b4f7c381c2ceef50cb2cd68edc8e3d80.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 Decolonization or Independence Movements in Asia, Africa, & the Middle East 1920 s – 1980 s
Decolonization or Independence Movements in Asia, Africa, & the Middle East 1920 s – 1980 s
 Overview By the mid-20 th century, many colonies in Africa, Asia & the Middle East had “freed” themselves from European dominance. Decolonization is the term historians have used to describe this process
Overview By the mid-20 th century, many colonies in Africa, Asia & the Middle East had “freed” themselves from European dominance. Decolonization is the term historians have used to describe this process
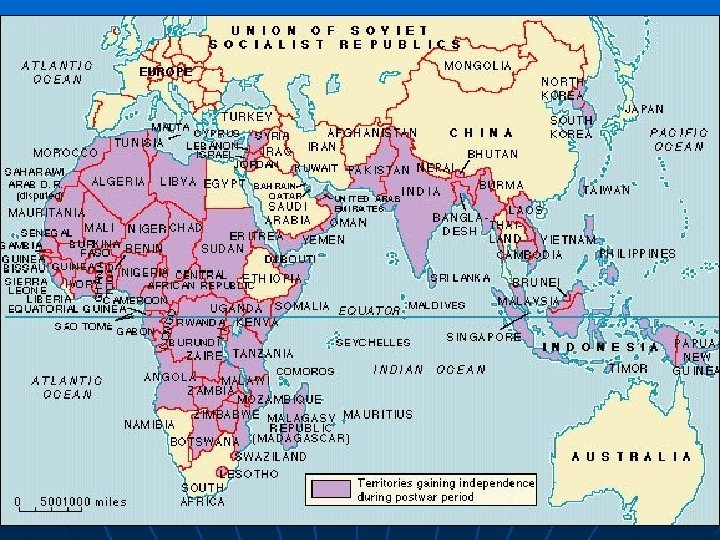
 WHY? : Causes of Decolonization What forces led to the end of European colonial empires? n Education & information acquired by Asians & Africans. “Lessons” on equality, democracy, revolution, government, natural rights, etc. caused people to take action for freedom. n World Wars Asians and Africans questioned European “progress” The winners of both wars talked of freedom. . .
WHY? : Causes of Decolonization What forces led to the end of European colonial empires? n Education & information acquired by Asians & Africans. “Lessons” on equality, democracy, revolution, government, natural rights, etc. caused people to take action for freedom. n World Wars Asians and Africans questioned European “progress” The winners of both wars talked of freedom. . .
 Decolonization: HOW The many differing African & Asian groups used a variety of elements in their efforts to gain independence. Some of these include. . . n n n Nationalism Military force / violence Mass demonstrations Economic boycotts Government representation & democratic processes Indigenous religious beliefs & symbols
Decolonization: HOW The many differing African & Asian groups used a variety of elements in their efforts to gain independence. Some of these include. . . n n n Nationalism Military force / violence Mass demonstrations Economic boycotts Government representation & democratic processes Indigenous religious beliefs & symbols
 Colonial Repercussions of the WWII n n Some defeated powers forced to give up colonies. North Africa was able to exploit German occupation of France to build institutions of self -government. Economically, Britain, Belgium & Netherlands devastated by war, difficult to re-establish colonial rule. War’s principal victors – U. S. , U. S. S. R. & China – follow anti-imperialist stances. UN (post WW 2) provides a forum for decolonization process. India (1947) & Ghana (1957) sponsor antiimperial movements.
Colonial Repercussions of the WWII n n Some defeated powers forced to give up colonies. North Africa was able to exploit German occupation of France to build institutions of self -government. Economically, Britain, Belgium & Netherlands devastated by war, difficult to re-establish colonial rule. War’s principal victors – U. S. , U. S. S. R. & China – follow anti-imperialist stances. UN (post WW 2) provides a forum for decolonization process. India (1947) & Ghana (1957) sponsor antiimperial movements.
 EFFECTS of Decolonization Were mixed n Problems remained Economic Dependency Little industrialization Poverty Tribal, racial, religious differences
EFFECTS of Decolonization Were mixed n Problems remained Economic Dependency Little industrialization Poverty Tribal, racial, religious differences
 Decolonization in INDIA
Decolonization in INDIA
 Mohandas ‘Mahatma’ Gandhi n n Passed English bar - lawyer for Indian merchants in South Africa. Gandhi’s answer to a spiritual theory of social action – Satyagraha - “soul force”. A tactic using nonviolent resistance or civil disobedience.
Mohandas ‘Mahatma’ Gandhi n n Passed English bar - lawyer for Indian merchants in South Africa. Gandhi’s answer to a spiritual theory of social action – Satyagraha - “soul force”. A tactic using nonviolent resistance or civil disobedience.
 A ‘Revolution’ in Indian politics Gandhi’s Satyagraha “What do you think? Wherein in courage required – in blowing others to pieces from behind a cannon, or with a smiling face to approach a cannon and be blown to pieces? . . . Believe me that a man devoid of courage and manhood can never be a passive resister. ” n
A ‘Revolution’ in Indian politics Gandhi’s Satyagraha “What do you think? Wherein in courage required – in blowing others to pieces from behind a cannon, or with a smiling face to approach a cannon and be blown to pieces? . . . Believe me that a man devoid of courage and manhood can never be a passive resister. ” n
 Gandhi in India n 1915: back in India - Dressed in traditional clothing- crisscrossed India on third-class trains listening to common people to understand their plight.
Gandhi in India n 1915: back in India - Dressed in traditional clothing- crisscrossed India on third-class trains listening to common people to understand their plight.
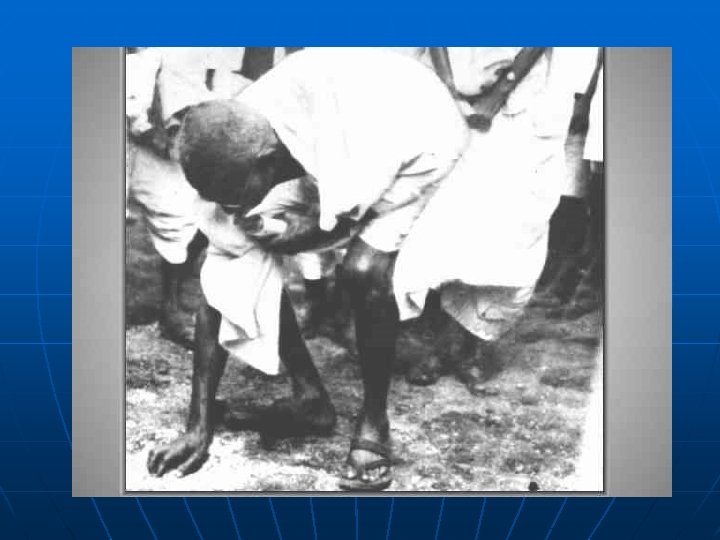
 The British Back Down 1931 - released Gandhi from jail & negotiated with him as an equal. n 1935 - Indian got a new constitution. n 1942 - called on British to “Quit India” – civil disorder campaign – arrested & jailed. n
The British Back Down 1931 - released Gandhi from jail & negotiated with him as an equal. n 1935 - Indian got a new constitution. n 1942 - called on British to “Quit India” – civil disorder campaign – arrested & jailed. n
 The Muslim League n n Led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah (18761948) Feared Hindu domination of an independent India ruled by Congress Party. Made Muslim separation from Hindu majority a nationalist issue. In 1940 Jinnah told a Muslim League conference that Britain should give Indian Hindus & Muslims separate homelands –
The Muslim League n n Led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah (18761948) Feared Hindu domination of an independent India ruled by Congress Party. Made Muslim separation from Hindu majority a nationalist issue. In 1940 Jinnah told a Muslim League conference that Britain should give Indian Hindus & Muslims separate homelands –
 Independence But Partition n Britain agreed to speedy independence in 1945, but murderous clashes between Hindus and Muslims in 1946 led to a delay. In the end. . . n n India’s last Viceroy, Lord Mountbatten (1900 -1979) proposed partition. Both sides agreed. One fifth of humanity gained independence on August 14 th 1947.
