e79945c539a974f5eccf0de93c749116.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Deindustri alization in the Core • Relative decline in industrial employment – Automation • Reinvestment in higher profit areas – Sunbelt states (non-union) – Semi-periphery and Periphery
Deindustri alization in the Core • Relative decline in industrial employment – Automation • Reinvestment in higher profit areas – Sunbelt states (non-union) – Semi-periphery and Periphery
 http: //www. whatisanamericancar. com/ Right to Work States RTW is a state law that prohibits employers and unions from requiring an employee to pay dues or fees to a union in order to keep his or her job. Currently, 22 states have right-towork laws. While right-to-work laws do NOT allow individual workers to negotiate their own contracts, they do protect a worker from having to involuntarily support a union. Advantages? Disadvantages?
http: //www. whatisanamericancar. com/ Right to Work States RTW is a state law that prohibits employers and unions from requiring an employee to pay dues or fees to a union in order to keep his or her job. Currently, 22 states have right-towork laws. While right-to-work laws do NOT allow individual workers to negotiate their own contracts, they do protect a worker from having to involuntarily support a union. Advantages? Disadvantages?
 Consultant: Atlanta's traffic is endangering its growth Published on: 12/17/07 Metro Atlanta's traffic congestion is endangering its future growth, according to one of the nation's top site selection experts, who advises companies on where to send their jobs. Atlanta's traffic problem has put it "at the point of no return, " said Dennis J. Donovan. Clients of his company, New Jersey-based WDG Consulting, include at any given time about a third of the Fortune 500 companies. And something new is happening in his client meetings that didn't in the 1990's, Donovan said. "Up until seven or eight years ago when we had Atlanta on a recommended short list" for places to relocate or expand a business, "we rarely heard grumbling, " he said. That has changed. Now, he said, when Atlanta shows up on a short list, "Every one of our companies, every one of them, says, 'Boy, isn't there a lot of traffic down there? '" While he had not yet seen his own clients refuse to consider Atlanta, he said he believes that some companies are quietly rejecting Atlanta because of traffic. He cited Mead. Westvaco, which relocated its headquarters —and hundreds of new jobs— to Richmond, Va. , instead of Atlanta because of traffic. Lots of places have transportation funding problems, but Atlanta's congestion is the second worst in the nation, Donovan noted, and "the planning and funding to make sure this wouldn't happen hasn't been done. “ Donovan made his comments to the Metro Atlanta Chamber of Commerce, which backed a bill this year allowing counties to group together as a region and put funding for regional projects to voter referendum.
Consultant: Atlanta's traffic is endangering its growth Published on: 12/17/07 Metro Atlanta's traffic congestion is endangering its future growth, according to one of the nation's top site selection experts, who advises companies on where to send their jobs. Atlanta's traffic problem has put it "at the point of no return, " said Dennis J. Donovan. Clients of his company, New Jersey-based WDG Consulting, include at any given time about a third of the Fortune 500 companies. And something new is happening in his client meetings that didn't in the 1990's, Donovan said. "Up until seven or eight years ago when we had Atlanta on a recommended short list" for places to relocate or expand a business, "we rarely heard grumbling, " he said. That has changed. Now, he said, when Atlanta shows up on a short list, "Every one of our companies, every one of them, says, 'Boy, isn't there a lot of traffic down there? '" While he had not yet seen his own clients refuse to consider Atlanta, he said he believes that some companies are quietly rejecting Atlanta because of traffic. He cited Mead. Westvaco, which relocated its headquarters —and hundreds of new jobs— to Richmond, Va. , instead of Atlanta because of traffic. Lots of places have transportation funding problems, but Atlanta's congestion is the second worst in the nation, Donovan noted, and "the planning and funding to make sure this wouldn't happen hasn't been done. “ Donovan made his comments to the Metro Atlanta Chamber of Commerce, which backed a bill this year allowing counties to group together as a region and put funding for regional projects to voter referendum.
 Basic vs. Non-Basic • The basic sector of an economy includes any industry that brings in money from outside the area. • The non-basic sector includes all industry that supports the local community and circulates money amongst local industries. • This can drive you crazy b/c some jobs are both basic and non-basic!
Basic vs. Non-Basic • The basic sector of an economy includes any industry that brings in money from outside the area. • The non-basic sector includes all industry that supports the local community and circulates money amongst local industries. • This can drive you crazy b/c some jobs are both basic and non-basic!
