0f65bc87b840be867cb31caf13d5e4a0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 Definition: Total Quality Management n n Total Quality Management (TQ, QM or TQM) and Six Sigma (6 ) are sweeping “culture change” efforts to position a company for greater customer satisfaction, profitability and competitiveness. TQM may be defined as managing the entire organization so that it excels on all dimensions of products and services that are important to the customer. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 1
Definition: Total Quality Management n n Total Quality Management (TQ, QM or TQM) and Six Sigma (6 ) are sweeping “culture change” efforts to position a company for greater customer satisfaction, profitability and competitiveness. TQM may be defined as managing the entire organization so that it excels on all dimensions of products and services that are important to the customer. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 1
 Quality Descriptions Design Quality (Features) vs. Conformance Quality Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 2
Quality Descriptions Design Quality (Features) vs. Conformance Quality Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 2
 Conformance Quality • Meeting Our Customer’s Requirements • Doing (the Right) Things Right the First Time; Freedom from Failure (Defects) • Consistency (Reduction in Variation) • Continuous Improvement • Quality in Everything We Do Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 3
Conformance Quality • Meeting Our Customer’s Requirements • Doing (the Right) Things Right the First Time; Freedom from Failure (Defects) • Consistency (Reduction in Variation) • Continuous Improvement • Quality in Everything We Do Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 3
 Quality Management History ØFrederick Winslow Taylor wrote Principles of Scientific Management in 1911 ØWalter A. Shewhart used statistics in quality control and inspection, and showed that productivity improves when variation is reduced (1924); wrote Economic Control of Manufactured Product in 1931 ØW. Edwards Deming and Joseph M. Juran, students of Shewhart, went to Japan in 1950; began transformation from “shoddy” to “world class” goods ØIn 1960, Dr. K. Ishikawa formalized “quality circles” - the use of small groups to eliminate variation and improve processes Ø In the late ‘ 70’s and early 80’s: - Deming returned from Japan to write Out of the Crisis, and began his famous 4 -day seminars in the United States - Phil Crosby wrote Quality is Free - NBC ran “If Japan can do it, why can’t we? ” - Motorola began 6 Sigma Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 4
Quality Management History ØFrederick Winslow Taylor wrote Principles of Scientific Management in 1911 ØWalter A. Shewhart used statistics in quality control and inspection, and showed that productivity improves when variation is reduced (1924); wrote Economic Control of Manufactured Product in 1931 ØW. Edwards Deming and Joseph M. Juran, students of Shewhart, went to Japan in 1950; began transformation from “shoddy” to “world class” goods ØIn 1960, Dr. K. Ishikawa formalized “quality circles” - the use of small groups to eliminate variation and improve processes Ø In the late ‘ 70’s and early 80’s: - Deming returned from Japan to write Out of the Crisis, and began his famous 4 -day seminars in the United States - Phil Crosby wrote Quality is Free - NBC ran “If Japan can do it, why can’t we? ” - Motorola began 6 Sigma Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 4
 Quality Management History “On the assembly line at the Ford Motor Company in 1923, most of the workers producing Model T’s were immigrants and could not speak English. Many were also illiterate. Workers learned their trade by modeling the actions of other workers. They were unable to plan, problem-solve, and make decisions. As a result, the Taylor scientific school of management flourished, and MBAs and industrial engineers were invented to do this work. Today, however, the workforce is educated. Workers know what is needed to improve their jobs, and companies that do not tap into this significant source of knowledge will truly be at a competitive disadvantage. ” Joseph M. Juran (1991) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 5
Quality Management History “On the assembly line at the Ford Motor Company in 1923, most of the workers producing Model T’s were immigrants and could not speak English. Many were also illiterate. Workers learned their trade by modeling the actions of other workers. They were unable to plan, problem-solve, and make decisions. As a result, the Taylor scientific school of management flourished, and MBAs and industrial engineers were invented to do this work. Today, however, the workforce is educated. Workers know what is needed to improve their jobs, and companies that do not tap into this significant source of knowledge will truly be at a competitive disadvantage. ” Joseph M. Juran (1991) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 5
