0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Definite Clause Grammars t. k. prasad@wright. edu http: //www. knoesis. org/tkprasad/ cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 1
Definite Clause Grammars t. k. prasad@wright. edu http: //www. knoesis. org/tkprasad/ cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 1
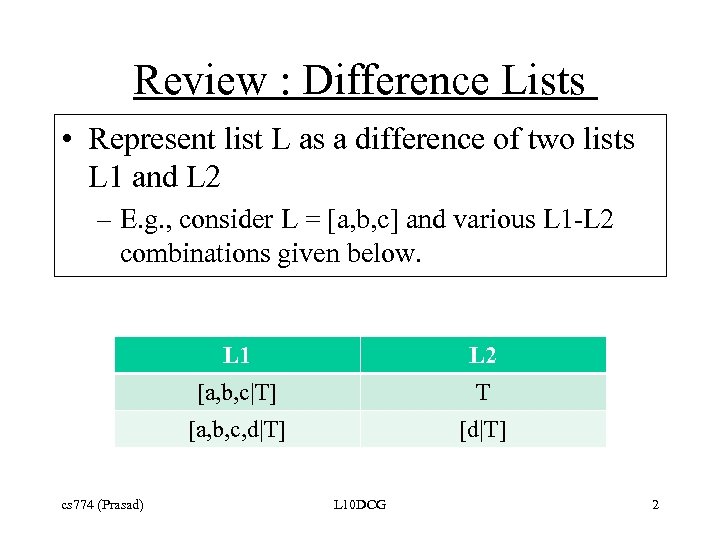 Review : Difference Lists • Represent list L as a difference of two lists L 1 and L 2 – E. g. , consider L = [a, b, c] and various L 1 -L 2 combinations given below. L 1 [a, b, c|T] T [a, b, c, d|T] cs 774 (Prasad) L 2 [d|T] L 10 DCG 2
Review : Difference Lists • Represent list L as a difference of two lists L 1 and L 2 – E. g. , consider L = [a, b, c] and various L 1 -L 2 combinations given below. L 1 [a, b, c|T] T [a, b, c, d|T] cs 774 (Prasad) L 2 [d|T] L 10 DCG 2
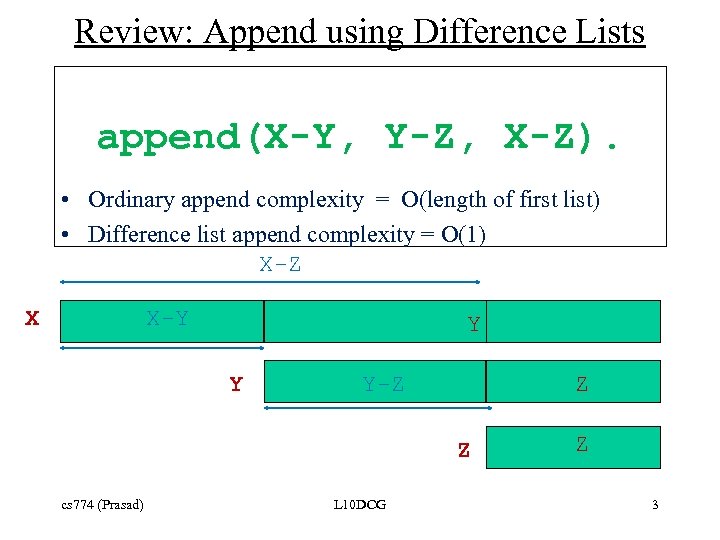 Review: Append using Difference Lists append(X-Y, Y-Z, X-Z). • Ordinary append complexity = O(length of first list) • Difference list append complexity = O(1) X-Z X X-Y Y Y Y-Z Z Z cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG Z 3
Review: Append using Difference Lists append(X-Y, Y-Z, X-Z). • Ordinary append complexity = O(length of first list) • Difference list append complexity = O(1) X-Z X X-Y Y Y Y-Z Z Z cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG Z 3
 DCGs • Mechanize attribute grammar formalism (a generalization of CFG) – Executable specification • Use difference lists for efficiency • Translation from DCGs to Prolog clauses is automatic cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 4
DCGs • Mechanize attribute grammar formalism (a generalization of CFG) – Executable specification • Use difference lists for efficiency • Translation from DCGs to Prolog clauses is automatic cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 4
 Sample Applications of DCGs • Coding recursive descent backtracking parser • Encoding and checking context-sensitive constraints • Simple NLP • In general, enabling syntax directed translation • E. g. , VHDL Parser-Pretty Printer cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 5
Sample Applications of DCGs • Coding recursive descent backtracking parser • Encoding and checking context-sensitive constraints • Simple NLP • In general, enabling syntax directed translation • E. g. , VHDL Parser-Pretty Printer cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 5