 Why do you want a lot of new basic jobs in your community? • Multiplier Effect = one basic job produces two nonbasic jobs (as opposed to…) Bob, the world’s best psychologist, has clients from all over the world. He gets paid about $1, 000 per hour. His office is in Atlanta and he spends about 90% of his salary inside the city limits. He therefore helps employ many waiters, grocery store clerks, cooks…
Why do you want a lot of new basic jobs in your community? • Multiplier Effect = one basic job produces two nonbasic jobs (as opposed to…) Bob, the world’s best psychologist, has clients from all over the world. He gets paid about $1, 000 per hour. His office is in Atlanta and he spends about 90% of his salary inside the city limits. He therefore helps employ many waiters, grocery store clerks, cooks…
 The Probably-Not-Going-to-Multiply Effect
The Probably-Not-Going-to-Multiply Effect
 Proximity to Cheap Labor • Outsourcing a decision by a corporation to turn over much of the responsibility for production to independent suppliers – Low level tasks look 4 cheap labor • Call centers and tax accountants to Bangalore • Textile manufacturers in East Asia, Latin America – Opposite of vertical integration employ someone else to perform a task b/c cheaper & more efficient • Outsourcing “New International Division of Labor” – Process raw materials near supply – Labor-intensive work where labor is cheap – Skilled labor: R&D, Capital, Marketing, Sales = CORE – Unskilled labor: Factory assembly = periphery/semiperiphery http: //www. metatube. com/en/videos/10420/The-Simpsons-India. Outsourcing/ Homer’s job gets outsourced to India
Proximity to Cheap Labor • Outsourcing a decision by a corporation to turn over much of the responsibility for production to independent suppliers – Low level tasks look 4 cheap labor • Call centers and tax accountants to Bangalore • Textile manufacturers in East Asia, Latin America – Opposite of vertical integration employ someone else to perform a task b/c cheaper & more efficient • Outsourcing “New International Division of Labor” – Process raw materials near supply – Labor-intensive work where labor is cheap – Skilled labor: R&D, Capital, Marketing, Sales = CORE – Unskilled labor: Factory assembly = periphery/semiperiphery http: //www. metatube. com/en/videos/10420/The-Simpsons-India. Outsourcing/ Homer’s job gets outsourced to India
 Proximity to Skilled Labor • Old days: Fordism – One worker: one task – Specialization = unskilled labor – Repetitive motion leads to stress injuries • Now in high-tech industries: Post-Fordism – Work tasks spread out throughout the world • Outsourcing/New Internat’l division of labor – Work in teams performing many tasks – Workers solve problems for several tasks in a team (more flexible)
Proximity to Skilled Labor • Old days: Fordism – One worker: one task – Specialization = unskilled labor – Repetitive motion leads to stress injuries • Now in high-tech industries: Post-Fordism – Work tasks spread out throughout the world • Outsourcing/New Internat’l division of labor – Work in teams performing many tasks – Workers solve problems for several tasks in a team (more flexible)
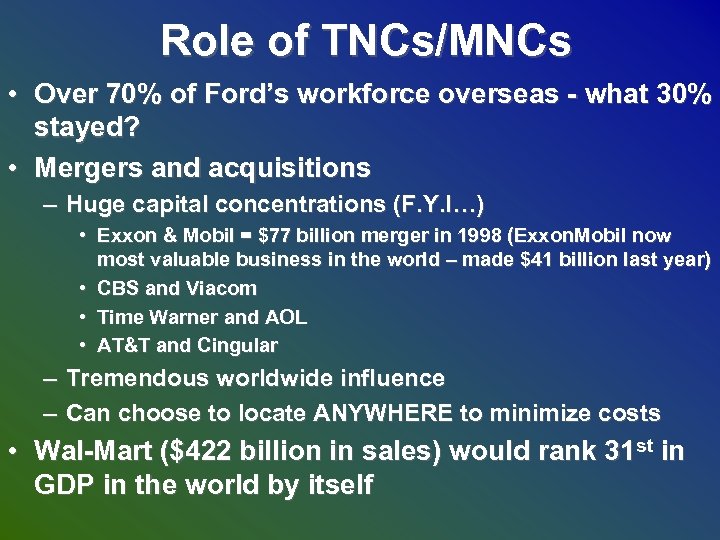 Role of TNCs/MNCs • Over 70% of Ford’s workforce overseas - what 30% stayed? • Mergers and acquisitions – Huge capital concentrations (F. Y. I…) • Exxon & Mobil = $77 billion merger in 1998 (Exxon. Mobil now most valuable business in the world – made $41 billion last year) • CBS and Viacom • Time Warner and AOL • AT&T and Cingular – Tremendous worldwide influence – Can choose to locate ANYWHERE to minimize costs • Wal-Mart ($422 billion in sales) would rank 31 st in GDP in the world by itself
Role of TNCs/MNCs • Over 70% of Ford’s workforce overseas - what 30% stayed? • Mergers and acquisitions – Huge capital concentrations (F. Y. I…) • Exxon & Mobil = $77 billion merger in 1998 (Exxon. Mobil now most valuable business in the world – made $41 billion last year) • CBS and Viacom • Time Warner and AOL • AT&T and Cingular – Tremendous worldwide influence – Can choose to locate ANYWHERE to minimize costs • Wal-Mart ($422 billion in sales) would rank 31 st in GDP in the world by itself
 MNCs/TNCs cont. • Conglomerate corporations more and more common – Companies in different industries merge together – Example – Kraft • • • Kool – Aid A 1 Steak Sauce Maxwell House Capri. Sun Lunchables
MNCs/TNCs cont. • Conglomerate corporations more and more common – Companies in different industries merge together – Example – Kraft • • • Kool – Aid A 1 Steak Sauce Maxwell House Capri. Sun Lunchables
 Changing Industrial Practices • Just-in-Time Delivery – Companies minimize storage costs – Need proximal suppliers 4 timely delivery – Industry moving back to core (closer to customers) – Combination of cheap labor while meeting J-I-T delivery could be next? ? ? • Problems: – Strikes? – Weather? – War/Terrorist Attacks?
Changing Industrial Practices • Just-in-Time Delivery – Companies minimize storage costs – Need proximal suppliers 4 timely delivery – Industry moving back to core (closer to customers) – Combination of cheap labor while meeting J-I-T delivery could be next? ? ? • Problems: – Strikes? – Weather? – War/Terrorist Attacks?