Independence But Partition n Britain agreed to speedy independence in 1945, but murderous clashes between Hindus and Muslims in 1946 led to a delay. In the end. . . n n India’s last Viceroy, Lord Mountbatten (1900 -1979) proposed partition. Both sides agreed. One fifth of humanity gained independence on August 14 th 1947.
 Indian Independence Aug 15 1947
Indian Independence Aug 15 1947

 The Tragedy of Partition n n Massacres and mass expulsions. 100, 000 slaughtered & five million refugees Gandhi said “What is there to celebrate? I see nothing but rivers of death. ” Gandhi was gunned down in January 1948 by a Hindu fanatic, while announcing a fast to protest Hindu persecution of Muslims.
The Tragedy of Partition n n Massacres and mass expulsions. 100, 000 slaughtered & five million refugees Gandhi said “What is there to celebrate? I see nothing but rivers of death. ” Gandhi was gunned down in January 1948 by a Hindu fanatic, while announcing a fast to protest Hindu persecution of Muslims.
 Refugees
Refugees
 Modern India n n n Largest democracy in the world Jawaharlal Nehru became the first prime minister for the next 17 years Democracy, Unity, & Economic Modernization Challenges: n n Kashmir= years of conflict that continues today Cold War alignment= NON Alignment Movement Industrialization= slow but coming Social and cultural issues= continuous challenges with progress Caste system Economic Women’s rights
Modern India n n n Largest democracy in the world Jawaharlal Nehru became the first prime minister for the next 17 years Democracy, Unity, & Economic Modernization Challenges: n n Kashmir= years of conflict that continues today Cold War alignment= NON Alignment Movement Industrialization= slow but coming Social and cultural issues= continuous challenges with progress Caste system Economic Women’s rights
 Kashmir Border both India & Pakistan Hindu leader with large Muslim populations 1947 -Pakistan invaded leading Kashmir to align with India fighting cont. ’d until 1949. Cease fire lead to 1/3 control by Pakistan 2/3 by India. 1962 - China seized part of Kashmir 1972 - Indian and Pakistani forces fought again Today: tensions continue and flare up intermittently
Kashmir Border both India & Pakistan Hindu leader with large Muslim populations 1947 -Pakistan invaded leading Kashmir to align with India fighting cont. ’d until 1949. Cease fire lead to 1/3 control by Pakistan 2/3 by India. 1962 - China seized part of Kashmir 1972 - Indian and Pakistani forces fought again Today: tensions continue and flare up intermittently
 Nehru’s Family Rules n n n 1964 Nehru dies Congress Party left with no strong leader 1966 Indira Gandhi becomes Prime Minister (Nehru’s daughter) 1980 re-elected (after a short period out of office) Increased food/grain production Faced a threat from Sikh extremist agitating for an independent state 1984 500 were killed in a violent demonstrations 2 months later her Sikh bodyguards shot her n 1984 -89 Rajiv Gandhi leader / charged with corruption 1991 killed by a bomb while campaigning near Madra
Nehru’s Family Rules n n n 1964 Nehru dies Congress Party left with no strong leader 1966 Indira Gandhi becomes Prime Minister (Nehru’s daughter) 1980 re-elected (after a short period out of office) Increased food/grain production Faced a threat from Sikh extremist agitating for an independent state 1984 500 were killed in a violent demonstrations 2 months later her Sikh bodyguards shot her n 1984 -89 Rajiv Gandhi leader / charged with corruption 1991 killed by a bomb while campaigning near Madra
 Indira Gandhi Assassinated
Indira Gandhi Assassinated
 Pakistan (1947) & Sri Lanka (1948) Both suffer from religious & ethic conflicts Pakistan n n 47’ Divided E/W; Separated by India Ethnically/culturally different; same religion 1971 - W. Pakistan became independent Bangladesh After 1958 Pakistan went through a series of military coups Ali Bhutto lead after the civil war 77’ Gen. Zia removed him Bhutto later executed for corruption Gen. Zia dies in a plane crash Benazir Bhutto elected 2 ‘Xs 96’ removed from office after period of disorder More military coup ensued Benazir Bhutto ran again in 07’ she was assassinated Sri Lanka n n n ¾ = 16 mill Buddhists 1/5 = Tamils (Hindu) Tamil militants want a separate nation 83’ India tried unsuccessfully to help disarm the Tamils to end the violence. May 2009 Tamil “Tigers” leader killed, they lose, civil war over!?
Pakistan (1947) & Sri Lanka (1948) Both suffer from religious & ethic conflicts Pakistan n n 47’ Divided E/W; Separated by India Ethnically/culturally different; same religion 1971 - W. Pakistan became independent Bangladesh After 1958 Pakistan went through a series of military coups Ali Bhutto lead after the civil war 77’ Gen. Zia removed him Bhutto later executed for corruption Gen. Zia dies in a plane crash Benazir Bhutto elected 2 ‘Xs 96’ removed from office after period of disorder More military coup ensued Benazir Bhutto ran again in 07’ she was assassinated Sri Lanka n n n ¾ = 16 mill Buddhists 1/5 = Tamils (Hindu) Tamil militants want a separate nation 83’ India tried unsuccessfully to help disarm the Tamils to end the violence. May 2009 Tamil “Tigers” leader killed, they lose, civil war over!?
 Summary: Decolonization in India n n Nationalist protests & revolutionary activities led to repression by British officials in the 19 th & 20 th c. Gandhi launches a nationalists movement against British rule using civil disobedience World Wars & broken promises by the British led to a greater desire for Independence as Hindu-Muslim splits became more pronounced. 1947 – India was granted independence by the British.
Summary: Decolonization in India n n Nationalist protests & revolutionary activities led to repression by British officials in the 19 th & 20 th c. Gandhi launches a nationalists movement against British rule using civil disobedience World Wars & broken promises by the British led to a greater desire for Independence as Hindu-Muslim splits became more pronounced. 1947 – India was granted independence by the British.