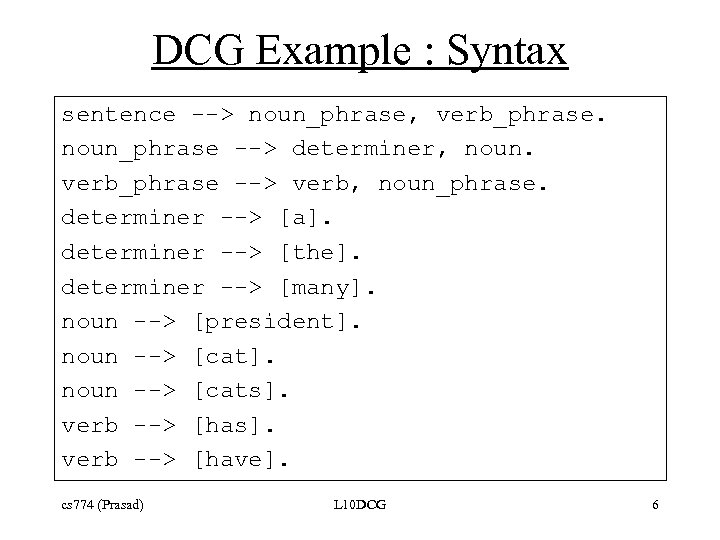 DCG Example : Syntax sentence --> noun_phrase, verb_phrase. noun_phrase --> determiner, noun. verb_phrase --> verb, noun_phrase. determiner --> [a]. determiner --> [the]. determiner --> [many]. noun --> [president]. noun --> [cats]. verb --> [have]. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 6
DCG Example : Syntax sentence --> noun_phrase, verb_phrase. noun_phrase --> determiner, noun. verb_phrase --> verb, noun_phrase. determiner --> [a]. determiner --> [the]. determiner --> [many]. noun --> [president]. noun --> [cats]. verb --> [have]. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 6
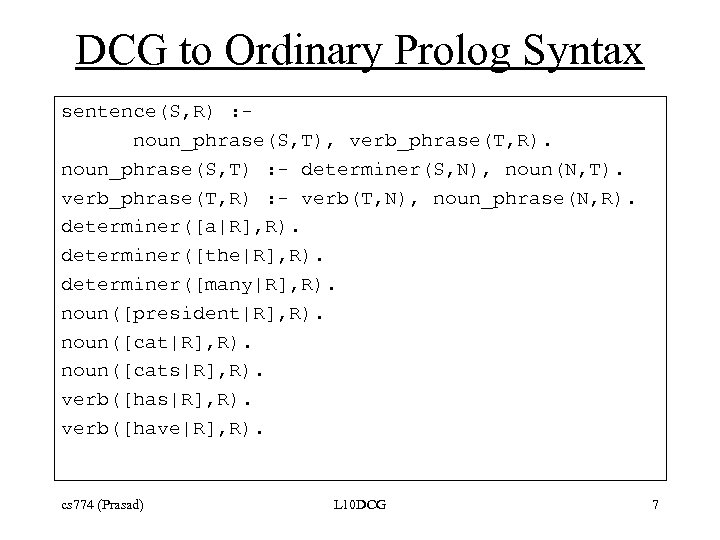 DCG to Ordinary Prolog Syntax sentence(S, R) : noun_phrase(S, T), verb_phrase(T, R). noun_phrase(S, T) : - determiner(S, N), noun(N, T). verb_phrase(T, R) : - verb(T, N), noun_phrase(N, R). determiner([a|R], R). determiner([the|R], R). determiner([many|R], R). noun([president|R], R). noun([cats|R], R). verb([have|R], R). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 7
DCG to Ordinary Prolog Syntax sentence(S, R) : noun_phrase(S, T), verb_phrase(T, R). noun_phrase(S, T) : - determiner(S, N), noun(N, T). verb_phrase(T, R) : - verb(T, N), noun_phrase(N, R). determiner([a|R], R). determiner([the|R], R). determiner([many|R], R). noun([president|R], R). noun([cats|R], R). verb([have|R], R). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 7
![Queries ? - sentence([the, president, has, a, cat], []). ? - sentence([the, cats, have, Queries ? - sentence([the, president, has, a, cat], []). ? - sentence([the, cats, have,](https://present5.com/presentation/0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216/image-8.jpg) Queries ? - sentence([the, president, has, a, cat], []). ? - sentence([the, cats, have, a, president], []). ? - sentence([a, cats, has, the, cat, president], [president]). ? - sentence([a, cats, has, the, cat, President], [President]). • Each non-terminal takes two lists as arguments. • In difference list representation, they together stand for a single list. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 8
Queries ? - sentence([the, president, has, a, cat], []). ? - sentence([the, cats, have, a, president], []). ? - sentence([a, cats, has, the, cat, president], [president]). ? - sentence([a, cats, has, the, cat, President], [President]). • Each non-terminal takes two lists as arguments. • In difference list representation, they together stand for a single list. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 8