 Services • Provide a human need/desire and get $$$ for it • Tertiary • Quaternary • Quinary • Rubenstein (preferred method): – Consumer services – retail, education, health, and leisure – Business services – professional, financial, transportation/information – Public services – security and protection
Services • Provide a human need/desire and get $$$ for it • Tertiary • Quaternary • Quinary • Rubenstein (preferred method): – Consumer services – retail, education, health, and leisure – Business services – professional, financial, transportation/information – Public services – security and protection
 Gravity Model • Predicts that the optimal location of a service is directly related to the number of people in the area and inversely related to the distance people must travel to access it
Gravity Model • Predicts that the optimal location of a service is directly related to the number of people in the area and inversely related to the distance people must travel to access it
 Walter Christaller Die Zentralen Orte in Suddeutschland Central Places in Southern Germany Originally published in 1933, translated into English in 1966 Expanded on by others – Losch’s Zone of Profitability; Brian Berry, etc.
Walter Christaller Die Zentralen Orte in Suddeutschland Central Places in Southern Germany Originally published in 1933, translated into English in 1966 Expanded on by others – Losch’s Zone of Profitability; Brian Berry, etc.
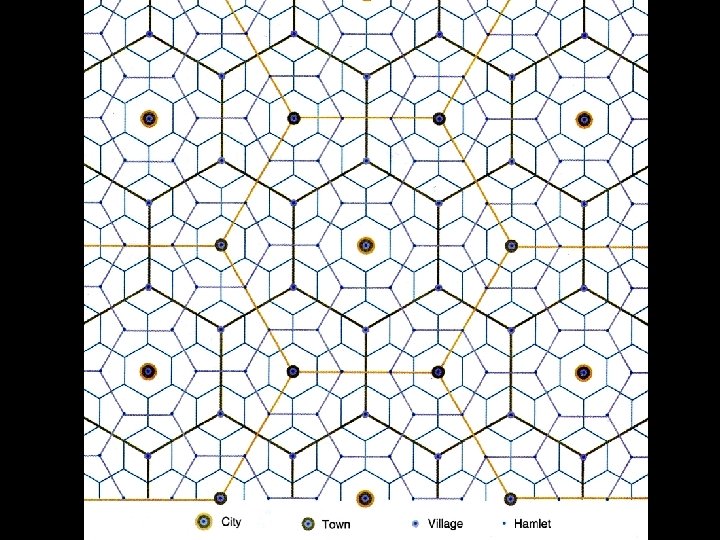
 Central Place Theory: Christaller • First Some Terminology – Central Place – market center where goods/services are exchanged w/ surrounding customers • Cities/towns usually serve this function • Area serviced = market area/hinterland (nodal region) – Range = distance people willing to travel 4 something • (Groceries v. medical care) • (TIME! Not distance) – Threshold = minimum # of people (customers) needed to sustain a business (viable) • Kroger needs 30, 000 – Breaking Point = line where customers will choose to go to another business for a service/good
Central Place Theory: Christaller • First Some Terminology – Central Place – market center where goods/services are exchanged w/ surrounding customers • Cities/towns usually serve this function • Area serviced = market area/hinterland (nodal region) – Range = distance people willing to travel 4 something • (Groceries v. medical care) • (TIME! Not distance) – Threshold = minimum # of people (customers) needed to sustain a business (viable) • Kroger needs 30, 000 – Breaking Point = line where customers will choose to go to another business for a service/good
 Central Place Theory cont. • Central Place Theory attempts to explain the pattern of settlements & Urban Hierarchy = – Hamlet – Village – Town – City – Mega city – World city
Central Place Theory cont. • Central Place Theory attempts to explain the pattern of settlements & Urban Hierarchy = – Hamlet – Village – Town – City – Mega city – World city
 What shape should hamlet’s, village’s, town’s, etc. economic reach or hinterland be? Why?
What shape should hamlet’s, village’s, town’s, etc. economic reach or hinterland be? Why?
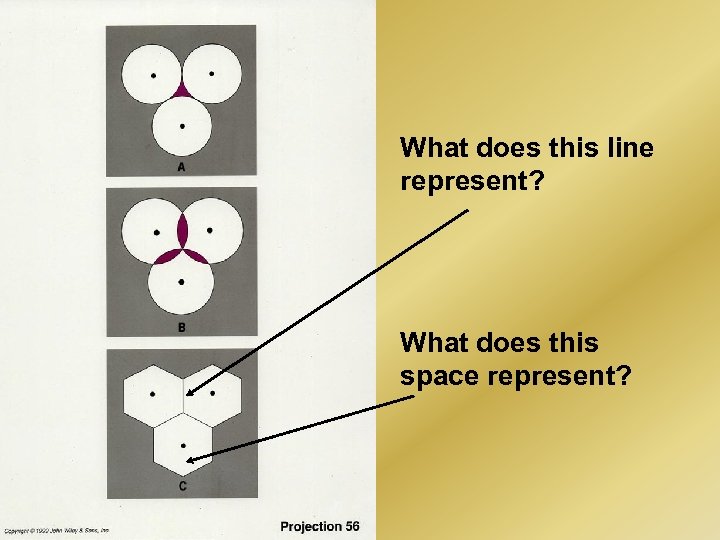 What does this line represent? What does this space represent?
What does this line represent? What does this space represent?
