77e7bf4cd263c2902e76566a9c33c036.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Defense Related Policy and Procurement Developments in UK as well as within US British Embassy team: Jonathan Hoyle – Minister (Defence Materiel) Adrian Baguley - Defence Science and Technology Counsellor Andrew Radcliffe – Defence Equipment Counsellor Bill Cruickshank – Attache Defence Equipment (Legal) British Defence Staff
Defense Related Policy and Procurement Developments in UK as well as within US British Embassy team: Jonathan Hoyle – Minister (Defence Materiel) Adrian Baguley - Defence Science and Technology Counsellor Andrew Radcliffe – Defence Equipment Counsellor Bill Cruickshank – Attache Defence Equipment (Legal) British Defence Staff
 Agenda • • • General Policy Overview & Global Context Facts & Figures Procurement Science & Technology Industrial Strategy Conclusions British Defence Staff
Agenda • • • General Policy Overview & Global Context Facts & Figures Procurement Science & Technology Industrial Strategy Conclusions British Defence Staff
 General Policy Overview & Global Context British Defence Staff
General Policy Overview & Global Context British Defence Staff
 The UK Defence Policy Vision • • Defending the UK and its interests Strengthening international peace and stability A force for good in the world Achieved by being: – Fit for the challenge of today – Ready for the tasks of tomorrow – Capable of building for the future British Defence Staff
The UK Defence Policy Vision • • Defending the UK and its interests Strengthening international peace and stability A force for good in the world Achieved by being: – Fit for the challenge of today – Ready for the tasks of tomorrow – Capable of building for the future British Defence Staff
 New Threats and Instabilities • We face new challenges and unpredictable conditions. • Strategy must evolve to reflect these new realities. • This means: – Evolving strategy and military doctrine that is flexible and geared to changing conditions. – Behaving with speed, flexibility and creativity. British Defence Staff
New Threats and Instabilities • We face new challenges and unpredictable conditions. • Strategy must evolve to reflect these new realities. • This means: – Evolving strategy and military doctrine that is flexible and geared to changing conditions. – Behaving with speed, flexibility and creativity. British Defence Staff
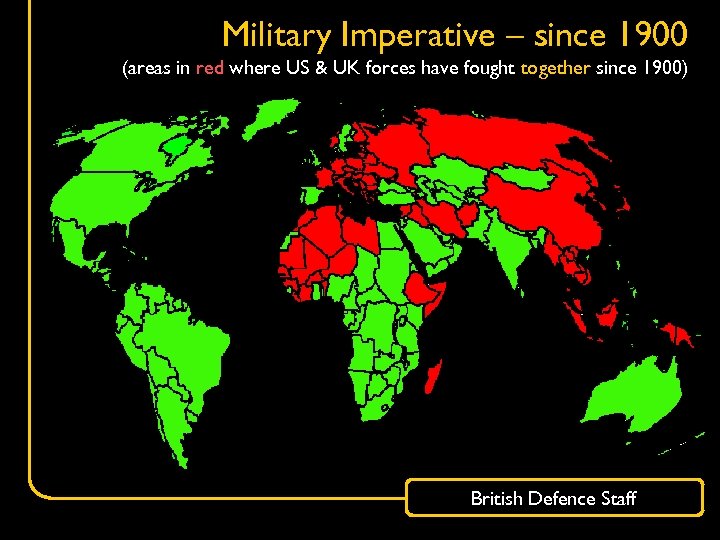 Military Imperative – since 1900 (areas in red where US & UK forces have fought together since 1900) British Defence Staff
Military Imperative – since 1900 (areas in red where US & UK forces have fought together since 1900) British Defence Staff
