8cd676881400932fcde2c6d11802299c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
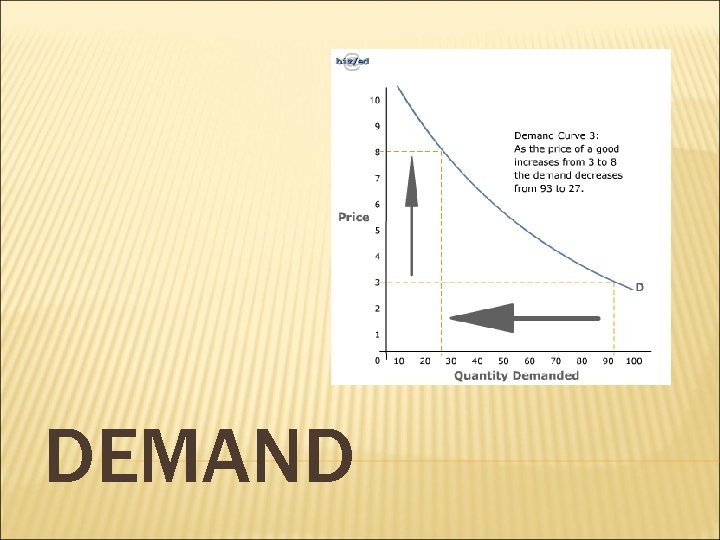 DEMAND
DEMAND
 DEMAND SCHEDULES AND DEMAND CURVES (SECTION 6. 1)
DEMAND SCHEDULES AND DEMAND CURVES (SECTION 6. 1)
 WHAT IS MICROECONOMICS? branch of economics that examines individuals’ choices concerning 1 product/firm/industry
WHAT IS MICROECONOMICS? branch of economics that examines individuals’ choices concerning 1 product/firm/industry
 WHAT IS DEMAND? quantities (Q) of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices (P) during a given period of time
WHAT IS DEMAND? quantities (Q) of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices (P) during a given period of time
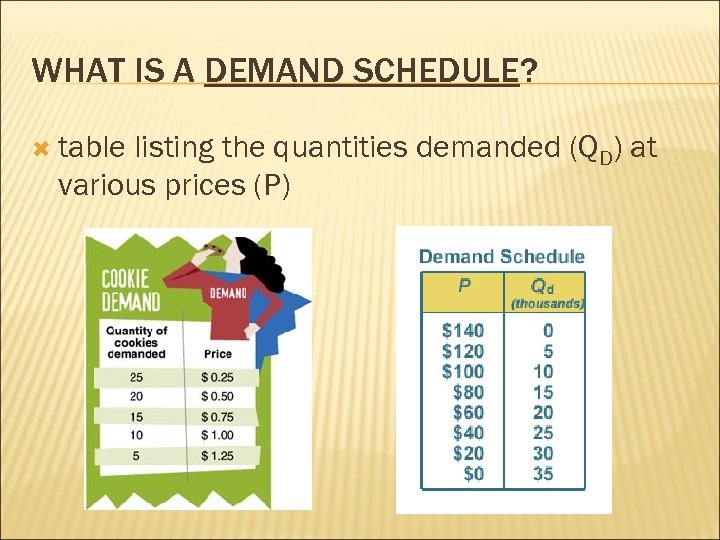 WHAT IS A DEMAND SCHEDULE? table listing the quantities demanded (QD) at various prices (P)
WHAT IS A DEMAND SCHEDULE? table listing the quantities demanded (QD) at various prices (P)
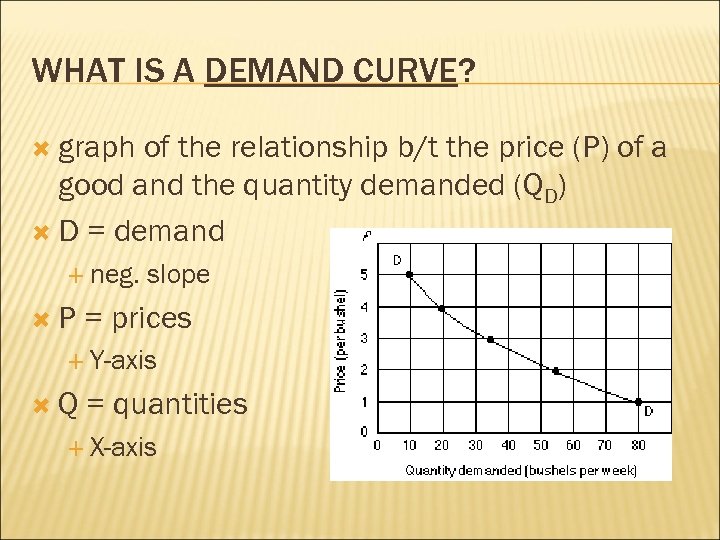 WHAT IS A DEMAND CURVE? graph of the relationship b/t the price (P) of a good and the quantity demanded (QD) D = demand neg. P slope = prices Y-axis Q = quantities X-axis
WHAT IS A DEMAND CURVE? graph of the relationship b/t the price (P) of a good and the quantity demanded (QD) D = demand neg. P slope = prices Y-axis Q = quantities X-axis
 THE LAW OF DEMAND (SECTION 6. 2)
THE LAW OF DEMAND (SECTION 6. 2)
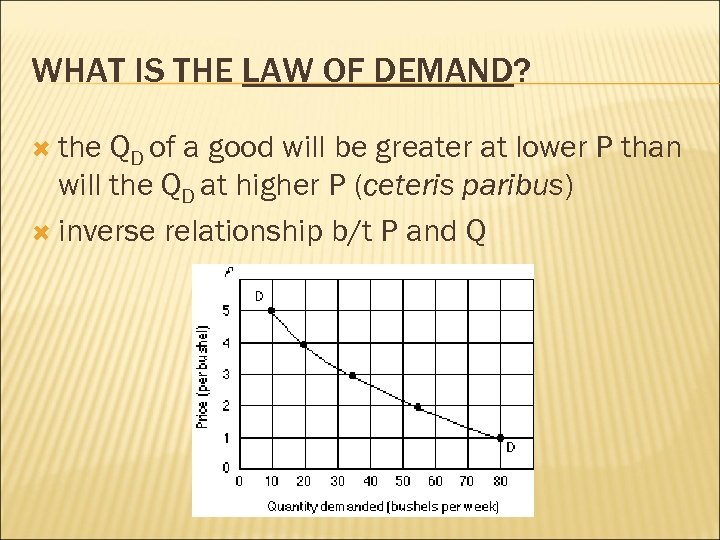 WHAT IS THE LAW OF DEMAND? the QD of a good will be greater at lower P than will the QD at higher P (ceteris paribus) inverse relationship b/t P and Q
WHAT IS THE LAW OF DEMAND? the QD of a good will be greater at lower P than will the QD at higher P (ceteris paribus) inverse relationship b/t P and Q
 WHY IS THE LAW OF DEMAND TRUE? 1. 2. 3. diminishing marginal utility income effect substitution effect
WHY IS THE LAW OF DEMAND TRUE? 1. 2. 3. diminishing marginal utility income effect substitution effect
 1. DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY
1. DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY
 WHAT IS UTILITY? utility: amt. of satisfaction one receives from consuming a good total utility (TU): total amt. of satisfaction from consuming an amt. of goods marginal utility (MU): amt. of satisfaction from consuming 1 more unit of a good