 Trends (general similarities): What trends did you notice with these countries and the Decolonization process? India Economic: lack of industrialization ? s of who will rule; how will they rule=conflict Political: Social: Ethnic/religious conflicts n n n Muslim Hindu (incl. Tamil) Sikh Look for such trends in the problems facing decolonizing countries n Economic
Trends (general similarities): What trends did you notice with these countries and the Decolonization process? India Economic: lack of industrialization ? s of who will rule; how will they rule=conflict Political: Social: Ethnic/religious conflicts n n n Muslim Hindu (incl. Tamil) Sikh Look for such trends in the problems facing decolonizing countries n Economic
 Singapore
Singapore
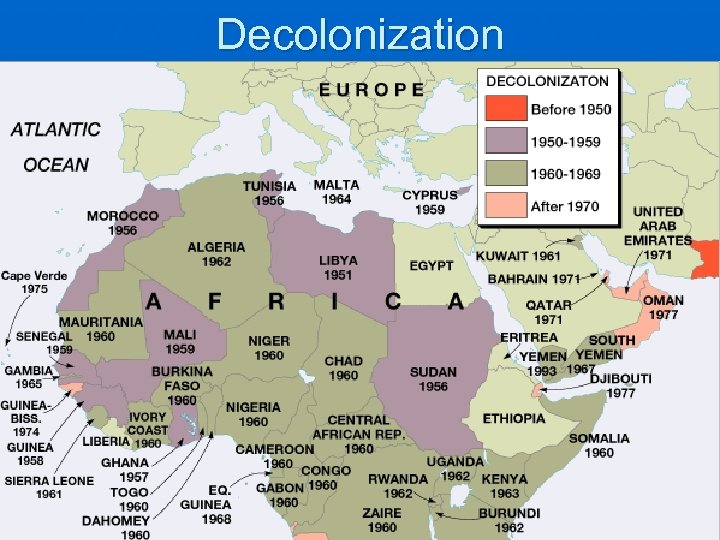
 Colonization in Africa Europeans had divided up the continent n Exploited the resources n Left the region unprepared (no experience) to rule themselves In addition, … n Borders imposed by the Europeans caused many problems (Berlin Conference n of 1884) Separated similar cultures Enclosed traditional enemies
Colonization in Africa Europeans had divided up the continent n Exploited the resources n Left the region unprepared (no experience) to rule themselves In addition, … n Borders imposed by the Europeans caused many problems (Berlin Conference n of 1884) Separated similar cultures Enclosed traditional enemies
 Independence Two major methods in Africa: Negotiated Independence: Long or short term deal between European power and African colony Incomplete Decolonization: White settler minority population given political power over black majority
Independence Two major methods in Africa: Negotiated Independence: Long or short term deal between European power and African colony Incomplete Decolonization: White settler minority population given political power over black majority
 The Road to Independence n Interwar years: an educated middle class began to develop Went to US for college Influenced by American Culture (Harlem Renaissance, Black activist & leaders) n n Pan African Congresses 1919/1921 Negritude Movement began in among French speaking Africans/lead by Leopold Senghor Celebrated African culture, heritage, & values n WWII African soldiers fought along side Europeans Became unwilling to accept colonial domination Europeans began to ? The cost of mainitaining the colonies
The Road to Independence n Interwar years: an educated middle class began to develop Went to US for college Influenced by American Culture (Harlem Renaissance, Black activist & leaders) n n Pan African Congresses 1919/1921 Negritude Movement began in among French speaking Africans/lead by Leopold Senghor Celebrated African culture, heritage, & values n WWII African soldiers fought along side Europeans Became unwilling to accept colonial domination Europeans began to ? The cost of mainitaining the colonies
 Decolonization in Africa: Post WWII Europeans were ready to decolonize n n When? British wanted to Prepare the colonies for self rule How? Allowed more Africans to be elected to the legislative Council Africans wanted elected, not nominated rep. s n Where? Gold Coast first Kwame Nkrumah (US ed. & Former teacher) began Non violent protest for elected rep. s n n Strikes, boycotts When? Succeeded in getting INDEPENDENCE in 1957 Renamed: Ghana Commonwealth) (1 st African lead country to joint the British Nkrumah became first Prime Minister
Decolonization in Africa: Post WWII Europeans were ready to decolonize n n When? British wanted to Prepare the colonies for self rule How? Allowed more Africans to be elected to the legislative Council Africans wanted elected, not nominated rep. s n Where? Gold Coast first Kwame Nkrumah (US ed. & Former teacher) began Non violent protest for elected rep. s n n Strikes, boycotts When? Succeeded in getting INDEPENDENCE in 1957 Renamed: Ghana Commonwealth) (1 st African lead country to joint the British Nkrumah became first Prime Minister
 Ghana. asf n Independent Ghana 3: 45 -8. 42 Nkrumah = 1 st Prime Minister & then President for life Pushed thru expensive development plans & econ. Projects n Roads, schools, healthcare facilities These $$$ projects quickly crippled the country & STRENGTHED his opposition n n n Influenced by Marcus Garvey (separatist who wanted Africa for Africans) Helped organize Pan African meetings in 1945 & 53. 1963 he influenced the development of the (OAU) Organization of African Unity Criticized for spending too much times on Pan African efforts & neglecting economic problems 1966 while he was in China the Ghana army & police seized power 1966 -Present: has gone back & forth btwn military & civililand gov’t. s & it
Ghana. asf n Independent Ghana 3: 45 -8. 42 Nkrumah = 1 st Prime Minister & then President for life Pushed thru expensive development plans & econ. Projects n Roads, schools, healthcare facilities These $$$ projects quickly crippled the country & STRENGTHED his opposition n n n Influenced by Marcus Garvey (separatist who wanted Africa for Africans) Helped organize Pan African meetings in 1945 & 53. 1963 he influenced the development of the (OAU) Organization of African Unity Criticized for spending too much times on Pan African efforts & neglecting economic problems 1966 while he was in China the Ghana army & police seized power 1966 -Present: has gone back & forth btwn military & civililand gov’t. s & it
 Decolonization
Decolonization
 n n British settlers controlled prime farmland in North & fiercely resisted Decolonization there Forced to accept Independence due to: the strong, popular leadership of Nationalist Jomo Kenyatta (Kikuyu educated in London) & The rise of the Mau secret society made up of mostly Kikuyu farmers forced out by British farmers Mau’s aim: frighten the white farmers into leaving n n n Kenyatta was not a Mau but he did not oppose them either 1963 Independence was granted but only after 10, 000 Kenyans & 100 whites were killed Jomo Kenyatta became President Independent Worked to unite the various ethnic /language. Kenya groups Nairobi (capital) grew into a major business center
n n British settlers controlled prime farmland in North & fiercely resisted Decolonization there Forced to accept Independence due to: the strong, popular leadership of Nationalist Jomo Kenyatta (Kikuyu educated in London) & The rise of the Mau secret society made up of mostly Kikuyu farmers forced out by British farmers Mau’s aim: frighten the white farmers into leaving n n n Kenyatta was not a Mau but he did not oppose them either 1963 Independence was granted but only after 10, 000 Kenyans & 100 whites were killed Jomo Kenyatta became President Independent Worked to unite the various ethnic /language. Kenya groups Nairobi (capital) grew into a major business center