 DCG Example: Number Agreement sentence --> noun_phrase(N), verb_phrase(N). noun_phrase(N) --> determiner(N), noun(N). verb_phrase(N) --> verb(N), noun_phrase(_). determiner(sgular) --> [a]. determiner(_) --> [the]. determiner(plural) --> [many]. noun(sgular) noun(plural) verb(sgular) verb(plural) cs 774 (Prasad) --> --> --> [president]. [cats]. [have]. L 10 DCG 9
DCG Example: Number Agreement sentence --> noun_phrase(N), verb_phrase(N). noun_phrase(N) --> determiner(N), noun(N). verb_phrase(N) --> verb(N), noun_phrase(_). determiner(sgular) --> [a]. determiner(_) --> [the]. determiner(plural) --> [many]. noun(sgular) noun(plural) verb(sgular) verb(plural) cs 774 (Prasad) --> --> --> [president]. [cats]. [have]. L 10 DCG 9
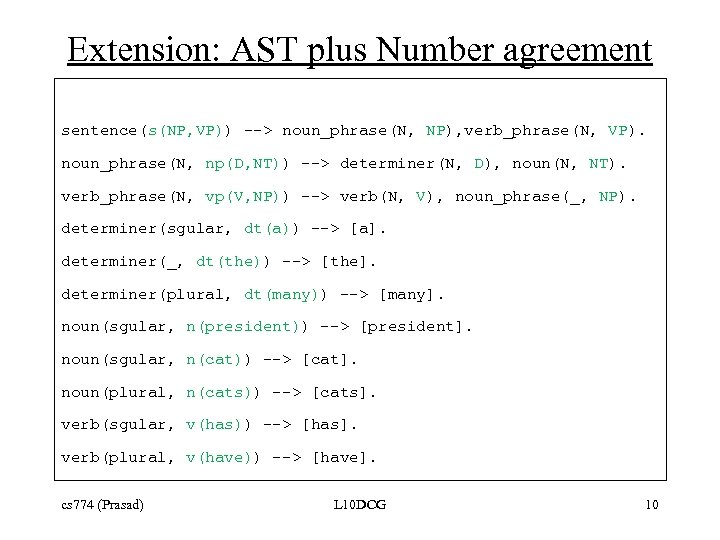 Extension: AST plus Number agreement sentence(s(NP, VP)) --> noun_phrase(N, NP), verb_phrase(N, VP). noun_phrase(N, np(D, NT)) --> determiner(N, D), noun(N, NT). verb_phrase(N, vp(V, NP)) --> verb(N, V), noun_phrase(_, NP). determiner(sgular, dt(a)) --> [a]. determiner(_, dt(the)) --> [the]. determiner(plural, dt(many)) --> [many]. noun(sgular, n(president)) --> [president]. noun(sgular, n(cat)) --> [cat]. noun(plural, n(cats)) --> [cats]. verb(sgular, v(has)) --> [has]. verb(plural, v(have)) --> [have]. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 10
Extension: AST plus Number agreement sentence(s(NP, VP)) --> noun_phrase(N, NP), verb_phrase(N, VP). noun_phrase(N, np(D, NT)) --> determiner(N, D), noun(N, NT). verb_phrase(N, vp(V, NP)) --> verb(N, V), noun_phrase(_, NP). determiner(sgular, dt(a)) --> [a]. determiner(_, dt(the)) --> [the]. determiner(plural, dt(many)) --> [many]. noun(sgular, n(president)) --> [president]. noun(sgular, n(cat)) --> [cat]. noun(plural, n(cats)) --> [cats]. verb(sgular, v(has)) --> [has]. verb(plural, v(have)) --> [have]. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 10
![Queries ? - sentence(T, [the, president, has, a, cat], []). T = s(np(dt(the), n(president)), Queries ? - sentence(T, [the, president, has, a, cat], []). T = s(np(dt(the), n(president)),](https://present5.com/presentation/0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216/image-11.jpg) Queries ? - sentence(T, [the, president, has, a, cat], []). T = s(np(dt(the), n(president)), vp(v(has), np(dt(a), n(cat)))) ; ? - sentence(T, [the, cats, have, a, president|X], X). ? - sentence(T, [a, cats, has, the, cat, preside], [preside]). • Each non-terminal takes two lists as arguments for input sentences, and additional arguments for the static semantics (e. g. , number, AST, etc). • Number disagreement causes the last query to fail. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 11