 Central Place Theory cont. • Central Places compete w/ each other 4 services & goods • Thus, larger the city, greater the distance between it & its rivals • BUT, how can you explain Dallas/Ft. Worth? BOSNYWASH? St. Paul/Minneapolis?
Central Place Theory cont. • Central Places compete w/ each other 4 services & goods • Thus, larger the city, greater the distance between it & its rivals • BUT, how can you explain Dallas/Ft. Worth? BOSNYWASH? St. Paul/Minneapolis?
 Would you travel farther to buy a new car or the week’s groceries? To buy a new car Would you travel farther to see your family physician or a heart specialist? To see a heart specialist Would you travel farther to go to elementary school or to go to high school? To go to high school
Would you travel farther to buy a new car or the week’s groceries? To buy a new car Would you travel farther to see your family physician or a heart specialist? To see a heart specialist Would you travel farther to go to elementary school or to go to high school? To go to high school
 A Hierarchy of Educational Services City: College Town: High School Village: Elementary School Hamlet: No Schools
A Hierarchy of Educational Services City: College Town: High School Village: Elementary School Hamlet: No Schools
 Why do we not ever see a perfect central place hierarchy? • Physical geography is important! Topography and hydrography interfere. • Consumer behavior is determined by more than economic considerations. • The automobile has made long-distance travel popular (cheap and easy). • People make multiple-purpose shopping trips, often bypassing the smallest places. • The Internet has made it unnecessary to have customers nearby. • Anything else that Christaller failed to address?
Why do we not ever see a perfect central place hierarchy? • Physical geography is important! Topography and hydrography interfere. • Consumer behavior is determined by more than economic considerations. • The automobile has made long-distance travel popular (cheap and easy). • People make multiple-purpose shopping trips, often bypassing the smallest places. • The Internet has made it unnecessary to have customers nearby. • Anything else that Christaller failed to address?
 Recent Developments w/ Industry/Services 1. Homogenization of global tastes – World cars: Toyota Carolla best selling car ever (Ford Fiesta, Honda Civic, etc. (Emissions, mpg, meets environ. standards for many countries) – Clothes, foods, insurance… – Bland moderate foods vs. extreme flavors – What concept does this represent? ? ? • Globalization – every urban place looks the same/provides the same goods/services
Recent Developments w/ Industry/Services 1. Homogenization of global tastes – World cars: Toyota Carolla best selling car ever (Ford Fiesta, Honda Civic, etc. (Emissions, mpg, meets environ. standards for many countries) – Clothes, foods, insurance… – Bland moderate foods vs. extreme flavors – What concept does this represent? ? ? • Globalization – every urban place looks the same/provides the same goods/services
 Recent Dev. w/ Services 2. Tourism’s Rise (11% of all jobs worldwide) – World’s largest industry/service – Outside of agriculture, the largest employer – Medical tourism http: //www. cnn. com/2010/HEALTH/04/26/cheaper. surgery/index. html? hpt=C 1 – Ecotourism – Indigenous people’s culture sustained or eroded? ? • Problems? ? – Capital Flight – Environmental Issues
Recent Dev. w/ Services 2. Tourism’s Rise (11% of all jobs worldwide) – World’s largest industry/service – Outside of agriculture, the largest employer – Medical tourism http: //www. cnn. com/2010/HEALTH/04/26/cheaper. surgery/index. html? hpt=C 1 – Ecotourism – Indigenous people’s culture sustained or eroded? ? • Problems? ? – Capital Flight – Environmental Issues
 Recent Dev. w/ Services 3. Advances in Telecommunication changes how business is done – NASDAQ no trading floor; all digital – “Back offices” outside the CBD headquarters in India, Ireland, Kenya – Telecommuting reduces transportation costs/traffic issues – Call centers – Claim-processing relocates to places w/: • Low labor costs • English speakers
Recent Dev. w/ Services 3. Advances in Telecommunication changes how business is done – NASDAQ no trading floor; all digital – “Back offices” outside the CBD headquarters in India, Ireland, Kenya – Telecommuting reduces transportation costs/traffic issues – Call centers – Claim-processing relocates to places w/: • Low labor costs • English speakers

 Recent Dev. w/ Ind. /Ser. 5. Suburbanization of Services – Services historically locate near CBD (Central Business District) • Provides more customers for higher threshold services • Attracts people from further distances (higher range services) – As land values increase in CBD… • People/Services move to suburbs/overseas • Land used more intensively (vertical geography) – Rise of skyscrapers – Underground activities • Manufacturing relocating to suburbs/rural areas
Recent Dev. w/ Ind. /Ser. 5. Suburbanization of Services – Services historically locate near CBD (Central Business District) • Provides more customers for higher threshold services • Attracts people from further distances (higher range services) – As land values increase in CBD… • People/Services move to suburbs/overseas • Land used more intensively (vertical geography) – Rise of skyscrapers – Underground activities • Manufacturing relocating to suburbs/rural areas
 Urbanization
Urbanization
 Urbanization’s History % people living in urban settings: 1800: 3% 1850: 6% 1900: 14% 1950: 25% 2000: 47% 2013: ? Urban (city limits) + suburbs tied to central business district = Metropolitan Statistical Area http: //en. wikipedia. org/wi ki/Atlanta_metropolitan _area#Major_Edge_citi es_. 28 from_Atlanta_ed ge_cities. 29
Urbanization’s History % people living in urban settings: 1800: 3% 1850: 6% 1900: 14% 1950: 25% 2000: 47% 2013: ? Urban (city limits) + suburbs tied to central business district = Metropolitan Statistical Area http: //en. wikipedia. org/wi ki/Atlanta_metropolitan _area#Major_Edge_citi es_. 28 from_Atlanta_ed ge_cities. 29
 Urban Banana • Crescent-shaped zone of early urbanization extending across Eurasia from England to Japan • If you include eastern USA it should be called “urban snake!”
