27 M VA records stolen • July 2006 — My. Space worm • January 2007 – TJ Maxx discloses 45 M accounts exposed • February 2007 — Wordpress backdoor • March 2007 — John Mc. Cain's My. Space page defaced • April 2007 — IRS grants extensions to Turbo. Tax online filers
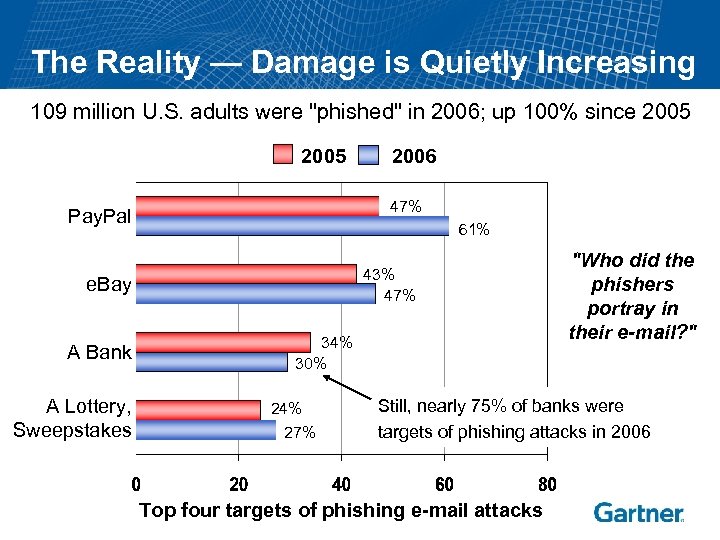
The Reality — Damage is Quietly Increasing 109 million U. S. adults were "phished" in 2006; up 100% since 2005 47% Pay. Pal 61% 43% 47% e. Bay A Bank A Lottery, Sweepstakes 2006 34% 30% 24% 27% "Who did the phishers portray in their e-mail? " Still, nearly 75% of banks were targets of phishing attacks in 2006 Top four targets of phishing e-mail attacks
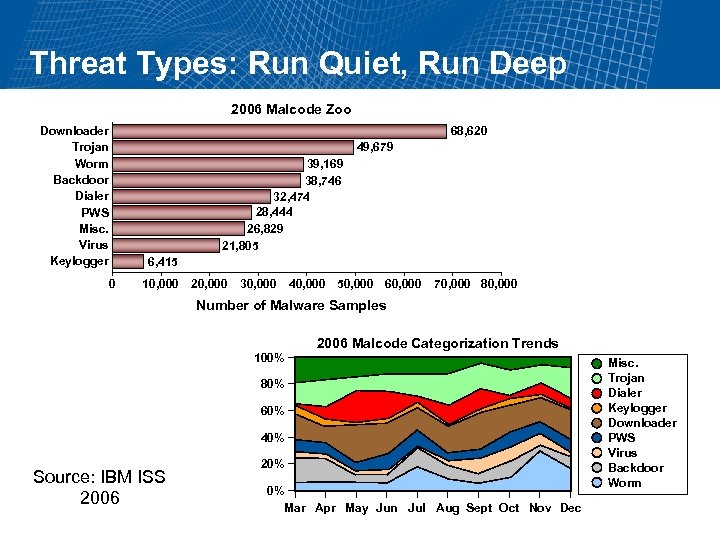
Threat Types: Run Quiet, Run Deep 2006 Malcode Zoo Downloader Trojan Worm Backdoor Dialer PWS Misc. Virus Keylogger 0 68, 620 49, 679 39, 169 38, 746 32, 474 28, 444 26, 829 21, 805 6, 415 10, 000 20, 000 30, 000 40, 000 50, 000 60, 000 70, 000 80, 000 Number of Malware Samples 100% 2006 Malcode Categorization Trends 80% 60% 40% Source: IBM ISS 2006 20% 0% Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Misc. Trojan Dialer Keylogger Downloader PWS Virus Backdoor Worm
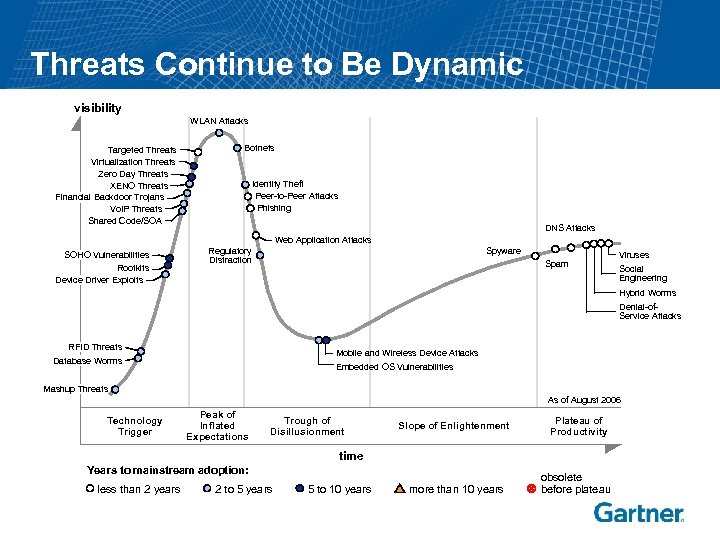