 • 1978 Kenyatta died • Succeeded by Daniel arap Moi • Faced more & more opposition to ONE Party Rule • University strikes and protests = DEATHS for some students & put pressure on Moi to move more toward Democracy • 1990 s economy suffered / ethnic conflict cont. d / charges of corruption toward Moi’s govt • 2007 -08: evidence of election corruption and ethnic violence blackened the election
• 1978 Kenyatta died • Succeeded by Daniel arap Moi • Faced more & more opposition to ONE Party Rule • University strikes and protests = DEATHS for some students & put pressure on Moi to move more toward Democracy • 1990 s economy suffered / ethnic conflict cont. d / charges of corruption toward Moi’s govt • 2007 -08: evidence of election corruption and ethnic violence blackened the election
 Belgian Congo n Most Exploited African Colony Ruthlessly plundered for resources (rubber & copper), slave labor, drained wealth No social services & no preparation
Belgian Congo n Most Exploited African Colony Ruthlessly plundered for resources (rubber & copper), slave labor, drained wealth No social services & no preparation
 History congo (Zaire). asf Independent Congo : 56 -1: 49; 1: 49 -2: 39 n 1960 - granted independence Renamed Zaire 1967 -95 Tumultuous process n Internal conflict & Outside n (UN & USSR) intervention Patrice Lumumba 1 st prime minister Ruled a divided country (He controlled the North) In the SE (Mineral rich Katanga region / copper) Moise Tshombe declared SE independent of the rest Tshombe backed by Belgian mining co. Lumumba 1 st asked UN for help against Tshombe, then he turned to the USSR Colonel Mobutu (first working for Lumumba) led a military coup to over throw Lumumba & turned him over to Tshombe Lumumba was murdered shortly after Tshombe ruled briefly until 1965 when Mobutu overthru him & seized power in a bloodless coup
History congo (Zaire). asf Independent Congo : 56 -1: 49; 1: 49 -2: 39 n 1960 - granted independence Renamed Zaire 1967 -95 Tumultuous process n Internal conflict & Outside n (UN & USSR) intervention Patrice Lumumba 1 st prime minister Ruled a divided country (He controlled the North) In the SE (Mineral rich Katanga region / copper) Moise Tshombe declared SE independent of the rest Tshombe backed by Belgian mining co. Lumumba 1 st asked UN for help against Tshombe, then he turned to the USSR Colonel Mobutu (first working for Lumumba) led a military coup to over throw Lumumba & turned him over to Tshombe Lumumba was murdered shortly after Tshombe ruled briefly until 1965 when Mobutu overthru him & seized power in a bloodless coup
 n n n n Ruled 32 yrs Mobutu Used a combo of force, 1 party rule & bribes Zaire’s mineral wealth & natural resources made it 1 of the richest in Africa Under Mobutu it became 1 of the poorest He is believed to have looted the country for billions Mobutu resisted many attempted rebellions & ethnic clashes 1997 Laurent Kabila took over after a 7 month long civil war Banned all political parties Promised transition to democracy & election by 1999 Never Happened
n n n n Ruled 32 yrs Mobutu Used a combo of force, 1 party rule & bribes Zaire’s mineral wealth & natural resources made it 1 of the richest in Africa Under Mobutu it became 1 of the poorest He is believed to have looted the country for billions Mobutu resisted many attempted rebellions & ethnic clashes 1997 Laurent Kabila took over after a 7 month long civil war Banned all political parties Promised transition to democracy & election by 1999 Never Happened
 Pre-WWI
Pre-WWI
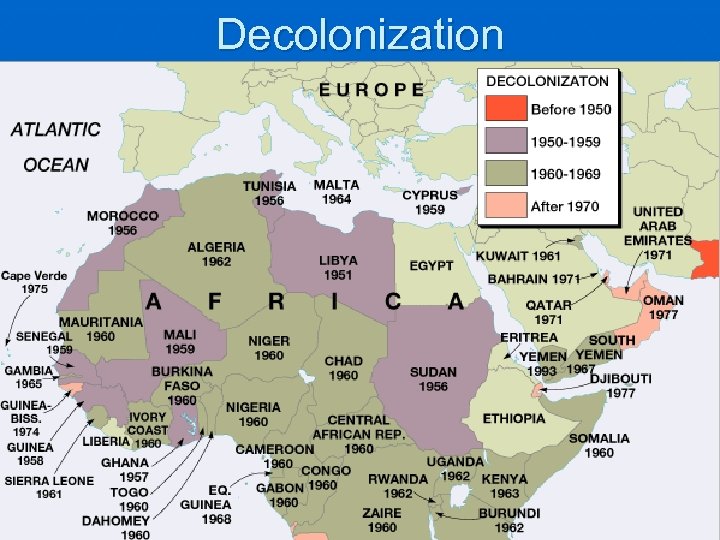 Decolonization
Decolonization
 Algeria Colonization France was the primary colonizer in North Africa n Population: n 1 million french colonists / 9 million Arab & Berber Muslims n n Colonists were unwilling to leave w/o a fight France attempted assimilation but not a reality
Algeria Colonization France was the primary colonizer in North Africa n Population: n 1 million french colonists / 9 million Arab & Berber Muslims n n Colonists were unwilling to leave w/o a fight France attempted assimilation but not a reality
 Independents Algeria n n 1945 - French troops fired on Algerian nationalist who were demonstrating--killing thousands of Muslims & 100 s of Europeans 1954 -Algerian National Liberation Front (FLN) moved to fight for independence FLN used guerrilla tactics at home but diplomacy (talk) internationally n n n French sent ½ million troops to stop them Both sides committed atrocities European settlers began calling for De Gaulle to return as president in France to restore order in the colonies
Independents Algeria n n 1945 - French troops fired on Algerian nationalist who were demonstrating--killing thousands of Muslims & 100 s of Europeans 1954 -Algerian National Liberation Front (FLN) moved to fight for independence FLN used guerrilla tactics at home but diplomacy (talk) internationally n n n French sent ½ million troops to stop them Both sides committed atrocities European settlers began calling for De Gaulle to return as president in France to restore order in the colonies
 De Gaulle & Algeria n 1958 - De Gaulle returned to power He concluded that Algeria count not be held by force France let go of most of its African possessions n 1962 - a referendum set up the conditions for independence Transfer of power planned March -750, 000 settlers fled Algeria July 1962 = Independence n Ahmed Ben Bella (FLN leader, imprisoned by French) became prime minister & then President Reestablished order Began land refors Developed new plans for education n 1965 - he was overthrown by his Chief of Staff!
De Gaulle & Algeria n 1958 - De Gaulle returned to power He concluded that Algeria count not be held by force France let go of most of its African possessions n 1962 - a referendum set up the conditions for independence Transfer of power planned March -750, 000 settlers fled Algeria July 1962 = Independence n Ahmed Ben Bella (FLN leader, imprisoned by French) became prime minister & then President Reestablished order Began land refors Developed new plans for education n 1965 - he was overthrown by his Chief of Staff!