Queries ? - sentence(T, [the, president, has, a, cat], []). T = s(np(dt(the), n(president)), vp(v(has), np(dt(a), n(cat)))) ; ? - sentence(T, [the, cats, have, a, president|X], X). ? - sentence(T, [a, cats, has, the, cat, preside], [preside]). • Each non-terminal takes two lists as arguments for input sentences, and additional arguments for the static semantics (e. g. , number, AST, etc). • Number disagreement causes the last query to fail. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 11
![Prefix Expression DCG expr --> [if], expr, [then], expr, [else], expr --> [’+’], expr Prefix Expression DCG expr --> [if], expr, [then], expr, [else], expr --> [’+’], expr](https://present5.com/presentation/0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216/image-12.jpg) Prefix Expression DCG expr --> [if], expr, [then], expr, [else], expr --> [’+’], expr --> [’*’], expr --> [m]. expr --> [n]. expr --> [a]. expr --> [b]. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 12
Prefix Expression DCG expr --> [if], expr, [then], expr, [else], expr --> [’+’], expr --> [’*’], expr --> [m]. expr --> [n]. expr --> [a]. expr --> [b]. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 12
![Queries ? -expr([’*’, m, n], []). ? -expr([m, ’*’, n], []). ? -expr([’*’, m, Queries ? -expr([’*’, m, n], []). ? -expr([m, ’*’, n], []). ? -expr([’*’, m,](https://present5.com/presentation/0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216/image-13.jpg) Queries ? -expr([’*’, m, n], []). ? -expr([m, ’*’, n], []). ? -expr([’*’, m, ’+’, ’a’, n, n], [n]). ? -expr([if, a, then, m, else, n], []). ? -expr([if, a, then, a, else, ’*’, m, n], []). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 13
Queries ? -expr([’*’, m, n], []). ? -expr([m, ’*’, n], []). ? -expr([’*’, m, ’+’, ’a’, n, n], [n]). ? -expr([if, a, then, m, else, n], []). ? -expr([if, a, then, a, else, ’*’, m, n], []). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 13
![Prefix Expression DCG : Type Checking Version t. Expr(T) --> [if], t. Expr(bool), [then], Prefix Expression DCG : Type Checking Version t. Expr(T) --> [if], t. Expr(bool), [then],](https://present5.com/presentation/0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216/image-14.jpg) Prefix Expression DCG : Type Checking Version t. Expr(T) --> [if], t. Expr(bool), [then], t. Expr(T), [else], t. Expr(T) --> [’+’], t. Expr(T) --> [’*’], t. Expr(T). t. Expr(int) --> [m]. t. Expr(int) --> [n]. t. Expr(bool) --> [a]. t. Expr(bool) --> [b]. • Assume that + and * are overloaded for int and bool. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 14