Threats Continue to Be Dynamic visibility WLAN Attacks Targeted Threats Virtualization Threats Zero Day Threats XENO Threats Financial Backdoor Trojans Vo. IP Threats Shared Code/SOA Botnets Identity Theft Peer-to-Peer Attacks Phishing DNS Attacks Web Application Attacks SOHO Vulnerabilities Rootkits Device Driver Exploits Regulatory Distraction Spyware Spam Viruses Social Engineering Hybrid Worms Denial-of. Service Attacks RFID Threats Database Worms Mobile and Wireless Device Attacks Embedded OS Vulnerabilities Mashup Threats As of August 2006 Technology Trigger Peak of Inflated Expectations Trough of Disillusionment Slope of Enlightenment Plateau of Productivity time Years to mainstream adoption: less than 2 years 2 to 5 years 5 to 10 years more than 10 years obsolete before plateau
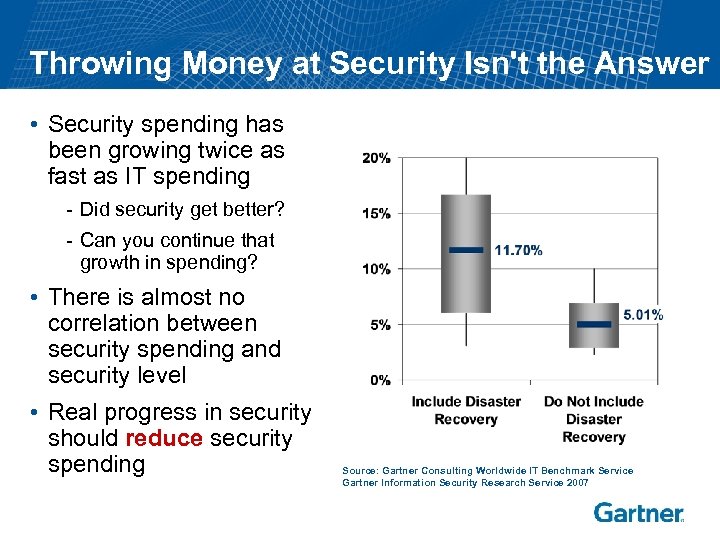
Throwing Money at Security Isn't the Answer • Security spending has been growing twice as fast as IT spending - Did security get better? - Can you continue that growth in spending? • There is almost no correlation between security spending and security level • Real progress in security should reduce security spending Source: Gartner Consulting Worldwide IT Benchmark Service Gartner Information Security Research Service 2007

Coping Checklist q Avoid the compliance trap q Buy the most secure stuff q Demand security processes that can transition to "operationalization" q Measure and move up the security program maturity cycle
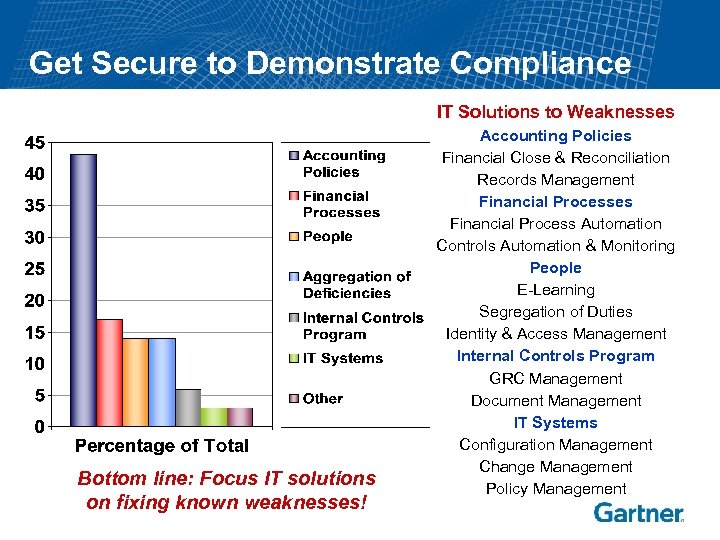