WHAT IS UTILITY? utility: amt. of satisfaction one receives from consuming a good total utility (TU): total amt. of satisfaction from consuming an amt. of goods marginal utility (MU): amt. of satisfaction from consuming 1 more unit of a good
 WHAT IS DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY? as additional units of a product are consumed, the additional satisfaction starts to
WHAT IS DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY? as additional units of a product are consumed, the additional satisfaction starts to
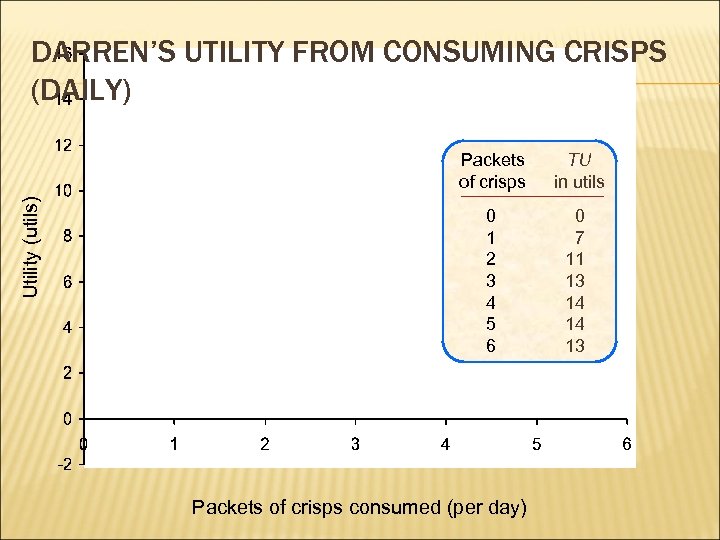 DARREN’S UTILITY FROM CONSUMING CRISPS (DAILY) Utility (utils) Packets of crisps TU in utils 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 7 11 13 14 14 13 Packets of crisps consumed (per day)
DARREN’S UTILITY FROM CONSUMING CRISPS (DAILY) Utility (utils) Packets of crisps TU in utils 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 7 11 13 14 14 13 Packets of crisps consumed (per day)
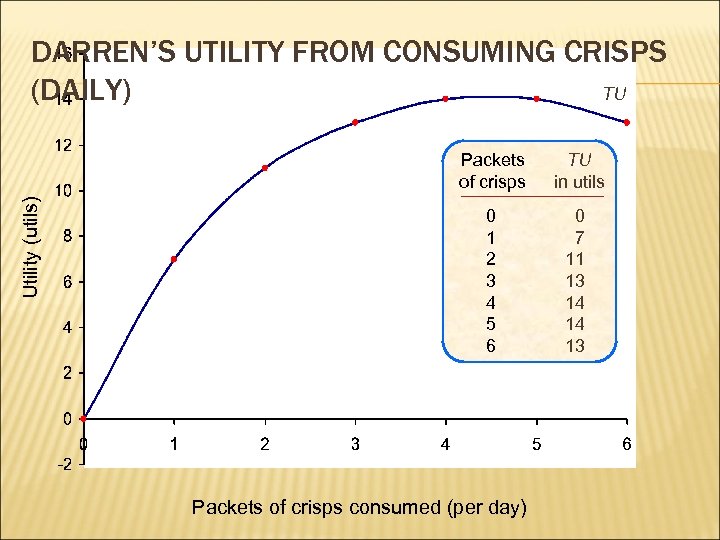 DARREN’S UTILITY FROM CONSUMING CRISPS (DAILY) TU Utility (utils) Packets of crisps TU in utils 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 7 11 13 14 14 13 Packets of crisps consumed (per day)
DARREN’S UTILITY FROM CONSUMING CRISPS (DAILY) TU Utility (utils) Packets of crisps TU in utils 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 7 11 13 14 14 13 Packets of crisps consumed (per day)
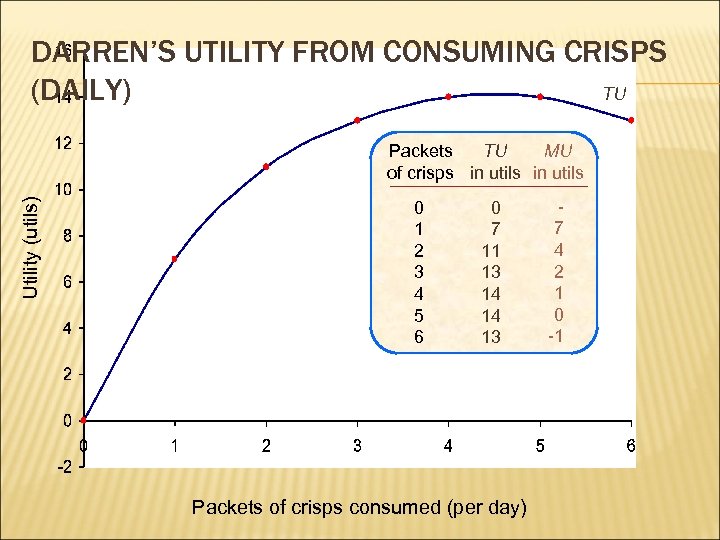 DARREN’S UTILITY FROM CONSUMING CRISPS (DAILY) TU Utility (utils) MU Packets TU of crisps in utils 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 7 11 13 14 14 13 Packets of crisps consumed (per day) 7 4 2 1 0 -1
DARREN’S UTILITY FROM CONSUMING CRISPS (DAILY) TU Utility (utils) MU Packets TU of crisps in utils 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 7 11 13 14 14 13 Packets of crisps consumed (per day) 7 4 2 1 0 -1
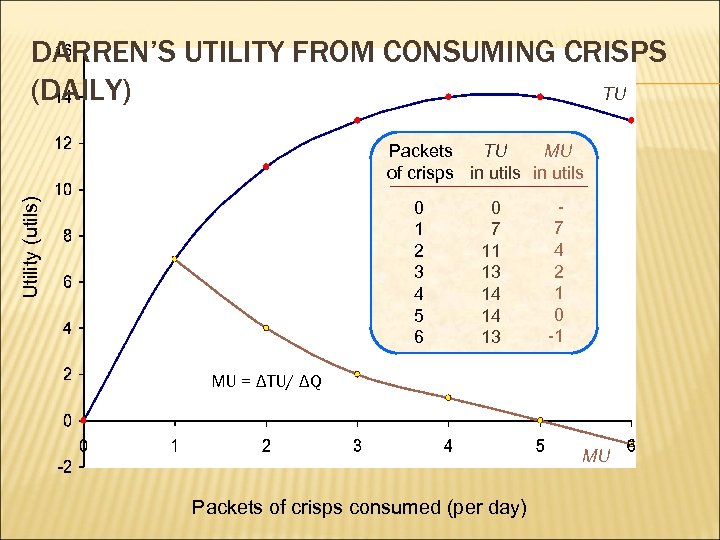 DARREN’S UTILITY FROM CONSUMING CRISPS (DAILY) TU Utility (utils) MU Packets TU of crisps in utils 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 7 11 13 14 14 13 7 4 2 1 0 -1 MU = ΔTU/ ΔQ MU Packets of crisps consumed (per day)