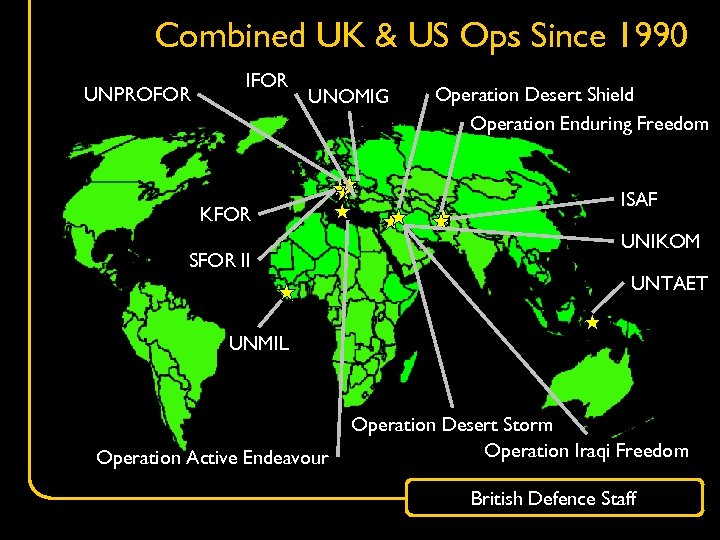 Combined UK & US Ops Since 1990 UNPROFOR IFOR UNOMIG KFOR SFOR II Operation Desert Shield Operation Enduring Freedom ISAF UNIKOM UNTAET UNMIL Operation Active Endeavour Operation Desert Storm Operation Iraqi Freedom British Defence Staff
Combined UK & US Ops Since 1990 UNPROFOR IFOR UNOMIG KFOR SFOR II Operation Desert Shield Operation Enduring Freedom ISAF UNIKOM UNTAET UNMIL Operation Active Endeavour Operation Desert Storm Operation Iraqi Freedom British Defence Staff
 UK Defence Policy vis-à-vis US “ Maintenance of the transatlantic relationship is fundamental to our security and defence policy” “ Our Armed Forces will need to be inter-operable with US Command & Control structures” British Defence Staff
UK Defence Policy vis-à-vis US “ Maintenance of the transatlantic relationship is fundamental to our security and defence policy” “ Our Armed Forces will need to be inter-operable with US Command & Control structures” British Defence Staff
 March 2003 - Iraq 1 Marine Expeditionary Force 3 Commando Brigade 15 Marine Expeditionary Unit British Defence Staff
March 2003 - Iraq 1 Marine Expeditionary Force 3 Commando Brigade 15 Marine Expeditionary Unit British Defence Staff
 Facts & Figures British Defence Staff
Facts & Figures British Defence Staff
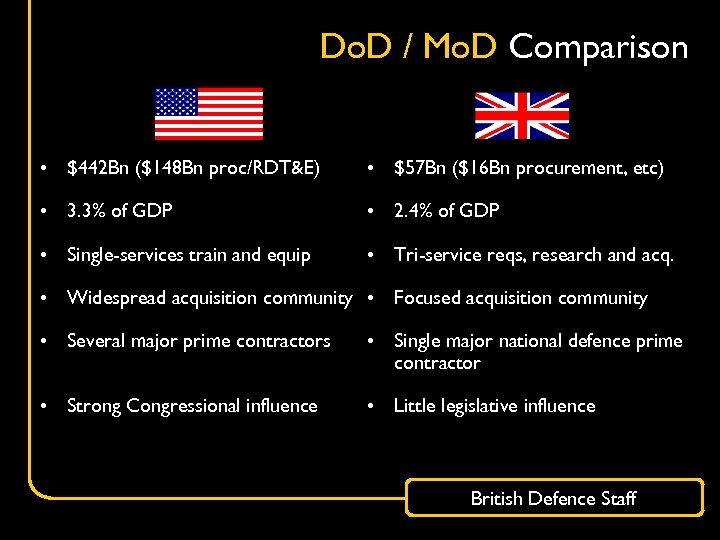 Do. D / Mo. D Comparison • $442 Bn ($148 Bn proc/RDT&E) • $57 Bn ($16 Bn procurement, etc) • 3. 3% of GDP • 2. 4% of GDP • Single-services train and equip • Tri-service reqs, research and acq. • Widespread acquisition community • Focused acquisition community • Several major prime contractors • Single major national defence prime contractor • Strong Congressional influence • Little legislative influence British Defence Staff
Do. D / Mo. D Comparison • $442 Bn ($148 Bn proc/RDT&E) • $57 Bn ($16 Bn procurement, etc) • 3. 3% of GDP • 2. 4% of GDP • Single-services train and equip • Tri-service reqs, research and acq. • Widespread acquisition community • Focused acquisition community • Several major prime contractors • Single major national defence prime contractor • Strong Congressional influence • Little legislative influence British Defence Staff
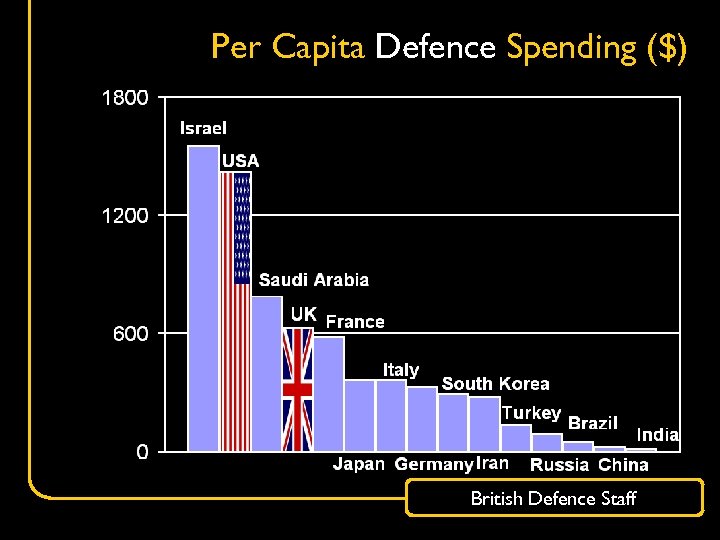 Per Capita Defence Spending ($) British Defence Staff
Per Capita Defence Spending ($) British Defence Staff
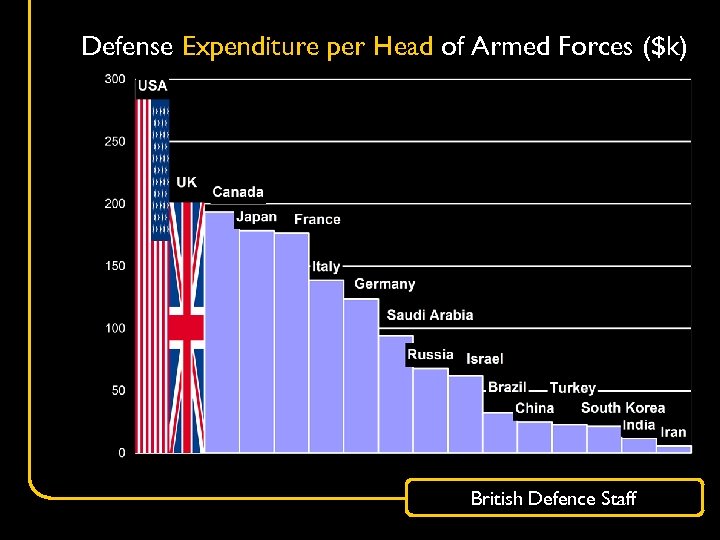 Defense Expenditure per Head of Armed Forces ($k) British Defence Staff
Defense Expenditure per Head of Armed Forces ($k) British Defence Staff
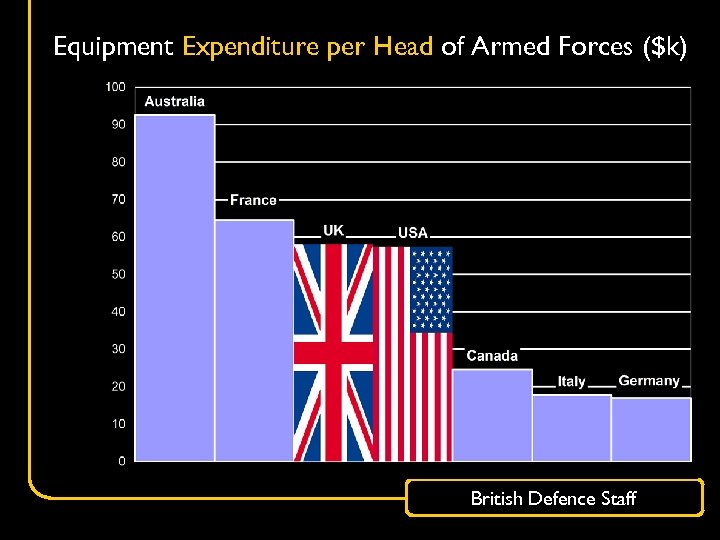 Equipment Expenditure per Head of Armed Forces ($k) British Defence Staff