Urban Banana • Crescent-shaped zone of early urbanization extending across Eurasia from England to Japan • If you include eastern USA it should be called “urban snake!”
 Late 20 th/ 21 st Century Urban Trends • Increase in service jobs + higher standard of living/affordable cars + Interstate Highway System = commuting development of suburbs • Suburbanization - 50 percent of Americans live in suburbs • Diversified economic base for each city • “Edge cities” develop (no need for CBD travel)
Late 20 th/ 21 st Century Urban Trends • Increase in service jobs + higher standard of living/affordable cars + Interstate Highway System = commuting development of suburbs • Suburbanization - 50 percent of Americans live in suburbs • Diversified economic base for each city • “Edge cities” develop (no need for CBD travel)
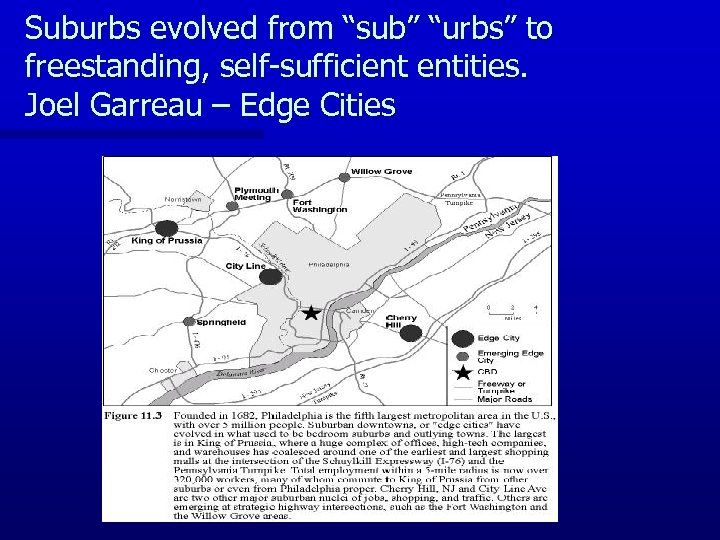 Suburbs evolved from “sub” “urbs” to freestanding, self-sufficient entities. Joel Garreau – Edge Cities
Suburbs evolved from “sub” “urbs” to freestanding, self-sufficient entities. Joel Garreau – Edge Cities
 Late 20 th/ 21 st Century Urban Trends • Problems with new trends? – Urban sprawl – Increasing mobility decreases sense of community & increases pollution – Traffic Congestion/Rush hour problems telecommuting – Degradation of wildlife habitat – Semi-periphery/periphery urbanizing too rapidly (development can’t keep up) “squatter settlements”
Late 20 th/ 21 st Century Urban Trends • Problems with new trends? – Urban sprawl – Increasing mobility decreases sense of community & increases pollution – Traffic Congestion/Rush hour problems telecommuting – Degradation of wildlife habitat – Semi-periphery/periphery urbanizing too rapidly (development can’t keep up) “squatter settlements”
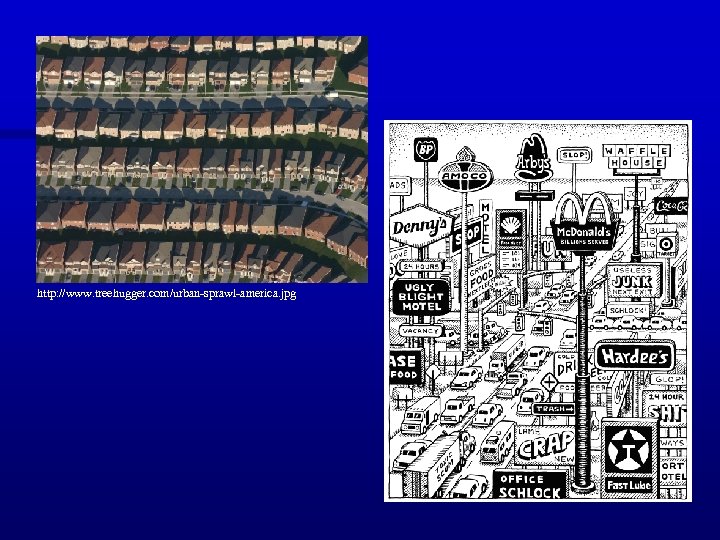 http: //www. treehugger. com/urban-sprawl-america. jpg
http: //www. treehugger. com/urban-sprawl-america. jpg
 onlinegeography. wikispaces. com/S+-+Urban+Sprawl
onlinegeography. wikispaces. com/S+-+Urban+Sprawl