 Secular & Religious Conflict over Power n 1965 -1988 - attempt to modernize & industrialize were undermined when world oil prices plunged (1985 -86) Unemployment & broken promises lead to an Islamic revival n Riots in 1988 against the secular govt occurred Islamic Salvation Front (FIS) won in 1990 & 91 elections Ruling govt refused the election results Civil War broke out Islamic militants vs govt
Secular & Religious Conflict over Power n 1965 -1988 - attempt to modernize & industrialize were undermined when world oil prices plunged (1985 -86) Unemployment & broken promises lead to an Islamic revival n Riots in 1988 against the secular govt occurred Islamic Salvation Front (FIS) won in 1990 & 91 elections Ruling govt refused the election results Civil War broke out Islamic militants vs govt
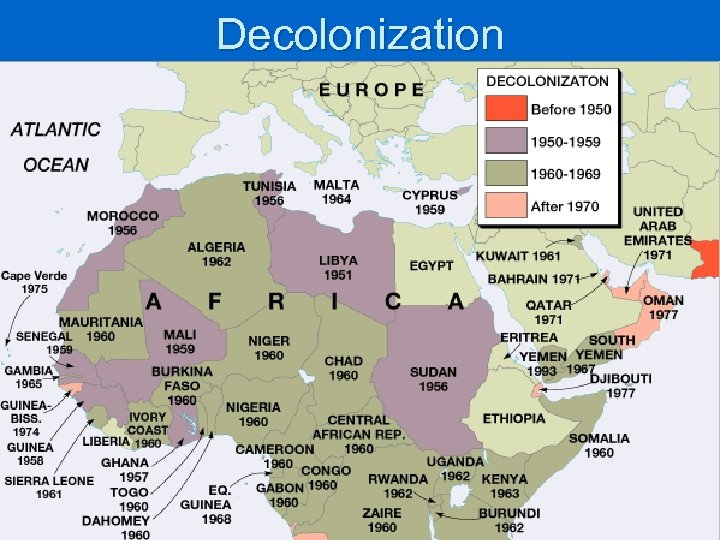 Decolonization
Decolonization
 Angola n n Portugal = 1 st to imperialize Africa; and the last to leave Made no preparation to assist their colonies into independence No education; health facilities & little commerce n However, some Angolans did gain an education & they heard about other African countries gaining independence & became inspired
Angola n n Portugal = 1 st to imperialize Africa; and the last to leave Made no preparation to assist their colonies into independence No education; health facilities & little commerce n However, some Angolans did gain an education & they heard about other African countries gaining independence & became inspired
 n 1960 s- 3 Revolutionaries Groups emerged. Independent Angola Each supported by different foreign powers Portugal sent 50, 000 troops to down the rebellions $$$$$ costing ½ of Portugal total nation budget $$$ Discontent WITHIN Portugal over colonial wars led to the military toppling the govt. there! n n n 1975 - Portuguese withdrew from Angola w/out formally handing power over to any one group Lack pf preparation for independence was made worse when a Communist (MPLA) group seized of power next Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) took control of the capital & declared
n 1960 s- 3 Revolutionaries Groups emerged. Independent Angola Each supported by different foreign powers Portugal sent 50, 000 troops to down the rebellions $$$$$ costing ½ of Portugal total nation budget $$$ Discontent WITHIN Portugal over colonial wars led to the military toppling the govt. there! n n n 1975 - Portuguese withdrew from Angola w/out formally handing power over to any one group Lack pf preparation for independence was made worse when a Communist (MPLA) group seized of power next Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) took control of the capital & declared
 Civil War in Angola MPLA got help from Cuba & the USSR FNLA (National Front for the Liberation of Angola) got help from Zaire and the US [they faded away] The MPLA was also opposed by UNITA (National Union for the Total Independence of Angola) who got help from So. Africa & the US 1988 - the US with consent from the USSR pressed for a settlement among the MPLA, UNITA, So. Africa & Cuba n n n 1989 a Cease fire went into effect 1995 the parties began discussion about representation of EACH group in the govt. Negotiations broke down and a long bloody cifil war continues today. Multiple elections have been planned
Civil War in Angola MPLA got help from Cuba & the USSR FNLA (National Front for the Liberation of Angola) got help from Zaire and the US [they faded away] The MPLA was also opposed by UNITA (National Union for the Total Independence of Angola) who got help from So. Africa & the US 1988 - the US with consent from the USSR pressed for a settlement among the MPLA, UNITA, So. Africa & Cuba n n n 1989 a Cease fire went into effect 1995 the parties began discussion about representation of EACH group in the govt. Negotiations broke down and a long bloody cifil war continues today. Multiple elections have been planned
 Results of Decolonization Elites gained power n Initial political parties reflected ethnic, regional, or religious groups n Power was often gained by corrupt African “strongmen” (dictators) who ignored the social needs of people n Economic dependency continued. n Political turmoil and instability continued n
Results of Decolonization Elites gained power n Initial political parties reflected ethnic, regional, or religious groups n Power was often gained by corrupt African “strongmen” (dictators) who ignored the social needs of people n Economic dependency continued. n Political turmoil and instability continued n
 Conflict in the Middle East
Conflict in the Middle East
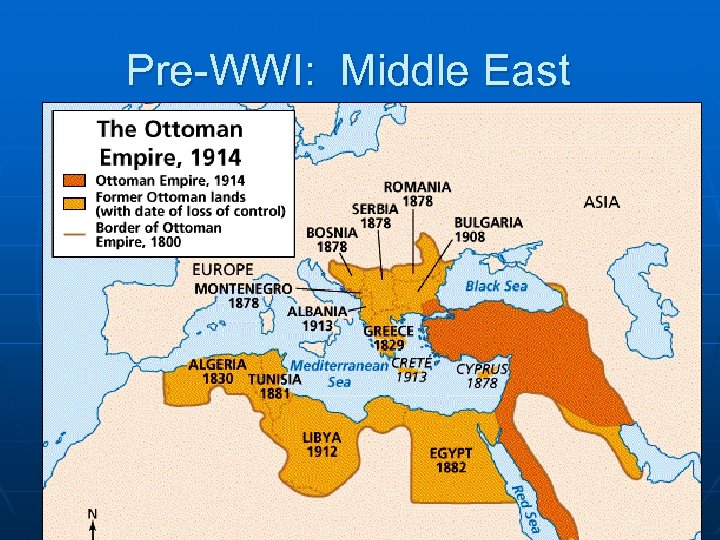 Pre-WWI: Middle East
Pre-WWI: Middle East