 Quality Management History “Knowledge-worker productivity is the biggest of the 21 st-century management challenges. In the developed countries, it is their first survival requirement. In no other way can the developed countries hope to maintain themselves, let alone to maintain their leadership and their standards of living. ” Peter F. Drucker (1999) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 6
Quality Management History “Knowledge-worker productivity is the biggest of the 21 st-century management challenges. In the developed countries, it is their first survival requirement. In no other way can the developed countries hope to maintain themselves, let alone to maintain their leadership and their standards of living. ” Peter F. Drucker (1999) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 6
 Quality Management History Deming’s 14 Points 1. Create constancy of purpose for improvement 2. Adopt a new philosophy 3. Cease dependence on mass inspection 4. Do not award business on price alone 5. Work continually on the system of production and service 6. Institute Modern methods of training 7. Institute modern methods of supervision of workers 8. Drive out fear 9. Break down barriers between departments 10. Eliminate slogans, exhortations, and targets for the work force 11. Eliminate numerical quotas 12. Remove barriers preventing pride of workmanship 13. Institute a vigorous program of education and retraining 14. Take action to accomplish the transformation Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 7
Quality Management History Deming’s 14 Points 1. Create constancy of purpose for improvement 2. Adopt a new philosophy 3. Cease dependence on mass inspection 4. Do not award business on price alone 5. Work continually on the system of production and service 6. Institute Modern methods of training 7. Institute modern methods of supervision of workers 8. Drive out fear 9. Break down barriers between departments 10. Eliminate slogans, exhortations, and targets for the work force 11. Eliminate numerical quotas 12. Remove barriers preventing pride of workmanship 13. Institute a vigorous program of education and retraining 14. Take action to accomplish the transformation Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 7
 A Quality Management System Is… n n n A belief in the employee’s ability to solve problems A belief that people doing the work are best able to improve it A belief that everyone is responsible for quality
A Quality Management System Is… n n n A belief in the employee’s ability to solve problems A belief that people doing the work are best able to improve it A belief that everyone is responsible for quality
 Quality Management History Deming’s Concept of “Profound Knowledge” Ø Understanding (and appreciation) of Systems - optimizing sub-systems sub-optimizes the total system - the majority of defects come from systems, the responsibility of management (e. g. , machines not in good order, defective material) Ø Knowledge of Statistics (variation, capability, uncertainty in data, etc. ) - to identify where problems are, and point managers and workers toward solutions Ø Knowledge of Psychology (Motivation) - people are afraid of failing and not being recognized, so they fear how data will be used against them Ø Theory of Knowledge - understanding that management in any form is a prediction, and is based on assumptions Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 9
Quality Management History Deming’s Concept of “Profound Knowledge” Ø Understanding (and appreciation) of Systems - optimizing sub-systems sub-optimizes the total system - the majority of defects come from systems, the responsibility of management (e. g. , machines not in good order, defective material) Ø Knowledge of Statistics (variation, capability, uncertainty in data, etc. ) - to identify where problems are, and point managers and workers toward solutions Ø Knowledge of Psychology (Motivation) - people are afraid of failing and not being recognized, so they fear how data will be used against them Ø Theory of Knowledge - understanding that management in any form is a prediction, and is based on assumptions Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 9
 Elements for Success n n n n n Management Support/Involvement Mission Statement Proper Planning Customer and Bottom Line Focus Measurement Empowerment/Shared Leadership Teamwork/Effective Meetings Continuous Process Improvement Dedicated Resources/Training
Elements for Success n n n n n Management Support/Involvement Mission Statement Proper Planning Customer and Bottom Line Focus Measurement Empowerment/Shared Leadership Teamwork/Effective Meetings Continuous Process Improvement Dedicated Resources/Training