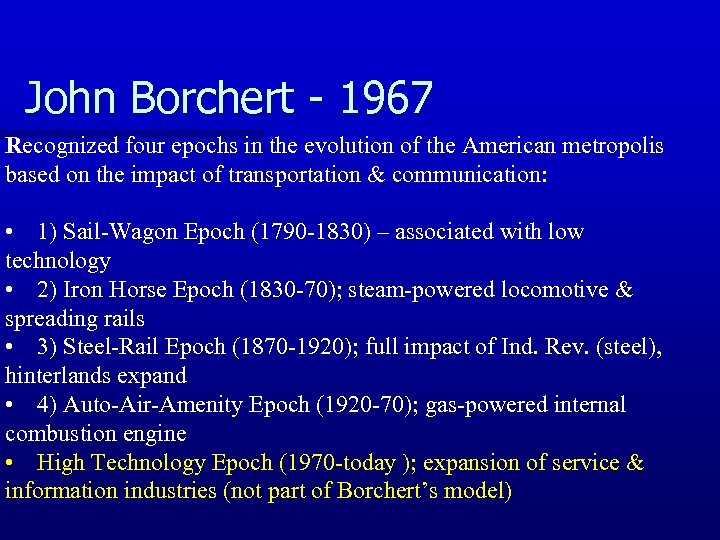 John Borchert - 1967 Recognized four epochs in the evolution of the American metropolis based on the impact of transportation & communication: • 1) Sail-Wagon Epoch (1790 -1830) – associated with low technology • 2) Iron Horse Epoch (1830 -70); steam-powered locomotive & spreading rails • 3) Steel-Rail Epoch (1870 -1920); full impact of Ind. Rev. (steel), hinterlands expand • 4) Auto-Air-Amenity Epoch (1920 -70); gas-powered internal combustion engine • High Technology Epoch (1970 -today ); expansion of service & information industries (not part of Borchert’s model)
John Borchert - 1967 Recognized four epochs in the evolution of the American metropolis based on the impact of transportation & communication: • 1) Sail-Wagon Epoch (1790 -1830) – associated with low technology • 2) Iron Horse Epoch (1830 -70); steam-powered locomotive & spreading rails • 3) Steel-Rail Epoch (1870 -1920); full impact of Ind. Rev. (steel), hinterlands expand • 4) Auto-Air-Amenity Epoch (1920 -70); gas-powered internal combustion engine • High Technology Epoch (1970 -today ); expansion of service & information industries (not part of Borchert’s model)
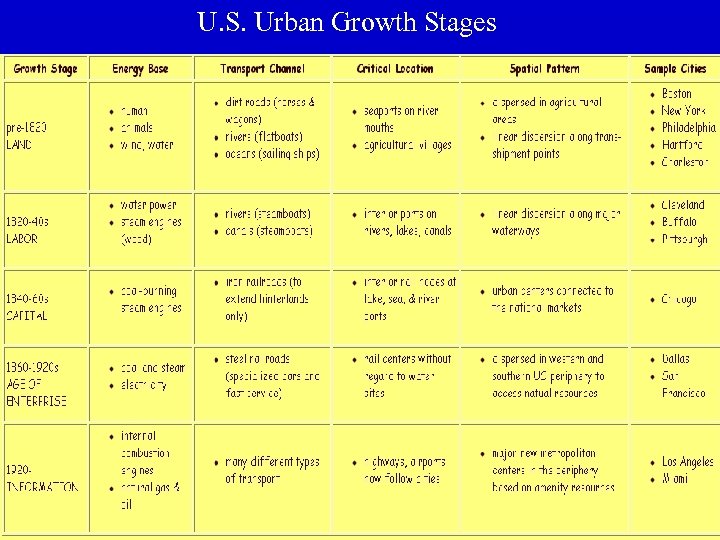 U. S. Urban Growth Stages
U. S. Urban Growth Stages
 Urban areas in LDC v. MDC • 8/10 largest cities in LDC & growing (NYC and Tokyo only ones in MDC) • Core are very urban (L. Amer. Exception)** • Fastest growing megacities are in South and East Asia • Africa lowest % urban BUT fastest urban growth • 300+ cities w/ 1 million+ people
Urban areas in LDC v. MDC • 8/10 largest cities in LDC & growing (NYC and Tokyo only ones in MDC) • Core are very urban (L. Amer. Exception)** • Fastest growing megacities are in South and East Asia • Africa lowest % urban BUT fastest urban growth • 300+ cities w/ 1 million+ people
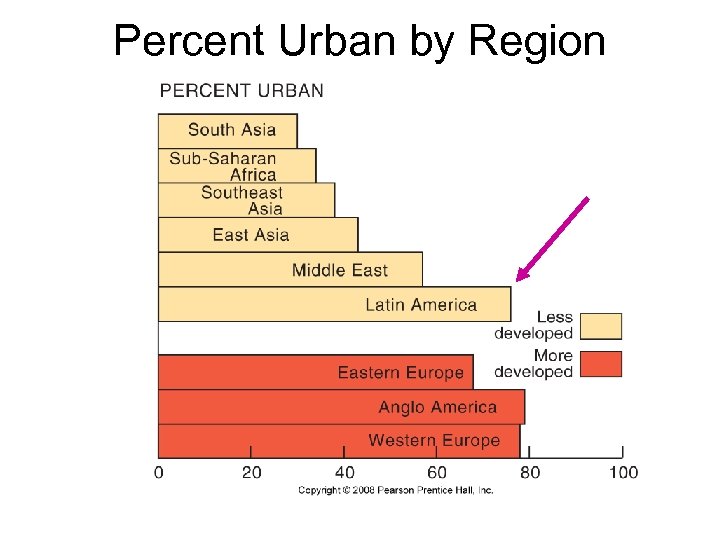 Percent Urban by Region Fig. 13 -2 b: Over 70% of people in MDCs live in urban areas. Although under half of the people in most of Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa are urban, Latin America and the Middle East have urban percentages comparable to MDCs.