 Palestine n Increased Jewish immigration n Requests for a Jewish Homeland (Zionism) n Increased tension btwn Jews & Palestinians (Arabs) as Jewish population continued to grow
Palestine n Increased Jewish immigration n Requests for a Jewish Homeland (Zionism) n Increased tension btwn Jews & Palestinians (Arabs) as Jewish population continued to grow
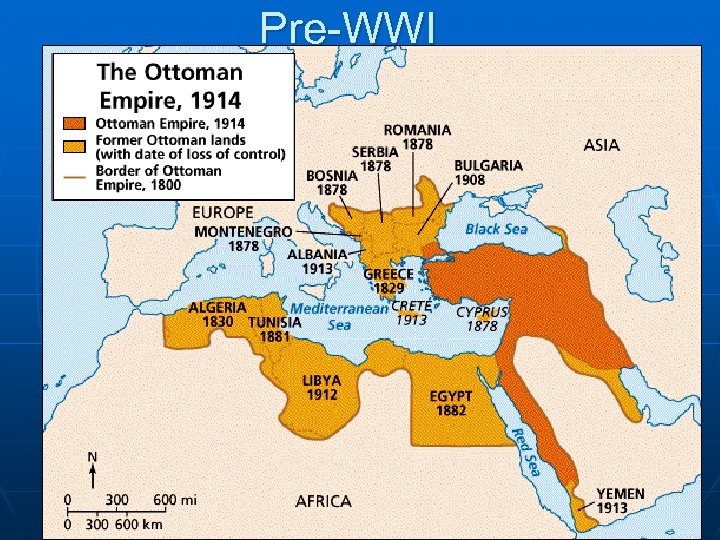
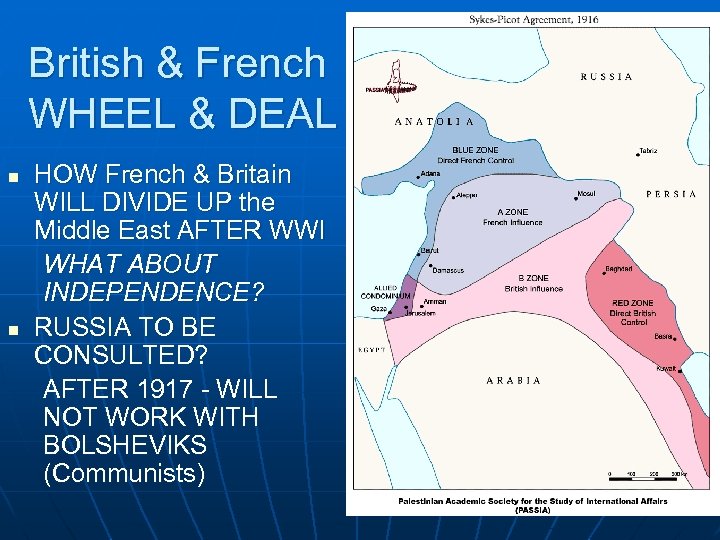 British & French WHEEL & DEAL n n HOW French & Britain WILL DIVIDE UP the Middle East AFTER WWI WHAT ABOUT INDEPENDENCE? RUSSIA TO BE CONSULTED? AFTER 1917 - WILL NOT WORK WITH BOLSHEVIKS (Communists)
British & French WHEEL & DEAL n n HOW French & Britain WILL DIVIDE UP the Middle East AFTER WWI WHAT ABOUT INDEPENDENCE? RUSSIA TO BE CONSULTED? AFTER 1917 - WILL NOT WORK WITH BOLSHEVIKS (Communists)
 END OF WWI n Arab regions expect British to hold to word And grant Independence n USSR angry supports Middle East MISTRUST!
END OF WWI n Arab regions expect British to hold to word And grant Independence n USSR angry supports Middle East MISTRUST!
 Treaty of Versailles n League of Nations attempts a solution: Mandate System n UK, France administer (oversee) regions until they’re “Ready” for independence n How is this different from a colony?
Treaty of Versailles n League of Nations attempts a solution: Mandate System n UK, France administer (oversee) regions until they’re “Ready” for independence n How is this different from a colony?
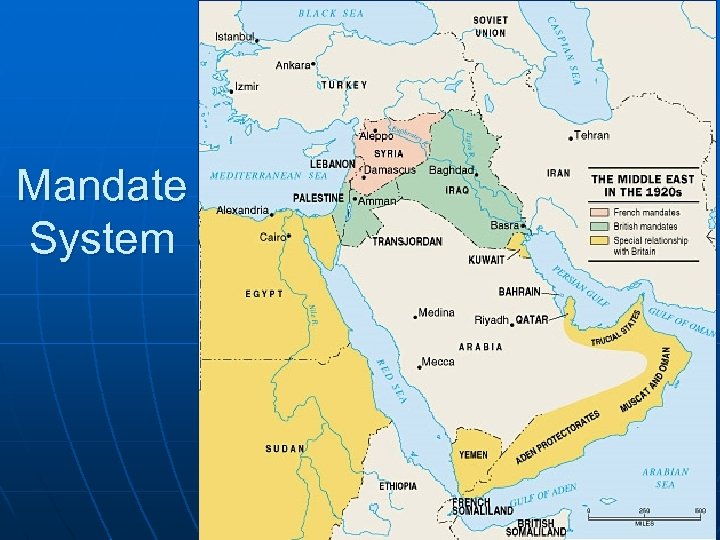 Mandate System
Mandate System
 Mandate System UK- Mandates of: n Persia (Iraq) Install puppet king Establish 75 -year-long oil concession
Mandate System UK- Mandates of: n Persia (Iraq) Install puppet king Establish 75 -year-long oil concession
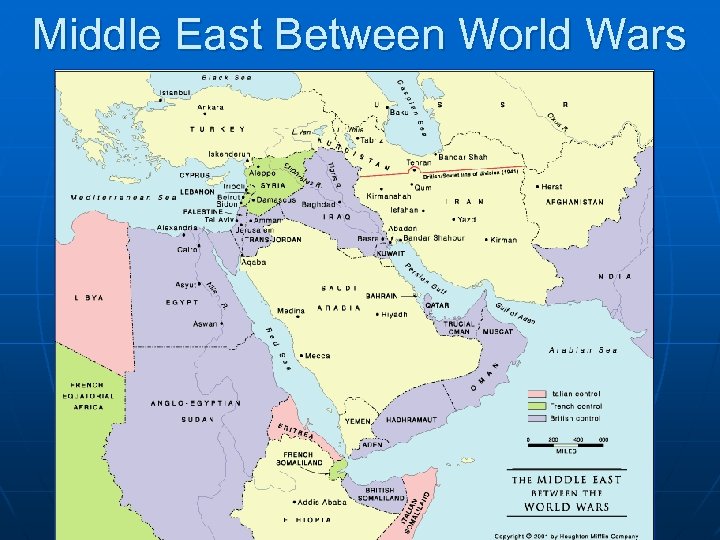 Middle East Between World Wars
Middle East Between World Wars
 Post-WWII Middle East Israel/Palestine n n Before WWI: Jews asked that a Jewish nation be carved out of the territory inhabited by the Palestinians under the Mandate of the British During WWI Britain feared the loss of support from both sides Balfour Agreement written (1917) Seemed to make promises to both sides English needed the support of both during WWII The terms were unworkable b/c they could not live together RESULT came after WWII: British can’t resolve the issue so they refer it to the “newly formed
Post-WWII Middle East Israel/Palestine n n Before WWI: Jews asked that a Jewish nation be carved out of the territory inhabited by the Palestinians under the Mandate of the British During WWI Britain feared the loss of support from both sides Balfour Agreement written (1917) Seemed to make promises to both sides English needed the support of both during WWII The terms were unworkable b/c they could not live together RESULT came after WWII: British can’t resolve the issue so they refer it to the “newly formed
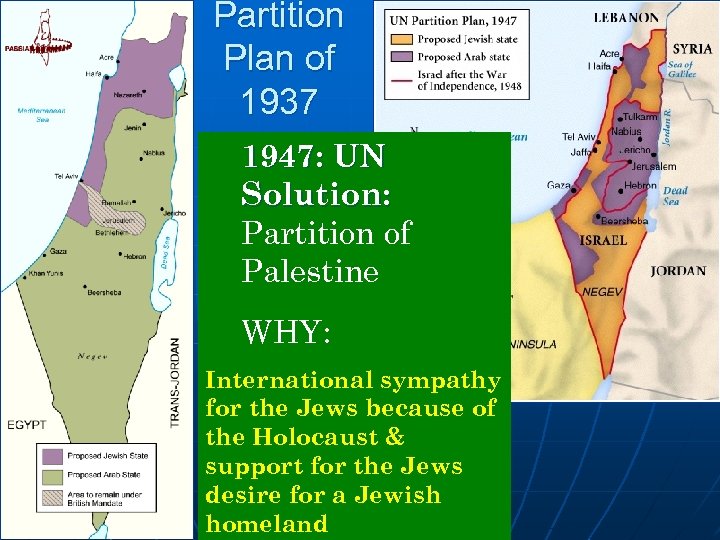 Partition Plan of 1937 1947: UN Solution: Partition of Palestine WHY: International sympathy for the Jews because of the Holocaust & support for the Jews desire for a Jewish homeland
Partition Plan of 1937 1947: UN Solution: Partition of Palestine WHY: International sympathy for the Jews because of the Holocaust & support for the Jews desire for a Jewish homeland
 Israel Becomes a State: May 14, 1948 n n Palestinians feared the increasing # of Jews would result in hardships 1920: 20 Arab Palestinian to 1 Jew / 1947: 2 to 1 Post- WWII Britain was weary of failed solution for the problem & deferred to the UN UN recommendation: PARTIITION of Palestine into a Palestinian state & a Jewish State Palestine = 66% of the Pop. & got 45% of the land / Jews = 34% of the Pop. & got 55% Jerusalem was to be an international city owned by neither. All Arab nations voted against this & Palestine rejected it completely The Jews welcomed the decision n Country of Israel declared by United Nations, 1948 ? of Palestinian rights, boundaries & access to things like water & farmland
Israel Becomes a State: May 14, 1948 n n Palestinians feared the increasing # of Jews would result in hardships 1920: 20 Arab Palestinian to 1 Jew / 1947: 2 to 1 Post- WWII Britain was weary of failed solution for the problem & deferred to the UN UN recommendation: PARTIITION of Palestine into a Palestinian state & a Jewish State Palestine = 66% of the Pop. & got 45% of the land / Jews = 34% of the Pop. & got 55% Jerusalem was to be an international city owned by neither. All Arab nations voted against this & Palestine rejected it completely The Jews welcomed the decision n Country of Israel declared by United Nations, 1948 ? of Palestinian rights, boundaries & access to things like water & farmland