DARREN’S UTILITY FROM CONSUMING CRISPS (DAILY) TU Utility (utils) MU Packets TU of crisps in utils 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 7 11 13 14 14 13 7 4 2 1 0 -1 MU = ΔTU/ ΔQ MU Packets of crisps consumed (per day)
 HOW DOES THE LAW OF DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY SUPPORT THE LAW OF DEMAND? the less of something you have, the more satisfaction you gain from each additional unit MU you gain from that product is higher you have willingness to pay more for it P are lower at higher QD because your additional satisfaction diminishes as you demand more
HOW DOES THE LAW OF DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY SUPPORT THE LAW OF DEMAND? the less of something you have, the more satisfaction you gain from each additional unit MU you gain from that product is higher you have willingness to pay more for it P are lower at higher QD because your additional satisfaction diminishes as you demand more
 2. INCOME EFFECT
2. INCOME EFFECT
 WHAT IS THE INCOME EFFECT? effect that or P has on buying power of income P = buying power (income seems )
WHAT IS THE INCOME EFFECT? effect that or P has on buying power of income P = buying power (income seems )
 3. SUBSTITUTION EFFECT
3. SUBSTITUTION EFFECT
 WHAT IS THE SUBSTITUTION EFFECT? the change in the mix of goods purchased as a result of or relative prices substitute: good that can be substituted for another butter vs. margarine coffee vs. tea perfect substitute: red pencil vs. yellow pencil
WHAT IS THE SUBSTITUTION EFFECT? the change in the mix of goods purchased as a result of or relative prices substitute: good that can be substituted for another butter vs. margarine coffee vs. tea perfect substitute: red pencil vs. yellow pencil
 HOW DOES THE SUBSTITUTION EFFECT SUPPORT THE LAW OF DEMAND? Example: If P of butter , you will buy margarine instead. QD of butter .
HOW DOES THE SUBSTITUTION EFFECT SUPPORT THE LAW OF DEMAND? Example: If P of butter , you will buy margarine instead. QD of butter .