Prefix Expression DCG : Type Checking Version t. Expr(T) --> [if], t. Expr(bool), [then], t. Expr(T), [else], t. Expr(T) --> [’+’], t. Expr(T) --> [’*’], t. Expr(T). t. Expr(int) --> [m]. t. Expr(int) --> [n]. t. Expr(bool) --> [a]. t. Expr(bool) --> [b]. • Assume that + and * are overloaded for int and bool. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 14
![Queries ? -t. Expr(T, [’*’, m, n], []). ? -t. Expr(T, [m, ’*’, n], Queries ? -t. Expr(T, [’*’, m, n], []). ? -t. Expr(T, [m, ’*’, n],](https://present5.com/presentation/0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216/image-15.jpg) Queries ? -t. Expr(T, [’*’, m, n], []). ? -t. Expr(T, [m, ’*’, n], []). ? -t. Expr(T, [’*’, m, ’+’, ’a’, n, n], [n]). ? -t. Expr(T, [if, a, then, m, else, n], []). T = int ; ? -t. Expr(T, [if, a, then, b, else, ’*’, m, n], []). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 15
Queries ? -t. Expr(T, [’*’, m, n], []). ? -t. Expr(T, [m, ’*’, n], []). ? -t. Expr(T, [’*’, m, ’+’, ’a’, n, n], [n]). ? -t. Expr(T, [if, a, then, m, else, n], []). T = int ; ? -t. Expr(T, [if, a, then, b, else, ’*’, m, n], []). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 15
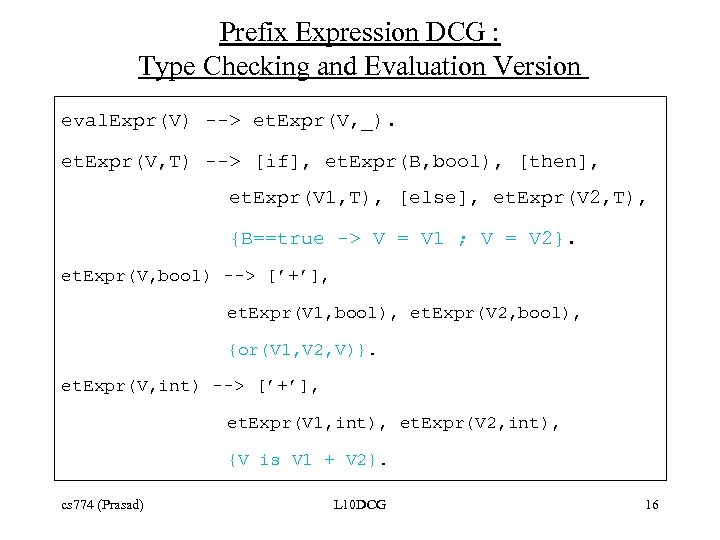 Prefix Expression DCG : Type Checking and Evaluation Version eval. Expr(V) --> et. Expr(V, _). et. Expr(V, T) --> [if], et. Expr(B, bool), [then], et. Expr(V 1, T), [else], et. Expr(V 2, T), {B==true -> V = V 1 ; V = V 2}. et. Expr(V, bool) --> [’+’], et. Expr(V 1, bool), et. Expr(V 2, bool), {or(V 1, V 2, V)}. et. Expr(V, int) --> [’+’], et. Expr(V 1, int), et. Expr(V 2, int), {V is V 1 + V 2}. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 16
Prefix Expression DCG : Type Checking and Evaluation Version eval. Expr(V) --> et. Expr(V, _). et. Expr(V, T) --> [if], et. Expr(B, bool), [then], et. Expr(V 1, T), [else], et. Expr(V 2, T), {B==true -> V = V 1 ; V = V 2}. et. Expr(V, bool) --> [’+’], et. Expr(V 1, bool), et. Expr(V 2, bool), {or(V 1, V 2, V)}. et. Expr(V, int) --> [’+’], et. Expr(V 1, int), et. Expr(V 2, int), {V is V 1 + V 2}. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 16
![(cont’d) et. Expr(V, bool) --> [’*’], et. Expr(V 1, bool), et. Expr(V 2, bool), (cont’d) et. Expr(V, bool) --> [’*’], et. Expr(V 1, bool), et. Expr(V 2, bool),](https://present5.com/presentation/0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216/image-17.jpg) (cont’d) et. Expr(V, bool) --> [’*’], et. Expr(V 1, bool), et. Expr(V 2, bool), {and(V 1, V 2, V)}. et. Expr(V, bool) --> [’*’], et. Expr(V 1, int), et. Expr(V 2, int), {V is V 1 * V 2}. et. Expr(V, int) --> [m], {value(m, V)}. et. Expr(V, int) --> [n], {value(n, V)}. et. Expr(V, bool) --> [a], {value(a, V)}. et. Expr(V, bool) --> [b], {value(b, V)}. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 17
