 Definition
Definition
 What is respiratory distress?
What is respiratory distress?
 Respiratory Definitions
Respiratory Definitions
 Goals of this presentation
Goals of this presentation
 My Philosophy of teaching:
My Philosophy of teaching:
 What is NOT Dyspnea?
What is NOT Dyspnea?
 Case 1
Case 1
 Case 1 – additional history
Case 1 – additional history
 Case 1
Case 1
 Approach to the patient with shortness of breath, or respiratory distress: the emergency approach.
Approach to the patient with shortness of breath, or respiratory distress: the emergency approach.
 1: Degree of urgency
1: Degree of urgency
 2. Assess patient.
2. Assess patient.
 3. Locate the problem
3. Locate the problem
 4. Correct it
4. Correct it
 Suspicion
Suspicion
 Ask (yourself) questions.
Ask (yourself) questions.
 What is the purpose of respiration:
What is the purpose of respiration:
 Abnormal atmosphere
Abnormal atmosphere
 Other substances
Other substances
 Mechanical Airway Obstruction
Mechanical Airway Obstruction
 Muscular / Chest Wall system
Muscular / Chest Wall system
 Air to blood interface:
Air to blood interface:
 Causes of dyspnea
Causes of dyspnea
 Tools to evaluate dyspnea
Tools to evaluate dyspnea
 What other tools?
What other tools?
 Additional items of history
Additional items of history
 Cough
Cough
 Aphorism
Aphorism
 Vital Signs
Vital Signs
 Vital Signs
Vital Signs
 Vital Signs:
Vital Signs:
 Pulse Ox
Pulse Ox
 VS - Combinations:
VS - Combinations:
 Focused exam
Focused exam
 Physical Exam
Physical Exam
 Scratch Test
Scratch Test
 Afferent neurons
Afferent neurons
 Efferent signals
Efferent signals
 Central Processing
Central Processing
 MRC Breathlessness Scale
MRC Breathlessness Scale
 Causes of dyspnea
Causes of dyspnea
 Chest radiography (CXR)
Chest radiography (CXR)
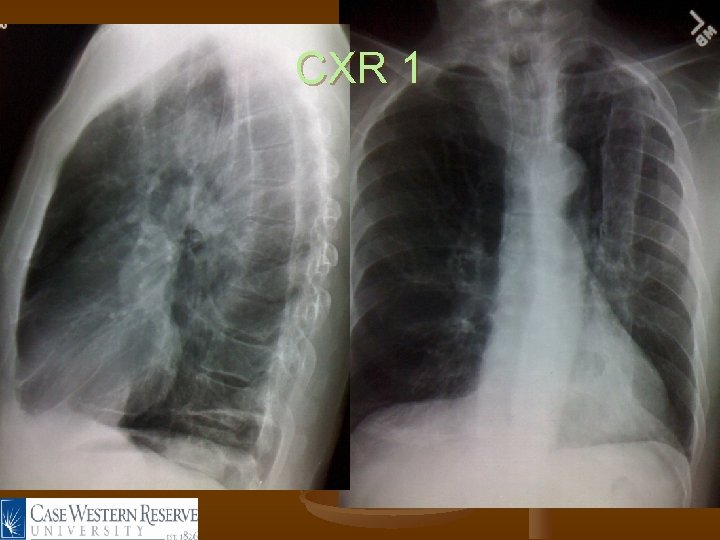 CXR 1
CXR 1
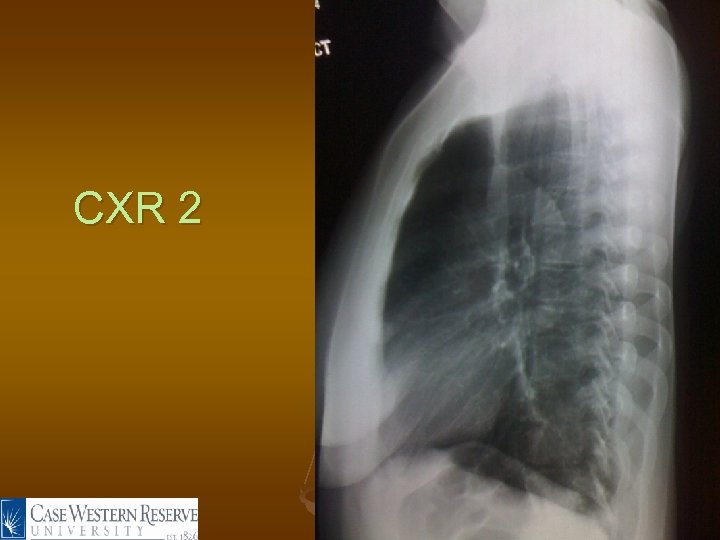 CXR 2
CXR 2
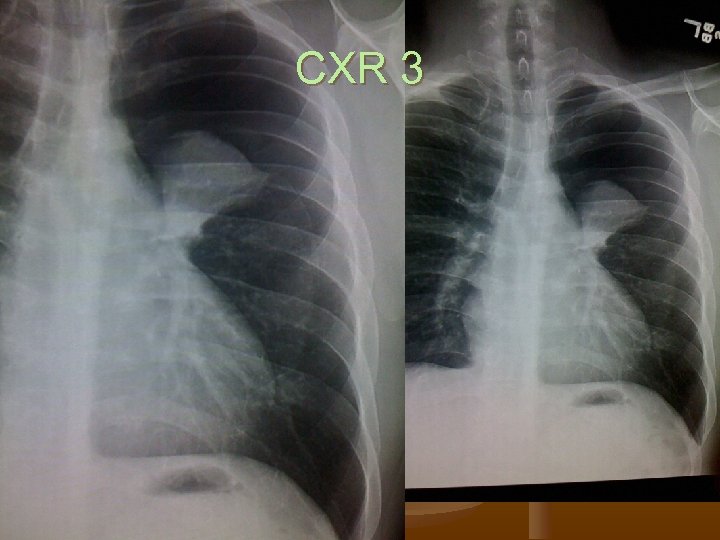 CXR 3
CXR 3
 ECG
ECG
 EKGs (TB Inserted)
EKGs (TB Inserted)
 Arterial Blood Gases (ABG)
Arterial Blood Gases (ABG)
 ABG and Acid base balance.
ABG and Acid base balance.
 p. H
p. H
 Pa. CO 2
Pa. CO 2
 Pa. O 2
Pa. O 2
 Ventilation / Perfusion Scanning (V/Q Scan)
Ventilation / Perfusion Scanning (V/Q Scan)
 CT Scan of the Chest
CT Scan of the Chest
 Ultrasonography & Echocardiography
Ultrasonography & Echocardiography
 Specific entities:
Specific entities:
 Asthma:
Asthma:
 Pulmonary edema:
Pulmonary edema:
 Pulmonary edema:
Pulmonary edema:
 Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema
 Diabetic Keto. Acidosis DKA
Diabetic Keto. Acidosis DKA
 Pneumo / hemo thorax.
Pneumo / hemo thorax.
 Pneumonia
Pneumonia
 Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary Embolism
 Emphysema
Emphysema
 CO poisoning:
CO poisoning:
 Cyanide poisoning:
Cyanide poisoning:
 Summary:
Summary:
 REFERENCES
REFERENCES