Equipment Expenditure per Head of Armed Forces ($k) British Defence Staff
 Procurement British Defence Staff
Procurement British Defence Staff
 Public Perception British Defence Staff
Public Perception British Defence Staff
 SMART Acquisition “To acquire Defence capability faster, cheaper, better and more effectively integrated. ” • • • Deliver within time, cost and performance parameters Integrate Reduce risk Cut the time for new technologies to be introduced Whole life approach Clear customer / supplier relationship British Defence Staff
SMART Acquisition “To acquire Defence capability faster, cheaper, better and more effectively integrated. ” • • • Deliver within time, cost and performance parameters Integrate Reduce risk Cut the time for new technologies to be introduced Whole life approach Clear customer / supplier relationship British Defence Staff
 A Vision… Joy delivery of thrilled by the news that the DPA had yet again succeeded in delivering key Cost reductions welcomed by defence chiefs reduced by more than ends British Defence Staff
A Vision… Joy delivery of thrilled by the news that the DPA had yet again succeeded in delivering key Cost reductions welcomed by defence chiefs reduced by more than ends British Defence Staff
 Major Project Report Headline Performance - Post Main Gate Projects MPR 2003 In-Year Cost Variation £ 3, 121 m In-year ISD slippage 144 months MPR 2004 £ 1, 731 m 62 months British Defence Staff
Major Project Report Headline Performance - Post Main Gate Projects MPR 2003 In-Year Cost Variation £ 3, 121 m In-year ISD slippage 144 months MPR 2004 £ 1, 731 m 62 months British Defence Staff
 Still More To Be Done. . . Ø Improve through-life management Ø Improve relationship with industry Ø Increase early investment to de-risk projects Ø Improve approach to project approvals Ø More effective performance/time/cost trade-off Ø Better skills planning, development & incentives Ø Improved corporate approach to business British Defence Staff
Still More To Be Done. . . Ø Improve through-life management Ø Improve relationship with industry Ø Increase early investment to de-risk projects Ø Improve approach to project approvals Ø More effective performance/time/cost trade-off Ø Better skills planning, development & incentives Ø Improved corporate approach to business British Defence Staff
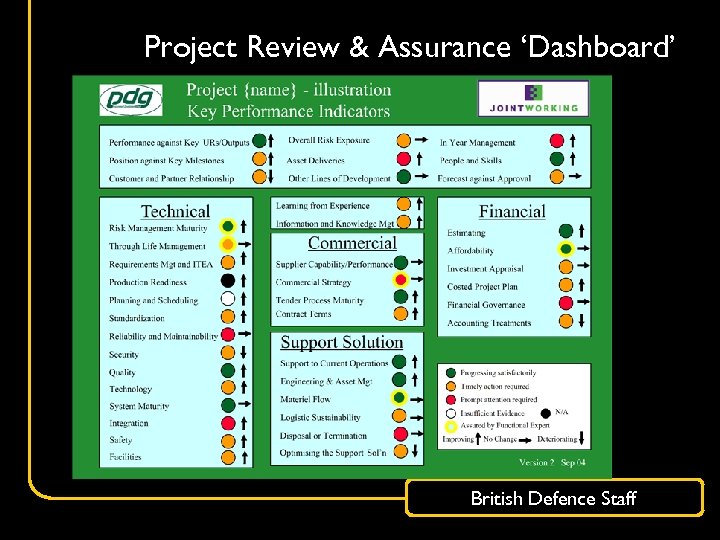 Project Review & Assurance ‘Dashboard’ British Defence Staff
Project Review & Assurance ‘Dashboard’ British Defence Staff
 Joint Strike Fighter • UK requires 150 JSF: – Replace RAF & RN Harriers – Equip 2 new carriers • US lead co-operative venture • UK is sole Level 1 Participant • BAES is major contractor British Defence Staff