(cont’d) et. Expr(V, bool) --> [’*’], et. Expr(V 1, bool), et. Expr(V 2, bool), {and(V 1, V 2, V)}. et. Expr(V, bool) --> [’*’], et. Expr(V 1, int), et. Expr(V 2, int), {V is V 1 * V 2}. et. Expr(V, int) --> [m], {value(m, V)}. et. Expr(V, int) --> [n], {value(n, V)}. et. Expr(V, bool) --> [a], {value(a, V)}. et. Expr(V, bool) --> [b], {value(b, V)}. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 17
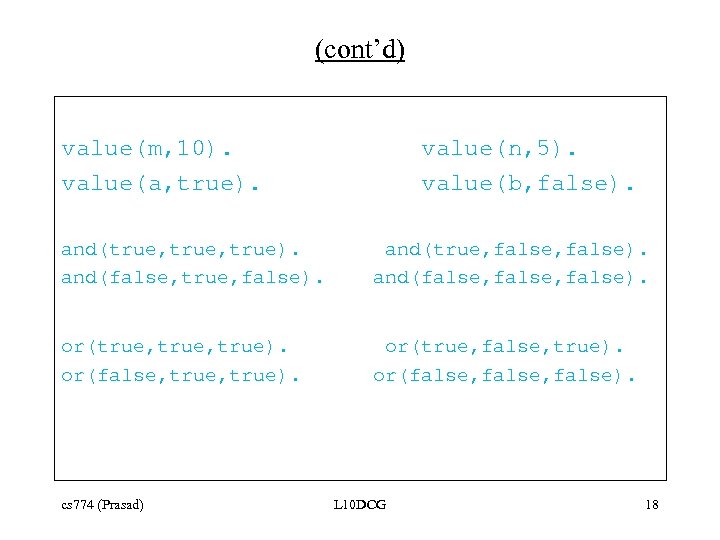 (cont’d) value(m, 10). value(a, true). value(n, 5). value(b, false). and(true, true). and(false, true, false). and(true, false). and(false, false). or(true, true). or(false, true). or(true, false, true). or(false, false). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 18
(cont’d) value(m, 10). value(a, true). value(n, 5). value(b, false). and(true, true). and(false, true, false). and(true, false). and(false, false). or(true, true). or(false, true). or(true, false, true). or(false, false). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 18
 Prefix Expression DCG : AST Version tree. Expr(V) --> tr. Expr(V, _). tr. Expr(cond(B, V 1, V 2), T) --> [if], tr. Expr(B, bool), [then], tr. Expr(V 1, T), [else], tr. Expr(V 2, T). tr. Expr(or(V 1, V 2), bool) --> [’+’], tr. Expr(V 1, bool), tr. Expr(V 2, bool). tr. Expr(plus(V 1, V 2), int) --> [’+’], tr. Expr(V 1, int), tr. Expr(V 2, int). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 19
Prefix Expression DCG : AST Version tree. Expr(V) --> tr. Expr(V, _). tr. Expr(cond(B, V 1, V 2), T) --> [if], tr. Expr(B, bool), [then], tr. Expr(V 1, T), [else], tr. Expr(V 2, T). tr. Expr(or(V 1, V 2), bool) --> [’+’], tr. Expr(V 1, bool), tr. Expr(V 2, bool). tr. Expr(plus(V 1, V 2), int) --> [’+’], tr. Expr(V 1, int), tr. Expr(V 2, int). cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 19
![(cont’d) tr. Expr(and(V 1, V 2), bool) --> [’*’], tr. Expr(V 1, bool), tr. (cont’d) tr. Expr(and(V 1, V 2), bool) --> [’*’], tr. Expr(V 1, bool), tr.](https://present5.com/presentation/0d81dae0f568a4a09263d6b944599216/image-20.jpg) (cont’d) tr. Expr(and(V 1, V 2), bool) --> [’*’], tr. Expr(V 1, bool), tr. Expr(V 2, bool). tr. Expr(mul(V 1, V 2), int) --> [’*’], tr. Expr(V 1, int), tr. Expr(V 2, int). tr. Expr(m, int) --> [m]. tr. Expr(n, int) --> [n]. tr. Expr(a, bool) --> [a]. tr. Expr(b, bool) --> [b]. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 20
