Demand_Curve.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 16

Demand Curve The presentation is made by Dmitry Kulinchenko Group 1 -2

Contents Linear Function Definition of Demand Function Generalized Demand Function Factors Affecting Demand Function Slope Parameters

Linear Function Definition An algebraic equation in which the highest degree term in the variable or variables is of the first degree. The graph of such an equation is a straight line if there are two variables. In linear equation there are two variable names independent variable and dependent variable.

Linear Equation A common form of a linear equation in the two variables x and y is y = mx + c Where 'x' and 'y' are the coordinates of the points that satisfy the function and so lie on the straight line graph. 'm' is the gradient of the straight line graph, and 'c' is the 'y intercept' of the straight line graph.
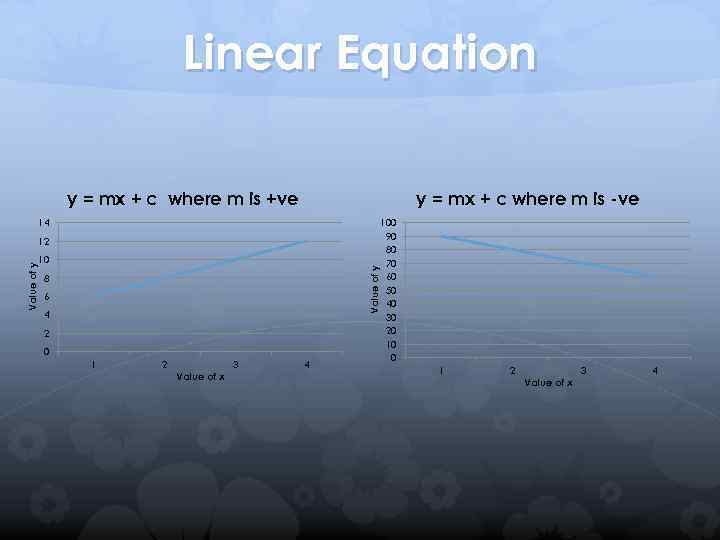
Linear Equation y = mx + c where m is +ve y = mx + c where m is -ve 14 12 Value of y 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 Value of x 3 4 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1 2 Value of x 3 4

Definition of Demand is the amount of goods and services that consumers in a market are willing and able to purchase during a given period of time
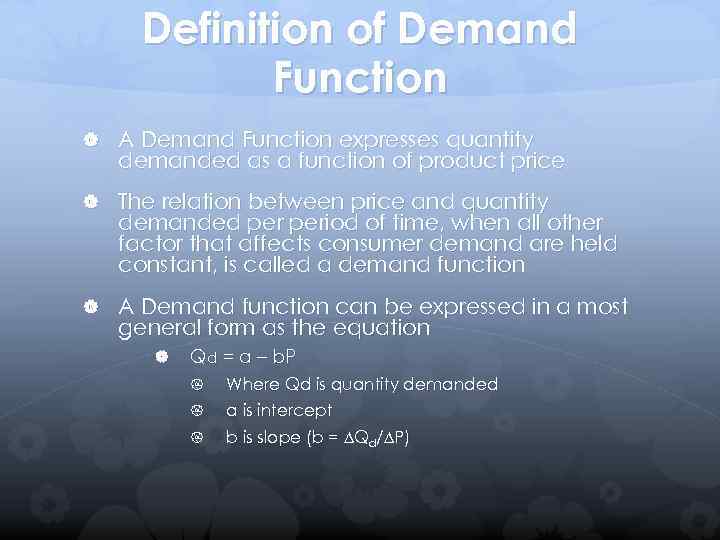
Definition of Demand Function A Demand Function expresses quantity demanded as a function of product price The relation between price and quantity demanded period of time, when all other factor that affects consumer demand are held constant, is called a demand function A Demand function can be expressed in a most general form as the equation Qd = a – b. P Where Qd is quantity demanded a is intercept b is slope (b = Qd/ P)