Percent Urban by Region Fig. 13 -2 b: Over 70% of people in MDCs live in urban areas. Although under half of the people in most of Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa are urban, Latin America and the Middle East have urban percentages comparable to MDCs.
 Specialized cities • One/two industries/services dominate = “Functional Specialization” – ex: Dalton Ga. = carpet manufacturing – ex: Lost Wages… Las Vegas, NV. • Why do modern cities want a diversified economic base? • Fact: As cities grow Functional Specialization decreases.
Specialized cities • One/two industries/services dominate = “Functional Specialization” – ex: Dalton Ga. = carpet manufacturing – ex: Lost Wages… Las Vegas, NV. • Why do modern cities want a diversified economic base? • Fact: As cities grow Functional Specialization decreases.
 World Cities • Control centers for major decisionmaking/economic interests – Economics (NY, London, Tokyo) – Political: (D. C. , Brussels = EU, NYC = UN) – Fashion (Milan)
World Cities • Control centers for major decisionmaking/economic interests – Economics (NY, London, Tokyo) – Political: (D. C. , Brussels = EU, NYC = UN) – Fashion (Milan)
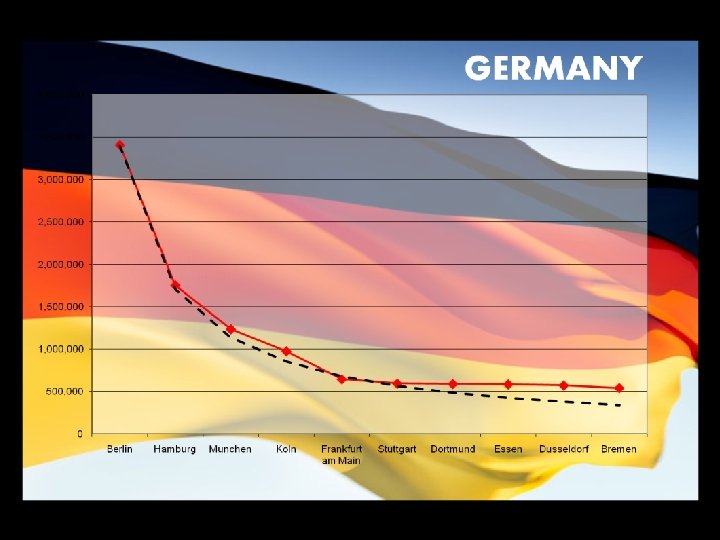
 Rank-Size Rule • (May not apply in LDC) Applies pretty well to U. S. and to Germany. (rank = “n” Population = (1/n)pop. of largest city 1/1 = biggest city without peer 4 th in size = ¼ of size of #1 • Ex: city X is 5 th largest and the largest has 100, 000 people… pop. of city X? ? ?
Rank-Size Rule • (May not apply in LDC) Applies pretty well to U. S. and to Germany. (rank = “n” Population = (1/n)pop. of largest city 1/1 = biggest city without peer 4 th in size = ¼ of size of #1 • Ex: city X is 5 th largest and the largest has 100, 000 people… pop. of city X? ? ?
 Primate City Rule • #1 city is MORE THAN 2 x pop. of #2 city – Core: UK and France – Periphery: Nigeria, Argentina, Mexico • Problems w/ countries w/ primate city – No uniform development – People have access to goods/services t/o country? ? • Solution Forward capital – moving the capital to achieve a certain goal – Abuja, Nigeria – Brasilia, Brazil Achieve more even development of the country
Primate City Rule • #1 city is MORE THAN 2 x pop. of #2 city – Core: UK and France – Periphery: Nigeria, Argentina, Mexico • Problems w/ countries w/ primate city – No uniform development – People have access to goods/services t/o country? ? • Solution Forward capital – moving the capital to achieve a certain goal – Abuja, Nigeria – Brasilia, Brazil Achieve more even development of the country
 4 More Dumb Models That Hurt Your Head: Models of Urban Structure