 UN Partition Plan, 1947 Effect: Full Scale Arab Israeli war!- Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia & Syria invaded Israel 1 st of many Arab-Israeli Wars (56, 67, 73, 2006). This ended w/in months in Israel’s Victory. Israel had strong
UN Partition Plan, 1947 Effect: Full Scale Arab Israeli war!- Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia & Syria invaded Israel 1 st of many Arab-Israeli Wars (56, 67, 73, 2006). This ended w/in months in Israel’s Victory. Israel had strong
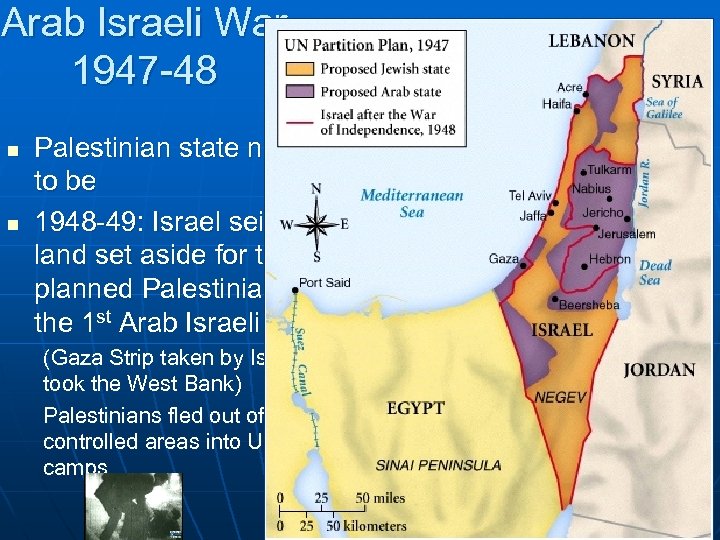 Arab Israeli War 1947 -48 n n Palestinian state never came to be 1948 -49: Israel seized half the land set aside for the UN planned Palestinian state in the 1 st Arab Israeli War (Gaza Strip taken by Israel & Jordan took the West Bank) Palestinians fled out of Jewish controlled areas into UN refugee camps
Arab Israeli War 1947 -48 n n Palestinian state never came to be 1948 -49: Israel seized half the land set aside for the UN planned Palestinian state in the 1 st Arab Israeli War (Gaza Strip taken by Israel & Jordan took the West Bank) Palestinians fled out of Jewish controlled areas into UN refugee camps
 1956 Second Arab-Israeli War: Suez Crisis n Egypt seized the Suez Canal from French & British businesses Pres. Nasser (Egypt) was angry b/c the US & Britain stopped financial support for the building of the Aswan Dam n British & French made an agreement with Israel Military air support if Israel marched on the Canal – they did & took it Egypt lost the canal, BUT… n Pressure from the international community (incl. US/USSR) forced Israel & the European Allies to withdraw & leave Egypt in charge of
1956 Second Arab-Israeli War: Suez Crisis n Egypt seized the Suez Canal from French & British businesses Pres. Nasser (Egypt) was angry b/c the US & Britain stopped financial support for the building of the Aswan Dam n British & French made an agreement with Israel Military air support if Israel marched on the Canal – they did & took it Egypt lost the canal, BUT… n Pressure from the international community (incl. US/USSR) forced Israel & the European Allies to withdraw & leave Egypt in charge of
 1967: Six- Day War Tensions Grew: n n n By early 1967, Pres. Nasser & his Arab allies, helped by USSR tanks & aircraft, moved to close off the Gulf of Aqaba (Israel’s outlet to the Red Sea) Threatened, Israel attacked airfields in Egypt, Iran, Jordan, & Syria Safe from air attacks, Israeli ground forces struck FAST on 3 Fronts War ended in 6 days. Israel lost 800 troops Arabs lost > 15, 000 Results: Israel militarily occupied & then annexed the old city of Jerusalem, the Sinai Peninsula, the Golan Heights & the West Bank. (providing a buffer btwn Israel & the Arab states) Palestinians living in the newly occupied Jerusalem were
1967: Six- Day War Tensions Grew: n n n By early 1967, Pres. Nasser & his Arab allies, helped by USSR tanks & aircraft, moved to close off the Gulf of Aqaba (Israel’s outlet to the Red Sea) Threatened, Israel attacked airfields in Egypt, Iran, Jordan, & Syria Safe from air attacks, Israeli ground forces struck FAST on 3 Fronts War ended in 6 days. Israel lost 800 troops Arabs lost > 15, 000 Results: Israel militarily occupied & then annexed the old city of Jerusalem, the Sinai Peninsula, the Golan Heights & the West Bank. (providing a buffer btwn Israel & the Arab states) Palestinians living in the newly occupied Jerusalem were
 1973 Yom Kippur War n n n Egypt’s new Pres. Anwar Sadat, planned a joint Arab attack on the holiest Jewish holiday Surprised! Israel incurred heavy casualties & lost some of the territory lost in 1967 Israeli prime minister, Golda Meir launched a counter attack & regained most of the lost territory. An “uneasy” TRUCE (NOT a Peace Treaty) was agreed to after several weeks of fighting
1973 Yom Kippur War n n n Egypt’s new Pres. Anwar Sadat, planned a joint Arab attack on the holiest Jewish holiday Surprised! Israel incurred heavy casualties & lost some of the territory lost in 1967 Israeli prime minister, Golda Meir launched a counter attack & regained most of the lost territory. An “uneasy” TRUCE (NOT a Peace Treaty) was agreed to after several weeks of fighting
 Land for Peace! n n n 1977: 4 yrs following the Yom Kippur War, Anwar Sadat offered Peace for Land! NO ARAB COUNTRY HAD EVER RECONGNIZED ISRAEL’S RIGHT TO EXIST!! Terms of Peace: Israel would have to recognize the rights of Palesinians & withdraw from territory seized in 1967 from Egypt, Jordan & Syria 1978: US Pres. Carter invited Sadat & Israeli prime minister Menachem Begin to Camp David to discuss an agreement 13 days of talks lead to THE CAMP DAVID ACCORDS: Egypt recognizing Israel as a state & Israel agreed to return the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt. Ending 30 years of hostilities btwn the 2 countries Sadat was assassinated later (1981 Muslim extremists