 Benchmarking 1. Identify those processes needing improvement. 2. Identify a firm that is the world leader in performing the process (Library & WWW). 3. Contact the managers of that company and make a personal visit to interview managers and workers. 4. Analyze data Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 11
Benchmarking 1. Identify those processes needing improvement. 2. Identify a firm that is the world leader in performing the process (Library & WWW). 3. Contact the managers of that company and make a personal visit to interview managers and workers. 4. Analyze data Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 11
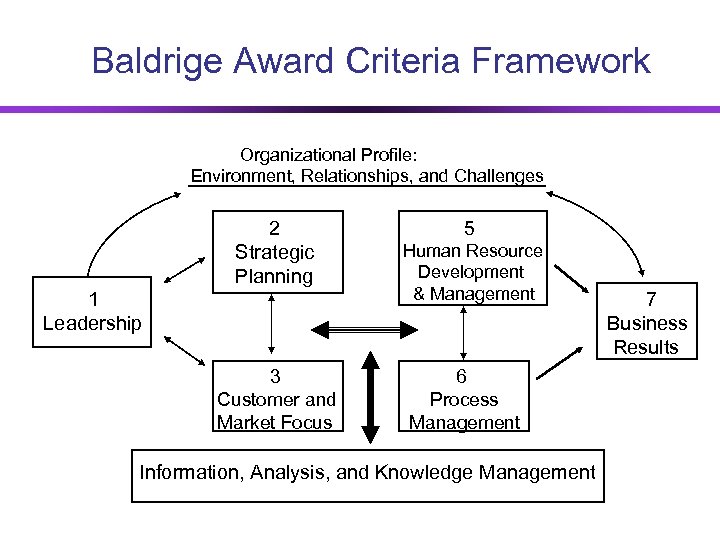 Baldrige Award Criteria Framework Organizational Profile: Environment, Relationships, and Challenges 2 Strategic Planning 1 Leadership 3 Customer and Market Focus 5 Human Resource Development & Management 6 Process Management Information, Analysis, and Knowledge Management 7 Business Results
Baldrige Award Criteria Framework Organizational Profile: Environment, Relationships, and Challenges 2 Strategic Planning 1 Leadership 3 Customer and Market Focus 5 Human Resource Development & Management 6 Process Management Information, Analysis, and Knowledge Management 7 Business Results
 Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award (2004) 1. 0 Leadership (120 points) 2. 0 Strategic Planning (85 points) 3. 0 Customer and Market Focus (85 points) 4. 0 Information and Analysis (90 points) 5. 0 Human Resource Focus (85 Points) 6. 0 Process Management (85 points) 7. 0 Business Results (450 points) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 13
Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award (2004) 1. 0 Leadership (120 points) 2. 0 Strategic Planning (85 points) 3. 0 Customer and Market Focus (85 points) 4. 0 Information and Analysis (90 points) 5. 0 Human Resource Focus (85 Points) 6. 0 Process Management (85 points) 7. 0 Business Results (450 points) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 13
 Categories for the Baldrige Award n Manufacturing companies or subsidiaries that: produce and sell manufactured products or manufacturing processes or n produce agricultural, mining, or construction products. n n n Service companies or subsidiaries that sell service Small businesses Education Institutions Health Care Organizations Non-Profit (new) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 14
Categories for the Baldrige Award n Manufacturing companies or subsidiaries that: produce and sell manufactured products or manufacturing processes or n produce agricultural, mining, or construction products. n n n Service companies or subsidiaries that sell service Small businesses Education Institutions Health Care Organizations Non-Profit (new) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 14
 Characteristics of a Baldrige Award Winner n n n The companies formulated a vision of quality and how they would achieve it. Senior management was actively involved. Companies carefully planned and organized their quality effort to insure effective initiation. n They vigorously controlled the overall process. n Studies have shown MBA Winners’ success. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 15
Characteristics of a Baldrige Award Winner n n n The companies formulated a vision of quality and how they would achieve it. Senior management was actively involved. Companies carefully planned and organized their quality effort to insure effective initiation. n They vigorously controlled the overall process. n Studies have shown MBA Winners’ success. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 15
 ISO 9000 n Series of standards agreed upon by the International Organization for Standardization(ISO) n Adopted in 1987 n More than 100 countries n A prerequisite for global competition? n ISO 9000 directs you to: n document what you do and then do as you documented. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 16
ISO 9000 n Series of standards agreed upon by the International Organization for Standardization(ISO) n Adopted in 1987 n More than 100 countries n A prerequisite for global competition? n ISO 9000 directs you to: n document what you do and then do as you documented. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 16
 ISO 9000 Series n 9001 n n 9002 n n Model for Quality Assurance in Design, Production Installation, and Servicing. Model for Quality Assurance in Production and Installation 9003 n Model for Quality Assurance in Final Inspection Test Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 17
ISO 9000 Series n 9001 n n 9002 n n Model for Quality Assurance in Design, Production Installation, and Servicing. Model for Quality Assurance in Production and Installation 9003 n Model for Quality Assurance in Final Inspection Test Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 17
 Three Forms of Certification 1. First party: A firm audits itself against ISO 9000 standards. 2. Second party: A customer audits supplier. 3. Third party: A "qualified" national or international standards or certifying agency serves as auditor. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 18