 MARKETS & THE LAW OF DEMAND market demand schedule/curve: P and QD for all consumers of a good combined (the market) same principles apply to market as individuals
MARKETS & THE LAW OF DEMAND market demand schedule/curve: P and QD for all consumers of a good combined (the market) same principles apply to market as individuals
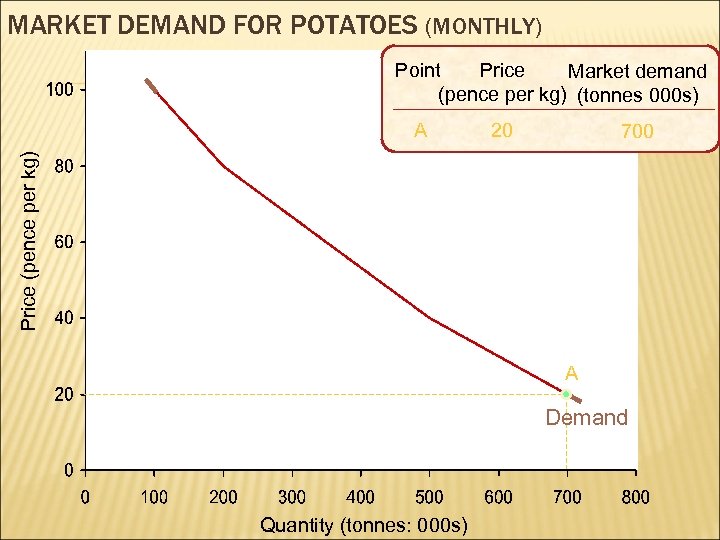 MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) 20 700 Price (pence per kg) A A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) 20 700 Price (pence per kg) A A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
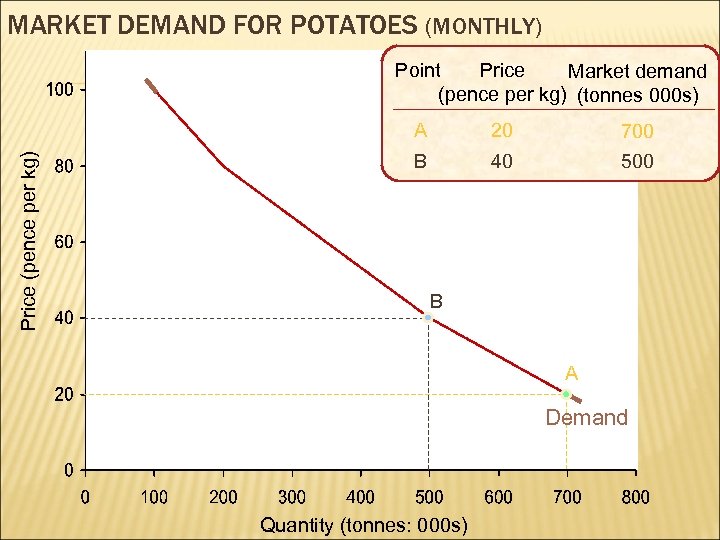 MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) Price (pence per kg) A 20 700 B 40 500 B A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) Price (pence per kg) A 20 700 B 40 500 B A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
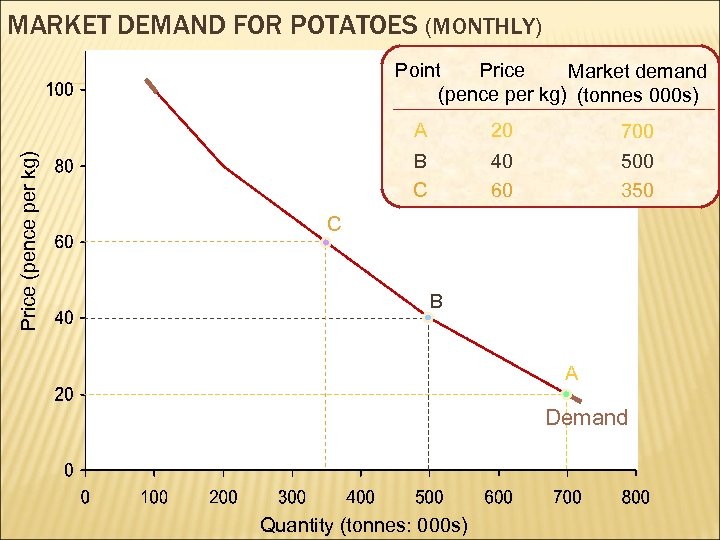 MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) Price (pence per kg) A 20 700 B C 40 60 500 350 C B A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) Price (pence per kg) A 20 700 B C 40 60 500 350 C B A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
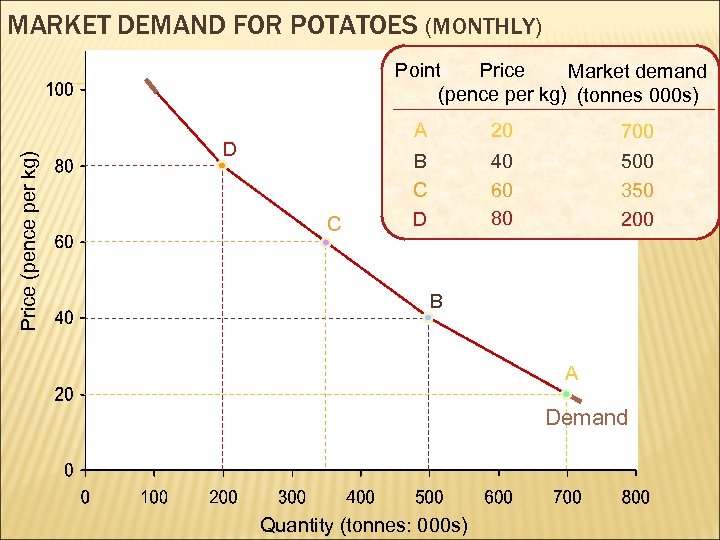 MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Price (pence per kg) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) A D C 20 700 B C D 40 60 80 500 350 200 B A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Price (pence per kg) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) A D C 20 700 B C D 40 60 80 500 350 200 B A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
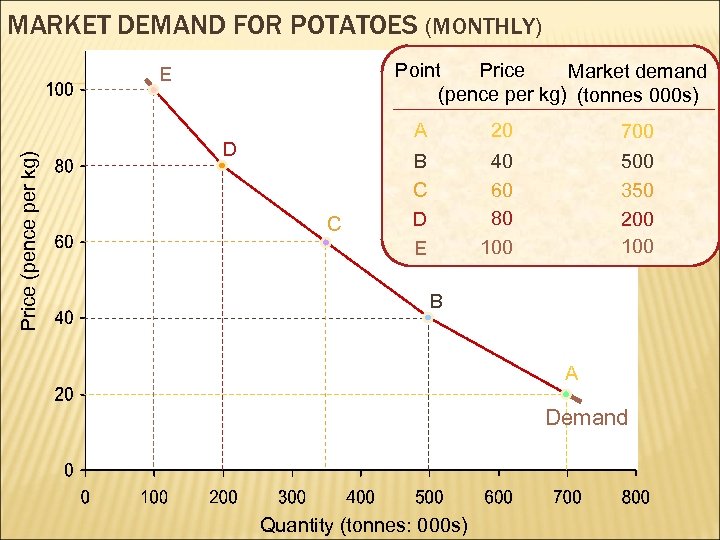 MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) Price (pence per kg) E A D C 20 700 B C D E 40 60 80 100 500 350 200 100 B A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
MARKET DEMAND FOR POTATOES (MONTHLY) Point Price Market demand (pence per kg) (tonnes 000 s) Price (pence per kg) E A D C 20 700 B C D E 40 60 80 100 500 350 200 100 B A Demand Quantity (tonnes: 000 s)
 DETERMINANTS OF DEMAND (SECTION 6. 3)
DETERMINANTS OF DEMAND (SECTION 6. 3)