Get Secure to Demonstrate Compliance IT Solutions to Weaknesses Bottom line: Focus IT solutions on fixing known weaknesses! Accounting Policies Financial Close & Reconciliation Records Management Financial Processes Financial Process Automation Controls Automation & Monitoring People E-Learning Segregation of Duties Identity & Access Management Internal Controls Program GRC Management Document Management IT Systems Configuration Management Change Management Policy Management
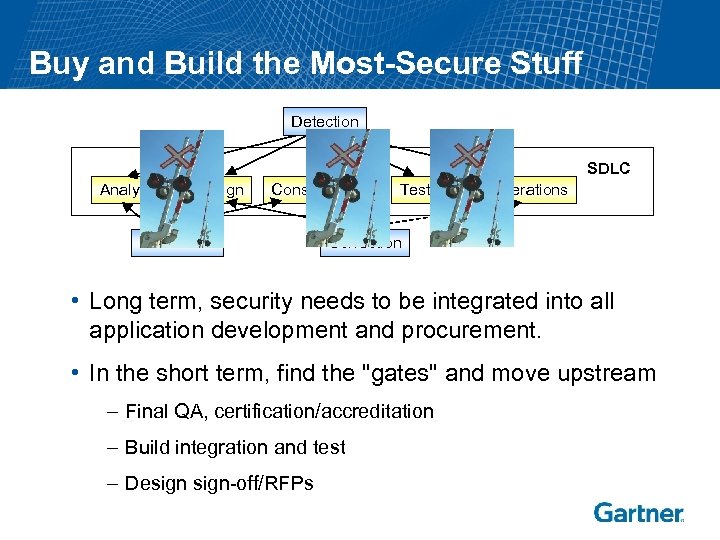
Buy and Build the Most-Secure Stuff Detection SDLC Analysis Design Construction Prevention Testing Operations Correction • Long term, security needs to be integrated into all application development and procurement. • In the short term, find the "gates" and move upstream – Final QA, certification/accreditation – Build integration and test – Design-off/RFPs
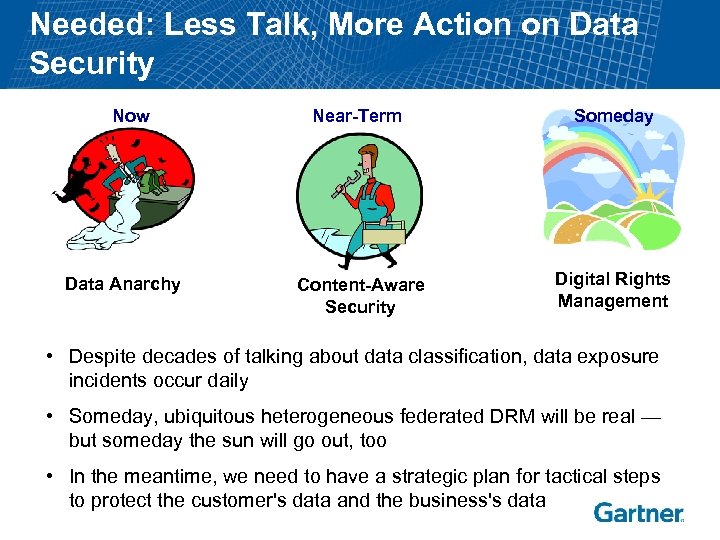
Needed: Less Talk, More Action on Data Security Now Data Anarchy Near-Term Someday Content-Aware Security Digital Rights Management • Despite decades of talking about data classification, data exposure incidents occur daily • Someday, ubiquitous heterogeneous federated DRM will be real — but someday the sun will go out, too • In the meantime, we need to have a strategic plan for tactical steps to protect the customer's data and the business's data