Joint Strike Fighter • UK requires 150 JSF: – Replace RAF & RN Harriers – Equip 2 new carriers • US lead co-operative venture • UK is sole Level 1 Participant • BAES is major contractor British Defence Staff
 Future Strategic Tanker Aircraft • Replace 28 VC 10’s / Tristars • High replacement capital cost • Air. Tanker Consortium Selected – Airbus A 330 • FSTA contracts for a ‘service’: – 5 -8 aircraft needed for training etc. – Rising to ~20 during peak operations – Contractor uses aircraft commercially (for freight and passengers) when not required by RAF British Defence Staff
Future Strategic Tanker Aircraft • Replace 28 VC 10’s / Tristars • High replacement capital cost • Air. Tanker Consortium Selected – Airbus A 330 • FSTA contracts for a ‘service’: – 5 -8 aircraft needed for training etc. – Rising to ~20 during peak operations – Contractor uses aircraft commercially (for freight and passengers) when not required by RAF British Defence Staff
 ASTOR • World-leading airborne Ground Surveillance system – First to interleave Ground Moving Target Indication (GMTI) & Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) – 3 operators (c. f. E 10’s 35) – 5 aircraft, first flight imminent • Contract is with US firm (Raytheon) British Defence Staff
ASTOR • World-leading airborne Ground Surveillance system – First to interleave Ground Moving Target Indication (GMTI) & Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) – 3 operators (c. f. E 10’s 35) – 5 aircraft, first flight imminent • Contract is with US firm (Raytheon) British Defence Staff
 A 400 M • European Multinational Airlifter – 7 nations – 180 aircraft • Clear requirement for European airlift capability – Only current capability is small UK C-17 fleet British Defence Staff
A 400 M • European Multinational Airlifter – 7 nations – 180 aircraft • Clear requirement for European airlift capability – Only current capability is small UK C-17 fleet British Defence Staff
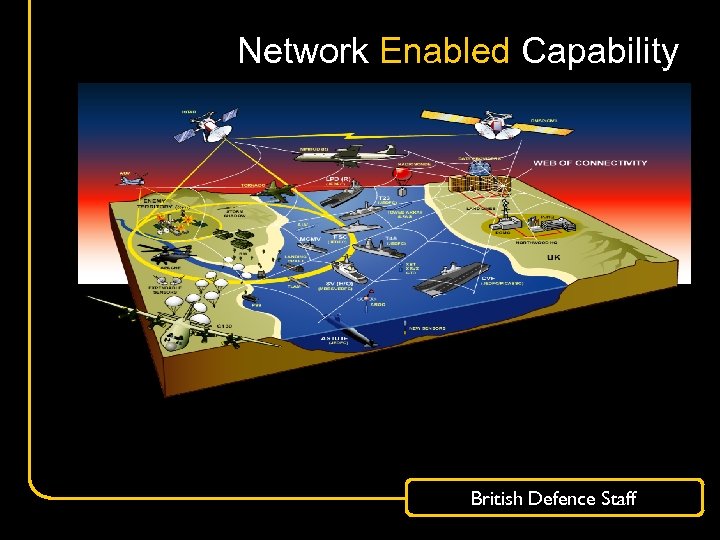 Network Enabled Capability British Defence Staff
Network Enabled Capability British Defence Staff
 Science & Technology British Defence Staff
Science & Technology British Defence Staff
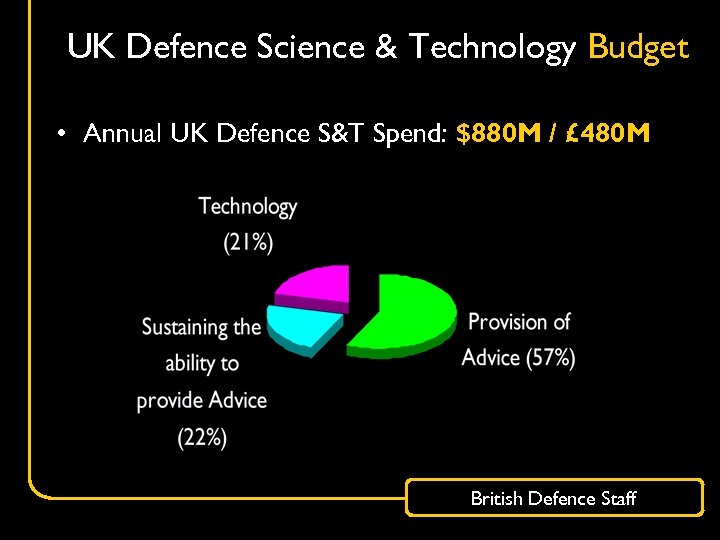 UK Defence Science & Technology Budget • Annual UK Defence S&T Spend: $880 M / £ 480 M British Defence Staff
UK Defence Science & Technology Budget • Annual UK Defence S&T Spend: $880 M / £ 480 M British Defence Staff