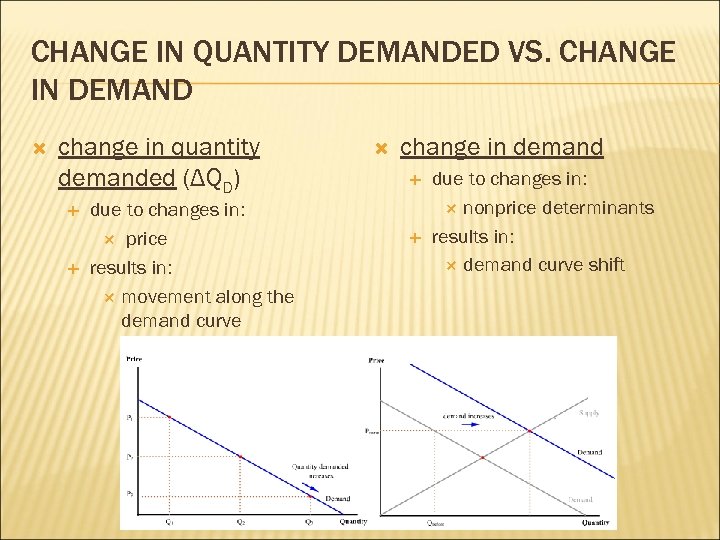 CHANGE IN QUANTITY DEMANDED VS. CHANGE IN DEMAND change in quantity demanded (ΔQD) due to changes in: price results in: movement along the demand curve change in demand due to changes in: nonprice determinants results in: demand curve shift
CHANGE IN QUANTITY DEMANDED VS. CHANGE IN DEMAND change in quantity demanded (ΔQD) due to changes in: price results in: movement along the demand curve change in demand due to changes in: nonprice determinants results in: demand curve shift
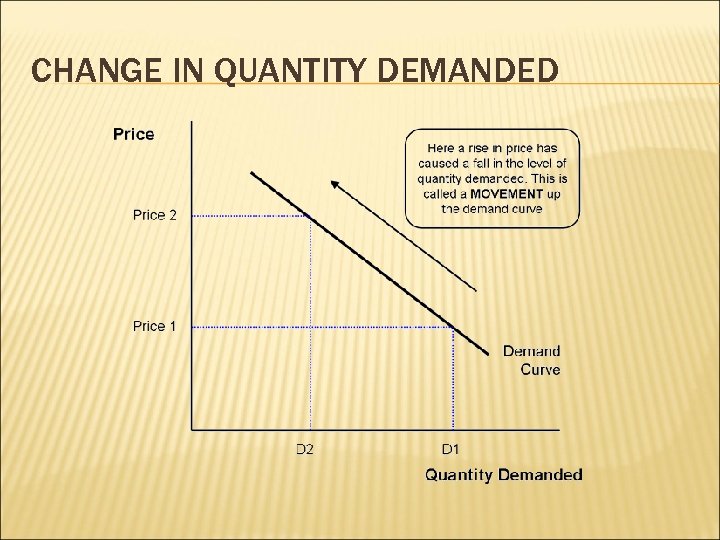 CHANGE IN QUANTITY DEMANDED
CHANGE IN QUANTITY DEMANDED
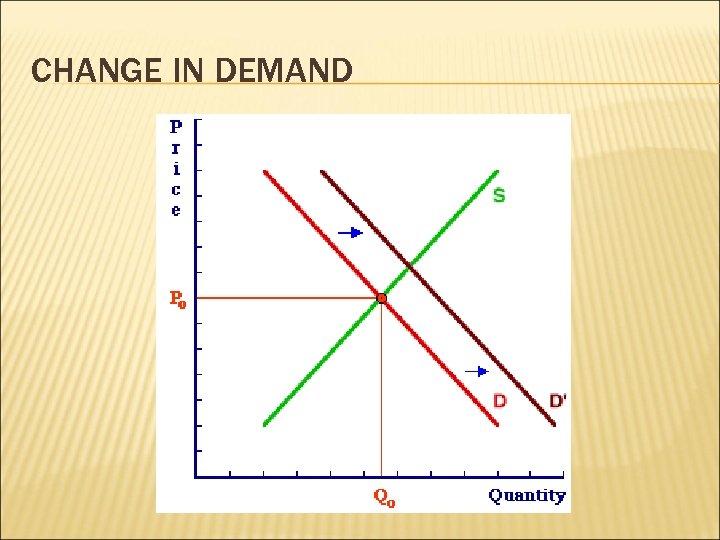 CHANGE IN DEMAND
CHANGE IN DEMAND
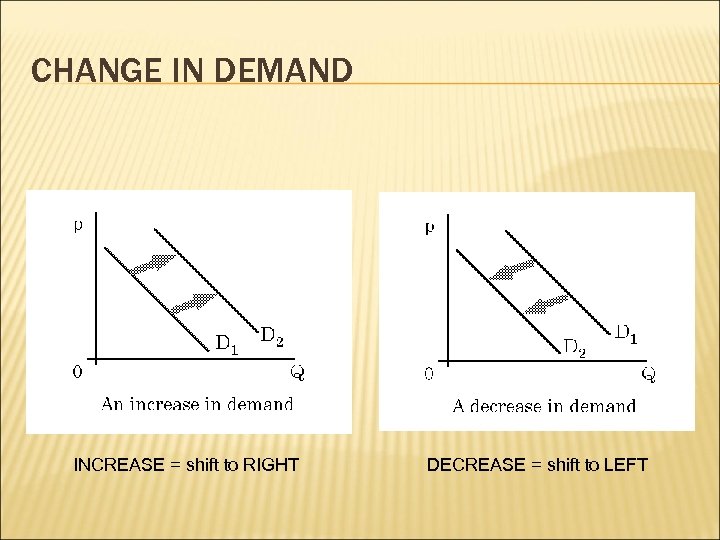 CHANGE IN DEMAND INCREASE = shift to RIGHT DECREASE = shift to LEFT
CHANGE IN DEMAND INCREASE = shift to RIGHT DECREASE = shift to LEFT
 NONPRICE DETERMINANTS OF DEMAND 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Income Tastes & preferences Prices of related goods Expectations of future prices Population size
NONPRICE DETERMINANTS OF DEMAND 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Income Tastes & preferences Prices of related goods Expectations of future prices Population size
 1. INCOME normal goods: demand as personal income inferior goods: demand as personal income (“Spam effect”)
1. INCOME normal goods: demand as personal income inferior goods: demand as personal income (“Spam effect”)
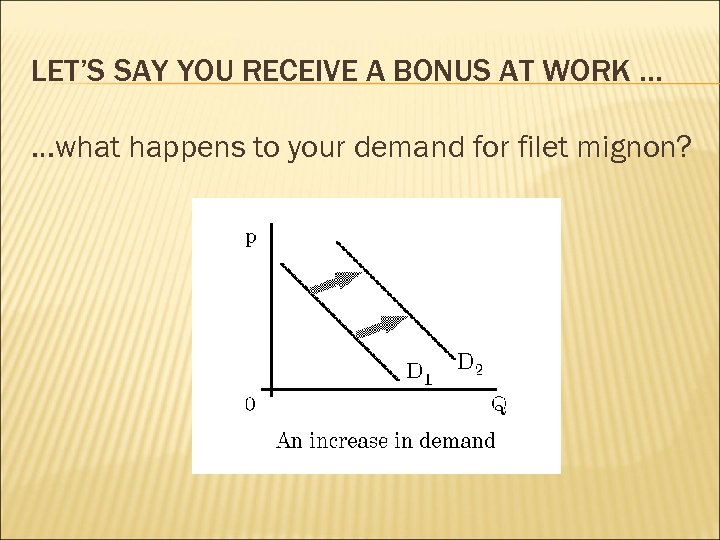 LET’S SAY YOU RECEIVE A BONUS AT WORK … …what happens to your demand for filet mignon?
LET’S SAY YOU RECEIVE A BONUS AT WORK … …what happens to your demand for filet mignon?
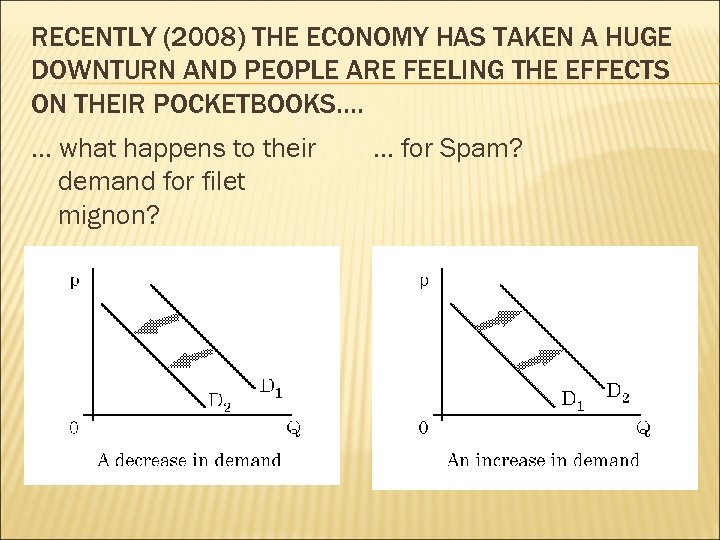 RECENTLY (2008) THE ECONOMY HAS TAKEN A HUGE DOWNTURN AND PEOPLE ARE FEELING THE EFFECTS ON THEIR POCKETBOOKS…. … what happens to their demand for filet mignon? … for Spam?
RECENTLY (2008) THE ECONOMY HAS TAKEN A HUGE DOWNTURN AND PEOPLE ARE FEELING THE EFFECTS ON THEIR POCKETBOOKS…. … what happens to their demand for filet mignon? … for Spam?
 2. TASTES & PREFERENCES Hybrids, especially the Toyota Prius The “Friends” Haircut
2. TASTES & PREFERENCES Hybrids, especially the Toyota Prius The “Friends” Haircut
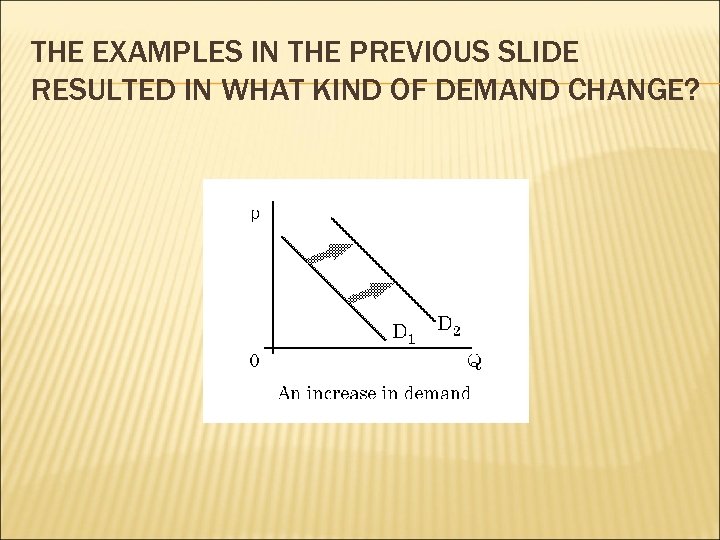 THE EXAMPLES IN THE PREVIOUS SLIDE RESULTED IN WHAT KIND OF DEMAND CHANGE?