(cont’d) tr. Expr(and(V 1, V 2), bool) --> [’*’], tr. Expr(V 1, bool), tr. Expr(V 2, bool). tr. Expr(mul(V 1, V 2), int) --> [’*’], tr. Expr(V 1, int), tr. Expr(V 2, int). tr. Expr(m, int) --> [m]. tr. Expr(n, int) --> [n]. tr. Expr(a, bool) --> [a]. tr. Expr(b, bool) --> [b]. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 20
 Other Compiler Operations • From parse tree and type information, one can: – compute (stack) storage requirements for variables and for expression evaluation – generate assembly code (with coercion instructions if necessary) – transform/simplify expression • Ref: http: //www. cs. wright. edu/~tkprasad/papers/Attribute-Grammars. pdf cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 21
Other Compiler Operations • From parse tree and type information, one can: – compute (stack) storage requirements for variables and for expression evaluation – generate assembly code (with coercion instructions if necessary) – transform/simplify expression • Ref: http: //www. cs. wright. edu/~tkprasad/papers/Attribute-Grammars. pdf cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 21
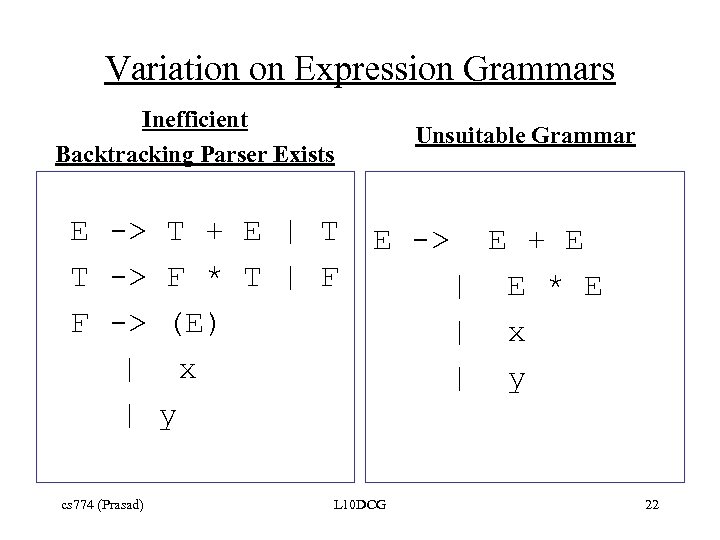 Variation on Expression Grammars Inefficient Backtracking Parser Exists E -> T + E | T T -> F * T | F F -> (E) | x | y cs 774 (Prasad) Unsuitable Grammar E -> L 10 DCG E + E | E * E | x | y 22
Variation on Expression Grammars Inefficient Backtracking Parser Exists E -> T + E | T T -> F * T | F F -> (E) | x | y cs 774 (Prasad) Unsuitable Grammar E -> L 10 DCG E + E | E * E | x | y 22
 RELATIONSHIP TO ATTRIBUTE GRAMMARS cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 23
RELATIONSHIP TO ATTRIBUTE GRAMMARS cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 23
 Attribute Grammars • Formalism for specifying semantics based on contextfree grammars (BNF) § Static semantics (context-sensitive aspects) § Type checking and type inference § Compatibility between procedure definition and call § Dynamic semantics • • Associate attributes with terminals and nonterminals Associate attribute computation rules with productions CS 784 (Prasad) L 167 AG 24
Attribute Grammars • Formalism for specifying semantics based on contextfree grammars (BNF) § Static semantics (context-sensitive aspects) § Type checking and type inference § Compatibility between procedure definition and call § Dynamic semantics • • Associate attributes with terminals and nonterminals Associate attribute computation rules with productions CS 784 (Prasad) L 167 AG 24