 UK Science & Technology Priorities For Directed Research • • • Command structures and decision support for NCW Information and data management Detection and identification of difficult targets, BDA and Combat Id Unmanned systems Precision weapons, including for HDBT CBR detection and countermeasures Improved mobile communications Recruitment, retention, reduced manning and duty of care Detection and disruption of explosive devices Technology Insertion Modelling and simulation for effects based operations, experimentation, urban ops, human systems and logistics supply chain British Defence Staff
UK Science & Technology Priorities For Directed Research • • • Command structures and decision support for NCW Information and data management Detection and identification of difficult targets, BDA and Combat Id Unmanned systems Precision weapons, including for HDBT CBR detection and countermeasures Improved mobile communications Recruitment, retention, reduced manning and duty of care Detection and disruption of explosive devices Technology Insertion Modelling and simulation for effects based operations, experimentation, urban ops, human systems and logistics supply chain British Defence Staff
 UK Science & Technology Priorities For Innovative Research • • • Autonomous systems Wireless sensor networks Generic biological detection and countermeasures Novel sensor and processing technology Active or Multifunctional material technologies Technology enabling low cost, low maintenance or high availability systems Technologies to reduce environmental impact Information systems Power Sources British Defence Staff
UK Science & Technology Priorities For Innovative Research • • • Autonomous systems Wireless sensor networks Generic biological detection and countermeasures Novel sensor and processing technology Active or Multifunctional material technologies Technology enabling low cost, low maintenance or high availability systems Technologies to reduce environmental impact Information systems Power Sources British Defence Staff
 Towers of Excellence – Partnership with industry – Focus resources on priority areas – Improve transition and pull -through • British Defence Staff
Towers of Excellence – Partnership with industry – Focus resources on priority areas – Improve transition and pull -through • British Defence Staff
 Defence Technology Centres – Development of enabling-level technologies – Formal collaboration between Mo. D, industry and academia Data Information Fusion Defence Technology Centre British Defence Staff
Defence Technology Centres – Development of enabling-level technologies – Formal collaboration between Mo. D, industry and academia Data Information Fusion Defence Technology Centre British Defence Staff
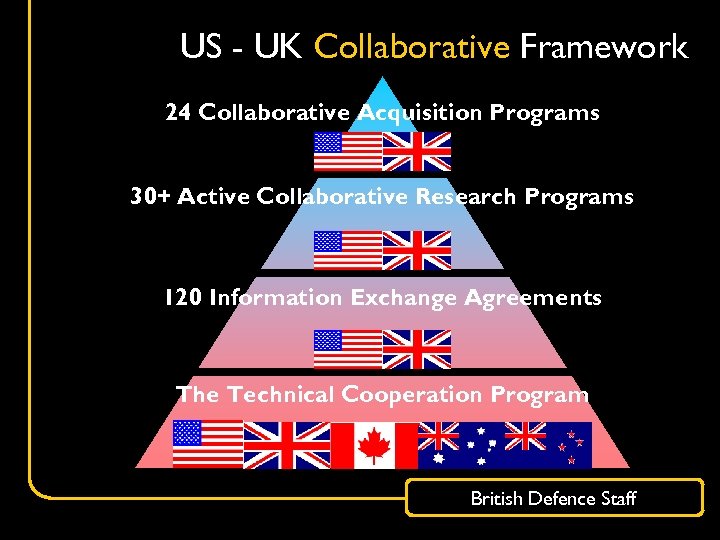 US - UK Collaborative Framework 24 Collaborative Acquisition Programs 30+ Active Collaborative Research Programs 120 Information Exchange Agreements The Technical Cooperation Program British Defence Staff