THE EXAMPLES IN THE PREVIOUS SLIDE RESULTED IN WHAT KIND OF DEMAND CHANGE?
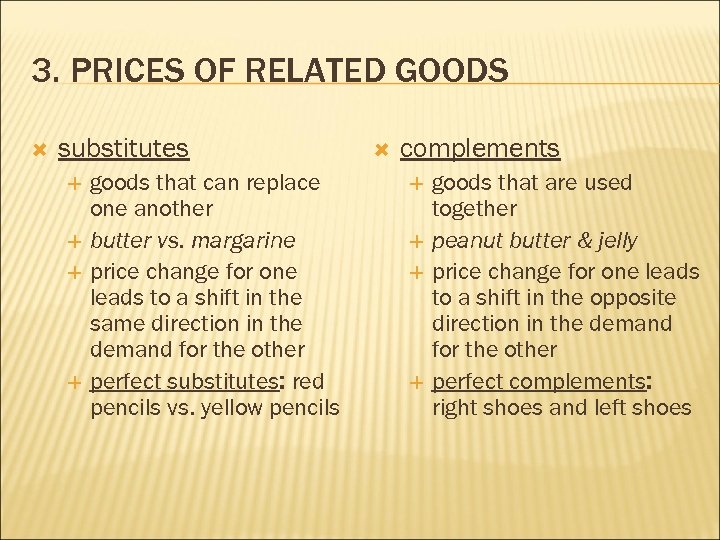 3. PRICES OF RELATED GOODS substitutes goods that can replace one another butter vs. margarine price change for one leads to a shift in the same direction in the demand for the other perfect substitutes: red pencils vs. yellow pencils complements goods that are used together peanut butter & jelly price change for one leads to a shift in the opposite direction in the demand for the other perfect complements: right shoes and left shoes
3. PRICES OF RELATED GOODS substitutes goods that can replace one another butter vs. margarine price change for one leads to a shift in the same direction in the demand for the other perfect substitutes: red pencils vs. yellow pencils complements goods that are used together peanut butter & jelly price change for one leads to a shift in the opposite direction in the demand for the other perfect complements: right shoes and left shoes
 LET’S SAY THE PRICE OF BUTTER SKYROCKETS… … what happens to demand for margarine?
LET’S SAY THE PRICE OF BUTTER SKYROCKETS… … what happens to demand for margarine?
 A BLIGHT ATTACKS THE PEANUT CROP, AND AS A RESULT THE PRICE OF PEANUT BUTTER GOES UP… … what happens to demand for jelly?
A BLIGHT ATTACKS THE PEANUT CROP, AND AS A RESULT THE PRICE OF PEANUT BUTTER GOES UP… … what happens to demand for jelly?
 4. EXPECTATIONS OF FUTURE PRICES future ΔP and current ΔD move in the same direction Ex. speculative buying. Google stock? H 20 before a hurricane
4. EXPECTATIONS OF FUTURE PRICES future ΔP and current ΔD move in the same direction Ex. speculative buying. Google stock? H 20 before a hurricane
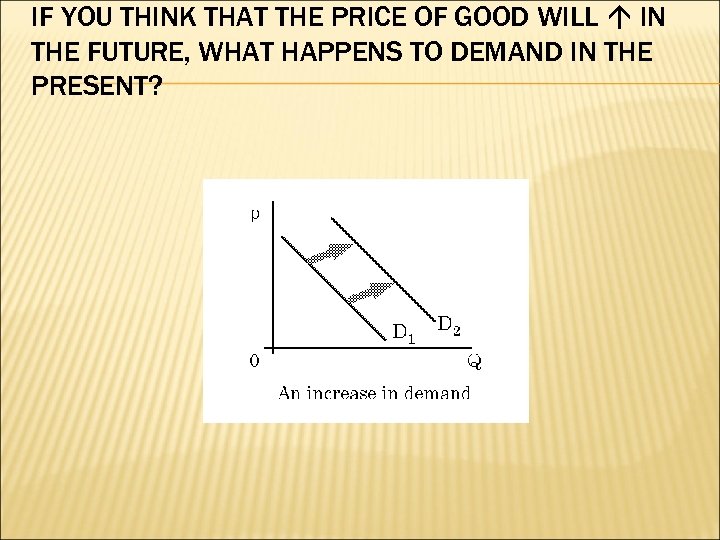 IF YOU THINK THAT THE PRICE OF GOOD WILL IN THE FUTURE, WHAT HAPPENS TO DEMAND IN THE PRESENT?
IF YOU THINK THAT THE PRICE OF GOOD WILL IN THE FUTURE, WHAT HAPPENS TO DEMAND IN THE PRESENT?