4 More Dumb Models That Hurt Your Head: Models of Urban Structure
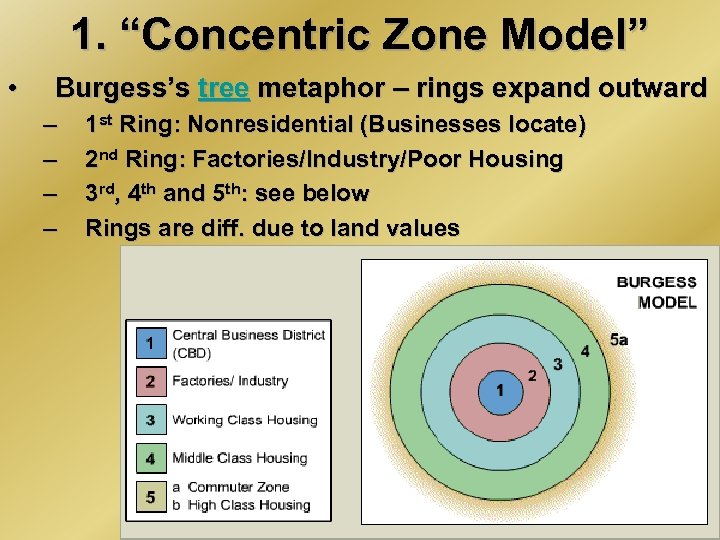 1. “Concentric Zone Model” • Burgess’s tree metaphor – rings expand outward – – 1 st Ring: Nonresidential (Businesses locate) 2 nd Ring: Factories/Industry/Poor Housing 3 rd, 4 th and 5 th: see below Rings are diff. due to land values
1. “Concentric Zone Model” • Burgess’s tree metaphor – rings expand outward – – 1 st Ring: Nonresidential (Businesses locate) 2 nd Ring: Factories/Industry/Poor Housing 3 rd, 4 th and 5 th: see below Rings are diff. due to land values
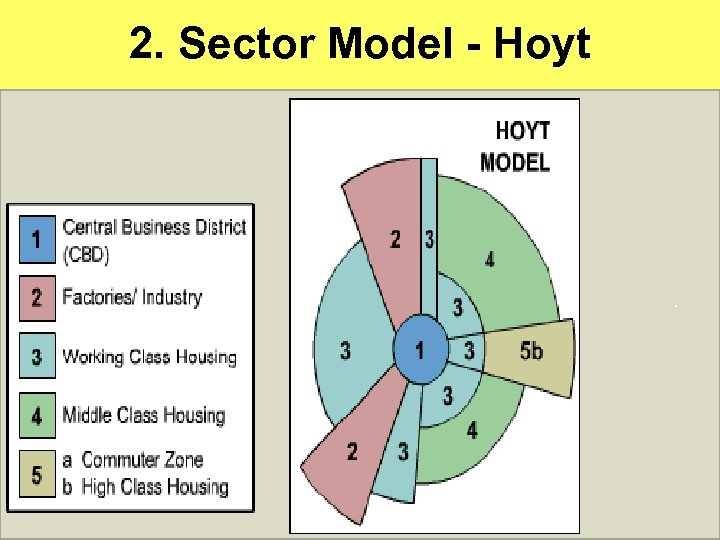 2. Sector Model - Hoyt
2. Sector Model - Hoyt
 “Sector Model” • Hoyt’s “expanding pizza” metaphor • CBD w/ spokes – Each has diff. levels of dev. /housing – Each centered around mode of infrastructure – Ex: Mexico City & Atlanta • Pizza slices expand w/ the infrastructure • “Other side of the tracks” • Very similar to Burgess
“Sector Model” • Hoyt’s “expanding pizza” metaphor • CBD w/ spokes – Each has diff. levels of dev. /housing – Each centered around mode of infrastructure – Ex: Mexico City & Atlanta • Pizza slices expand w/ the infrastructure • “Other side of the tracks” • Very similar to Burgess
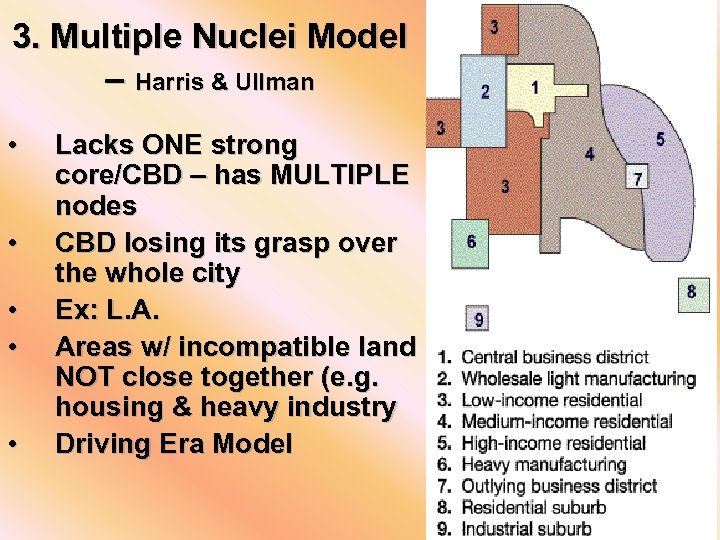 3. Multiple Nuclei Model – Harris & Ullman • • • Lacks ONE strong core/CBD – has MULTIPLE nodes CBD losing its grasp over the whole city Ex: L. A. Areas w/ incompatible land NOT close together (e. g. housing & heavy industry Driving Era Model
3. Multiple Nuclei Model – Harris & Ullman • • • Lacks ONE strong core/CBD – has MULTIPLE nodes CBD losing its grasp over the whole city Ex: L. A. Areas w/ incompatible land NOT close together (e. g. housing & heavy industry Driving Era Model
 4. Urban Realms – Hartshorn and Muller • • • Problems w/ other models: People increasingly NOT working in CBD Multiple metropolitan areas interact – each area functions separately in some ways Outer cities became more self-sufficient (what do we call these cities? ) – Duplicate certain functions of central city – Regional shopping centers become CBD’s of the outer nuclei – Business/Industrial parks locating outside the central city
4. Urban Realms – Hartshorn and Muller • • • Problems w/ other models: People increasingly NOT working in CBD Multiple metropolitan areas interact – each area functions separately in some ways Outer cities became more self-sufficient (what do we call these cities? ) – Duplicate certain functions of central city – Regional shopping centers become CBD’s of the outer nuclei – Business/Industrial parks locating outside the central city