Three Forms of Certification 1. First party: A firm audits itself against ISO 9000 standards. 2. Second party: A customer audits supplier. 3. Third party: A "qualified" national or international standards or certifying agency serves as auditor. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 18
 ISO 9000 versus the Baldrige Award n n n Which should we pursue first? What are the differences between the two? Do you have to be ISO 9000 certified before going for the Baldrige Award? Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 19
ISO 9000 versus the Baldrige Award n n n Which should we pursue first? What are the differences between the two? Do you have to be ISO 9000 certified before going for the Baldrige Award? Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 19
 ISO 9000 versus the Baldrige Award Baldrige QS 9000 ISO 9000 Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Evans and Lindsay The Management and Control of Quality, Southwestern Books, p 536. 20
ISO 9000 versus the Baldrige Award Baldrige QS 9000 ISO 9000 Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Evans and Lindsay The Management and Control of Quality, Southwestern Books, p 536. 20
 Costs of Quality: Categories n Appraisal costs n Prevention costs n Internal failure costs n External failure costs Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 21
Costs of Quality: Categories n Appraisal costs n Prevention costs n Internal failure costs n External failure costs Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 21
 The 1 -10 -100 Rule 1 10 100 · Defects caught at their source cost the organization $1. · Defects caught outside of the source department but within the organization cost $10. · Defects that reach the external customer cost $100! Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 22
The 1 -10 -100 Rule 1 10 100 · Defects caught at their source cost the organization $1. · Defects caught outside of the source department but within the organization cost $10. · Defects that reach the external customer cost $100! Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 22
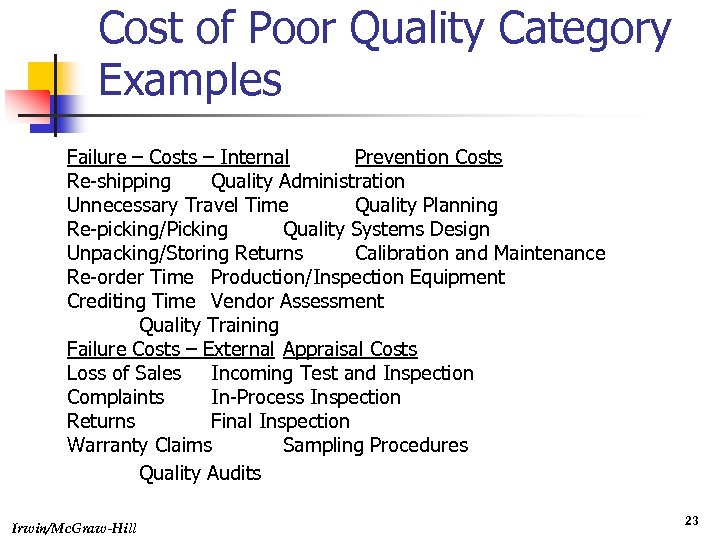 Cost of Poor Quality Category Examples Failure – Costs – Internal Prevention Costs Re-shipping Quality Administration Unnecessary Travel Time Quality Planning Re-picking/Picking Quality Systems Design Unpacking/Storing Returns Calibration and Maintenance Re-order Time Production/Inspection Equipment Crediting Time Vendor Assessment Quality Training Failure Costs – External Appraisal Costs Loss of Sales Incoming Test and Inspection Complaints In-Process Inspection Returns Final Inspection Warranty Claims Sampling Procedures Quality Audits Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 23
Cost of Poor Quality Category Examples Failure – Costs – Internal Prevention Costs Re-shipping Quality Administration Unnecessary Travel Time Quality Planning Re-picking/Picking Quality Systems Design Unpacking/Storing Returns Calibration and Maintenance Re-order Time Production/Inspection Equipment Crediting Time Vendor Assessment Quality Training Failure Costs – External Appraisal Costs Loss of Sales Incoming Test and Inspection Complaints In-Process Inspection Returns Final Inspection Warranty Claims Sampling Procedures Quality Audits Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 23
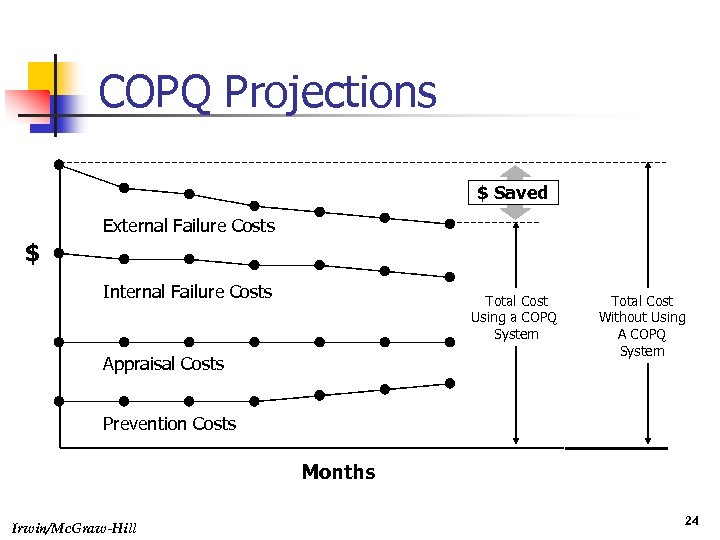 COPQ Projections $ Saved External Failure Costs $ Internal Failure Costs Total Cost Using a COPQ System Appraisal Costs Total Cost Without Using A COPQ System Prevention Costs Months Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 24
COPQ Projections $ Saved External Failure Costs $ Internal Failure Costs Total Cost Using a COPQ System Appraisal Costs Total Cost Without Using A COPQ System Prevention Costs Months Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 24
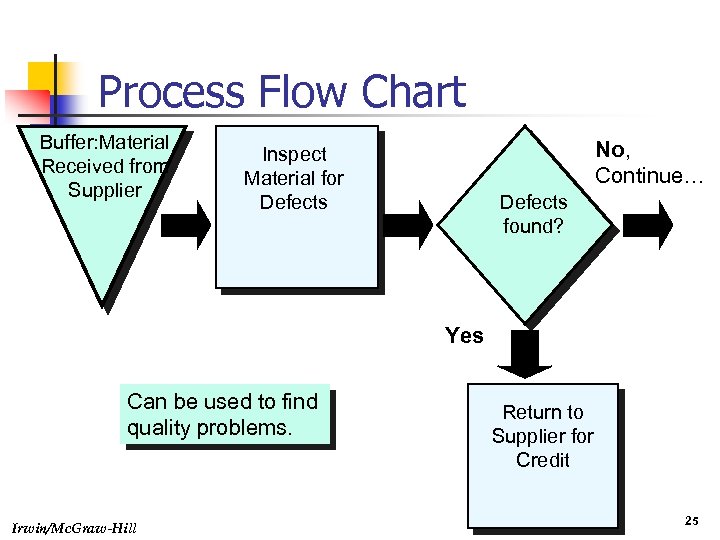 Process Flow Chart Buffer: Material Received from Supplier No, Continue… Inspect Material for Defects found? Yes Can be used to find quality problems. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Return to Supplier for Credit 25
Process Flow Chart Buffer: Material Received from Supplier No, Continue… Inspect Material for Defects found? Yes Can be used to find quality problems. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Return to Supplier for Credit 25
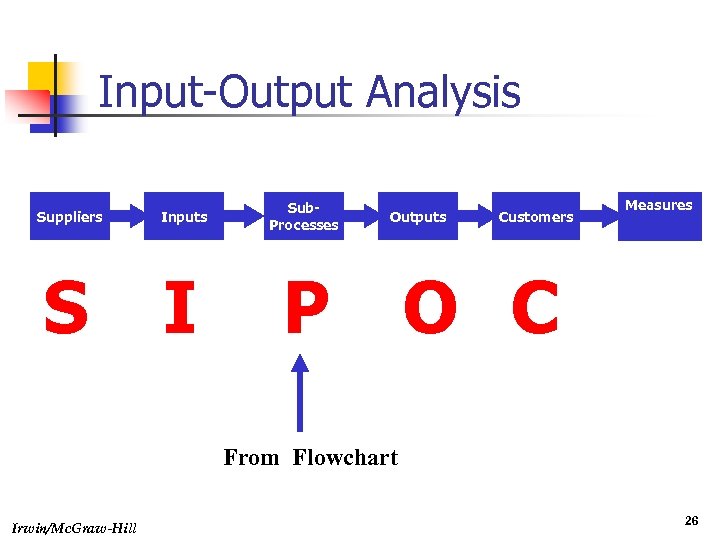 Input-Output Analysis Suppliers Inputs Sub. Processes S I P Outputs Customers Measures O C From Flowchart Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 26
Input-Output Analysis Suppliers Inputs Sub. Processes S I P Outputs Customers Measures O C From Flowchart Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 26