Land for Peace! n n n 1977: 4 yrs following the Yom Kippur War, Anwar Sadat offered Peace for Land! NO ARAB COUNTRY HAD EVER RECONGNIZED ISRAEL’S RIGHT TO EXIST!! Terms of Peace: Israel would have to recognize the rights of Palesinians & withdraw from territory seized in 1967 from Egypt, Jordan & Syria 1978: US Pres. Carter invited Sadat & Israeli prime minister Menachem Begin to Camp David to discuss an agreement 13 days of talks lead to THE CAMP DAVID ACCORDS: Egypt recognizing Israel as a state & Israel agreed to return the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt. Ending 30 years of hostilities btwn the 2 countries Sadat was assassinated later (1981 Muslim extremists
 The Palestinian Side n n n Israel was unwilling to give up territories seized for security & began building settlements on the West Bank & Gaza Strip Palestinians living in Israel resented Israeli rule The PLO (Palestinian Liberation Organization) & its leader, Yasir Arafat attracted many angry Palestinians 1970 s & 80 s military wing of the PLO conducted many armed struggles against Israel n Israel took a hard line against them Bombing suspected bases in Palestinian towns 1982: Israel’s army invaded Lebanon looking for PLO strongholds n Israel became involved in Lebanon’s civil war & were forced to withdraw n n n 1987 - 1990 s: Palestinians began to express their frustration in a widespread campaign of civil disobedience (boycotts, demonstrations, attacks on soldiers & rock throwing by teens) called the intifada (uprising) Intifada continued with little progress toward an end BUT… Public opinion began to swing away from the Israelis This ongoing conflict over occupied territories led to
The Palestinian Side n n n Israel was unwilling to give up territories seized for security & began building settlements on the West Bank & Gaza Strip Palestinians living in Israel resented Israeli rule The PLO (Palestinian Liberation Organization) & its leader, Yasir Arafat attracted many angry Palestinians 1970 s & 80 s military wing of the PLO conducted many armed struggles against Israel n Israel took a hard line against them Bombing suspected bases in Palestinian towns 1982: Israel’s army invaded Lebanon looking for PLO strongholds n Israel became involved in Lebanon’s civil war & were forced to withdraw n n n 1987 - 1990 s: Palestinians began to express their frustration in a widespread campaign of civil disobedience (boycotts, demonstrations, attacks on soldiers & rock throwing by teens) called the intifada (uprising) Intifada continued with little progress toward an end BUT… Public opinion began to swing away from the Israelis This ongoing conflict over occupied territories led to
 Peace Talk: The Declaration of Principles n n n 1993: secret talks in Oslo, Norway = a surprise agreement btwn Israeli prime minister Yitzhak Rabin & Yasir Arafat The Declaration of Principles Negotiated to grant the Palestinians self–rule in the Gaza Strip & the West Bank 1995: Rabin was assassinated by a right-wing Jewish extremist who opposed concessions to Palestine Benjamin Netanyahu succeeded Rabin & opposed the Peace Plan but he did make efforts to honor it 1997: he met with Arafat to work out plans fr a partial Israeli withdrawal; from Hebron on the West Bank.
Peace Talk: The Declaration of Principles n n n 1993: secret talks in Oslo, Norway = a surprise agreement btwn Israeli prime minister Yitzhak Rabin & Yasir Arafat The Declaration of Principles Negotiated to grant the Palestinians self–rule in the Gaza Strip & the West Bank 1995: Rabin was assassinated by a right-wing Jewish extremist who opposed concessions to Palestine Benjamin Netanyahu succeeded Rabin & opposed the Peace Plan but he did make efforts to honor it 1997: he met with Arafat to work out plans fr a partial Israeli withdrawal; from Hebron on the West Bank.
 2000 s n n n 2001 - Ariel Sharon became leader & moved away from withdrawal 2004 - Hamas wins election in Palestine (international community doesn’t acknowledge them) 2006 - Hamas kidnapped Israeli soldiers & Israel retaliated with air strikes 2008 -09 - Hamas bombed Israel from the Gaza Strip & Israel retaliated with war & blockades Today: Netanyahu is prime minister again & he supports settlement vs. withdrawal
2000 s n n n 2001 - Ariel Sharon became leader & moved away from withdrawal 2004 - Hamas wins election in Palestine (international community doesn’t acknowledge them) 2006 - Hamas kidnapped Israeli soldiers & Israel retaliated with air strikes 2008 -09 - Hamas bombed Israel from the Gaza Strip & Israel retaliated with war & blockades Today: Netanyahu is prime minister again & he supports settlement vs. withdrawal
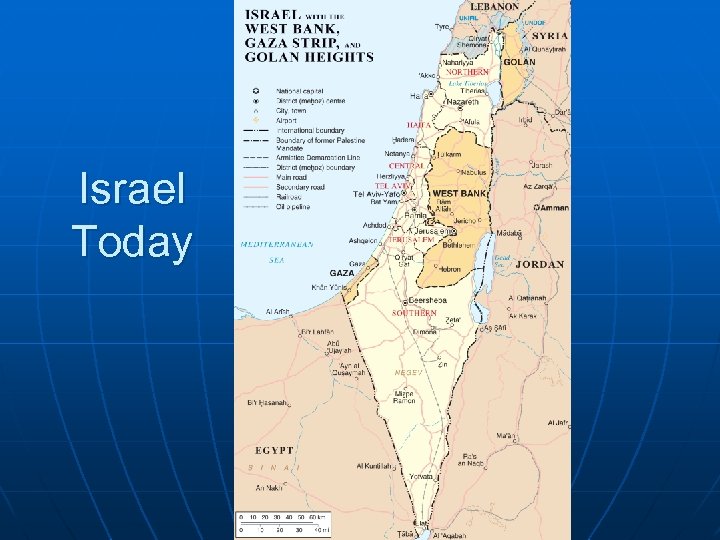 Israel Today
Israel Today