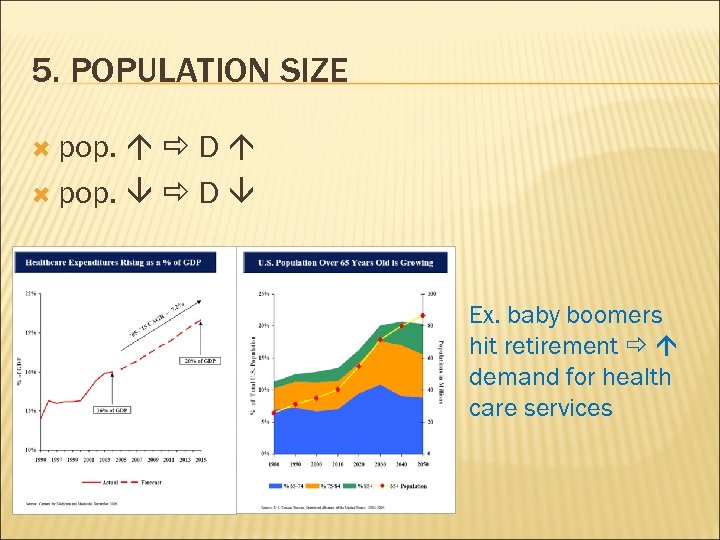 5. POPULATION SIZE pop. D Ex. baby boomers hit retirement demand for health care services
5. POPULATION SIZE pop. D Ex. baby boomers hit retirement demand for health care services
 PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (SECTION 6. 4)
PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (SECTION 6. 4)
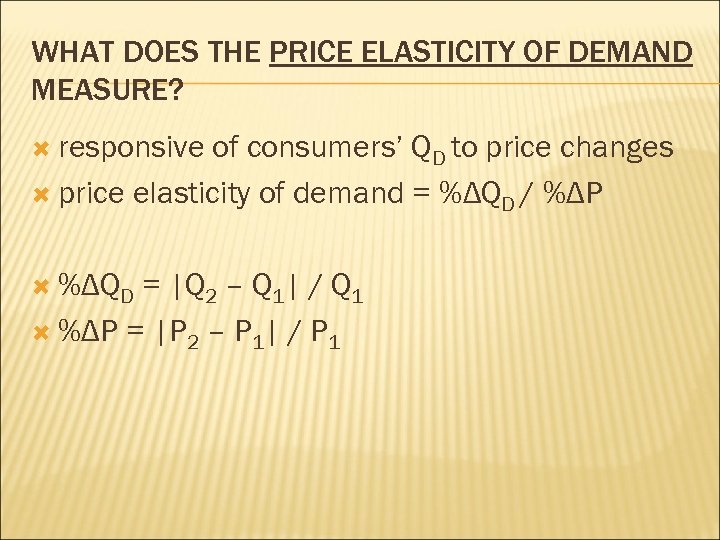 WHAT DOES THE PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND MEASURE? responsive of consumers’ QD to price changes price elasticity of demand = %ΔQD / %ΔP %ΔQD = |Q 2 – Q 1| / Q 1 %ΔP = |P 2 – P 1| / P 1
WHAT DOES THE PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND MEASURE? responsive of consumers’ QD to price changes price elasticity of demand = %ΔQD / %ΔP %ΔQD = |Q 2 – Q 1| / Q 1 %ΔP = |P 2 – P 1| / P 1
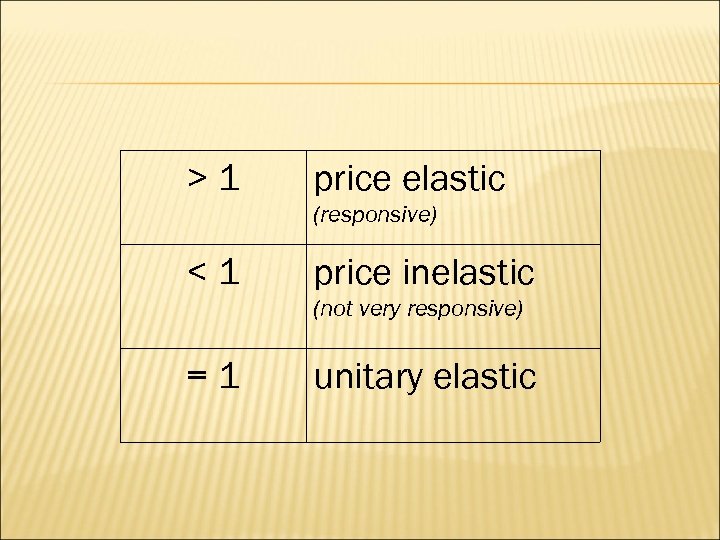 >1 price elastic (responsive) <1 price inelastic (not very responsive) =1 unitary elastic
>1 price elastic (responsive) <1 price inelastic (not very responsive) =1 unitary elastic
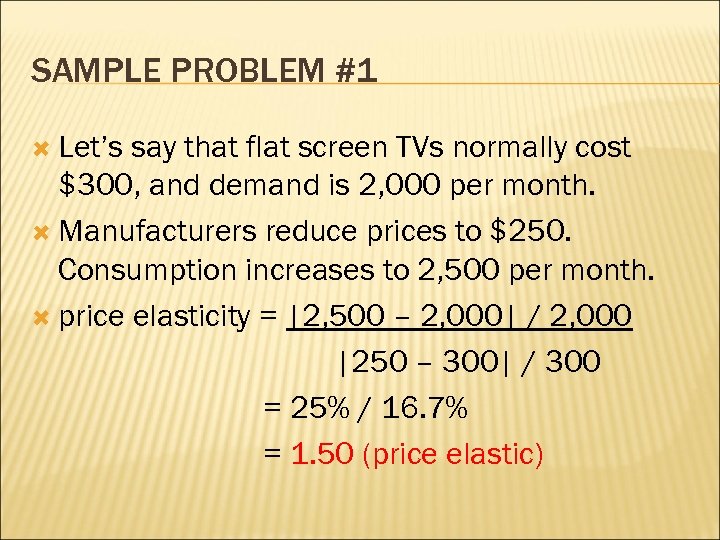 SAMPLE PROBLEM #1 Let’s say that flat screen TVs normally cost $300, and demand is 2, 000 per month. Manufacturers reduce prices to $250. Consumption increases to 2, 500 per month. price elasticity = |2, 500 – 2, 000| / 2, 000 |250 – 300| / 300 = 25% / 16. 7% = 1. 50 (price elastic)
SAMPLE PROBLEM #1 Let’s say that flat screen TVs normally cost $300, and demand is 2, 000 per month. Manufacturers reduce prices to $250. Consumption increases to 2, 500 per month. price elasticity = |2, 500 – 2, 000| / 2, 000 |250 – 300| / 300 = 25% / 16. 7% = 1. 50 (price elastic)
 SAMPLE PROBLEM #2 In April, gas cost $3 per gallon, and demand was 10, 000 gallons per day. In May, gas rose to $3. 50 per gallon, and demand slipped to 9, 750 gallons per day. price elasticity = |9, 750 – 10, 000| / 10, 000 |3. 50 – 3| / 3 = 2. 5% / 16. 7% = 0. 15 (price inelastic)
SAMPLE PROBLEM #2 In April, gas cost $3 per gallon, and demand was 10, 000 gallons per day. In May, gas rose to $3. 50 per gallon, and demand slipped to 9, 750 gallons per day. price elasticity = |9, 750 – 10, 000| / 10, 000 |3. 50 – 3| / 3 = 2. 5% / 16. 7% = 0. 15 (price inelastic)
 FACTORS DETERMINING ELASTICITY 1. ability to substitute 2. proportion of budget spent on good 3. more substitutes = more elastic more expensive item = more elastic length of time to permit changes more time = more elastic
FACTORS DETERMINING ELASTICITY 1. ability to substitute 2. proportion of budget spent on good 3. more substitutes = more elastic more expensive item = more elastic length of time to permit changes more time = more elastic