US - UK Collaborative Framework 24 Collaborative Acquisition Programs 30+ Active Collaborative Research Programs 120 Information Exchange Agreements The Technical Cooperation Program British Defence Staff
 Cooperative Research Programmes (12 new programmes totaling >$230 m commenced in 2004) British Defence Staff
Cooperative Research Programmes (12 new programmes totaling >$230 m commenced in 2004) British Defence Staff
 Industry’s role in Cooperation • Seeking to increase involvement of UK/US supplier bases in S+T collaboration – National research is being increasingly contracted out to non-government bodies – Better prepare for technology transition – Early engagement increases viability of downstream procurement collaboration • Can be achieved: – Via government – industry contracting – Through government and industry partnerships British Defence Staff
Industry’s role in Cooperation • Seeking to increase involvement of UK/US supplier bases in S+T collaboration – National research is being increasingly contracted out to non-government bodies – Better prepare for technology transition – Early engagement increases viability of downstream procurement collaboration • Can be achieved: – Via government – industry contracting – Through government and industry partnerships British Defence Staff
 International Technology Alliance • A new model of collaboration • UK/US government, industry and academic partnership • Network & Information Sciences – – Network Theory Security across a system of systems Sensor information processing and delivery Distributed coalition planning and decision making • Competition in progress – ITA begins work early 2006 British Defence Staff
International Technology Alliance • A new model of collaboration • UK/US government, industry and academic partnership • Network & Information Sciences – – Network Theory Security across a system of systems Sensor information processing and delivery Distributed coalition planning and decision making • Competition in progress – ITA begins work early 2006 British Defence Staff
 Industrial Strategy British Defence Staff
Industrial Strategy British Defence Staff
 UK Defence Industrial Policy • Healthy & globally competitive defence industry - to provide the Armed Forces with: – the equipment they require – at best value for the taxpayer • UK defence industry = suppliers who create: – – value employment technology intellectual assets • Open & fair competition is the bedrock: – improved flow of info / tech across borders – no market distortion but wide range of factors British Defence Staff