 Example SIPOC - Specifying Equipment Selection and Installation Procedures at Coca-Cola USA Suppliers Inputs Process Outputs Customers Technical Information Developing Installation Cost Reduction Programs Equipment Burger King Selection Guide Mc. Donald’s Equipment Sales Prestige Manuals Developing Equipment Selection Policies and Procedures Technology Cost/ Benefit Matrix Designing Installation Policies and Procedures Installation Time Standards Coca-Cola Fountain Technical Questions Customer Input Installation Guidelines Coca-Cola Fountain Equipment Suppliers Measures Number of Entities Using Guidelines Installation Audit Ratings Survey of Users Effectively Using Selection Guidelines Installation Rating System Installation Design Guidelines Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Customers 27
Example SIPOC - Specifying Equipment Selection and Installation Procedures at Coca-Cola USA Suppliers Inputs Process Outputs Customers Technical Information Developing Installation Cost Reduction Programs Equipment Burger King Selection Guide Mc. Donald’s Equipment Sales Prestige Manuals Developing Equipment Selection Policies and Procedures Technology Cost/ Benefit Matrix Designing Installation Policies and Procedures Installation Time Standards Coca-Cola Fountain Technical Questions Customer Input Installation Guidelines Coca-Cola Fountain Equipment Suppliers Measures Number of Entities Using Guidelines Installation Audit Ratings Survey of Users Effectively Using Selection Guidelines Installation Rating System Installation Design Guidelines Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Customers 27
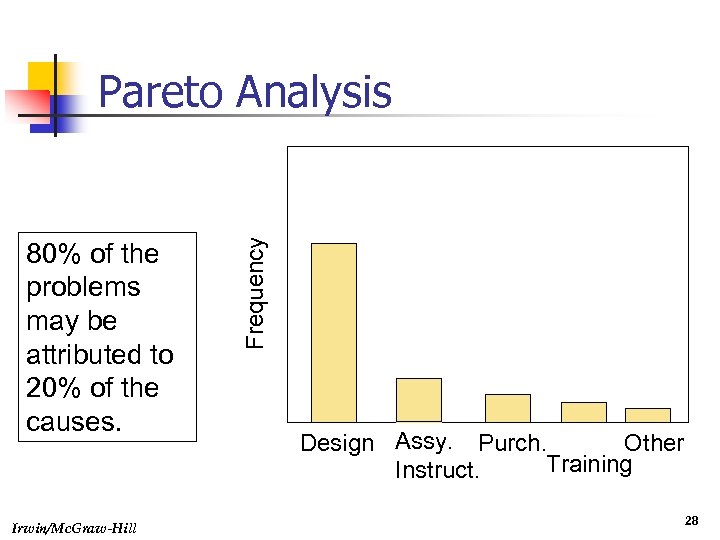 80% of the problems may be attributed to 20% of the causes. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Frequency Pareto Analysis Design Assy. Purch. Other Training Instruct. 28
80% of the problems may be attributed to 20% of the causes. Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Frequency Pareto Analysis Design Assy. Purch. Other Training Instruct. 28
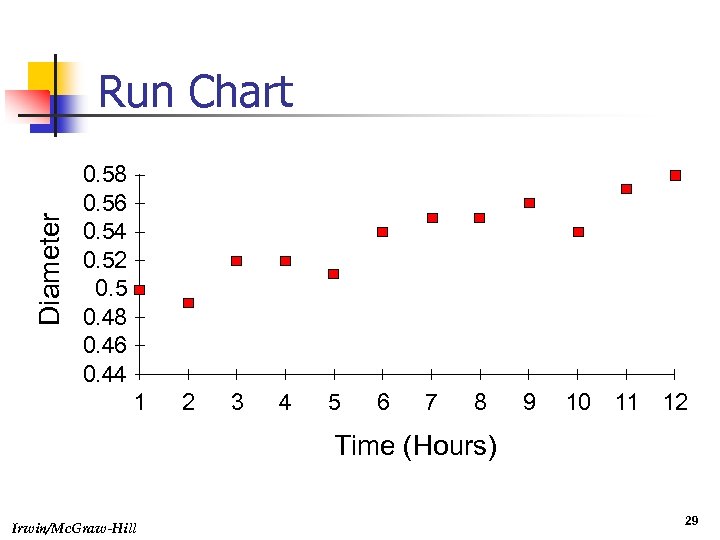 Diameter Run Chart 0. 58 0. 56 0. 54 0. 52 0. 5 0. 48 0. 46 0. 44 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Time (Hours) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 29
Diameter Run Chart 0. 58 0. 56 0. 54 0. 52 0. 5 0. 48 0. 46 0. 44 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Time (Hours) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 29
 Frequency Histogram Data Ranges Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 30
Frequency Histogram Data Ranges Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 30
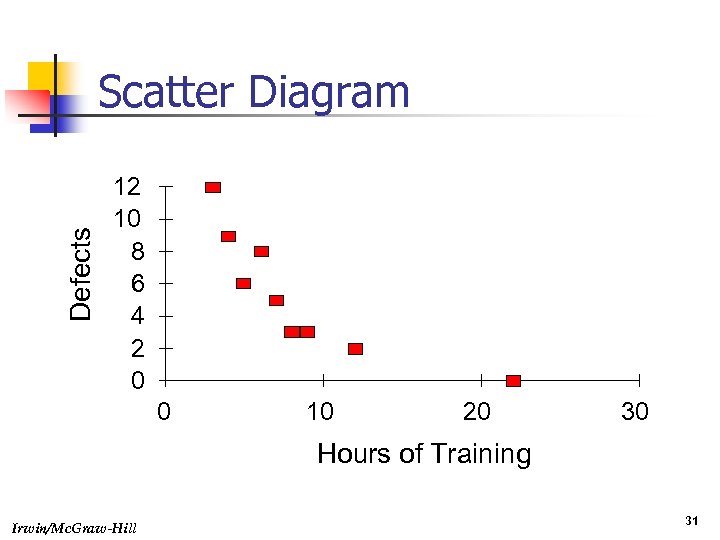 Defects Scatter Diagram 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 10 20 30 Hours of Training Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 31
Defects Scatter Diagram 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 10 20 30 Hours of Training Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 31
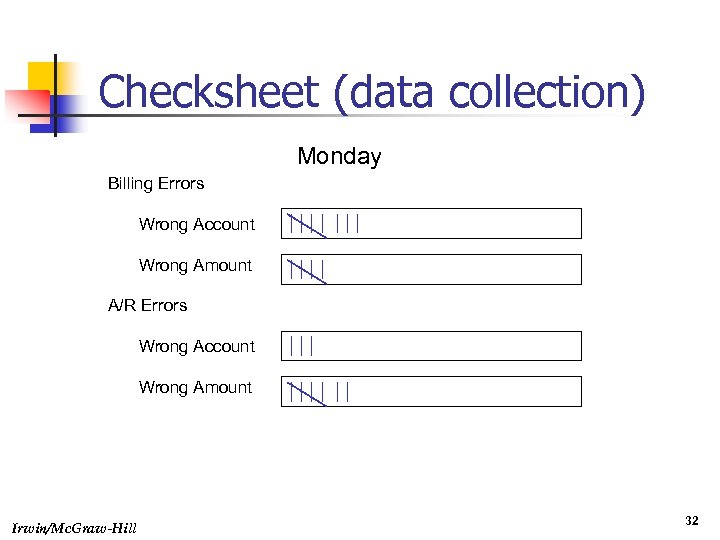 Checksheet (data collection) Monday Billing Errors Wrong Account Wrong Amount A/R Errors Wrong Account Wrong Amount Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 32
Checksheet (data collection) Monday Billing Errors Wrong Account Wrong Amount A/R Errors Wrong Account Wrong Amount Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 32
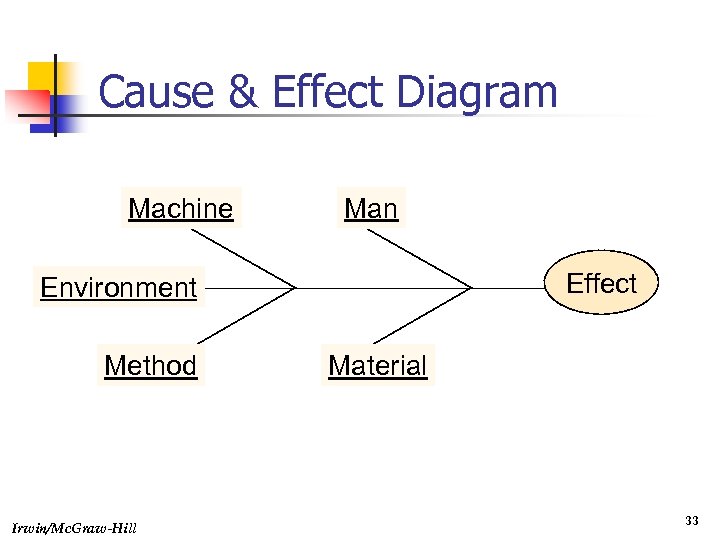 Cause & Effect Diagram Machine Man Effect Environment Method Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Material 33
Cause & Effect Diagram Machine Man Effect Environment Method Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Material 33
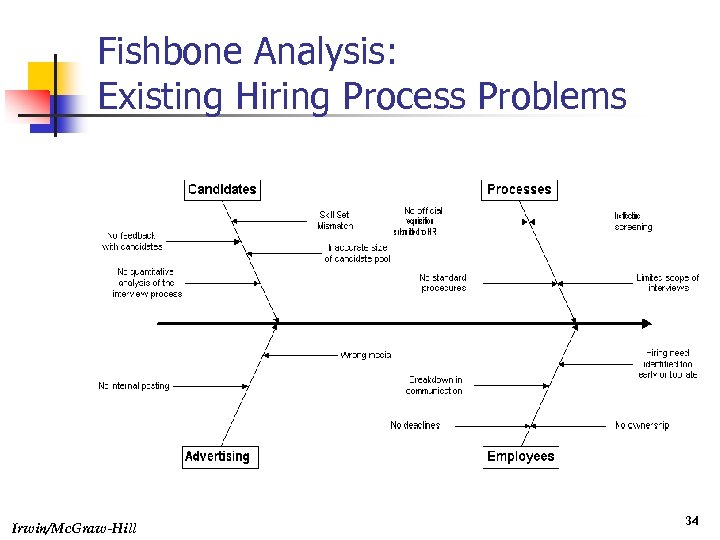 Fishbone Analysis: Existing Hiring Process Problems Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 34
Fishbone Analysis: Existing Hiring Process Problems Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 34
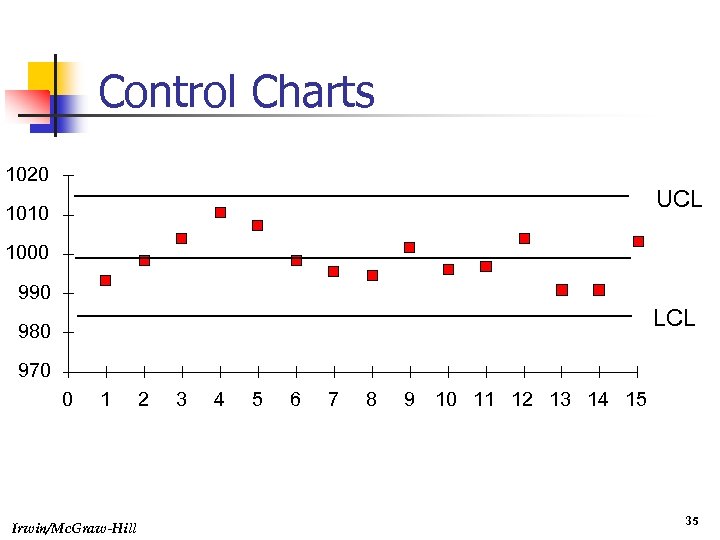 Control Charts 1020 UCL 1010 1000 990 LCL 980 970 0 1 Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 35
Control Charts 1020 UCL 1010 1000 990 LCL 980 970 0 1 Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 35
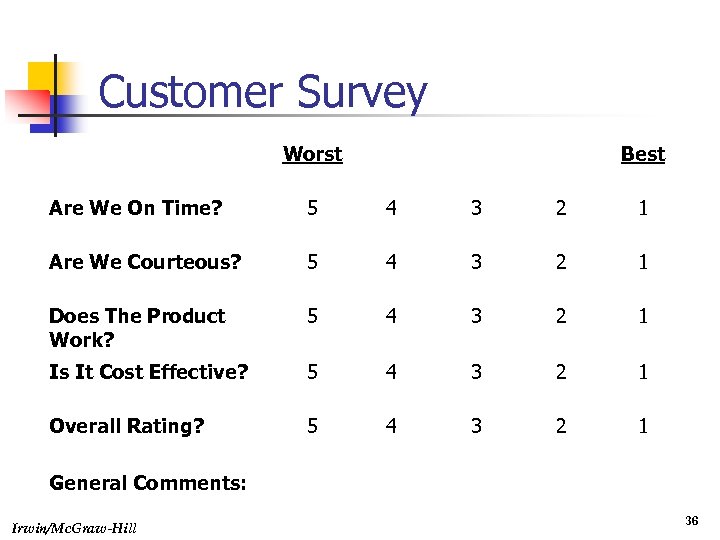 Customer Survey Worst Best Are We On Time? 5 4 3 2 1 Are We Courteous? 5 4 3 2 1 Does The Product Work? 5 4 3 2 1 Is It Cost Effective? 5 4 3 2 1 Overall Rating? 5 4 3 2 1 General Comments: Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 36
Customer Survey Worst Best Are We On Time? 5 4 3 2 1 Are We Courteous? 5 4 3 2 1 Does The Product Work? 5 4 3 2 1 Is It Cost Effective? 5 4 3 2 1 Overall Rating? 5 4 3 2 1 General Comments: Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 36