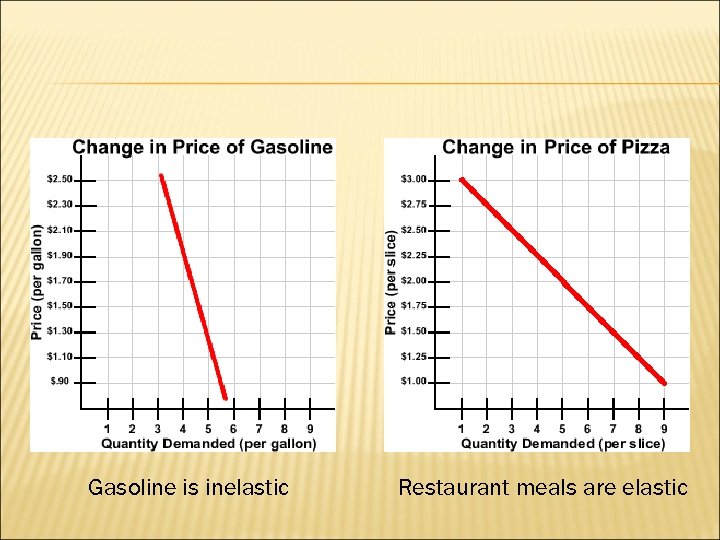 Gasoline is inelastic Restaurant meals are elastic
Gasoline is inelastic Restaurant meals are elastic
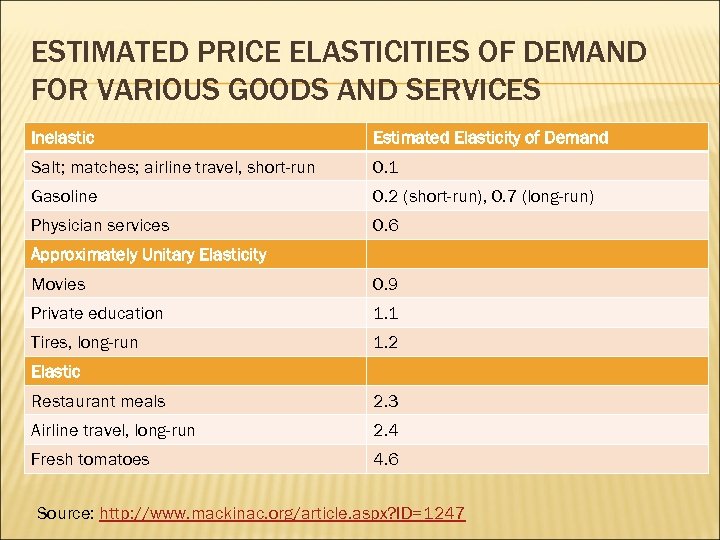 ESTIMATED PRICE ELASTICITIES OF DEMAND FOR VARIOUS GOODS AND SERVICES Inelastic Estimated Elasticity of Demand Salt; matches; airline travel, short-run 0. 1 Gasoline 0. 2 (short-run), 0. 7 (long-run) Physician services 0. 6 Approximately Unitary Elasticity Movies 0. 9 Private education 1. 1 Tires, long-run 1. 2 Elastic Restaurant meals 2. 3 Airline travel, long-run 2. 4 Fresh tomatoes 4. 6 Source: http: //www. mackinac. org/article. aspx? ID=1247
ESTIMATED PRICE ELASTICITIES OF DEMAND FOR VARIOUS GOODS AND SERVICES Inelastic Estimated Elasticity of Demand Salt; matches; airline travel, short-run 0. 1 Gasoline 0. 2 (short-run), 0. 7 (long-run) Physician services 0. 6 Approximately Unitary Elasticity Movies 0. 9 Private education 1. 1 Tires, long-run 1. 2 Elastic Restaurant meals 2. 3 Airline travel, long-run 2. 4 Fresh tomatoes 4. 6 Source: http: //www. mackinac. org/article. aspx? ID=1247
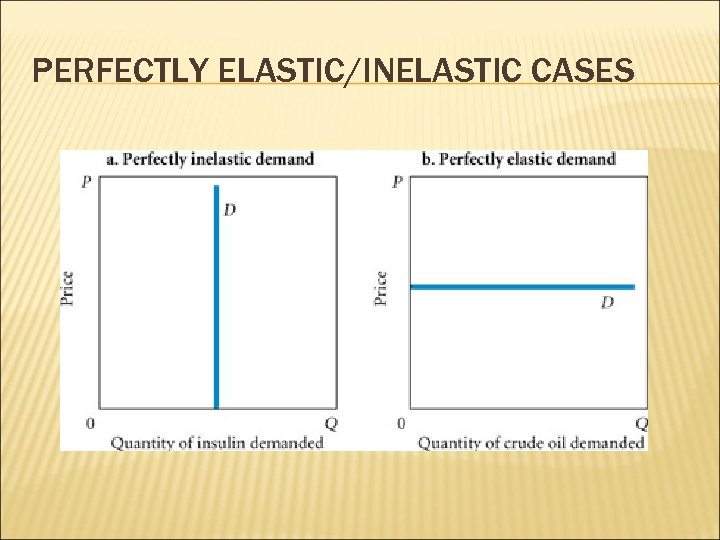 PERFECTLY ELASTIC/INELASTIC CASES
PERFECTLY ELASTIC/INELASTIC CASES
 TOTAL REVENUE total amount of money a company receives from sales of a product TR = P x Q
TOTAL REVENUE total amount of money a company receives from sales of a product TR = P x Q
 SAMPLE PROBLEM Edie’s Little Bakeshop sells scones for $1. 50 each and sells 600 per month. What is her total revenue? TR = P x Q = ($1. 50)(600) = $900
SAMPLE PROBLEM Edie’s Little Bakeshop sells scones for $1. 50 each and sells 600 per month. What is her total revenue? TR = P x Q = ($1. 50)(600) = $900
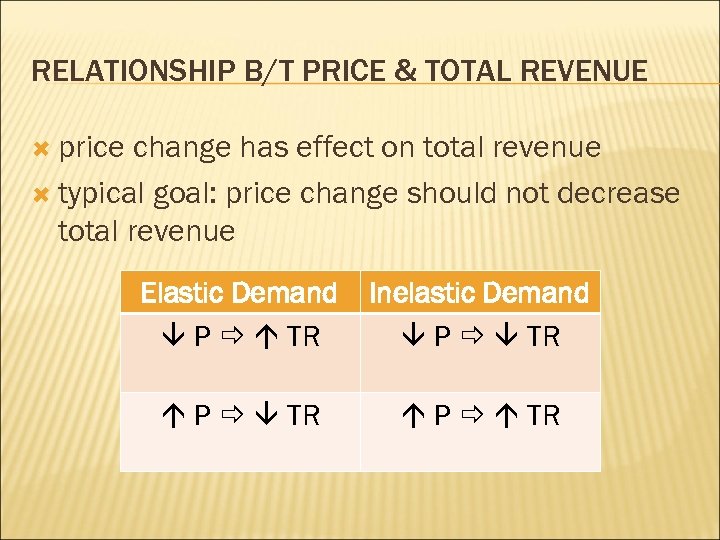 RELATIONSHIP B/T PRICE & TOTAL REVENUE price change has effect on total revenue typical goal: price change should not decrease total revenue Elastic Demand P TR Inelastic Demand P TR
RELATIONSHIP B/T PRICE & TOTAL REVENUE price change has effect on total revenue typical goal: price change should not decrease total revenue Elastic Demand P TR Inelastic Demand P TR
 BACK TO PRICE ELASTICITY SAMPLE PROBLEM #1 (TVS) Should manufacturers reduce the price to $250? TR 1 = ($300)(2, 000) = $600, 000 TR 2 = ($250)(2, 500) = $625, 000 YES, because total revenue increases.
BACK TO PRICE ELASTICITY SAMPLE PROBLEM #1 (TVS) Should manufacturers reduce the price to $250? TR 1 = ($300)(2, 000) = $600, 000 TR 2 = ($250)(2, 500) = $625, 000 YES, because total revenue increases.