Generalized Demand Function Quantity Demanded Qd = a + b. P + c. I + d. P + e. T + f. Pe + g. N R b, c, d, e, f and g are slope parameters P = Price of the goods or services I = Consumers Income PR = Price of related goods or services T = Taste pattern of consumers Pe = Expected price of the goods in some future period N = Number of Consumers in the market
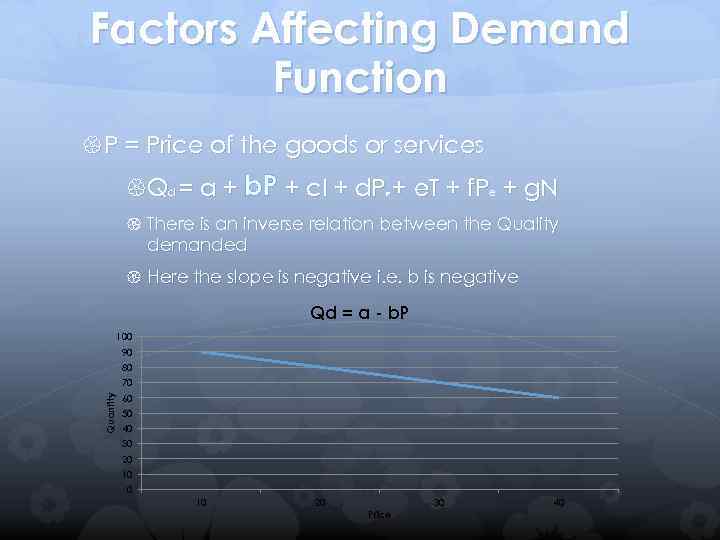
Factors Affecting Demand Function P = Price of the goods or services Qd = a + b. P + c. I + d. P + e. T + f. Pe + g. N R There is an inverse relation between the Quality demanded Here the slope is negative i. e. b is negative Qd = a - b. P 100 90 80 Quantity 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 20 Price 30 40
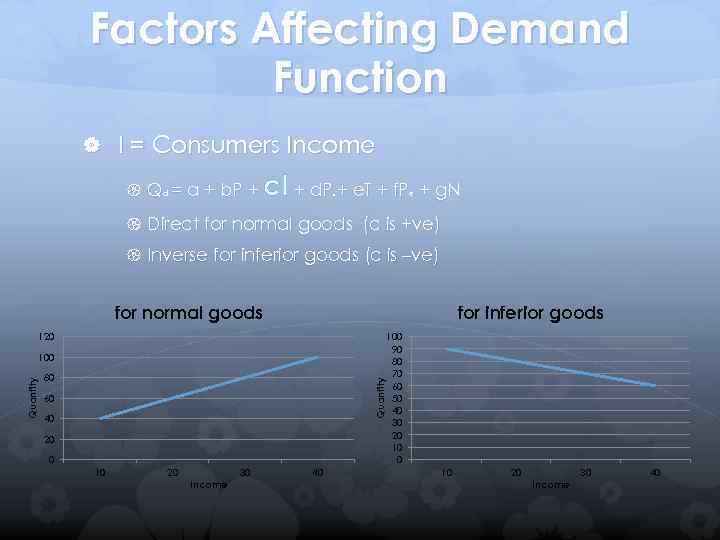
Factors Affecting Demand Function I = Consumers Income Qd = a + b. P + c. I + d. P + e. T + f. P + g. N e R Direct for normal goods (c is +ve) Inverse for inferior goods (c is –ve) for normal goods for inferior goods 120 80 Quantity 100 60 40 20 0 10 20 Income 30 40 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 20 Income 30 40
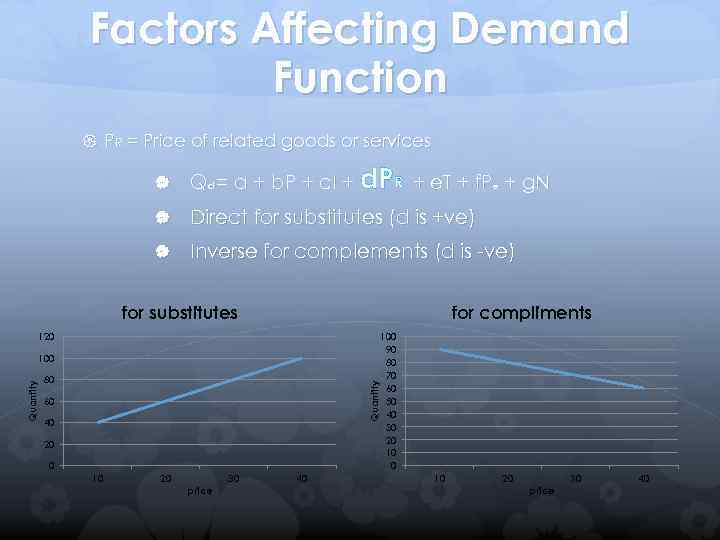
Factors Affecting Demand Function PR = Price of related goods or services Qd = a + b. P + c. I + d. PR + e. T + f. P + g. N Direct for substitutes (d is +ve) Inverse for complements (d is -ve) e for substitutes for compliments 120 80 Quantity 100 60 40 20 0 10 20 price 30 40 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 20 price 30 40

Factors Affecting Demand Function T = Taste pattern of consumers Qd = a + b. P + c. I + d. P + e. T + f. P + g. N It has the direct relation (e is +ve) R e

Factors Affecting Demand Function Pe = Expected price of the goods in some future period Qd = a + b. P + c. I + d. P + e. T + f. Pe + g. N It has the direct relation (f is +ve) R

Factors Affecting Demand Function N = Number of Consumers in the market Qd = a + b. P + c. I + d. P + e. T + f. P + g. N It has the direct relation (g is +ve) R e
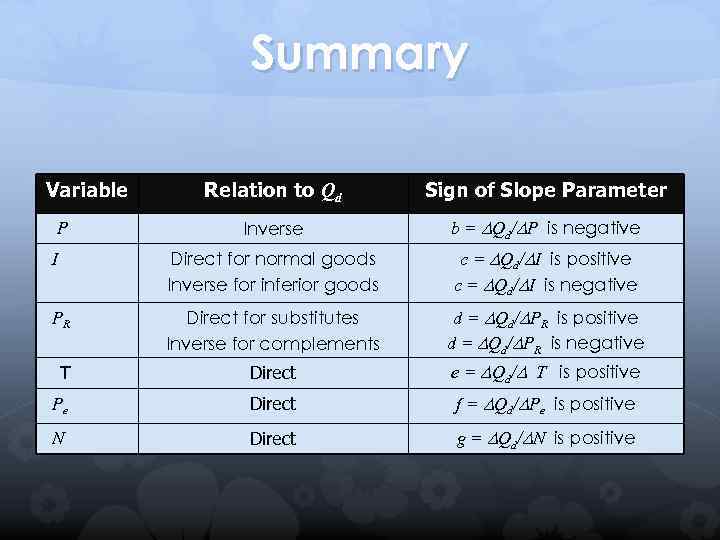
Summary Relation to Qd Sign of Slope Parameter Inverse b = Qd/ P is negative I Direct for normal goods Inverse for inferior goods c = Qd/ I is positive c = Qd/ I is negative PR Direct for substitutes Inverse for complements d = Qd/ PR is positive d = Qd/ PR is negative T Direct e = Qd/ T is positive Pe Direct f = Qd/ Pe is positive N Direct g = Qd/ N is positive Variable P

Thank You
Demand_Curve.pptx