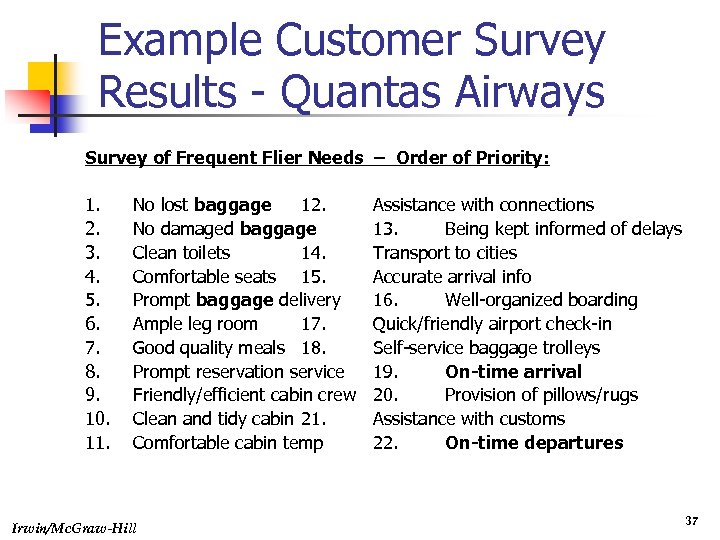 Example Customer Survey Results - Quantas Airways Survey of Frequent Flier Needs – Order of Priority: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. No lost baggage 12. No damaged baggage Clean toilets 14. Comfortable seats 15. Prompt baggage delivery Ample leg room 17. Good quality meals 18. Prompt reservation service Friendly/efficient cabin crew Clean and tidy cabin 21. Comfortable cabin temp Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Assistance with connections 13. Being kept informed of delays Transport to cities Accurate arrival info 16. Well-organized boarding Quick/friendly airport check-in Self-service baggage trolleys 19. On-time arrival 20. Provision of pillows/rugs Assistance with customs 22. On-time departures 37
Example Customer Survey Results - Quantas Airways Survey of Frequent Flier Needs – Order of Priority: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. No lost baggage 12. No damaged baggage Clean toilets 14. Comfortable seats 15. Prompt baggage delivery Ample leg room 17. Good quality meals 18. Prompt reservation service Friendly/efficient cabin crew Clean and tidy cabin 21. Comfortable cabin temp Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Assistance with connections 13. Being kept informed of delays Transport to cities Accurate arrival info 16. Well-organized boarding Quick/friendly airport check-in Self-service baggage trolleys 19. On-time arrival 20. Provision of pillows/rugs Assistance with customs 22. On-time departures 37
 Continuous Improvement Process Orlando Remanufacturing And Distribution Center Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 38
Continuous Improvement Process Orlando Remanufacturing And Distribution Center Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 38
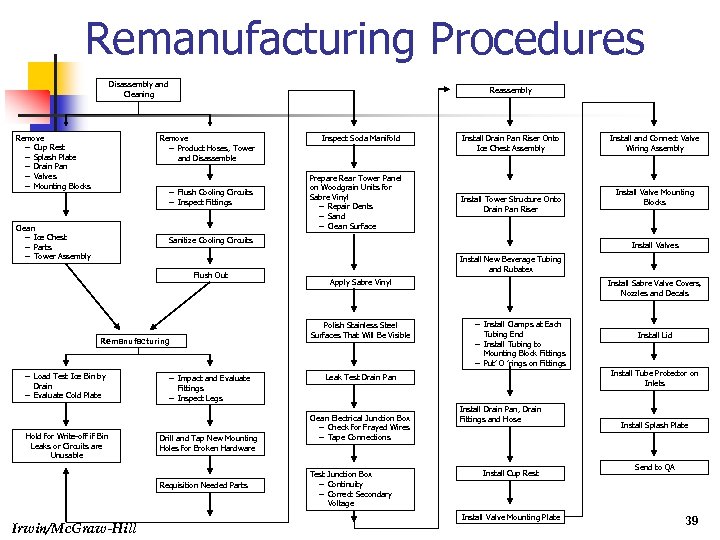 Remanufacturing Procedures Disassembly and Cleaning Remove – Cup Rest – Splash Plate – Drain Pan – Valves – Mounting Blocks Reassembly Remove – Product Hoses, Tower and Disassemble – Flush Cooling Circuits – Inspect Fittings Clean – Ice Chest – Parts – Tower Assembly Inspect Soda Manifold Prepare Rear Tower Panel on Woodgrain Units for Sabre Vinyl – Repair Dents – Sand – Clean Surface Install Drain Pan Riser Onto Ice Chest Assembly Install Tower Structure Onto Drain Pan Riser Sanitize Cooling Circuits Flush Out Remanufacturing Install and Connect Valve Wiring Assembly Install Valve Mounting Blocks Install Valves Install New Beverage Tubing and Rubatex Apply Sabre Vinyl Polish Stainless Steel Surfaces That Will Be Visible Install Sabre Valve Covers, Nozzles and Decals – Install Clamps at Each Tubing End – Install Tubing to Install Lid Mounting Block Fittings – Put’ O ’rings on Fittings – Load Test Ice Bin by Drain – Evaluate Cold Plate Hold for Write-off if Bin Leaks or Circuits are Unusable – Impact and Evaluate Drill and Tap New Mounting Holes for Broken Hardware Requisition Needed Parts Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Install Tube Protector on Inlets Leak Test Drain Pan Fittings – Inspect Legs Clean Electrical Junction Box – Check for Frayed Wires – Tape Connections Test Junction Box – Continuity – Correct Secondary Voltage Install Drain Pan, Drain Fittings and Hose Install Cup Rest Install Valve Mounting Plate Install Splash Plate Send to QA 39
Remanufacturing Procedures Disassembly and Cleaning Remove – Cup Rest – Splash Plate – Drain Pan – Valves – Mounting Blocks Reassembly Remove – Product Hoses, Tower and Disassemble – Flush Cooling Circuits – Inspect Fittings Clean – Ice Chest – Parts – Tower Assembly Inspect Soda Manifold Prepare Rear Tower Panel on Woodgrain Units for Sabre Vinyl – Repair Dents – Sand – Clean Surface Install Drain Pan Riser Onto Ice Chest Assembly Install Tower Structure Onto Drain Pan Riser Sanitize Cooling Circuits Flush Out Remanufacturing Install and Connect Valve Wiring Assembly Install Valve Mounting Blocks Install Valves Install New Beverage Tubing and Rubatex Apply Sabre Vinyl Polish Stainless Steel Surfaces That Will Be Visible Install Sabre Valve Covers, Nozzles and Decals – Install Clamps at Each Tubing End – Install Tubing to Install Lid Mounting Block Fittings – Put’ O ’rings on Fittings – Load Test Ice Bin by Drain – Evaluate Cold Plate Hold for Write-off if Bin Leaks or Circuits are Unusable – Impact and Evaluate Drill and Tap New Mounting Holes for Broken Hardware Requisition Needed Parts Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Install Tube Protector on Inlets Leak Test Drain Pan Fittings – Inspect Legs Clean Electrical Junction Box – Check for Frayed Wires – Tape Connections Test Junction Box – Continuity – Correct Secondary Voltage Install Drain Pan, Drain Fittings and Hose Install Cup Rest Install Valve Mounting Plate Install Splash Plate Send to QA 39
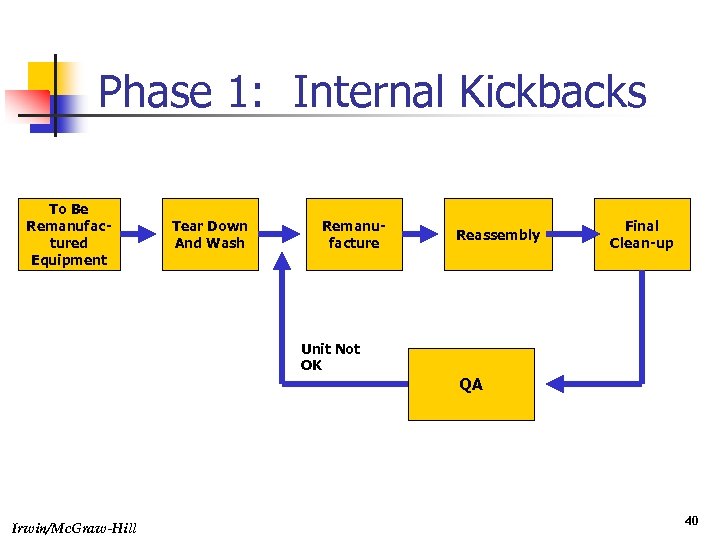 Phase 1: Internal Kickbacks To Be Remanufactured Equipment Tear Down And Wash Remanufacture Reassembly Final Clean-up Unit Not OK QA Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 40
Phase 1: Internal Kickbacks To Be Remanufactured Equipment Tear Down And Wash Remanufacture Reassembly Final Clean-up Unit Not OK QA Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 40