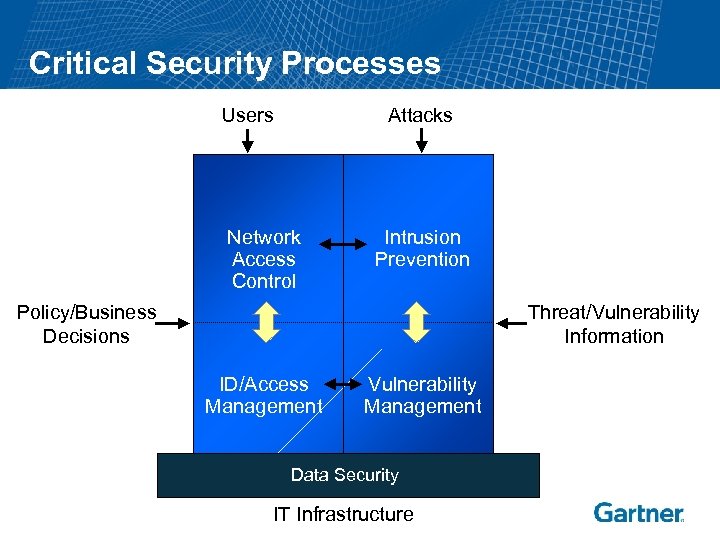
Critical Security Processes Users Attacks Network Access Control Intrusion Prevention Policy/Business Decisions Threat/Vulnerability Information ID/Access Management Vulnerability Management Data Security IT Infrastructure
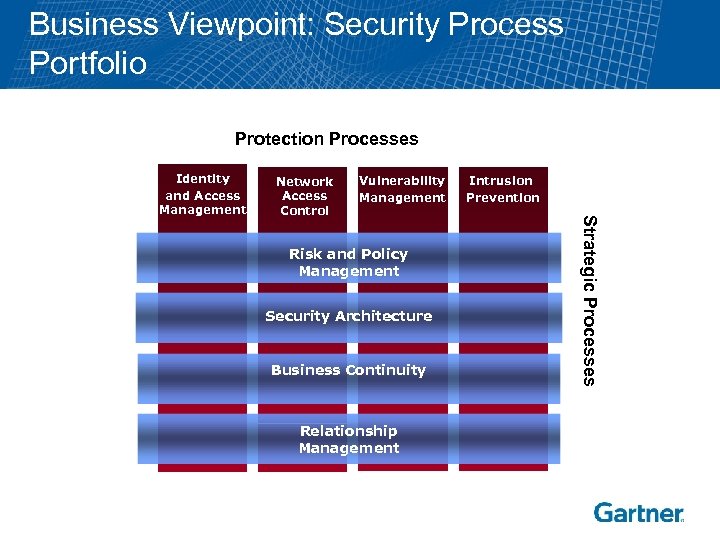
Business Viewpoint: Security Process Portfolio Protection Processes Network Access Control Vulnerability Management Risk and Policy Management Security Architecture Business Continuity Relationship Management Intrusion Prevention Strategic Processes Identity and Access Management
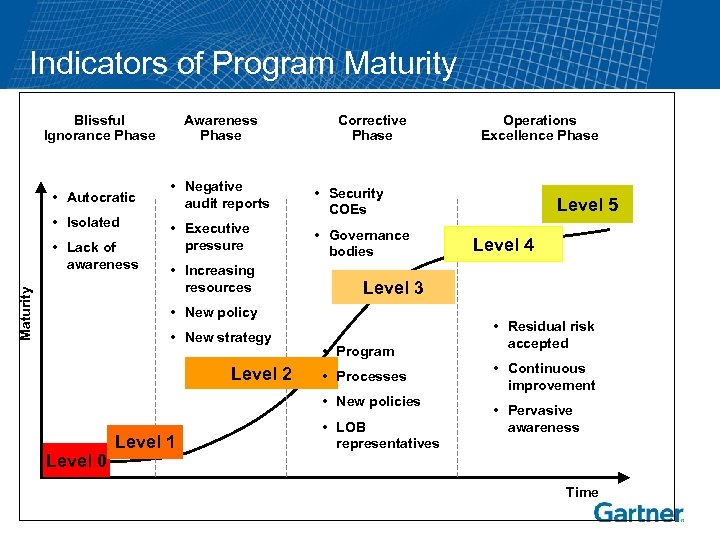
Indicators of Program Maturity Blissful Ignorance Phase • Autocratic • Isolated Maturity • Lack of awareness Awareness Phase Corrective Phase • Negative audit reports • Security COEs • Executive pressure • Governance bodies • Increasing resources • New strategy Level 2 • Program • Processes • New policies Level 1 Level 5 Level 4 Level 3 • New policy Level 0 Operations Excellence Phase • LOB representatives • Residual risk accepted • Continuous improvement • Pervasive awareness Time
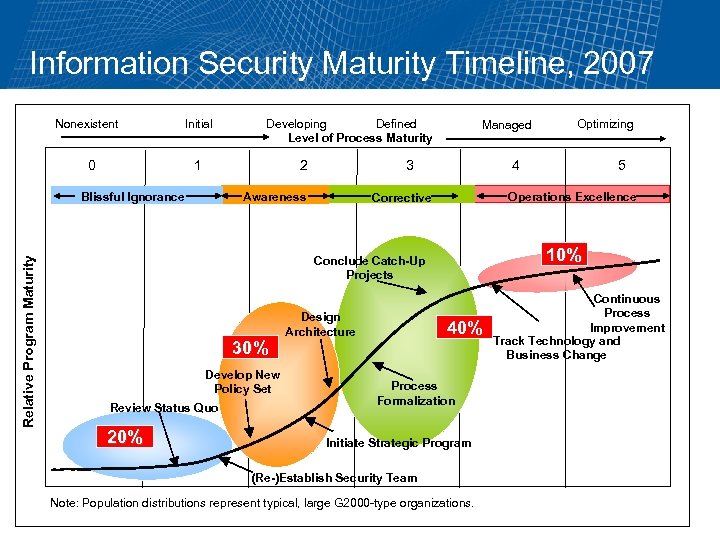