UK Defence Industrial Policy • Healthy & globally competitive defence industry - to provide the Armed Forces with: – the equipment they require – at best value for the taxpayer • UK defence industry = suppliers who create: – – value employment technology intellectual assets • Open & fair competition is the bedrock: – improved flow of info / tech across borders – no market distortion but wide range of factors British Defence Staff
 UK Defence Industrial Strategy (DIS) • Recently announced. • Will build on the Defence Industrial Policy. • Address some of the more difficult questions surrounding future of the defence industrial base. • Intended to develop clearer joint understanding between Gov & Industry of essential technologies and capabilities. • Publish before end 2005. British Defence Staff
UK Defence Industrial Strategy (DIS) • Recently announced. • Will build on the Defence Industrial Policy. • Address some of the more difficult questions surrounding future of the defence industrial base. • Intended to develop clearer joint understanding between Gov & Industry of essential technologies and capabilities. • Publish before end 2005. British Defence Staff
 DIS Way Forward • Will not address all industrial sectors by year end to the same depth. • Work has to be prioritised. • Major decisions required shortly on key acquisitions such as the Future Carrier project. • DIS will concentrate on: – – – Shipbuilding and support Fixed wing aircraft (Inc. UAVs) Rotorcraft Guided weapons General munitions Armoured fighting vehicles British Defence Staff
DIS Way Forward • Will not address all industrial sectors by year end to the same depth. • Work has to be prioritised. • Major decisions required shortly on key acquisitions such as the Future Carrier project. • DIS will concentrate on: – – – Shipbuilding and support Fixed wing aircraft (Inc. UAVs) Rotorcraft Guided weapons General munitions Armoured fighting vehicles British Defence Staff
 DIS Expectations • DIS will require change for Mo. D and wider government as well as supply side. • This will include: – – – Reassessing the use of competition at different stages. Optimising contract durations to encourage investment. Fresh approaches to demonstrating value for money. Challenging structures, policies and processes. Being more open and transparent. British Defence Staff
DIS Expectations • DIS will require change for Mo. D and wider government as well as supply side. • This will include: – – – Reassessing the use of competition at different stages. Optimising contract durations to encourage investment. Fresh approaches to demonstrating value for money. Challenging structures, policies and processes. Being more open and transparent. British Defence Staff