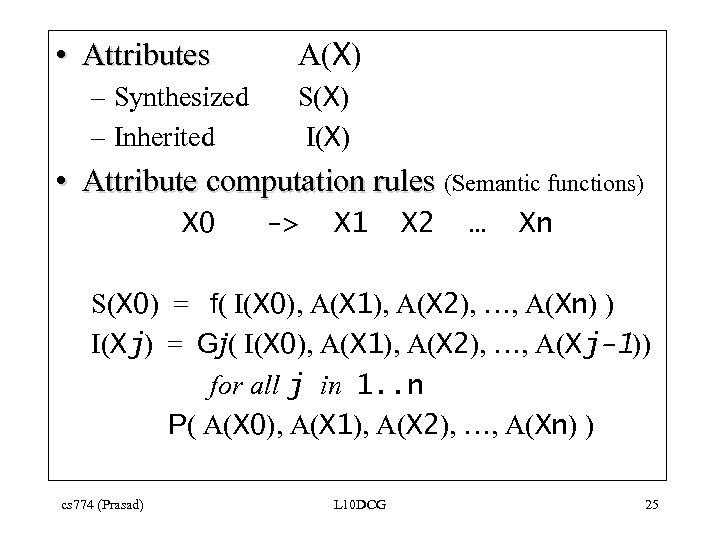 • Attributes – Synthesized – Inherited A(X) S(X) I(X) • Attribute computation rules (Semantic functions) X 0 -> X 1 X 2 … Xn S(X 0) = f( I(X 0), A(X 1), A(X 2), …, A(Xn) ) I(Xj) = Gj( I(X 0), A(X 1), A(X 2), …, A(Xj-1)) for all j in 1. . n P( A(X 0), A(X 1), A(X 2), …, A(Xn) ) cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 25
• Attributes – Synthesized – Inherited A(X) S(X) I(X) • Attribute computation rules (Semantic functions) X 0 -> X 1 X 2 … Xn S(X 0) = f( I(X 0), A(X 1), A(X 2), …, A(Xn) ) I(Xj) = Gj( I(X 0), A(X 1), A(X 2), …, A(Xj-1)) for all j in 1. . n P( A(X 0), A(X 1), A(X 2), …, A(Xn) ) cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 25
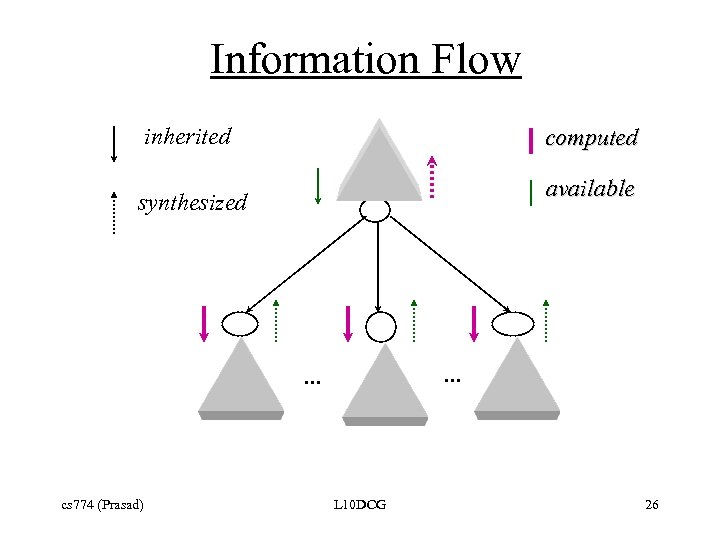 Information Flow inherited computed available synthesized . . . cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 26
Information Flow inherited computed available synthesized . . . cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 26
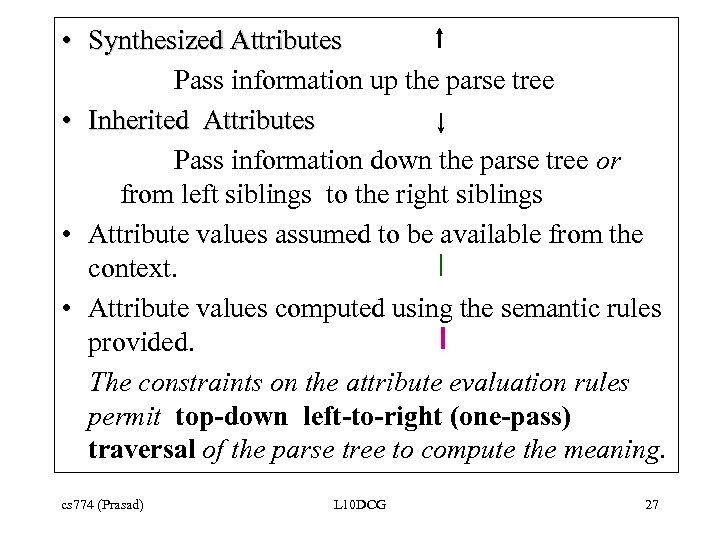 • Synthesized Attributes Pass information up the parse tree • Inherited Attributes Pass information down the parse tree or from left siblings to the right siblings • Attribute values assumed to be available from the context. • Attribute values computed using the semantic rules provided. The constraints on the attribute evaluation rules permit top-down left-to-right (one-pass) traversal of the parse tree to compute the meaning. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 27
• Synthesized Attributes Pass information up the parse tree • Inherited Attributes Pass information down the parse tree or from left siblings to the right siblings • Attribute values assumed to be available from the context. • Attribute values computed using the semantic rules provided. The constraints on the attribute evaluation rules permit top-down left-to-right (one-pass) traversal of the parse tree to compute the meaning. cs 774 (Prasad) L 10 DCG 27
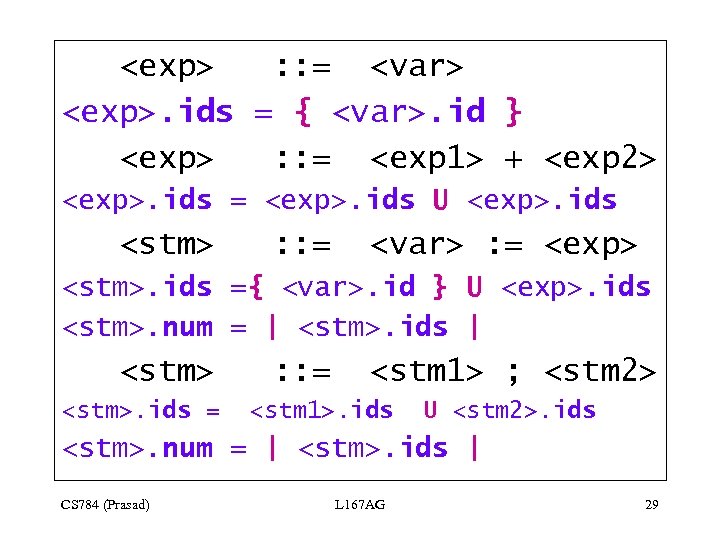
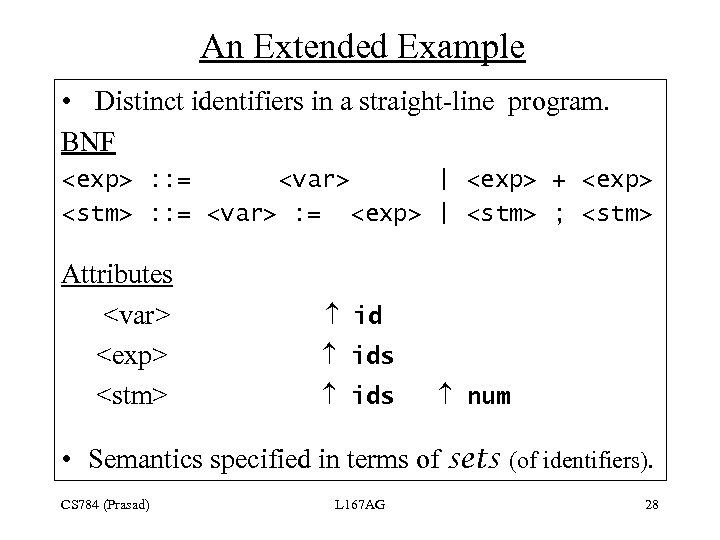 An Extended Example • Distinct identifiers in a straight-line program. BNF
An Extended Example • Distinct identifiers in a straight-line program. BNF
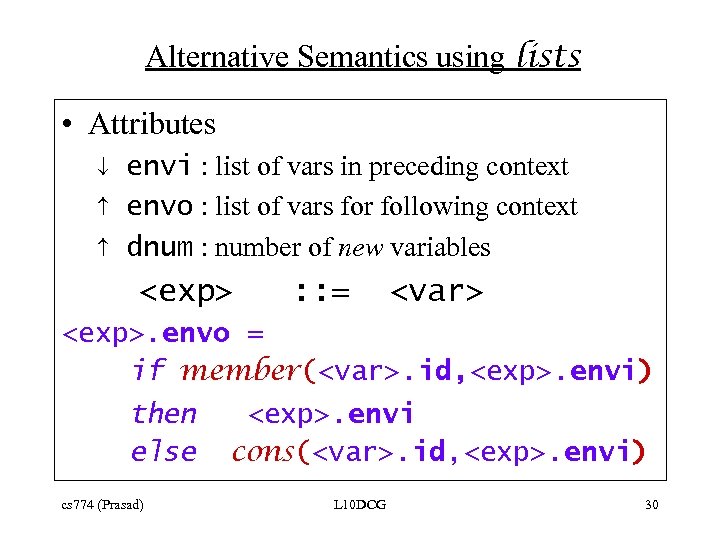 Alternative Semantics using lists • Attributes envi : list of vars in preceding context envo : list of vars for following context dnum : number of new variables
Alternative Semantics using lists • Attributes envi : list of vars in preceding context envo : list of vars for following context dnum : number of new variables
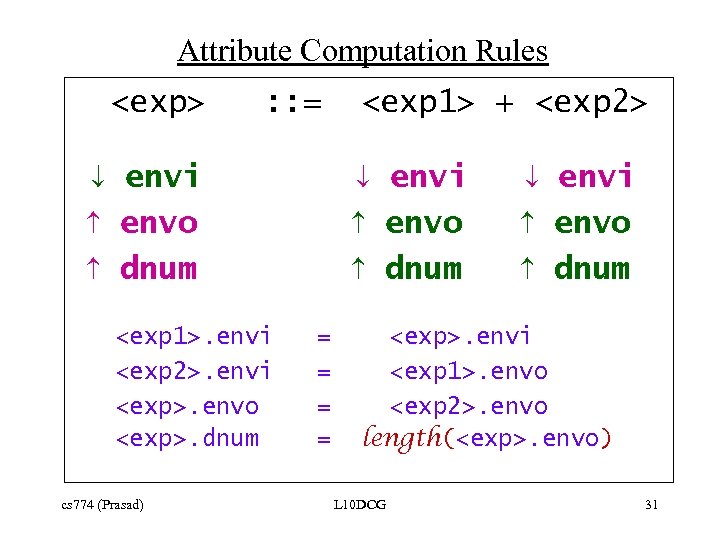 Attribute Computation Rules
Attribute Computation Rules