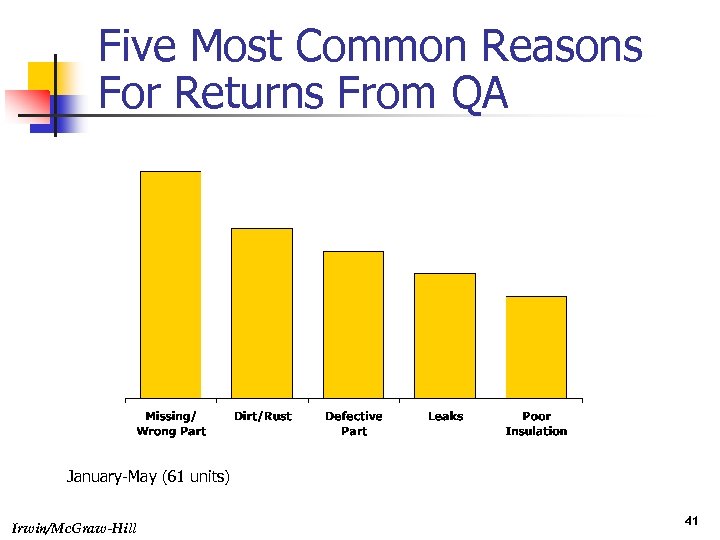 Five Most Common Reasons For Returns From QA January-May (61 units) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 41
Five Most Common Reasons For Returns From QA January-May (61 units) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 41
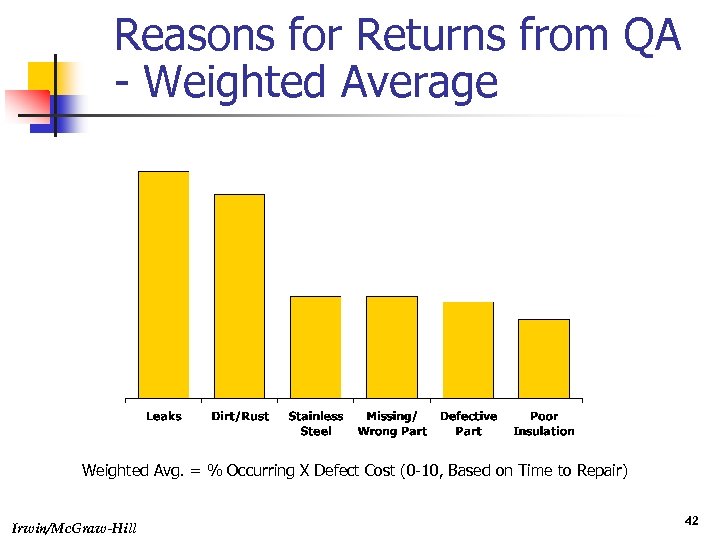 Reasons for Returns from QA - Weighted Average Weighted Avg. = % Occurring X Defect Cost (0 -10, Based on Time to Repair) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 42
Reasons for Returns from QA - Weighted Average Weighted Avg. = % Occurring X Defect Cost (0 -10, Based on Time to Repair) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 42
 Why Dirt? Methods n n Need to Rinse Parts off after Sandblasting Need Better Procedure for Determining What to Remanufacture Based on its Condition Machines n Best tools for $$? Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Materials n n Cleaning Compounds watered down Need Larger Wire Brushes People n n Need More Training More Attention to Detail – Do it Right the First Time Environment n Dust/Humidity n Poor Lighting n Space Limitations Measurement n QA Manager Fixes Some Things Without Informing the Technicians 43
Why Dirt? Methods n n Need to Rinse Parts off after Sandblasting Need Better Procedure for Determining What to Remanufacture Based on its Condition Machines n Best tools for $$? Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Materials n n Cleaning Compounds watered down Need Larger Wire Brushes People n n Need More Training More Attention to Detail – Do it Right the First Time Environment n Dust/Humidity n Poor Lighting n Space Limitations Measurement n QA Manager Fixes Some Things Without Informing the Technicians 43
 Why Leaks? Environment n n High Temperatures in Warehouse Poor Lighting Methods n n Softening Tubing with Water that’s Too Hot Need to Check Units for All Possible Ways They Could Leak Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Materials n n n Bad Tubing “O” Rings Out of Spec n n “O” Rings Too Old (Dry) People n Machines Use Wrong Clamps Don’t Crimp Properly Forget to Connect Bad Dispenser Design Need Rims That Make it Easier to Install Tubing Measurement n n No Testing for Leaks Prior to QA Need to ID by Mfr. /Model Which Units Leak the Most 44
Why Leaks? Environment n n High Temperatures in Warehouse Poor Lighting Methods n n Softening Tubing with Water that’s Too Hot Need to Check Units for All Possible Ways They Could Leak Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Materials n n n Bad Tubing “O” Rings Out of Spec n n “O” Rings Too Old (Dry) People n Machines Use Wrong Clamps Don’t Crimp Properly Forget to Connect Bad Dispenser Design Need Rims That Make it Easier to Install Tubing Measurement n n No Testing for Leaks Prior to QA Need to ID by Mfr. /Model Which Units Leak the Most 44
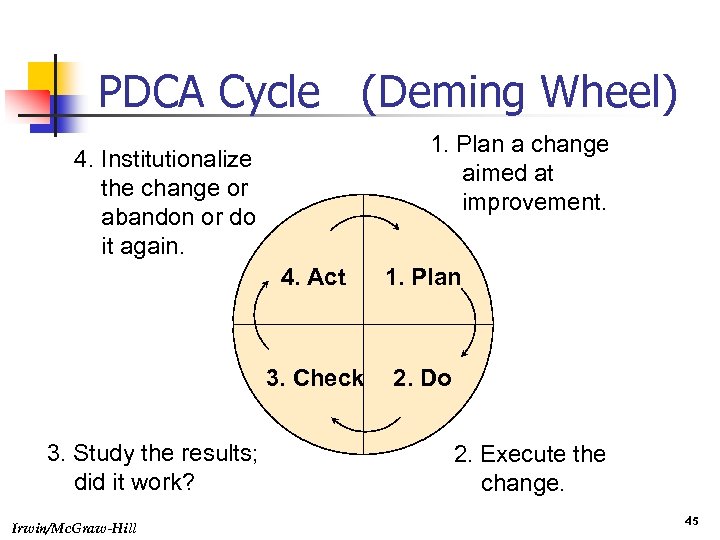 PDCA Cycle (Deming Wheel) 1. Plan a change aimed at improvement. 4. Institutionalize the change or abandon or do it again. 4. Act 3. Check 3. Study the results; did it work? Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 1. Plan 2. Do 2. Execute the change. 45
PDCA Cycle (Deming Wheel) 1. Plan a change aimed at improvement. 4. Institutionalize the change or abandon or do it again. 4. Act 3. Check 3. Study the results; did it work? Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 1. Plan 2. Do 2. Execute the change. 45
 What is Six Sigma? • A sweeping culture change effort to position a company for greater customer satisfaction, profitability and competitiveness (developed by Motorola in the late 1970’s) • A goal of near perfection in meeting customer requirements • A comprehensive and flexible system for achieving, sustaining and maximizing business success; uniquely driven by close understanding of customer needs, disciplined use of facts, data, and statistical analysis, and diligent attention to managing, improving and reinventing business processes Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 46
What is Six Sigma? • A sweeping culture change effort to position a company for greater customer satisfaction, profitability and competitiveness (developed by Motorola in the late 1970’s) • A goal of near perfection in meeting customer requirements • A comprehensive and flexible system for achieving, sustaining and maximizing business success; uniquely driven by close understanding of customer needs, disciplined use of facts, data, and statistical analysis, and diligent attention to managing, improving and reinventing business processes Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill 46
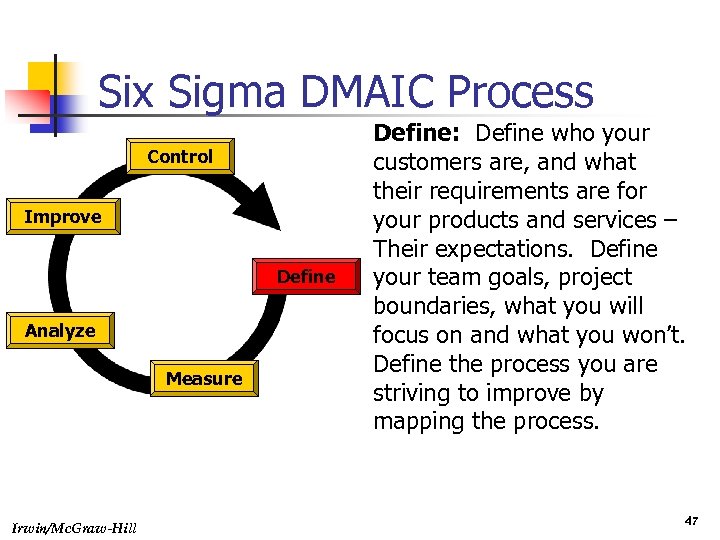 Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Define: Define who your customers are, and what their requirements are for your products and services – Their expectations. Define your team goals, project boundaries, what you will focus on and what you won’t. Define the process you are striving to improve by mapping the process. 47
Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Define: Define who your customers are, and what their requirements are for your products and services – Their expectations. Define your team goals, project boundaries, what you will focus on and what you won’t. Define the process you are striving to improve by mapping the process. 47
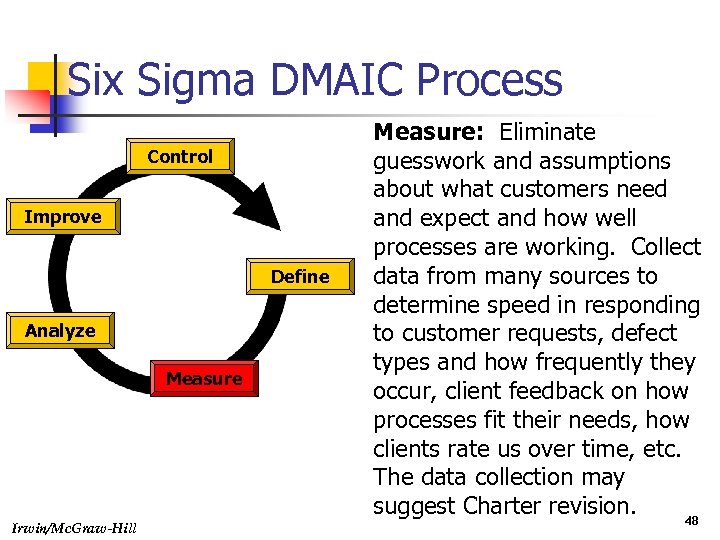 Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Measure: Eliminate guesswork and assumptions about what customers need and expect and how well processes are working. Collect data from many sources to determine speed in responding to customer requests, defect types and how frequently they occur, client feedback on how processes fit their needs, how clients rate us over time, etc. The data collection may suggest Charter revision. 48
Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Measure: Eliminate guesswork and assumptions about what customers need and expect and how well processes are working. Collect data from many sources to determine speed in responding to customer requests, defect types and how frequently they occur, client feedback on how processes fit their needs, how clients rate us over time, etc. The data collection may suggest Charter revision. 48
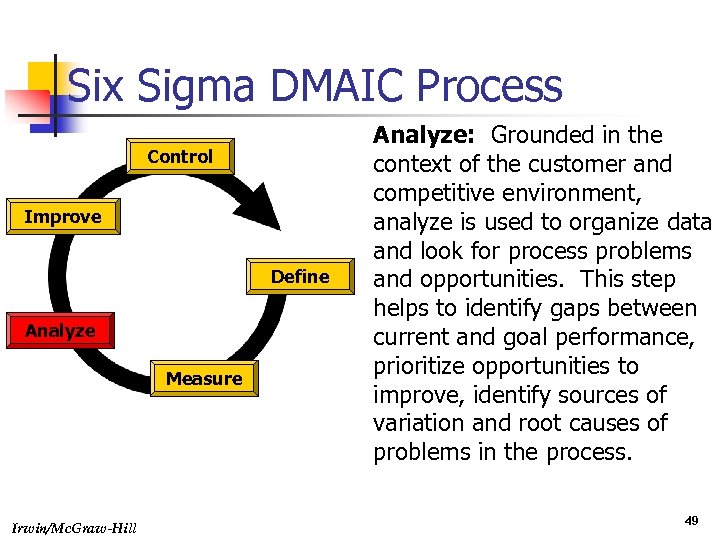 Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Analyze: Grounded in the context of the customer and competitive environment, analyze is used to organize data and look for process problems and opportunities. This step helps to identify gaps between current and goal performance, prioritize opportunities to improve, identify sources of variation and root causes of problems in the process. 49
Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Analyze: Grounded in the context of the customer and competitive environment, analyze is used to organize data and look for process problems and opportunities. This step helps to identify gaps between current and goal performance, prioritize opportunities to improve, identify sources of variation and root causes of problems in the process. 49
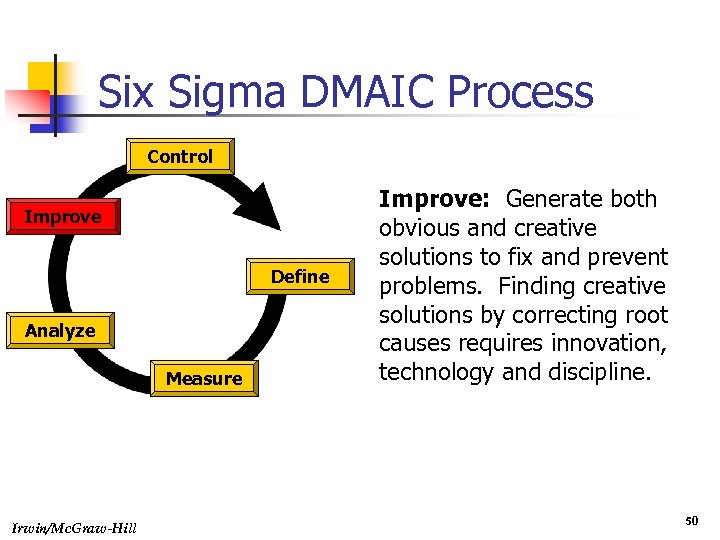 Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Improve: Generate both obvious and creative solutions to fix and prevent problems. Finding creative solutions by correcting root causes requires innovation, technology and discipline. 50
Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Improve: Generate both obvious and creative solutions to fix and prevent problems. Finding creative solutions by correcting root causes requires innovation, technology and discipline. 50
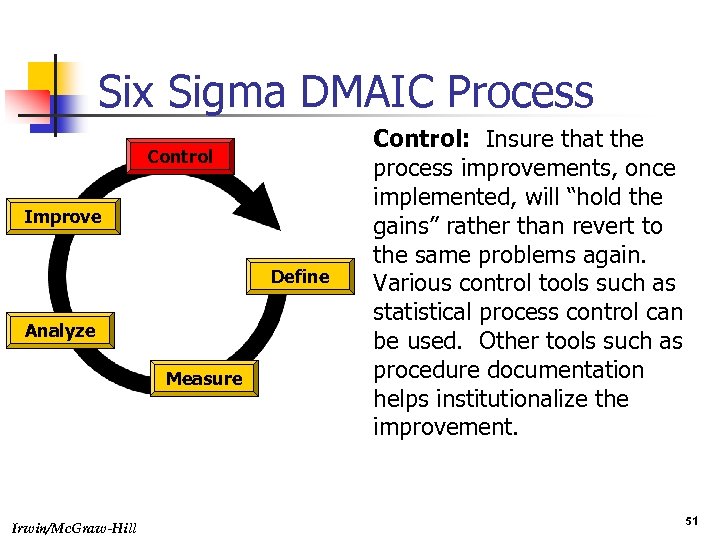 Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Control: Insure that the process improvements, once implemented, will “hold the gains” rather than revert to the same problems again. Various control tools such as statistical process control can be used. Other tools such as procedure documentation helps institutionalize the improvement. 51
Six Sigma DMAIC Process Control Improve Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Control: Insure that the process improvements, once implemented, will “hold the gains” rather than revert to the same problems again. Various control tools such as statistical process control can be used. Other tools such as procedure documentation helps institutionalize the improvement. 51
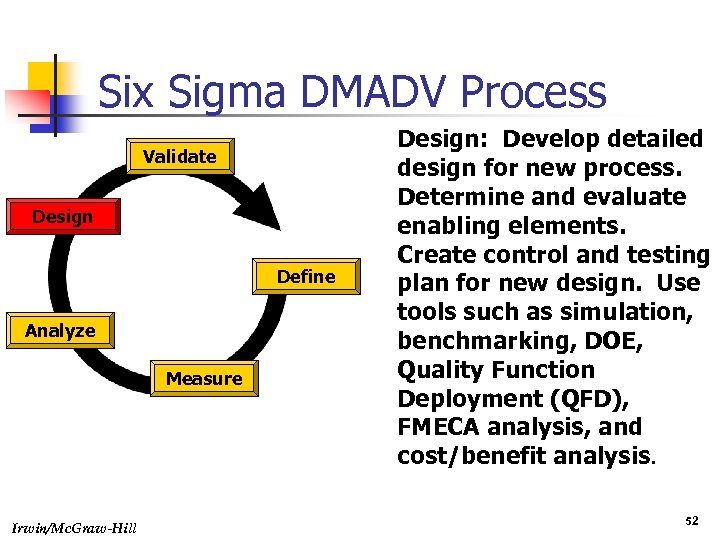 Six Sigma DMADV Process Validate Design Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Design: Develop detailed design for new process. Determine and evaluate enabling elements. Create control and testing plan for new design. Use tools such as simulation, benchmarking, DOE, Quality Function Deployment (QFD), FMECA analysis, and cost/benefit analysis. 52
Six Sigma DMADV Process Validate Design Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Design: Develop detailed design for new process. Determine and evaluate enabling elements. Create control and testing plan for new design. Use tools such as simulation, benchmarking, DOE, Quality Function Deployment (QFD), FMECA analysis, and cost/benefit analysis. 52
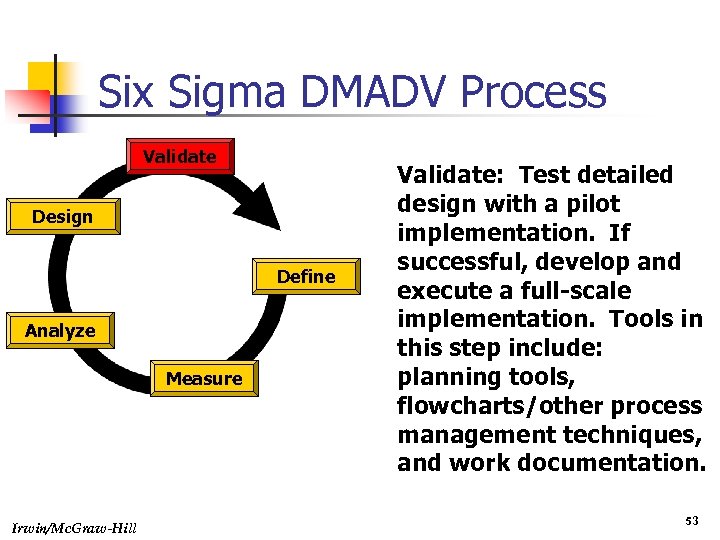 Six Sigma DMADV Process Validate Design Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Validate: Test detailed design with a pilot implementation. If successful, develop and execute a full-scale implementation. Tools in this step include: planning tools, flowcharts/other process management techniques, and work documentation. 53
Six Sigma DMADV Process Validate Design Define Analyze Measure Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Validate: Test detailed design with a pilot implementation. If successful, develop and execute a full-scale implementation. Tools in this step include: planning tools, flowcharts/other process management techniques, and work documentation. 53