 DIS International Context “We also need to be clear on the relationship with other technologies and equipment, developed by our allies. We – the Mo. D and industry – need to think carefully about where, and how, we match, complement, or disinvest in areas compared to key allies. I explicitly include continental Europe in that. ” Lord Drayson, Minister (Defence Procurement) 15 September 2005 British Defence Staff
DIS International Context “We also need to be clear on the relationship with other technologies and equipment, developed by our allies. We – the Mo. D and industry – need to think carefully about where, and how, we match, complement, or disinvest in areas compared to key allies. I explicitly include continental Europe in that. ” Lord Drayson, Minister (Defence Procurement) 15 September 2005 British Defence Staff
 Conclusions British Defence Staff
Conclusions British Defence Staff
 Immediate Challenges • Sustaining an adequate defence industrial base on an inadequate defence budget • Investing in new technology, developing new processes: – NCW / NEC – UAVs / UCAVs / UUVs – Pulling R&D through into production • Interoperability and transatlantic cooperation: – Making the JSF work – Protectionism – Information sharing – Technology transfer restrictions • Growing the talent - skills for industry & government British Defence Staff
Immediate Challenges • Sustaining an adequate defence industrial base on an inadequate defence budget • Investing in new technology, developing new processes: – NCW / NEC – UAVs / UCAVs / UUVs – Pulling R&D through into production • Interoperability and transatlantic cooperation: – Making the JSF work – Protectionism – Information sharing – Technology transfer restrictions • Growing the talent - skills for industry & government British Defence Staff
 • Military Imperative Why Cooperate? – Improved interoperability – More capable allies – increased burden-sharing – Lessons identified / learnt • Fiscal Imperative – Reduced research and acquisition costs • Intellectual Imperative – Wider intellectual pool – Peer review • Technology Imperative – Access to unique capabilities – Improved technology access British Defence Staff
• Military Imperative Why Cooperate? – Improved interoperability – More capable allies – increased burden-sharing – Lessons identified / learnt • Fiscal Imperative – Reduced research and acquisition costs • Intellectual Imperative – Wider intellectual pool – Peer review • Technology Imperative – Access to unique capabilities – Improved technology access British Defence Staff
 Questions? British Defence Staff
Questions? British Defence Staff