Information Security Maturity Timeline, 2007 Nonexistent 0 Initial 1 2 Blissful Ignorance Relative Program Maturity Developing Defined Level of Process Maturity Managed 3 Awareness 4 10% Conclude Catch-Up Projects 30% Develop New Policy Set Review Status Quo 20% 5 Operations Excellence Corrective Design Architecture Optimizing 40% Process Formalization Initiate Strategic Program (Re-)Establish Security Team Note: Population distributions represent typical, large G 2000 -type organizations. Continuous Process Improvement Track Technology and Business Change
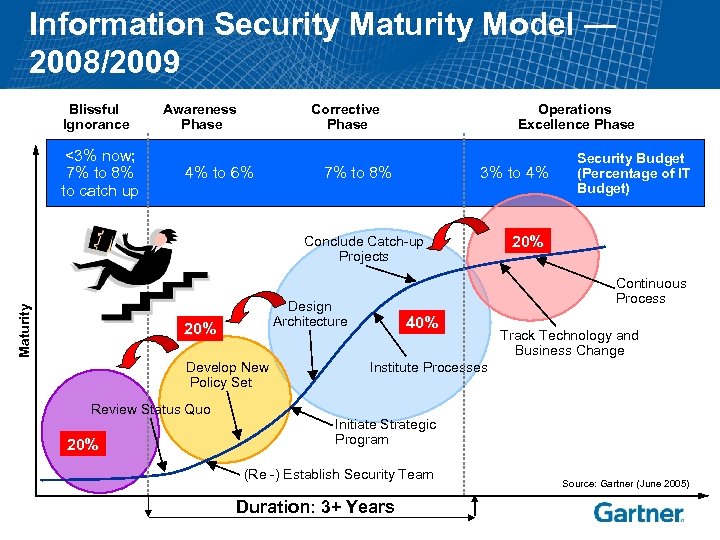
Information Security Maturity Model — 2008/2009 Blissful Ignorance <3% now; 7% to 8% to catch up Awareness Phase Corrective Phase 4% to 6% Operations Excellence Phase 7% to 8% 3% to 4% Maturity Conclude Catch-up Projects Develop New Policy Set Review Status Quo 20% Continuous Process Design Architecture 20% Security Budget (Percentage of IT Budget) 40% Track Technology and Business Change Institute Processes Initiate Strategic Program (Re -) Establish Security Team Duration: 3+ Years Source: Gartner (June 2005)

Call to Action ü Getting to Security 3. 0 means driving change – Change how IT is bought or built – Change how business solutions are developed – Change who pays for what security controls – Change how you spend 75% of your time ü If you can't change something right away, find the decision gate and change that ü Security might be a journey but it better have destinations along the way
253c65873328ca202854f8df6e684ea6.ppt